Abstract
Background
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and Parkinson’s disease (PD) are the top two common neurodegenerative diseases in elderly. Recent studies found the α-synuclein have a key role in AD. Although many clinical and pathological features between AD and PD are shared, the genetic association between them remains unclear, especially whether α-synuclein in PD genetically alters AD risk.
Results
We did not obtain any significant result (OR = 0.918, 95% CI: 0.782–1.076, P = 0.291) in MR analysis between PD and AD risk. In MR between α-synuclein in PD with AD risk, we only extracted rs356182 as the IV through a strict screening process. The result indicated a significant association based on IVW method (OR = 0.638, 95% CI: 0.485–0.838, P = 1.20E-03). In order to examine the robustness of the IVW method, we used other three complementary analytical methods and also obtained consistent results.
Conclusion
The overall PD genetic risk factors did not predict AD risk, but the α-synuclein susceptibility genetic variants in PD reduce the AD risk. We believe that our findings may help to understand the association between them, which may be useful for future genetic studies for both diseases.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1186/s12881-018-0721-7) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, α-synuclein, Mendelian randomization, Genetic association
Background
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and Parkinson’s disease (PD) are the top two common neurodegenerative diseases [1]. In 2015, AD and PD respectively affected about 29.8 million and 6.2 million people worldwide [2]. AD is characterized by a progressive decline in memory, language, problem solving and other cognitive functions [3]. The neuropathological changes of AD are mainly manifested as brain atrophy and the accumulation of abundant extracellular Aβ plaques and intraneuronal neurofibrillary tau tangles [4, 5]. The patients suffering from PD show slow movements, tremor, gait and balance disturbances and other behavioral problems [6]. The main pathological characteristics of PD are the progressive degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra and the presence of Lewy bodies, which are made of abnormal filaments composed of α-synuclein [7, 8].
The two neurodegenerative diseases share many clinical and pathological features. Because of the toxicity of the α-synuclein or Aβ42 and tau proteins, so many similar cascades of neuronal reactions leading to progressive neurodegeneration occur in PD and AD patients. The overlapping pathological changes of AD and PD include activation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta, mitogen-activated protein kinases, cell cycle reentry and oxidative stress, etc. [9]. As we all know, mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is associated with the risk of progression to AD. However, MCI was recently also recognized as a kind of subtype predicting progression to PD [10, 11]. About 25% of non-demented patients with PD meet neuropsychological test criteria for MCI [12] and more than 50% of them eventually develop dementia [11]. All of these suggest that the two neurodegenerative diseases are probably the risk factor of each other.
In addition to the similarities between AD and PD, some potential mechanisms linking these two neurodegenerative diseases were found recently, especially the α-synuclein and Lewy pathology in AD. Several studies found that up to 50% AD patients exhibited extra aggregation of α-synuclein into Lewy bodies [13, 14]. Statistic test did not identify any significant difference of α-synuclein levels in cerebrospinal fluid between AD and PD patients [15]. In transgenic mice, the accumulation of α-synuclein could significantly disrupt cognition [14]. A similar study found that the α-synuclein in the transgenic mice could also massive increase apolipoprotein E (ApoE) levels and accelerate the accumulation of insoluble mouse Aβ [16]. Furthermore, the cerebrospinal fluid total α-synuclein levels contributed to the differential diagnosis of AD versus other dementias [17]. In the familial AD patients with presenilin 1 (PSEN1) mutations, which is most commonly associated with familial forms of AD, the notable interaction between α-synuclein and PSEN1 was identified in post-mortem brain tissue [9]. Our previously study conducted an interaction network using genome-wide association studies (GWASs) data and found the significant interaction among AD and PD susceptibility genes [7]. All of these evidences suggest a further investigation for the potential genetic mechanisms linking PD to AD, particularly the role that the α-synuclein plays in AD.
In recent years, large-scale GWAS identified some common genetic variants and provided insights into the genetics of AD and PD, including α-synuclein coding gene Synuclein Alpha (SNCA) 18,19. The large-scale GWAS datasets provide tremendous support for investigating the potential genetic association between PD and AD risk by Mendelian randomization analytical method (MR). MR is conceptually similar to randomized controlled trials (RCT) and can be applied to investigate the causality of biomarkers in disease etiology based on GWAS summary data20,21. In our study, we conducted a MR analysis with the lead single nucleotide polymorphisms (lead SNPs, which showed the strongest association in GWAS) from PD susceptibility loci. Here, these lead SNPs defined as instrumental variable (IV). In the results of sensitivity analysis of the MR between PD and AD risk, we found that the absence of SNCA lead SNP would massive decrease the statistical significance. Considering the reported role of α-synuclein in AD pathology, we further performed a MR to investigate the genetic association of the α-synuclein and AD risk.
Materials and methods
Study design
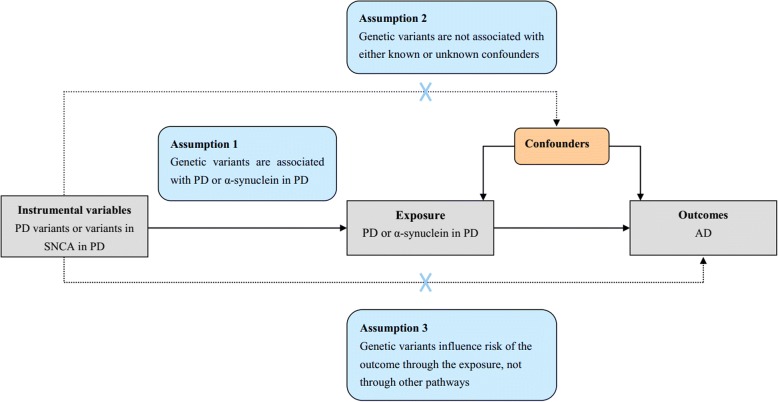
MR is based on the premise that the human genetic variants are randomly distributed in the population [18, 19]. These genetic variants are largely not associated with confounders and can be used as IVs to estimate the causal association of exposures (PD, α-synuclein in PD) with an outcome (AD) [18, 19]. The MR is based on three principal assumptions (Fig. 1), which have been widely described in recent studies [18, 19]. First, the genetic variants selected to be IVs should be associated with the exposures (PD, α-synuclein in PD) (assumption 1 in Fig. 1) 20,22. Second, the genetic variants should not be associated with confounders (assumption 2 in Fig. 1) [18, 19]. Third, genetic variants should affect the risk of the outcome (AD) only through the exposure (PD or α-synuclein in PD) (assumption 3 in Fig. 1) 20,22. The second and third assumptions are collectively known as independence from pleiotropy [18, 19]. This study is based on the publicly available, large-scale GWAS summary datasets, and the genetic variants are SNPs. All participants gave informed consent in all these corresponding original studies.
Fig. 1.
Mendelian randomization assumptions. The Mendelian randomization is based on three principal assumptions, which have been widely described in recent studies [18, 29]. First, the genetic variants selected to be IVs should be associated with the exposure (PD or α-synuclein in PD) (assumption 1) [18, 29]. Second, the genetic variants should not be associated with confounders (assumption 2) [18, 29]. Third, genetic variants should affect the risk of the outcome (AD) only through the exposure (PD or α-synuclein in PD) (assumption 3) [18, 29]
PD GWAS dataset
Here, we first used PD susceptibility SNPs as the IVs that from the most large-scale PD GWAS dataset [20]. This GWAS included 428,235 individuals (26,035 PD cases and 403,190 controls) consisting of 416,518 individuals in discovery stage and 21,679 individuals in replication stage [20]. The final joint analysis identified 17 novel loci associated with PD with the genome-wide significance (P < 5.00E-08) [20]. We extracted lead SNPs information of each locus from the joint analysis results except rs601999, which did not provide sufficient data. We also obtained 27 genome-wide significant loci from other more earlier GWASs23,24. But the basic lead SNPs information of these 27 loci were extracted from the discovery stage of the most large-scale GWAS [19]. All these 43 lead SNPs were independent [20].
Reported SNCA mutations in PD
We acquired the PD susceptibility SNCA lead SNPs through a rigorous screening process. We first searched all previous GWASs which reported SNCA as a PD susceptibility locus. Afterwards, we obtained the lead SNPs from each GWAS. However, we would exclude the lead SNP when they were not reported by GWAS of European ethnicity. When a lead SNP is reported by more than one GWAS, we would extract the summary statistics from the most large-scale GWAS because of its greater statistic power. When several lead SNPs were in linkage disequilibrium (LD), we would choose the one from the most large-scale GWAS. We searched the LD information by using the HaploReg v4.1, which based on LD data from 1000 Genomes Project (CEU) [21].
Finally, we only selected one lead SNP from 7 unduplicated lead SNPs. The sources and the detailed information about the 7 SNPs are described in Table 1. We excluded the SNPs rs11931074, rs8180209 and rs6532194 because they were reported in GWASs of Asian ethnicity. We then found that all of the rest 4 SNPs were located in SNCA. Considering the rs356182 was overwhelmingly significantly associated with PD risk in the most large-scale PD GWAS [20], we selected this genetic variant as tagged SNP to perform MR analysis.
Table 1.
Characteristics of 7 SNCA genetic variants reported in PD GWASs
| SNP | Chr:BPa | Reported year | Source | Reported ancestry | LD (r2)b | Function class | EA | NEA | EAF | OR (95% CI) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs356182 | 4: 90626111 | 2017 | Chang D [20] | European | 1 | Intron variant | G | A | 0.404 | 1.33 (1.30–1.36) | 5.21E-123 |
| rs356219 | 4:89716450 | 2012 | Lill CM [47] | Caucasian | 0.76 | Intron variant | G | A | 0.41 | 1.29 (1.25–1.33) | 6.00E-65 |
| rs356220 | 4:89720189 | 2014 | Hill-Burns EM [48] | European | 0.51 | Intron variant | T | C | 0.364 | 1.38 (1.24–1.52) | 3.00E-11 |
| rs2736990 | 4:89757390 | 2010 | Edwards DL [49] | Caucasian | 0.48 | Intron variant | G | A | 0.52 | 1.30 (1.18–1.43) | 6.74E-8 |
| rs8180209 | 4:89723303 | 2017 | Foo JN [50] | Han Chinese | NAc | Intron variant | A | G | 0.07 | 0.41 (NAd) | 1.02E-32 |
| rs11931074 | 4:89718364 | 2009 | Satake W [51] | Japanese | NAc | Intron variant | G | T | 0.36 | 1.37 (1.27–1.48) | 7.35E-17 |
| rs6532194 | 4:89859751 | 2012 | Lill CM [47] | Asian | NAc | Intergenic variant | T | C | 0.40 | 1.29 (1.20–1.39) | 4.91E-11 |
aChr:BP, Chromosome:Position
brepresent the r2 value of linkage disequilibrium (LD) between the selected genetic variant and the tagged mutation rs356182. The range of r2 is 0–1, the greater the value of r2, the stronger the linkage disequilibrium
cThe genetic variants were not reported in European (or Caucasian) populations
dThe 95% CI of OR was not available
AD GWAS dataset
The AD GWAS dataset was downloaded from the large-scale meta-analysis, which was performed by the International Genomics of Alzheimer’s Project (IGAP) [22]. In stage 1, the IGAP genotyped and imputed 7,055,881 SNPs, and performed a meta-analysis of four GWAS datasets including 17,008 cases and 37,154 controls of European descent [22]. All patients with AD satisfied the NINCDS-ADRDA criteria or DSM-IV guidelines [22]. Here, we would extract the summary statistics of the 43 lead SNPs from stage 1 results of the AD GWAS.
Pleiotropy analysis
In MR study, there is a potential violation of assumption 2 and 3 through pleiotropy that a genetic instrument is associated with a study outcome through biological pathways outside the interest exposure. Here, we performed an assessment for pleiotropy to assure that all the selected genetic variants do not exert effects on AD risk through biological pathways independent of PD pathological changes. Five steps were taken to reduce the risk of pleiotropy. In stage 1, nine potentially modifiable risk factors, which were reported in a major review about dementia risk factors, were considered [23]. The nine risk factors consisted of low levels of education, midlife hearing loss, physical inactivity, high blood pressure (hypertension), type 2 diabetes, obesity, smoking, depression, and social isolation [23]. We excluded obesity because a recent MR study reported that this trait as well as body mass index (BMI) is not genetically associated with AD risk [24]. In stage 2, we investigated whether the dietary factors are the potential confounders [23, 25]. The UK Biobank datasets were available [26]. Some studies reported that alcohol play an important role in AD risk, so we considered it as a potential confounder in stage 3 [27]. In stage 4, we evaluated the potential pleiotropic associations of IVs with AD biomarkers, which contain cerebrospinal fluid tau, phosphorylated tau (ptau) and Aβ42 [28]. In last stage, we selected MR-Egger intercept test to evaluate the potential pleiotropic associations of these genetic variants with potential confounders. Here, we provided more detailed information about the selected exposures and counterpart GWASs are described in Additional file 1.
Mendelian randomization analysis
We conducted two MR analyses to investigate the genetic association between PD and AD risk and the genetic association between α-synuclein in PD and AD risk. Until now, four different MR analytical methods have been well established including inverse-variance weighted meta-analysis (IVW), weighted median regression, MR-Egger regression and maximum-likelihood regression [18, 29]. However, the IVW has more statistical power than the other three methods [30]. The detailed information of IVW were described in Additional file 2. Particularly, MR-Egger regression always including a wide confidence intervals even the null hypothesis [30]. Therefore, we selected the IVW as the main analytical method to perform the MR analysis, as did in previous MR studies [19, 29].
Besides, in MR analysis of PD and AD risk, we also selected the weighted median regression, MR-Egger regression and maximum-likelihood method as the complementary analytical methods to examine the robustness of the IVW estimate. MR-Egger could also provide a statistical test the presence of potential pleiotropy, and account for this potential pleiotropy [31]. If there was no clear evidence of pleiotropy, we would expect all the four tests to give consistent estimates. We also performed a sensitivity analysis using the leave-one-out permutation method. In the MR analysis between α-synuclein in PD and AD risk, we only selected maximum-likelihood method as complementary analytical method because of the quantitative limitation of IV.
All analyses were conducted using the R package ‘MendelianRandomization’ [32]. We choose P < 0.05 as discriminant criterion for statistical significant result of the MR study.
Results
Instrumental variable
In MR analysis between PD and AD risk, we obtained 43 SNPs associated with PD as potential IVs. However, one of these 43 genetic variants as well as its proxy genetic variants were not available in stage 1 dataset of AD GWAS. The genetic variant was rs143918452 and we excluded it from the IVs. All the rest SNPs could map to genes implicated in PD pathology pathways, including autophagy, mitochondria, immune system, lysosome and endocytosis, etc. [20, 33, 34].
In MR analysis between α-synuclein in PD and AD risk, we only selected rs356182 after a rigorous screening process. As we all know, α-synuclein plays an important role in almost all PD pathology pathways. The genetic variants at SNCA locus (coding α-synuclein) can alter the risk of PD and even lead to monogenic and severe early-onset forms PD [34]. The rs356182 were reported as lead SNP of SNCA locus in most PD GWASs, which was also the strongest association signal in the most large-scale PD GWAS [20]. Recently, some studies found that rs356182 was associated with a specific SNCA 5′ untranslated region transcript isoform and regular the SNCA expression in brain [35, 36]. The firm and reliable association between rs356182 and α-synuclein make the SNP perfectly meet the requirements of IV.
Pleiotropy of instrumental variables
We identified that rs11343 and rs17649553 were significantly associated with years of education in stage1 (P = 1.20E-4 and P = 2.33E-07 respectively). We also found that rs17649553 was associated with Vitamin in stage 2 and continuous alcohol in stage 3. In stage 2, rs9275326 was associated with vitamin C, vitamin B9 and mineral supplements with P = 6.42E-04, 1.95E-09 and 2.63E-06. There were no genetic variants associated with AD biomarker. In stage 5, the MR-Egger intercept test showed no significant intercept (MR-Egger intercept β = 0.003; P = 0.717) in these genetic variants. By iteratively pruning the corresponding variant list, we also didn’t find any significant intercept. The detailed information about the pleiotropy of these genetic variants is described in Table S1-S3 in Additional file 3 and Table S4 in Additional file 4.
In summary, our pleiotropy analysis showed that rs11343, rs17649553 and rs9275326 may have potential violation of assumption 2 and 3 through pleiotropy. To meet the MR assumptions (Fig. 1), we excluded these variants in following analyses. The rest 39 genetic variants which used in following analyses were detailed described in Table 2.
Table 2.
Characteristics of 39 genetic variants in PD and AD GWAS datasets
| SNP | Chr | Pos | Nearby Genes | EA | NEA | EAFa | PD | AD GWAS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Betab | SE | P value | Betab | SE | P value | |||||||
| rs10797576 | 1 | 232,664,611 | SIPA1L2 | T | C | 0.127 | 0.113 | 0.014 | 8.41E-13 | 0.006 | 0.022 | 0.795 |
| rs10906923 | 10 | 15,569,598 | FAM171A1 | A | C | 0.461 | 0.073 | 0.014 | 1.35E-8 | −0.033 | 0.017 | 0.051 |
| rs11060180 | 12 | 123,303,586 | OGFOD2 | A | G | 0.748 | 0.105 | 0.011 | 2.05E-20 | 0.032 | 0.019 | 0.081 |
| rs11158026 | 14 | 55,348,869 | GCH1 | C | T | 0.490 | 0.094 | 0.011 | 4.30E-16 | −0.002 | 0.017 | 0.894 |
| rs115185635 | 3 | 87,520,857 | CHMP2B | C | G | 0.012 | 0.191 | 0.048 | 1.22E-4 | −0.022 | 0.058 | 0.702 |
| rs11724635 | 4 | 15,737,101 | FAM200B, CD38 | A | C | 0.408 | 0.105 | 0.011 | 1.22E-19 | −0.032 | 0.016 | 0.040 |
| rs117896735 | 10 | 121,536,327 | BAG3 | A | G | 0.004 | 0.501 | 0.057 | 2.23E-19 | 0.133 | 0.086 | 0.119 |
| rs12456492 | 18 | 40,673,380 | SYT4 | G | A | 0.330 | 0.095 | 0.012 | 5.56E-16 | 0.009 | 0.017 | 0.589 |
| rs12497850 | 3 | 48,748,989 | NCKIPSD, CDC71 | T | G | 0.731 | 0.073 | 0.014 | 9.16E-9 | 0.028 | 0.017 | 0.088 |
| rs12637471 | 3 | 182,762,437 | MCCC1 | G | A | 0.663 | 0.163 | 0.015 | 2.11E-30 | 0.002 | 0.019 | 0.909 |
| rs13294100 | 9 | 17,579,690 | SH3GL2 | G | T | 0.457 | 0.083 | 0.014 | 4.84E-13 | 0.013 | 0.017 | 0.453 |
| rs14235 | 16 | 31,121,793 | ZNF646, KAT8 | A | G | 0.359 | 0.077 | 0.009 | 5.44E-12 | 0.041 | 0.016 | 0.011 |
| rs1474055 | 2 | 169,110,394 | STK39 | T | C | 0.201 | 0.186 | 0.018 | 5.68E-26 | 0.004 | 0.024 | 0.881 |
| rs1555399 | 14 | 67,984,370 | TMEM229B | T | A | 0.607 | 0.086 | 0.012 | 9.61E-11 | −0.021 | 0.016 | 0.194 |
| rs199347 | 7 | 23,293,746 | KLHL7, NUPL2, GPNMB | A | G | 0.483 | 0.094 | 0.011 | 3.51E-18 | −0.033 | 0.016 | 0.039 |
| rs2280104 | 8 | 22,525,980 | SORBS3, PDLIM2, C8orf58, BIN3 | T | C | 0.265 | 0.068 | 0.012 | 2.53E-8 | −0.002 | 0.016 | 0.923 |
| rs2414739 | 15 | 61,994,134 | VPS13C | A | G | 0.679 | 0.094 | 0.011 | 3.94E-14 | −8.00E-04 | 0.017 | 0.964 |
| rs2694528 | 5 | 60,273,923 | ELOVL7 | C | A | 0.135 | 0.140 | 0.020 | 4.84E-15 | −0.028 | 0.027 | 0.305 |
| rs2740594 | 8 | 11,707,174 | CTSB | A | G | 0.893 | 0.086 | 0.012 | 5.91E-12 | 0.002 | 0.018 | 0.926 |
| rs329648 | 11 | 133,765,367 | MIR4697 | T | C | 0.465 | 0.086 | 0.012 | 1.11E-13 | −0.007 | 0.018 | 0.701 |
| rs34043159 | 2 | 102,413,116 | IL1R2 | C | T | 0.332 | 0.077 | 0.009 | 5.48E-11 | 0.006 | 0.016 | 0.695 |
| rs34311866 | 4 | 951,947 | TMEM175,DGKQ | C | T | 0.140 | 0.207 | 0.014 | 1.47E-50 | 0.009 | 0.021 | 0.685 |
| rs353116 | 2 | 166,133,632 | SCN3A | C | T | 0.557 | 0.062 | 0.011 | 2.98E-8 | 0.038 | 0.016 | 0.021 |
| rs356182 | 4 | 90,626,111 | SNCA | G | A | 0.404 | 0.285 | 0.012 | 5.21E-123 | −0.056 | 0.017 | 0.001 |
| rs35749011 | 1 | 155,135,036 | GBA | A | G | 0.005 | 0.545 | 0.044 | 2.59E-35 | 0.188 | 0.071 | 0.008 |
| rs3793947 | 11 | 83,544,472 | DLG2 | G | A | 0.570 | 0.073 | 0.011 | 3.72E-9 | −0.010 | 0.016 | 0.525 |
| rs4073221 | 3 | 18,277,488 | SATB1 | G | T | 0.062 | 0.095 | 0.016 | 1.57E-8 | 0.007 | 0.023 | 0.754 |
| rs4653767 | 1 | 226,916,078 | ITPKB | T | C | 0.726 | 0.083 | 0.011 | 1.63E-11 | −0.005 | 0.017 | 0.756 |
| rs4784227 | 16 | 52,599,188 | TOX3 | T | C | 0.200 | 0.086 | 0.014 | 9.75E-11 | −0.010 | 0.018 | 0.580 |
| rs591323 | 8 | 16,697,091 | MICU3 | G | A | 0.635 | 0.094 | 0.014 | 2.38E-11 | −0.002 | 0.018 | 0.930 |
| rs62120679 | 19 | 2,363,319 | LSM7 | T | C | 0.426 | 0.077 | 0.014 | 6.64E-7 | −0.004 | 0.022 | 0.843 |
| rs6430538 | 2 | 135,539,967 | TMEM163,CCNT2 | C | T | 0.189 | 0.117 | 0.011 | 8.24E-24 | −0.047 | 0.017 | 0.006 |
| rs6812193 | 4 | 77,198,986 | FAM47E | C | T | 0.687 | 0.083 | 0.011 | 1.43E-14 | −0.017 | 0.016 | 0.310 |
| rs76904798 | 12 | 40,614,434 | LRRK2 | T | C | 0.132 | 0.140 | 0.015 | 1.21E-19 | −0.016 | 0.022 | 0.483 |
| rs78738012 | 4 | 114,360,372 | ANK2, CAMK2D | C | T | 0.039 | 0.122 | 0.018 | 4.78E-11 | −0.012 | 0.029 | 0.680 |
| rs8005172 | 14 | 88,472,612 | GALC | T | C | 0.434 | 0.077 | 0.012 | 8.77E-11 | −0.021 | 0.016 | 0.171 |
| rs8118008 | 20 | 3,168,166 | DDRGK1 | A | G | 0.540 | 0.068 | 0.012 | 1.99E-6 | 0.014 | 0.018 | 0.432 |
| rs823118 | 1 | 205,723,572 | NUCKS1, SLC41A1 | T | C | 0.411 | 0.117 | 0.011 | 1.12E-23 | −0.003 | 0.016 | 0.846 |
| rs9468199 | 6 | 27,681,215 | ZNF184 | A | G | 0.300 | 0.104 | 0.014 | 1.46E-12 | 0.044 | 0.022 | 0.046 |
SNP single-nucleotide polymorphism, Chr Chromosome, Pos Position, EA Effect Allele, NEA Non-Effect Allele, EAF Effect Allele Frequency, PD Parkinson’s disease, AD Alzheimer’s disease, GWAS genome-wide association studies, SE standard error
aFrequency of the effect allele in 1000 Genomes Project (CEU)
bBeta is the regression coefficient based on the effect allele. Beta > 0 and Beta < 0 means that this effect allele regulates increased and reduced PD or AD risk, respectively
Mendelian randomization between PD and AD risk
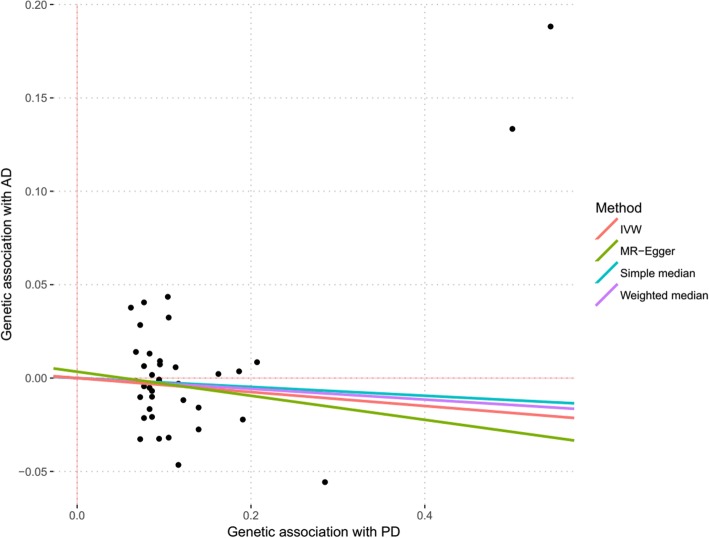
Using the remaining 39 genetic variants, IVW analysis showed that the genetically predicted PD was not significantly associated with AD risk (OR = 0.918, 95% CI: 0.782–1.076, P = 0.291). Furthermore, all of the weighted median estimate (OR = 1.069, 95% CI: 0.769–1.140, P = 0.509), MR-Egger estimate (OR = 0.863, 95% CI: 0.593–1.253, P = 0.437) and maximum-likelihood estimate (OR = 0.916, 95% CI: 0.780–1.076, P = 0.292) were consistent with the IVW estimate in terms of direction and magnitude. Meanwhile, the MR-Egger intercept test showed no significant intercept (β = 0.003, P = 0.717) between these 39 variants. Figure 2 shows individual genetic estimates from each of the 39 genetic variants using different methods.
Fig. 2.
Individual genetic estimates from each of 39 genetic variants using different methods. This scatter plot show individual causal estimates from each of 6 genetic variants associated with PD on the x-axis and AD risk on the y-axis. The continuous line represents the causal estimate of PD on AD risk
Sensitivity analysis between PD and AD risk
To further test the stability of these estimates, we sequentially removed each genetic variant in the MR analysis. The direction and precision of the genetic estimates between PD and the risk of AD remained largely unchanged using these MR methods except maximum-likelihood method (Table 3). In spite the exclusion of rs356182 notably increased the significance of the association between PD and AD risk, it is P value still not reach 0.05.
Table 3.
sensitivity analysis of the association between PD and AD risk
| SNPa | P value | SNPa | P value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IVWb | Wei-Medc | MR-Eggerd | IVWb | Wei-Medc | MR-Eggerd | ||
| rs10797576 | 0.281 | 0.600 | 0.437 | rs34043159 | 0.277 | 0.596 | 0.465 |
| rs10906923 | 0.365 | 0.653 | 0.348 | rs34311866 | 0.245 | 0.608 | 0.346 |
| rs11060180 | 0.200 | 0.598 | 0.422 | rs353116 | 0.204 | 0.593 | 0.606 |
| rs11158026 | 0.299 | 0.660 | 0.444 | rs356182 | 0.991 | 0.649 | 0.313 |
| rs115185635 | 0.307 | 0.654 | 0.454 | rs35749011 | 0.117 | 0.592 | 0.075 |
| rs11724635 | 0.419 | 0.653 | 0.441 | rs3793947 | 0.320 | 0.651 | 0.418 |
| rs117896735 | 0.207 | 0.597 | 0.240 | rs4073221 | 0.283 | 0.594 | 0.446 |
| rs12456492 | 0.264 | 0.599 | 0.450 | rs4653767 | 0.307 | 0.653 | 0.438 |
| rs12497850 | 0.222 | 0.594 | 0.527 | rs4784227 | 0.318 | 0.652 | 0.433 |
| rs12637471 | 0.277 | 0.608 | 0.411 | rs591323 | 0.297 | 0.596 | 0.444 |
| rs13294100 | 0.260 | 0.597 | 0.468 | rs62120679 | 0.302 | 0.649 | 0.440 |
| rs14235 | 0.172 | 0.593 | 0.547 | rs6430538 | 0.473 | 0.648 | 0.482 |
| rs1474055 | 0.277 | 0.605 | 0.406 | rs6812193 | 0.340 | 0.653 | 0.414 |
| rs1555399 | 0.355 | 0.652 | 0.408 | rs76904798 | 0.331 | 0.656 | 0.465 |
| rs199347 | 0.404 | 0.651 | 0.405 | rs78738012 | 0.310 | 0.652 | 0.448 |
| rs2280104 | 0.299 | 0.647 | 0.445 | rs8005172 | 0.353 | 0.652 | 0.385 |
| rs2414739 | 0.295 | 0.599 | 0.445 | rs8118008 | 0.267 | 0.594 | 0.490 |
| rs2694528 | 0.341 | 0.654 | 0.474 | rs823118 | 0.301 | 0.662 | 0.442 |
| rs2740594 | 0.290 | 0.597 | 0.449 | rs9468199 | 0.201 | 0.596 | 0.422 |
| rs329648 | 0.311 | 0.654 | 0.437 | ||||
athe SNP that was excluded in sensitivity analysis
bIVW, Inverse-variance weighted meta-analysis
cWei-Med, Weighted median
dMR-Egger, MR-Egger regression
Mendelian randomization between α-synuclein in PD and AD risk
Using rs356182 as IV, IVW analysis showed that the genetically changed PD α-synuclein was significantly associated with a reduced AD risk (OR = 0.638, 95% CI: 0.485–0.838, P = 1.20E-03). The maximum-likelihood estimate (OR = 0.60, 95% CI: 0.34–1.06, P = 0.08) was completely consistent with the IVW estimate.
Discussion
In this study, we firstly selected 39 SNPs as IVs to investigate the association between PD and AD risk by using MR methods. However, we didn’t identify any significant results with all P values greater than 0.2. In the sensitivity analysis, we found that in the absence of rs356182, the P value of the IVW result rose to nearly 1. Considering some PD patients exhibited AD characteristics as described in the introduction, we secondly selected rs356182 as IV and conducted another one MR. The results of this MR indicated that the α-synuclein in PD was significantly associated with AD risk. The consistent results of different MR methods increased the credibility of our findings.
Besides the similar clinical and neuropathological similarities as we all know, amounts of genetic overlap between AD and PD were also discovered42,43. The evaluation of the α-synuclein functional characterization in AD can be traced back to the last century [37]. From then on, a lot of evidences supported the discovery as described in introduction. Recently, many studies have found the potential genetic association between AD and PD [38–42]. A trans-pQTL study discovered the PD risk variant rs12456492 affects expression of AD-associated protein CD33 in peripheral monocytes [41]. Genetic association study proved rs76904798 of LRRK2 significantly reduce late-onset AD risk in Han Chinese [43]. The AD risk factor SORL1 had been identified to be associated with PD recently [38].
The rs356182 locates in the intron of SNCA, which is the coding gene of α-synuclein. In addition to the key role of α-synuclein in PD, rs356182 can defines PD endophenotype in different levels [36, 44, 45]. In our study, the association between α-synuclein and AD identified by rs356182 as IV greatly supported and extended the genetic overlap of AD and PD. The effect size of the IV was the regression coefficient between SNCA loci (the counts of effect allele) and PD. Therefore our results suggested that the α-synuclein function in PD probably causes AD pathological changes. This conclusion supported the phenomenon that some PD patients meet neuropsychological test criteria for MCI [12].
But the overall genetic risk factors of PD were not statistically associated with AD risk in our study. It can’t be ignored that PD is a complex disease with so many pathogenic factors leading to kinds of pathological changes19,41. However, there may be only one kind of the PD pathological changes is genetically associated with AD risk. And including all the PD pathogenic factors will reduce or even eliminate this genetic association statistically. A similar MR study investigated the association between type 2 diabetes (T2D) and AD [46]. They chose mechanism-specific genetic variants as IVs to overcome this problem [46]. And they found only insulin sensitivity genetic variants in T2D are associated with AD risk (OR = 1.17; 95% CI: 1.02–1.34) [46]. However, there are ambiguous boundaries between different pathogenic mechanisms in PD. Furthermore, one genetic variant is probably involved in many pathological pathways. That means the IVs of the mechanism-specific in PD may violate the MR assumptions. So we adopted the molecular-specific genetic variants as the IV in our study.
Nevertheless, we still could not exclude all the other possible pathways besides the PD pathological pathway that α-synuclein play roles in AD. In other words, the potential pleiotropy of the rs356182 may be the biggest problem in the study. That’s the insufficient of MR and selecting one genetic variant as IV expands this deficiency. Another limitation of our study is the absence of a well PD pathogenic mechanism division method. Overcoming these problems will greatly improve our understanding about the effect of PD pathological changes on AD risk.
Conclusions
As we all know, PD and AD have many clinical and pathological features. However, there is little genetic proof for the association between these neurodegenerative diseases. In this MR study, we investigated the genetic roles of PD and its molecular pathological changes in AD. The results indicated only the α-synuclein in PD was genetically associated with AD risk. The pleiotropy analysis demonstrated all of the 39 PD susceptibility SNPs used as IVs were not linked with any reported AD risk factors. Future studies could identify the potential biological process that linking the α-synuclein and AD. We believe this finding will help to understand the pathology of AD and PD, which will stimulate subsequent research.
Additional files
A more detailed description about the selected exposures and counterpart GWASs. And how we conducted the pleiotropy analysis with these datasets. (DOCX 95 kb)
Statistical description of Inverse-variance weighted method. (DOCX 71 kb)
The genetic association between PD susceptibility SNPs with potential AD risk factors. (XLSX 18 kb)
The results of the MR-Egger intercept test. (XLSX 10 kb)
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Guiyou Liu and Dr. Lin Jiao of the School of Life Science and Technology for their technical and linguistic assistance.
Funding
Publication costs are funded by funding from the National Key R&D Program of China (2016YFC1202302 and 2017YFSF090117), Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (F2015006), the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61822108 and 61571152), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (AUGA5710001716).
Availability of data and materials
The summary statistics used as IVs of the MR study are included within the articles and its Additional files. The datasets of the AD GWAS are available from the IGAP on reasonable request.
About this supplement
This article has been published as part of BMC Medical Genetics Volume 19 Supplement 1, 2018: Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Genome Informatics (GIW 2018): medical genetics. The full contents of the supplement are available online at https://bmcmedgenet.biomedcentral.com/articles/supplements/volume-19-supplement-1.
Abbreviations
- AD
Alzheimer’s disease
- CI
Confidence interval
- GWAS
Genome-wide association study
- IGAP
International Genomics of Alzheimer’s Project
- IV
Instrumental variable
- IVW
Inverse-variance weighted meta-analysis
- LD
Linkage disequilibrium
- MCI
Mild cognitive impairment
- MR
Mendelian randomization
- OR
Odd ratio
- PD
Parkinson’s disease
- pQTL
Protein quantitative trait loci
- RCT
Randomized controlled trial
- SNP
Single nucleotide polymorphism
- T2D
Type 2 diabetes
Authors’ contributions
QHJ and SLJ proposed and designed the research. ZFH extracted and processed the GWAS data with assistance from RT, PPW, WYZ, PR, and ML. ZFH preformed most of the statistical analyses. ZFH wrote the article with assistance from RT. QHJ supervised the writing and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Consent for publication
All authors agree to publish this article.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Zhifa Han, Email: zhifahan@foxmail.com.
Rui Tian, Email: xiaoxing110@foxmail.com.
Peng Ren, Email: 747667111@qq.com.
Wenyang Zhou, Email: 13408139@qq.com.
Pingping Wang, Email: wangpp220@hotmail.com.
Meng Luo, Email: slaket0628@hotmail.com.
Shuilin Jin, Email: jinsl@hit.edu.cn.
Qinghua Jiang, Email: qhjiang@hit.edu.cn.
References
- 1.Nussbaum RL, Ellis CE. Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(14):1356–1364. doi: 10.1056/NEJM2003ra020003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Disease GBD, Injury I, Prevalence C. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388(10053):1545–1602. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Alzheimer's A. 2016 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimer's & dementia : the journal of the Alzheimer's Association. 2016;12(4):459–509. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2016.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ballard C, Gauthier S, Corbett A, Brayne C, Aarsland D, Jones E. Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 2011;377(9770):1019–1031. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61349-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Goedert M. NEURODEGENERATION. Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases: The prion concept in relation to assembled Abeta, tau, and alpha-synuclein. Science. 2015;349(6248):1255555. doi: 10.1126/science.1255555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sveinbjornsdottir S. The clinical symptoms of Parkinson's disease. J Neurochem. 2016;139(Suppl 1):318–324. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Liu G, Bao X, Jiang Y, Liao M, Jiang Q, Feng R, Zhang L, Ma G, Chen Z, Wang G, et al. Identifying the association between Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson’s disease using genome-wide association studies and protein-protein interaction network. Mol Neurobiol. 2015;52(3):1629–1636. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-8946-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Davie CA. A review of Parkinson's disease. Br Med Bull. 2008;86:109–127. doi: 10.1093/bmb/ldn013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Majd S, Power JH, Grantham HJ. Neuronal response in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease: the effect of toxic proteins on intracellular pathways. BMC Neurosci. 2015;16:69. doi: 10.1186/s12868-015-0211-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Yarnall AJ, Rochester L, Burn DJ. Mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease. Age Ageing. 2013;42(5):567–576. doi: 10.1093/ageing/aft085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Caballol N, Marti MJ, Tolosa E. Cognitive dysfunction and dementia in Parkinson disease. Movement disorders : official journal of the Movement Disorder Society. 2007;22(Suppl 17):S358–S366. doi: 10.1002/mds.21677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Aarsland D, Bronnick K, Williams-Gray C, Weintraub D, Marder K, Kulisevsky J, Burn D, Barone P, Pagonabarraga J, Allcock L, et al. Mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson disease: a multicenter pooled analysis. Neurology. 2010;75(12):1062–1069. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181f39d0e. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hamilton RL. Lewy bodies in Alzheimer's disease: a neuropathological review of 145 cases using alpha-synuclein immunohistochemistry. Brain Pathol. 2000;10(3):378–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2000.tb00269.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Clinton LK, Blurton-Jones M, Myczek K, Trojanowski JQ, LaFerla FM. Synergistic interactions between Abeta, tau, and alpha-synuclein: acceleration of neuropathology and cognitive decline. J Neurosci. 2010;30(21):7281–7289. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0490-10.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Parnetti L, Chiasserini D, Bellomo G, Giannandrea D, De Carlo C, Qureshi MM, Ardah MT, Varghese S, Bonanni L, Borroni B, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid tau/alpha-synuclein ratio in Parkinson's disease and degenerative dementias. Mov Disord. 2011;26(8):1428–1435. doi: 10.1002/mds.23670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gallardo G, Schluter OM, Sudhof TC. A molecular pathway of neurodegeneration linking alpha-synuclein to ApoE and Abeta peptides. Nat Neurosci. 2008;11(3):301–308. doi: 10.1038/nn2058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Shi M, Tang L, Toledo JB, Ginghina C, Wang H, Aro P, Jensen PH, Weintraub D, Chen-Plotkin AS, Irwin DJ, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid alpha-synuclein contributes to the differential diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2018;14(8):1052-62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 18.Davey Smith G, Hemani G. Mendelian randomization: genetic anchors for causal inference in epidemiological studies. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23(R1):R89–R98. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Emdin CA, Khera AV, Natarajan P, Klarin D, Zekavat SM, Hsiao AJ, Kathiresan S. Genetic Association of Waist-to-hip Ratio with Cardiometabolic Traits, type 2 diabetes, and coronary heart disease. Jama. 2017;317(6):626–634. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.21042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chang D, Nalls MA, Hallgrimsdottir IB, Hunkapiller J, van der Brug M, Cai F, Kerchner GA, Ayalon G, International Parkinson's disease genomics C, and Me research T et al. A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies identifies 17 new Parkinson's disease risk loci. Nat Genet. 2017;49(10):1511–1516. doi: 10.1038/ng.3955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ward LD, Kellis M. HaploReg: a resource for exploring chromatin states, conservation, and regulatory motif alterations within sets of genetically linked variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40(Database issue):D930–D934. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lambert JC, Ibrahim-Verbaas CA, Harold D, Naj AC, Sims R, Bellenguez C, DeStafano AL, Bis JC, Beecham GW, Grenier-Boley B, et al. Meta-analysis of 74,046 individuals identifies 11 new susceptibility loci for Alzheimer's disease. Nat Genet. 2013;45(12):1452–1458. doi: 10.1038/ng.2802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Livingston G, Sommerlad A, Orgeta V, Costafreda SG, Huntley J, Ames D, Ballard C, Banerjee S, Burns A, Cohen-Mansfield J, et al. Dementia prevention, intervention, and care. Lancet. 2017;390(10113):2673–2734. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31363-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mukherjee S, Walter S, Kauwe JSK, Saykin AJ, Bennett DA, Larson EB, Crane PK, Glymour MM, Adult changes in thought study I, religious orders SM et al. Genetically predicted body mass index and Alzheimer's disease-related phenotypes in three large samples: Mendelian randomization analyses. Alzheimers Dement. 2015;11(12):1439–1451. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2015.05.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Luchsinger JA, Mayeux R. Dietary factors and Alzheimer's disease. The Lancet Neurology. 2004;3(10):579–587. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(04)00878-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sudlow C, Gallacher J, Allen N, Beral V, Burton P, Danesh J, Downey P, Elliott P, Green J, Landray M, et al. UK biobank: an open access resource for identifying the causes of a wide range of complex diseases of middle and old age. PLoS Med. 2015;12(3):e1001779. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Venkataraman A, Kalk N, Sewell G, Ritchie CW, Lingford-Hughes A. Alcohol and Alzheimer's disease-does alcohol dependence contribute to Beta-amyloid deposition, Neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease? Alcohol Alcohol. 2017;52(2):151–158. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/agw101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Deming Y, Li Z, Kapoor M, Harari O, Del-Aguila JL, Black K, Carrell D, Cai Y, Fernandez MV, Budde J, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies four novel loci associated with Alzheimer's endophenotypes and disease modifiers. Acta Neuropathol. 2017;133(5):839–856. doi: 10.1007/s00401-017-1685-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Boef AG, Dekkers OM, le Cessie S. Mendelian randomization studies: a review of the approaches used and the quality of reporting. Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44(2):496–511. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyv071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Noyce AJ, Kia DA, Hemani G, Nicolas A, Price TR, De Pablo-Fernandez E, Haycock PC, Lewis PA, Foltynie T, Davey Smith G, et al. Estimating the causal influence of body mass index on risk of Parkinson disease: a Mendelian randomisation study. PLoS Med. 2017;14(6):e1002314. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Dale CE, Fatemifar G, Palmer TM, White J, Prieto-Merino D, Zabaneh D, Engmann JEL, Shah T, Wong A, Warren HR, et al. Causal associations of adiposity and body fat distribution with coronary heart disease, stroke subtypes, and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a Mendelian randomization analysis. Circulation. 2017;135(24):2373–2388. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.026560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Yavorska OO, Burgess S. MendelianRandomization: an R package for performing Mendelian randomization analyses using summarized data. Int J Epidemiol. 2017;46(6):1734–1739. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyx034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Deng H, Wang P, Jankovic J. The genetics of Parkinson disease. Ageing Res Rev. 2018;42:72–85. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2017.12.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Billingsley KJ, Bandres-Ciga S, Saez-Atienzar S, Singleton AB. Genetic risk factors in Parkinson's disease. Cell and tissue research. 2018;373(1):9–20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 35.Pihlstrom L, Blauwendraat C, Cappelletti C, Berge-Seidl V, Langmyhr M, Henriksen SP, van de Berg WDJ, Gibbs JR, Cookson MR, International Parkinson disease genomics C et al. A comprehensive analysis of SNCA-related genetic risk in sporadic parkinson disease. Ann Neurol. 2018;84(1):117–129. doi: 10.1002/ana.25274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Cooper CA, Jain N, Gallagher MD, Weintraub D, Xie SX, Berlyand Y, Espay AJ, Quinn J, Edwards KL, Montine T, et al. Common variant rs356182 near SNCA defines a Parkinson's disease endophenotype. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2017;4(1):15–25. doi: 10.1002/acn3.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hashimoto M, Masliah E. Alpha-synuclein in Lewy body disease and Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Pathol. 1999;9(4):707–720. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.1999.tb00552.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Maple-Grodem J, Chung J, Lunde KA, Tzoulis C, Tysnes OB, Pedersen KF, Alves G. Alzheimer disease associated variants in SORL1 accelerate dementia development in Parkinson disease. Neurosci Lett. 2018;674:123–126. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2018.03.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ferrari R, Wang Y, Vandrovcova J, Guelfi S, Witeolar A, Karch CM, Schork AJ, Fan CC, Brewer JB, International FTDGC et al. Genetic architecture of sporadic frontotemporal dementia and overlap with Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2017;88(2):152–164. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2016-314411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Singleton A, Hardy J. The evolution of genetics: Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. Neuron. 2016;90(6):1154–1163. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.05.040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Chan G, White CC, Winn PA, Cimpean M, Replogle JM, Glick LR, Cuerdon NE, Ryan KJ, Johnson KA, Schneider JA, et al. Trans-pQTL study identifies immune crosstalk between Parkinson and Alzheimer loci. Neurology Genetics. 2016;2(4):e90. doi: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000000090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Belin AC, Bjork BF, Westerlund M, Galter D, Sydow O, Lind C, Pernold K, Rosvall L, Hakansson A, Winblad B, et al. Association study of two genetic variants in mitochondrial transcription factor a (TFAM) in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. Neurosci Lett. 2007;420(3):257–262. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2007.05.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zhu XC, Cao L, Tan MS, Jiang T, Wang HF, Lu H, Tan CC, Zhang W, Tan L, Yu JT. Association of Parkinson's disease GWAS-linked loci with Alzheimer's disease in Han Chinese. Mol Neurobiol. 2017;54(1):308–318. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9649-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Karimi-Moghadam A, Charsouei S, Bell B, Jabalameli MR. Parkinson disease from Mendelian forms to genetic susceptibility: new molecular insights into the neurodegeneration process. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2018;38(6):1153–1178. doi: 10.1007/s10571-018-0587-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Campelo C, Silva RH. Genetic variants in SNCA and the risk of sporadic Parkinson's disease and clinical outcomes: a review. Parkinson’s disease. 2017;2017:4318416. doi: 10.1155/2017/4318416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Walter S, Marden JR, Kubzansky LD, Mayeda ER, Crane PK, Chang SC, Cornelis M, Rehkopf DH, Mukherjee S, Glymour MM. Diabetic phenotypes and late-life dementia risk: a mechanism-specific Mendelian randomization study. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2016;30(1):15–20. doi: 10.1097/WAD.0000000000000128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Lill CM, Roehr JT, McQueen MB, Kavvoura FK, Bagade S, Schjeide BM, Schjeide LM, Meissner E, Zauft U, Allen NC, et al. Comprehensive research synopsis and systematic meta-analyses in Parkinson's disease genetics: the PDGene database. PLoS Genet. 2012;8(3):e1002548. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Hill-Burns EM, Wissemann WT, Hamza TH, Factor SA, Zabetian CP, Payami H. Identification of a novel Parkinson's disease locus via stratified genome-wide association study. BMC Genomics. 2014;15:118. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Edwards TL, Scott WK, Almonte C, Burt A, Powell EH, Beecham GW, Wang L, Zuchner S, Konidari I, Wang G, et al. Genome-wide association study confirms SNPs in SNCA and the MAPT region as common risk factors for Parkinson disease. Ann Hum Genet. 2010;74(2):97–109. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.2009.00560.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Foo JN, Tan LC, Irwan ID, Au WL, Low HQ, Prakash KM, Ahmad-Annuar A, Bei J, Chan AY, Chen CM, et al. Genome-wide association study of Parkinson's disease in east Asians. Hum Mol Genet. 2017;26(1):226–232. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Satake W, Nakabayashi Y, Mizuta I, Hirota Y, Ito C, Kubo M, Kawaguchi T, Tsunoda T, Watanabe M, Takeda A, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies common variants at four loci as genetic risk factors for Parkinson's disease. Nat Genet. 2009;41(12):1303–1307. doi: 10.1038/ng.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
A more detailed description about the selected exposures and counterpart GWASs. And how we conducted the pleiotropy analysis with these datasets. (DOCX 95 kb)
Statistical description of Inverse-variance weighted method. (DOCX 71 kb)
The genetic association between PD susceptibility SNPs with potential AD risk factors. (XLSX 18 kb)
The results of the MR-Egger intercept test. (XLSX 10 kb)
Data Availability Statement
The summary statistics used as IVs of the MR study are included within the articles and its Additional files. The datasets of the AD GWAS are available from the IGAP on reasonable request.