Abstract
Dynamin copolymerizes with cortactin to form a ring-like complex that bundles and stabilizes actin filaments. Actin bundle formation is crucial for generation of filopodia and lamellipodia, which guide migration, invasion, and metastasis of cancer cells. However, it is unknown how the dynamin-cortactin complex regulates actin bundle formation. The present study investigated phosphorylation of cortactin by cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5) and its effect on actin bundle formation by the dynamin-cortactin complex. CDK5 directly phosphorylated cortactin at T145/T219 in vitro. Phosphomimetic mutants in which one or both of these threonine residues was substituted by aspartate were used. The three phosphomimetic mutants (T145D, T219D and T145DT219D) had a decreased affinity for F-actin. Furthermore, electron microscopy demonstrated that these phosphomimetic mutants could not form a ring-like complex with dynamin 1. Consistently, the dynamin 1-phosphomimetic cortactin complexes exhibited decreased actin-bundling activity. Expression of the phosphomimetic mutants resulted in not only aberrant lamellipodia and short filopodia but also cell migration in NG108-15 glioma-derived cells. These results indicate that phosphorylation of cortactin by CDK5 regulates formation of lamellipodia and filopodia by modulating dynamin 1/cortactin-dependent actin bundling. Taken together, these findings suggest that CDK5 is a potential molecular target for anticancer therapy.
Keywords: cortactin, actin, bundle, cyclin-dependent kinase 5, dynamin
Introduction
Two- or three-dimensional actin assembly is a prerequisite for formation of actin-rich protrusions such as lamellipodia and filopodia, which are required for migration, invasion, and metastasis of cancer cells (1). Actin filaments in lamellipodia exhibit complex branching and combine with each other to form a mesh-like structure, while those in filopodia are bundled by various actin-crosslinking and -binding proteins (2).
The F-actin-binding protein cortactin contributes to cell migration and invasion (3) and has three functional domains: an N-terminal acidic region that binds to the Arp2/3 complex, an F-actin-binding cortactin repeat region that contains 6.5 tandem repeats, and a C-terminal Src homology 3 (SH3) region that binds to proline-rich domain (PRD)-containing proteins, such as dynamin (4-6), Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP) (7) and WASP-interacting protein (8).
Dynamin, a well-known endocytic protein required for vesicle scission, copolymerizes with cortactin to form a ring-like complex via an interaction between the PRD of dynamin and the SH3 domain of cortactin, and this complex bundles and stabilizes actin filaments (5,6). Actin bundling by the dynamin-cortactin complex regulates formation of filopodia in human neuroblastoma cells (5) and non-small lung carcinoma cells (6) and is thus implicated in cell motility. However, the mechanism by which this complex regulates actin bundling is largely unknown.
Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5) is a proline-directed serine/threonine kinase belonging to the cyclin-dependent kinase family (9). The role of CDK5 has been mostly studied in terminally differentiated cells, including neurons and neuroendocrine cells. CDK5 contributes to neurite outgrowth, neuronal migration, and neuronal and β cell differentiation (10,11). In addition, it has recently been demonstrated that CDK5 is highly expressed in several cancer cell lines and tissues, suggesting this kinase is functionally associated with tumorigenesis and/or malignancy (12). Furthermore, CDK5 participates in actin-based cancer cell motility, including migration, invasion (13) and metastasis of pancreatic cancer cells (14). However, it remains unknown whether CDK5-mediated phosphorylation regulates actin-based motility.
The present study investigated phosphorylation of cortactin by CDK5 in vitro and its effect on actin bundling and complex formation with dynamin in vitro and in glioma-derived cells. The potential roles of CDK5 and cortactin in anticancer therapy are also discussed.
Materials and methods
Antibodies and reagents
A rabbit polyclonal antibody against c-myc (C3956) and a mouse monoclonal antibody against β-actin (clone AC-15) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA (Darmstadt, Germany). A mouse monoclonal antibody against c-myc (sc-40) was purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc. (Dallas, TX, USA). Mouse monoclonal antibodies against cortactin (clone 4F-11; cat. no. 05-180) and CDK5 (clone DC17; cat. no. 05-364) were purchased from EMD Millipore (Billerica, MA, USA). Rabbit polyclonal anti-dynamin 1 antibodies (PA1-660), Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated anti-rabbit immunoglobulin G (IgG; cat. no. A21206), rhodamine-conjugated anti-mouse IgG (cat. no. R6393), rhodamine- (cat. no. R415) or Alexa Fluor 488-labeled phalloidin (cat. no. A12379), Horseradish peroxidase-coniugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (H+L; cat. no. 31460) and rabbit anti-mouse IgG (H+L; cat. no. 31450) were purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. (Waltham, MA, USA).
Cell culture
NG108-15 (HB-12317) cells were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA, USA) and cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; cat. no. 26140079) (both from Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) at 37°C in 5% CO2. To induce differentiation of NG108-15 cells, cells were treated with 1 mM dibutyryl-cyclic-AMP (cat. no. D0627; Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) at 37°C for 48 h.
Expression and purification of cortactin and its mutants
cDNA encoding full-length rat cortactin was produced as previously described (5). Glutathione-S-transferase (GST)-tagged W525K, T145D, T219D, T145DT219D and T145AT219A mutants were generated by mutating cortactin in pGEX-6P using a QuickChange Site-Directed Mutagenesis kit (Agilent Technologies, Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA). GST-tagged proteins were expressed in Escherichia coli (cat. no. 200131; Agilent Technologies, Inc.) and purified as described previously (5). Histidine-tagged human dynamin 1 was expressed using the Bac-to-Bac baculoviral expression system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) and purified as described previously (5). Purified dynamin solutions were concentrated using Centriplus YM50 (EMD Millipore). Protein solutions (1-2 mg/ml protein) were stored at −80°C and thawed at 37°C prior to use.
For protein expression in cells, wild-type (WT) cortactin and the T145D, T219D and T145DT219D mutants were separately subcloned into the pEF1 myc-His vector (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) as EcoRI/XbaI fragments. The nucleotide sequences of the constructs were verified using a BigDye Terminator v3.1 Cycle Sequencing kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). These vectors were transfected using Lipofectamine LTX (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) according to the manufacturer’s manual. Following 48 h of transfection, transfected cells were used for subsequent experiments.
Fluorescence microscopy
NG108-15 cells were fixed for 15 min in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) and processed for immunofluorescence analysis as described previously (6). To measure filopodial length, non-transfected cells and those transfected with WT or mutant cortactin were fixed as described above and stained with Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated phalloidin (1:40) for 1 h. All steps were performed at room temperature. Digital images of actin-rich structures, including filopodia, lamellipodia, and cellular protrusions, were acquired at ×100 magnification. Up to three filopodia per cellular protrusion were randomly selected, and their lengths were measured using ImageJ software, version 1.40g (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA).
Migration assay
NG108-15 cells (1.6×105/well) in a 6-well plate were transfected with 2.5 µg of myc-tagged WT or T145DT219D cortactin using Lipofectamine LTX. Following 6 h transfection, cells were re-seeded in 35 mm glass base dishes (with grid; AGC Techno Glass Co., Ltd., Shizuoka, Japan) precoated with poly-L-lysin, and further cultured with 10% FBS/DMEM for 48 h. Time-lapsed imaging of the cells was performed using differential interference contrast microscopy (DIC) at ×100 magnification for 4 h at 30-sec intervals. During the experiments, the cells were maintained at 37°C under 5% CO2. To determine the WT or T145DT219D cortactin expressing cells, cells were stained with anti-myc antibodies (1:300) at room temperature for 1 h following the time lapse-imaging. Images were acquired by MetaMorph software version 7.8.13.0. (Universal Imaging, Inc., Bedford Hills, NY, USA). The migration path was processed using ImageJ, Adobe Photoshop CS3 version 10 or Illustrator CS3 software version 13 (Adobe Systems, Inc., San Jose, CA, USA).
Phosphorylation assay
In vitro phosphorylation reactions were performed in cytosolic buffer (25 mM HEPES-KOH, 25 mM KCl, 2.5 mM magnesium acetate and 100 mM potassium glutamate, pH 7.2) containing 0.5 mM ATP and 300 dpm/pmol [γ32P]-ATP. Purified WT, T145AT219A cortactin or dynamin 1 was incubated with 1 µg/ml recombinant CDK5/p35 (Merck KGaA) at 30°C for 1 h. Reactions were terminated by addition of SDS sample buffer and subsequent boiling. The reaction products were analyzed by SDS-PAGE in 10% polyacrylamide gel followed by SYPRO Orange staining at room temperature for 1 h and autoradiography. Autoradiography images were scanned using a FLA7000 Imager (Fuji Photo Film Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). The results were obtained from independent two experiments.
Actin-crosslinking assay
Non-muscle actin (Cytoskeleton, Inc., Denver, CO, USA) was polymerized in F-buffer (5 mM Tris-HCl, 0.5 mM DTT, 0.2 mM CaCl2, 2 mM MgCl2, 50 mM KCl and 1 mM ATP, pH 7.5) for 1 h. Thereafter, 3.3 µM F-actin was incubated with 5 µM WT cortactin or its phosphomimetic mutants alone or together with dynamin 1 for 1 h, and then with 3 µM Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated phalloidin for an additional 30 min. Samples were dispersed on glass slides and mounted. All steps were performed at room temperature. Cross-linked or bundled F-actin was observed under epifluorescence microscopy at ×400 magnification. When necessary, images were processed using Adobe Photoshop CS3 or Illustrator CS3 software.
In vitro actin assembly assay
Actin assembly was quantified using pyrene-actin as described previously (5). Briefly, 11.4 µM pyrene-actin (AP05; Cytoskeleton, Inc.) prepared in assay buffer (5 mM Tris-HCl, 50 mM KCl, 2 mM MgCl2, 0.2 mM CaCl2 and 1 mM ATP, pH 7.5) was incubated for 60-90 min in a microtiter plate (Sumitomo Bakelite Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). Pyrene fluorescence at 407 nm (10-nm slit width) was then measured using a fluorescence microplate reader (MTP-600F; Corona Electric Co., Ltd., Ibaraki, Japan) with an excitation wavelength of 365 nm. All steps were performed at room temperature.
Pulldown assay
The GST pulldown assay was performed as described previously (5). GST-fusion proteins (10 µg) bound to glutathione-Sepharose beads (GE Healthcare Life Sciences, Little Chalfont, UK) were incubated with 5 µg recombinant dynamin 1 prepared in 0.1% Tween-20, 100 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2 and 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.8), and a protease inhibitor cocktail tablet (Roche Diagnostics, Basel, Switzerland) at 4°C for 1 h. Bead-bound dynamin 1 was separated by centrifugation at 1,300 × g at 4°C for 3 min, and SDS sample buffer was added to the sample. After boiling at 95°C for 5 min, the beads were analyzed by SDS-PAGE in 10% polyacrylamide gel followed by western blotting.
Preparation of cells and whole brain homogenate
NG108-15 cells (1×106 cells) or whole brains of 10 male mice (C57BL/6J; age, 6 weeks; 22-27 g; Japan SLC, Inc., Hamamatsu, Japan) were homogenized in PBS containing a protease inhibitor cocktail tablet (Roche Diagnostics) with a Potter-type glass-Teflon homogenizer. The homogenate was centrifuged at 20,000 × g for 30 min at 4°C. The supernatant was sampled in SDS sample buffer. Samples were boiled for 5 min and subjected to western blotting.
Western blotting
Samples were subjected to SDS-PAGE in 10% polyacrylamide gel and transferred electrophoretically to a nitrocellulose membranes (cat. no. 10600003; GE Healthcare Life Sciences). The membrane was blocked with 140 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), containing 0.1% Tween-20 and 5% skimmed milk for 4 h at room temperature, and incubated with primary antibodies (1:1,000) for 2 h followed by incubation with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies (1:10,000) for 1 h. Bands were visualized using the ECL western blotting detection system (cat. no. RPN2106; GE Healthcare Life Sciences).
Protein assay
Protein concentration was determined using a bicinchoninic acid assay kit (cat. no. 23235; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) with bovine serum albumin as the standard.
Morphometric analysis
To measure filopodial length, NG108-15 cells transfected with WT or mutant cortactin were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 min and stained with Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated phalloidin (1:40) for 1 h. All steps were performed at room temperature. Actin-rich cellular protrusions with lamellipodia and filopodia at their tips were imaged. Digital images were acquired at ×600 magnification. Up to three filopodia per growth cone were randomly selected, and their lengths were measured using ImageJ software, version 1.40g.
Electron microscopy
Dynamin 1-cortactin complexes were negatively stained as described previously (5). Briefly, complexes were formed by incubating 1 µM dynamin 1 and 1 µM cortactin in cytosolic buffer at 37°C for 15 min. Samples were absorbed onto a Formvar- and carbon-coated copper grid and stained with 1.5% uranyl acetate prepared in ddH2O at room temperature for 2 min. For morphometric analysis of ring complex formation, negatively-stained samples with a similar density were imaged at ×20,000 magnification using a transmission electron microscope (H7650; Hitachi, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). A total of 6 regions of interest, corresponding to 0.84 µm2, were randomly selected and the number of ring complexes was counted. The dynamin 1-cortactin complexes observed were divided into the following four categories according to the completeness of their circular shape: Closed rings, incomplete rings that were ≥75% closed, incomplete rings that were >50% and <75% closed, and rod-like or irregularly shaped structures that were >60 nm in length.
Mass spectrometry analysis
Phosphorylation sites in cortactin were identified by mass spectrometry, as described previously (15). Briefly, cortactin was phosphorylated in vitro by CDK5 and separated by SDS-PAGE in 10% polyacrylamide gel. Polypeptide bands corresponding to cortactin were excised from the gel and digested with trypsin (Promega Corporation, Madison, WI, USA). Digested peptides were extracted with acetonitrile and subjected to matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-MS; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.).
Ethics and Animal Use Statement
The present study was conducted in strict accordance to the recommendations in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals in Japan. Animals were housed at 23±2°C with a 12-h light/dark cycle and free access to water and standard rodent chow in the Department of Animal Resources of Okayama University. All surgery was performed under general anesthesia with sevoflurane, and all efforts were made to minimize animal suffering. After sacrificing mice, whole brains were removed.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using KaleidaGraph software for Macintosh, version 4.1 (Synergy Software, Inc., Essex Junction, VT, USA). One-way analysis of variance and Tukey’s least significant difference post hoc test were used to compare multiple groups. Student’s t-test was used to compare two groups. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
CDK5 directly phosphorylates recombinant cortactin
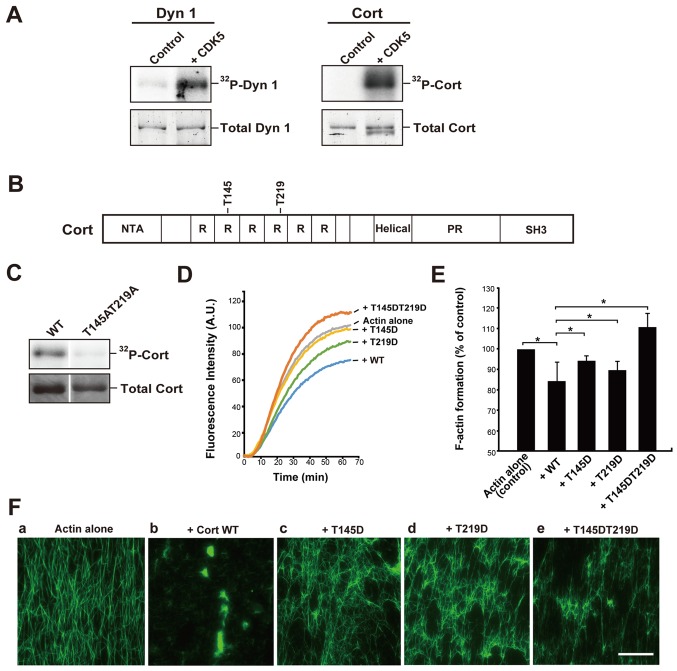
Dynamin 1 is reported to be an endogenous substrate of CDK5, and this phosphorylation is implicated in the regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis (16,17). Consistent with previous results, CDK5/p35 clearly phosphorylated recombinant dynamin 1 (Fig. 1A). Under the same conditions, CDK5/p35 also markedly phosphorylated cortactin in the presence of [γ32P]-ATP (Fig. 1A). Next, the phosphorylation sites, T145 and T219, were determined by MALDI-MS (Fig. 1B). Cortactin substitution mutant with alanine residues replacing T145 and T219 (Cort T145AT219A) exhibited only trace CDK5 radiolabeling (Fig. 1C). The two phosphorylation sites, T145 and T219, are located in the F-actin-binding cortactin repeat region of cortactin (RRRRRR 1/2; Fig. 1B).
Figure 1.
CDK5 directly phosphorylates Cort in vitro and this phosphorylation alters the interaction between Cort and F-actin. (A) Dyn 1 or Cort was incubated with or without 1 µg/ml CDK5 in the presence of [γ32P]-ATP. 32P-Dyn1 and 32P-Cort was then analyzed by SDS-PAGE and visualized by autoradiography (upper panels). Total protein was stained with SYPRO Orange (bottom panels). Proteins were incubated without CDK5 as a control. (B) Sites phosphorylated by CDK5 in Cort (T145 and T219) identified by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry analysis. These residues are located in the second and fourth Cort R units. (C) Verification of the identified phosphorylation sites in Cort. WT Cort (left) and a Cort mutant in which the T145/T219 phosphorylation sites were substituted with alanine (right) at 3.2 µg were incubated with CDK5/p35 and [γ32P]-ATP for 1 h. Total Cort stained with coomassie brilliant blue is presented (bottom). 32P-Cort was detected by autoradiography. (D) In vitro actin polymerization in the presence of WT Cort or the T145D, T219D, or T145DT219D mutant. Actin polymerization was initiated by adding K+ and Mg2+. Actin filament formation was measured by determining the change in the fluorescence intensity of pyrene-actin. (E) F-actin formation at 1 h following initiation of actin polymerization with or without WT Cort or the T145D, T219D or T145DT219D mutant was measured by analyzing pyrene-actin fluorescence. Actin alone was used as a control. The mean ± standard error of the mean of 3-6 independent experiments is plotted. *P<0.05. (F) Phosphorylation of Cort by CDK5 decreases its actin-crosslinking capability. (a) Actin alone appeared as individual filaments. (b) Tightly cross-linked F-actin in the presence of WT Cort (+Cort WT). Partially assembled filaments were observed in the presence of the (c) T145D, (d) T219D or (e) T145DT219D mutants. Preformed F-actin (3.3 µM) was incubated with or without the indicated proteins (5 µM each; b-e). F-actin was stained with Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated phalloidin. Scale bar, 30 µm. CDK5, cyclin-dependent kinase 5; Dyn 1, dynamin 1; Cort, cortactin; 32P, phosphorylated; WT, wild-type; NTA, N-terminal acidic region; R, repeat; PR, a proline-rich region; SH3, Src homology 3.
Phosphorylation of cortactin by CDK5 alters the interaction between cortactin and F-actin
The finding that the phosphorylation sites were located in the F-actin-binding region of cortactin suggested that this phosphorylation affects the binding affinity of cortactin for F-actin (Fig. 1B). To investigate this, the kinetics of in vitro F-actin formation in the presence or absence of WT cortactin or the phosphomimetic mutants were examined. To imitate phosphorylation, residues T145 and/or T219 were substituted by aspartate. Pyrene-labeled monomeric actin was polymerized in the presence of high concentrations of K+ and Mg2+. In the absence of cortactin, actin polymerization plateaued at 1 h. Addition of WT cortactin reduced the K+/Mg2+-dependent actin polymerization rate and decreased F-actin formation by ~15% at 1 h (Fig. 1D and E). Addition of the T145D or T219D mutant decreased F-actin formation by 5-10%. However, the T145DT219D mutant had no inhibitory effect (Fig. 1D and E). These results suggest that phosphorylation of the T145 and/or T219 residues of cortactin by CDK5 disrupts binding between cortactin and F-actin.
Next, it was investigated whether phosphorylation of cortactin by CDK5 affects its actin-crosslinking activity in vitro. Preformed F-actin was incubated with or without WT cortactin or the T145D, T219D or T145DT219D mutant and then stabilized and visualized using fluorescent phalloidin. F-actin alone appeared as individual filaments in fluorescence microscopy (Fig. 1Fa). Addition of WT cortactin led to marked crosslinking of these filaments (Fig. 1Fb), as previously reported (5,6). However, each of the phosphomimetic mutants had a reduced actin-crosslinking capacity (Fig. 1Fc-e).
Phosphorylation of cortactin by CDK5 decreases actin bundling by the dynamin 1-cortactin complex, but does not affect binding of cortactin to dynamin 1
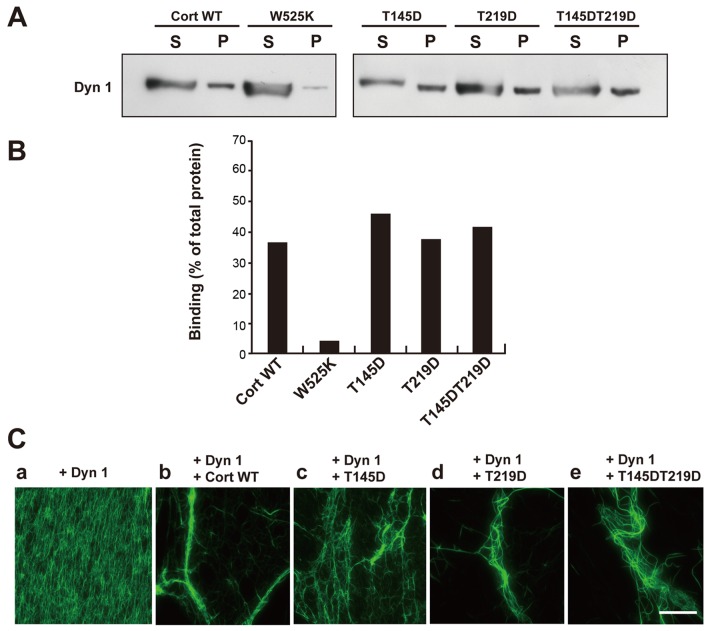
Next, the effect of cortactin phosphorylation by CDK5 on binding of cortactin to dynamin 1 was examined. Pulldown assays demonstrated that WT cortactin and the T145D, T219D and T145DT219D mutants bound to dynamin 1 comparably (Fig. 2A and B). By contrast, W525K, a mutant incapable of binding to dynamin 1 (18), exhibited little binding. Thus, phosphorylation of cortactin by CDK5 has little effect on its binding to dynamin 1.
Figure 2.
Phosphorylation of Cort by cyclin-dependent kinase 5 decreases actin bundling by the Dyn 1-Cort complex, but does not affect binding between Dyn 1 and Cort. (A) GST pulldown assay demonstrating that GST-tagged WT Cort and the T145D, T219D, and T145DT219D mutant bound to Dyn 1 comparably. The Cort Src homology 3 point mutant W525K hardly bound to Dyn 1. (B) The ratio of Dyn 1 co-precipitated with WT or mutant Cort relative to the total amount of Dyn 1. Levels were estimated by densitometry. The results were obtained in two independent experiments. (C) Dyn 1-mutant Cort complexes caused defective actin bundling. (a) The presence of Dyn 1 did not lead to any visible change of F-actin. (b) Long and thick actin bundles formed in the presence of Dyn 1 and WT Cort. Partially and loosely bundled short actin filaments were observed in the presence of Dyn 1 and the (c) T145D, (d) T219D or (e) T145DT219D mutant. Preformed F-actin (3.3 µM) was incubated with or without the indicated proteins (5 µM each; a-e). F-actin labeled with Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated phalloidin was visualized under fluorescence microscopy. Scale bar, 30 µm. Cort, cortactin; Dyn 1, dynamin 1; GST, glutathione-S-transferase; WT, wild-type; S, supernatant; P, pellet.
Formation of F-actin bundles by dynamin 1 and WT cortactin or the phosphomimetic mutants was examined visually. Addition of dynamin 1 alone to F-actin did not lead to any visible changes (Fig. 2Ca). Incubation of F-actin with dynamin 1 and WT cortactin led to formation of long and thick F-actin bundles (Fig. 2Cb). Partially bundled and short F-actin filaments were observed upon incubation of the phosphomimetic mutants and dynamin 1 with F-actin (Fig. 2Cc-e). These findings suggest that phosphorylation of the T145 and T219 residues of cortactin reduces actin bundling by the dynamin 1-cortactin complex.
Cortactin phosphorylated by CDK5 fails to form a ring-like complex with dynamin 1
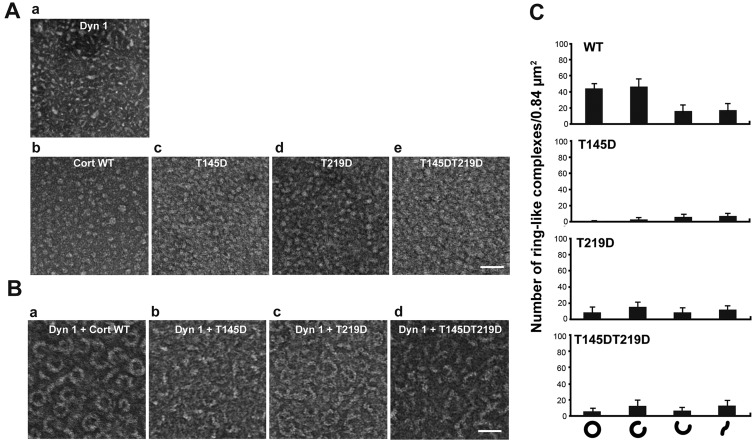
Dynamin 1 co-assembles with cortactin into a ring-like complex, the shape of which is ‘open’ or ‘closed’ depending on the guanine nucleotide conditions (5). Structural changes are required for actin bundling (5). Formation of this ring-like complex was examined by negative-staining electron microscopy. WT cortactin and the T145D, T219D, T145DT219D mutants alone had a granular shape with a diameter of 3-7 nm (Fig. 3Ab-e). Dynamin 1 alone was short and had a rod-like shape (Fig. 3Aa). Consistent with the previous report (5), WT cortactin and dynamin 1 copolymerized into ring-like complexes with an outer diameter of 34.8±3.1 nm and an inner diameter of 23.5±3.1 nm (n=30; Fig. 3Ba). Formation of ring-like complexes was markedly decreased upon incubation of dynamin 1 with each of the phosphomimetic mutants (Fig. 3B and C). These results suggest that phosphorylation of cortactin by CDK5 altered the higher order structure of the dynamin 1-cortactin complex.
Figure 3.
Phosphomimetic Cort mutants cannot form a ring-like complex with Dyn 1. (A) Electron micrographs of negatively-stained Dyn 1, WT Cort and Cort mutants. Scale bar, 50 nm. (B) Electron micrographs demonstrating that Cort phosphomimetic mutants cannot form ring-like complex with Dyn 1. Scale bar, 50 nm. (C) Morphometric analysis of the ring-like complexes formed in (B). Rings were divided into four categories according to the level to which the ring was closed. Cort, cortactin; Dyn 1, dynamin 1; WT, wild-type.
Cells expressing cortactin phosphomimetic mutants exhibit aberrant lamellipodia and short filopodia
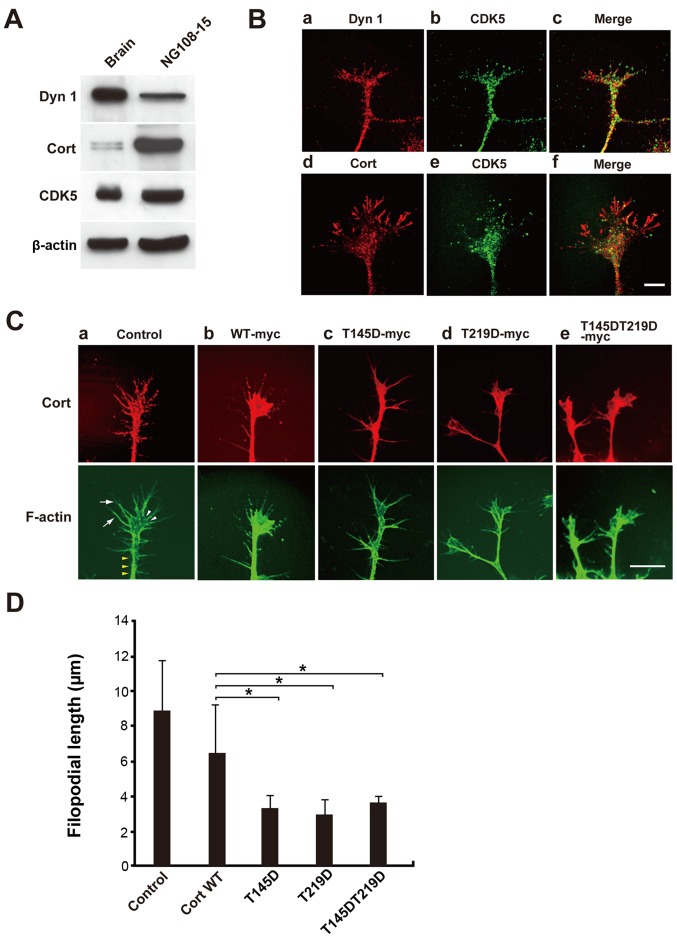
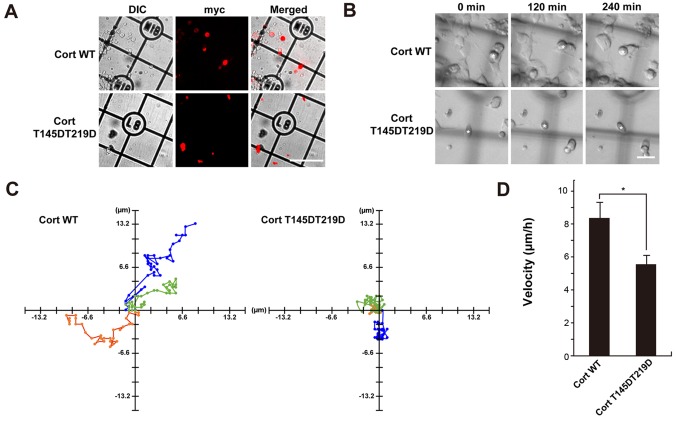
Finally, the effect of cortactin phosphorylation by CDK5 on formation of pseudopodia in NG108-15 glioma-derived cells was examined. Many actin-rich protrusions with lamellipodia and filopodia at their tips formed in NG108-15 cells (19). Dynamin 1, cortactin, and CDK5 were detected in the cell lysate by western blotting (Fig. 4A). Endogenous dynamin 1, cortactin, and CDK5 colocalized in foci along filopodia in immunofluorescence analysis (Fig. 4B). Next, NG108-15 cells were transfected with c-myc-tagged WT cortactin, T145D, T219D or T145DT219D and formation of filo-podia was examined. Filopodia were clearly observed in cells expressing c-myc-tagged WT cortactin, similar to non-transfected cells (Fig. 4Ca and b). Filopodial length was 8.9±2.9 nm in control cells and 6.5±2.8 nm in WT cortactin-expressing cells. By contrast, T145D, T219D and T145DT219D were diffusely distributed in filopodia (Fig. 4Cc-e). Expression of each phosphomimetic mutant led to deformation of lamellipodia (Fig. 4Cb-e), and filopodial length was ~50% shorter in cells expressing a phosphomimetic mutant than in cells expressing WT cortactin (Fig. 4D). The effect of phosphorylation mimetic mutant, T145DT219D on cell migration of time-lapse DIC imaging was further determined. Cells with cortactin mutant were identified by immunofluorescence microscopy following the live-imaging (Fig. 5A). Cells with T145DT219D exhibited defective migration capability compared with that of WT-cortactin-expressing cells (Fig. 5B and C). Furthermore, migration velocity of T145DT219D expressing cells was slower than that of WT-cortactin expressing cells (Fig. 5D). These results suggest that phosphorylation of cortactin by CDK5 modulates not only formation of lamellipodia and filopodia but also cell migration.
Figure 4.
NG108-15 cells expressing phosphomimetic Cort mutants exhibit aberrant lamellipodia and short filopodia. (A) Expression of Dyn 1, Cort and CDK5 in NG108-15 cell lysates was confirmed by western blotting. In total, 10 µg of mouse brain homogenate or 20 µg of NG108-15 cell lysate was loaded per lane. (B) Immunofluorescence analysis showing that endogenous Dyn 1, Cort and CDK5 partially colocalized in lamellipodia and filopodia of NG108-15 cells. Scale bar, 10 µm. (C) NG108-15 cells were not transfected (a; control) or transfected with c-myc-tagged (b) WT Cort or the (c) T145D, (d) T219D or (e) T145DT219D mutant, fixed, and stained with a monoclonal anti-c-myc antibody (red). F-actin was stained with Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated phalloidin (green). (Ca) Typical cellular protrusion (yellow arrow heads), lamellipodia (white arrow heads) and filopodia (white arrows) are presented. Filipodia were markedly shorter in T145D-, T219D- and T145DT219D-expressing cells than in WT Cort-expressing cells. Scale bar, 10 µm. (D) Morphometric analysis of filopodial length in (C). Data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean of 33-60 filopodia per experimental condition (n=3 independent experiments; *P<0.05). Cort, cortactin; Dyn 1, dynamin 1; CDK5, cyclin-dependent kinase 5; WT, wild-type.
Figure 5.
Expression of T145DT219D Cort mutant decreases migration in NG108-15 cells. (A) Identification of myc-tagged Cort expressing cells. Cells were cultured on glass base dish with grid at 37°C under 5% CO2 during the experiment. Following the DIC-live imaging, cells were identified by the immuno-staining with anti-myc antibodies. Scale bar, 150 µm. (B) Time lapse DIC image of WT- or T145DT219D-Cort expressing NG108-15 cells. Asterisks indicate cells expressing exogenous Cort. Scale bar, 30 µm. (C) Migration paths of cells with WT (left)- or T145DT219D (right)-Cort were traced for 2 h. Three representative, independent cells (green, orange or blue corresponds with each cell) analyzed are presented. (D) Migration velocity of WT- or T145DT219D-Cort expressing cells. Data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean of migration length per 1 h calculated from 5 cells. *P<0.05. Cort, cortactin; DIC, differential interference contrast microscopy; WT, wild-type.
Discussion
Cortactin and dynamin have been independently implicated in migration, invasion and metastasis of cancer cells (3,20). It was recently reported that cortactin and dynamin form a ring-like complex that bundles and stabilizes actin filaments (5,6). The actin bundling is essential for formation of actin-rich protrusions in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells (5) and migration of H1299 human non-small cell lung carcinoma cells (6). However, the regulatory mechanism of actin bundling is largely unknown. Dynamin 1 is a substrate of CDK5 (16,17). Furthermore, recent reports implicated CDK5 in cancer progression and aggressiveness (12). Therefore, the potential regulation of cortactin function by CDK5 was investigated in vitro and in vivo.
It was demonstrated that CDK5 directly phosphorylated cortactin in vitro. In addition, MALDI-MS analysis identified T145 and T219 as the phosphorylation sites of cortactin. To investigate the effects of this phosphorylation, three phosphomimetic mutants of cortactin (T145D, T219D and T145DT219D) were prepared by substituting T145 and/or T219 with aspartate. These mutants exhibited reduced binding to F-actin. F-actin bundles formed by the dynamin 1-mutant cortactin complex dissociated more or were looser than those formed by the dynamin 1-WT cortactin complex. Although the T145D, T219D, and T145DT219D mutants bound to dynamin 1, they could not form a ring-like complex. Filopodia were shorter and lamellipodia were smaller in rat glioma-derived NG108-15 cells expressing each phosphomimetic mutant than in those expressing WT cortactin (Fig. 4). Furthermore, T145DT219D mutant expressing cells exhibited significant decreased cell migration compared with that of WT expressing cells (Fig. 5). These results strongly suggest that phosphorylation of cortactin by CDK5 regulates formation of pseudopodia by modulating actin bundle formation in vivo.
CDK5 has been investigated in terminally differentiated cells, such as neurons and neuroendocrine cells (10,11). In synapses, phosphorylation of dynamin 1 by CDK5 is crucial for regulation of endocytosis, and dynamin 1 is phosphorylated at S774 and S778 in rats and sheep (16) as well as T780 in bovine (17). CDK5 also phosphorylates endophilin 1 (21) and amphiphysin 1 (17,22), a physiological binding partner of dynamin 1. Co-phosphorylation of dynamin 1 and amphiphysin 1 by CDK5 leads to defective formation of the dynamin 1-amphiphysin 1 complex and strongly inhibits endocytosis (17). In the present study, phosphorylation of cortactin by CDK5 not only decreased the interaction between cortactin and F-actin, but also disrupted formation of the ring-like dynamin 1-cortactin complex. These two effects may regulate actin bundling. Co-phosphorylation of dynamin 1 and its binding partner likely controls endocytic activity in vivo. Actin regulation by co-phosphorylation of dynamin 1 and cortactin would be possible. The effect of co-phosphorylation of dynamin 1 and cortactin on complex formation and actin bundling should be investigated in detail in the future.
Brain-derived cancer cells, including glioma-derived cells, and tissues highly express CDK5, and this kinase is implicated in proliferation (23) and invasion (24) of cancer cells, and development and progression of tumors (25). NG108-15 glioma-derived cells expressed dynamin 1, cortactin, and CDK5, and these proteins colocalized in filopodia and lamellipodia.
The present study demonstrates that CDK5 phosphorylates two threonine residues (T145 and T219) of cortactin. Martin et al (26) previously exhaustively examined cortactin phosphorylation sites in human embryonic kidney 293 cells by mass spectrometry. However, they did not identify T145 and T219 as phosphorylation sites. Phosphorylation of cortactin by CDK5 might differ between brain-derived and non-neuronal cells as expression of this kinase is lower in the latter cells than in the former cells.
In conclusion, cortactin was identified as a novel substrate of CDK5. Phosphorylation of cortactin by CDK5 decreased the actin-bundling activity of the dynamin 1-cortactin complex and consequently reduced pseudopodal formation, which is required for migration, invasion and metastasis of cancer cells. Most molecular targets of current anticancer drugs are involved in cell division or DNA replication. Therefore, targeting of dynamin-dependent actin dynamics via modulation of CDK5 activity may be a more effective anticancer therapy, especially for brain-derived tumors. Further studies are required to determine the precise mechanism(s) by which intracellular phosphorylation modulates actin bundling by the dynamin 1-cortactin complex.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dai Shimizu (Okayama University, Okayama, Japan) and Natsuki Wakita (Okayama University, Okayama, Japan) for technical assistance.
Funding
The present study was supported in part by grants from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports, and Culture of Japan (grant nos. 16K10756 to TA and 17K08808 to HY).
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Authors’ contributions
HY and KTa designed research and wrote the paper. HY, TA, YM, EO and TT performed mutant protein construction, protein purification and actin bundling experiments. TA and YM performed electron microscopy. EO, TML, KS and KF performed immunofluorescent microscopy, cell migration assay and analyzed data. FYW and KTo identified phosphorylation sites by MALDI-MS. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All procedures and animal protocols were approved by the Committee on the Ethics of Animal Experimentation at Okayama University (Okayama, Japan; approval no. OKU-2015052 and OKU-2018109).
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- 1.Arjonen A, Kaukonen R, Ivaska J. Filopodia and adhesion in cancer cell motility. Cell Adhes Migr. 2011;5:421–430. doi: 10.4161/cam.5.5.17723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ridley AJ. Life at the leading edge. Cell. 2011;145:1012–1022. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.MacGrath SM, Koleske AJ. Cortactin in cell migration and cancer at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2012;125:1621–1626. doi: 10.1242/jcs.093781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.McNiven MA, Kim L, Krueger EW, Orth JD, Cao H, Wong TW. Regulated interactions between dynamin and the actin-binding protein cortactin modulate cell shape. J Cell Biol. 2000;151:187–198. doi: 10.1083/jcb.151.1.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Yamada H, Abe T, Satoh A, Okazaki N, Tago S, Kobayashi K, Yoshida Y, Oda Y, Watanabe M, Tomizawa K, et al. Stabilization of actin bundles by a dynamin 1/cortactin ring complex is necessary for growth cone filopodia. J Neurosci. 2013;33:4514–4526. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2762-12.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yamada H, Takeda T, Michiue H, Abe T, Takei K. Actin bundling by dynamin 2 and cortactin is implicated in cell migration by stabilizing filopodia in human non-small cell lung carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 2016;49:877–886. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Weaver AM, Heuser JE, Karginov AV, Lee WL, Parsons JT, Cooper JA. Interaction of cortactin and N-WASp with Arp2/3 complex. Curr Biol. 2002;12:1270–1278. doi: 10.1016/S0960-9822(02)01035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kinley AW, Weed SA, Weaver AM, Karginov AV, Bissonette E, Cooper JA, Parsons JT. Cortactin interacts with WIP in regulating Arp2/3 activation and membrane protrusion. Curr Biol. 2003;13:384–393. doi: 10.1016/S0960-9822(03)00107-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Contreras-Vallejos E, Utreras E, Gonzalez-Billault C. Going out of the brain: Non-nervous system physiological and pathological functions of Cdk5. Cell Signal. 2012;24:44–52. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.08.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Nikolic M, Dudek H, Kwon YT, Ramos YF, Tsai LH. The cdk5/p35 kinase is essential for neurite outgrowth during neuronal differentiation. Genes Dev. 1996;10:816–825. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.7.816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Liu KC, Leuckx G, Sakano D, Seymour PA, Mattsson CL, Rautio L, Staels W, Verdonck Y, Serup P, Kume S, et al. Inhibition of Cdk5 Promotes β-Cell Differentiation From Ductal Progenitors. Diabetes. 2018;67:58–70. doi: 10.2337/db16-1587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Pozo K, Bibb JA. The emerging role of Cdk5 in cancer. Trends Cancer. 2016;2:606–618. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2016.09.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Quintavalle M, Elia L, Price JH, Heynen-Genel S, Courtneidge SA. A cell-based high-content screening assay reveals activators and inhibitors of cancer cell invasion. Sci Signal. 2011;4:ra49. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2002032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Feldmann G, Mishra A, Hong SM, Bisht S, Strock CJ, Ball DW, Goggins M, Maitra A, Nelkin BD. Inhibiting the cyclin-dependent kinase CDK5 blocks pancreatic cancer formation and progression through the suppression of Ras-Ral signaling. Cancer Res. 2010;70:4460–4469. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-1107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yamada H, Kikuchi T, Masumoto T, Wei FY, Abe T, Takeda T, Nishiki T, Tomizawa K, Watanabe M, Matsui H, et al. Possible role of cortactin phosphorylation by protein kinase Cα in actin-bundle formation at growth cone. Biol Cell. 2015;107:319–330. doi: 10.1111/boc.201500032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tan TC, Valova VA, Malladi CS, Graham ME, Berven LA, Jupp OJ, Hansra G, McClure SJ, Sarcevic B, Boadle RA, et al. Cdk5 is essential for synaptic vesicle endocytosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2003;5:701–710. doi: 10.1038/ncb1020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tomizawa K, Sunada S, Lu YF, Oda Y, Kinuta M, Ohshima T, Saito T, Wei FY, Matsushita M, Li ST, et al. Cophosphorylation of amphiphysin I and dynamin I by Cdk5 regulates clathrin-mediated endocytosis of synaptic vesicles. J Cell Biol. 2003;163:813–824. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200308110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Schafer DA, Weed SA, Binns D, Karginov AV, Parsons JT, Cooper JA. Dynamin2 and cortactin regulate actin assembly and filament organization. Curr Biol. 2002;12:1852–1857. doi: 10.1016/S0960-9822(02)01228-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Nozumi M, Nakagawa H, Miki H, Takenawa T, Miyamoto S. Differential localization of WAVE isoforms in filopodia and lamellipodia of the neuronal growth cone. J Cell Sci. 2003;116:239–246. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Jeannot P, Besson A. Cortactin function in invadopodia. Small GTPases. 2017 Dec 31; doi: 10.1080/21541248.2017.1405773. Epub ahead of print. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wong AS, Lee RH, Cheung AY, Yeung PK, Chung SK, Cheung ZH, Ip NY. Cdk5-mediated phosphorylation of endophilin B1 is required for induced autophagy in models of Parkinson’s disease. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13:568–579. doi: 10.1038/ncb2217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Liang S, Wei FY, Wu YM, Tanabe K, Abe T, Oda Y, Yoshida Y, Yamada H, Matsui H, Tomizawa K, et al. Major Cdk5-dependent phosphorylation sites of amphiphysin 1 are implicated in the regulation of the membrane binding and endocytosis. J Neurochem. 2007;102:1466–1476. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Moutal A, Villa LS, Yeon SK, Householder KT, Park KD, Sirianni RW, Khanna R. CRMP2 Phosphorylation Drives Glioblastoma Cell Proliferation. Mol Neurobiol. 2018;55:4403–4416. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0653-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Liu R, Tian B, Gearing M, Hunter S, Ye K, Mao Z. Cdk5-mediated regulation of the PIKE-A-Akt pathway and glioblastoma cell invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:7570–7575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0712306105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Yushan R, Wenjie C, Suning H, Yiwu D, Tengfei Z, Madushi WM, Feifei L, Changwen Z, Xin W, Roodrajeetsing G, et al. Insights into the clinical value of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 in glioma: A retrospective study. World J Surg Oncol. 2015;13:223. doi: 10.1186/s12957-015-0629-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Martin KH, Jeffery ED, Grigera PR, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Parsons JT. Cortactin phosphorylation sites mapped by mass spectrometry. J Cell Sci. 2006;119:2851–2853. doi: 10.1242/jcs.03034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.