Abstract
A rapidly aging population along with the increasing burden of patients with chronic conditions in Asia requires efficient health systems with integrated care. Although some efforts to integrate primary care and hospital care in Asia are underway, overall care delivery remains fragmented and diverse, eg, in terms of medical electronic record sharing and availability, patient registries, and empowerment of primary health care providers to handle chronic illnesses. The primary care sector requires more robust and effective initiatives targeted at specific diseases, particularly chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, depression, and dementia. This can be achieved through integrated care – a health care model of collaborative care provision. For successful implementation of integrated care policy, key stakeholders need a thorough understanding of the high-risk patient population and relevant resources to tackle the imminent population demographic shift due to the extremely rapid rate of increase in the aging population in Asia.
Keywords: Asia, aging, integrated health care, primary care
Integrated care health systems: Introduction
In medicine, the “integrated care” model refers to practice that seeks to improve patients’ health and experience from health care delivery systems.1,2 However, according to the World Health Organization (WHO), there is no existing unifying definition for integrated care.2 This is because of “the polymorphous nature of integrated care itself” (WHO 2016, Page 3, Line 6).2 According to the WHO, the vision of people-centered integrated health care is to provide the following: 1) equal access to health care service of quality (universal health coverage); 2) individualized services that cater to patients’ need and preferences; 3) coordinated services that facilitate comprehensiveness, safety, effectiveness, timeliness, and efficiency across the continuum of health care; and 4) supportive working environments with motivated and competent health care workers.3 Though still controversial in its definition and implementation, the benefits of integrated care have been widely acknowledged and it has been adapted extensively in North America and Europe, especially for the management of patients with chronic diseases.4–7
Rapidly aging populations, as well as the increased burden of patients with chronic conditions and complex needs, call for health systems with comprehensive care.8 This requires not only good coordination between interdisciplinary health providers to reduce existing fragmentation of care, but also effective changes in funding and policy models.9,10 To align with the vision, five key strategies for implementation have been suggested by the WHO: 1) engaging and empowering the population, 2) reinforcing accountability and governance, 3) adapting a suitable care model, 4) coordinating services within and between sectors, and 5) building a conducive environment.2
Methodology
An Advisory Board Meeting on “Integrated Care” health systems for “Individualized” patient care in Asia was held on June 2, 2018, in Singapore. The meeting aimed to define and document significant unmet needs for care integration, share best practices and capabilities in various countries in Asia, and generate ideas and actions for change. The meeting featured presentations on integrated care programs being implemented in countries represented at the meeting, including the Primary Care Networks system in Singapore; service delivery networks, the family medicine residency training program, and the privately funded Family Doctor program in the Philippines; the Gwangmyeong project in Korea; and an integrated system-based program and individualized service plan for chronic care in Thailand. This article is based on discussions during that meeting.
Literature search methodology
An electronic search of PubMed and Google Scholar was conducted to source relevant articles in English language using a combination of MeSH terms and keywords including “Integrated care health systems”, “clinical practice in Asia”, “patient registries”, “burden of disease in Asia”, “primary care practice in Asia”, “aging population in Asia”, and “universal health coverage in Asia”. Relevant articles included randomized controlled trials, surveillance, outcome studies, and expert opinions. Bibliographies of relevant articles were manually screened to broaden the literature search. No restrictions were set with respect to the year or type of publication.
Burden of aging population and population demographics shift in Asia
According to the WHO, there are more than 400 million people around the world with insufficient access to basic health care. When this is combined with increased life expectancy and high chronic disease prevalence, there is a need for long-term comprehensive care and interventions.3 It has been widely recognized that a population-based health approach is the right strategy to maximize benefits and improve performance of health care systems.11,12
Globally, the proportion of people aged >60 years will approximately double from 12% to 22% between 2015 and 2020.3 By 2050, 80% of the older population will be residing in low- and middle-income nations.3 This trend is even more obvious in Asia. In 2016, around 12.4% of the population in this region was ≥60 years of age.13 By 2050, the proportion is projected to increase to approximately 25% (around 1.3 billion people).13 In addition, developing nations in Asia are experiencing a much more rapid rate of population aging compared with developed nations (Table 1).
Table 1.
Aging pace in different countries across the world
| Countries | Aging pace (years)a |
|---|---|
| France | 115 |
| Sweden | 85 |
| China | 25 |
| Singapore/Thailand | 22 |
| Vietnam | 19 |
Notes: France and Sweden, which are developed countries from the west, have taken ~80–120 years to become an aged society. However, both developing and developed countries from the east will turn into an aged society in much more rapid time, approximately four to five times faster. This means that countries in Asia will have much less time to adapt to this drastic demographic shift.
Aging pace refers to the time needed to shift from an aging society to an aged society. Created from United Nations ESCAP.13
With increasing average life expectancy as a result of better health care and technology advancements, the increase in proportion and absolute number of the oldest old (those aged ≥80 years) also adds additional burden to the current health care system. In 2016, this group accounted for ~1.5% of the population in Asia (68 million people).13 By 2050, it is projected that the proportion will increase to 5% (258 million people; Table 2).13 This rise will have serious implications for both appropriate and long-term health care provision. It is logical that these rapid changes in population demographics in Asia warrant immediate action by policy makers to quickly address the unmet needs of appropriate and long-term health care for the aged population.
Table 2.
Absolute and proportion of aged population (≥60 years old and ≥80 years old) across the world for the year 1950, 2000, and 2050
| Major regions | Population ≥60 years old | Population ≥80 years old | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absolute population (millions) | Proportion of total population (%) | Absolute population (millions) | Proportion of total population (%) | |||||||||
| 1950 | 2000 | 2050 | 1950 | 2000 | 2050 | 1950 | 2000 | 2050 | 1950 | 2000 | 2050 | |
| World | 205 | 606 | 1,907 | 8 | 10 | 21 | 14 | 69 | 377 | 7 | 11 | 20 |
| More developed regionsa | 95 | 232 | 394 | 12 | 19 | 32 | 9 | 37 | 113 | 9 | 16 | 29 |
| Less developed regionsb | 110 | 375 | 1,514 | 6 | 8 | 20 | 5 | 32 | 265 | 5 | 9 | 17 |
| Africa | 12 | 40 | 183 | 5 | 5 | 10 | 1 | 3 | 20 | 5 | 7 | 11 |
| Asia | 95 | 322 | 1,191 | 7 | 9 | 23 | 4 | 29 | 225 | 5 | 9 | 19 |
| Europe | 66 | 147 | 222 | 12 | 20 | 35 | 6 | 21 | 60 | 8 | 14 | 27 |
| Latin America and the Caribbean | 10 | 42 | 184 | 6 | 8 | 24 | 1 | 5 | 38 | 7 | 12 | 21 |
| Northern America | 21 | 51 | 117 | 12 | 16 | 26 | 2 | 10 | 33 | 9 | 20 | 28 |
| Oceania | 1 | 4 | 11 | 11 | 13 | 25 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 9 | 17 | 25 |
Notes: Both concepts are derived from the socioeconomic status of the nations. In Asia, when projected to 2050, the proportion of ≥60 years old population will account for approximately a quarter of the total population. The proportion of the oldest old “≥80 years old population” will also reach approximately a fifth of the total population by 2050, translating to about 225 million people. More immediate actions needed to be done to cater to the unmet needs of our massively aged population.
More developed regions refer to nations in Europe, Northern America, Australia, New Zealand, and Japan.
Less developed regions consist of all nations in Africa, Asia (except for Japan), Latin America, the Caribbean. Data from United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs/Population Division.14
Integrated care systems for efficient and effective health management
Progress toward improved coordination across stakeholders in health care settings can enable better continuity of care and patient services.1,15 There is an established association between integrated care and a decrease in hospital admissions and readmission incidents, reduced average hospital stay, improvement in patient adherence to treatment, increased quality of life, and reduced health care expenditure (Figure 1).5,6,16 These benefits extend not only to adult patients with chronic disease, but also to the elderly population.5,17,18 Furthermore, admission to either hospital or a nursing home occurs much later and less often in elderly patients managed in an integrated care setting. In developing regions such as Africa and Asia, integrated care also has recognized benefits and is recommended to help relieve the health care burden.19–21
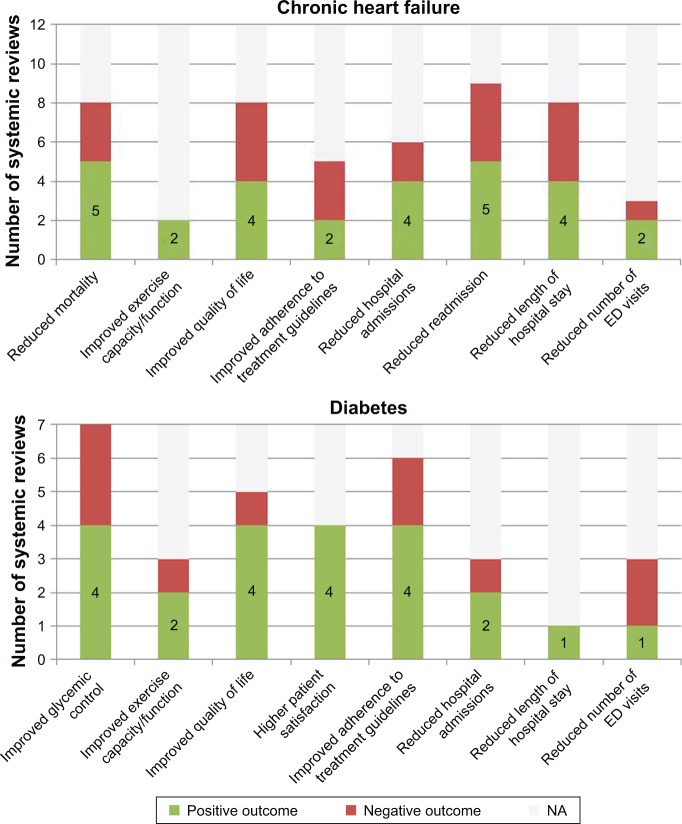
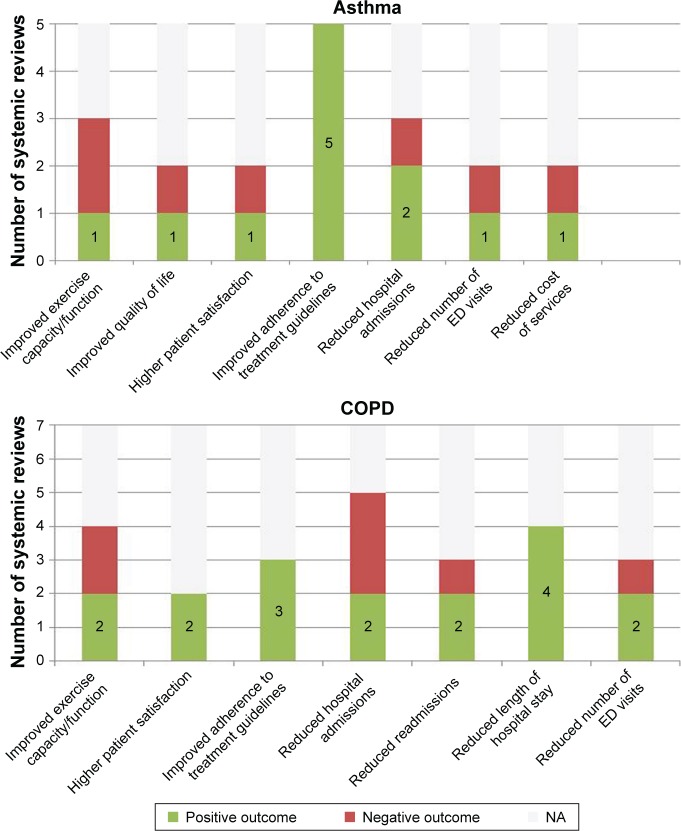
Figure 1.
Overall results from 27 systematic reviews on effects of integrated care models for adults with chronic conditions.
Notes: Positive outcome: reviews showing positive trends or significant (P<0.05) improvements associated with integrated care models. Negative outcome: reviews showing insignificant (P<0.05) improvements associated with integrated care models. NA: reviews that do not examine this outcome. Twenty-seven systematic reviews were identified for the meta-analysis of the integrated care conditions for adults with chronic conditions, including chronic heart failure (12 reviews), diabetes mellitus (7 reviews), COPD (7 reviews), and asthma (5 reviews). Most reviews show that integrated care models do have beneficial impacts on the clinical and functions results for the patients, the patients’ overall experience, care process, and health care resources usage. Specifically, there is a significant reduction in hospital admission and readmission for patients with chronic heart failure and diabetes, improvement in adherence to treatment guidelines in patients with diabetes, COPD, and asthma, and increase in quality of life in patients with diabetes. Data from Martínez-González et al.6
Abbreviations: ED, emergency department; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Burden of disease and health care systems across Asia
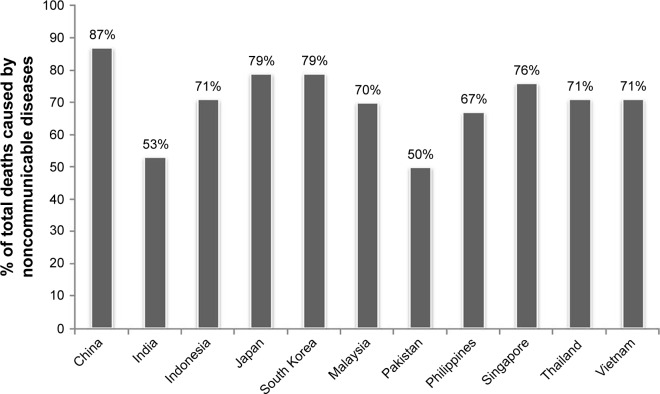
One consequence of the rapidly aging population in Asia is the increasing trend of noncommunicable diseases (NCDs). Mortality due to NCDs is increasing, accounting for >70% of deaths across Asia since 2014 (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Percentage of total deaths caused by non-communicable diseases in Asia in 2014.
Notes: Noncommunicable diseases refer to diseases or medical conditions that are not caused by any infectious agents. Also referred to as chronic diseases, they generally have long duration with slow progression and fall under four main types: cardiovascular diseases, chronic respiratory diseases, cancer, and diabetes. Noncommunicable diseases are the leading cause of death worldwide. In Asia, the mortality percentage caused by noncommunicable diseases stands at the average of 55%, and it is still on the rise. This rise affects both developed and developing regions alike. Data from WHO.22
This increasing trend for death from NCDs is reflected by the top five diseases in terms of mortality burden across Asian countries. Within the region, cardiovascular disease and cancer are consistently among the top five causes of death in all Asian countries.22 Chronic respiratory diseases and diabetes are also in the top five diseases in terms of mortality burden in the majority of Asian countries.22 Other leading causes of mortality, such as communicable diseases, injuries, cerebrovascular diseases, and Alzheimer’s disease, vary from country to country.22
In developed regions, such as China, Singapore, South Korea, Japan, and Hong Kong, major concerns relate to the aging population, falling birth rates, rising costs, and rising rates of NCDs.23 In less developed regions, such as India, Indonesia, Philippines, Thailand, and Vietnam, poverty and inequality are still significant issues.24 The key concerns are the triple disease burden, namely existing communicable diseases, emerging and re-emerging communicable diseases, and the increasing prevalence of noncommunicable, lifestyle-related diseases.25,26 Other major health care system constraints in these countries relate to poor accessibility, availability, and affordability of health care, characterized by the nonavailability of drugs, lack of advanced laboratory facilities and equipment, a severely constrained health workforce, poorly funded public health systems, unequal distribution of health care resources leading to overburdened public institutions, and poor health care delivery mechanisms.27
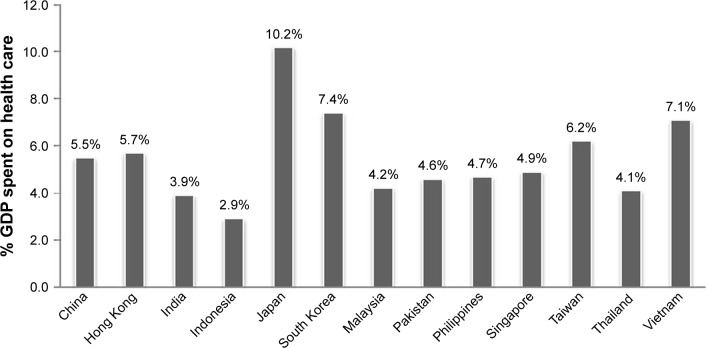
It is also important to note the wide variations in health care policies and reimbursement systems across Asia. The percentage of gross domestic product (GDP) spent on health care differs between countries (Figure 3), but averages to 5.5%. In general, the percentage of GDP spent on health care in Asia is less than in Europe and North America.
Figure 3.
Percentage GDP spent on health care across different countries in Asia.
Notes: Japan and South Korea generally have the highest spending on health care. Across the region, the average percentage spending on health care is 5.5% of total GDP spent. Data from Hong Kong are from 2016. Data from the rest of the countries are from 2014. Data from various sources. Hong Kong,28 India,29 Taiwan,30 other countries.31
Abbreviation: GDP, gross domestic product.
The reimbursement system in Asia mainly consists of government assistance, out-of-pocket and prepaid private spending. For more developed countries with established health care systems and better government reimbursements, the reimbursement system aims to transition toward providing universal health coverage. Japan has now nearly achieved universal health coverage under two insurance schemes, with long-term care insurance to cater to older patients living with morbidities.32 South Korea also aims to implement universal health coverage; however, cost sharing is generally quite high, resulting in people still relying largely on private insurance.33 Thailand achieved universal health coverage in 2002 with three public health insurance schemes covering the entire population.34 China also appears to be working toward a universal health care approach.35 In Indonesia, the universal health scheme was started in 2014 and is expected to cover the whole population in 2019.26 In the Philippines, PHILHEALTH (the national insurance agency) provides limited support because patients are still liable for substantial copayments.36 There has been a national reform of this system in place under the principles of universal health coverage.
Less developed nations rely on development assistance for health as well as private health insurance due to limited government-assisted reimbursement. Their reimbursement systems are still undergoing transformation to achieve universal health coverage, and out-of-pocket expenses with private health insurance still account for the majority of health care cost. Therefore, low-income patients face greater barriers to adequate health care due to the pressure of out-of-pocket payments in the absence of government reimbursement.33,37
Across Asia, efforts for integration between primary care and hospital care are underway to help relieve the health care burden, especially in the setting of increasing NCD burden. Each country has its own integrated care initiatives based on the local context, such as medical electronic record sharing and availability, patient registries, and empowerment of primary care health providers to handle chronic illness. These initiatives are targeted at specific conditions, which differ between countries, but are mostly aimed at chronic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, depression, and dementia (Table 3).
Table 3.
Integration activities between primary care and hospital care across Asia
| Countries | Integration activities between primary care and hospital care |
|---|---|
| China | • Primary care networks based on community health centers with different models of ownership and managements38–41 |
| Hong Kong | • Integrated diabetes care • The Hong Kong Reference Framework for Preventive Care for Older Adults42 • Unified medical information system23 |
| India | • Diabetes and hypertension via the mWellcare trial43 • Maternal and neonatal outcomes |
| Indonesia | • GERMAS – empowerment of primary care providers26 • Perinatal depression44 • Electronic integrated antenatal care45 |
| Japan | • Long-term care insurance provides institutional, home, and community based benefits under a case manager21,32,46 • Example: dementia care as detailed under “Five-Year Plan for Promotion of Measures Against Dementia (Orange Plan)” |
| South Korea | • Large-scale databases/registries that are tied to the universal health care scheme33 |
| Malaysia | • Limited integration where primary care physicians report lack of communication with peers. Tele-primary care was launched as a potential record-keeping system; limited clinics have it47–49 |
| Philippines | • First Line Diabetes Care Project50 • Introduction of electronic medical records and enforced gatekeeping are part of the government’s plan36 |
| Singapore | • Primary Care Networks initiative51 • Primary Care Dementia Clinic52 |
| Taiwan | • Family Practice Integrated Care Project53 • Integrated Health and Long-term Care Study54,55 |
| Thailand | • CKD trial: ESCORT based on Integrated CKD Care program56 |
| Vietnam | • The MOH’s Direction of Healthcare Activities program is focused on the transfer of skills to lower level hospitals to support community-oriented activities at primary level57 • Health information systems are limited58 |
Notes: Countries across Asian regions have started to try or establish many integrated care activities based on the local context. This can include medical electronic records sharing and availability, patient registries, empowering of primary care health providers to handle chronic illness patients, etc. Most existing integrated care activities aim at chronic diseases and conditions. These initiatives have been proved to be effective in improving patient’s experience and care. Created from various sources (as per cited).
Abbreviations: GERMAS, Gerakan Masyarakat Hidup Sehat/Community Movement for Healthy Life; CKD, chronic kidney disease; ESCORT, Effectiveness of Integrated Care on Delaying Progression stage 3–4 Chronic Kidney Disease in Rural Communities of Thailand; MOH, Ministry of Health.
More efforts toward integration are needed because there is a general lack of integration between public and private services to share the burden of NCDs, and prevention strategies require collaboration of primary and secondary care.47,59
Role of patient registries and clinical indicators in “integrated care health systems”
In integrated care, patient registries are important for medical collaboration and are integral to the seamless exchange of information.60 Put simply, a patient registry comprises records of standardized information related to an individual patient’s diagnosis, treatment, care regimen, and outcomes across multiple sites for comparison and analysis.58 More specifically, a registry refers to a database or collection of records or repository of certain information.61 Generally, patient registries refer to registries specifically used for health-related information, distinguishing them from other types of information record.58,62 As per the WHO definition, a patient registry can be understood as “a file of documents containing uniform information about individual persons, collected in a systematic and comprehensive way, in order to serve a predetermined purpose” (Brooke EM, 1974, Page 2, Lines 14–16).63 The term is often interchangeable with other terms, including outcome registry, disease registry, clinical data registry, or clinical registry.64,65
Patient registries for transforming patient information into improved outcomes
The benefits of patient registries are established and widely acknowledged. They play a pivotal role in population health management, which in turn leads to overall improvement in quality, efficiency, and safety.66 Patient registries promote public reporting, prospective and retrospective observational research, and improvement in both professional development and care service.58 Given their observational nature, registries can provide real-time information on patient outcomes, effectiveness and safety in real-world clinical practice.58 Multidisciplinary collaboration is central to integrated care, and this requires practitioners and health care staff to have a thorough understanding of patients’ needs and status in real time to improve outcomes.1 Centralized real-time data from a patient registry enables appropriately coordinated care that caters to specific patients’ needs.60 This is particularly important in management of chronic conditions and improvement of overall health status in patient populations.60
Patient registries also help to identify variation in practices and outcomes, allowing practitioners and researchers to identify targets for improvement. In addition to monitoring patient outcomes and disease trends, data from registries can also be used to motivate improvements and provide benchmarks to individual GP clinics. Moreover, patient registries can help to provide practitioners and researchers with a comprehensive overview of different patient populations and a better understanding of specific disease characteristics.58,67 Information can be extracted to provide insights into disease incidence, natural course, prognostic factors, appropriate therapeutic regimen and timing, and long-term effects (desired and adverse) for different interventions.67–70
From a patient perspective, patient registries can provide benefits when it comes to regimen decision and tracking, as well as expectation management.71 For example, if a patient registry follows the natural course of a specific disease, it can enable patients to be better informed about their condition from reliable and scientifically accurate sources, and to anticipate progression of their condition.69,70 Sufficient data can also allow practitioners and patients to understand causes of disease, identify the appropriate therapeutic regimen, anticipate potential adverse effects, and provide suitable high-quality care.69,70,72 For different diseases, patients can be informed about the latest treatments and potentially sign up for participation in clinical trials for which they qualify.58
Operation of patient registries in the absence of sophisticated IT systems
Essentially, a patient registry is information management.73,74 With large volumes of data to store, process, tabulate, and analyze, registries require a sophisticated technology system.73,74 However, information technology (IT) infrastructure and literacy across Asia is inconsistent; the strength of IT/technology development and literacy is usually proportional to a nation or region’s development status.75 In addition, electronic medical record (eMR) systems are relatively uncommon in Asian health care settings because many older doctors are not very comfortable with computers and using new technology. This, in combination with the poorly resourced settings, highlights the need for simplified systems for manually transferring handwritten notes into predesigned spreadsheets. It should be noted that while the manual transfer of handwritten case notes to an electronic format carries the potential for human errors, a sophisticated eMR is not necessary to operate a patient registry in a primary care setting. Manual entry is more appropriate for disease-specific registries because the scope is narrower.
Precautions and operations while setting up a registry
Registries differ in size, resources, and scope depending on their purpose and the availability of resources.58 They can involve common vs rare conditions, include extensive or limited data, operate over long or short periods of time, and/or have generous or limited funding.58,76 Thus, the nature of clinical practice needs to be taken into account during the design and implementation of a patient registry.
Ideally, patient registry programs should not be too complicated to operate in the medical setting, yet gather sufficient data to allow care integration and analysis. Registry design should be flexible enough to accommodate additional data, new treatment regimens, expansion to different populations and geographical locations, and to allow expansion into new areas of research if required.58,76 Furthermore, case report forms (CRFs) should be designed alongside registries to ensure they list all relevant parameters to be recorded during patient assessment. For countries with better technology infrastructure, CRFs and registries should ideally be converted to eMRs.
One concern when setting up patient registries is patient privacy and confidentiality. These important factors need to be given high priority from the planning phase right through until data collection and analysis. Data and information security must be in place to secure the highly sensitive confidential data.75 In addition, secondary use of data should be governed by a strict protocol and surveillance to ensure privacy and ethical data handling.75 Access to patient data in the patient registry should be limited to prespecified individuals, with different levels of data access in accordance to their role.
Future directions for implementation of these health systems for rapidly aging population in Asia
Prioritization of patient and clinical pathway for integrations
Despite the holistic nature of integrated care, it is not a system that caters to all.77,78 There is no single integrated care model that suits all settings, contexts, and circumstances.77,78 Specific care settings and specific perspectives need to be taken into consideration when evaluating different integrated care initiatives,1,77 and relevant stakeholders should be engaged at different levels.1,77 High-quality and robust evidence is required to help stakeholders make informed decisions on the development of integrated care.1 The involvement of a variety of stakeholders in implementation of integrated care means that it may take time to realize outcomes and assess the effectiveness of such programs.1,2 Therefore, in the first instance, initiatives should focus on complex and highly prevalent clinical conditions that require urgent attention and have proven effective in other settings.
Given the burden of chronic conditions, particularly NCDs, in Asia (Figure 2), cardiovascular diseases, chronic respiratory diseases, diabetes, and cancer are obviously targets for integrated health care. Indeed, most efforts for integrated care around the world focus on chronic conditions, especially cardiovascular and chronic respiratory diseases, and these have proven successful (Figure 1).20 Therefore, cardiovascular and chronic respiratory conditions would appear to be good starting points for integrated care programs in Asia, and should be prioritized in the region.
Empowering health providers and patients
Integrated care is required when patient needs cannot be met by a single health care professional or medical provider, but instead requires coordinated support from different providers, including both professional and informal care.79 This will involve renegotiation and transformation of current organization and policies, which has major implications for current legislation and funding, professional qualifications, and both management and governance.80 This is a big challenge to overcome. Thus, it is more practical to first address the issue on a smaller scale: the patients, the health care providers, and the community.
A step-wise solution is needed to facilitate the practical implementation of integrated care. Assistance can be provided to empower health care providers and patients, while providing a supportive physical, mental, and social patient-centric environment.81 To align with this, patients should be the main focus, with care built on a multidisciplinary foundation. This can include a wide variety of health care practitioners and individuals, including nurse counselors, care coordinators, patients, and patient family counselors. Given that patient counseling is an integral part of primary care (to promote prevention, awareness, and adherence), nursing and allied health care professionals should be trained to provide this service, thus reducing the burden on doctors. Greater involvement of nonphysician health care professionals will facilitate better understanding of the patient’s perception of disease and allows patients to be more involved in their treatment plan. The patient’s family also plays an important role when it comes to individualized care, and family intervention and family counseling should not be overlooked. Other resources can be utilized if available; eg, a social worker could be assigned to check on patient progress, and to work with families to ensure better patient outcomes.
It is also important that the patient’s perspective is taken into consideration. Integrated care should include care from both health care professionals and other care providers.80 Measures to facilitate more patient involvement can include provision of health cards or a monitoring booklet, or enrollment in a patient registry (if acceptable to the patient and if technology permits). Patients should have individualized records to keep a detailed record of their medical conditions, laboratory test results, and treatments; this will help to actively engage them as participants in the management of their health, and facilitate discussions with doctors across different specialties.
In addition to education materials, patients should have access to an online, commercial-free, balanced, health-information platform that is relevant to local health priorities and ideally could be promoted by doctors. A reliable health care information platform is also a good tool to allow patients and their families to proactively seek information to better understand their disease and its management. This is especially important in the Asian region, where most patients have difficulty accessing reliable sources of information about their health care issues and treatments. Therefore, a regional, independent, online platform should be established to provide patients and physicians with unbiased and balanced information. In the absence of online access, simplified patient education materials are required. Content across all platforms can be independently developed by specialists, validated by professional bodies or societies prior to publication, and promoted by physicians who have a role to direct patients to appropriate medical websites for further information.
Partnerships
Engagement with and assistance from stakeholders that have direct or indirect roles in driving more efficient health care, such as the pharmaceutical industry, nongovernmental organizations (NGOs) and patient groups, can help to reduce some of the strains on the health care system, and empower both health care professionals and patients, especially in resource-poor communities.
Patients and the wider community can develop initiatives to enable a more supportive environment and to effectively highlight the patient perspective to policy makers and researchers. Patients with different conditions, especially rare or chronic diseases such as cancer or diabetes, can come together to establish support groups. These cooperative support groups could play an important role in increasing patients’ proactive involvement in their own health, support other patients, and increase public awareness of their conditions.
There has been considerable support for different initiatives driven by several NGOs around the world. For example, the WHO, United Nations Children’s Fund, and Asian Development Bank are actively involved in enhancing health care in many developing and resource-poor regions of Asia and Africa. Along with updating health statistics in the local context, these NGOs have been successful in driving better and healthier lifestyles for patients through partnerships with local governments, hospitals, and universities. More investment and partnerships are required to drive this informal community-based health care model.
One of the pharmaceutical industry’s priorities relates to medical capability-building with institutions and associations. Thus, they could also be involved by supporting continuing medical education of doctors, nurses, and other allied health professionals to promote best practice principles for integrated care. The pharmaceutical industry also has the capacity to reach out and improve patient education by a variety of means, including patient education materials and support for health information platforms. Collaboration with patient-initiated support groups is another way for industry to empower more patients to manage their health, especially in resource-poor communities.
Conclusion
Immediate appropriate interventions and changes in policy implementation are required to address the projected health care needs of the rapidly aging population in Asia, and manage the demographic shift toward an aging society. This necessitates effective collaboration between not only researchers and policy makers, but also institutions, industries, and communities so that an effective and timely solution to the impending demographic shift in the Asian region can be achieved.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr Chin Kwang Chong and Dr Thuan Wee Koh, Frontier Healthcare Group, Singapore; Dr Weon Young Lee, Department of Preventive Medicine, Hung-Ang University, Republic of Korea; Dr Martha Umali and Dr Rana Palma Mendoza, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of the Philippines, Philippines; Dr Kidaphol Wadhanakul, Bhumirajanagarindra Kidney Institute Hospital, Thailand; and Dr Krishna Suvarnabhumi, Department of Family Medicine and Preventive Medicine, Prince of Songkla University, Thailand, for their valuable insights during the advisory board meeting, which were critical for drafting this article. The authors would also like to thank Tanaya Bharatan, Scientific Communications, Pfizer, for editorial support, and Dr Chandrashekhar N Potkar, Regional Medical Affairs APAC, Pfizer, for his valuable comments during design of the article. The authors sincerely appreciate the timely support for English language editing assistance provided by Nicola Ryan, on behalf of Transform Medical Communications.
Footnotes
Author contributions
All authors were involved in conception, design, analysis, and interpretation of data. All authors were also involved in preparation of the manuscript, revising it for scientific content, gave final approval before its submission for publication, and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Disclosure
This paper was compiled based on discussions during an advisory board meeting on “Integrated Care Health Systems for Individualized Patient Care in Asia” held in Singapore on June 2, 2018, attended by the co-authors and sponsored by Pfizer. None of the authors received any honorarium for the preparation of the article. Dr Vicknesh Welluppillai is an employee of Pfizer. Dr Sajita Setia was an employee of Pfizer at the time the advisory board meeting took place. Ms Thuy Linh Tran underwent indirect patient care pharmacy training for 3 months at Pfizer, Singapore. This publication contains personal views and opinions of authors and no inference should be derived related to their current or previous employers. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
References
- 1.Shaw S, Rosen R, Rumbold B. An overview of integrated care in the NHS: what is integrated care? 2011. [Accessed July 16, 2018]. Available from: https://www.nuf-fieldtrust.org.uk/files/2017-01/what-is-integrated-care-report-web-final.pdf.
- 2.World Health Organization Integrated care models: an overview. 2016. [Accessed July 16, 2018]. Available from: http://www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0005/322475/Integrated-care-models-overview.pdf.
- 3.World Health Organization Framework on integrated, people-centred health services: report by the Secretariat. 2016. [Accessed July 19, 2018]. Available from: http://apps.who.int/gb/ebwha/pdf_files/WHA69/A69_39-en.pdf.
- 4.Ouwens M, Wollersheim H, Hermens R, Hulscher M, Grol R. Integrated care programmes for chronically ill patients: a review of systematic reviews. Int J Qual Health Care. 2005;17(2):141–146. doi: 10.1093/intqhc/mzi016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bernabei R, Landi F, Gambassi G, et al. Randomised trial of impact of model of integrated care and case management for older people living in the community. BMJ. 1998;316(7141):1348–1351. doi: 10.1136/bmj.316.7141.1348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Martínez-González NA, Berchtold P, Ullman K, Busato A, Egger M. Integrated care programmes for adults with chronic conditions: a meta-review. Int J Qual Health Care. 2014;26(5):561–570. doi: 10.1093/intqhc/mzu071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tsiachristas A, Lionis C, Yfantopoulos J. Bridging knowledge to develop an action plan for integrated care for chronic diseases in Greece. Int J Integr Care. 2015;15:e040. doi: 10.5334/ijic.2228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hall P, Weaver L. Interdisciplinary education and teamwork: a long and winding road. Med Educ. 2001;35(9):867–875. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2923.2001.00919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Xyrichis A, Ream E. Teamwork: a concept analysis. J Adv Nurs. 2008;61(2):232–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2648.2007.04496.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Nancarrow SA, Booth A, Ariss S, Smith T, Enderby P, Roots A. Ten principles of good interdisciplinary team work. Hum Resour Health. 2013;11:19. doi: 10.1186/1478-4491-11-19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gullery C, Hamilton G. Towards integrated person-centred healthcare – the Canterbury journey. Future Healthc J. 2015;2(2):111–116. doi: 10.7861/futurehosp.2-2-111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Landon BE, Grumbach K, Wallace PJ. Integrating public health and primary care systems: potential strategies from an IOM report. JAMA. 2012;308(5):461–462. doi: 10.1001/jama.2012.8227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.United Nations ESCAP Ageing in Asia and the Pacific: overview. 2017. [Accessed July 17, 2018]. Available from: https://www.unescap.org/resources/ageing-asia-and-pacific-overview.
- 14.United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs Population Division. Living arrangement of older persons around the world. 2005. [Accessed July 17, 2018]. Available from: http://www.un.org/esa/population/publications/livingarrangement/report.htm.
- 15.RAND Europe National evaluation of the Department of Health’s integrated care pilots. 2012. [Accessed July 17, 2018]. Available from: https://www.rand.org/content/dam/rand/pubs/technical_reports/2012/RAND_TR1164.pdf. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 16.Lars E, Keith B. Complex adaptive systems for management of integrated care. Leadersh Health Serv. 2012;25(1):39–51. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Reed J, Cook G, Childs S, Mccormack B. A literature review to explore integrated care for older people. Int J Integr Care. 2005;5:e17. doi: 10.5334/ijic.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Windham BG, Bennett RG, Gottlieb S. Care management interventions for older patients with congestive heart failure. Am J Manag Care. 2003;9(6):447–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Marais DL, Petersen I. Health system governance to support integrated mental health care in South Africa: challenges and opportunities. Int J Ment Health Syst. 2015;9(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s13033-015-0004-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sun X, Tang W, Ye T, Zhang Y, Wen B, Zhang L. Integrated care: a comprehensive bibliometric analysis and literature review. Int J Integr Care. 2014;14:e017. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Morikawa M. Towards community-based integrated care: trends and issues in Japan’s long-term care policy. Int J Integr Care. 2014;14:e005. doi: 10.5334/ijic.1066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.World Health Organization Noncommunicable diseases country profiles 2014. 2014. [Accessed July 19, 2018]. Available from: http://www.who.int/nmh/publications/ncd-profiles-2014/en/
- 23.Kong X, Yang Y, Gao J, et al. Overview of the health care system in Hong Kong and its referential significance to mainland China. J Chin Med Assoc. 2015;78(10):569–573. doi: 10.1016/j.jcma.2015.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Balisacan A, Edillon R, Faye A, Piza S. Rural poverty in Southeast Asia: issues, policies, and challenges. Asian J Agric Dev. 2005;2:25–38. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Pati S, Sharma K, Zodpey S, Chauhan K, Dobe M. Health promotion education in India: present landscape and future vistas. Glob J Health Sci. 2012;4(4):159–167. doi: 10.5539/gjhs.v4n4p159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Moeloek NF. Indonesia national health policy in the transition of disease burden and health insurance coverage. Med J Indones. 2017;26(1):3. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Mohanan M, Hay K, Mor N. Quality of health care in India: challenges, priorities, and the road ahead. Health Aff (Project Hope) 2016;35(10):1753–1758. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2016.0676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Department of Health The Government of the Hongkong Special Administrative Region. Health facts of Hongkong. 2018. [Accessed July 17, 2018]. http://www.dh.gov.hk/english/statistics/statistics_hs/files/Health_Statistics_pamphlet_E.pdf.
- 29.Ministry of Health and Family Welfare Government of India. National Health Accounts Estimates for India. 2017. [AccessedJuly 17, 2018]. https://mohfw.gov.in/sites/default/files/National%20Health%20Accounts%20Estimates%20Report%20201415.pdf.
- 30.The Commonwealth Fund International Health Care System Profiles: The Taiwan Health Care System. 2018. [Accessed July 19, 2018]. Available from: https://international.commonwealthfund.org/countries/taiwan/
- 31.World Health Organization. WHO Country Profiles. 2018. [Accessed July 19, 2018]. Available from: http://www.who.int/countries/en/
- 32.Health and Global Policy Institute Japan Health Policy NOW. 2018. [Accessed July 19, 2018]. Available from: http://japanhpn.org/en/healthpolicy/
- 33.Kwon S, Busse R. South Korea: an interesting case to study. Health Policy. 2016;120(6):577–579. doi: 10.1016/j.healthpol.2016.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Thammatacharee NO, Suphanchaimat R, Patcharanarumol W. Thailand’s universal health coverage scheme. Econ Polit Wkly. 2012;47(8):53–57. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Dai G, Deng F, Ramaprasad A, Syn T. China’s national health policies: an ontological analysis. Online J Public Health Inform. 2016;8(3):e196. doi: 10.5210/ojphi.v8i3.7052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Republic of Philippines: Department of Health Philippine Health Agenda: Healthy Philippines 2022. 2016. [Accessed July 19, 2018]. Available from: https://www.doh.gov.ph/philippine_health_agenda.
- 37.World Health Organization . Regional Office for the Western Pacific. The Philippines Health System Review 1. Manila: WHO Regional Office for the Western Pacific 2011; [Accessed July 20, 2018]. Available from: http://iris.wpro.who.int/handle/10665.1/5536. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hu R, Liao Y, du Z, Hao Y, Liang H, Shi L. Types of health care facilities and the quality of primary care: a study of characteristics and experiences of Chinese patients in Guangdong Province, China. BMC Health Serv Res. 2016;16(a):335. doi: 10.1186/s12913-016-1604-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wang HH, Wong SY, Wong MC, et al. Patients’ experiences in different models of community health centers in southern China. Ann Fam Med. 2013;11(6):517–526. doi: 10.1370/afm.1545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Shi L, Lee DC, Liang H, et al. Community health centers and primary care access and quality for chronically-ill patients – a case-comparison study of urban Guangdong Province, China. Int J Equity Health. 2015;14(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s12939-015-0222-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Qian Y, Hou Z, Wang W, Zhang D, Yan F. Integrated care reform in urban China: a qualitative study on design, supporting environment and implementation. Int J Equity Health. 2017;16(1):185. doi: 10.1186/s12939-017-0686-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ng IHY, Cheung KKT, Yau TTL, Chow E, Ozaki R, Chan JCN. Evolution of diabetes care in Hong Kong: from the Hong Kong Diabetes Register to JADE-PEARL Program to RAMP and PEP Program. Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(1):17–32. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2018.33.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Jha D, Gupta P, Ajay VS, et al. Protocol for the mWellcare trial: a multicentre, cluster randomised, 12-month, controlled trial to compare the effectiveness of mWellcare, an mHealth system for an integrated management of patients with hypertension and diabetes, versus enhanced usual care in India. BMJ Open. 2017;7(8):e014851. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-014851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Surjaningrum ER, Minas H, Jorm AF, Kakuma R. The feasibility of a role for community health workers in integrated mental health care for perinatal depression: a qualitative study from Surabaya, Indonesia. Int J Ment Health Syst. 2018;12:27. doi: 10.1186/s13033-018-0208-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Markam H, Hochheiser H, Kuntoro K, Notobroto HB. Exploring midwives’ need and intention to adopt electronic integrated antenatal care. Perspect Health Inf Manag. 2018;15(Winter):1e. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Tsutsui T. Implementation process and challenges for the community-based integrated care system in Japan. Int J Integr Care. 2014;14:e002. doi: 10.5334/ijic.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Mimi O, Tong S, Nordin S, et al. A comparison of morbidity patterns in public and private primary care clinics in Malaysia. Malays Fam Physician. 2011;6(1):19–25. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Sellappans R, Lai PS, Ng CJ. Challenges faced by primary care physicians when prescribing for patients with chronic diseases in a teaching hospital in Malaysia: a qualitative study. BMJ Open. 2015;5(8):e007817. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-007817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Lim HM, Sivasampu S, Khoo EM, Mohamad Noh K. Chasm in primary care provision in a universal health system: findings from a nationally representative survey of health facilities in Malaysia. PLoS One. 2017;12(2):e0172229. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ku GM, Kegels G. Integrating chronic care with primary care activities: enriching healthcare staff knowledge and skills and improving glycemic control of a cohort of people with diabetes through the First Line Diabetes Care Project in the Philippines. Glob Health Action. 2014;7:25286. doi: 10.3402/gha.v7.25286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Ministry of Health: Singapore Ministry of Health 2018 Budget Initiatives. 2018. [Accessed November 22, 2018]. Available from: https://www.moh.gov.sg/our-healthcare-system/healthcare-services-and-facilities/primary-care-networks.
- 52.Saxena N, George PP, Teo KW, et al. Evaluation of an integrated primary care-led dementia shared care program in Singapore: an effectiveness and cost-effectiveness study. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2018;18(3):479–486. doi: 10.1111/ggi.13196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Jan CF, Chiu TY, Chen CY, Guo FR, Lee MC. A 10-year review of health care reform on Family Practice Integrated Care Project-Taiwan experience. Fam Pract. 2018;35(4):352–357. doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmx111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Lee M-C. Integrated care and training in family practice in the 21st century: Taiwan as an example. Fam Med Community Health. 2016;4(1):57–59. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Glavin Y-FW. Integrated health and long-term care in Taiwan. Int J Integr Care. 2017;17(5):A94. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Jiamjariyapon T, Ingsathit A, Pongpirul K, et al. Effectiveness of integrated care on delaying progression of stage 3–4 chronic kidney disease in rural communities of Thailand (ESCORT study): a cluster randomized controlled trial. BMC Nephrol. 2017;18(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12882-016-0414-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Takashima K, Wada K, Tra TT, Smith DR. A review of Vietnam’s healthcare reform through the Direction of Healthcare Activities (DOHA) Environ Health Prev Med. 2017;22(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s12199-017-0682-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.AHRQ Methods for Effective Health Care . In: Registries for Evaluating Patient Outcomes: A User’s Guide. Gliklich RE, Dreyer NA, Leavy MB, editors. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Ariffin F, Ramli AS, Daud MH, et al. Feasibility of implementing chronic care model in the Malaysian public primary care setting. Med J Malaysia. 2017;72(2):106–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Liaw S-T, Taggart J, Yu H, Rahimi A. Electronic health records and disease registries to support integrated care in a health neighbourhood: an ontology-based methodology. AMIA Summits Transl Sci Proc. 2014;2014:50–54. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Merriam-Webster Webster’s English Dictionary. 2018. [Accessed July 20, 2018]. Available from: https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/registry.
- 62.World Federation of Hemophilia Benefits of a national patient registry: Fact Sheet. 2007. [Accessed July 19, 2018]. Available from: http://www1.wfh.org/publication/files/pdf-1381.pdf.
- 63.Brooke EM. The Current and Future Use of Registers in Health Information Systems. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1974. [Accessed July 19, 2018]. Publication No. 8. Available from: http://www.who.int/iris/handle/10665/36936. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Dokholyan RS, Muhlbaier LH, Falletta JM, et al. Regulatory and ethical considerations for linking clinical and administrative databases. Am Heart J. 2009;157(6):971–982. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2009.03.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Hammill BG, Hernandez AF, Peterson ED, Fonarow GC, Schulman KA, Curtis LH. Linking inpatient clinical registry data to Medicare claims data using indirect identifiers. Am Heart J. 2009;157(6):995–1000. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2009.04.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Wright A, Mcglinchey EA, Poon EG, Jenter CA, Bates DW, Simon SR. Ability to generate patient registries among practices with and without electronic health records. J Med Internet Res. 2009;11(3):e31. doi: 10.2196/jmir.1166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Trotter JP. Patient registries: a new gold standard for “real world” research. Ochsner J. 2002;4(4):211–214. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Data Plus Research Top benefits of patient registries. 2017. [Accessed July 19, 2018]. Available from: https://www.dataplus-research.com/top-benefits-of-patient-registries/
- 69.Durborow M, Aljallad K, Call J, Menos M, Scherzer NJ. The benefits of patient-centered patient registries. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(15_suppl):e21625–e21625. [Google Scholar]
- 70.Hoque DME, Kumari V, Hoque M, Ruseckaite R, Romero L, Evans SM. Impact of clinical registries on quality of patient care and clinical outcomes: a systematic review. PLoS One. 2017;12(9):e0183667. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0183667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Freeman JV, Simon DN, Go AS, et al. Outcomes Registry for Better Informed Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation (ORBIT-AF) Investigators and Patients Association between atrial fibrillation symptoms, quality of life, and patient outcomes. Results from the outcomes registry for better informed treatment of atrial fibrillation (ORBIT-AF) Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2015;8(4):393–402. doi: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.114.001303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Williams AM, Allingham RR, Beckwith HS, Liu PJ, Santiago-Turla C, Muir KW. Patient and family attitudes about an eye donation registry for research. Curr Eye Res. 2013;38(9):945–951. doi: 10.3109/02713683.2013.800890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.World Health Organization . International Agency for Research on Cancer. Cancer Registration: Principles and Methods. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 1991. [Accessed July 17, 2018]. http://www.iarc.fr/en/publications/pdfs-online/epi/sp95/index.php. [Google Scholar]
- 74.Workman TA. AHRQ Methods for Effective Health Care Engaging Patients in Information Sharing and Data Collection: The Role of Patient-Powered Registries and Research Networks. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Stone SF. Asia’s infrastructure challenges: issues of institutional capacity. ADBI working paper series. 2008. [Accessed November 22, 2018]. Available from: https://www.adb.org/sites/default/files/publication/155981/adbi-wp126.pdf.
- 76.Somanath M, Nair A, Mohanty R, Barick U, Gowda A, Patil A. Good practices in the conduct of a patient registry. Int J Med Res Health Sci. 2016;5(4):22–26. [Google Scholar]
- 77.Lyngsø AM, Godtfredsen NS, Høst D, Frølich A. Instruments to assess integrated care: a systematic review. Int J Integr Care. 2014;14:e027. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Béland F, Hollander MJ. Integrated models of care delivery for the frail elderly: international perspectives. Gac Sanit. 2011;25(Suppl 2):138–146. doi: 10.1016/j.gaceta.2011.09.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Fabbricotti IN. Integrated care in Europe: description and comparison of integrated care in six EU countries. Int J Integr Care. 2003;3(4):e05. [Google Scholar]
- 80.Nies H. Communities as co-producers in integrated care. Int J Integr Care. 2014;14:e022. doi: 10.5334/ijic.1589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Huber M, Knottnerus JA, Green L, et al. How should we define health? BMJ. 2011;343:d4163. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d4163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]