Abstract
Background
Coronary artery disease including acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is mainly caused by atherosclerosis, an inflammatory and metabolic disease. Autophagy has been demonstrated to play critical roles in lipid metabolism and inflammation. Altered autophagic activity has been reported in AMI patients. However, molecular basis for dysfunctional autophagy in AMI remains unexplained.
Methods
In this study, the promoter of the ATG7 gene, encoding a core protein for autophagy, was genetically and functionally analyzed in large cohorts of AMI patients (n = 355) and ethnic‐matched healthy controls (n = 363). Related molecular mechanisms were also explored.
Results
A total of 19 DNA sequence variants (DSVs) including single‐nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were found in the ATG7 gene promoter. Two novel DSVs and five SNPs were only identified in AMI patients group. These DSVs and SNPs, except one SNP, significantly altered the transcriptional activity of the ATG7 gene promoter in both HEK‐293 and H9c2 cells (p < 0.05). Further electrophoretic mobility shift assay revealed that the DSVs and SNPs evidently affected the binding of transcription factors.
Conclusions
ATG7 gene DSVs and SNPs identified in AMI patients may alter the transcriptional activity of the ATG7 gene promoter and change ATG7 level, contributing to the AMI development as a rare risk factor.
Keywords: acute myocardial infarction, ATG7, autophagy, DNA sequence variants, genetics, promoter
1. INTRODUCTION
Coronary artery disease (CAD) including acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is a common complex disease that is caused by atherosclerosis, an inflammatory and metabolic disease. Dysregulated lipid metabolism and inflammation have been shown to play critical roles in the initiation and progression of atherosclerosis and its complications, particularly plaque rupture and subsequent AMI (Connelly, Shalaurova, & Otvos, 2016; Shapiro & Fazio, 2016). Genome‐wide association studies have revealed a great number of genetic loci for CAD and AMI, some of which are associated with lipid metabolism and inflammation. However, the collective genetic loci could explain only <10% of cases (Assimes & Roberts, 2016). Therefore, genetic causes and molecular mechanisms for CAD and AMI remain largely unclear.
Autophagy is an evolutionally conserved cellular process to maintain cell homeostasis by delivering cytoplasmic contents to lysosomes for degradation. In mammals, autophagy has three subtypes, macroautophagy, microautophagy, and chaperone‐mediated autophagy. Macroautophagy (hereafter referred as autophagy) mainly degrades long‐lived macromolecules and damaged organelles and has been extensively studied. Autophagy is involved in many physiological processes, including lipid metabolism and inflammation. Altered autophagic activity has been implicated in a wide range of human diseases, including cardiovascular diseases (Lavandero, Chiong, Rothermel, & Hill, 2015). In the cardiovascular system, autophagic activity occurs in all cell types including cardiomyocytes, cardiac fibroblasts, vascular smooth muscle cells, vascular endothelial cells, and macrophages. A window of optimal autophagic activity is critical to the maintenance of cardiovascular homeostasis and function. Excessive or insufficient levels of autophagic flux can each contribute to the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases, such as atherosclerosis, cardiomyopathy, and AMI (Bravo‐San Pedro, Kroemer, & Galluzzi, 2017; Gatica, Chiong, Lavandero, & Klionsky, 2015; Lavandero et al., 2015).
To date, more than 30 autophagy‐related (ATG) proteins have been identified in the formation of autophagosome (Mizushima, Yoshimori, & Ohsumi, 2011). ATG7 (OMIM: 608760) acts as an E1‐like activating enzyme and facilitates both microtubule‐associated protein light chain 3 (LC3)‐phosphatidylethanolamine and ATG12 conjugation, which play important roles in autophagosome biogenesis in autophagy. ATG7 has been shown to play a pleiotropic function in development and human diseases (Xiong, 2015). Homozygous knockout of ATG7 gene in mice is neonatally lethal, and autophagy is not upregulated during starvation (Komatsu et al., 2005). Tissue‐specific deletion of ATG7 gene and subsequent defective autophagy has been widely studied, including cardiomyocytes, vascular endothelial cells, and smooth muscle cells. Conditional knockout of ATG7 gene in cardiomyocyte leads to severe contractile dysfunction, myofibrillar disarray, and vacuolar cardiomyocytes (Li et al., 2016). In a mouse model of cardiomyopathy, cardiac‐specific overexpression of ATG7 gene and enhanced autophagy improve cardiac performance by decreasing interstitial fibrosis, ameliorating ventricular dysfunction, decreasing cardiac hypertrophy, and reducing intracellular aggregates (Bhuiyan et al., 2013). In neonatal rat cardiomyocytes, ATG7 induces basal autophagy and attenuates the accumulation of misfolded proteins and aggregates (Pattison, Osinska, & Robbins, 2011). In vascular smooth muscle cells, ATG7 gene deletion alters contractility and Ca²⁺ homeostasis (Michiels, Fransen, De Munck, De Meyer, & Martinet, 2015). In endothelial cells, ATG7 gene deletion results in higher levels of intracellular lipid accumulation (Torisu et al., 2016).
Dysregulated gene expression has been implicated in many human common diseases (Lee & Young, 2013). In previous studies, we have reported altered autophagic activity in CAD and AMI patients by examining LC3 gene expression levels (Wu, Wei et al., 2011; Wu, Liu et al., 2011). However, molecular basis for dysfunctional autophagy in AMI remains unexplained. As ATG7 is one of core proteins for autophagy, we postulated that dysregulated ATG7 gene expression may lead to altered autophagic activity, playing an important role in the development of CAD and AMI. In this study, we genetically and functionally analyzed the promoter of ATG7 gene in large cohort of AMI patients and ethnic‐matched healthy controls.
2. MATERIAL AND METHODS
2.1. Study population
Acute myocardial infarction patients (n = 355, male 265, female 90, median age 63.00 years) were recruited during the period April 2014 to April 2016, from Cardiac Care Unit, Division of Cardiology, Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical University, Jining, Shandong, China. AMI patients were diagnosed with medical records, physical examination, electrocardiogram, and three‐dimensional echocardiography. Ethnic‐matched healthy controls (n = 363, male 188, female 175, median age 51.00 years) were recruited from the Physical Examination Center in the same hospital. The controls with CAD family history were excluded from this study. The study was approved by the Human Ethic Committee of Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical University and conducted according to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
2.2. Direct DNA sequencing
Peripheral blood leukocytes were isolated from vein blood, and genomic DNAs were extracted. ATG7 gene promoter region (from −1145 bp to +112 bp to the transcription start site) was directly sequenced. Two overlapped DNA fragments, 698 bp (−1145 bp ~ −448 bp) and 622 bp (−510 bp~+112 bp), were generated by PCR. PCR primers were designed based on genomic sequence of the human ATG7 gene (NCBI, NC_000003.12; Table 1). PCR products were bidirectionally sequenced with Applied Biosystems 3500XL genetic analyzer. The DNA sequences were aligned and compared with the wild‐type ATG7 gene promoter.
Table 1.
PCR primers for the ATG7 gene promoter
| PCR primersa | Sequences | Location | Positionb (bp) | Products (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sequencing | ||||
| ATG7‐F1 | 5′‐GGTTCCTTCTCTCCCACCTC‐3′ | 11271179 | −1145 | 698 |
| ATG7‐R1 | 5′‐ACTGGACAGGTGTTGAAG ‐3′ | 11271876 | −448 | |
| ATG7‐F2 | 5′‐GCCTTACAGGCCAGACAGA‐3′ | 11271814 | −510 | 622 |
| ATG7‐R2 | 5′‐CTTACCGCCGCTCAACTT‐3′ | 11272435 | +112 | |
| Functioning | ||||
| ATG7‐F | 5′‐(KpnI)‐ACGGAGTCTCGCTCTGTCGC‐3′ | 11271242 | −1082 | 1194 |
| ATG7‐R | 5′‐(HindIII)‐CTTACCGCCGCTCAACTTCC ‐3′ | 11272435 | +112 | |
aPCR primers are designed based on the genomic DNA sequence of the ATG7 gene (NC_000003.12). bThe transcription start site (TSS) is at the position of 11272324 (+1).
2.3. Functional analysis with dual‐luciferase reporter assay
Wild‐type and variant ATG7 gene promoters were subcloned into firefly luciferase reporter vector (pGL3‐basic) to construct expression vectors. These expression vectors were then transfected into cultured cells, and dual‐luciferase activities were examined. Briefly, DNA fragments of wild‐type and variant ATG7 gene promoters (1194 bp, from −1082 bp to +112 bp to the transcription start site) were generated by PCR and inserted into the KpnI and Hind III sites of pGL3‐basic to generate expression vectors. The PCR primers are shown in Table 1. Designated expression vectors were transiently transfected into human embryonic kidney cells (HEK‐293) or rat cardiomyocyte line cells (H9c2). Forty‐eight hours post‐transfection, the cells were collected and lysed. Dual‐luciferase activities were measured using dual‐luciferase reporter assay system on a Promega Glomax 20/20 luminometer. Vector pRL‐TK expressing renilla luciferase was used as an internal control for transfection efficiency. Empty vector pGL3‐basic was used as a negative control. The transcriptional activities of the ATG7 gene promoters were represented as ratios of firefly luciferase activities over renilla luciferase activities. Transcriptional activity of the wild‐type ATG7 gene promoter was designed as 100%. All the experiments were repeated three times independently, in triplicate.
2.4. Nuclear extracts preparation and electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA)
Nuclear extracts were prepared from HEK‐293 and H9c2 cells using NE‐PER® Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Extraction Reagents (Thermo Scientific, Rockford, IL, USA). Protein concentrations were determined with Bio‐Rad protein assay. EMSA examining DNA–protein interactions was carried out using LightShift® Chemiluminescent EMSA kit (Thermo Scientific, Rockford, IL, USA). DNA‐protein binding reaction was carried out with nuclear extracts (3.0 μg) and double‐stranded biotinylated oligonucleotides (30 bp) containing wild‐type and variant DNA sequence of the ATG7 gene promoter. After 20 min at room temperature, the reaction mixtures were loaded onto a native 6% polyacrylamide gel in 0.5× TBE and run at 100 V for 1 hr, which were subsequently transferred onto a nylon membrane (Thermo Scientific, Rockford, IL, USA) at 100V for 30 min. The oligonucleotides were cross‐linked to the membrane using the UV Stratalinker 1800 (Stratagene, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The biotin‐labeled oligonucleotides were then detected by chemiluminescence.
2.5. Statistical analysis
The quantitative data were represented as mean ± SEM and compared by a standard Student's t test. DSV frequencies in AMI patients and controls were analyzed and compared with SPSS v13.0. p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. RESULTS
3.1. The DSVs identified in AMI patients and controls
A total of 19 DNA sequence variants (DSVs), including 12 single‐nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), were identified in this study population. Locations and frequencies of the DSVs are depicted in Figure 1 and summarized in Table 2. Two novel heterozygous DSVs, g.11271467C>T and g.11272338G>A, and five heterozygous SNPs, g.11271281T>C (rs2594975), g.11271763G>A (rs76708041), g.11272004C>G (rs550744886), g.11272071G>A (rs544484285), and g.11272355A>G (rs2606729), were found in nine AMI patients. In the 1000 Genome Project, frequencies of C allele in g.11271281T>C (rs2594975) and G allele in g.11272355A>G (rs2606729) were 100% in Han Chinese people. These DSVs and SNPs were not found in controls. Sequencing chromatograms of these DSVs and SNPs are shown in Figure 1b. Four novel heterozygous DSVs, g.11271319G>C, g.11271431C>T, g.11271576G>C, and g.11272227G>T, were only identified in controls, the sequencing chromatograms of which are shown in Figure 1c. In addition, one novel heterozygous DSV and seven SNPs were found in both AMI patients and controls with similar frequencies (p > 0.05).
Figure 1.
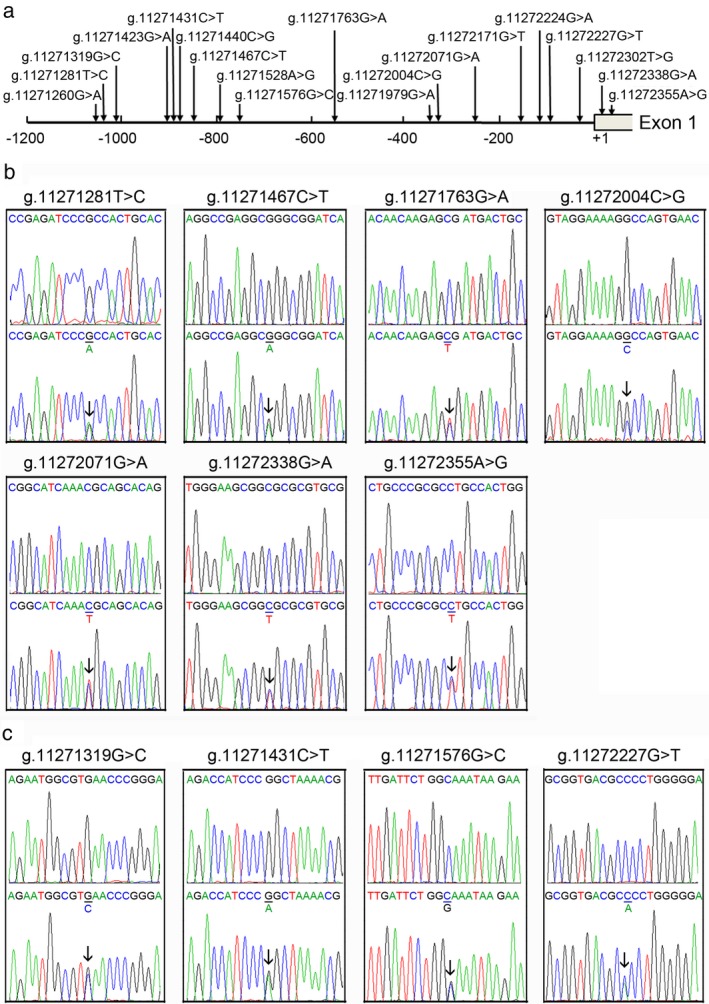
Locations and sequencing chromatograms of the DSVs and SNPs in the ATG7 gene promoter. (a) Locations of the DSVs and SNPs. The numbers represent the genomic DNA sequences of the human ATG7 gene (Genbank accession number NC_000003.12) upstream to the transcription start site (at the position of 11272264), which is set as +1. (b) Sequencing chromatograms of the DSVs and SNPs in AMI patients. (c) Sequencing chromatograms of the DSVs in controls. Top panels show wild‐type DNA sequences, and bottom panels heterozygous DSVs and SNPs, which are marked with arrows. For the DSV g.11271319G>C, sequence orientation is forward and all others are reverse
Table 2.
The DSVs in the ATG7 gene promoter in AMI patients and controls
| DSVs | Genotypes | Location[Link] (bp) | Controls (n = 363) | AMI (n = 355) | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g.11271260G>A | GA | −1064 | 1 | 1 | 1.000 |
| g.11271281T>C (rs2594975) | TC | −1043 | 0 | 2 | ‐ |
| g.11271319G>C | GC | −1005 | 1 | 0 | ‐ |
| g.11271423G>A (rs533883497) | GA | −901 | 1 | 1 | 1.000 |
| g.11271431C>T | CT | −893 | 1 | 0 | ‐ |
| g.11271440C>G (rs181704508) | CG | −884 | 26 | 28 | 0.778 |
| g.11271467C>T | CT | −857 | 0 | 1 | ‐ |
| g.11271528A>G (rs11714563) | AA | −796 | 176 | 165 | 0.730 |
| AG | 157 | 163 | |||
| GG | 30 | 27 | |||
| g.11271576G>C | GC | −748 | 1 | 0 | ‐ |
| g.11271763G>A (rs76708041) | GA | −561 | 0 | 1 | ‐ |
| g.11271979G>A (rs552163870) | GA | −345 | 2 | 5 | 0.282 |
| g.11272004C>G (rs550744886) | CG | −320 | 0 | 2 | ‐ |
| g.11272071G>A (rs544484285) | GA | −253 | 0 | 1 | ‐ |
| g.11272171G>T (rs140788185) | GT | −153 | 4 | 6 | 0.542 |
| g.11272224G>A (rs2594971) | GG | −100 | 48 | 45 | 0.206 |
| GA | 168 | 187 | |||
| AA | ‐ | 147 | 123 | ||
| g.11272227G>T | GT | −97 | 1 | 0 | ‐ |
| g.11272302T>G (rs142065270) | TT | −22 | 359 | 348 | 0.477 |
| TG | 4 | 6 | |||
| GG | 0 | 1 | |||
| g.11272338G>A | GA | +15 | 0 | 1 | ‐ |
| g.11272355A>G (rs2606729) | AG | +32 | 0 | 1 | ‐ |
DSVs are located upstream (‐) or downstream (+) to the transcription start site of ATG7 gene at 11272324 of NC_000003.12.
3.2. DSV‐related putative binding sites for transcription factors
To determine whether the DSVs and SNPs identified in AMI patients affected putative binding sites for transcription factors, the ATG7 gene promoter was analyzed with JASPAR program (http://jaspar.genereg.net/). The DSVs identified in AMI patients may abolish, create, and modify the putative binding sites for transcription factors, which are summarized in Table 3. The SNP g.11271281T>C (rs2594975) may abolish a binding site for zinc finger protein 354C (ZF354C), a ubiquitously expressed transcriptional repressor. The DSV g.11271467C>T may abolish a binding site for THAP domain containing 1 (THAP1), a C2CH THAP‐type zinc finger factor with roles in proliferation, apoptosis, cell cycle, chromosome segregation, chromatin modification, and transcriptional regulation. The SNP g.11271763G>A (rs76708041) may modify the binding site for GATA binding protein 2 (GATA2), a transcriptional activator involved in the development and proliferation of hematopoietic and endocrine cell lineages. The SNP g.11272004C>G (rs550744886) may create the binding sites for Rhox homeobox family member 1 (RHOXF1), a transcription factor that may play a role in human reproduction, and NF‐kappaB‐related factors. The SNP g.11272071G>A (rs544484285) may abolish the binding site for transcription factor 7‐like 2 (TCF7L2), which is highly expressed in fat. The DSV g.11272338G>A may modify the binding site for nuclear respiratory factor 1 (NRF1), which regulates cellular growth and nuclear genes required for respiration, heme biosynthesis, and mitochondrial DNA transcription and replication. The SNP g.11272355A>G (rs2606729) may modify the binding site for nuclear factor 1 X‐type (NFIX), a SMAD/NF‐1 DNA‐binding domain transcriptional activator.
Table 3.
Predicted binding sites for transcription factors affected by the DSVs and SNPs
| DSVs/SNPs | Create/abolish/modify | Transcription factors |
|---|---|---|
| g.11271281T>C (rs2594975) | Abolish | zinc finger protein 354C (ZF354C), |
| g.11271467C>T | Abolish | C2CH THAP‐type zinc finger factor THAP domain containing 1 (THAP1) |
| g.11271763G>A (rs76708041) | Modify | GATA binding protein 2 (GATA2) |
| g.11272004C>G (rs550744886) | Create | Rhox homeobox family member 1 (RHOXF1) |
| g.11272071G>A (rs544484285) | Abolish | transcription factor 7 like 2 (TCF7L2) |
| g.11272338G>A | Modify | nuclear respiratory factor 1 (NRF1) |
| g.11272355A>G (rs2606729) | Modify | nuclear factor 1 X‐type (NFIX) |
3.3. Functional analysis of the DSVs by dual‐luciferase reporter assay
Wild‐type and variant ATG7 gene promoters were subcloned into luciferase reporter vector (pGL3‐basic) to generate expression vectors, including empty pGL3‐basic (negative control), pGL3‐WT (wild‐type ATG7 gene promoter), pGL3‐11271281T, pGL3‐11271431T, pGL3‐11271467T, pGL3‐11271576C, pGL3‐11271763A, pGL3‐11272004G, pGL3‐11272071A, pGL3‐11272171T, pGL3‐11272227G>T, pGL3‐11272338A, and pGL3‐11272355A. The expression vectors were transfected into HEK‐293 and H9c2 cells, and dual‐luciferase activities were assayed.
In HEK‐293 cells, the DSV (g.11271467C>T) and the SNPs [g.11271763G>A (rs76708041), g.11272004C>G (rs550744886), g.11272071G>A (rs544484285), and g.11272355A>G (rs2606729)] identified in AMI patients significantly decreased the transcriptional activity of the ATG7 gene promoter (p < 0.01). In contrast, the DSV (g.11272338G>A) and the SNP [g.11271281T>C (rs2594975)] identified in AMI patients significantly increased the transcriptional activity of the ATG7 gene promoter (p < 0.01). As expected, the DSVs (g.11271319G>C, g.11271431C>T, g.11271576G>C, and g.11272227G>T) identified in controls and the SNP [g.11272171G>T (rs140788185)] found in both AMI patients and controls did not affect the activity of the ATG7 gene promoter (p > 0.05; Figure 2a).
Figure 2.
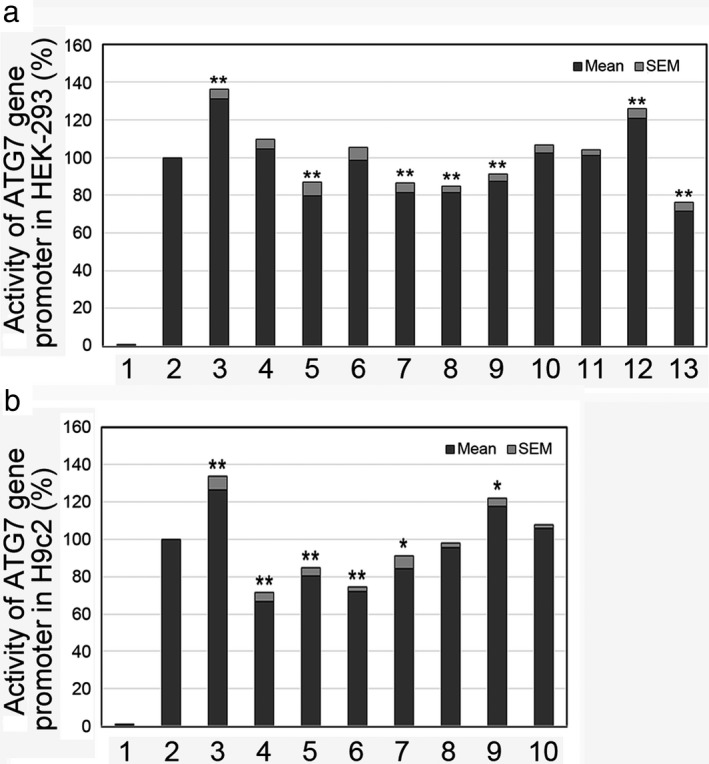
Relative transcriptional activity of wild‐type and variant ATG7 gene promoters. Wild‐type and variant ATG7 gene promoters were cloned into reporter gene vector pGL3 and transfected into cultured cells. The transfected cells were collected, and dual‐luciferase activities were assayed. Empty vector pGL3‐basic was used as a negative control. Transcriptional activity of the wild‐type ATG7 gene promoter was designed as 100%. Relative activities of ATG7 gene promoters were calculated. (a) Relative activities of wild‐type and variant ATG7 gene promoters in HEK‐293 cells. Lanes 1, pGL3‐basic; 2, pGL3‐WT; 3, pGL3‐11271281T; 4, pGL3‐11271431T; 5, pGL3‐11271467T; 6, pGL3‐11271576C; 7, pGL3‐11271763A; 8, pGL3‐11272004G; 9, pGL3‐11272071A; 10, pGL3‐11272171T; 11, pGL3‐11272227G>T; 12, pGL3‐11272338A; and 13, pGL3‐11272355A. (b) Relative activities of wild‐type and variant ATG7 gene promoters in H9c2 cells. Lanes 1, pGL3‐basic; 2, pGL3‐WT; 3, pGL3‐11271281T; 4, pGL3‐11271467T; 5, pGL3‐11271763A; 6, pGL3‐11272004G; 7, pGL3‐11272071A; 8, pGL3‐11272171T; 9, pGL3‐11272338A; and 10, pGL3‐11272355A. WT, wild type. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01
To further determine the tissue‐specific effects of the DSVs and SNPs in cardiomyocytes, the activity of wild‐type and variant ATG7 gene promoters were examined in H9c2 cells. All the DSVs and SNPs found in AMI patients, except one SNP, exhibited similar effects on the transcriptional activity of ATG7 gene (p < 0.05; Figure 2b). The SNP [g.11272355A>G (rs2606729)] did not significantly affect the transcriptional activity of ATG7 gene promoter in H9c2 cells, indicating its tissue‐specific effect (p > 0.05). Therefore, the DSVs and SNPs identified in AMI patients significantly altered the activity of the ATG7 gene promoter in both HEK‐293 and H9c2 cells.
3.4. The binding for transcription factors affected by the DSVs
To investigate whether the DSVs and SNPs affected the binding for transcription factors, EMSA was performed with wild‐type or variant oligonucleotides. The sequences of the DSVs and SNPs are shown in Table 4. The results showed that the SNP [g.11272004C>G (rs550744886)] reduced the binding of a transcription factor, which was weakly expressed in H9c2 cells. The predicted creation of RHOXF1 binding site may not exist or beyond the detection of EMSA. The DSV g.11272338G>A enhanced the binding of a transcription factor. The SNP [g.11272355A>G (rs2606729)] enhanced the binding of a transcription factor in HEK‐293 cells (Figure 3). Interestingly, this SNP [g.11272355A>G (rs2606729)] did significantly decrease the transcriptional activity of the ATG7 gene promoter in HEK‐293 cells, but had no effect in H9c2 cells, indicating its tissue‐specific effects (Figure 2a,b). The DSV g.11271467C>T did not affect the binding of transcription factors, likely due to the sensitivity of EMSA (Figure 3). Similarly, other DSVs and SNPs found in AMI patients did not evidently affect the binding of transcription factors (not shown). Taken together, the DSVs and SNPs altered ATG7 gene promoter activity by affecting the binding of transcription factors. Further work will be needed to identify these transcription factors.
Table 4.
The double‐stranded biotinylated oligonucleotides for the EMSA
| DSVs | Oligonucleotide sequences | Locations |
|---|---|---|
| g.11271281T>C (rs2594975) | 5′‐GCTGGAGTGCAGTGG(T/C)GGGATCTCGGCT‐3′ | 11271266‐11271295 |
| g.11271467C>T | 5′‐ACCTCGTGATCCGCC(C/T)GCCTCGGCCTCCCA‐3′ | 11271452‐11271481 |
| g.11271763G>A (rs76708041) | 5′‐TTAATAGCAGTCATC(G/A)CTCTTGTTGTTATG‐3′ | 11271748‐11271777 |
| g.11272004C>G (rs550744886) | 5′‐GTCGACGTTCACTGG(C/G)CTTTTCCTACTAAA‐3′ | 11271989‐11272018 |
| g.11272071G>A (rs544484285) | 5′‐TGGCCCCTGTGCTGC(G/A)TTTGATGCCGCCTC‐3′ | 11272056‐11272085 |
| g.11272338G>A | 5′‐CCTTTGCGCACGCGC(G/A)CCGCTTCCCAGTGG‐3′ | 11272323‐11272352 |
| g.11272355A>G (rs2606729) | 5′‐CGCTTCCCAGTGGCA(A/G)GCGCGGGCAGGACC‐3′ | 11272340‐11272369 |
Figure 3.
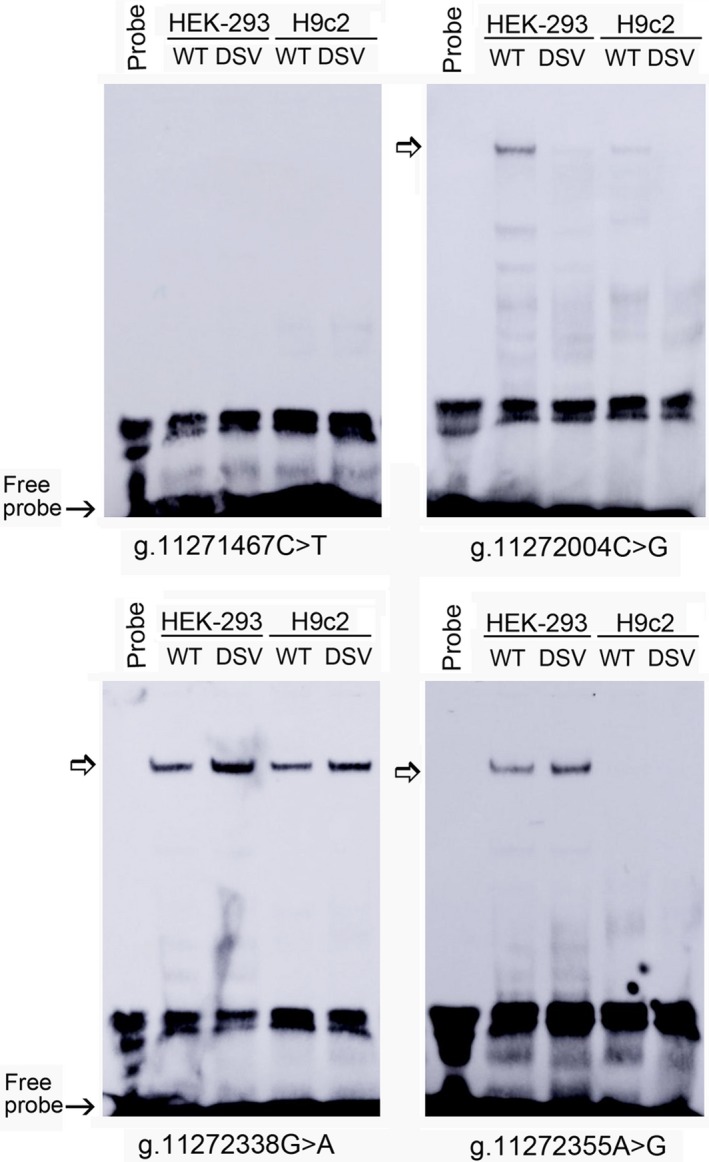
EMSA of biotin‐labeled oligonucleotides containing DSVs and SNPs. Wild‐type and variant oligonucleotides (30 bp) were designed and labeled with biotin for the DSVs and SNPs identified in AMI patients, including g.11271467C>T, g.11272004C>G, g.11272338G>A, and g.11272355A>G. EMSA was conducted with biotinylated oligonucleotides and the nuclear extracts from HEK‐293 and H9c2 cells. Free probe was marked with an arrow at the bottom. The affected binding for transcription factors was marked with an open arrow
4. DISCUSSION
Recently, low‐frequency and rare genetic variants have been suggested to account for the missing heritability as a major cause for human diseases (Lettre, 2014). Previous studies have shown that the polymorphism (V471A) in ATG7 gene that substitutes alanine for valine has been significantly associated with an earlier onset of Huntington's disease (HD) (Metzger et al., 2010). An intron variant in ATG7 gene (rs8154) is significantly associated with breast cancer‐specific survival (Zhou et al., 2017). Lower and elevated ATG7 levels have been observed in the patients with ulcerative colitis and active eosinophilic esophagitis, respectively (Lankarani, Sepehrimanesh, Seghatoleslam, Hoseini, & Ghavami, 2017; Merves et al., 2016). In this study, we identified two novel DSVs and five SNPs in AMI patients, which significantly altered the transcriptional activity of ATG7 gene. Further EMSA revealed that one DSV and two SNPs evidently affected the binding of transcription factors. Collective frequency of the DSVs and SNPs in ATG7 gene promoter was 2.54% (9/355) in AMI patients. Therefore, these DSVs and SNPs may change ATG7 levels, contributing to the AMI development as a low‐frequency risk factor.
The human ATG7 gene has been mapped to chromosome 3p25.3 and is ubiquitously expressed in human adult and fetal tissues (Tanida et al., 2002). The promoter of the ATG7 gene has not been characterized in details. Heat shock factor 1 (HSF1), a master regulator of heat shock responses, directly binds to the ATG7 gene promoter and transcriptionally upregulating its expression (Desai et al., 2013). ATG7 gene has been validated as target of microRNA‐17 family (microRNA‐20a and microRNA‐17), which bind to the 3′ UTR of ATG7 gene mRNA (Guo, Mei, Li, Huang, & Yang, 2016). In HeLa cells, p300 acetyltransferase colocalizes and physically interacts with ATG7 in regulating autophagy (Lee & Finkel, 2009). In human umbilical vein endothelial cells, ATG7 interacts with acetylated FOXO1, a mediator of autophagy, in protecting cell survival from oxidative stress damage (Han et al., 2012). Therefore, the DSVs in the ATG7 gene promoter may change ATG7 levels.
Accumulating evidence suggests that ATG7 and autophagy play protective roles in cardiomyocytes, vascular endothelial cells, and smooth muscle cells (Michiels et al., 2015; Pattison et al., 2011; Torisu et al., 2016). Autophagy is an innate and potent process that protects cardiomyocytes from ischemic death during acute myocardial infarction in animal experiments (Orogo & Gustafsson, 2015). Autophagy also occurs in advanced atherosclerotic plaques and is protective for plaque stabilization (Schrijvers, De Meyer, & Martinet, 2011). In human atrial myofibroblasts, ATG7 gene knockdown decreases the fibrotic effect of transforming growth factor‐β1 (TGF‐β1) (Ghavami et al., 2015). In contrast, excessive autophagy is capable of provoking plaque destabilization and lesional thrombosis, leading finally to autophagic cell death (Martinet & De Meyer, 2009). Autophagy acts as a mechanism of cell death in atherosclerotic vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) (Jia, Cheng, Gangahar, & Agrawal, 2006). Overloading autophagy has been recognized as a deleterious process by excessive self‐digestion (Tai, Hu, Peng, Zhou, & Zheng, 2016). Endothelial‐specific deletion of ATG7 gene impairs the release of von Willebrand factor, which plays a major role in blood coagulation (Torisu et al., 2013). Taken together, the DSVs in ATG7 gene identified in AMI patients may increase or decrease ATG7 levels, which lead to defective or excessive autophagic activity, contributing to the development of atherosclerosis and AMI.
Non‐autophagic functions of ATG7 have been reported. In mouse embryonic fibroblasts, ATG7 could bind to the tumor suppressor p53 to regulate the expression of the cell cycle inhibitor p21(CDKN1A) gene, which is independent of its E1‐like enzymatic activity (Lee et al., 2012). ATG7 functions as cellular scaffolds in regulating phosphorylation of extracellular signal‐regulated kinase (ERK), which controls various aspects of cell physiology including proliferation (Martinez‐Lopez, Athonvarangkul, Mishall, Sahu, & Singh, 2013). ATG7 deficiency suppresses apoptosis and cell death induced by lysosomal photodamage (Kessel, Price, & Reiners, 2012). ATG7 directly interacts with caspase‐9 and represses its apoptotic activity, which is not related to its autophagic function (Han et al., 2014). ATG7 is involved in a process designated LC3‐associated phagocytosis, which is independent of autophagic process (Sanjuan et al., 2007). In addition, ATG7 is required for interferon gamma‐mediated host defense against virus replication (Hwang et al., 2012). Therefore, deficient or excessive ATG7 may interfere with inflammation, cell proliferation, and apoptosis, contributing to the development of cardiovascular diseases through its non‐autophagic function.
In conclusion, the ATG7 gene promoter was genetically and functionally analyzed in AMI patients and healthy controls in this study. The DSVs and SNPs were identified in AMI patients, which significantly altered the transcriptional activity of the ATG7 gene promoter. These DSV and two SNPs evidently affected the binding of transcription factors. Therefore, these DSVs and SNPs may change ATG7 level, contributing to AMI development through its autophagic and non‐autophagic functions as a low‐frequency risk factor.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81370271, 81400291, and 81870279) and Shandong Taishan Scholar Project, China (tshw201502063).
Zhang P, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Wang S, Pang S, Yan B. Functional variants of the ATG7 gene promoter in acute myocardial infarction. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2018;6:1209–1219. 10.1002/mgg3.508
REFERENCES
- Assimes, T. L. , & Roberts, R. (2016). Genetics: Implications for prevention and management of coronary artery disease. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 68, 2797–2818. 10.1016/j.jacc.2016.10.039 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhuiyan, M. S. , Pattison, J. S. , Osinska, H. , James, J. , Gulick, J. , McLendon, P. M. , … Robbins, J. (2013). Enhanced autophagy ameliorates cardiac proteinopathy. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 123, 5284–5297. 10.1172/JCI70877 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo‐San Pedro, J. M. , Kroemer, G. , & Galluzzi, L. (2017). Autophagy and mitophagy in cardiovascular disease. Circulation Research, 120, 1812–1824. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.311082 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connelly, M. A. , Shalaurova, I. , & Otvos, J. D. (2016). High‐density lipoprotein and inflammation in cardiovascular disease. Translational Research, 173, 7–18. 10.1016/j.trsl.2016.01.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai, S. , Liu, Z. , Yao, J. , Patel, N. , Chen, J. , Wu, Y. , … Tan, M. (2013). Heat shock factor 1 (HSF1) controls chemoresistance and autophagy through transcriptional regulation of autophagy‐related protein 7 (ATG7). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 288, 9165–9176. 10.1074/jbc.M112.422071 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatica, D. , Chiong, M. , Lavandero, S. , & Klionsky, D. J. (2015). Molecular mechanisms of autophagy in the cardiovascular system. Circulation Research, 116, 456–467. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.303788 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghavami, S. , Cunnington, R. H. , Gupta, S. , Yeganeh, B. , Filomeno, K. L. , Freed, D. H. , … Dixon, I. M. (2015). Autophagy is a regulator of TGF‐β1‐induced fibrogenesis in primary human atrial myofibroblasts. Cell Death & Disease, 6, e1696 10.1038/cddis.2015.36 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J. , Mei, Y. , Li, K. , Huang, X. , & Yang, H. (2016). Downregulation of miR‐17‐92a cluster promotes autophagy induction in response to celastrol treatment in prostate cancer cells. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 478, 804–810. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.08.029 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han, J. , Hou, W. , Goldstein, L. A. , Stolz, D. B. , Watkins, S. C. , & Rabinowich, H. (2014). A Complex between Atg7 and Caspase‐9: A novel mechanism of cross‐regulation between autophagy and apoptosis. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 289, 6485–6497. 10.1074/jbc.M113.536854 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han, J. , Pan, X. Y. , Xu, Y. , Xiao, Y. , An, Y. , Tie, L. , … Li, X. J. (2012). Curcumin induces autophagy to protect vascular endothelial cell survival from oxidative stress damage. Autophagy, 8, 812–825. 10.4161/auto.19471 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, S. , Maloney, N. S. , Bruinsma, M. W. , Goel, G. , Duan, E. , Zhang, L. , … Virgin, H. W. (2012). Nondegradative role of Atg5‐Atg12/Atg16L1 autophagy protein complex in antiviral activity of interferon gamma. Cell Host & Microbe, 11, 397–409. 10.1016/j.chom.2012.03.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jia, G. , Cheng, G. , Gangahar, D. M. , & Agrawal, D. K. (2006). Insulin‐like growth factor‐1 and TNF‐alpha regulate autophagy through c‐jun N‐terminal kinase and Akt pathways in human atherosclerotic vascular smooth cells. Immunology and Cell Biology, 84, 448–454. 10.1111/j.1440-1711.2006.01454.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessel, D. H. , Price, M. , & Reiners Jr, J. J. (2012). ATG7 deficiency suppresses apoptosis and cell death induced by lysosomal photodamage. Autophagy, 8, 1333–1341. 10.4161/auto.20792 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu, M. , Waguri, S. , Ueno, T. , Iwata, J. , Murata, S. , Tanida, I. , … Chiba, T. (2005). Impairment of starvation‐induced and constitutive autophagy in Atg7‐deficient mice. Journal of Cell Biology, 169, 425–434. 10.1083/jcb.200412022 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lankarani, K. B. , Sepehrimanesh, M. , Seghatoleslam, S. F. , Hoseini, S. E. , & Ghavami, S. (2017). Autophagy‐related protein 7 level in patients with ulcerative colitis. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology, 52, 468 10.1080/00365521.2016.1259655 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavandero, S. , Chiong, M. , Rothermel, B. A. , & Hill, J. A. (2015). Autophagy in cardiovascular biology. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 125, 55–64. 10.1172/JCI73943 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee, I. H. , & Finkel, T. (2009). Regulation of autophagy by the p300 acetyltransferase. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 284, 6322–6328. 10.1074/jbc.M807135200 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee, I. H. , Kawai, Y. , Fergusson, M. M. , Rovira, I. I. , Bishop, A. J. , Motoyama, N. , … Finkel, T. (2012). Atg7 modulates p53 activity to regulate cell cycle and survival during metabolic stress. Science, 336, 225–228. 10.1126/science.1218395 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee, T. I. , & Young, R. A. (2013). Transcriptional regulation and its misregulation in disease. Cell, 152, 1237–1251. 10.1016/j.cell.2013.02.014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lettre, G. (2014). Rare and low‐frequency variants in human common diseases and other complex traits. Journal of Medical Genetics, 51, 705–714. 10.1136/jmedgenet-2014-102437 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li, S. , Liu, C. , Gu, L. , Wang, L. , Shang, Y. , Liu, Q. , … Li, W. (2016). Autophagy protects cardiomyocytes from the myocardial ischaemia‐reperfusion injury through the clearance of CLP36. Open Biology, 6, 160177 10.1098/rsob.160177 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinet, W. , & De Meyer, G. R. (2009). Autophagy in atherosclerosis: A cell survival and death phenomenon with therapeutic potential. Circulation Research, 104, 304–317. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.188318 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez‐Lopez, N. , Athonvarangkul, D. , Mishall, P. , Sahu, S. , & Singh, R. (2013). Autophagy proteins regulate ERK phosphorylation. Nature Communications, 4, 2799 10.1038/ncomms3799 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merves, J. F. , Whelan, K. A. , Benitez, A. J. , Muir, A. B. , Furuta, G. T. , Wang, M. L. , … Nakagawa, H. (2016). ATG7 Gene Expression as a Novel Tissue Biomarker in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. American Journal of Gastroenterology, 111, 151–153. 10.1038/ajg.2015.404 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger, S. , Saukko, M. , Van Che, H. , Tong, L. , Puder, Y. , Riess, O. , & Nguyen, H. P. (2010). Age at onset in Huntington's disease is modified by the autophagy pathway: Implication of the V471A polymorphism in Atg7. Human Genetics, 128, 453–459. 10.1007/s00439-010-0873-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michiels, C. F. , Fransen, P. , De Munck, D. G. , De Meyer, G. R. , & Martinet, W. (2015). Defective autophagy in vascular smooth muscle cells alters contractility and Ca²⁺ homeostasis in mice. American Journal of Physiology. Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 308, H557–H567. 10.1152/ajpheart.00659.2014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima, N. , Yoshimori, T. , & Ohsumi, Y. (2011). The role of Atg proteins in autophagosome formation. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology, 27, 107–132. 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-092910-154005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orogo, A. M. , & Gustafsson, Å. B. (2015). Therapeutic targeting of autophagy: Potential and concerns in treating cardiovascular disease. Circulation Research, 116, 489–503. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.303791 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattison, J. S. , Osinska, H. , & Robbins, J. (2011). Atg7 induces basal autophagy and rescues autophagic deficiency in CryABR120G cardiomyocytes. Circulation Research, 109, 151–160. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.237339 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanjuan, M. A. , Dillon, C. P. , Tait, S. W. , Moshiach, S. , Dorsey, F. , Connell, S. , … Green, D. R. (2007). Toll‐like receptor signalling in macrophages links the autophagy pathway to phagocytosis. Nature, 450, 1253–1257. 10.1038/nature06421 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrijvers, D. M. , De Meyer, G. R. , & Martinet, W. (2011). Autophagy in atherosclerosis: A potential drug target for plaque stabilization. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 31, 2787–2791. 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.224899 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, M. D. , & Fazio, S. (2016). From Lipids to Inflammation: New Approaches to Reducing Atherosclerotic Risk. Circulation Research, 118, 732–749. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306471 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai, S. , Hu, X. Q. , Peng, D. Q. , Zhou, S. H. , & Zheng, X. L. (2016). The roles of autophagy in vascular smooth muscle cells. International Journal of Cardiology, 211, 1–6. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.02.128 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanida, I. , Tanida‐Miyake, E. , Nishitani, T. , Komatsu, M. , Yamazaki, H. , Ueno, T. , & Kominami, E. (2002). Murine Apg12p has a substrate preference for murine Apg7p over three Apg8p homologs. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 292, 256–262. 10.1006/bbrc.2002.6645 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torisu, K. , Singh, K. K. , Torisu, T. , Lovren, F. , Liu, J. , Pan, Y. , … Finkel, T. (2016). Intact endothelial autophagy is required to maintain vascular lipid homeostasis. Aging Cell, 15, 187–191. 10.1111/acel.12423 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torisu, T. , Torisu, K. , Lee, I. H. , Liu, J. , Malide, D. , Combs, C. A. , … Finkel, T. (2013). Autophagy regulates endothelial cell processing, maturation and secretion of von Willebrand factor. Nature Medicine, 19, 1281–1287. 10.1038/nm.3288 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G. , Liu, L. , Huang, J. , Pang, S. , Wei, G. , Cui, Y. , & Yan, B. (2011). Alterations of autophagic‐lysosomal system in the peripheral leukocytes of patients with myocardial infarction. Clinica Chimica Acta, 412, 1567–1571. 10.1016/j.cca.2011.05.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G. , Wei, G. , Huang, J. , Pang, S. , Liu, L. , & Yan, B. (2011). Decreased gene expression of LC3 in peripheral leucocytes of patients with coronary artery disease. European Journal of Clinical Investigation, 41, 958–963. 10.1111/j.1365-2362.2011.02486.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, J. (2015). Atg7 in development and disease: Panacea or Pandora's Box? Protein Cell, 6, 722–734. 10.1007/s13238-015-0195-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J. , Hang, D. , Jiang, Y. , Chen, J. , Han, J. , Zhou, W. , … Dai, J. (2017). Evaluation of genetic variants in autophagy pathway genes as prognostic biomarkers for breast cancer. Gene, 627, 549–555. 10.1016/j.gene.2017.06.053 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


