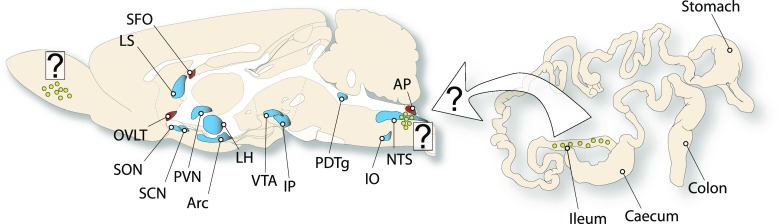
Figure 1.
GLP-1 interactions with the brain. GLP-1–producing cells (yellow circles) are found in areas including the ileum, olfactory bulb, and hindbrain. GLP-1–responsive structures in the brain are far more distributed and include structures behind (blue) and outside of (red) the blood-brain barrier, a subset of which are represented in this schematic. Knowing which source of GLP-1 acts on which of the responsive structures is important in order to understand the role of endogenous GLP-1 in the control of the diverse effects of GLP-1; question marks highlight the lack of detail in current knowledge about the sources of GLP-1 to these and other GLP-1–responsive sites. The article by Holt et al. (7) offers an important step toward this understanding. AP, area postrema; Arc, arcuate hypothalamic nucleus; IO, inferior olive; IP, interpeduncular nucleus; LH, lateral hypothalamus; LS, lateral septum; OVLT, organum vasculosum of the lamina terminalis; PDTg, posterodorsal tegmental nucleus; PVN, paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus; SCN, suprachiasmatic nucleus; SFO, subfornical organ; SON, supraoptic nucleus; VTA, ventral tegmental area.