ABSTRACT
Background
Professionalism, which encompasses behavioral, ethical, and related domains, is a core competency of medical practice. While observer-based instruments to assess medical professionalism are available, information on their psychometric properties and utility is limited.
Objective
We systematically reviewed the psychometric properties and utility of existing observer-based instruments for assessing professionalism in medical trainees.
Methods
After selecting eligible studies, we employed the COnsensus-based Standards for the selection of health Measurement INstruments (COSMIN) criteria to score study methodological quality. We identified eligible instruments and performed quality assessment of psychometric properties for each selected instrument. We scored the utility of each instrument based on the ability to distinguish performance levels over time, availability of objective scoring criteria, validity evidence in medical students and residents, and instrument length.
Results
Ten instruments from 16 studies met criteria for consideration, with studies having acceptable methodological quality. Psychometric properties were variably assessed. Among 10 instruments, the Education Outcomes Service (EOS) group questionnaire and Professionalism Mini-Evaluation Exercise (P-MEX) possessed the best psychometric properties, with the P-MEX scoring higher on utility than the EOS group questionnaire.
Conclusions
We identified 2 instruments with best psychometric properties, with 1 also showing acceptable utility for assessing professionalism in trainees. The P-MEX may be an option for program directors to adopt as an observer-based instrument for formative assessment of medical professionalism. Further studies of the 2 instruments to aggregate additional validity evidence is recommended, particularly in the domain of content validity before they are used in specific cultural settings and in summative assessments.
Introduction
Medical professionalism is defined as “the habitual and judicious use of communication, knowledge, technical skills, clinical reasoning, emotions, values, and reflection in daily practice for the benefit of the individual and community being served.”1 Professionalism is critical to trust between physicians and patients as well as the medical community and the public.2 Assessing professionalism is essential to medical education because professionalism in practice is central to a physician's social contract with society.3,4 Despite growing recognition of its importance, the lack of a consensus definition of professionalism limits its effective operationalization.5 While approaches such as critical incident reporting have been used to recognize when professional breaches occur, the need for trainee assessment and program evaluation necessitates quantitative and objective positive measures of professionalism to track the demonstration of competence and assess curricular effectiveness.6 Valid and reliable instruments that can discriminate levels of professionalism and identify lapses to facilitate remediation and further training are needed.
Many instruments have been developed to assess medical professionalism as a comprehensive stand-alone construct or as a facet of clinical competence.7 There is a tendency for programs to use multiple instruments, and selecting the most suitable instrument for a given program can be challenging for educators.5,8 Workplace- and observer-based assessments allow for the systematic assessment of professionalism by different assessors in various clinical contexts,8 which may complement other assessment modes such as self- and peer assessments. Observer-based instruments are in keeping with the current trend of adopting entrustable professional activities.9
Previous systematic reviews of professionalism measures have focused on different assessment methods, including direct observation, self-administered rating forms, patient surveys, and paper-based ratings.10–12 The most recent review concluded that studies were of limited methodological quality and recommended only 3 of 74 existing instruments as psychometrically sound; of note, 2 of these were from studies involving nurses.10 There were no current systematic reviews that focus on observer-based instruments to assess medical professionalism13 and on the utility of the instruments. The primary aim of this study was to identify observer-based instruments for use by program directors and to examine their psychometric properties and utility for practical application.
Methods
We performed a systematic review in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic review and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) checklist (provided as online supplemental material).
Search Strategies
We searched the PubMed, Scopus, ERIC, and PsycINFO databases from their inception to July 2018. The search strategy was adapted and revised from a previous systematic review14 in consultation with a medical librarian, and the full search strategy is provided as online supplemental material. Our focus was on observer-based instruments that measured professionalism.
Study Selection
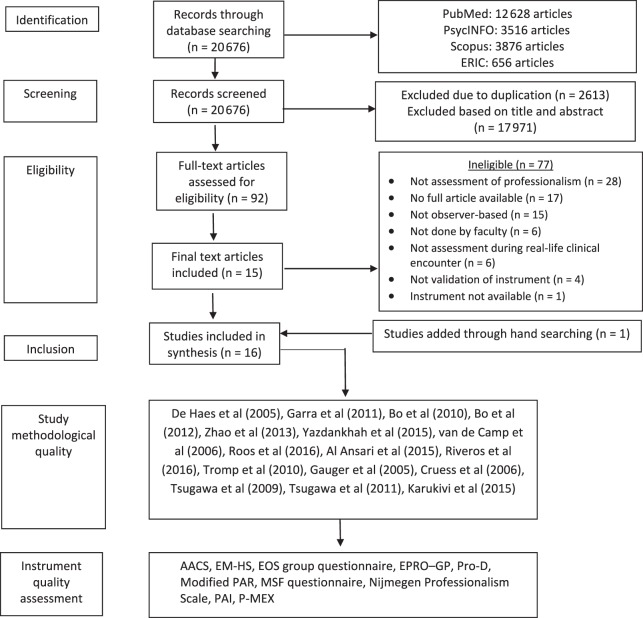
Inclusion criteria were English-language, full-text original studies on the validation of observer-based instruments, or questionnaires assessing or measuring medical professionalism of residents and medical students. Instruments had to be applied to the evaluation of professionalism in an actual clinical setting or context (see Figure). We excluded articles not in English, studies of professionalism in other health disciplines, and review articles. Duplicate studies were removed using EndNote X8 (Clarivate Analytics, Philadelphia, PA), and cross-checked by the researchers. Studies that met inclusion criteria were independently screened by 2 researchers (J.K.P. and H.G.) based on titles and abstracts. Full-text studies selected were independently read and assessed for eligibility, and the reference lists were hand-searched for additional eligible studies. Disagreements in the selection process were resolved by discussion with a third researcher (Y.H.K.).
Figure.
Flowchart Showing Process for Inclusion and Quality Assessment of Articles
Abbreviations: AACS, Amsterdam Attitude and Communication Scale; EM-HS, Emergency Medicine Humanism Scale; EOS, Education Outcome Service group questionnaire; EPRO-GP, Evaluation of Professional Behavior in General Practice; Pro-D, German Professionalism Scale; PAR, Physician Achievement Review; MSF, multisource feedback; PAI, Professionalism Assessment Instrument; P-MEX, Professionalism Mini-Evaluation Exercise.
The study did not involve human subjects and did not require Institutional Review Board approval.
Data Extraction
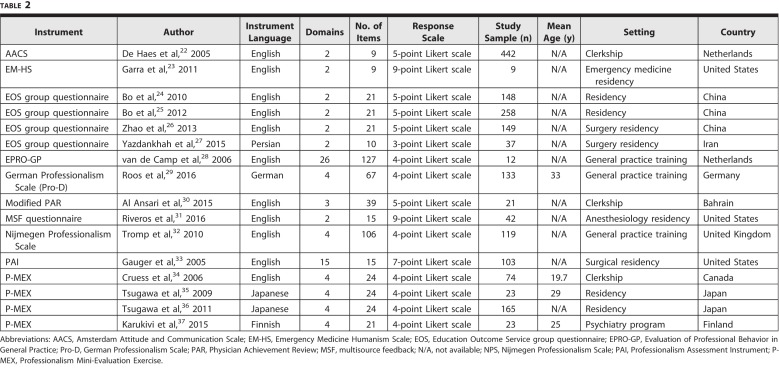
For studies deemed eligible, data were extracted independently by 2 researchers (H.G. and Y.S.) using a standardized data extraction form. The following data were extracted: general characteristics of each instrument (name of instrument, author, language, number of domains, number of items, and response categories) and characteristics of study samples (sample size, age, settings, and country).
Study Methodological Quality and Instrument Psychometric Property
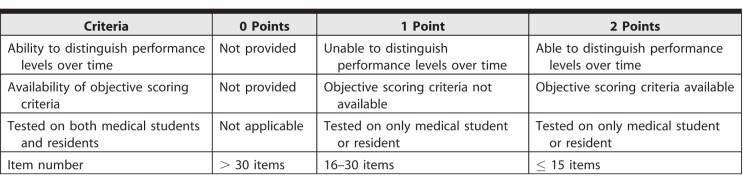
We performed 3 levels of quality assessment. First, 2 researchers (K.P. and H.G.) independently assessed each study using the COnsensus-based Standards for the selection of health Measurement INstruments (COSMIN) checklist (Figure). Disagreements were resolved by a third reviewer (Y.H.K.). We selected the COSMIN checklist because it is a consensus-based tool for study appraisal involving instruments.15,16 The checklist addresses 9 criteria: content validity, structural validity, internal consistency, cross-cultural validity measurement invariance, reliability, measurement error, criterion validity, hypotheses testing for construct validity, and responsiveness. The checklist is presented in boxes, with each box comprising items to assess the study methodological quality for each criterion. Items are rated on a 4-point scale, which includes the ratings inadequate, doubtful, adequate, or very good.17 As there is no accepted “gold standard” for assessing professionalism, we did not assess criterion validity of the studies. Second, we assessed the psychometric quality of each instrument using an adapted version of the Prinsen et al criteria18 to synthesize evidence that supported the measurement properties of instruments (see Figure). Third, we assessed the utility of each instrument for real-world practicality using prespecified criteria, including the ability to distinguish performance over time, objective scoring criteria, validity for use in medical students and residents, and number of items.
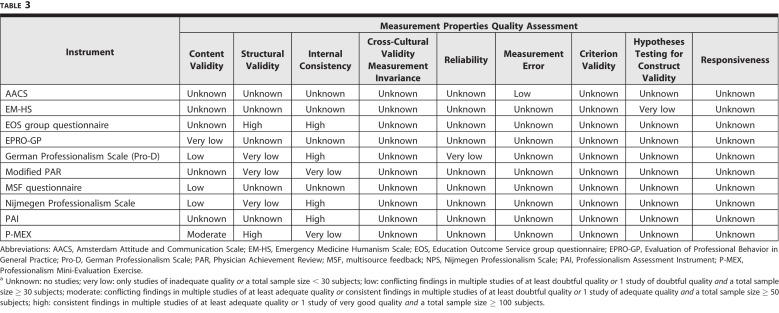
The quality of evidence was graded for psychometric properties, taking into account the number of studies, the methodological quality of the studies, the consistency of the results of the measurement properties, and the total sample size.18 The ratings for the level of evidence for the psychometric properties were as follows:
Unknown: No study
Very low: Only studies of inadequate quality or a total sample size < 30 subjects
Low: Conflicting findings in multiple studies of at least doubtful quality or 1 study of doubtful quality and a total sample size ≥ 30 subjects
Moderate: Conflicting findings in multiple studies of at least adequate quality or consistent findings in multiple studies of at least doubtful quality or 1 study of adequate quality and a total sample size ≥ 50 subjects
High: Consistent findings in multiple studies of at least adequate quality or 1 study of very good quality and a total sample size ≥ 100 subjects18
Instrument Utility and Scoring
We developed a utility scale using criteria from other studies.19–21 The 4 criteria chosen were (1) the ability to distinguish performance levels over time; (2) the availability of objective scoring criteria; (3) the utility for medical students and residents; and (4) the number of items, with a maximum of 8 points (see Table 1) and a higher utility score indicating greater feasibility of implementation.
Table 1.
Utility Scoring Criteria Checklist
Results
Search Results
The electronic search yielded 20 676 article titles after removal of duplicates. Articles were reviewed by title and abstract, and 17 971 articles that did not meet inclusion criteria were removed. A second review of 92 full-text articles resulted in the selection of 15 articles after the removal of articles that did not examine professionalism but other constructs such as empathy. One article was added after hand-searching published systematic reviews. Sixteen articles assessing 10 observer-based instruments were included in this review and quality assessment (see the Figure).
The 16 studies examined 10 instruments: the Amsterdam Attitude and Communication Scale (AACS),22 the Emergency Medicine Humanism Scale (EM-HS),23 the Education Outcome Service (EOS) group questionnaire,24–27 the Evaluation of Professional Behavior in General Practice (EPRO-GP),28 the German Professionalism Scale (Pro-D),29 the modified Physician Achievement Review (PAR),30 the multisource feedback (MSF) questionnaire,31 the Nijmegen Professionalism Scale,32 the Professionalism Assessment Instrument (PAI),33 and the Professionalism Mini-Evaluation Exercise (P-MEX).34–37 Four instruments assessed residents and medical students (the EPRO-GP, Pro-D, Nijmegen Professionalism Scale, and P-MEX). Each instrument was assessed in 1 study except for P-MEX and the EOS group questionnaire, which were assessed in 4 individual studies.
All 10 instruments measured professionalism as a single construct with multiple domains (see Table 2 and online supplemental material). The instruments varied in item number from 9 to 127. Study sample size ranged from 9 to 442 participants. All instruments used a Likert scale (ranging from 3 to 9 points) to measure professionalism. Four instruments (P-MEX, EPRO-GP, Nijmegen Professionalism Scale, and Pro-D) were tested in medical students and residents.13,35–40 The AACS and EM-HS had the lowest number of items at 9, while the EPRO-GP had the most at 127.
Table 2.
Characteristics of Studies Included in Systematic Review
COSMIN Methodological Quality Assessment
Methodological quality was generally adequate for 9 studies (provided as online supplemental material). The structural validity psychometric property was the most commonly assessed, being the focus of 9 studies (56%). Eight studies assessed internal consistency, with 5 (63%) scoring adequate or very good. The 8 studies that assessed content validity had scores of doubtful. Inadequate methodological quality was observed for the single study that assessed reliability. Only 1 study assessed measurement error, and there were questions about its methodological quality.
Although translations were performed in 5 studies,27,36,37,39,42 no studies assessed cross-cultural validity. Lack of effective interventions was the main reason for the inadequate evaluation of responsiveness, as validating responsiveness required the assessment tool to be able to detect change over time after an intervention.
Psychometric Properties
The quality of psychometric properties varied for the 10 instruments that assessed it (Table 3). Internal consistency scored better than other criteria, with low or better levels (low, moderate, high) observed for 4 of 6 instruments (the EOS group questionnaire, Pro-D, Nijmegen Professionalism Scale, PAI). For structural validity, the EOS group questionnaire and the P-MEX scored high. Content validity had low levels of evidence overall, with the P-MEX scoring the highest with moderate quality.
Table 3.
Levels of Evidence for Combined Measurement Properties for Each Instrumenta
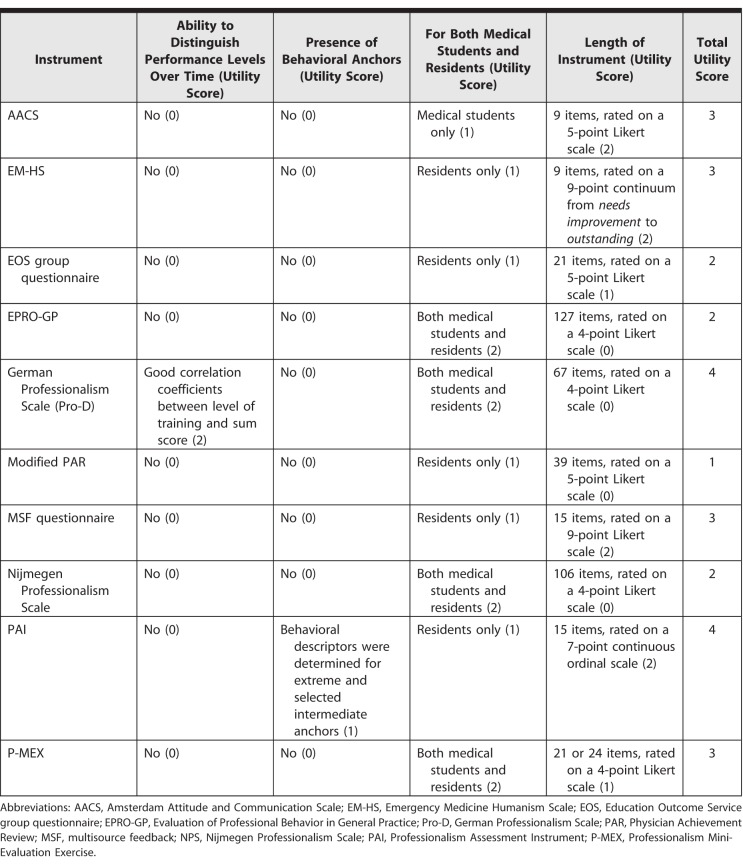
Utility Scores
Utility scoring for the 10 instruments ranged from 2 to 4 points (Table 4), with only the Pro-D showing good correlation coefficients between level of training and sum score. The ability of the instrument to distinguish performance level over time was not examined for the other instruments. Only the PAI provided behavioral descriptors/anchors for extreme and selected intermediate anchors. Based on the 4 utility criteria, the Pro-D and PAI had the highest score at 4 points.
Table 4.
Utility of Each Instrument
Discussion
We identified 16 studies assessing 10 instruments for assessing medical professionalism, with instruments showing varying quality. The P-MEX performed best relative to evidence for measurement properties and adequate utility scoring among the available instruments. Considering the psychometric properties and utility, the P-MEX may be the most suitable instrument for assessing medical professionalism in medical trainees due to evidence to support its measurement properties and higher utility.
For many instruments, methodological quality assessed via the COSMIN checklist and the level of evidence synthesized was very low to low. Our findings are similar to those reported in a systematic review of instruments for measuring communication skills in students and residents using an objective structured clinical examination,41 where the authors identified 8 psychometrically tested scales from 12 studies, often of poor methodological and psychometric quality. Compared with 32 instruments to measure technical surgical skills among residents42 and 55 instruments for assessing clinical competencies in medical students and residents,43 the number of professionalism assessment instruments meeting quality criteria was lower. This may reflect challenges educators face in defining and assessing this competency.
Our study has limitations. First, the number of studies available for evidence synthesis was limited, and we may have missed studies published in languages other than English. The utility assessment tool was developed by the authors, based on previous reports, but was not evaluated further for evidence.19–21
Our review showed inadequate investigation of content validity of assessment tools for medical professionalism, and future studies are needed to identify the relevant domains of medical professionalism. It is important for future studies to assess the validity of instruments across different cultural contexts, as definitions of professionalism may differ among national and cultural contexts.
Conclusion
Our review found that the P-MEX has the best evidence for measurement properties and adequate utility scoring among available instruments for assessing medical professionalism. This too may be an option for program directors to adopt as an observer-based instrument for the formative assessment of professionalism in trainees. Further aggregation of validity evidence for instruments is recommended, particularly in the domain of content validity before implementation in a specific cultural setting or for summative assessments.
Supplementary Material
References
- 1.Armitage-Chan E. Assessing professionalism: a theoretical framework for defining clinical rotation assessment criteria. J Vet Med Educ. 2016;43(4):364–371. doi: 10.3138/jvme.1215-194R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Goold SD, Lipkin M. The doctor-patient relationship: challenges, opportunities, and strategies. J Gen Intern Med. 1999;14(suppl 1):26–33. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1497.1999.00267.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Livingston EH, Ginsburg S, Levinson W. Introducing JAMA professionalism. JAMA. 2016;316(7):720–721. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.9854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hodges BD, Ginsburg S, Cruess R, et al. Assessment of professionalism: recommendations from the Ottawa 2010 Conference. Med Teach. 2011;33(5):354–363. doi: 10.3109/0142159X.2011.577300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Goldie J. Assessment of professionalism: a consolidation of current thinking. Med Teach. 2013;35(2):e952–e956. doi: 10.3109/0142159X.2012.714888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.van Mook WN, Gorter SL, O'Sullivan H, et al. Approaches to professional behaviour assessment: tools in the professionalism toolbox. Eur J Intern Med. 2009;20(8):e153–e157. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2009.07.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Veloski JJ, Fields SK, Boex JR, et al. Measuring professionalism: a review of studies with instruments reported in the literature between 1982 and 2002. Acad Med. 2005;80(4):366–370. doi: 10.1097/00001888-200504000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Passi V, Doug M, Peile JT, et al. Developing medical professionalism in future doctors: a systematic review. Int J Med Educ. 2010;1:19–29. [Google Scholar]
- 9.ten Cate O. Nuts and bolts of entrustable professional activities. J Grad Med Educ. 2013;5(1):157–158. doi: 10.4300/JGME-D-12-00380.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Li H, Ding N, Zhang Y, et al. Assessing medical professionalism: a systematic review of instruments and their measurement properties. PLOS ONE. 2017;12(5):e0177321. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lynch DC, Surdyk PM, Eiser AR. Assessing professionalism: a review of the literature. Med Teach. 2004;26(4):366–373. doi: 10.1080/01421590410001696434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wilkinson TJ, Wade WB, Knock LD. A blueprint to assess professionalism: results of a systematic review. Acad Med. 2009;84(5):551–558. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0b013e31819fbaa2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Tromp F, Vernooij-Dassen M, Kramer A, et al. Behavioural elements of professionalism: assessment of a fundamental concept in medical care. Med Teach. 2010;32(4):e161–e169. doi: 10.3109/01421590903544728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Honghe L, Ding N, Zhang Y, et al. Assessing medical professionalism: a systematic review of instruments and their measurement properties. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(5):e0177321. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Prinsen CAC, Mokkink LB, Bouter LM, et al. COSMIN guideline for systematic reviews of patient-reported outcome measures. Qual Life Res. 2018;27(5):1147–1157. doi: 10.1007/s11136-018-1798-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mokkink LB, de Vet HCW, Prinsen CAC, et al. COSMIN risk of bias checklist for systematic reviews of patient-reported outcome measures. Qual Life Res. 2018;27(5):1171–1179. doi: 10.1007/s11136-017-1765-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Terwee CB, Mokkink LB, Knol DL, et al. Rating the methodological quality in systematic reviews of studies on measurement properties: a scoring system for the COSMIN checklist. Qual Life Res. 2012;21(4):651–657. doi: 10.1007/s11136-011-9960-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Prinsen CAC, Vohra S, Rose MR, et al. How to select outcome measurement instruments for outcomes included in a “Core Outcome Set”—a practical guideline. Trials. 2016;17(1):449. doi: 10.1186/s13063-016-1555-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ferrarello F, Bianchi VAM, Baccini M, et al. Tools for observational gait analysis in patients with stroke: a systematic review. Phys Ther. 2013;93(12):1673–1685. doi: 10.2522/ptj.20120344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Tyson SF, Connell LA. How to measure balance in clinical practice. A systematic review of the psychometrics and clinical utility of measures of balance activity for neurological conditions. Clin Rehabil. 2009;23(9):824–840. doi: 10.1177/0269215509335018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Tyson S, Connell L. The psychometric properties and clinical utility of measures of walking and mobility in neurological conditions: a systematic review. Clin Rehabil. 2009;23(11):1018–1033. doi: 10.1177/0269215509339004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.De Haes JCJM, Oort FJ, Hulsman RL. Summative assessment of medical students' communication skills and professional attitudes through observation in clinical practice. Med Teach. 2005;27(7):583–589. doi: 10.1080/01421590500061378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Garra G, Wackett A. Thode H. Feasibility and reliability of a multisource feedback tool for emergency medicine residents. J Grad Med Educ. 2011;3(3):356–360. doi: 10.4300/JGME-D-10-00173.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bo Q, Zhao Y, Sun B. Evaluation of residents in professionalism and communication skills in south China. Saudi Med J. 2010;31(11):1260–1265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bo Q, Zhao YH, Sun BZ. Assessment of resident physicians in professionalism, interpersonal and communication skills: a multisource feedback. Int J Med Sci. 2012;9(3):228–236. doi: 10.7150/ijms.3353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Zhao Y, Zhang X, Chang Q, et al. Psychometric characteristics of the 360 degrees feedback scales in professionalism and interpersonal and communication skills assessment of surgery residents in China. J Surg Educ. 2013;70(5):628–635. doi: 10.1016/j.jsurg.2013.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Yazdankhah A, Tayefeh Norooz M, Ahmadi Amoli H, et al. Using 360-degree multi-source feedback to evaluate professionalism in surgery departments: an Iranian perspective. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2015;29(1):1088–1094. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Van De Camp K, Vernooij-Dassen M, Grol R, et al. Professionalism in general practice: development of an instrument to assess professional behaviour in general practitioner trainees. Med Educ. 2006;40(1):43–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2929.2005.02346.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Roos M, Pfisterer D, Krug D, et al. Adaptation, psychometric properties and feasibility of the Professionalism Scale Germany. Z Evid Fortbild Qual Gesundheitswes. 2016;113:66–75. doi: 10.1016/j.zefq.2016.04.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Al Ansari A, Al Khalifa K, Al Azzawi M, et al. Cross-cultural challenges for assessing medical professionalism among clerkship physicians in a Middle Eastern country (Bahrain): feasibility and psychometric properties of multisource feedback. Adv Med Educ Pract. 2015;6:509–515. doi: 10.2147/AMEP.S86068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Riveros R, Kimatian S, Castro P, et al. Multisource feedback in professionalism for anesthesia residents. J Clin Anesth. 2016;34:32–40. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2016.03.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Tromp F, Vernooij-Dassen M, Kramer A, et al. Behavioural elements of professionalism: assessment of a fundamental concept in medical care. Med Teach. 2010;32(4):e161–e169. doi: 10.3109/01421590903544728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Gauger PG, Gruppen LD, Minter RM, et al. Initial use of a novel instrument to measure professionalism in surgical residents. Am J Surg. 2005;189(4):479–487. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2004.09.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Cruess R, McIlroy JH, Cruess S, et al. The professionalism mini-evaluation exercise: a preliminary investigation. Acad Med. 2006;81(suppl 10):74–78. doi: 10.1097/00001888-200610001-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Tsugawa Y, Tokuda Y, Ohbu S, et al. Professionalism mini-evaluation exercise for medical residents in Japan: a pilot study. Med Educ. 2009;43(10):968–973. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2923.2009.03437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tsugawa Y, Ohbu S, Cruess R, et al. Introducing the professionalism mini-evaluation exercise (p-MEX) in Japan: results from a multicenter, cross-sectional study. Acad Med. 2011;86(8):1026–1031. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0b013e3182222ba0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Karukivi M, Kortekangas-Savolainen O, Saxen U, et al. Professionalism mini-evaluation exercise in Finland: a preliminary investigation introducing the Finnish version of the P-MEX instrument. J Adv Med Educ Prof. 2015;3(4):154–158. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Cruess R, McIlroy JH, Cruess S, et al. The professionalism mini-evaluation exercise: a preliminary investigation. Acad Med. 2006;81(suppl 10):74–78. doi: 10.1097/00001888-200610001-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.van de Camp K, Vernooij-Dassen M, Grol R, et al. Professionalism in general practice: development of an instrument to assess professional behaviour in general practitioner trainees. Med Educ. 2006;40(1):43–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2929.2005.02346.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Roos M, Pfisterer D, Krug D, et al. Adaptation, psychometric properties and feasibility of the Professionalism Scale Germany. Z Evid Fortbild Qual Gesundhwes. 2016;113:66–75. doi: 10.1016/j.zefq.2016.04.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Cömert M, Zill JM, Christalle E, et al. Assessing communication skills of medical students in objective structured clinical examinations (OSCE)—a systematic review of rating scales. PLOS ONE. 2016;11(3):e0152717. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Fahim C, Wagner N, Nousiainen MT, et al. Assessment of technical skills competence in the operating room: a systematic and scoping review. Acad Med. 2018;93(5):794–808. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000001902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kogan JR, Holmboe ES, Hauer KE. Tools for direct observation and assessment of clinical skills of medical trainees: a systematic review. JAMA. 2009;302(12):1316–1326. doi: 10.1001/jama.2009.1365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.