Abstract
The sirtuins (SIRTs) are a family of highly conserved histone deacetylases (HDACs) consisting of seven members (SIRT1-SIRT7). Over the past few decades, SIRT1 has been the most extensively studied and garnered tremendous attention in the scientific community due to its emerging role in cancer biology. However, its biological role in the regulation of oral cancer is not yet fully understood. Owing to contradictory findings regarding the role of SIRT1 in oral cancer, debate about it continues. The present study discusses the biological roles and potential therapeutic implications of SIRT1 in precancerous oral lesions and oral cancer.
Keywords: sirtuin, oral cancer, betel quid, transforming growth factor beta
1. Introduction
The sirtuin family proteins (SIRT) are class III histone deacetylases (HDACs) comprised of seven members (SIRT1-7). Sirtuin proteins are widely expressed in normal tissues and reported to be involved in several biological processes (1–4) (Fig. 1). SIRT1 was the first family member to be discovered and is still the most studied. Its biological role in cancer has been studied extensively, yet there are conflicting results regarding the association between the two as SIRT1 is known to suppress or promote cancer depending on its cellular content or type (2–4). The expression level of SIRT1 has been shown to play an important role in the pathogenesis of oral cancer (5–8), the sixth most frequent cancer worldwide, with oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) being, by far, the commonest single entity, accounting for about 90% of all malignancies in the oral cavity and posing a major public health problem in many Asian countries (9). The etiologies of oral cancer include betel quid chewing, smoking, alcohol consumption, genetic predisposition, and viruses, including human papillomavirus (HPV) (9,10). The overall 5-year survival rates for patients with OSCC (ranging from 34 to 62.9%) have not significantly improved for decades in spite of advances in the field of oncology. These findings underscore the importance of encouraging new areas of research on factors that modify oral cancer and therapeutic targets to treat it. The purpose of this review is to summarize the findings of recent publications on SIRT1 with regard to oral cancer and to discuss its importance as a possible therapeutic agent. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first review evaluating the biological role of SIRT1 in the modulation of oral cancer.
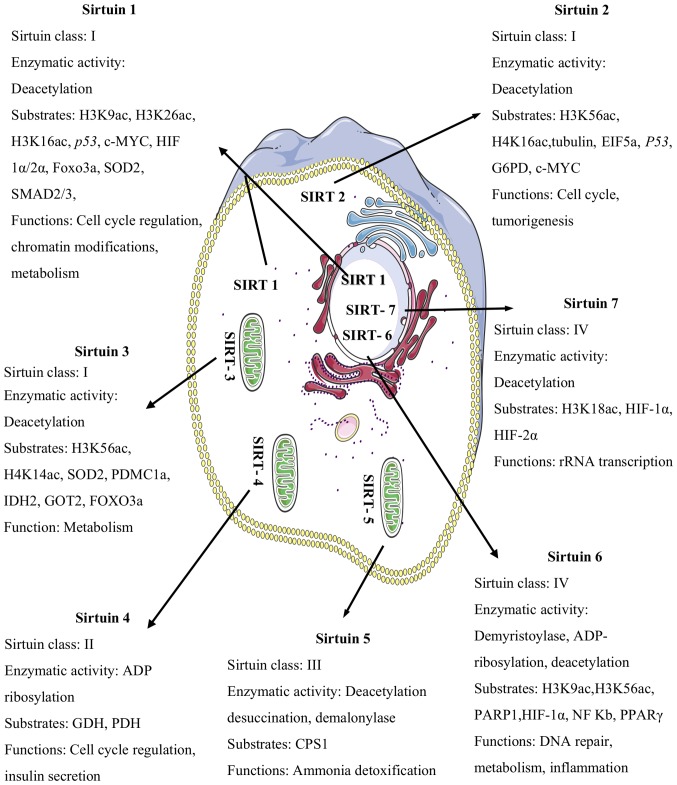
Figure 1.
The subcellular localizations of sirtuins, their enzymatic activities, substrates, and functions: H3K9ac, H3K26ac, H3K16ac, HIF-1α/2α, Foxo3a, SOD2, SMAD2/3, H3K56ac, H4K16ac, EIF5a, G6PD, H4K14ac, IDH2, GOT2, ADP; GDH, PDH, CPS1, PARP1, NF-Kb and PPAR-γ. SIRT1 is predominantly located in the nucleus, and also in the cytosol. SIRT2 is localized in the cytosol. SIRT3, SIRT4, and SIRT5 are mitochondrial proteins. SIRT6 and SIRT7 are localized in the nucleus. H3K9ac, histone H3 lysine 9 acetylation; H3K26ac, histone H3 lysine 26 acetylation; H3K16ac, histone H3 lysine 16 acetylation; HIF-1α/2α, hypoxia-inducible factor-1/2 alpha; Foxo3a, forkhead box o3 alpha; SOD2, superoxide dismutase 2; SMAD2/3, mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 2/3; H3K56ac, histone H3 lysine 56 acetylation; H4K16ac, histone H4 lysine 16 acetylation; EIF5a, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5a; G6PD, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; H4K14ac, histone H4 lysine 14 acetylation; IDH2, isocitrate dehydrogenase 2; GOT2, glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase; ADP, adenosine diphosphate; GDH, glutamate dehydrogenase; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; CPS1, carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1; PARP1, poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1; NF-Kb, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; PPAR-γ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors gamma.
2. Overview of SIRT1 functions
SIRT1 is a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)-dependent class III HDAC protein. High levels of NAD+ induce SIRT1 activity, whereas high NADH levels inhibit its function. Due to its localization, SIRT1 is capable of deacetylating lysine residues on nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins, which is thought to affect their stability, transcriptional activity, and translocation (1). Over the years, SIRT1 has been a major point of focus in biomedical research due to its diversified roles in various pathophysiological states (2–4). It plays contradictory roles in cancer and has an elaborate network of interactions that are directly involved in tumour biology (11–23) (Table I).
Table I.
Overview of SIRT1 functions.
| Author, year | Function | Substrates | Effects of SIRT1 | (Refs.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peters et al, 2001 | Genomic stability | H3K9Ac, H4K16Ac, | Modification of chromatin through the | (11) |
| Vaquero et al, 2004 | H1K26Ac, Suv39h1, | formation of heterochromatin structure | (12) | |
| Vaquero et al, 2007 | TERT | and positive regulation of telomere length | (13) | |
| Palacios et al, 2010 | (14) | |||
| Wang et al, 2008 | DNA repair | γ-H2AX, BRCA1, | Induction of HR and NHEJ-mediated DNA | (4) |
| Sawada et al, 2003 | Rad51, MRN complex, | repair | (17) | |
| Yuan et al, 2007 | Ku70, Bax | Induction of formation of NBSI (nibrin) foci | (15) | |
| Jeong et al, 2007 | and direct recruitment to DNA damage sites | (16) | ||
| Induction of Ku70-dependent DNA repair signalling | ||||
| Brunet et al, 2004 | Stress response | p53, Foxo3a, p300, | Inhibition of apoptosis and promote DNA | (18) |
| Motta et al, 2004 | set7/9, MnSOD | repair by deacetylase p53 | (20) | |
| Kobayashi et al, 2005 | Promotion of cell survival during oxidative | (19) | ||
| Chua et al, 2005 | stress by inducing DNA repair in cooperation | (21) | ||
| Yi et al, 2010 | with Foxo1 | (22) | ||
| Peng et al, 2011 | DNA methylation | DNMT1, DNMT3b | Alteration of DNMTs enzymatic activity by deacetylating different lysines | (23) |
H3K9ac, histone H3 lysine 9 acetylation; H4K16ac, histone H4 lysine 16 acetylation; H1K26ac, histone H1 lysine 26 acetylation; Suv39h1, suppressor of variegation 3–9 homolog 1; TERT, telomerase reverse transcriptase; γ-H2AX, phosphorylated form of variant histone H2AX; BRCA1, breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein; Rad51, DNA repair protein Rad51 homolog 1; MRN complex, Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 complex; Ku70, X-ray repair cross-complementing 6; Bax, BCL2 associated × protein; HR, homologous recombination; NHEJ, nonhomologous end joining; Foxo3a, forkhead box o3 α; p300, E1A binding protein p300; Set7/9, Set domain containing lysine methyltransferase 7; MnSOD, manganese-containing superoxide dismutase; Foxo1, forkhead box protein o1; DNMT1, DNA methyltransferase 1; DNMT3b, DNA methyltransferase 3 β.
3. SIRT1 and tumour development
SIRT1 plays a key role in epigenetic regulation of gene expression by changing the structure of chromatin. It has been reported to deacetylate both histone and non-histone proteins. Deacetylation of histones by SIRT1 has been shown to induce chromatin condensation, whereas acetylation by histone acetyltransferases (HATs) causes chromatin decondensation. This balance is crucial for normal cellular functions, and any disturbance of it will be related to cancer (24). SIRT1-mediated deacetylation of non-histone proteins has been suggested to be more important in cancer than histones (24,25). In tumour biology, SIRT1 seems to play contradictory roles and deregulation of SIRT1 expression has frequently been reported in many human malignancies (4,26–38) (Table II).
Table II.
SIRT1 and tumour development.
| A, Tumor promoter | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Author, year | Effects of SIRT1 | Types of tumour | (Refs.) |
| Huffman et al, 2007 | Inhibition of HIC-1 expression via epigenetic modification | Prostate cancer | (26) |
| Chen et al, 2012 | Induction of expression of c-Myc, EMT markers; thereby | HCC | (27) |
| Hao et al, 2014 | increasing resistance to the chemotherapeutic agent | (28) | |
| Chen et al, 2014 | Induction of genomic instability by maintaining the characteristics of CSCs | CRC | (29) |
| Zhao et al, 2013 | Induction of chemoresistance via dysregulation of HIC-1 | Pancreatic carcinoma | (30) |
| Stunkel et al, 2007 | Survival and proliferation of cancer cells | Colon carcinoma | (31) |
| Ford et al, 2005 | Induction of growth and survival | Cervical cancer | (32) |
| Induction of c-Myc activity | Thyroid carcinoma | ||
| He et al, 2016 | Induction of metastatic phenotype of cancerous cells | ESCC | (33) |
| Hida et al, 2007 | Dysregulation of the RB1 pathway | NMSC | (34) |
| Bradbury et al, 2005 | Induction of drug resistance | AML | (35) |
| B, Tumor suppressor | |||
| Author, year | Effects of SIRT1 | Types of tumour | (Refs.) |
| Wang et al, 2008 | Maintenance of genomic integrity & activation of | Glioblastoma | (4) |
| DNA repair mechanisms | Ovarian cancer | ||
| Hepatic cancer | |||
| Breast cancer | |||
| Bladder cancer | |||
| Prostate cancer | |||
| Jung et al, 2012 | Maintenance of genetic integrity and inhibition of β catenin, | CRC | (36) |
| Jang et al, 2013 | survivin expression | (37) | |
| Firestein et al, 2008 | Deacetylation and suppression of β-catenin | Colon cancer | (38) |
HIC1, hypermethylated in cancer 1; AFP, α-fetoprotein; TERT, telomerase reverse transcriptase; EMT, epithelial mesenchymal transition; CSCs, cancer stem cells; RB1, retinoblastoma 1; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; CRC, colorectal carcinoma; ESCC, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; NMSC, nonmelanoma skin cancer; AML, acute myeloid leukemia; β catenin, catenin β 1.
On the one hand, SIRT1 has been reported to deacetylate and inactivate p53, thereby allowing cells to bypass p53-induced apoptosis (22,39). Similarly, during cellular oxidative stress, SIRT1-mediated deacetylation of forkhead box O3 alpha (Foxo3a) has been shown to induce cell survival rather than apoptosis (4,22,39). This is good for normal cells to prolong their lifespan but in tumour cells, this effect is not at all desirable since it aggravates tumour growth. Meanwhile, overexpression of SIRT1 has been demonstrated to induce angiogenesis in cancer cells via increases in the expression of angiogenic growth factors (40). Taken together, these studies suggest that SIRT1 may bring more nutrition to cancer cells and lead to their enhanced growth, proliferation, and survival.
As opposed to what occurs during cellular oxidative stress, SIRT1 has been shown to induce mitochondrial translocation of p53, leading to enhanced p53-independent mitochondrial apoptosis (22). The DNA repair mechanisms and genomic stability functions of SIRT1 imply a protective effect against cancer (reviewed in 2–4). Therefore, the question arises as to whether SIRT1 acts primarily as an oncogene or a tumour suppressor. It is, however, strongly evident that SIRT1 is a critical regulator in the pathogenesis of tumours. To clarify the contradictory roles of SIRT1 in tumorigenesis, further studies are necessary.
4. Modulation of SIRT1 in oral cancer
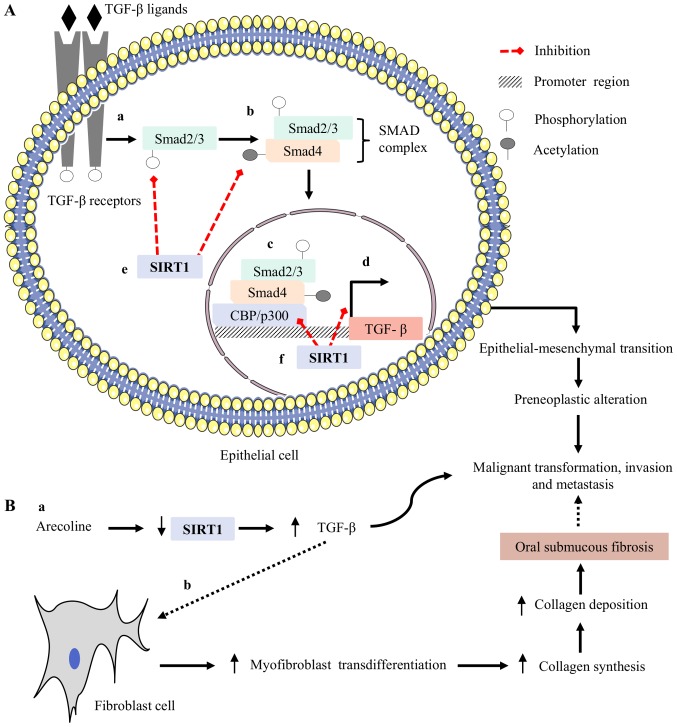
The regulatory role of SIRT1 in oral cancer is vigorously debated owing to the belief that it can have both tumorigenic and non-tumorigenic roles (5–8) (Table III). Altered levels of SIRT1 expression have a significant impact on the pathophysiology of oral cancer. Downregulation of SIRT1 expression is correlated with the metastatic phenotype, whereas upregulation of this protein results in opposite effects (5–8). It has been reported that stable expression of SIRT1 aids in maintaining epithelial integrity by inducing the expression of epithelial-cadherin (E-cadherin), and this contributes to the prevention of both invasion and metastasis in oral cancer (5–7). Conflicting data have also been reported for prostate carcinoma. It has been reported that SIRT1 mediates deacetylation of histone H3, causing transcriptional repression of E-cadherin and leading to invasion and metastasis (41). However, SIRT1 has been demonstrated to inhibit transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β)-mediated malignant transformation, invasion and metastasis in oral cancer (5). TGF-β is a growth factor and its overexpression has been frequently reported to be involved in precancerous oral lesions, leading to oral cancer (42,43). Increased expression of TGF-β has been shown to enhance malignant transformation, invasion and metastasis in oral epithelial cells by inducing its downstream targets (5–6,43). Similarly, overexpressed TGF-β acts on fibroblasts and has been reported to increase myofibroblastic transdifferentiation (42,43). Myofibroblasts are the major source for collagen synthesis in the extracellular matrix (ECM) of connective tissues, and continuous increases in the deposition of collagen lead to the pathogenesis of oral submucous fibrosis (OSF), a precancerous condition (42,43) (Fig. 2). The malignant transformation rate in patients with OSF ranges from 7–13% (10). SIRT1 has been shown to induce transcriptional suppression of TGF-β-mediated downstream targets in fibroblasts and to prevent malignant transformation (44). Based on these observations, SIRT1 may have the ability to prevent malignant transformation, invasion, and metastasis.
Table III.
Regulatory role of SIRT1 in oral cancer.
| Author, year | Type of function | Role of SIRT1 | (Refs.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chen et al, 2014 | Tumour suppressor | Maintenance of epithelial polarity by increases the expression of | (5) |
| Kang et al, 2017 | E-cadherin | (6) | |
| Murofushi et al, 2017 | Suppression of expression of N-cadherin and vimentin | (7) | |
| Downregulation of genes involved in migration and invasion, such as | |||
| CSK2A2, FRA1, ACTB, and SLUG | |||
| Downregulation of TGF-β downstream targets | |||
| Induction of p21 and G1/S phase cell cycle arrest | |||
| Xiong et al, 2011 | Tumour promoter | Induction of cisplatin resistance by increasing the expression of annexin A4, stathmin, SOD2 and thioredoxin | (8) |
| Induction of growth and survival of cancerous cells |
SOD2, superoxide dismutase 2; CSK2A2, casein kinase II subunit α; FRA1, fos related antigen 1; ACTB, beta-actin; SLUG, snail family transcriptional repressor 2, TGF-β, transforming growth factor β.
Figure 2.
Possible regulatory mechanism of SIRT1 in oral cancer induced by betel quid chewing: (A, a) TGF-β is a growth factor and its overexpression has been frequently reported in precancerous oral lesions leading to oral cancer, The TGF-β ligand binds to its receptor and induces the phosphorylation of smad2/3; (A, b) phosphorylated smad2/3 binds with acetylated smad4 and forms a complex known as the SMAD complex; (A, c, d) this SMAD complex translocates to the nucleus and binds with its co-activator CBP/p300, a histone acetyltransferase, and induces TGF-β-mediated invasion and metastasis. (A, e) SIRT1 can inhibit phosphorylation of smad2/3 and remove acetyl groups from smad4 protein. These effects help to prevent the formation of the SMAD complex; (A, f) at the nucleus, SIRT1 binds in the promoter region of TGF-β, inhibits CBP/p300-mediated acetylation via the deacetylation mechanism and results in transcriptional suppression of TGF-β-mediated malignant transformation, invasion, and metastasis in the oral mucosa of betel quid chewers. (B, a) Arecoline is the major alkaloid in betel quid, and is known to downregulate SIRT1 expression in oral epithelial cells, leading to enhanced TGF-β-mediated invasion and metastasis; (B, b) arecoline-mediated downregulation of SIRT1, followed by upregulation of TGF-β, acts on fibroblasts and enhances the pathogenesis of OSF, a precancerous condition. SIRT1, sirtuin 1; TGF-β, transforming growth factor beta; OSF, oral submucous fibrosis.
Recently, our group evaluated a significant association between arecoline and the expression of SIRT1 in oral epithelial cells. Arecoline, the major alkaloid in betel quid, has been reported to be involved in the pathogenesis of oral cancer by facilitating the cellular transformation and transcriptional repression of tumour suppressor genes (TSGs) (10,45,46). We discovered that arecoline significantly induced DNA hypermethylation, followed by downregulation of SIRT1 expression in oral epithelial cells. The frequency of DNA hypermethylation was found to be associated with precancerous oral lesions (data not shown). Our data suggest that arecoline-mediated downregulation of SIRT1 expression may be involved in the initial stage of transformation of normal cells to oral cancer and the development of precancerous oral lesions induced by betel quid chewing. Our results fit well with the observation of an association of SIRT1 and TGF-β, wherein arecoline-mediated downregulation of SIRT1 expression in oral epithelial cells fails to prevent TGF-β-induced malignant transformation in the oral mucosa of betel quid chewers. Taken together, these results suggest that SIRT1 could serve as a tumour suppressor in oral cancer. However, it remains unclear how it directly affects this process.
Conversely, despite evidence of the tumour-suppressing effects of SIRT1, some studies have demonstrated the promoting effects of this protein (8). Upregulation of annexin A4 has been shown to promote the progression and chemoresistance of numerous tumours (47). Overexpression of SIRT1 has been reported to induce cisplatin resistance in oral cancer by elevating the level of annexin A4 (8), and chemical inhibitors of SIRT1 significantly abolish this action (8). Hypoxia within the tumour microenvironment has a well-documented role to promote tumorigenesis. Recent reports investigating the role of SIRT1 under hypoxia have demonstrated that it promotes tumorigenesis via incorporation with hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1α) (48). Based on these findings, SIRT1 might have a significant tumour-inducing effect. Thus, further studies are needed to clarify this issue and evaluate new therapeutic approaches.
5. Therapeutic potential of HDACs in malignancy
Activators and inhibitors of HDACs have been developed in recent years and, to date, three histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACis) have received United States Food and Drug Administration approval for therapeutic use (49–63) (Table IV).
Table IV.
HDAC inhibitors/activators in the treatment of various tumours.
| Author, year | HDAC inhibitors (class I, II, IV) | Clinical status | (Refs.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ceccacci et al, 2016 | Vorinostat | Approved for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma | (49) |
| Panobinostat | Approved for multiple myeloma | ||
| Romidepsin | Approved for peripheral T-cell lymphoma | ||
| HDAC inhibitors (Class III) | |||
| Ceccacci et al, 2016 | NAM (SIRT 1–6) | Phase III clinical trial-laryngeal cancer | (49) |
| Hu et al, 2014 | Leukemia, prostate carcinoma | (50) | |
| Jin et al, 2015 | Tenovin-6 (SIRT 1–2) | Chronic myeloblastic leukemia | (51) |
| Dai et al, 2016 | Acute myeloblastic leukemia | (52) | |
| Eckschlager et al, 2017 | BDF4 (1/2a/-b/2d) (SIRT 1–2) | Colon carcinoma, glioblastoma | (53) |
| Eckschlager et al, 2017 | Sirtinol (SIRT 1–2) | Breast, lung and prostate carcinomas | (53) |
| Ota et al, 2006 | (54) | ||
| Eckschlager et al, 2017 | EX-527 (SIRT 1) | Leukaemia | (53) |
| Süssmuth et al, 2015 | Phase I/II clinical trials-Huntington disease | (56) | |
| Bhalla et al, 2017 | (55) | ||
| Heltweg et al, 2006 | CMB (SIRT 1–2) | Burkitt lymphoma | (57) |
| Kalle et al, 2010 | JGB-1741 (SIRT 1) | Breast cancer | (58) |
| Eckschlager et al, 2017 | AC-93253 (SIRT 1–3) | Prostate, pancreas and lung carcinoma | (53) |
| Lai et al, 2017 | (59) | ||
| Lara et al, 2009 | Salermide (SIRT 1–2) | Colorectal carcinoma | (61) |
| Rotili et al, 2012 | (60) | ||
| HDAC activators (Class III) | |||
| Jiang et al, 2017 | Resveratrol (SIRT1) | Leukemia, prostate carcinoma and skin cancer | (62) |
| Chauhan et al, 2011 | SRT1720 (SIRT1) | Multiple myeloma | (63) |
Vorinostat, suberanilohydroxamic acid; NAM, nicotinamide; BDF4, benzodeazoxaflavins; Sirtinol, sir two inhibitor naphthol; CMB, cambinol.
The use of HDACis in combination with conventional chemotherapeutic agents has already been reported to be a promising strategy against oral cancer (64–71) (Table V). The class III HDAC SIRT1 is considered to be both a promoter and suppressor. Inhibitors of SIRT1 have attracted interest and been found to induce apoptosis in various cancer cell lines. Similarly, activators of SIRT1 have been shown to possess the ability to prevent numerous cancers, including leukaemia, skin cancer, prostate cancer and multiple myeloma (25,34,62,63,72). Therefore, the conflicting data reported in the literature support the use of both activators and inhibitors of SIRT1 as strategies for cancer therapy; hence, care needs to be taken regarding the cytotoxicity and the dose of this protein when it is administered as a therapeutic agent.
Table V.
HDACis in oral squamous cell carcinoma treatment.
| Author, year | HDACis | Effects | Mechanism | (Refs.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suzuki et al, 2009 | Vorinostat | Induction of chemosensitization | Maintainence of epithelial polarity | (66) |
| Bruzzese et al, 2011 | to cisplatin, thereby increasing | Induction of p53, CytC, and | (65) | |
| Tasoulas et al, 2015 | apoptosis and inhibiting survival, proliferation, migration, and invasion | caspase-3 dependent apoptosis | (64) | |
| Tasoulas et al, 2015 | Trichostatin A | Induction of chemosensitization | Increased cathepsin activity and | (64) |
| Eriksson et al, 2013 | to cisplatin | reduced LAMP-2 level | (67) | |
| Tasoulas et al, 2015 | Benzamide | Increase in radiation-induced cell | Induction of G1/S phase cell | (64) |
| Sato et al, 2006 | cycle arrest and apoptosis | cycle arrest | (68) | |
| Tasoulas et al, 2015 | Depsipeptide | Induction of apoptosis and cell | Induction of p21 and G2/M arrest | (64) |
| Sato et al, 2006 | cycle arrest | (68) | ||
| Tasoulas et al, 2015 | Valproic acid +5 | Inhibition of proliferation and | Induction of H3 and H4 acetylation | (64) |
| Shoji et al, 2012 | azacytidine | induces radiosensitization | and decrease of Rad51 expression | (69) |
| Gan et al, 2012 | (70) | |||
| Gong et al, 2010 | Sodium butyrate | Suppression of growth and proliferation | Induction of p27 expression and caspase-dependent apoptosis | (71) |
| Downregulation of Akt pathway |
Vorinostat, suberanilohydroxamic acid; CytC, Cytochrome c; LAMP-2, lysosomal-associated membrane protein 2; Rad51, DNA repair protein Rad51 homolog 1; Akt, protein kinase B; HDACis, histone deacetylase inhibitors.
6. Future research perspectives and possible therapeutic applications of SIRT1 in oral cancer
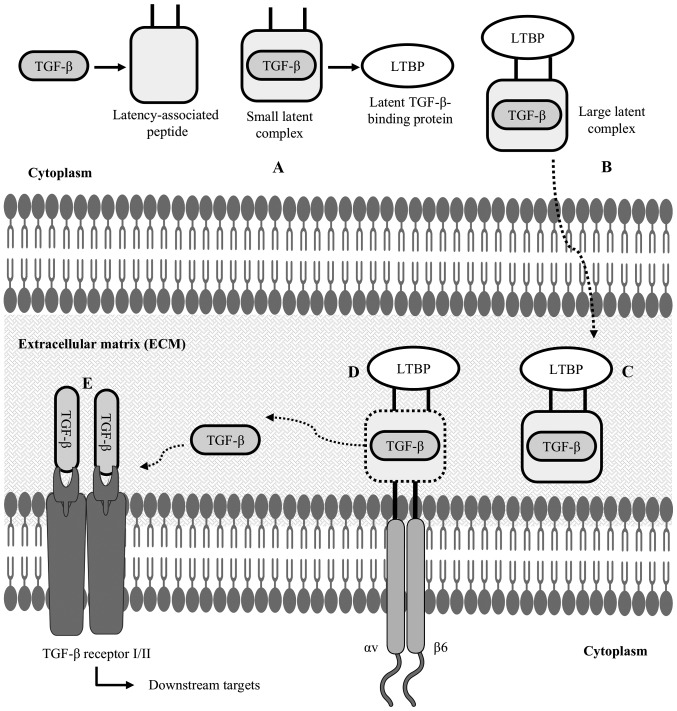
In spite of being involved in various physiological and pathological processes, the effects of altered SIRT1 expression in oral cancer are inconsistent. Reactive oxygen species (ROSs) are the strongest risk factor associated with the pathogenesis of oral cancer (10). Habits such as betel quid chewing have been reported to induce generation of ROSs in the oral epithelium and lead to genetic instability by damaging DNA and other macromolecules (10,45). SIRT1 has been shown to increase the synthesis of antioxidant enzymes such as glutathione and superoxide dismutase 2 and prevent ROS-mediated genomic alterations (73). Consistent with this premise, it is hypothesized that SIRT1 may play a significant role in inhibiting the synthesis of ROSs and prevent DNA and macromolecule damage in the oral mucosa of betel quid chewers. Further studies are thus warranted to evaluate the regulatory mechanism of SIRT1 in ROS generation in oral epithelial cells. Moreover, as demonstrated in some of the studies cited above, SIRT1 may prevent TGF-β-mediated invasion and metastasis in oral cancer (5,42,43). TGF-β is a growth factor and remains hidden in its inactive state in the ECM (74). αvβ6 integrin has been shown to facilitate the activation of the TGF-β downstream pathway by allowing it to bind with its receptors (74) (Fig. 3).
Figure 3.
Latent TGF-β structure and activation of TGF-β: (A) after synthesizing TGF-β inside the cytoplasm of a cell, LAP forms a straightjacket around the TGF-β, resulting in a small latent complex; (B) this small latent complex binds to LTBP to form a LLC; (C) this is an inactive state of TGF-β, which is now secreted in the ECM; (D) in the ECM, cell-associated αvβ6 integrin binds to the arginyl-glycyl-aspartic acid (RGD) domain of the latency-associated peptide, cleaving the LTBP interaction; (E) TGF-β is then released from the LAP, allowing it to interact with its receptor and activate TGF-β-mediated downstream targets. LAP, latency-associated peptide; LTBP, latent TGF-β-binding protein; LLC, large latent complex; ECM, extracellular matrix.
αv is the only integrin that can form a dimer with β6, and β6 integrin is normally not expressed in healthy adult epithelial cells, whereas its overexpression is associated with preneoplastic epithelial phenotypes. As a result, formation of a stable αvβ6 integrin dimer is related to TGF-β-mediated invasion and metastasis in the oral epithelium (75). CREB-binding protein (CBP) is a HAT and it has been reported that CBP mediates acetylation in the promoter region of β6 integrin and induces its expression in preneoplastic epithelium. This induced expression of β6 integrin enhances the formation of αvβ6 dimers and results in invasion and metastasis in oral cancer (76). Since SIRT1 is a deacetylase, it is hypothesized that it may induce transcriptional suppression of β6 integrin via deacetylation in the promoter region and prevent invasion and metastasis in oral cancer. Thus, further studies are warranted to evaluate the use of SIRT1-based therapeutic approaches in oral cancer.
7. Concluding remarks
Based on results of the studies referred to above and our current data, it is hypothesized that SIRT1 may play a significant tumour-suppressive role in oral cancer. Future studies will undoubtedly pinpoint the molecular mechanisms via which SIRT1 influences oral carcinogenesis and identify efficacious SIRT1 activators for the prevention or treatment of precancerous oral lesions that can lead to oral cancer.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
No funding was received.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the present study are not publicly available due to the data containing information that may compromise the consent of the participants but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Authors' contributions
SI and YA conducted the literature review and wrote the manuscript. OU and IC contributed to the study design and the writing of the manuscript, and made corrections. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- 1.Carafa V, Rotili D, Forgione M, Cuomo F, Serretiello E, Hailu GS, Jarho E, Lahtela-Kakkonen M, Mai A, Altucci L. Sirtuin functions and modulation: From chemistry to the clinic. Clin Epigenetics. 2016;8:61. doi: 10.1186/s13148-016-0224-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Deng CX. SIRT1, is it a tumor promoter or tumor suppressor? Int J Biol Sci. 2009;5:147–152. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.5.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bosch-Presegué L, Vaquero A. The dual role of sirtuins in cancer. Genes Cancer. 2011;2:648–662. doi: 10.1177/1947601911417862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wang RH, Sengupta K, Li C, Kim HS, Cao L, Xiao C, Kim S, Xu X, Zheng Y, Chilton B, et al. Impaired DNA damage response, genome instability, and tumorigenesis in SIRT1 mutant mice. Cancer Cell. 2008;14:312–323. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.09.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chen IC, Chiang WF, Huang HH, Chen PF, Shen YY, Chiang HC. Role of SIRT1 in regulation of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis. Mol Cancer. 2014;13:254. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kang YY, Sun FL, Zhang Y, Wang Z. SIRT1 acts as a potential tumor suppressor in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Chin Med Assoc. 2018;81:416–422. doi: 10.1016/j.jcma.2017.09.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Murofushi T, Tsuda H, Mikami Y, Yamaguchi Y, Suzuki N. CAY10591, a SIRT1 activator, suppresses cell growth, invasion, and migration in gingival epithelial carcinoma cells. J Oral Sci. 2017;59:415–423. doi: 10.2334/josnusd.16-0696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Xiong P, Li YX, Tang YT, Chen HG. Proteomic analyses of Sirt1-mediated cisplatin resistance in OSCC cell line. Protein J. 2011;30:499–508. doi: 10.1007/s10930-011-9354-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Warnakulasuriya S. Global epidemiology of oral and oropharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol. 2009;45:309–316. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2008.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans: Betel-quid and areca-nut chewing and some areca-nut-derived nitrosamines. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum. 2004;85:1–334. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Peters AH, O'Carroll D, Scherthan H, Mechtler K, Sauer S, Schöfer C, Weipoltshammer K, Pagani M, Lachner M, Kohlmaier A, et al. Loss of the Suv39h histone methyltransferases impairs mammalian heterochromatin and genome stability. Cell. 2001;107:323–337. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00542-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Vaquero A, Scher M, Lee D, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Reinberg D. Human SirT1 interacts with histone H1 and promotes formation of facultative heterochromatin. Mol Cell. 2004;16:93–105. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2004.08.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Vaquero A, Scher M, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Serrano L, Reinberg D. SIRT1 regulates the histone methyl-transferase SUV39H1 during heterochromatin formation. Nature. 2007;450:440–444. doi: 10.1038/nature06268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Palacios JA, Herranz D, De Bonis ML, Velasco S, Serrano M, Blasco MA. SIRT1 contributes to telomere maintenance and augments global homologous recombination. J Cell Biol. 2010;191:1299–1313. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201005160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yuan Z, Zhang X, Sengupta N, Lane WS, Seto E. SIRT1 regulates the function of the Nijmegen breakage syndrome protein. Mol Cell. 2007;27:149–162. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.05.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jeong J, Juhn K, Lee H, Kim SH, Min BH, Lee KM, Cho MH, Park GH, Lee KH. SIRT1 promotes DNA repair activity and deacetylation of Ku70. Exp Mol Med. 2007;39:8–13. doi: 10.1038/emm.2007.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sawada M, Sun W, Hayes P, Leskov K, Boothman DA, Matsuyama S. Ku70 suppresses the apoptotic translocation of Bax to mitochondria. Nat Cell Biol. 2003;5:320–329. doi: 10.1038/ncb950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Brunet A, Sweeney LB, Sturgill JF, Chua KF, Greer PL, Lin Y, Tran H, Ross SE, Mostoslavsky R, Cohen HY, et al. Stress-dependent regulation of FOXO transcription factors by the SIRT1 deacetylase. Science. 2004;303:2011–2015. doi: 10.1126/science.1094637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kobayashi Y, Furukawa-Hibi Y, Chen C, Horio Y, Isobe K, Ikeda K, Motoyama N. SIRT1 is a critical regulator of FOXO-mediated transcription in response to oxidative stress. Int J Mol Med. 2005;16:237–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Motta MC, Divecha N, Lemieux M, Kamel C, Chen D, Gu W, Bultsma Y, McBurney M, Guarente L. Mammalian SIRT1 represses forkhead transcription factors. Cell. 2004;116:551–563. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00126-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chua KF, Mostoslavsky R, Lombard DB, Pang WW, Saito S, Franco S, Kaushal D, Cheng HL, Fischer MR, Stokes N, et al. Mammalian SIRT1 limits replicative life span in response to chronic genotoxic stress. Cell Metab. 2005;2:67–76. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2005.06.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Yi J, Luo J. SIRT1 and p53, effect on cancer, senescence and beyond. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1804:1684–1689. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2010.05.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Peng L, Yuan Z, Ling H, Fukasawa K, Robertson K, Olashaw N, Koomen J, Chen J, Lane WS, Seto E. SIRT1 deacetylates the DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) protein and alters its activities. Mol Cell Biol. 2011;31:4720–4734. doi: 10.1128/MCB.06147-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Glozak MA, Sengupta N, Zhang X, Seto E. Acetylation and deacetylation of non-histone proteins. Gene. 2005;363:15–23. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2005.09.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Glozak MA, Seto E. Histone deacetylases and cancer. Oncogene. 2007;26:5420–5432. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Huffman DM, Grizzle WE, Bamman MM, Kim JS, Eltoum IA, Elgavish A, Nagy TR. SIRT1 is significantly elevated in mouse and human prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2007;67:6612–6618. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chen HC, Jeng YM, Yuan RH, Hsu HC, Chen YL. SIRT1 promotes tumorigenesis and resistance to chemotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma and its expression predicts poor prognosis. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19:2011–2019. doi: 10.1245/s10434-011-2159-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hao C, Zhu PX, Yang X, Han ZP, Jiang JH, Zong C, Zhang XG, Liu WT, Zhao QD, Fan TT, et al. Overexpression of SIRT1 promotes metastasis through an epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:978. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chen X, Sun K, Jiao S, Cai N, Zhao X, Zou H, Xie Y, Wang Z, Zhong M, Wei L. High levels of SIRT1 expression enhance tumorigenesis and associate with a poor prognosis of colorectal carcinoma patients. Sci Rep. 2014;4:7481. doi: 10.1038/srep07481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zhao G, Qin Q, Zhang J, Liu Y, Deng S, Liu L, Wang B, Tian K, Wang C. Hypermethylation of HIC1 promoter and aberrant expression of HIC1/SIRT1 might contribute to the carcinogenesis of pancreatic cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20(Suppl 3):S301–S311. doi: 10.1245/s10434-012-2364-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Stunkel W, Peh BK, Tan YC, Nayagam VM, Wang X, Salto-Tellez M, Ni B, Entzeroth M, Wood J. Function of the SIRT1 protein deacetylase in cancer. Biotechnol J. 2007;2:1360–1368. doi: 10.1002/biot.200700087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ford J, Jiang M, Milner J. Cancer-specific functions of SIRT1 enable human epithelial cancer cell growth and survival. Cancer Res. 2005;65:10457–10463. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.He Z, Yi J, Jin L, Pan B, Chen L, Song H. Overexpression of Sirtuin-1 is associated with poor clinical outcome in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2016;37:7139–7148. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4459-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hida Y, Kubo Y, Murao K, Arase S. Strong expression of a longevity-related protein, SIRT1, in Bowen's disease. Arch Dermatol Res. 2007;299:103–106. doi: 10.1007/s00403-006-0725-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Bradbury CA, Khanim FL, Hayden R, Bunce CM, White DA, Drayson MT, Craddock C, Turner BM. Histone deacetylases in acute myeloid leukaemia show a distinctive pattern of expression that changes selectively in response to deacetylase inhibitors. Leukemia. 2005;19:1751–1759. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2403910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Jung W, Hong KD, Jung WY, Lee E, Shin BK, Kim HK, Kim A, Kim BH. SIRT1 expression is associated with good prognosis in colorectal cancer. Korean J Pathol. 2013;47:332–339. doi: 10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.4.332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Jang SH, Min KW, Paik SS, Jang KS. Loss of SIRT1 histone deacetylase expression associates with tumour progression in colorectal adenocarcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 2012;65:735–739. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2012-200685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Firestein R, Blander G, Michan S, Oberdoerffer P, Ogino S, Campbell J, Bhimavarapu A, Luikenhuis S, de Cabo R, Fuchs C, et al. The SIRT1 deacetylase suppresses intestinal tumorigenesis and colon cancer growth. PLoS One. 2008;3:e2020. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Voelter-Mahlknecht S, Mahlknecht U. The sirtuins in the pathogenesis of cancer. Clin Epigenetics. 2010;1:71–83. doi: 10.1007/s13148-010-0008-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Potente M, Ghaeni L, Baldessari D, Mostoslavsky R, Rossig L, Dequiedt F, Haendeler J, Mione M, Dejana E, Alt FW, et al. SIRT1 controls endothelial angiogenic functions during vascular growth. Genes Dev. 2007;21:2644–2658. doi: 10.1101/gad.435107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Byles V, Zhu L, Lovaas JD, Chmilewski LK, Wang J, Faller DV, Dai Y. SIRT1 induces EMT by cooperating with EMT transcription factors and enhances prostate cancer cell migration and metastasis. Oncogene. 2012;31:4619–4629. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Verrecchia F, Mauviel A. Transforming growth factor-beta and fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13:3056–3062. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i22.3056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ekanayaka RP, Tilakaratne WM. Oral submucous fibrosis: Review on mechanisms of malignant transformation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2016;122:192–199. doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2015.12.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Chang YC, Lin CW, Yu CC, Wang BY, Huang YH, Hsieh YC, Kuo YL, Chang WW. Resveratrol suppresses myofibroblast activity of human buccal mucosal fibroblasts through the epigenetic inhibition of ZEB1 expression. Oncotarget. 2016;7:12137–12149. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Uehara O, Takimoto K, Morikawa T, Harada F, Takai R, Adhikari BR, Itatsu R, Nakamura T, Yoshida K, Matsuoka H, et al. Upregulated expression of MMP-9 in gingival epithelial cells induced by prolonged stimulation with arecoline. Oncol Lett. 2017;14:1186–1192. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Chiba I, Muthumala M, Yamazaki Y, Uz Zaman A, Iizuka T, Amemiya A, Shibata T, Kashiwazaki H, Sugiura C, Fukuda H. Characteristics of mutations in the p53 gene of oral squamous-cell carcinomas associated with betel-quid chewing in Sri Lanka. Int J Cancer. 1998;77:839–842. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19980911)77:6<839::AID-IJC7>3.0.CO;2-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wei B, Guo C, Liu S, Sun MZ. Annexin A4 and cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 2015;447:72–78. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2015.05.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Laemmle A, Lechleiter A, Roh V, Schwarz C, Portmann S, Furer C, Keogh A, Tschan MP, Candinas D, Vorburger SA, Stroka D. Inhibition of SIRT1 impairs the accumulation and transcriptional activity of HIF-1α protein under hypoxic conditions. PLoS One. 2012;7:e33433. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Ceccacci E, Minucci S. Inhibition of histone deacetylases in cancer therapy: Lessons from leukaemia. Br J Cancer. 2016;114:605–611. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2016.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Hu J, Jing H, Lin H. Sirtuin inhibitors as anticancer agents. Future Med Chem. 2014;6:945–966. doi: 10.4155/fmc.14.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Jin Y, Cao Q, Chen C, Du X, Jin B, Pan J. Tenovin-6-mediated inhibition of SIRT1/2 induces apoptosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) cells and eliminates ALL stem/progenitor cells. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:226. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1282-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Dai W, Zhou J, Jin B, Pan J. Class III-specific HDAC inhibitor Tenovin-6 induces apoptosis, suppresses migration and eliminates cancer stem cells in uveal melanoma. Sci Rep. 2016;6:22622. doi: 10.1038/srep22622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Eckschlager T, Plch J, Stiborova M, Hrabeta J. Histone deacetylase inhibitors as anticancer drugs. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(pii):E1414. doi: 10.3390/ijms18071414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Ota H, Tokunaga E, Chang K, Hikasa M, Iijima K, Eto M, Kozaki K, Akishita M, Ouchi Y, Kaneki M. Sirt1 inhibitor, Sirtinol, induces senescence-like growth arrest with attenuated Ras-MAPK signaling in human cancer cells. Oncogene. 2006;25:176–185. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Bhalla S, Gordon LI. Functional characterization of NAD dependent de-acetylases SIRT1 and SIRT2 in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) Cancer Biol Ther. 2016;17:300–309. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2016.1139246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Süssmuth SD, Haider S, Landwehrmeyer GB, Farmer R, Frost C, Tripepi G, Andersen CA, Di Bacco M, Lamanna C, Diodato E, et al. An exploratory double-blind, randomized clinical trial with selisistat, a SirT1 inhibitor, in patients with Huntington's disease. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2015;79:465–476. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Heltweg B, Gatbonton T, Schuler AD, Posakony J, Li H, Goehle S, Kollipara R, Depinho RA, Gu Y, Simon JA, Bedalov A. Antitumor activity of a small-molecule inhibitor of human silent information regulator 2 enzymes. Cancer Res. 2006;66:4368–4377. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Kalle AM, Mallika A, Badiger J, Alinakhi, Talukdar P, Sachchidanand Inhibition of SIRT1 by a small molecule induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;401:13–19. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.08.118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Lai YH, Lin SY, Wu YS, Chen HW, Chen JJW. AC-93253 iodide, a novel Src inhibitor, suppresses NSCLC progression by modulating multiple Src-related signaling pathways. J Hematol Oncol. 2017;10:172. doi: 10.1186/s13045-017-0539-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Rotili D, Tarantino D, Nebbioso A, Paolini C, Huidobro C, Lara E, Mellini P, Lenoci A, Pezzi R, Botta G, et al. Discovery of salermide-related sirtuin inhibitors: Binding mode studies and antiproliferative effects in cancer cells including cancer stem cells. J Med Chem. 2012;55:10937–10947. doi: 10.1021/jm3011614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Lara E, Mai A, Calvanese V, Altucci L, Lopez Nieva P, Martinez Chantar ML, Varela Rey M, Rotili D, Nebbioso A, Ropero S, et al. Salermide, a Sirtuin inhibitor with a strong cancer-specific proapoptotic effect. Oncogene. 2009;28:781–791. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Jiang Z, Chen K, Cheng L, Yan B, Qian W, Cao J, Li J, Wu E, Ma Q, Yang W. Resveratrol and cancer treatment: Updates. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2017;1403:59–69. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Chauhan D, Bandi M, Singh AV, Ray A, Raje N, Richardson P, Anderson KC. Preclinical evaluation of a novel SIRT1 modulator SRT1720 in multiple myeloma cells. Br J Haematol. 2011;155:588–598. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2011.08888.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Tasoulas J, Giaginis C, Patsouris E, Manolis E, Theocharis S. Histone deacetylase inhibitors in oral squamous cell carcinoma treatment. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2015;24:69–78. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2014.952368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Bruzzese F, Leone A, Rocco M, Carbone C, Piro G, Caraglia M, Di Gennaro E, Budillon A. HDAC inhibitor vorinostat enhances the antitumor effect of gefitinib in squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck by modulating ErbB receptor expression and reverting EMT. J Cell Physiol. 2011;226:2378–2390. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Suzuki M, Endo M, Shinohara F, Echigo S, Rikiishi H. Enhancement of cisplatin cytotoxicity by SAHA involves endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2009;64:1115–1122. doi: 10.1007/s00280-009-0969-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Eriksson I, Joosten M, Roberg K, Ollinger K. The histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A reduces lysosomal pH and enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis. Exp Cell Res. 2013;319:12–20. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2012.10.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Sato T, Suzuki M, Sato Y, Echigo S, Rikiishi H. Sequence-dependent interaction between cisplatin and histone deacetylase inhibitors in human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 2006;28:1233–1241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Shoji M, Ninomiya I, Makino I, Kinoshita J, Nakamura K, Oyama K, Nakagawara H, Fujita H, Tajima H, Takamura H, et al. Valproic acid, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, enhances radiosensitivity in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 2012;40:2140–2146. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2012.1416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Gan CP, Hamid S, Hor SY, Zain RB, Ismail SM, Wan Mustafa WM, Teo SH, Saunders N, Cheong SC. Valproic acid: growth inhibition of head and neck cancer by induction of terminal differentiation and senescence. Head Neck. 2012;34:344–353. doi: 10.1002/hed.21734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Gong L, Wang WM, Ji Y, Wang Y, Li DW. Effects of sodium butyrate on proliferation of human oral squamous carcinoma cell line and expression of p27Kip1. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2010;45:619–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Lin Z, Fang D. The roles of SIRT1 in cancer. Genes Cancer. 2013;4:97–104. doi: 10.1177/1947601912475079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Salminen A, Kaarniranta K, Kauppinen A. Crosstalk between oxidative stress and SIRT1: Impact on the ageing process. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14:3834–3859. doi: 10.3390/ijms14023834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Agarwal SK. Integrins and cadherins as therapeutic targets in fibrosis. Front Pharmacol. 2014;5:131. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2014.00131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Xue H, Atakilit A, Zhu W, Li X, Ramos DM, Pytela R. Role of the avb6 integrin in human oral squamous cell carcinoma growth in vivo and in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;288:610–618. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.5813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Xu M, Yin L, Cai Y, Hu Q, Huang J, Ji Q, Hu Y, Huang W, Liu F, Shi S, Deng X. Epigenetic regulation of integrin β6 transcription induced by TGF-β1 in human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119:4193–4204. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the present study are not publicly available due to the data containing information that may compromise the consent of the participants but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.