Abstract
Background: The American Medical Association (AMA) and National Institutes of Health (NIH) recommend that patient education materials be written at no higher than a sixth-grade reading level. Methods: We examined 100 online educational materials for the 10 hand conditions most commonly treated by hand surgeons, as reported by the American Society for Surgery of the Hand. The listed conditions were carpal tunnel syndrome, basal joint arthritis of the thumb, de Quervain syndrome, Dupuytren’s contracture, ganglion cysts, hand fractures, trigger finger, extensor tendon injuries, flexor tendon injuries, and mallet finger. Following a Google search for each condition, we analyzed the 10 most visited websites for each disorder utilizing the Flesch-Kincaid formula. Results: The average grade reading level of the 100 websites studied was 9.49 with a reading ease of 53.03 (“fairly difficult high school”). Only 29% of the websites were at or below the national average of an eighth-grade reading level. Carpal tunnel syndrome had the highest average grade reading level at 10.32 (standard deviation: 1.52), whereas hand fractures had the lowest at 8.14 (2.03). Every hand condition in this study had an average readability at or above the ninth-grade reading level. Conclusions: The most frequently accessed materials for common maladies of the hand exceed both the readability limits recommended by the AMA and NIH, and the average reading ability of most US adults. Therefore, the most commonly accessed websites pertaining to hand pathology may not be comprehended by the audience for which it is intended.
Keywords: readability, ASSH, Flesch-Kincaid, Google, hand conditions, reading level
Introduction
Traditionally, the patient-to-hand surgeon interaction has been a patriarchal relationship in which the care provider disseminates information and treatment options based on the patient’s medical history and physical exam. However, with the advent of the Internet, patients are now able to learn about their symptoms and diagnosis outside of the physician’s office.7,21 Patients’ increased access encourages autonomy but poses unique challenges to physicians. Increased access to information on the Internet has also led to patients sharing less information with their physician, and even fewer office visits as the information on the web is often used to supplant the in-office visit.4,9,19 Due to the evolving dynamic between the patient and orthopaedic surgeon, there has been an emphasis to provide patients with written or electronic material to enrich their understanding of their condition and the available treatment options.
The value of online patient education material is dependent on the readers’ ability to understand the information that is presented. An objective way of assessing the effectiveness of online patient educational materials is by grading their readability. Readability is defined as the grade level of school one must complete to comprehend the text in a passage and is an indirect determinant of a person’s comprehension of health information.2,18,19,22 Although it may be intuitive to assume that an individual’s reading level is synonymous with the highest level of education attained, it is in fact its own entity, with most people reading at a level that is 5 grades lower than their highest level of scholastic achievement.2,5,19
Studies have traditionally utilized the Flesch-Kincaid (FK) grading scale to assess the readability of online orthopaedic patient education materials, which has consistently documented a disparity between the national average eighth-grade reading level and the available online patient educational material.8,18 A recent US literacy survey found that nearly half of the US population is “functionally illiterate,” less than fifth-grade reading level, or “marginally illiterate,” sixth- to eighth-grade reading level, despite the fact that 25% of these individuals graduated from high school. Due to this startling statistic, several prominent health organizations, including the American Medical Association (AMA) and National Institutes of Health (NIH), have recommended that written patient education materials have a readability score no higher than the sixth-grade level to have the desired effect of improving patient’s health literacy.1,5,9,18
Previous studies have described the quality and readability of online patient education materials from specific websites, based on specific conditions and search terms. We utilized this model and chose to assess the quality of information available on the Internet of the 10 most common hand conditions according to the American Society for Surgery of the Hand (ASSH). This list of the most common conditions hand surgeons treat encompassed carpal tunnel syndrome, basal joint arthritis of the thumb, de Quervain syndrome, Dupuytren’s contracture, ganglion cysts, hand fractures, trigger finger, extensor tendon injuries, flexor tendon injuries, and mallet finger. We hypothesized that the reading level of the most accessed websites of these common hand ailments would be well above the recommended sixth-grade reading level given the complexity of the pathology and treatment plans of these disorders.
Materials and Methods
The materials needed for this study were a computer with Internet access, Microsoft word, and Microsoft Excel programs. Each of the 10 hand conditions were entered into the search engine, Google, as they appeared on the ASSH website: “carpal tunnel syndrome,” “arthritis - base of the thumb,” “de Quervain syndrome,” “Dupuytren’s disease,” “extensor tendon injuries,” “flexor tendon injuries,” “ganglion cysts,” “hand fractures,” “mallet finger,” and “trigger finger.” Thus, following a Google search for each condition, we selected and analyzed the 10 most visited websites for each disorder. In total, there were 100 patient education entries, which were analyzed for grade-level readability using the FK formula, a widely used and validated tool to evaluate the text reading level. The formulas of the FK grade reading level, 0.39 × (average number of words per sentence) + 11.8 × (average number of syllables per word) − 15.59, and FK reading ease, 206.835 − 1.015 × (average number of words per sentence) − 84.6 × (average number of syllables per word), were initially developed by the US Military, and thus have been the focus of research and have been validated extensively.12,15,19 The practicality and applicability of the FK grade formula has further enhanced its role in assessing readability as this formula has been incorporated into many word processors, which allow the calculation to be completed with a simple set of key strokes in a matter of seconds.19
The readability for each website was performed after skeletonizing each entry of all content but written text, and pasting it into the Microsoft Word 2011 Document program using MAC. The text was then highlighted, and the “Spelling and Grammar” function was activated with the “Show Readability Statistics” option enabled. Therefore, following the spelling and grammar check, the FK grade reading level of the text was automatically calculated by Microsoft Word, and the data were subsequently entered into Microsoft Excel for analysis.
Interpretations
The FK analysis gives us 2 useful metrics: the FK grade level and the FK reading ease. The first is the FK grade-level score, which is the grade level one must complete to comprehend a given text. If the score for a given website ended in a decimal 0.4 or lower, it was rounded down to the grade level below, and if the score was 0.5 or above, it was rounded up to the next grade. For example, an FK grade level score of 6.32 was considered meeting sixth-grade reading level criteria, whereas a score of 7.61 was interpreted to exceed the seventh grade and meet the eighth-grade reading level. As for the FK reading ease, the higher the score, the easier the text is to comprehend. This score can be interpreted as follows:
0-29: Very difficult postgraduate
30-49: Difficult college
50-59: Fairly difficult high school
60-69: Standard eighth to ninth grade
70-79: Fairly easy seventh grade
80-89: Easy fifth to sixth grade
90-100: Very easy fourth to fifth grade.
Results
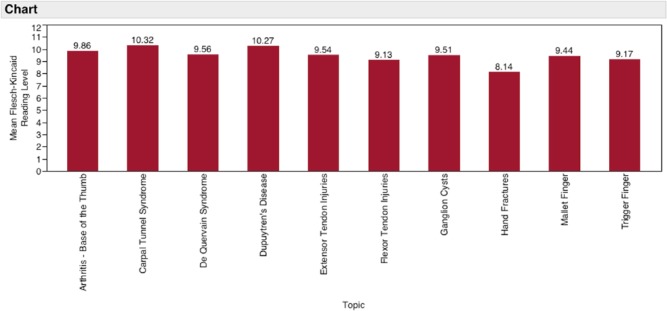
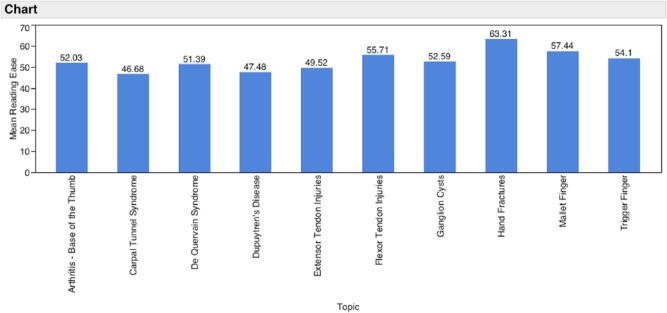
Figure 1 shows the distribution of average FK grade reading level of the 10 hand conditions analyzed in this study. The average readability of all conditions combined was 9.49. Figure 2 shows the distribution of average FK reading ease with a combined average of 53.03. Carpal tunnel syndrome had both the lowest average reading ease and highest grade reading level with scores of 46.8, and 10.32, respectively, while hand fractures had the highest reading ease at 63.31, and the lowest average grade reading level at 8.14—still above the recommended sixth-grade reading level. Every other hand condition in this study had an average readability at or above the ninth-grade reading level. Table 1 displays each website analyzed with its corresponding FK scores.
Figure 1.
Mean Flesch-Kincaid grade level by condition.
Figure 2.
Mean Flesch-Kincaid reading ease by condition.
Table 1.
Flesch-Kincaid Scores and Sources.
Note. NIH = National Institutes of Health; NHS = National Health Service; UCSF = University of California, San Francisco.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
The FK grade reading level of the 10 most visited websites for carpal tunnel syndrome were collected with a mean grade reading level of 10.32 and a standard deviation of 1.52. Not one of the carpal tunnel syndrome websites were at the recommended sixth-grade reading level, and only 2 of the websites were at or below the eighth-grade reading level, which is the national average. The average of the FK reading ease scores was 46.8, interpreted as “difficult college.”
Arthritis - Base of the Thumb
The FK grade reading level of the 10 most visited websites for thumb basal joint arthritis had a mean grade reading level of 9.86 with a standard deviation of 1.48. Not one website was at the recommended sixth-grade reading level, and 1 site was at or below the eighth-grade reading level. The average of the FK reading ease scores was 52.03, interpreted as “fairly difficult high school.”
De Quervain Syndrome
The FK grade reading level of the 10 most visited websites for de Quervain syndrome had a mean of 9.56 with a standard deviation of 1.88. None of the websites met the recommended sixth-grade reading level, and 3 sites were at or below the eighth-grade reading level. The average of the FK reading ease scores was 51.39, interpreted as “fairly difficult high school.”
Dupuytren’s Disease
The FK grade reading level of the 10 most visited websites for Dupuytren’s disease had a mean of 10.27 with a standard deviation of 1.33. Not one website was at the recommended sixth-grade reading level, and 1 site was at or below the eighth-grade reading level. The average of the FK reading ease scores was 47.48, interpreted as “difficult college.”
Extensor Tendon Injuries
The FK grade reading level of the 10 most visited websites for extensor tendon injuries had a mean grade reading level of 9.54 with a standard deviation of 2.24. Two of the sites met the recommended sixth-grade reading level, and 3 of the sites were at or below the eighth-grade reading level. The average of the FK reading ease scores was 49.52, interpreted as “fairly difficult high school.”
Flexor Tendon Injuries
The FK grade reading level of the 10 most visited websites for flexor tendon injuries had a mean of 9.13 with a standard deviation of 2.12. None of the websites met the recommended sixth-grade reading level; however, 5 out of the 10 websites met the national average of the eighth-grade reading level. The average of the FK reading ease scores was 55.71, interpreted as “fairly difficult high school.”
Ganglion Cysts
The FK grade reading level of the 10 most visited websites for ganglion cysts had a mean of 9.51 with a standard deviation of 1.66. Not one of the websites met the recommended sixth-grade reading level, and 2 of the websites were at or below the eighth-grade reading level. The average of the FK reading ease scores was 52.59, interpreted as “fairly difficult high school.”
Hand Fractures
The FK grade reading level of the 10 most visited websites for hand fractures had a mean of 8.14 with a standard deviation of 2.03. Two of the websites met the recommended sixth-grade reading level, and 5 out of the 10 websites met the national average of the eighth-grade reading level. The average of the FK reading ease scores was 63.31, interpreted as “standard eighth to ninth grade.”
Mallet Finger
The FK grade reading level of the 10 most visited websites for mallet finger had a mean of 9.44 with a standard deviation of 1.92. One of the websites met the recommended sixth-grade reading level, and 3 of the websites were at or below the eighth-grade reading level. The average of the FK reading ease scores was 57.44, interpreted as “fairly difficult high school.”
Trigger Finger
The FK grade reading level of the 10 most visited websites for trigger finger had a mean of 9.17 with a standard deviation of 1.90. Not one of the websites met the recommended sixth-grade reading level, and 4 of the websites were at or below the eighth-grade reading level. The average of the FK reading ease scores was 54.1, interpreted as “fairly difficult high school.”
Discussion
The Internet has emerged as the preferred platform to provide patient education materials, journal articles, treatment options, individual physician information and to facilitate overall patient care.6,7,13,19,21-23 Everyday, more than 8 million Americans will access the Internet with the intention of obtaining health information for themselves or for a relative.10,11 The impact this content has on patients was substantiated in several reports, which documented that the information obtained on the Internet directly influenced patients’ final decision regarding their course of treatment.5,10,18-20 One method of effectively capitalizing on this free, ubiquitous, and publicly available resource is to ensure that the medical information is presented on this platform at a level understandable to the general population.
This study shows that, on average, the patients of hand surgeons must read well above the recommended sixth-grade reading level to absorb the content provided in the most accessed websites. In fact, only 5 out of the 100 websites met the sixth-grade reading level. The implications are significant, in that it suggests a large proportion of hand patients utilizing the Internet to gather information have difficulty with comprehension of the available content. While we did not study the average reading level of patients visiting the offices of hand surgeons, it is unlikely significantly different than patients of other practices, and thus, the general population. An individual’s health literacy is one of the single best predictors of their health status.2,3,14 Health literacy is defined as one’s capacity to obtain, interpret, and understand the basic health information necessary to make an appropriate health decision.10 As such, a large proportion of the patient population is functionally illiterate or experiences difficulty synthesizing information from lengthy texts10,16,20; online patient education material written beyond the recommended level substantially diminishes the value of the message, and is associated with poor health status, increased hospitalization rate, poor compliance, and increased cost.8,19
In comparing the readability of the different hand conditions, the more complex pathology such as carpal tunnel syndrome, Dupuytren’s disease, and basal thumb arthritis had higher average readability levels than the acute injuries such as fracture, tendon damage, and mallet finger. This underscores the point that the subject matter of some conditions may be inherently too complex to adequately convey to the masses via written text. One website for carpal tunnel syndrome even had a reading ease score of 28, which corresponds to “very difficult postgraduate.” One solution to address the inevitably complex subject matter of some of these hand conditions is to supplement or replace the written text of websites with illustrations and videos. Many physicians utilize models and or illustrations/diagrams in their office visits to help delineate information more simply; thus, websites can also benefit from this practice. In addition to the audiovisual aids, revisions to the text resulting in simpler words, shorter sentences, and a reduction of medical terminology would aid in the making the material more understandable.5 Wang et al demonstrated that substitution of medical terminology with simple words improved readability levels by an average of 0.6 grade levels.20
There are several limitations to this study. While the FK scoring system is the most widely used and validated method to measure readability, it has been criticized because it is not infallible. One study reported that computer coding for the formula could lead to imprecision because colons and semicolons are interpreted as periods; this biases toward easier grade levels as sentences appear shorter.5,17 Furthermore, given the inherent prevalence of larger words in medical vernacular, the FK scores are skewed relatively higher based on its formulaic equation. Another limitation of this study is the inability to account for the variability in websites that patients may encounter when researching these common hand conditions on the Internet. The Google search engine utilizes a complex algorithm to generate “top searches” based on a host of variables such as the type of device (desktop, laptop, smartphone), search history, browser, and geographic location. Thus, different patients can get different search results. Also, the content of many web pages is often written with goals in mind other than purely patient education. Marketing and search engine optimization often influences the style, character, and content of many web pages. Moreover, our study did not account for those patients who use a search engine other than Google, which may yield different websites, or they may use different search terms in said search engine. Last, we used an indirect method of measuring the grade reading level of websites in comparison with the national average. Thus our results do not take into account the geographic differences in socioeconomic status and Internet access among patients throughout the United States, which would have major implications in medical literacy.
To our knowledge, this is the first study to investigate the readability of a comprehensive set of conditions that hand surgeons commonly treat. While previous studies interested in the online readability of these conditions focused on specific specialty-related organizations such as the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) or the AASH, our study is unique in that we utilized a popular search engine, considering that 40% to 60% of Internet searches are medically related.11 We believe that utilizing the Google search engine, rather than focusing on patient education materials from specialty organizations, allowed us to reproduce the Internet research habits of the lay public11 and better anticipate the materials that people without formal medical training would access.
Our study shows that the most commonly accessed online patient education information regarding hand pathology exceeds the readability level recommended by the AMA and NIH, and is above the average reading level of the majority of US adults. Given the fact that these are the most commonly visited websites by the lay public, there needs to be a greater emphasis on tailoring the information regarding hand pathology to the literacy of our patient population so that they can better inform and empower themselves as the websites intended.
Footnotes
Ethical Approval: This study was approved by our institutional review board.
Statement of Human and Animal Rights: This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Statement of Informed Consent: Informed consent was not needed, as there were not any human subjects involved in this study.
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Funding: The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
References
- 1. Albright J, de Guzman C, Acebo P, et al. Readability of patient education materials: implications for clinical practice. Appl Nurs Res. 1996;9(3):139-143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Badarudeen S, Sabharwal S. Assessing readability of patient education materials: current role in orthopaedics. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(10):2572-2580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Baker DW, Parker RM, Williams MV, et al. The relationship of patient reading ability to self-reported health and use of health services. Am J Public Health. 1997;87(6):1027-1030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Beredjiklian P, Bozentka D, Steinberg D, et al. Evaluating the source and content of orthopaedic information on the internet. The case of carpal tunnel syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82-A(11):1540-1543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Bluman E, Foley R, Chiodo C. Readability of the patient education section of the AOFAS website. Foot Ankle Int. 2009;30(4):287-291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Brooks BA. Using the Internet for patient education. Orthop Nurs. 2001;20:69-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Diaz J, Griffith R, Ng J, et al. Patients’ use of the Internet for medical information. J Gen Intern Med. 2002;17:180-185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Doak CC, Doak LG, Root JH. Teaching Patients With Low Literacy Skills. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: J.B. Lippincott; 1996. [Google Scholar]
- 9. Doak LG, Doak CC, Meade CD. Strategies to improve cancer education materials. Oncol Nurs Forum. 1996;23:1305-1312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Eltorai A, Sharma P, Wang J, et al. Most American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons’ online patient education material exceeds average patient reading level. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(4):1181-1186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Fox S. Online health search 2006. Pew Internet and American Life Project; http://www.pewinternet.org/2006/10/29/online-health-search-2006/. Published October 29, 2006. Accessed July 31, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 12. Friedman DB, Hoffman-Goetz L. A systematic review of readability and comprehension instruments used for print and web-based cancer information. Health Educ Behav. 2006;33:352-373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Heap J, Dezfuli B, Bennett D, et al. The Internet as a source of information for De Quervain’s tendinitis. Hand. 2014;10(1):131-136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Johnson K, Weiss BD. How long does it take to assess literacy skills in clinical practice? J Am Board Fam Med. 2008;21(3):211-214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Kincaid JP, Fishburne RP, Rogers RL, et al. Derivation of New Readability Formulas (Automated Readability Index, Fog Count and Flesch Reading Ease Formula) for Navy Enlisted Personnel. Orlando, FL: Institute for Simulation and Training; 1975:56. [Google Scholar]
- 16. Kirsch IS, Jungeblut A, Jenkins L, et al. Adult Literacy in America: A First Look at the Results of the National Adult Literacy Survey. Washington, DC: National Center for Education Statistics; 1993. [Google Scholar]
- 17. Ludbrook J. Readability of original articles in surgical journals. ANZ J Surg. 2006;76(11):1038-1040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Polishchuk D, Hashem J, Sabharwal S. Readability of online patient education materials on adult reconstruction Web sites. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(5):716-719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Sabharwal S, Badarudeen S, Unes Kunju S. Readability of online patient education materials from the AAOS web site. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(5):1245-1250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Wang S, Capo J, Orillaza N. Readability and comprehensibility of patient education material in hand-related web sites. J Hand Surg Am. 2009;34:1308-1315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Wolf J, Ritter M, Arnold-Peter CW, et al. Access and use of the internet in a hand surgery population. Hand Surg. 2004;9(1):29-33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Yi PH, Chang MM, Haughom BD, et al. Readability of patient education materials from the AAHS. Hand. 2014;9(3):393-394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Yi PH, Ganta A, Hussein KI, et al. Readability of arthroscopy-related patient education materials from the American academy of orthopaedic surgeons and arthroscopy association of north America Web sites. Arthroscopy. 2013;29(6):1108-1112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]