Abstract
We model the transmission of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) by six differential equations that represent the reactions between HBV with DNA-containing capsids, the hepatocytes, the antibodies and the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) cells. The intracellular delay and treatment are integrated into the model. The existence of the optimal control pair is supported and the characterization of this pair is given by the Pontryagin’s minimum principle. Note that one of them describes the effectiveness of medical treatment in restraining viral production, while the second stands for the success of drug treatment in blocking new infections. Using the finite difference approximation, the optimality system is derived and solved numerically. Finally, the numerical simulations are illustrated in order to determine the role of optimal treatment in preventing viral replication.
Keywords: HBV virus, abaptive immune response, treatment, numerical simulation
1. Introduction
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infects hepatocytes and causes approximately one million deaths annually [1]. With more than 257 million infected persons; HBV is considered a global public health problem [2]. This dangerous epidemic can be easily transmitted through contact with infected body fluids [3]. After transmission of the infection, HBV can cause acute or chronic illness [4]. Many mathematical models have been developed in order to study and model the dynamics of this serious viral infection [5,6,7,8]. All these models include the interaction between HBV and both the healthy and infected liver cells. The models which include the adaptive immune response in fighting the free viruses and in reducing the infected cells have been studied [9,10,11,12]. This adaptive immunity is represented by cytotoxic T-lymphocytes (CTL) and antibody immune responses. The mathematical analysis of HBV viral infection with HBV DNA-containing capsids was determined [13,14,15,16,17]. It has also been noted that the infected liver cells release the HBV DNA-containing capsids under the form of mature viruses after being enveloped by both cellular membrane lipids and viral envelope proteins [18,19]. More recently, the optimal control of HBV infection including HBV DNA-containing capsids and CTL immune response was studied [17]. In this paper, we are interested in the same problem, but we will introduce antibodies into this model. This work is motivated by the role of antibodies in reducing the viral infection severity [20,21,22]; thus it will be important to consider such an interesting element in studying the HBV viral dynamics. The model under consideration will be stated under the form of the following nonlinear system of six differential equations:
| (1) |
The uninfected cells X are produced with an average s, die with a rate , and become infected by the virus with a rate k. Infected cells Y die with an average and are killed by the CTL immune system with an average p. The constant is the death average of infected but still not virus-producing cells. The intracellular delay, , stands for the time needed for infected cells to produce new viruses after viral entry. The term is the probability of surviving between and t. The capsids D are produced with a rate a, they are transmitted to blood with a rate and die with a rate . The free viruses V grow with a rate , decay at a rate u and are neutralized by antibodies with a rate q. Antibodies W expand in response to free virus with a rate g and decay at a rate h. CTLs Z develop in response to viral antigen derived from infected cells with a rate c and decay in the absence of antigenic stimulation with a rate b. Finally, and denote the efficiency of pegylated interferon (PEG IFN) and lamivudine (LMV) drugs, respectively. It is noteworthy to mention that the main function of the PEG IFN drug is to block new infections of the healthy hepatocytes in the liver, while the prime role of the second drug, LMV, is to stop viral production [16,17].
The organization of this paper is as follows. The next section is concerned to the analysis of the model. Section 3 is devoted to an optimization analysis of our suggested viral infection model. In Section 4, we construct an appropriate numerical algorithm and show some numerical simulations. The last section concludes the work.
2. Analysis of the Model
2.1. Non-Negativity and Boundedness of Solutions
The model (1) represents a system of six delayed differential equations. For such kind of problems, initial functions have to be stated and the functional framework needs to be specified. Let be the Banach space of continuous mapping from to supplied by the sup-norm . The initial functions of the problem verify the following:
| (2) |
Also, for biological reasons, these six initial functions , , , , and have to be non-negative:
| (3) |
We have the following result about the boundedness and the positivity of any solutions of the system (1):
Theorem 1.
For any initial functions , , , , and verifying (2) and (3), the system (1) has an unique solution; moreover, this solution is non-negative and bounded for all .
Proof.
By the classical theory of the functional differential equations (see for instance [23], and the references therein), we know that there is a unique local solution to system (1) in , where is a finite number.
By using the system (1), we have
and
By recursive argument we get that , this proves the positivity of solutions in .
For the boundedness result of all the solutions, we will consider the following functional:
Therefore, when we use (1), we have
because of the fact , we have , from which, it follows
Assuming that , we obtain
then,
this shows that is bounded, and so are the other functions , , , , and . Therefore, every local solution can be prolonged up to any time , which means that the solution exists globally. ☐
2.2. Steady States
By simple calculation the system (1) has the following disease free equilibrium
Indeed, the system (1) has four steady states other than :
where
| (4) |
where
| (5) |
where
and
where
3. Mathematical Analysis of the Optimal Control
3.1. The Optimization Problem
To state the optimization problem, we first suppose that and vary in time. The problem (1) becomes then
| (6) |
For this problem, we will have the following result of the boundedness and the positivity of any solutions:
Theorem 2.
For any initial conditions , , , , and verifying (2) and (3), the system (6) has a unique solution; moreover, this solution is non-negative and bounded for all .
Proof.
Using the classical theory of the functional differential equations [23], it is clear to see that there is a unique local solution to system (1) in .
From the system (6), we have
and
from all these previous equalities, we deduce that all solutions are non-negative in .
About the boundedness, we will prove that the solutions are bounded in each interval such that .
We will begin with . Let , from the first equation of system (6), we obtain
so,
this means that X is bounded.
From the second equation of (6), we obtain
since and , it follows
therefore,
since and from (2) and (3), we have the fact that is bounded, then Y is also bounded.
From the third equation of (6), we obtain
since , it follows
this inequality implies that
from the boundedness result of I, one can conclude that D is bounded.
From the fourth equation of (6), we obtain
then,
from the boundedness result of D, we conclude that V is also bounded.
From both the fourth and the fifth equations of (6), we obtain
then
from the boundedness results of D and V, we deduce that W is bounded.
From the second and the last equation of system (6), we obtain
then
from the boundedness results of X, Y and V, it follows the result that Z is bounded.
By following the same analysis as before, for each single interval with , one can conclude that all the solutions are bounded for all . Therefore, every local solution can be prolonged up to any time , which means that the solution exists globally. ☐
Let us consider the following objective functional:
| (7) |
where is the time period of therapy and the two positive constants and are based on the benefit-cost of the therapy and , respectively. The two control functions, and are supposed to be bounded and also Lebesgue integrable. Our main purpose is to maximize the objective functional defined in the Equation (7) by maximizing the number of the uninfected cells, increasing the CTL immune responses and the antibodies, decreasing the viral load and also decreasing the cost of treatment. That means, we are seeking an optimal control pair such that
| (8) |
where is the control set given by
| (9) |
3.2. An Optimal Control Existence Result
The two optimal control pair existence result can be obtained via the results [24,25]. Indeed, we have the following result:
Theorem 3.
There exists an optimal control such that
(10)
Proof.
To use the existence result [24], we should first check the following properties
- (C1)
The set of the corresponding state variables and controls is nonempty.
- (C2)
The set is closed and convex.
- (C3)
The right hand side of the state system is bounded by a linear function in the state and control variables.
- (C4)
The integrand of the objective functional is concave on .
- (C5)
There exists an and two constants , such that the integrand of the objective functional satisfieswhere
(11)
(12) The boundedness of the state system equations with the two controls (6) ensures us the existence of a solution. We can therefore deduce that the set of controls and the corresponding state variables are non-empty, this gives us the condition . The control set is convex and closed by definition, which ensures the condition . Moreover, since the system of state is bi-linear in , , the right hand-side of (6) verifies condition , using the fact that the solutions are bounded. About the condition , we obtain the Hessian matrix for I as follows,
(13) its determinant is stated as follows,
then I is concave on .
For the condition , we have
(14) with depends on the upper bound on X, W, Z, and . We deduce that there exists an optimal control pair such that
☐
3.3. The Optimality System
To prove the necessary conditions for the optimal control problem, we will use the Pontryagin’s minimum principle [26]. This principle changes (6), (7) and (9) into a problem of maximizing of an Hamiltonian, T, pointwise with respect to and : where the for is an adjoint variables and for is the system dynamics defined by
| (15) |
By the Pontryagin’s minimum principle with the delay fact in state [26], we have the following theorem:
Theorem 4.
For any optimal control pair , and any solutions (6), there exists an adjoint variables, , , , , and satisfying
(16) where the transversality conditions
(17) Moreover, the optimal control as follows,
(18)
Proof.
The transversality conditions and adjoint equations as follows,
(19) The two optimal controls and can be solved from the optimality conditions,
By the definition of , we obtain
If we replace and in the systems (6), we have the following optimality system:
then,
(20)
(21) ☐
4. Numerical Results
To illustrate the numerical simulations, we implement and solved numerically our optimality system by the finite difference approximation method [27,28,29]. We obtain the following algorithm (Algorithm 1):
| Algorithm 1: The forward-backward finite difference numerical scheme. |
|
Using values of parameters from [12,17]; i.e., , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , and . The role of the two parameters and is to calibrate the terms size in the system equations.
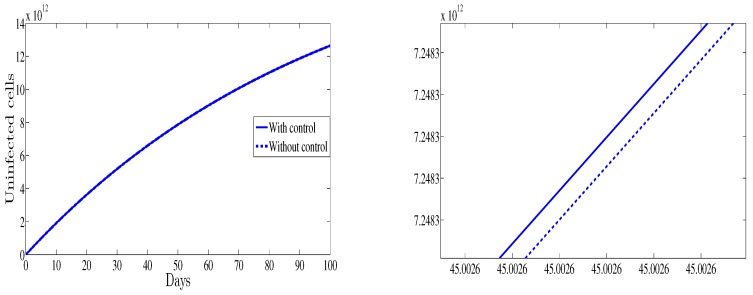
Figure 1 depicts the evolution of the uninfected cells as function of time for both cases with and without control therapy. It is shown that with control the number of the uninfected cells is higher than those observed for the case without control. This result support the fact that the control strategy is to maximize the number of the healthy cells.
Figure 1.
The evolution of the healthy cells (left) vs. time and a zoomed in region (right).
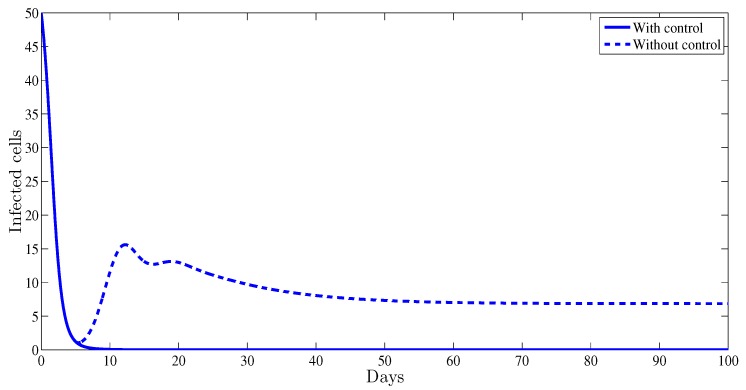
From Figure 2, one can observe that the plot representing the infected cells with control strategy converges towards , however without any control therapy it converges towards , which proves that administrating this treatment will help the patient by a significant reduction of the infected cells.
Figure 2.
The evolution of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) infected cells vs. time.
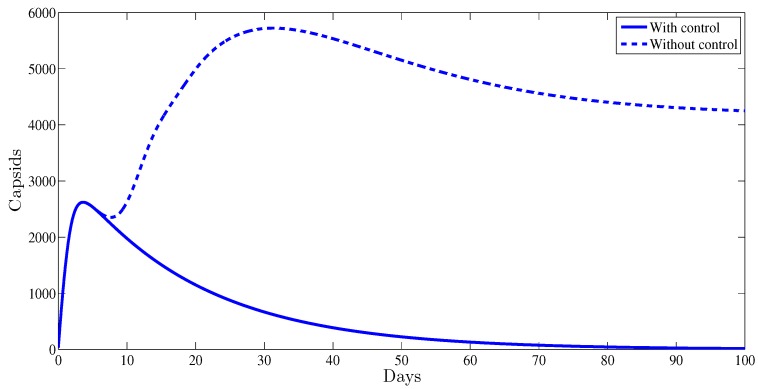
Figure 3 illustrates the evolution of the capsids during the period of observation. It was established that with a control strategy, the amount of capsids vanishes after the first weeks of the administrated therapy. Meanwhile, without any control strategy this number remains at very high positive level, .
Figure 3.
The evolution of HBV capsids vs. time.
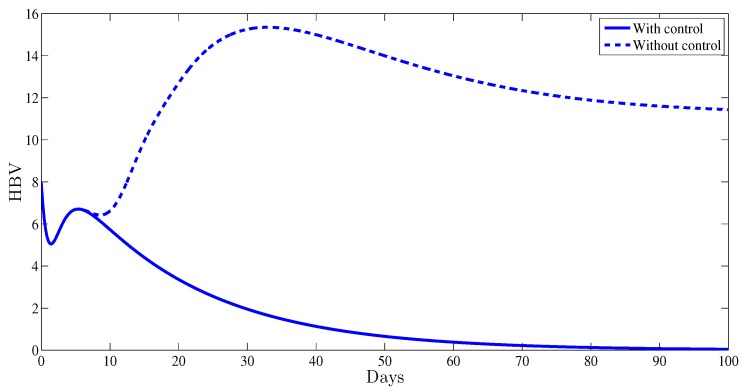
The role of the two administrated therapy controls is also remarked in Figure 4. It was shown that with therapy control, the number of virions dies out after the first weeks of therapy, while without any control strategy it remains equal to . This indicates clearly the impact of the administrated therapy in controlling the HBV viral replication.
Figure 4.
The free HBV virions as function of time.
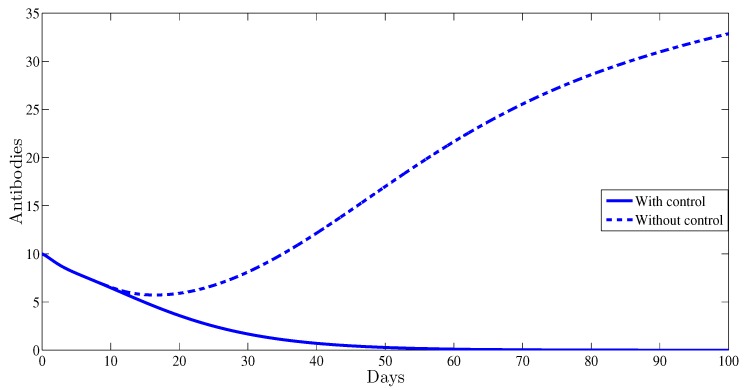
The antibody immune response is clearly affected by the control. This is illustrated in Figure 5; indeed, with control, the curve of antibodies converges towards zero; however, without any control strategy it converges towards which clearly indicates the importance of adding the antibody component to HBV viral dynamics.
Figure 5.
The evolution of antibodies as function of time.
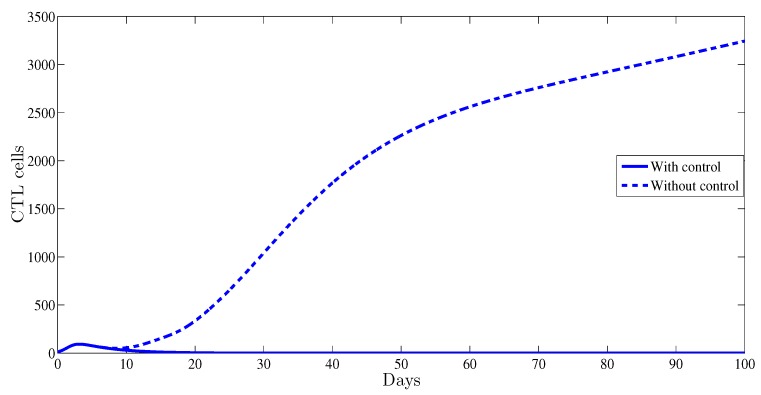
The CTL cell dynamics are also affected by the optimal control. This is shown in Figure 6; indeed, with control, the curve of CTL cells converges towards zero; however, without any control it converges towards a high level of ; this reveals the role of the CTL component in blocking HBV viral infection.
Figure 6.
The behavior of the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) immune response as function of time.
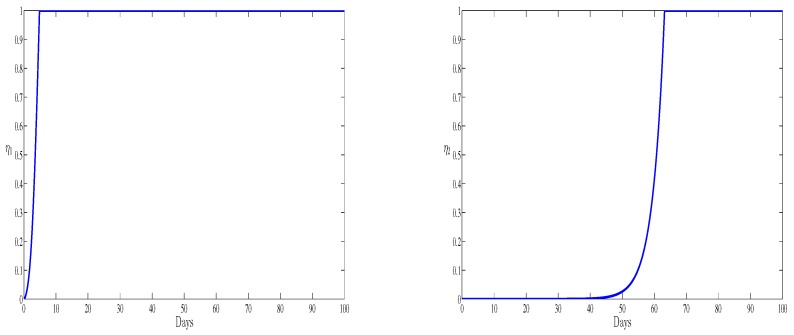
The two optimal controls and representing inhibiting new infections and blocking viral replication are represented in Figure 7. The two curves present the treatment administration schedule for the period of observation. Both of the controls start from zero and when the first immune boosting drug is administered at full scale, the second drug is at its lowest for the first days of observation. During the last days of observation both the therapies should be administrated at their full scales. In this case the new infection is totally blocked. It is worthy to notice that if we compare the numerical simulation of this paper and the recent work [17], we remark that the antibodies have a clear effect in maximizing the level of the healthy cells and reducing the amount of the free viruses. Also, we remark that the presence of antibodies improves the effectiveness of both treatments after the first 60 days by reaching their maximum value. However, without antibodies, only the second treatment presents efficacy (see [17]) which leads to the elimination of HBV viruses. The obtained numerical results show that with antibodies and the optimal control, we observe a significant reduce of the HBV infection. All our numerical simulations will performed during the acute HBV infection period. This period is also known as the early stage of the infection [12,30]; however it will be very useful to predict infection for a chronic type of the infection.
Figure 7.
The optimal control (left) and the optimal control (right) versus time.
5. Conclusions
We have modeled HBV in regards to intracellular behavior, capsids and adaptive immunity. The considered adaptive immune system is represented by the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte cells and the antibodies. The model under consideration includes six nonlinear differential equations that describe the dynamics that occur between hepatitis B free viruses (HBV), HBV DNA-containing capsids, hepatocytes, the antibodies and the CTL cells. An intracellular infection time delay and the effect of two drugs are incorporated into the suggested model. We have established the existence and uniqueness of the optimal controls via Pontryagin’s maximum principle. The problem was implemented and solved numerically using backward and forward finite numerical difference schemes. It was established that with the two administrated optimal therapies, the amount of the healthy hepatocytes increases considerably while the number of infected hepatocytes decreases remarkably. Moreover, it was also shown that, with the control strategy, the viral load decreases significantly comparing with the model without control case, and this may boost the patient’s life quality. Finally, we would like to mention that the used optimal controllers are given by open-loop, it will be useful to test other feedback control methods as a new predictive control model.
Author Contributions
J.D. and K.A. discussed the mathematical model. They wrote the paper and established the theoritical findings. J.D. carried out the numerical simuations.
Funding
The authors would like to thank the Moroccan CNRST “Centre National de Recherche Scientique et Technique” and the French CNRS “Centre National de Recherche Scientique” for the support of the research project in form of the PICS project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Kane M. Global programme for control of hepatitis B infection. Vaccine. 1995;13:547–549. doi: 10.1016/0264-410X(95)80050-N. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.World Health Organization . WHO Web Site; 2018. [(accessed on 19 July 2018)]. Progress toward Access to Hepatitis B Treatment Worldwide. Available online: http://www.who.int/hepatitis/news-events/cdc-hepatitis-b-article/en/ [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lavanchy D. Hepatitis B virus epidemiology, disease burden, treatment, and current and emerging prevention and control measures. J. Viral Hepat. 2004;11:97–107. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2893.2003.00487.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ciupe S.M., Ribeiro R.M., Nelson P.W., Perelson A.S. Modeling the mechanisms of acute hepatitis B virus infection. J. Theor. Biol. 2007;247:23–35. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2007.02.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Nowak M.A., Bonhoeffer S., Hill A.M., Boehme R., Thomas H.C., McDade H. Viral dynamics in hepatitis B virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1996;93:4398–4402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.9.4398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wang K., Wang W. Propagation of HBV with spatial dependence. Math. Biosci. 2007;210:78–95. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2007.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zheng Y., Min L., Ji Y., Su Y., Kuang Y. Global stability of endemic equilibrium point of basic virus infection model with application to HBV infection. J. Syst. Sci. Complex. 2010;23:1221–1230. doi: 10.1007/s11424-010-8467-0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Li J., Wang K., Yang Y. Dynamical behaviors of an HBV infection model with logistic hepatocyte growth. Math. Comput. Model. 2011;54:704–711. doi: 10.1016/j.mcm.2011.03.013. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Yousfi N., Hattaf K., Tridane A. Modeling the adaptive immune response in HBV infection. J. Math. Biol. 2011;63:933–957. doi: 10.1007/s00285-010-0397-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Jiang C., Wang W. Complete classification of global dynamics of a virus model with immune responses. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B. 2014;19:1087–1103. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Meskaf A., Allali K., Tabit Y. Optimal control of a delayed hepatitis B viral infection model with cytotoxic T-lymphocyte and antibody responses. Int. J. Dyn. Control. 2017;5:893–902. doi: 10.1007/s40435-016-0231-4. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Allali K., Meskaf A., Tridane A. Mathematical Modeling of the Adaptive Immune Responses in the Early Stage of the HBV Infection. Int. J. Differ. Equ. 2018;2018:6710575. doi: 10.1155/2018/6710575. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Manna K., Chakrabarty S.P. Chronic hepatitis B infection and HBV DNA-containing capsids: Modeling and analysis. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2015;22:383–395. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2014.08.036. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Manna K., Chakrabarty S.P. Global stability and a non-standard finite difference scheme for a diffusion driven HBV model with capsids. J. Differ. Equ. Appl. 2015;21:918–933. doi: 10.1080/10236198.2015.1056524. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Manna K., Chakrabarty S.P. Global stability of one and two discrete delay models for chronic hepatitis B infection with HBV DNA-containing capsids. Comput. Appl. Math. 2017;36:525–536. doi: 10.1007/s40314-015-0242-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Manna K., Chakrabarty S.P. Combination therapy of pegylated interferon and lamivudine and optimal controls for chronic hepatitis B infection. Int. J. Dynam. Control. 2018;6:354–368. doi: 10.1007/s40435-017-0306-x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Danane J., Meskaf A., Allali K. Optimal control of a delayed hepatitis B viral infection model with HBV DNA-containing capsids and CTL immune response. Optim. Control Appl. Methods. 2018;39:1262–1272. doi: 10.1002/oca.2407. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bruss V. Envelopment of the hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid. Virus Res. 2004;106:199–209. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2004.08.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ganem D., Prince A.M. Hepatitis B virus infection: Natural history and clinical consequences. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004;350:1118–1129. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra031087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ochsenbein A.F., Fehr T., Lutz C., Suter M., Brombacher F., Hengartner H., Zinkernagel R.M. Control of early viral and bacterial distribution and disease by natural antibodies. Science. 1999;286:2156–2159. doi: 10.1126/science.286.5447.2156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Aasa-Chapman M.M., Hayman A., Newton P., Cornforth D., Williams I., Borrow P., Balfe P., McKnight A. Development of the antibody response in acute HIV-1 infection. AIDS. 2004;18:371–381. doi: 10.1097/00002030-200402200-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Puoti M., Zonaro A., Ravaggi A., Marin M.G., Castelnuovo F., Cariani E. Hepatitis C virus RNA and antibody response in the clinical course of acute hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology. 1992;16:877–881. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840160404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hale J., Verduyn Lunel S.M. Introduction to Functional Differential Equations. Springer; New York, NY, USA: 1993. p. 99. Applied Mathematical Science. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Fleming W.H., Rishel R.W. Deterministic and Stochastic Optimal Control. Springer; New York, NY, USA: 1975. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lukes D.L. Differential Equations: Classical to Controlled, of Mathematics in Science and Engineering. Academic Press; New York, NY, USA: 1982. p. 162. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Göllmann L., Kern D., Maurer H. Optimal control problems with delays in state and control variables subject to mixed control-state constraints. Optim. Control Appl. Methods. 2009;30:341–365. doi: 10.1002/oca.843. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hattaf K., Yousfi N. Optimal control of a delayed HIV infection model with immune response using an efficient numerical method. ISRN Biomath. 2012 doi: 10.5402/2012/215124. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Laarabi H., Abta A., Hattaf K. Optimal control of a delayed SIRS epidemic model with vaccination and treatment. Acta Biotheor. 2015;63:87–97. doi: 10.1007/s10441-015-9244-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chen L., Hattaf K., Sun J. Optimal control of a delayed SLBS computer virus model. Physica A. 2015;427:244–250. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2015.02.048. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Yan Z., Tan W., Zhao W., Dan Y., Wang X., Mao Q., Wang Y., Deng G. Regulatory polymorphisms in the IL-10 gene promoter and HBV-related acute liver failure in the Chinese population. J. Viral Hepat. 2009;16:775–783. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2009.01139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]