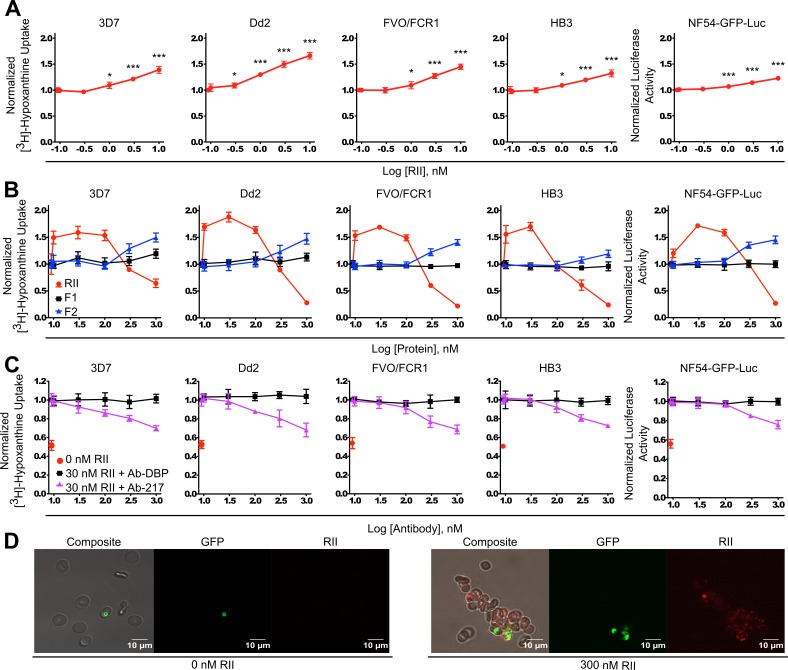
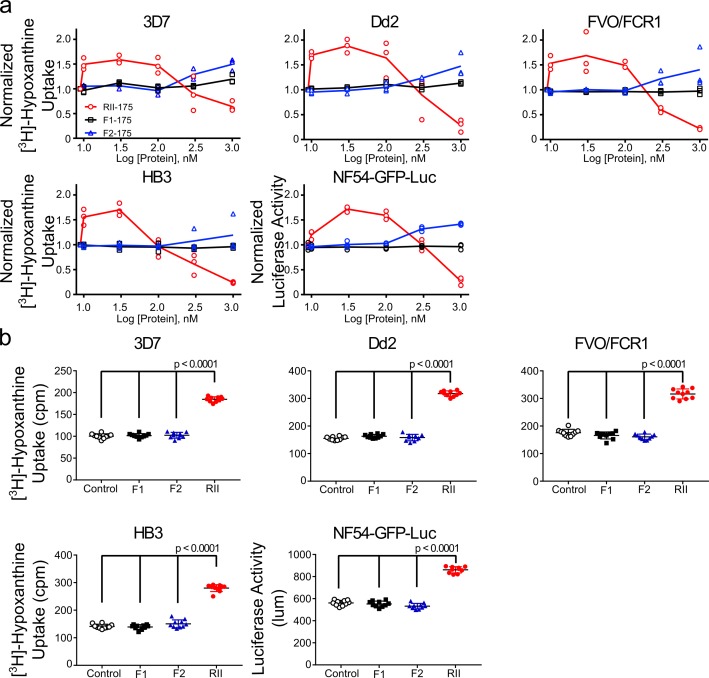
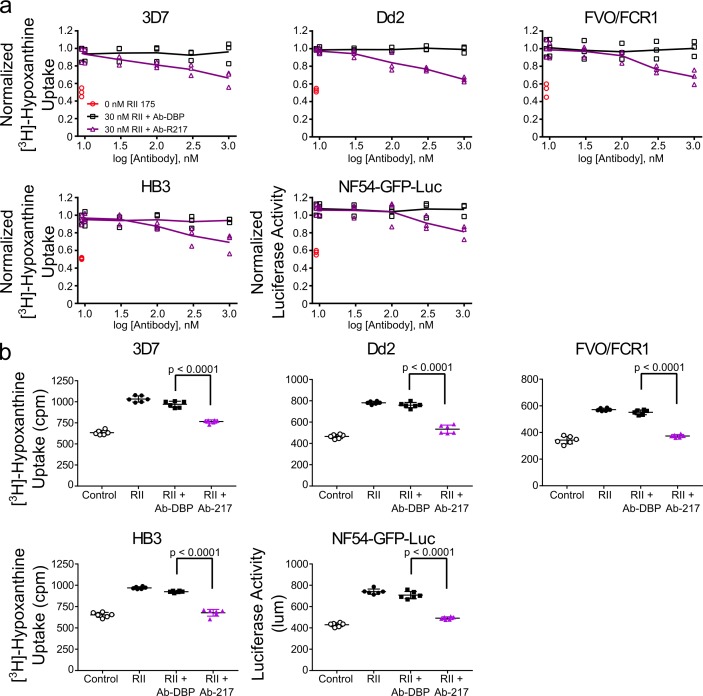
Figure 3. Recombinant EBA-175 RII causes RBC clustering in parasite culture and enhances parasite growth.
(A) Effects of picomolar to low nanomolar RII on parasite growth assessed by [3H]-hypoxanthine uptake for 3D7, Dd2, FVO/FCR1, HB3 strains, and the luciferase activity for NF54-GFP-luc strain (far right). Data shown are mean ± SD of three biological replicates for all strains. Significance (*, p<0.05; ***, p<0.001) (B) Uptake of [3H]-hypoxanthine into parasite nucleic acids by 3D7, Dd2, FVO/FCR1, HB3 strains, and the luciferase activity in NF54-GFP-luc strain (far right), in the presence or absence of RII, F1 or F2 at varying concentrations (10 nM – 1 μM range) for 96 hr. Results are shown as mean ± SD of three biological replicates. (C) Ab-217 (purple line) inhibition of RII-mediated growth enhancement, control Ab Ab-DBP (black line). Results are shown as mean ± SD of three biological replicates. (D) Microscopy analysis of NF54-GFP parasites (green) in RII-induced clusters (red).