Abstract
Cancer is the second leading cause of mortality worldwide. More importantly, the mortality rates for cancer are increasing. In China, lung cancer, liver cancer and gastric cancer are the top three leading causes of mortality in males, whereas lung cancer, gastric cancer and liver cancer are ranked the top three causes of mortality in females. Exosomes are extracellular vesicles that are produced and released by many different cells; these vesicles have a size range between 30 and 100 nm in diameter, and contain a lipid bilayer. Exosomes exist in various bodily fluids, contain plentiful amounts of nucleic acids and proteins, and shuttle these materials between cells to mediate the development of cancers. The present review summarizes the composition of exosomes and methods for their isolation and then intensively highlights the latest findings on the contributions of exosomal microRNAs (miRNAs) and proteins to lung cancer, liver cancer and gastric cancer. Taken together, exosomal miRNAs and proteins may be used as noninvasive, novel biomarkers for cancer diagnosis, prognosis or precision treatment owing to their ability to promote tumor progression and metastasis, and their ability to regulate the immune response and tumor cell sensitivity to chemotherapy drugs.
Keywords: exosomes, exosomal miRNAs, exosomal proteins, high mortality cancers
1. Introduction
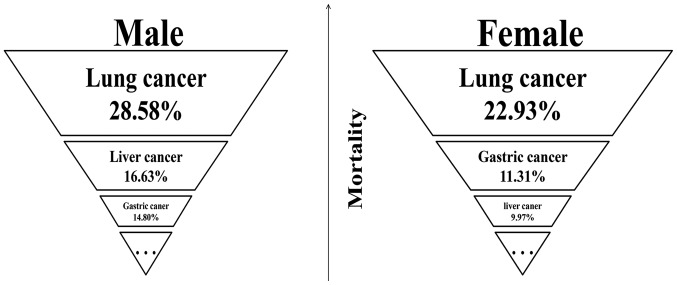
Cancer is the second leading cause of death globally (1). In China, the numbers of newly diagnosed cases and deaths were approximately 3.0 million and 1.9 million, respectively, in 2010 (2). According to 2013 data, lung cancer, liver cancer and gastric cancer are the top three leading causes of mortality in males in China, whereas lung cancer, gastric cancer and liver cancer are the top three leading causes of mortality in females (3) (Fig. 1).
Figure 1.
Top three mortality cancers in China, 2013. Liver cancer and gastric cancer are the top three leading causes of mortality in males. Lung cancer, gastric cancer and liver cancer are ranked the top three causes of mortality in females.
A growing number of studies have focused on the biology, function and clinical implications of exosomes in cancers (4,5), and it has been demonstrated that exosomal miRNAs and proteins can act as tumor biomarkers for clinical diagnosis or prognosis and that exosomes shuttle between cells to exchange genetic material, which promotes tumor progression, metastasis and prognosis; regulates the immune response; and affects the sensitivity of tumor cells to chemotherapy drugs (6–8). Therefore, exosomal miRNAs and proteins potentially play critical roles in cancers with high mortality rates.
2. Exosome composition
Exosomes are extracellular vesicles (EVs) that are produced and released by many different cells; and these vesicles range in size from 30 to 100 nm in diameter and contain a lipid bilayer (9,10). Proteins, DNA, mRNAs, miRNAs and lipids are enriched in exosomes (11). Exosomes transfer nucleic acids and proteins between different cells, leading to both the transportation of materials and cell-cell communication (6,12,13).
A set of distinct proteins are contained in exosomes (14), including heat-shock proteins (Hsp70, Hsp90), tetraspanins (CD9, CD81), ESCRT-related proteins (Alix, Tsg101), cytoskeletal proteins (actin, Tubulin) and GTPases (EEF1A1, EEF2) (15,16). These proteins are known to be involved in biogenesis, the sorting and secretion of exosomes (17), antigen presentation, the organization of membrane microdomains, the cytoskeleton, and the endosomal system (18,19). Typically, exosomes contain both cell-type specific proteins and proteins that are expressed in various cell types (20).
In addition to proteins, exosomes contain a significant amount of nucleic acids, including DNA, mRNAs, miRNAs, circular RNAs (circRNAs) and long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) (21). Of these, miRNAs are a class of well-known regulatory molecules that control posttranscriptional gene regulation (22). Increasing evidence has shown that exosomal miRNAs are associated with many diseases, such as cancers, diabetes and obesity (23–26). Interestingly, the miRNA content of exosomes is similar to that of the original tumor; thus, a series of studies has focused on exosomal miRNA profiles for cancer diagnostics (16). In particular, the shuttling of miRNAs may act as a tumor promoter or a tumor suppressor during tumorigenesis (27). Previous studies have uncovered exosomal miRNAs that are closely associated with tumorigenesis, metastasis and drug resistance in various kinds of cancers (28,29). All of these findings suggest that exosomal miRNAs play a pivotal role in the diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of cancers (30,31).
Additionally, cholesterols, diglycerides, phospholipids, glycerophospholipids, sphingomyelins and ceramides are enriched in exosomes (32). These lipids participate in exosome biogenesis, function and release. For example, the cellular trafficking of the tetraspanin CD82 to endosomes is regulated by the cholesterol content of the membrane, and ceramides can protect miRNAs from degradation by circulating RNases and govern the cellular distribution of the tetraspanin CD81. In addition, bioactive lipids such as prostaglandins, leukotrienes, fatty acids and lipid-related enzymes such as phospholipases A2 have been detected in exosomes (33).
3. Exosome isolation
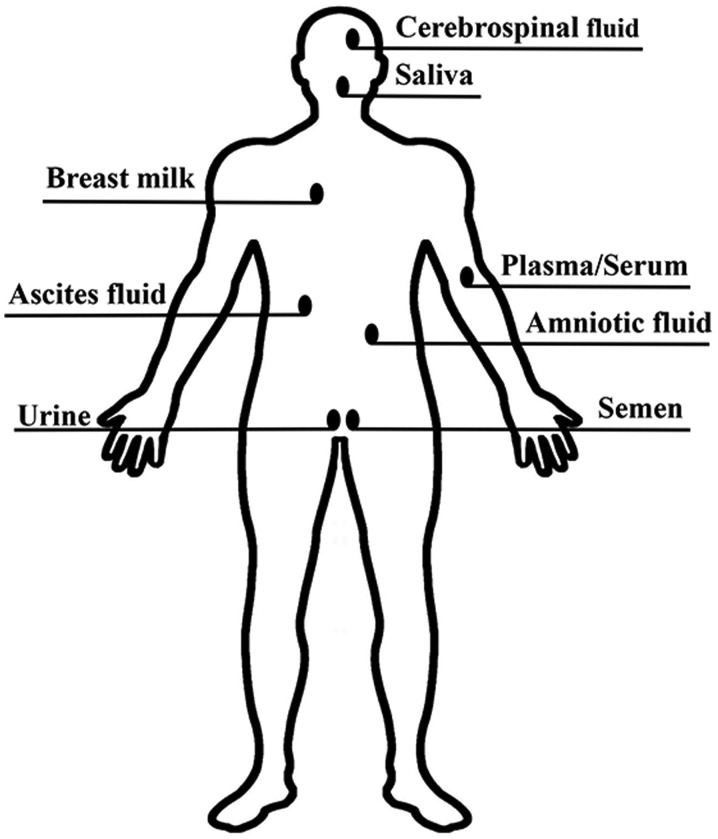
Exosomes secreted by various types of living cells have been detected in a diverse range of bodily fluids, including peripheral blood, saliva, cerebrospinal fluid, ascites fluid, amniotic fluid, urine, breast milk and semen (31,34) (Fig. 2). It is clear that the utility of exosomes goes beyond basic research and extends to clinical practice. For this reason, an efficient and accurate method for exosome isolation is crucial.
Figure 2.
Exosomes exist in various bodily fluids. Exosomes can be detected in peripheral blood, saliva, cerebrospinal fluid, ascites fluid, amniotic fluid, urine, breast milk, semen and other bodily fluids.
Here, we compare the common methods for exosome isolation (Table I), including ultracentrifugation (UC), ultrafiltration (UF), immunomagnetic beads, size exclusion chromatography (SEC) and ExoQuick™ (35,36). UC is a common and simple method (37); however, recent studies indicated that more contaminants were found in exosomes isolated by UC compared to other methods mainly due to the presence of albumins. Furthermore, the high-velocity ultracentrifugation process could cause some exosomes to rupture, resulting in exosome loss (38). Recently, the challenges of UC approach have been again discussed, the conventional biophysical UC cannot distinguish exosomes from lipoproteins and oncosomes, other types of small EVs with sedimentation velocities and gradient densities similar to those of exosomes (39). UF does not require special equipment, although it leads to a reduction in the membranes' lifespan and a low isolation efficiency (35,40). The use of immunomagnetic beads is an alternative method with high specificity and purity, but it is limited to exosomes with a known antigen and has a high reagent cost (35). Although SEC does not lead to significant albumin contamination, the efficiency is low (35,37,41). ExoQuick™ produces excellent reproducibility and sensitivity. However, the proprietary reagents exhibit contamination from unknown sources, and the polymer leads to protein aggregation (35,36,42,43). Moreover, the ExoQuick™ kit does not specifically precipitate exosomes, which means that other types of nanovesicles with similar sizes (30–100 nm) might also be coprecipitated (39). Recently, a new technique developed by the microfluidics community has been used to approach some of the problems with exosome isolation mentioned above. The most important feature of this method is exosome enrichment during isolation, which is beneficial for the detection of early-stage cancers. This microfluidics approach showed a superior recovery of 60–80% compared to the conventional techniques of UC (6%) and ExoQuick™ (30%) based on nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) (43).
Table I.
Comparison of exosome isolation methods.
| Author, year | Method | Principle | Advantages | Disadvantages | (Refs.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baranyai et al, 2015; Peterson et al, 2015 | UC | Separating the exosomes through differential mass, density and shape | • Available technology | • The high velocity ultracentrifugation process could cause some exosomes rupture that results in some exosomes loss | (37,38) |
| • Simple operation | |||||
| • Contaminated with albumin and IgG | |||||
| • Time consuming (16–20 h) | |||||
| Li et al, 2017; Zeringer et al, 2015 | UF | Depending on exosomal size or molecular weight | • No need of special equipment | • Clogging and vesicle trapping lead to reduce the membranes' lifetime and low isolation efficiency | (35,40) |
| • Good portability | |||||
| Li et al, 2017 | Immunom-agnetic beads | Specific exosomal antigens (receptors) can be captured by magnetic beads (ligands) | • High specificity and purity | • High reagent cost | (35) |
| • Low yield | |||||
| • No damage on the integrity of the exosomes' morphology and structure | |||||
| Li et al, 2017; Baranyai et al, 2015; Taylor and Shah, 2015 | SEC | A porous stationary phase is utilized to sort exosomes out according to the size | • Obtaining high-purity exosomes without significant albumin contamination | • Require dedicated equipment | (35,37,41) |
| • Low efficiency | |||||
| • Excellent reproducibility and sensitivity | |||||
| Li et al, 2017; Caradec et al, 2014; Ban et al, 2015 | ExoQuick™ | By the precipitation approach | • Efficient (around 100%) and reproducible | • Isolation procedure should be under acidic conditions (pH=4) | (35,36,42) |
| • Decreasing albumin contamination | • Polymer precipitates protein aggregation | ||||
| • Fast (within 30 min) |
UC, ultracentrifugation; UF, ultrafiltration; SEC, size exclusion chromatography.
Indeed, the high quantity and purity of exosomes are extremely important for exosomal biology studies. Thus, western blotting should be used to determine whether exosomal protein markers (Alix, Tsg101, Hsp70 or others) are present in exosome isolations (44). Simultaneously, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is often utilized to observe exosome morphology, NTA is used to measure particle size, and the bicinchoninic acid assay (BCA) is performed to examine the protein concentration of exosomes (45). Additionally, to ensure the sensitivity of isolations and achieve a robust result, pre-analytical factors should be taken into consideration (Table II) (46,47).
Table II.
Pre-analytical considerations.
| Author, year | Pre-analytical considerations | (Refs.) |
|---|---|---|
| Muller et al, 2014; Witwer et al, 2013 | Venous blood from patients or healthy volunteers is collected into tubes without heparin-based anticoagulants, EDTA may be more appropriate. | (46,47) |
| Witwer et al, 2013 | Blood should be processed quickly at room temperature. | (47) |
| Witwer et al, 2013 | Collected blood should be handled gently and tubes should be vertically positioned prior to centrifugation. | (47) |
| Witwer et al, 2013 | Both plasma and serum can be used, but most studies indicate the isolation of exosomes prefers to plasma. | (47) |
| Muller et al, 2014 | Harvested plasma or serum should be immediately used or stored at −80°C. | (46) |
4. Exosomal miRNAs and proteins in lung cancer
The latest report showed that lung cancer caused approximately 597,000 deaths in China in 2013 (3). Of lung cancer cases, approximately 95% are non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) (48), which together represent the most common cause of cancer-related death globally (49,50).
Serving as biomarkers
Exosomes and exosomal miRNAs differed between patients with lung cancer and controls (51). By comparing 12 specific tumor- and exosome-derived miRNAs (miR-17-3p, miR-21, miR-106a, miR-146, miR-155, miR-191, miR-192, miR-203, miR-205, miR-210, miR-212, and miR-214) in lung cancer, previous studies revealed that there was no significant difference between circulating miRNAs and tumor miRNAs, demonstrating that exosome-derived miRNAs can serve as diagnostic biomarkers for lung cancer (51). In a nude mouse model of subcutaneous primary and recurrent lung cancer xenografts in vivo, miR-21 and miR-155 were found to be up-regulated in serum exosomes derived from recurrent tumor-bearing nude mice compared to nontumor- or primary tumor-bearing nude mice (52), suggesting that these two miRNAs might be potential prognostic biomarkers for noninvasive diagnosis of recurrent lung cancer. In addition, Liu et al (53) first reported that elevation of plasma exosomal miR-23b-3p, miR-10b-5p and miR-21-5p predicted a significantly poor survival, implying that these three exosomal miRNAs could serve as independent prognostic biomarkers for NSCLC.
Exosomal membrane-bound proteins, for example, the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), NY-ESO-1 and CD91, are also promising diagnostic or prognostic biomarker candidates for lung cancer. Yamashita et al (54) demonstrated that the measurement of plasma exosomal proteins might be helpful for in vitro diagnosis, and exosomal EGFR was a potential diagnostic biomarker for the characterization of lung cancer. In NSCLC patients, exosomal NY-ESO-1 was a strong prognostic biomarker of poorer survival (55). CD91 expression was significantly increased in serum exosomes derived from patients with lung adenocarcinoma (ADC), and its detection power for early-stage patients was higher than that of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) (56).
Stimulating angiogenesis and inducing metastasis
Angiogenesis is essential for tumor growth, progression and metastasis (57). Liu et al (58) found that exosomal miR-21 derived from cigarette smoke extract (CSE)-transformed human bronchial epithelial (HBE) cells was elevated, and this increased exosomal miR-21 led to STAT3 activation and altered the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression of recipient cells, promoting CSE-induced angiogenesis and the malignant transformation of HBE cells. These results provided a novel intervention strategy to prevent carcinogenesis of lung cancer. In addition, hypoxic lung cancer cell (hypoxic CL1-5)-derived exosomal miR-23a enhanced neovascularization and tumor growth, and serum exosomal miR-23a was also elevated in patients with lung cancer. These findings provided strong evidence that an increase in exosomal miR-23a contributes to angiogenesis, intravasation and extravasation in lung cancer (59).
Exosomes play a fundamental role in the premetastatic niche and metastasis (4). Results from Fabbri et al (60) indicated that miRNAs (miR-21/29a) derived from lung cancer cell line (A549 and SK-MES) exosomes activate members of the Toll-like receptor (TLR) family (murine TLR7 and human TLR8) in immune cells, leading to a TLR-mediated prometastatic inflammatory response that might ultimately trigger tumor growth and metastasis.
Mediating cisplatin (DDP) resistance
Lung cancer cell-derived exosomes could confer DDP resistance to other cancer cells. Qin et al (61) established A549 cells that were resistant to DDP (A549/DDP). Compared with A549 exosomes, miR-100-5p was downregulated by 75% in A549/DDP cell exosomes. Lower expression of miR-100-5p induced DDP resistance in recipient cells (other lung cancer cell lines). miR-100-5p negatively regulated mTOR, the mammalian target of rapamycin, to alter the recipient lung cancer cells' resistance to DDP. Additionally, the chemosensitivity of NSCLC to DDP could be regulated by serum exosomal miR-146a-5p. The overexpression of miR-146a-5p reversed the resistance of A549/DDP cells by targeting Atg12 to inhibit autophagy (62). Furthermore, in a human bronchial epithelial cell (HBEC) model, exosomes derived from chemoresistant mesenchymal NSCLC cells were able to transfer chemoresistance and mesenchymal phenotypes to recipient cells, thereby enhancing resistance to gemcitabine and cisplatin/gemcitabine combination therapy (63).
5. Exosomal miRNAs and proteins in liver cancer
Liver cancer is a common malignancy with a high mortality rate both in China and around the world (64,65). Liver cancer includes primary liver cancer (PLC) and secondary liver cancer. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) are two different histologic types of PLC, which is the second most common cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide (66).
Serving as biomarkers
Differential expression of exosomal miRNAs in serum could serve as a diagnostic biomarker for HCC. Sohn et al (67) reported that the levels of serum exosomal miR-18a, miR-221, miR-222 and miR-224 were remarkably higher in HCC patients compared with patients with liver cirrhosis (LC) or chronic hepatitis B (CHB); however, the levels of serum exosomal miR-101, miR-106b, miR-122 and miR-195 were lower in HCC patients than in CHB patients. In addition, other studies have shown that expression of exosomal miR-21 and miR-125b was upregulated in HCC patients compared with CHB patients or healthy controls. More importantly, the levels of miR-21 and miR-125b were higher in exosomes than in serum samples (68,69).
Promoting proliferation, invasion and metastasis
Exosomal miRNAs could affect cellular gene expression and cellular behaviors in target cells (70). Wei et al (71) showed that exosomes derived from HCC cells (SMMC-7721, Hep3B, and Huh-7) could functionally deliver miRNAs to target cells and that Vps4A regulated the secretion and uptake of these miRNAs in hepatoma cells by utilizing exosomes as mediators. Vps4A-associated miRNAs are believed to regulate the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and promote the proliferation, invasion and metastasis of HCC cells. It has been suggested that a large number of protumorigenic RNAs and proteins, such as the MET proto-oncogene, caveolins (CAV1, CAV2) and an S100 family member (S100A4), are enriched in metastatic HCC-derived exosomes (72–74). Moreover, He et al (75) showed that uptake of these shuttling molecules in exosomes derived from motile HCC cell lines (HKCI-C3, HKCI-8 and MHCC97 L) markedly enhanced the invasive and migratory abilities of nonmotile immortalized hepatocyte (MIHA) cell lines by activating the PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling pathways and increasing the secretion of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP)-2 and MMP-9, which induced cell invasion.
Mediating sensitivity to sorafenib
Sorafenib is predominantly used for the treatment of liver cancer and can improve the overall survival of patients with advanced HCC (76). Exosomes may mediate sorafenib resistance in HCC cells. Guo et al (77) revealed that miR-122 contained in adipose tissue mesenchymal stem cell (AMSC) exosomes enhanced HCC cell sensitivity to chemotherapeutic agents. Compared with the control groups, the inhibitory effect of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) or sorafenib on HCC cells (HepG2 and Huh7) treated with AMSC-derived exosomes (122-Exo) was significantly enhanced, thereby providing a new strategy for HCC therapy. An important mechanism of sorafenib resistance is the overexpression of c-Met, a proto-oncogene that serves as a receptor for hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) in tumor cells (78). Further investigations confirmed that HGF upregulation and c-Met/AKT pathway activation triggered sorafenib resistance induced by exosomes derived from HCC cells (MHCC-97L and MHCC-97H), indicating that HGF/c-Met might be a possible target for decreasing sorafenib resistance of HCC cells (79).
6. Exosomal miRNAs and proteins in gastric cancer
Gastric cancer (GC), a malignant tumor of the digestive system, is the second leading cause of cancer-related death and the fourth most common cancer worldwide (80). Although its incidence and mortality have appreciably decreased globally over recent decades, the mortality of GC is still relatively high in Asia (81).
Serving as biomarkers
Recent research suggested that serum exosomal miR-19b-3p and miR-106a-5 could be potential biomarkers for the early diagnosis of GC (82). Additionally, Tokuhisa et al (83) assessed exosomal miRNA profiles in peritoneal fluid and found that miR-21 and miR-1225-5p might be prognostic biomarkers for peritoneal recurrence after curative GC resection. miR-10b-5p, miR-195-5p, miR-20a-3p and miR-296-5p were significantly upregulated in serum exosomes derived from patients with GC and were able to discriminate GC patients from healthy controls (84).
Promoting metastasis
miR-214, miR-221 and miR-222 are commonly upregulated in gastric cancer tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells (GC-MSCs) and tumor tissues; moreover, GC-MSC-derived exosomes deliver miR-221 to HGC-27 cells and promote the proliferation and migration (85). The serum exosomes of GC patients transport EGFR to liver cells, and EGFR activates HGF by suppressing miR-26a/b, stimulating the development of a liver-like microenvironment that promotes gastric cancer liver metastasis (86). In later studies, proliferation and Matrigel invasion of gastric cancer cells in the presence of exosomes derived from gastric cancer cells (SGC-7901) with either high (SGC/wt) or low (SGC/kd) CD97 expression were investigated, and the results indicated that CD97 promoted gastric cancer cell proliferation and invasion through exosome-mediated activation of the MAPK signaling pathway (87,88).
Regulating the immune response
Compared with exosomes derived from the untreated malignant ascites of GC patients, exosomes derived from heat-treated malignant ascites contained higher concentrations of the heat shock proteins Hsp70 and Hsp60, which might play an important role in inducing a tumor-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) response in vitro and are involved in the promotion of dendritic cell (DC) maturation (89). Additionally, HSPs have been identified as damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), a class of self-danger signals released by stressed cells that elicited immune responses. Mechanistically, HSPs respond to the innate immune system both directly with inflammation and indirectly by recruiting reinforcements (90). However, there is some evidence showing that HSPs have a dampening effect on the immune system under physiological conditions, indicating that HSPs are actually DAMPERs, a class of molecules that reduces the activity of the innate immune system (91).
Mediating DDP resistance
The level of miR-21 in exosomes derived from tumor-associated macrophages (M2 macrophages) has been shown to be increased, and exosomal miR-21 can be directly transferred from tumor-associated macrophages to gastric cancer cells, conferring DDP resistance to gastric cancer cells by downregulating PTEN and activating signaling through the PI3K/AKT pathway (92). However, exosome-delivered anti-miR-214 was able to reverse the resistance of gastric cancer cells to DDP, leading to suppressed migration in vitro, inhibited tumor growth in vivo, and increased cellular apoptosis (93). Additionally, MSC-derived exosomes significantly induced gastric cancer cell resistance to 5-FU both in vivo and ex vivo by activating the calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CaM-K)/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway (94).
7. Conclusion and future studies
Exosomes have established a role in cancer biology, immunology, drug sensitivity and clinical diagnosis. In particular, exosomal miRNAs and proteins play important roles in cancers with high mortality rates (lung cancer, liver cancer and gastric cancer) (Tables III and IV).
Table III.
Exosomal miRNAs in the top three mortality cancer types.
| A, Lung cancer | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author, year | miRNAs | Study design | Sample | Clinical significance | Approach | Performance | (Refs.) |
| Rabinowits et al, 2009 | miR-17-p/21/106a/146/155/191/192/203/205/210/212/214 | Case-control | Human plasma | Diagnostic biomarkers for NSCLC | Microarray | Increase | (51) |
| Munagala et al, 2016 | miR-21/155 | Animal model Cell model | Athymic nude mice H1299, Beas-2b | Possible prognostic markers for lung cancer recurrence | Microarray, qPCR | Increase | (52) |
| Liu et al, 2017 | miR-23b-3p/10b-5p/21-5p | Case-control | Human plasma | Independent non-invasive prognostic markers for NSCLC | qPCR | Increase | (53) |
| Liu et al, 2016 | miR-21 | Patients Cell model | Human serum CSE-transformed HBE cells | Promoting CSE-induced angiogenesis and malignant transformation of HBE cells | qPCR | Increase | (58) |
| Hsu et al, 2017 | miR-23a | Patients Cell model | Human serum Hypoxic CL1-5 | Stimulating the angiogenesis, intrava-sation and extravasation in lung cancer | qPCR | Increase | (59) |
| Fabbri et al, 2012 | miR-21/29a | Cell model, Animal model | A549, SK-MES WT B6 mice B6 TLR7−/−mice | Triggering tumour growth and metastasis | qPCR | Increase | (60) |
| Qin et al, 2017 | miR-100-5p | Cell model | A549/DDP | Altering the recipient lung cancer cells' resistance to DDP | Microarray, qPCR | Decrease | (61) |
| Yuwen et al, 2017 | miR-146a-5p | Patients Cell model | Human serum A549/DDP | Reversing the resistance of A549/DDP | qPCR | Increase | (62) |
| B, Liver cancer | |||||||
| Author, year | miRNAs | Study design | Sample | Clinical significance | Approach | Performance | (Refs.) |
| Sohn et al, 2015 | miR-18a/221/222/224 | Case-control | Human serum | Discriminating HCC from LC or CHB | qPCR | Increase | (67) |
| Sohn et al, 2015 | miR-101/106b/122/195 | Case-control | Human serum | Discriminating HCC from CHB | qPCR | Decrease | (67) |
| Wang et al, 2014; Liu et al, 2017 | miR-21/125b | Case-control | Human serum | Discriminating HCC from CHB or healthy controls | qPCR | Increase | (68,69) |
| Wei et al, 2015 | Vps4A-related miRNAs | Cell model | SMMC-7721, Hep3B, Huh-7 | Regulating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and promoting proliferation, invasion and metastasis of HCC cells | RNA sequencing | Increase | (71) |
| Lou et al, 2015 | miR-122 | Cell model | AMSC | Enhancing the effect 5-FU or sorafenib on HCC cells | qPCR | Increase | (77) |
| C, Gastric cancer | |||||||
| Author, year | miRNAs | Study design | Sample | Clinical significance | Approach | Performance | (Refs.) |
| Wang et al, 2017 | miR-19b-3p/106a-5 | Case-control | Human serum | Potential biomarkers for the early diagnosis of GC | qPCR | Increase | (82) |
| Tokuhisa, et al, 2015 | miR-21/1225-5p | Patients Cell model | Peritoneum lavage fluid, OCUM-2M OCUM-2MD3 | Prognostic biomarkers for peritoneal recurrence after curative GC resection | Microarray, qPCR | Increase | (83) |
| Huang et al, 2017 | miR-10b-5p/miR-195-5p/miR-20a-3p/miR-296-5p | Case-control | Human serum | Discriminating GC patients from healthy controls | qPCR | Increase | (84) |
| Wang et al, 2014 | miR-221 | Patients Cell model Animal model | Human tissue GC-MSCs BALB/cnu/nu nude mice | Promoting HGC-27 cells proliferation and migration | Microarray, qPCR | Increase | (85) |
| Zheng et al, 2017 | miR-21 | Cell model Animal model | M2 macrophages athymic C57-nudemice | Conferring DDP resistance in GC cells | Microarray, qPCR | Increase | (92) |
| Wang et al, 2018 | Anti-miR-214 | Cell model Animal model | SGC7901, SGC7901/DDP BALB/c-nude mice | Reversing the resistance of GC cells to DDP | qPCR | Increase | (93) |
NSCLC, non-small-cell lung cancer; CSE-transformed HBE cells, cigarette smoke extrac-transformed human bronchial epithelial cells. Hypoxic lung cancer cell, hypoxic CL1-5; DDP, cisplatin; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; LC, liver cirrhosis; CHB, chronic hepatitis B; AMSC, adipose tissue mesenchymal stem cell; 5-FU, 5-fluorouracil; GC, gastric cancer; GC-MSCs, gastric cancer tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells; qPCR, quantitative polymerase chain reaction.
Table IV.
Exosomal proteins in the top three mortality cancer types.
| A, Lung cancer | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author, year | Protein | Study design | Sample | Clinical significance | Approach | Performance | (Refs.) |
| Yamashita et al, 2017 | EGFR | Case-control | Human plasma | Potential diagnostic biomarker for characterization of lung cancer | ELISA | Increase | (54) |
| Sandfeld-Paulsen et al, 2016 | NY-ESO-1 | Case-control | Human plasma | A strongly prognostic markers for poor survival of NSCLC | Microarray | Increase | (55) |
| Ueda et al, 2014 | CD91 | Case-control | Human serum | Diagnostic markers for ADC | ELISA Mass spectrometry | Increase | (56) |
| B, Liver cancer | |||||||
| Author, year | Protein | Study design | Sample | Clinical significance | Approach | Performance | (Refs.) |
| He et al, 2015 | CAV1/CAV2/S100A4 | Cell model | HKCI-C3, HKCI-8 MHCC97L | Enhancing the invasive and migratory abilities of non-motile MIHA cells | Western blot Mass spectrometry | Increase | (75) |
| Qu et al, 2016 | HGF | Cell model Animal model | MHCC-97L, MHCC-97H BALB/c nu/nu mice | Improving sorafenib resistance of HCC cells | ELISA Western blot | Increase | (79) |
| C, Gastric cancer | |||||||
| Author, year | Protein | Study design | Sample | Clinical significance | Approach | Performance | (Refs.) |
| Zhang et al, 2017 | EGFR | Patients Animal model Cell model | Human serum/tissue BALB/c-nu nude mice SGC7901 | Promoting GC liver metastasis | ELISA Western blot | Increase | (86) |
| Li et al, 2015; Liu et al, 2016 | CD97 | Cell model | SGC-7901 | Promoting GC cells proliferation and invasion | Western blot | Increase | (87,88) |
| Zhong et al, 2011 | Hsp70, Hsp60 | Patients | Heat-treated malignant ascites | Inducing a CTL response in vitro and involving in the promotion of DC maturation | Western blot | Increase | (89) |
NSCLC, non-small-cell lung cancer; ADC, lung adenocarcinoma; MIHA, motile immortalized hepatocyte; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; CTL, cytotoxic T lymphocyte; DC, dendritic cell.
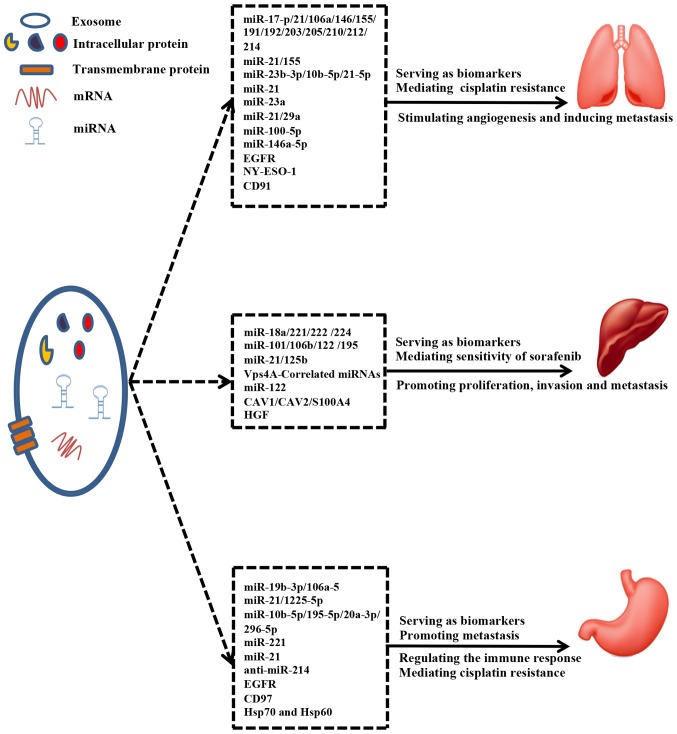
On one hand, existing data indicate that the packaging of miRNAs into exosomes is a selective process and that the levels of specific exosomal miRNAs and proteins are changed in exosomes upon tumorigenesis. For these reasons, exosomal miRNAs and proteins can be served as a class of novel biomarkers for clinical applications in high-mortality cancers. Moreover, the specificity, sensitivity and diagnostic value of exosomal miRNAs and proteins may be superior to that of traditional tumor markers. On the other hand, exosomal miRNAs and proteins are delivered between tumor cells to transmit information and modulate signaling pathways. Taken together, exosomal miRNAs and proteins perform the essential function of promoting tumor progression and metastasis as well as mediating the immune response and sensitivity of tumor cells to chemotherapy drugs (Fig. 3).
Figure 3.
Exosomal miRNAs and proteins play vital roles in high-mortality cancers. Exosomal miRNAs and proteins can be used as diagnostic or prognostic biomarkers, promote tumor progression and metastasis, and simultaneously regulate immune response and tumor cells' sensitivity to chemotherapy drugs.
In the future, more robust techniques, such as RNA-Seq and mass spectrometry, can be used for the detection, characterization and discovery of exosomal miRNAs and proteins. Moreover, exosomes could efficiently deliver chemotherapeutic agents to cells and tissues. Therefore, these bioengineered, drug-loaded exosomes can serve as promising exosome mimetics for effective chemotherapeutic agent delivery, which will be applied for the target treatment of malignant tumors. Currently, the majority of research on chemotherapy resistance and exosomal microRNAs focuses on cisplatin, and little is known about other drugs. To identify more sensitive and specific exosomal miRNAs and proteins to guide personal chemotherapy selection, future studies should further elucidate the role and underlying mechanism of exosomal miRNAs and proteins in more diverse cancers with more chemotherapy drugs.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 81772276) and the disciplines group construction project of Pudong Health Bureau of Shanghai (grant no. PWZxq2017-15).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Authors' contributions
LML was a major contributor in writing the manuscript. HL and XHL were responsible for the collection of the relevant literatures. HBH and SML revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
References
- 1.Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration, corp-author. Fitzmaurice C, Allen C, Barber RM, Barregard L, Bhutta ZA, Brenner H, Dicker DJ, Chimed-Orchir O, Dandona R, et al. Global, regional, and National cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 32 cancer groups, 1990 to 2015: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3:524–548. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.5688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chen W, Zheng R, Zhang S, Zhao P, Zeng H, Zou X. Report of cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2010. Ann Transl Med. 2014;2:61. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2305-5839.2014.04.05. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zheng R, Zeng H, Zhang S, Chen W. Estimates of cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2013. Chin J Cancer. 2017;36:66. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2017.01.08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Zhou L, Lv T, Zhang Q, Zhu Q, Zhan P, Zhu S, Zhang J, Song Y. The biology, function and clinical implications of exosomes in lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017;407:84–92. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Qi H, Liu C, Long L, Ren Y, Zhang S, Chang X, Qian X, Jia H, Zhao J, Sun J, et al. Blood exosomes endowed with magnetic and targeting properties for cancer therapy. ACS Nano. 2016;10:3323–3333. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b06939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Greening DW, Gopal SK, Xu R, Simpson RJ, Chen W. Exosomes and their roles in immune regulation and cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015;40:72–81. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.02.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Taylor DD, Gercel-Taylor C. Exosomes/microvesicles: Mediators of cancer-associated immunosuppressive microenvironments. Semin Immunopathol. 2011;33:441–454. doi: 10.1007/s00281-010-0234-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Zhao L, Liu W, Xiao J, Cao B. The role of exosomes and ‘exosomal shuttle microRNA’ in tumorigenesis and drug resistance. Cancer Lett. 2015;356:339–346. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.10.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kalluri R. The biology and function of exosomes in cancer. J Clin Invest. 2016;126:1208–1215. doi: 10.1172/JCI81135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Frydrychowicz M, Kolecka-Bednarczyk A, Madejczyk M, Yasar S, Dworacki G. Exosomes-structure, biogenesis and biological role in non-small-cell lung cancer. Scand J Immunol. 2015;81:2–10. doi: 10.1111/sji.12247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Aqil F, Munagala R, Jeyabalan J, Agrawal AK, Gupta R. Exosomes for the enhanced tissue bioavailability and efficacy of curcumin. AAPS J. 2017;19:1691–1702. doi: 10.1208/s12248-017-0154-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Simons M, Raposo G. Exosomes-vesicular carriers for intercellular communication. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009;21:575–581. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2009.03.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Schneider A, Simons M. Exosomes: Vesicular carriers for intercellular communication in neurodegenerative disorders. Cell Tissue Res. 2013;352:33–47. doi: 10.1007/s00441-012-1428-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mathivanan S, Ji H, Simpson RJ. Exosomes: Extracellular organelles important in intercellular communication. J Proteomics. 2010;73:1907–1920. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2010.06.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Villarroya-Beltri C, Baixauli F, Gutiérrez-Vázquez C, Sánchez-Madrid F, Mittelbrunn M. Sorting it out: Regulation of exosome loading. Semin Cancer Biol. 2014;28:3–13. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2014.04.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hannafon BN, Ding WQ. Intercellular communication by exosome-derived microRNAs in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14:14240–14269. doi: 10.3390/ijms140714240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Keerthikumar S, Chisanga D, Ariyaratne D, Al Saffar H, Anand S, Zhao K, Samuel M, Pathan M, Jois M, Chilamkurti N, et al. ExoCarta: A web-based compendium of exosomal cargo. J Mol Biol. 2016;428:688–692. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2015.09.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ludwig AK, Giebel B. Exosomes: Small vesicles participating in intercellular communication. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012;44:11–15. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2011.10.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Théry C, Zitvogel L, Amigorena S. Exosomes: Composition, biogenesis and function. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:569–579. doi: 10.1038/nri855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Iraci N, Leonardi T, Gessler F, Vega B, Pluchino S. Focus on extracellular vesicles: Physiological role and signalling properties of extracellular membrane vesicles. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17:171. doi: 10.3390/ijms17020171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Li W, Li C, Zhou T, Liu X, Liu X, Li X, Chen D. Role of exosomal proteins in cancer diagnosis. Mol Cancer. 2017;16:145. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0706-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hannafon BN, Carpenter KJ, Berry WL, Janknecht R, Dooley WC, Ding WQ. Exosome-mediated microRNA signaling from breast cancer cells is altered by the anti-angiogenesis agent docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) Mol Cancer. 2015;14:133. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0400-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kapetanakis NI, Baloche V, Busson P. Tumor exosomal microRNAs thwarting anti-tumor immune responses in nasopharyngeal carcinomas. Ann Transl Med. 2017;5:164. doi: 10.21037/atm.2017.03.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Thomou T, Mori MA, Dreyfuss JM, Konishi M, Sakaguchi M, Wolfrum C, Rao TN, Winnay JN, Garcia-Martin R, Grinspoon SK, et al. Adipose-derived circulating miRNAs regulate gene expression in other tissues. Nature. 2017;542:450–455. doi: 10.1038/nature21365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ying W, Riopel M, Bandyopadhyay G, Dong Y, Birmingham A, Seo JB, Ofrecio JM, Wollam J, Hernandez-Carretero A, Fu W, et al. Adipose tissue macrophage-derived exosomal miRNAs can modulate in vivo and in vitro insulin sensitivity. Cell. 2017;171:372–384.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.08.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Shi R, Zhao L, Cai W, Wei M, Zhou X, Yang G, Yuan L. Maternal exosomes in diabetes contribute to the cardiac development deficiency. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;483:602–608. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.12.097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Milane L, Singh A, Mattheolabakis G, Suresh M, Amiji MM. Exosome mediated communication within the tumor microenvironment. J Control Release. 2015;219:278–294. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.06.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ge Q, Zhou Y, Lu J, Bai Y, Xie X, Lu Z. miRNA in plasma exosome is stable under different storage conditions. Molecules. 2014;19:1568–1575. doi: 10.3390/molecules19021568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Pfeffer SR, Grossmann KF, Cassidy PB, Yang CH, Fan M, Kopelovich L, Leachman SA, Pfeffer LM. Detection of exosomal miRNAs in the plasma of melanoma patients. J Clin Med. 2015;4:2012–2027. doi: 10.3390/jcm4121957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Watahiki A, Macfarlane RJ, Gleave ME, Crea F, Wang Y, Helgason CD, Chi KN. Plasma miRNAs as biomarkers to identify patients with castration-resistant metastatic prostate cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14:7757–7770. doi: 10.3390/ijms14047757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Xu R, Greening DW, Rai A, Ji H, Simpson RJ. Highly-purified exosomes and shed microvesicles isolated from the human colon cancer cell line LIM1863 by sequential centrifugal ultrafiltration are biochemically and functionally distinct. Methods. 2015;87:11–25. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2015.04.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Subra C, Laulagnier K, Perret B, Record M. Exosome lipidomics unravels lipid sorting at the level of multivesicular bodies. Biochimie. 2007;89:205–212. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2006.10.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Record M, Carayon K, Poirot M, Silvente-Poirot S. Exosomes as new vesicular lipid transporters involved in cell-cell communication and various pathophysiologies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1841:108–120. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.10.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Raposo G, Stoorvogel W. Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol. 2013;200:373–383. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201211138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Li P, Kaslan M, Lee SH, Yao J, Gao Z. Progress in exosome isolation techniques. Theranostics. 2017;7:789–804. doi: 10.7150/thno.18133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Caradec J, Kharmate G, Hosseini-Beheshti E, Adomat H, Gleave M, Guns E. Reproducibility and efficiency of serum-derived exosome extraction methods. Clin Biochem. 2014;47:1286–1292. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2014.06.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Baranyai T, Herczeg K, Onódi Z, Voszka I, Módos K, Marton N, Nagy G, Mäger I, Wood MJ, El Andaloussi S, et al. Isolation of exosomes from blood plasma: Qualitative and quantitative comparison of ultracentrifugation and size exclusion chromatography methods. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0145686. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Peterson MF, Otoc N, Sethi JK, Gupta A, Antes TJ. Integrated systems for exosome investigation. Methods. 2015;87:31–45. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2015.04.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lu L, Risch HA. Exosomes: Potential for early detection in pancreatic cancer. Future Oncol. 2016;12:1081–1090. doi: 10.2217/fon-2015-0005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Zeringer E, Barta T, Li M, Vlassov AV. Strategies for isolation of exosomes. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2015;2015:319–323. doi: 10.1101/pdb.top074476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Taylor DD, Shah S. Methods of isolating extracellular vesicles impact down-stream analyses of their cargoes. Methods. 2015;87:3–10. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2015.02.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ban JJ, Lee M, Im W, Kim M. Low pH increases the yield of exosome isolation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;461:76–79. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.03.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Marczak S, Richards K, Ramshani Z, Smith E, Senapati S, Hill R, Go DB, Chang HC. Simultaneous isolation and preconcentration of exosomes by ion concentration polarization. Electrophoresis. 2018 Feb 27; doi: 10.1002/elps.201700491. (Epub ahead of print) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Tauro BJ, Greening DW, Mathias RA, Ji H, Mathivanan S, Scott AM, Simpson RJ. Comparison of ultracentrifugation, density gradient separation, and immunoaffinity capture methods for isolating human colon cancer cell line LIM1863-derived exosomes. Methods. 2012;56:293–304. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2012.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Vaswani K, Koh YQ, Almughlliq FB, Peiris HN, Mitchell MD. A method for the isolation and enrichment of purified bovine milk exosomes. Reprod Biol. 2017;17:341–348. doi: 10.1016/j.repbio.2017.09.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Muller L, Hong CS, Stolz DB, Watkins SC, Whiteside TL. Isolation of biologically-active exosomes from human plasma. J Immunol Methods. 2014;411:55–65. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2014.06.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Witwer KW, Buzás EI, Bemis LT, Bora A, Lässer C, Lötvall J, Nolte-'t Hoen EN, Piper MG, Sivaraman S, Skog J, et al. Standardization of sample collection, isolation and analysis methods in extracellular vesicle research. J Extracell Vesicles. 2013;2 doi: 10.3402/jev.v2i0.20360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Kadota T, Yoshioka Y, Fujita Y, Kuwano K, Ochiya T. Extracellular vesicles in lung cancer-From bench to bedside. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017;67:39–47. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Nanavaty P, Alvarez MS, Alberts WM. Lung cancer screening: Advantages, controversies, and applications. Cancer Control. 2014;21:9–14. doi: 10.1177/107327481402100102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Pletnikoff PP, Laukkanen JA, Tuomainen TP, Kauhanen J, Rauramaa R, Ronkainen K, Kurl S. Cardiorespiratory fitness, C-reactive protein and lung cancer risk: A prospective population-based cohort study. Eur J Cancer. 2015;51:1365–1370. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2015.04.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Rabinowits G, Gercel-Taylor C, Day JM, Taylor DD, Kloecker GH. Exosomal microRNA: A diagnostic marker for lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2009;10:42–46. doi: 10.3816/CLC.2009.n.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Munagala R, Aqil F, Gupta RC. Exosomal miRNAs as biomarkers of recurrent lung cancer. Tumour Biol. 2016;37:10703–10714. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-4939-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Liu Q, Yu Z, Yuan S, Xie W, Li C, Hu Z, Xiang Y, Wu N, Wu L, Bai L, Li Y. Circulating exosomal microRNAs as prognostic biomarkers for non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8:13048–13058. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Yamashita T, Kamada H, Kanasaki S, Maeda Y, Nagano K, Abe Y, Inoue M, Yoshioka Y, Tsutsumi Y, Katayama S, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor localized to exosome membranes as a possible biomarker for lung cancer diagnosis. Pharmazie. 2013;68:969–973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Sandfeld-Paulsen B, Aggerholm-Pedersen N, Bæk R, Jakobsen KR, Meldgaard P, Folkersen BH, Rasmussen TR, Varming K, Jørgensen MM, Sorensen BS. Exosomal proteins as prognostic biomarkers in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Oncol. 2016;10:1595–1602. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2016.10.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Ueda K, Ishikawa N, Tatsuguchi A, Saichi N, Fujii R, Nakagawa H. Antibody-coupled monolithic silica microtips for highthroughput molecular profiling of circulating exosomes. Sci Rep. 2014;4:6232. doi: 10.1038/srep06232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Ostrowski K, Kinsner A. Inhibition of angiogenesis in the treatment of tumors. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 2001;49:27–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Liu Y, Luo F, Wang B, Li H, Xu Y, Liu X, Shi L, Lu X, Xu W, Lu L, et al. STAT3-regulated exosomal miR-21 promotes angiogenesis and is involved in neoplastic processes of transformed human bronchial epithelial cells. Cancer Lett. 2016;370:125–135. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.10.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Hsu YL, Hung JY, Chang WA, Lin YS, Pan YC, Tsai PH, Wu CY, Kuo PL. Hypoxic lung cancer-secreted exosomal miR-23a increased angiogenesis and vascular permeability by targeting prolyl hydroxylase and tight junction protein ZO-1. Oncogene. 2017;36:4929–4942. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Fabbri M, Paone A, Calore F, Galli R, Gaudio E, Santhanam R, Lovat F, Fadda P, Mao C, Nuovo GJ, et al. MicroRNAs bind to Toll-like receptors to induce prometastatic inflammatory response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:E2110–E2116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1209414109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Qin X, Yu S, Zhou L, Shi M, Hu Y, Xu X, Shen B, Liu S, Yan D, Feng J. Cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cell-derived exosomes increase cisplatin resistance of recipient cells in exosomal miR-100-5p-dependent manner. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;12:3721–3733. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S131516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Yuwen DL, Sheng BB, Liu J, Wenyu W, Shu YQ. MiR-146a-5p level in serum exosomes predicts therapeutic effect of cisplatin in non-small cell lung cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21:2650–2658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Lobb RJ, van Amerongen R, Wiegmans A, Ham S, Larsen JE, Möller A. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal non-small cell lung cancer cells promote chemoresistance. Int J Cancer. 2017;141:614–620. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Wang FS, Fan JG, Zhang Z, Gao B, Wang HY. The global burden of liver disease: The major impact of China. Hepatology. 2014;60:2099–2108. doi: 10.1002/hep.27406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Li X, Xu WF. China's efforts to shed its title of ‘Leader in liver disease’. Drug Discov Ther. 2007;1:84–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Wong MC, Jiang JY, Goggins WB, Liang M, Fang Y, Fung FD, Leung C, Wang HH, Wong GL, Wong VW, Chan HL. International incidence and mortality trends of liver cancer: A global profile. Sci Rep. 2017;7:45846. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-15922-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Sohn W, Kim J, Kang SH, Yang SR, Cho JY, Cho HC, Shim SG, Paik YH. Serum exosomal microRNAs as novel biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp Mol Med. 2015;47:e184. doi: 10.1038/emm.2015.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Wang H, Hou L, Li A, Duan Y, Gao H, Song X. Expression of serum exosomal microRNA-21 in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:864894. doi: 10.1155/2014/864894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Liu W, Hu J, Zhou K, Chen F, Wang Z, Liao B, Dai Z, Cao Y, Fan J, Zhou J. Serum exosomal miR-125b is a novel prognostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2017;10:3843–3851. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S140062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Kogure T, Lin WL, Yan IK, Braconi C, Patel T. Intercellular nanovesicle-mediated microRNA transfer: A mechanism of environmental modulation of hepatocellular cancer cell growth. Hepatology. 2011;54:1237–1248. doi: 10.1002/hep.24504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Wei JX, Lv LH, Wan YL, Cao Y, Li GL, Lin HM, Zhou R, Shang CZ, Cao J, He H, et al. Vps4A functions as a tumor suppressor by regulating the secretion and uptake of exosomal microRNAs in human hepatoma cells. Hepatology. 2015;61:1284–1294. doi: 10.1002/hep.27660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Mishra SK, Siddique HR, Saleem M. S100A4 calcium-binding protein is key player in tumor progression and metastasis: Preclinical and clinical evidence. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012;31:163–172. doi: 10.1007/s10555-011-9338-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Tse EY, Ko FC, Tung EK, Chan LK, Lee TK, Ngan ES, Man K, Wong AS, Ng IO, Yam JW. Caveolin-1 overexpression is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma tumourigenesis and metastasis. J Pathol. 2012;226:645–653. doi: 10.1002/path.3957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Cokakli M, Erdal E, Nart D, Yilmaz F, Sagol O, Kilic M, Karademir S, Atabey N. Differential expression of Caveolin-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma: Correlation with differentiation state, motility and invasion. BMC Cancer. 2009;9:65. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-9-65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.He M, Qin H, Poon TC, Sze SC, Ding X, Co NN, Ngai SM, Chan TF, Wong N. Hepatocellular carcinoma-derived exosomes promote motility of immortalized hepatocyte through transfer of oncogenic proteins and RNAs. Carcinogenesis. 2015;36:1008–1018. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgv081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S, Kim JS, Luo R, Feng J, Ye S, Yang TS, et al. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:25–34. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70285-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Lou G, Song X, Yang F, Wu S, Wang J, Chen Z, Liu Y. Exosomes derived from miR-122-modified adipose tissue-derived MSCs increase chemosensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hematol Oncol. 2015;8:122. doi: 10.1186/s13045-015-0220-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.You H, Ding W, Dang H, Jiang Y, Rountree CB. c-Met represents a potential therapeutic target for personalized treatment in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2011;54:879–889. doi: 10.1002/hep.24450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Qu Z, Wu J, Wu J, Luo D, Jiang C, Ding Y. Exosomes derived from HCC cells induce sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma both in vivo and in vitro. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016;35:159. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0430-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Ferro A, Peleteiro B, Malvezzi M, Bosetti C, Bertuccio P, Levi F, Negri E, La Vecchia C, Lunet N. Worldwide trends in gastric cancer mortality (1980–2011), with predictions to 2015, and incidence by subtype. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50:1330–1344. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2014.01.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Peleteiro B, Severo M, La Vecchia C, Lunet N. Model-based patterns in stomach cancer mortality worldwide. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2014;23:524–531. doi: 10.1097/CEJ.0b013e328364f2b6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Wang N, Wang L, Yang Y, Gong L, Xiao B, Liu X. A serum exosomal microRNA panel as a potential biomarker test for gastric cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;493:1322–1328. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.10.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Tokuhisa M, Ichikawa Y, Kosaka N, Ochiya T, Yashiro M, Hirakawa K, Kosaka T, Makino H, Akiyama H, Kunisaki C, Endo I. Exosomal miRNAs from peritoneum lavage fluid as potential prognostic biomarkers of peritoneal metastasis in gastric cancer. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0130472. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Huang Z, Zhu D, Wu L, He M, Zhou X, Zhang L, Zhang H, Wang W, Zhu J, Cheng W, et al. Six serum-based miRNAs as potential diagnostic biomarkers for gastric cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2017;26:188–196. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-16-0607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Wang M, Zhao C, Shi H, Zhang B, Zhang L, Zhang X, Wang S, Wu X, Yang T, Huang F, et al. Deregulated microRNAs in gastric cancer tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Novel biomarkers and a mechanism for gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. 2014;110:1199–1210. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2014.14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Zhang H, Deng T, Liu R, Bai M, Zhou L, Wang X, Li S, Wang X, Yang H, Li J, et al. Exosome-delivered EGFR regulates liver microenvironment to promote gastric cancer liver metastasis. Nat Commun. 2017;8:15016. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Li C, Liu DR, Li GG, Wang HH, Li XW, Zhang W, Wu YL, Chen L. CD97 promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation and invasion through exosome-mediated MAPK signaling pathway. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:6215–6228. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i20.6215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Liu D, Li C, Trojanowicz B, Li X, Shi D, Zhan C, Wang Z, Chen L. CD97 promotion of gastric carcinoma lymphatic metastasis is exosome dependent. Gastric Cancer. 2016;19:754–766. doi: 10.1007/s10120-015-0523-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Zhong H, Yang Y, Ma S, Xiu F, Cai Z, Zhao H, Du L. Induction of a tumour-specific CTL response by exosomes isolated from heat-treated malignant ascites of gastric cancer patients. Int J Hyperthermia. 2011;27:604–611. doi: 10.3109/02656736.2011.564598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Broere F, van der Zee R, van Eden W. Heat shock proteins are no DAMPs, rather ‘DAMPERs’. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011;11:565. doi: 10.1038/nri2873-c2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.van Eden W, Spiering R, Broere F, van der Zee R. A case of mistaken identity: HSPs are no DAMPs but DAMPERs. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2012;17:281–292. doi: 10.1007/s12192-011-0311-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Zheng P, Chen L, Yuan X, Luo Q, Liu Y, Xie G, Ma Y, Shen L. Exosomal transfer of tumor-associated macrophage-derived miR-21 confers cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017;36:53. doi: 10.1186/s13046-017-0528-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Wang X, Zhang H, Bai M, Ning T, Ge S, Deng T, Liu R, Zhang L, Ying G, Ba Y. Exosomes serve as nanoparticles to deliver anti-miR-214 to reverse chemoresistance to cisplatin in gastric cancer. Mol Ther. 2018;26:774–783. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.01.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Ji R, Zhang B, Zhang X, Xue J, Yuan X, Yan Y, Wang M, Zhu W, Qian H, Xu W. Exosomes derived from human mesenchymal stem cells confer drug resistance in gastric cancer. Cell Cycle. 2015;14:2473–2483. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1005530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.