Abstract
Background
In 621 consecutive prostate cancer patients, the frequency of urinary tract infections (UTI) and marker loss was evaluated. They prophylactically received a single dose of non-broad-spectrum antibiotics and transrectal implantation of three thin needle fiducial markers, Gold Anchor ™ (GA).
Methods
The occurrence of UTIs, sepsis, hospitalization due to infection, and marker loss after implantation was assessed from the medical records containing notes from physicians and nurses from the day of implantation to the end of 29 fractions.
Results
UTIs occurred in two (0.3%) of the 621 patients. Neither sepsis nor hospitalization was noted. Loss/drop-out of three markers was noted among 1,863 markers implanted.
Conclusion
The use of thin needles for the implantation of fiducials appears to reduce the rate of infection despite the use of a single dose of non-broad-spectrum antibiotics as prophylaxis. The marker construct appears to provide stability in the tissues.
Keywords: prostate cancer, radiation therapy, infection, urinary tract infections (uti), complications, fiducial marker, radiation treatment, antibiotic prophylaxis, prostate sbrt, migration
Introduction
To minimize the complications associated with the implantation of fiducial markers for image-guided radiotherapy, a fine needle marker called Gold Anchor ™ (GA) for kilovoltage (kV) imaging was developed by Dr. I. Naslund at Radiumhemmet, Department of Oncology, Karolinska University Hospital, Stockholm. This idea came from decades of good experience of fine needle aspiration cytology with 25-gauge (G) needles, developed inhouse by Dr. Sixten Franzén in the 1950s [1]. This study evaluates the number of infections after the implantation of the GA markers in 621 prostate cancer patients receiving radiation therapy.
Materials and methods
We retrospectively studied the records of 621 consecutive prostate cancer patients who got GA implanted per rectum solely by one of the uro-oncologists (E. Castellanos) from January 2007 to January 2016 at our institution. Urinary tract infections (UTI), sepsis, and hospitalization, as well as notations of marker migration or loss, were analyzed.
Patients received neoadjuvant hormonal treatment for three months before external curative radiation treatment with 72.5 Gy in 29 fractions. The mean age of the patients was 72 years (range: 46-85 years).
Patients were told to use a Microlax® enema in the morning of the day of the procedure. A peroral single dose of Bactrim® Forte (sulfamethoxazole 1,600 mg and trimethoprim 320 mg) was given one hour before implantation to all patients. No pre-procedural rectal swabs, stool cultures, or preop urinary culture were obtained to guide the selection of antibiotics.
The GA markers implanted have a diameter of 0.28 or 0.40 mm, both available in 10- or 20-mm length. The markers are of pure gold with 0.5% pure iron in an alloy to enhance magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) visibility. They are preloaded in 25G (0.50 mm/0.020” outer diameter) or 22G (0.70 mm/0.028”) fine needles. This study employed 200-mm-long 22G needles, loaded with a 0.28 × 20-mm marker delivered in a single blister pack with the product code GA200-20. When the marker is pushed out of the needle with the stylet, it folds itself in the tissue into a ball shape. The diameter of the ball is greater than the diameter of the needle so that the expanded marker cannot move back into the needle tract when the needle is retracted.
In a lithotomy position, three GA markers per patient were implanted transrectally in prostate, placed in the right lobe in the base and apex and in the other lobe in the midgland to avoid marker overlapping during imaging for patient setup. The 22G marker needle has a diameter similar to that of a local anesthesia needle. Injection of the anesthetic would be more painful than implantation of the fiducials itself; therefore, no anesthesia was used. Consequently, only three thin punctures through the rectal wall were needed per patient. This procedure typically takes only a few minutes. Computed tomography (CT) and MRI scans for the treatment planning were typically obtained the same day or within two days after implantation. Patients were informed to report fever or any local side effects after implantation.
Orthogonal kV images were acquired at each fraction for positioning, and the patients received a daily follow-up of side-effects by the nurses and/or the uro-oncologists of the RT section. Data were stored in the Information Networks for Cancer (INCA) register, a Swedish IT platform to facilitate the follow-up and evaluation of the health outcomes and quality. Facts about UTI, sepsis, and hospitalization after implantation of GA have been derived from our Clinical Electronic Medical Records and the INCA register.
The criteria for UTI were an oral temperature above 38.0 °C and a positive urine culture. The criteria for sepsis were defined as a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection according to the Sepsis-3 definitions [2].
Results
All the 621 patients were followed up for side effects from the day of implantation to the end of 29 fractions. Two of them, 0.3%, had UTI.
In 2012, a 67-year-old man had UTI symptoms on the third day after implantation and was treated with ciprofloxacin 500 mg × 2 for one week without improvement. The urine culture showed resistant E. coli to ciprofloxacin, and he was given Bactrim® Forte 1 × 2 for seven days. This patient had a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level of 6.2, stadium T1c, Gleason score 3+3, and a prostate volume of 45 cm3.
In 2014, a 71-year-old man had UTI. He was successfully treated with ciprofloxacin 500 mg × 2 for one week. This patient had a PSA level of 4.5, stadium T1c, Gleason score 3+4, and a prostate volume of 24 cm3.
There was no sepsis and no hospitalization due to implantation. No loss of the 1,863 GA markers had been noted during the daily setup, except for three patients (0.16%) in which one of the three markers in each patient was implanted very close to a transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) cavity.
Discussion
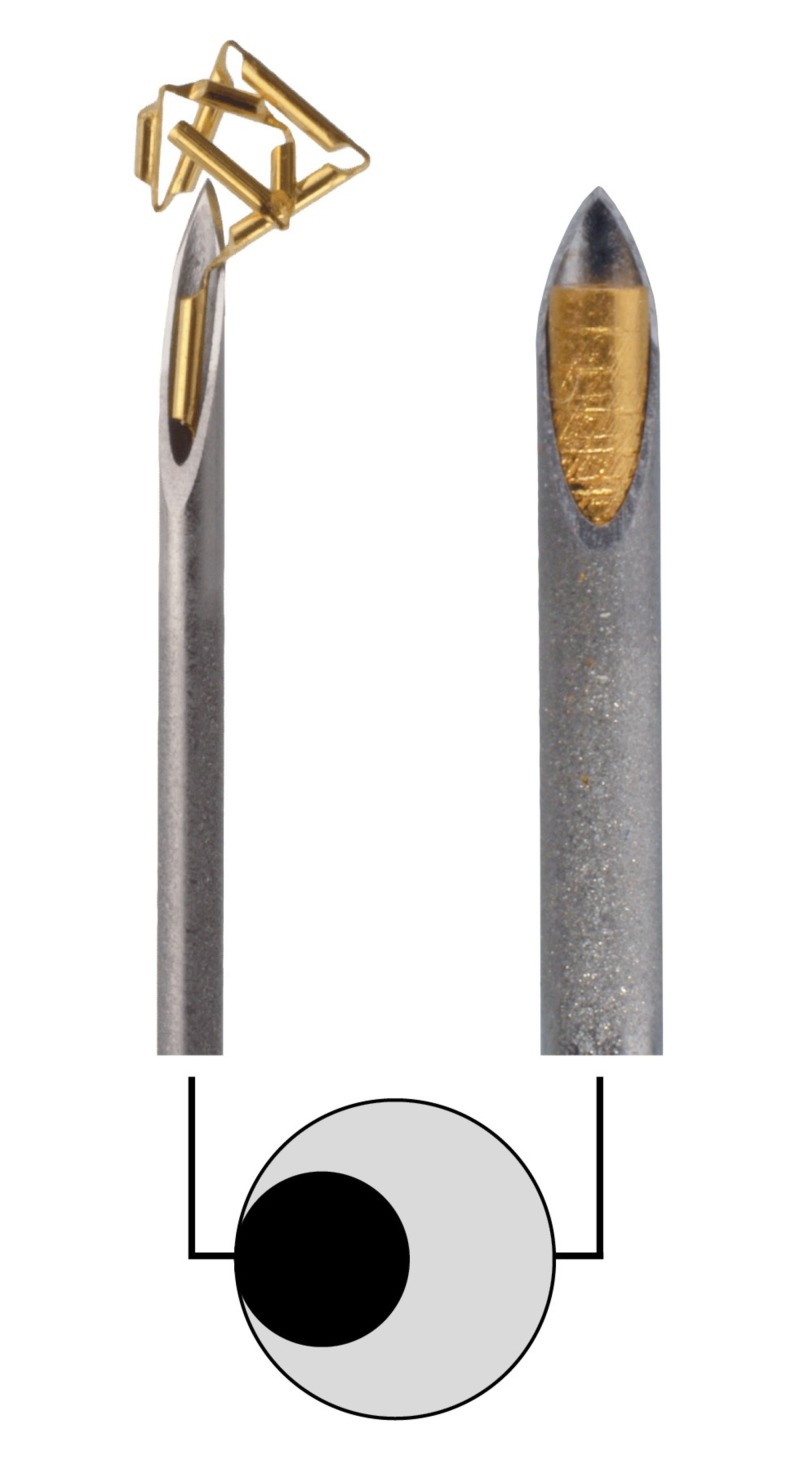
Traditionally, the fiducial markers had to be large enough to be visible on a megavoltage (MV) radiograph film or MV portal imaging devices. Therefore, it was a need to use 17-18G needles (1.47-1.25 mm/0.058-0.050” outer diameter) for the placement of fiducial markers. Despite improvements in the imaging technique, thick needles are still used for the implantation of large fiducial markers. The same type of thick needles, 17-18 G, are also used for prostate biopsies. Those needles have a three to four times larger cross-sectional area than the thin 22G needles used for GA in prostate (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Comparison in diameter between Gold Anchor™ needle to the left and an 18G traditional needle for fiducial markers. The cross-sectional area is three to four times larger for 18G and 17G needles compared to the 22G thin needle of 0.7 mm for Gold Anchor.
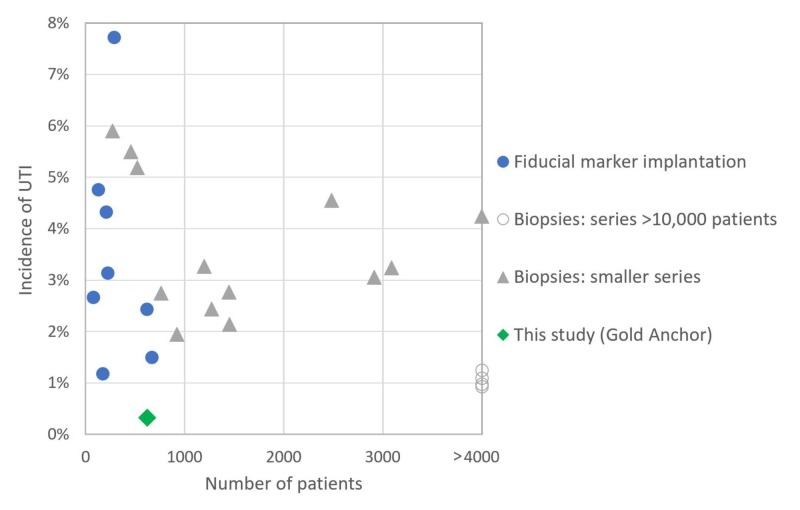
Figure 2 shows significant heterogeneity of the infection rates reported after transrectal biopsies or fiducial marker implantations [3-26].
Figure 2. Incidence of UTI after transrectal biopsy or fiducial marker implantation.
Table 1 shows the infection rates reported among patients after transrectal fiducial marker implantation [3-10]. Table 2 shows the infection rates after transrectal prostate biopsies in a large series [10-13], and Table 3 shows the same in a small series [14-26]. The studies were conducted in various ways, in different time periods and with different antibiotic prophylaxis, without targeted antibiotics guided by rectal swab. This prevents a direct comparison of the results but gives an estimate of the infection rates.
Table 1. Incidence of UTIs after transrectal fiducial marker implantation.
UTI: urinary tract infection
| Reference | Patients | UTI | UTI % |
| 3 | 126 | 6 | 4.8% |
| 4 | 223 | 7 | 3.1% |
| 5 | 615 | 15 | 2.4% |
| 6 | 75 | 2 | 2.7% |
| 7 | 169 | 2 | 1.2% |
| 8 | 285 | 22 | 7.7% |
| 9 | 208 | 9 | 4.3% |
| 10 | 666 | 10 | 1.5% |
| Sum | 2,367 | 73 | 3.1% |
Table 2. Incidence of UTIs after transrectal prostate biopsies in a large series.
UTI: urinary tract infection
| Reference | Patients | UTI | UTI % |
| 10 | 10,938 | 137 | 1.3% |
| 11 | 212,065 | 2,333 | 1.1% |
| 12 | 25,355 | 249 | 1.0% |
| 13 | 59,469 | 553 | 0.9% |
| Sum | 307,827 | 3,272 | 1.1% |
Table 3. Incidence of UTIs after transrectal biopsies in a smaller series.
UTI: urinary tract infection
| Reference | Patients | UTI | UTI % |
| 14 | 1,273 | 31 | 2.4% |
| 15 | 923 | 18 | 2.0% |
| 16 | 1,446 | 40 | 2.8% |
| 17 | 1,450 | 31 | 2.1% |
| 18 | 521 | 27 | 5.2% |
| 19 | 1.195 | 39 | 3.3% |
| 20 | 764 | 21 | 2.7% |
| 21 | 455 | 25 | 5.5% |
| 22 | 3,087 | 100 | 3.2% |
| 23 | 2,913 | 89 | 3.1% |
| 24 | 2,484 | 113 | 4.5% |
| 25 | 271 | 16 | 5.9% |
| 26 | 9,241 | 392 | 4.2% |
| Sum | 26,023 | 942 | 3.6% |
A reasonable assessment of these studies is that more than 2% of the patients developed UTI after 17-18G needle procedures. Although there are fewer rectal wall penetrations during marker implantation than during biopsy, the rates of UTIs reported seem to be similar to the rates after biopsies. One possible explanation is the development of bacterial resistance related to the use of the same antibiotics as for the prostate biopsy.
E. coli infection after transrectal biopsy of the prostate has become significantly more common since 2000 due to a dramatic increase in fluoroquinolone-resistant E. coli. [13]. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that new antibiotics are reserved for serious infections and not used for prophylaxis. The use of ciprofloxacin, belonging to the WATCH group, used to treat cystitis (a type of UTI), should be dramatically reduced to avoid further development of resistance. Furthermore, the third group, RESERVE, includes antibiotics such as colistin and some cephalosporins that should be considered as last-resort options and used only in the most severe circumstances when all other alternatives have failed, such as for life-threatening infections due to multidrug-resistant bacteria [27]. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently advised that in the treatment of uncomplicated UTIs, fluoroquinolones should be reserved for those who lack other options due to other complications besides development of resistance [28].
Conclusions
Infections after prostate biopsy and fiducial implantations with traditional 17G-18G needles are associated with the risk of UTI. In this study with 621 patients, we found a low UTI incidence after the transrectal implantation of Gold Anchor™ fine needle markers, despite the use of a non-broad-spectrum antibiotic prophylaxis. It is important to have a holistic view of all the inconvenient risks of healthcare efforts versus the benefits. Every part of the process is good to optimize. The use of small-diameter needles for the implantation of fiducial markers seems to reduce the rate of infections.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Cancer Society - Radiumhemmet Research Funds in Stockholm.
The content published in Cureus is the result of clinical experience and/or research by independent individuals or organizations. Cureus is not responsible for the scientific accuracy or reliability of data or conclusions published herein. All content published within Cureus is intended only for educational, research and reference purposes. Additionally, articles published within Cureus should not be deemed a suitable substitute for the advice of a qualified health care professional. Do not disregard or avoid professional medical advice due to content published within Cureus.
Funding Statement
This work was supported by grants from Cancer Society in Stockholm - Radiumhemmet research funds.
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Human Ethics
Consent was obtained by all participants in this study. Regional Ethical Review Board Stockholm issued approval 2006/620-3. Approved: Outcome studies on men who receive curative radiation therapy for prostate cancer - survival and side effects.
Animal Ethics
Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue.
References
- 1.Sixten Franzen, MD, PhD, Honorary Professor, 1919-2008. Waisman J, Skoog L, Tani E. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1002/cncr.23795. Cancer. 2008;5:285–286. doi: 10.1002/cncr.23795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3) Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymoour CW, et al. JAMA. 2016;8:801–810. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Insertion of intraprostate gold fiducial markers in prostate cancer treatment. Escudero JUJ, Peidro JP, de Campos MR, et al. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/268398789 Int J Nephrol Urol. 2010;2:265–272. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Patient-reported complications from fiducial marker implantation for prostate image-guided radiotherapy. Gill S, Li J, Thomas J, et al. Br J Radiol. 2012;85:1011–1017. doi: 10.1259/bjr/68127917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bacterial urinary tract infection after fiducial marker placement or prostate biopsy. Mendenhall WM, Costa JA, Williams CR, et al. Int J Particle Ther. 2014:745–758. doi: 10.14338/IJPT-16-00007.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Single-center experience in prostate fiducial marker placement: technique and midterm follow-up. Kably I, Bordegaray M, Shah K, et al. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2014;25:1125–1132. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2014.03.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fiducial marker implantation in prostate radiation therapy: complication rates and technique. Fawas ZS, Yassa M, Nguyen DH, Vavassis P. Cancer Radiother. 2014;18:736–739. doi: 10.1016/j.canrad.2014.07.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Infections after fiducial marker implantation for prostate radiotherapy: are we underestimating the risks? Loh J, Baker K, Sridharan S, et al. Radiat Oncol. 2015;10:1–5. doi: 10.1186/s13014-015-0347-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Infections after fiducial markers implantation for prostate radiation therapy, optimizing the antimicrobial prophylaxis. Clavel S, Gauthier-Pare AS, Duplan D, Fanizzi J, Rivest N, Haeck S. Int J Rad Onc Biol Phys. 2016:2663. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bacterial urinary tract infection after transrectal placement of fiducial markers prior to proton radiotherapy for prostate cancer. Mendenhall WM, Glassman G, Morris CG, et al. Int J Particle Ther. 2016:21–26. doi: 10.14338/IJPT-16-00007.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Complication rates of ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy: a nation-wide survey in Japan. Kakehi Y, Seiji Naito, Japanese Urological Association. Int J Urol. 2008;15:319–321. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2008.02048.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Infectious complications following transrectal ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy: new challenges in the era of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli. Williamson DA, Barrett LK, Rogers BA, Freeman JT, Hadway P, Paterson DL. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;57:267–274. doi: 10.1093/cid/cit193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fluoroquinolone-resistant Escherichia coli infections after transrectal biopsy of the prostate in the veterans affairs healthcare system. Saade EA, Suwantarat N, Zabarsky TF, Wilson B, Donskey CJ. Pathog Immun. 2016;1:243–257. doi: 10.20411/pai.v1i2.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.The incidence of fluoroquinolone resistant infections after prostate biopsy—are fluoroquinolones still effective prophylaxis? Feliciano J, Teper E, Ferrandino M, Macchia RJ, Glank W, Grunberger I, Colon I. J Urol. 2008;179:952–955. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2007.10.071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Risk factors for acute prostatitis after transrectal biopsy of the prostate. Kim SJ, Kim SII, Ahn HS, et al. Korean J Urol. 2010;51:426–430. doi: 10.4111/kju.2010.51.6.426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Emergence of fluoroquinolone-resistant Escherichia coli as cause of postprostate biopsy infection: implications for prophylaxis and treatment. Osama MZ, Vargo EH, Rajan R, Berglund R, Gordon S, Jones JS. Urology. 2011;5:1035–1041. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2010.12.067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Increasing risk of infectious complications after transrectal ultrasound-guided prostate biopsies: time to reassess antimicrobial prophylaxis? Carignan A, Roussy J-F, Lapointe V, Valiquette Louis, Sabbagh R, Pépin J. Eur Urol. 2012;62:453–459. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2012.04.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Infective complications after prostate biopsy: outcome of the global prevalence study of infections in urology (GPIU) 2010 and 2011, a prospective multinational multicentre prostate biopsy study. Wagenlehner FM, Van Oostrum E, Tenke P, et al. Eur Urol. 2013;63:521–527. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2012.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Febrile urinary tract infection after prostate biopsy and quinolone resistance. Choi JW, Kim THK, Chang KIH, et al. Korean J Urol. 2014;55:660–664. doi: 10.4111/kju.2014.55.10.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Clinical and microbiological determinants of infection after transrectal prostate biopsy. Liss MA, Johnson JR, Porter SB, et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2015;60:979–987. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciu1129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Comparative effectiveness of single versus combination antibiotic prophylaxis for infections after transrectal prostate biopsy. Marino K, Parlee A, Orlando R, Lerner L, Strymish J, Gupta K. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59:7273–7275. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01457-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Oral antibiotics in trans‑rectal prostate biopsy and its efficacy to reduce infectious complications: systematic review. Yaghi MD, Kehinde EO. Urol Ann. 2015;4:417–427. doi: 10.4103/0974-7796.164860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Prevalence, risk factors, and clinical relevance of fluoroquinolone-resistant organisms in rectal cultures: should we target antibiotic prophylaxis prior to prostate biopsy? Van Besien J, Uvin P, Van den Abeele AM, Merckx L. Adv Urol. 2016:1–7. doi: 10.1155/2016/5392107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.The role of targeted prophylactic antimicrobial therapy before transrectal ultrasonography-guided prostate biopsy in reducing infection rates: a systematic review. Cussans A, Somani BK, Basarab A, Dudderidge TJ. BJU Int. 2016:725–731. doi: 10.1111/bju.13402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Optimizing prophylactic antibiotic regimen in patients admitted for transrectal ultrasound-guided prostate biopsies: a prospective randomized study. Fahmy A, Rhashad H, Hohi M, Elabbadie A, Kotb A. Prostate Int. 2016;4:113–117. doi: 10.1016/j.prnil.2016.06.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Infectious complications and hospital admission after prostate biopsy in a European randomized trial. Loeb S, van den Heuvel S, Zhu X, Bangma CH, Schröder FH, Roobol MJ. Eur Urol. 2012;6:1110–1114. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2011.12.058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.WHO: The selection and use of essential medicines 2017, 27-31 March. [Oct;2018 ];http://www.who.int/medicines/publications/essentialmedicines/EML_2017_ExecutiveSummary.pdf 2017
- 28.FDA updates warnings for fluoroquinolone antibiotics on risks of mental health and low blood sugar adverse reactions. [Oct;2018 ];https://www.fda.gov/newsevents/newsroom/pressannouncements/ucm612995.htm 2018