Abstract
Gammadelta T (γδ-T) cells are strong candidates for adoptive immunotherapy in oncology due to their cytotoxicity, ease of expansion, and favorable safety profile. The development of γδ-T cell therapies would benefit from non-invasive cell-tracking methods and increased targeting to tumor sites. Here we report the use of [89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4 to track Vγ9Vδ2 T cells in vivo by positron emission tomography (PET). In vitro, we showed that 89Zr-labeled Vγ9Vδ2 T cells retained their viability, proliferative capacity, and anti-cancer cytotoxicity with minimal DNA damage for amounts of 89Zr ≤20 mBq/cell. Using a mouse xenograft model of human breast cancer, 89Zr-labeled γδ-T cells were tracked by PET imaging over 1 week. To increase tumor antigen expression, the mice were pre-treated with PEGylated liposomal alendronate. Liposomal alendronate, but not placebo liposomes or non-liposomal alendronate, significantly increased the 89Zr signal in the tumors, suggesting increased homing of γδ-T cells to the tumors. γδ-T cell trafficking to tumors occurred within 48 hr of administration. The presence of γδ-T cells in tumors, liver, and spleen was confirmed by histology. Our results demonstrate the suitability of [89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4 as a cell-labeling agent for therapeutic T cells and the potential benefits of liposomal bisphosphonate treatment before γδ-T cell administration.
Keywords: cancer immunotherapy, cell immunotherapy, liposome, PET, cell tracking, bisphosphonate, zirconium-89, nanomedicine
Graphical Abstract
Man et al. demonstrate that [89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4 allows in vivo PET imaging of therapeutic γδ-T cells over 1 week. Furthermore, the trafficking of γδ-T cells to the tumor is increased by treatment with a liposomal aminobisphosphonate drug. This radiotracer is potentially translatable for clinical trials of therapeutic T cells.
Introduction
Adoptive transfer of therapeutic T cells is a growing field in immuno-oncology, with spectacular clinical results against melanoma and hematological cancers.1, 2, 3 Gammadelta-T (γδ-T) cell therapy is one type of T cell therapy being explored, with recent data showing intra-tumoral γδ-T cells are the single most favorable prognostic immune cell infiltrate.4 γδ-T cells perform roles belonging to both adaptive and innate immunity, playing a significant role in anti-infectious and anti-tumor immune surveillance.5 Activated γδ-T cells are highly cytotoxic, enhance the function of other immune cells, and act as antigen-presenting cells.6 In humans, the Vγ9Vδ2 subtype of γδ-T cells represents 1%–5% of circulating CD3+ T cells.6 Their potent cytotoxicity and high proliferative capacity have made them candidates of choice for cancer immunotherapy.7
The unique activation of Vγ9Vδ2 cells by phosphoantigens such as isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP)8 allows them to discriminate between normal and metabolically disordered cells based on IPP expression levels.9 The activation and targeting of γδ-T cells to tumor tissue could, therefore, be improved by selectively increasing the presentation of phosphoantigens in cancer cells, for example, by using liposome- or nanocarrier-based formulations of aminobisphosphonate drugs (NBPs).10 NBPs (e.g., pamidronate, alendronate, and zoledronate),11 which increase the expression of IPP in target cells by inhibiting farnesyl diphosphate synthase, are hydrophilic molecules that accumulate in bone, but not in other tissues, and are rapidly cleared from the circulation. Encapsulating alendronate in liposomes has been shown to increase the therapeutic efficacy of γδ-T cells in preclinical models.12, 13
Clinical studies of γδ-T cell immunotherapy have shown a good safety profile and efficacy comparable to second-line anticancer therapies, but they have also highlighted the need for improvements.14, 15 Unknown aspects of adoptive γδ-T cell therapy include their in vivo distribution and kinetics of arrival at the tumor site. Whole-body imaging is highly useful in this context by enabling in vivo tracking of administered cells. Many techniques exist for non-invasive cell tracking;16, 17, 18 however, only nuclear imaging, and particularly positron emission tomography (PET), provides sensitive and quantitative, whole-body information with adequate spatiotemporal resolution. Hence, methods to radiolabel and track therapeutic cells using positron-emitting radionuclides are likely to become important tools for cell immunotherapy.19
PET tracking of T cells has been performed with radiolabeled antibodies, antibody fragments, or lipophilic small molecules20, 21 and by reporter-gene imaging.22 When genetic engineering is not required, e.g., for γδ-T cells, a clinically applicable alternative to reporter-gene imaging is direct cell labeling with PET radionuclides. Immune cells have long been imaged clinically by single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) in this manner, for example, using [111In]In(oxinate)3 and [99mTc]Tc-exametazime.19 In this regard, the clinically approved 8-hydroxyquinoline (oxine) has been recently shown to be an excellent ionophore for cell labeling with 89Zr (t1/2 = 78.4 hr, β+ = 22.3%).23, 24, 25 However, to the best of our knowledge, no study has evaluated its use for tracking γδ-T cells.
Here we report the first use of [89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4 for in vitro radiolabeling and in vivo tracking of human γδ-T cells, including the effects of radiolabeling on γδ-T cell functionality, proliferation, and DNA integrity. We applied this strategy in a xenograft model of breast cancer with an engineered cancer cell line that allows multimodal imaging to track tumor cells. A liposomal aminobisphosphonate was administered to increase T cell trafficking to the tumor.
Results
Radiotracer Labeling Efficiency and Retention in γδ-T Cells
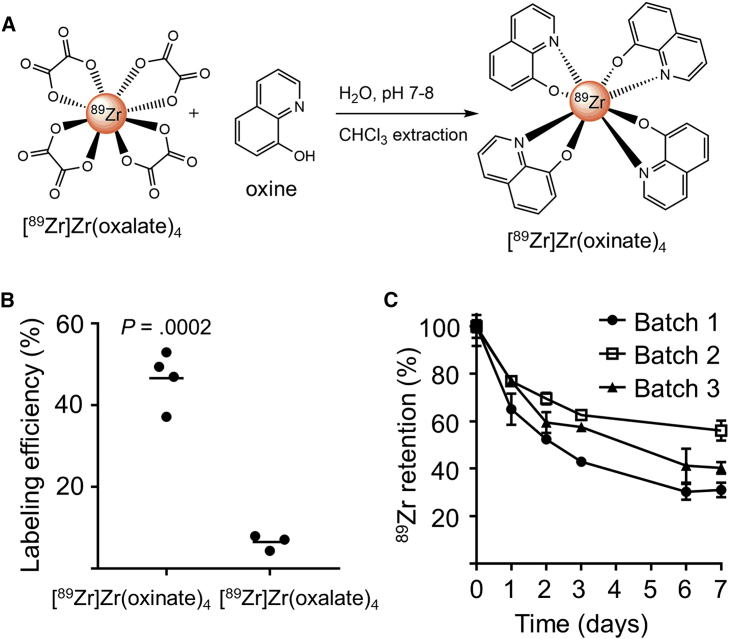
[89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4 was obtained by mixing neutralized [89Zr]Zr(oxalate)4 with 8-hydroxyquinoline dissolved in chloroform (Figure 1A). The radiochemical yield was 77.6% ± 11.8% (mean ± SD, N = 21), and radiochemical purity established by thin-layer radiochromatography was >95% (Figure S1). γδ-T cell labeling efficiency with [89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4 (46.6% ± 3.4%, N = 4) was significantly higher than with [89Zr]Zr(oxalate)4 (6.5% ± 1.1%, N = 3; Figure 1B). To optimize radiolabeling conditions, cells were incubated with [89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4 (6−600 mBq/cell) for 10, 20, or 30 min at 4°C, room temperature (RT), or 37°C. We found no significant difference between incubation times and temperatures (Figure S2).
Figure 1.
Radiotracer Synthesis and γδ-T Cell Radiolabeling
(A) [89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4 synthesis. (B) Labeling efficiencies of γδ-T cells incubated with 89Zr-based tracers (63.2 ± 7.9 mBq/cell) 20 min at RT. Mean of N = 3–4 individual experiments (unpaired t test). (C) 89Zr retention by γδ-T cells over 7 days after labeling with [89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4 (average incorporated activity: 34.3 ± 6.0 mBq/cell). Mean ± SEM of triplicate measures for 3 cell batches.
To study long-term tracer retention, radiolabeled γδ-T cells (25−40 mBq/cell) were cultured at 0.83 × 106 cells/mL. After 24 hr, the percentage of cell-associated 89Zr was 72.9% ± 6.8% of the original activity, and 42.4% ± 12.6% after 1 week (N = 3; Figure 1C).
In Vitro Assays of 89Zr-Radiolabeled γδ-T Cells
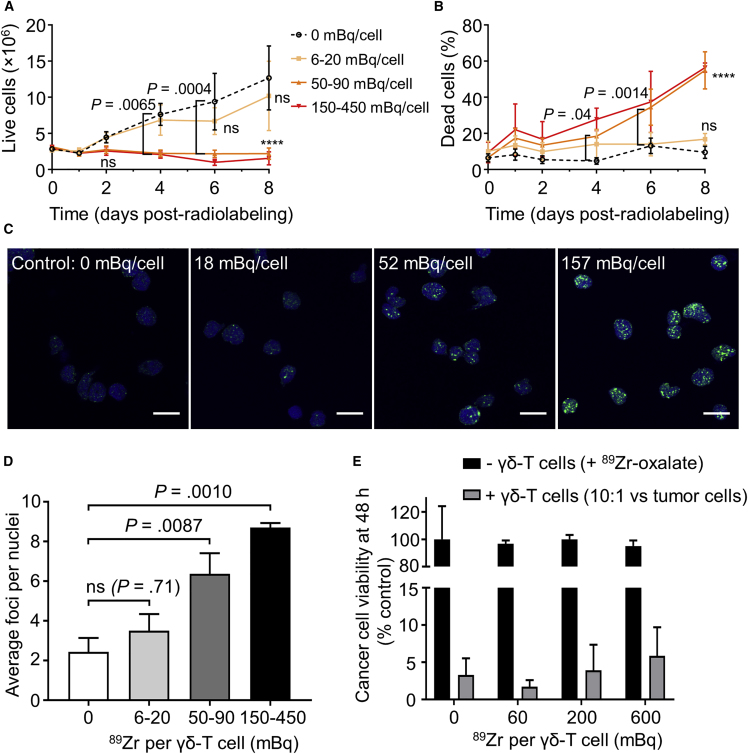
The purity of in vitro-expanded γδ-T cells plateaued 13−15 days post-isolation (Figure S3), at which point they were radiolabeled. Cells labeled with 6−20 mBq/cell proliferated similarly to unlabeled cells (p ≥ 0.05; Figure 2A), while cells labeled with more than 50 mBq/cell ceased to proliferate in vitro, indicating a dose-dependent effect of 89Zr on γδ-T cell proliferation. A similar dose dependency was observed on γδ-T cell death (Figure 2B) and DNA damage, evaluated by the formation of γH2AX foci26 1 hr after labeling (Figures 2C and 2D).
Figure 2.
Assays of 89Zr-Radiolabeled γδ-T Cells
(A and B) In vitro growth (A) and mortality (B) of radiolabeled γδ-T cells. Mean ± SEM of N = 4 independent experiments (except 150–450 mBq group, N = 2, not included in statistical analysis). ns: p > 0.05; ****p < 0.0001 versus unlabeled cells (2-way repeated-measures ANOVA, Dunnett’s correction for multiple comparisons). (C) Representative images of γ-H2AX foci (green) and nuclei (blue) in radiolabeled γδ-T cells (scale bars, 10 μm). (D) Average number of γ-H2AX foci per nuclei after radiolabeling. Mean ± SEM of N = 6, 5, 6, and 3 independent experiments (1-way ANOVA, Dunnett’s correction). (E) MDA-MB-231.hNIS-GFP tumor cell viability 48 hr after adding γδ-T cells or unchelated 89Zr, expressed as a percentage of control (tumor cells without γδ-T cells and 89Zr). Mean ± SEM of N = 3 independent experiments (2-way repeated-measures ANOVA, Dunnett’s correction).
To evaluate the cytotoxic ability of radiolabeled γδ-T cells, we quantified the survival of MDA-MB-231.hNIS-GFP cancer cell monolayers. γδ-T cells labeled with up to 600 mBq/cell showed no significant difference in cancer cell killing compared to unlabeled γδ-T cells (Figure 2E). As a control, adding 89Zr up to 3 Bq/cancer cell in the medium was not toxic to cancer cells in the absence of γδ-T cells. Even in 30-fold excess, γδ-T cells showed no toxicity toward cancer cells in the absence of aminobisphosphonate (Figure S4).
In Vivo PET Tracking of 89Zr-Radiolabeled γδ-T Cells
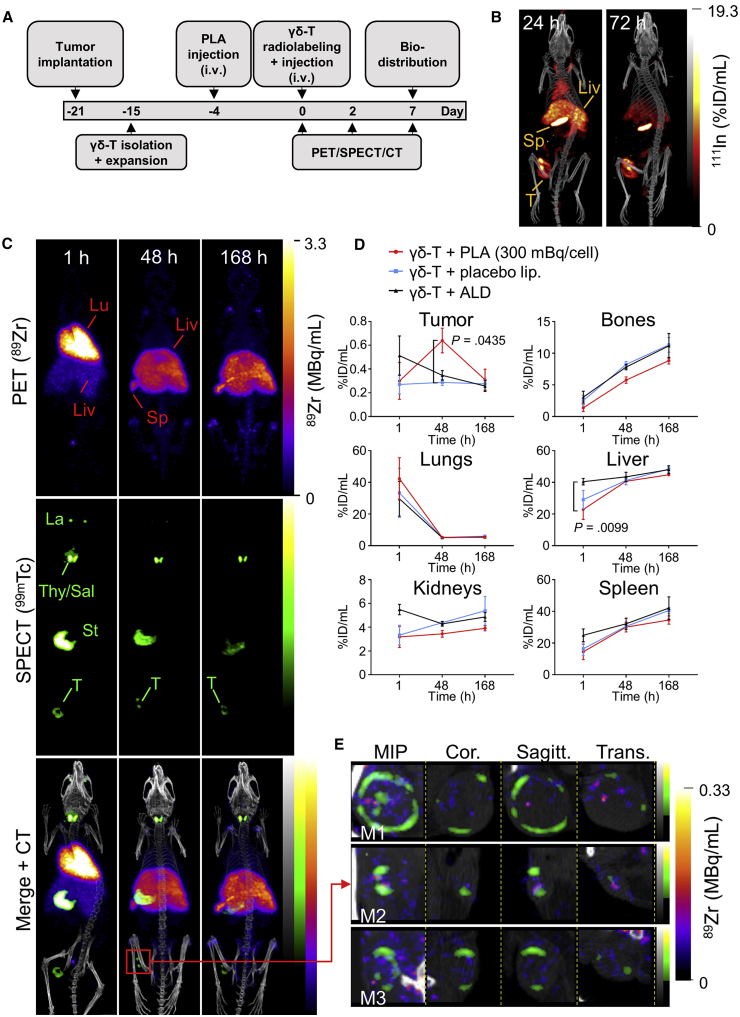
89Zr-radiolabeled γδ-T cells were administered intravenously in a mouse xenograft model of breast cancer followed by PET imaging at 1 hr, 48 hr, and 7 days after injection. We imaged the hNIS-expressing cancer cells by SPECT using 99mTcO4−.27 We also evaluated the effect of PLA on γδ-T cell homing to tumor sites. The study schedule is provided in Figure 3A.
Figure 3.
In Vivo Tracking of Radiolabeled γδ-T Cells
(A) Experiment schedule. (B) Representative SPECT-CT images of MDA-MB-231.hNIS-GFP xenograft NSG mice 24 and 72 hr after 111In-labeled PLA administration. (C) Representative PET, SPECT, and CT (merged) scans of a PLA-treated SCID/beige mouse at 1, 48, and 168 hr post-injection of γδ-T cells. Liv, liver; Lu, lungs; Sp, spleen; T, tumor. Endogenous murine NIS expression also results in radiotracer uptake, giving rise to the following signals: La, lacrimal glands; St, stomach; and Thy/Sal, thyroid/salivary glands. (D) Time-activity curves from image-based quantification of 89Zr in selected organs. Mean ± SEM of N = 3–4 animals (repeated-measures MM analysis, Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons). (E) Enlarged maximum intensity projection (MIP), coronal, sagittal, and transversal tumor views (merged PET- and SPECT-CT) in three PLA-treated mice (M1, M2, and M3), 48 hr after γδ-T cell injection.
The PLA dosing schedule was established using 111In-labeled PLA, showing significant PLA tumor accumulation within 24–72 hr of administration (Figure 3B; Table S1). The experimental group (PLA treated) received radiolabeled γδ-T cells + PLA (5 mg/kg alendronate). Control groups (non-PLA treated) received radiolabeled γδ-T cells with placebo liposomes, non-liposomal alendronate, or saline. An additional control group received γδ-T cells killed by freeze-thawing to compare bio-distributions of viable and non-viable cells.
SPECT showed uptake of 99mTcO4− in tumors and endogenous NIS-expressing organs (thyroid, salivary, and lacrimal glands and stomach; Figure 3C). At 1 hr after intravenous administration of 89Zr-radiolabeled γδ-T cells, PET revealed high amounts of radioactivity in the lungs in all groups, with signal also observed in the liver and spleen (Figures 3C and 3D). There was significantly higher uptake in the liver in the ALD group versus the PLA group. At tumor sites, the 89Zr signal was close to background (Figure S5). After 48 hr, 89Zr activity increased in the liver, spleen, and bones in all groups and decreased in the lungs. Uptake of 89Zr was observed at the tumor site only in the PLA group (Figure S5), suggesting the presence of radiolabeled γδ-T cells. Importantly, this was significantly higher in PLA-treated animals compared to control animals treated with non-liposomal alendronate (Figure 3D). Enlarged tumor views showed heterogeneity in tumor tissue, with live tissue, expressing a functional hNIS protein18, 27 and represented by a donut of 99mTc signal surrounding a core of non-viable tumor cells (Figure 3E). 89Zr signal in tumors was heterogeneous, with some co-localizing with 99mTc at the edges and foci of 89Zr signal inside the tumor. After 7 days, 89Zr activity remained high in the liver; increased in the spleen, bones, and kidneys; and was indistinguishable from background in tumors. Uptake values are provided in Table S2. Compared to other treatment groups, PET images of killed γδ-T cells showed a higher accumulation in the liver immediately after injection and increased uptake of 89Zr in the kidneys at later time points (Figure S6).
Ex Vivo Bio-distribution of 89Zr-Radiolabeled γδ-T Cells
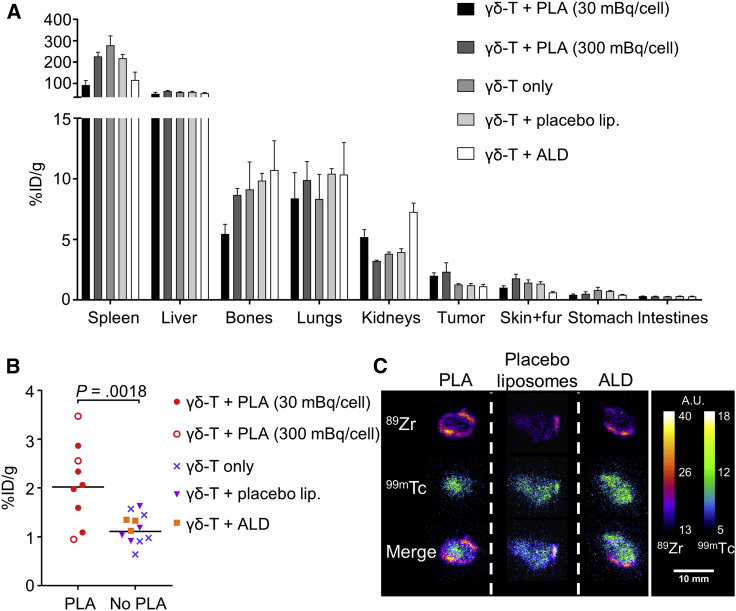
Ex vivo γ-counting 7 days post-administration of radiolabeled cells revealed a high concentration of 89Zr in the spleen (153.5% ± 88.8% injected dose [ID]/g averaged across all groups, N = 24) and liver (58.1% ± 10.6% ID/g, N = 24) in all groups, followed by lung and bone tissue (Figure 4A). Uptake of 89Zr in tumors from PLA-treated groups (2.1% ± 0.8% ID/g) was significantly higher than in non-PLA groups (1.2% ± 0.3% ID/g; Figure 4B), suggesting higher γδ-T cell numbers in PLA-treated tumors. Bone uptake of 89Zr in PLA-treated groups (6.5% ± 0.8% ID/g, N = 9) was significantly lower than in other groups (10.0% ± 1.1% ID/g, N = 12; p = 0.0238). Uptake in kidneys was significantly higher with killed γδ-T cells than in other treatment groups (Table S3). Uptake in other organs showed no major differences between treatment groups.
Figure 4.
PLA Treatment Increases the Accumulation of γδ-T Cells in Tumors
(A) Ex vivo bio-distribution of radiolabeled γδ-T cells, 7 days after γδ-T cell administration. Mean ± SEM of 89Zr uptake after PLA (N = 6 and 3, respectively), placebo liposomes (N = 4), non-liposomal alendronate (ALD; N = 3), or vehicle (N = 5) treatment. Data are from 3 pooled independent experiments (total N = 21). (B) Comparison of 89Zr accumulation in the tumor between PLA (N = 9) and non-PLA (N = 12) treatments (unpaired t test). (C) Artificially colored autoradiographs of tumor sections after PLA, placebo liposomes or non-liposomal alendronate (ALD) treatment. Images are representative of N = 3, 4, and 3 animals per group (scale bar, 10 mm).
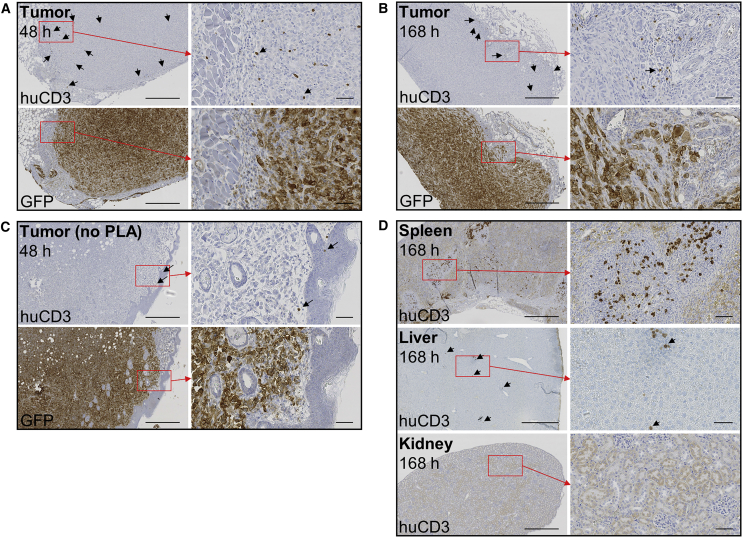
Tumor section autoradiographs showed a strong signal originating from hNIS-accumulated 99mTcO4−. Autoradiography was repeated after 4 days to allow for the decay of 99mTc and the capture 89Zr signal. Sections from PLA-treated animals showed increased 89Zr signal compared to non-PLA-treated animals. The 89Zr signal was higher in the tumor periphery, whereas the 99mTc signal was uniformly distributed (Figure 4C). γδ-T cell presence in tumors was demonstrated by immunohistochemistry. Human CD3-positive cells (>95% γδ-T cell receptor [TCR]+ at the time of administration; Figure S3) were visible in tumors 48 hr and 7 days after injection, both in the periphery and deeper regions (Figures 5A–5C; Figure S7). These cells were also visible in the spleen and liver after 7 days, but not in kidney sections (Figure 5D) or in control tissues of mice not administered γδ-T cells (Figure S8).
Figure 5.
Histology of γδ-T Cells
(A–C) Tumor sections 48 hr (A and C) or 7 days (B) after the injection of 89Zr-radiolabeled γδ-T cells into mice treated with PLA (A and B) or without PLA (C), stained for human CD3 (γδ-T cells) or GFP (tumor cells). Arrows indicate representative CD3+ cells. (D) Spleen, liver, and kidney sections 7 days after the administration of 89Zr-radiolabeled γδ-T cells. Sections are representative of N = 2–3 animals per time point. 6× (left) and 30× (right) magnification; scale bars, 500 μm (left) and 50 μm (right).
Discussion
[89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4 synthesis has been reported previously by our group23 and others.24, 25 The temperature-independent labeling efficiency of γδ-T cells with [89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4 suggests this is a passive process, in line with results from Sato et al.24 Sufficient radiotracer retention within cells is important to ensure that the imaging signal reflects labeled cells rather than free radiotracer bio-distribution. We observed an efflux of approximately half of the incorporated 89Zr over 1 week in vitro, which we believe does not interfere with in vivo imaging within this time frame. Uptake of 89Zr in the bone can be used to estimate the amount of tracer that leaked from the cells.25, 28 Retention of [89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4 is dependent on cell type, and our results are comparable to those observed with dendritic, bone marrow, and chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cells.23, 24, 25 Comparable levels of tracer efflux have been observed from lymphocytes labeled with [111In]In(oxinate)3,29, 30 the current gold standard for cell tracking by nuclear imaging.
A radiotracer for cell tracking must not significantly alter the phenotype, survival, proliferation capacity, and functionality of labeled cells. We demonstrated that the effects of [89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4 on γδ-T cell survival, proliferation capacity, and DNA damage were kept minimal for doses up to 20 mBq/cell but were significant at doses ≥50 mBq/cell. The cytotoxicity of radiolabeled γδ-T cells against the same tumor cells used for in vivo experiments was not affected by amounts of [89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4 of up to 600 mBq/cell, at least within 48 hr of radiolabeling. Cancer cell death was due to the combination of bisphosphonate treatment and γδ-T cells and not to the presence of 89Zr. Preserved cytotoxicity after radiolabeling, also recently observed in CAR-T cells by Weist et al.,25 is encouraging for the use of [89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4 as a T cell-tracking agent. However, the therapeutic efficacy of γδ-T cells presumably also relies on their in vivo proliferation ability; hence, we suggest that radiolabeling γδ-T cells with [89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4 should ideally not exceed 20 mBq/cell. This could lead to sensitivity issues on conventional PET scanners. Indeed, our experiments show that ex vivo gamma-counting tumors could reveal amounts of 89Zr indistinguishable from background in our PET imaging system at day 7. Assuming that a human cell-tracking study would require 37 MBq 89Zr31 and 109 γδ-T cells,14 this would equate to an average of 37 mBq/cell, which we have shown not to be excessively damaging to γδ-T cells. Upcoming developments in PET technology, such as total-body PET,32 should reduce the required 89Zr activity per cell (by a factor of 40) and overcome these sensitivity issues.
For in vivo studies, a xenograft model of human breast cancer in immunocompromised mice12, 33 was chosen, as mice do not possess a subset of T cells functionally equivalent to human Vγ9Vδ2 T cells.34 We tracked γδ-T cells radiolabeled with [89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4 (30−300 mBq/cell) by PET 1 hr, 48 hr, and 7 days after intravenous injection. We simultaneously used 99mTcO4− to visualize hNIS-expressing tumors by SPECT. The in vivo distribution of 89Zr-labeled γδ-T cells over time was similar to that observed in studies of adoptively transferred γδ-T35, 36 and other T cells.25, 37, 38 89Zr uptake was significantly increased in PLA-treated tumors, suggesting that PLA increases homing of these cells to the tumor site. Accumulation of γδ-T cells at the tumor site 48 hr after administration was also observed by others.35 Uptake values for the spleen and tumor determined by image-based quantification are lower than those determined by ex vivo bio-distribution. This can be explained by the small size of this organ and significant partial volume effect (spleen) and the liquid or necrotic tumor core that leaked upon dissection.
For instrument sensitivity reasons, some imaging studies were performed with higher doses of 89Zr than recommended above. However, the distinctly different distribution pattern observed with killed γδ-T cells suggests that radiolabeling with up to 300 mBq/cell, which preserved cytotoxic functionality in vitro over 48 hr, did not impair γδ-T cell trafficking and allowed us to track live cells. Furthermore, previous studies have shown that [89Zr]Zr(oxalate)4,28, 39 [89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4, and lysates from [89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4-labeled cells23 have distinct distribution patterns from intact cells labeled with [89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4. Cell concentrations during labeling and in vitro assays were in the range of 1−5 × 106/mL. In comparison, using in vitro 89Zr retention values, cell concentrations extrapolated from PET-computed tomography (CT) images in the organs showing the strongest 89Zr signal (spleen, liver, and lungs) would be in the range of 0.5−5 × 106 cells/mL. We therefore expect the DNA damage sustained by γδ-T cells, due to both self-irradiation and crossfire, after in vivo administration to be comparable to that observed in vitro. Considering the strong affinity of the 89Zr4+ ion for bone,28 the relatively low bone accumulation of 89Zr indicates limited efflux of weakly chelated 89Zr, and it suggests that 89Zr is mostly retained by γδ-T cells after injection. The lower accumulation of 89Zr in the bones of PLA-treated animals compared to other groups also suggests reduced efflux of 89Zr from γδ-T cells after PLA treatment.
Histology confirmed the presence of γδ-T cells in the tumors, spleen, and liver, using the CD3 marker.40 Immunohistochemistry and autoradiography suggest that γδ-T cells accumulated mostly at the periphery of the tumor. The small number of cells observed by immunohistochemistry precludes statistical comparison. Furthermore, these techniques can only image the solid portion of the tumor. PET imaging not only allowed visualization of the whole, intact tumors but additionally revealed heterogeneous distributions of 89Zr in tumors, which would be challenging to observe by histology. Combined with the non-invasive nature of PET imaging, this further highlights the value of using PET tracers such as [89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4 for cell tracking. The high uptake of 89Zr in the liver and spleen was mirrored by the large numbers of human CD3+ cells observed in these tissues, consistent with the bio-distribution of radiolabeled γδ-T cells. In contrast, the apparent absence of CD3+ cells in the kidneys, despite higher 89Zr uptake than in the tumor, and the fact that the kidney uptake of 89Zr was significantly higher in animals administered killed γδ-T cells than in other groups both suggest that the radioactivity detected in the kidneys corresponds to 89Zr progressively released from γδ-T cells in other organs. A limitation of directly labeling cells is that the radionuclide can leak out over time and be taken up by adjacent tissue. Although immunohistochemistry demonstrates the presence of the administered γδ-T cells in the tumors, this technique cannot determine whether the 89Zr signal originates from the γδ-T cells or from in situ-labeled bystander cells.
A critical aspect of this type of cellular immunotherapy is that the therapeutic cells must be activated at the target site and reach the tumor in sufficient numbers. γδ-T cell toxicity toward cancer cells is greatly amplified by bisphosphonates, suggesting a role for γδ-T cells in the anti-cancer properties of bisphosphonates.41 Here we sought to increase phosphoantigen expression in tumors by administering PLA, which delivers alendronate to the tumors in an untargeted fashion by virtue of the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect.42 Liposomal alendronate proved safer than other bisphosphonates and effective in potentiating γδ-T cell therapy.12, 43 We have previously shown that the tumor-to-background uptake ratio of PLA increases over time and is significant after 3 days.44 Here we observed that PLA administered 4 days in advance significantly increased the amount of 89Zr reaching the tumor within 48 hr of radiolabeled γδ-T cell administration. Our results suggest that γδ-T cells home to the tumor within 2 days and remain there for at least 5 days. This was not observed in any other treatment group, demonstrating the importance of encapsulating the aminobisphosphonate in a tumor-targeting vehicle.
Clinical imaging studies of therapeutic T cells with [111In]In(oxinate)3 have been performed by radiolabeling only a fraction of the total administered T cells,45, 46, 47 although evidence exists that distributing the total activity over a larger number of cells better preserves their proliferative abilities.48 Our results suggest that radiolabeling the entire batch of γδ-T cells with [89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4 might be the preferable option to avoid imaging excessively damaged cells. In two notable studies, γ-scintigraphy revealed T cell uptake in tumors using only 1−3 mBq 111In per cell.46, 49 Considering the increased sensitivity of PET over SPECT and expected improvements in PET technology, clinical imaging of T cell therapies using [89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4 is a credible prospect.
Conclusions
This study demonstrates the suitability of [89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4 as a PET tracer to track γδ-T cells in vivo, while previous work has shown the therapeutic efficacy of γδ-T cells in combination with PLA.12, 43 These objectives achieved, [89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4 can now be applied to answer fundamental questions in the preclinical and clinical development of γδ-T cell therapies, e.g., whether the accumulation of γδ-T cells at the tumor site or their distribution within the tumor correlates with therapeutic efficacy. Due to numerous molecular and cellular differences, the distribution of human γδ-T cells in an immunocompromised mouse model cannot fully predict their behavior in a human host. However, the results of this proof-of-principle study can be used to design a clinical trial that will answer the question of the distribution of γδ-T cells in humans after adoptive transfer.
Our results have implications for clinical translation, and they suggest using liposomal aminobisphosphonates as adjuncts to γδ-T cell therapy. In the context of clinical protocols involving repeated infusions of γδ-T cells,15 one can envisage the use of 89Zr-labeled cells for the first infusion, followed by PET imaging 24–72 hr later. The number of cells trafficking to the tumor sites would then be used to decide whether to pursue with additional treatment cycles. Cell radiolabeling with [89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4 is clinically translatable without significant methodological modifications, and the high similarity of [89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4 to the well-established [111In]In(oxinate)3 should facilitate regulatory approval. Our results support that T cell labeling with [89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4 is a realistic option for human studies and will benefit the development of cellular immunotherapy.
Materials and Methods
Experiment Approval
Animals experiments were approved by the UK Home Office under The Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act (1986), PPL reference 7008879 (Protocol 6), with local approval from King’s College London Research Ethics Committee (KCL-REC). Experiments using human T cells received approval from KCL-REC (Study Reference HR-16/17-3746). All donors provided written, informed consent.
Reagents, Animals, and Cells
Unless otherwise indicated, reagents were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich and Merck. Female SCID/beige (CB17.Cg-PrkdcscidLystbg-J/Crl) and Nod scid gamma (NSG) (NOD.Cg-Prkdcscid Il2rgtm1WjI/SzJ) mice (18−25 g, 10−20 weeks old) were obtained from Charles River (UK). γδ-T cells were obtained as described previously,12 using zoledronate (Novartis) and interleukin-2 (IL-2) (Novartis). Full details are provided in the Supplemental Materials and Methods. Population purity was assessed by flow cytometry (BD FACSCalibur), using pan-γδ TCR (IMMU510, Beckman Coulter B49175) and anti-CD3 (OKT3, BioLegend 317307) monoclonal antibodies. Data were analyzed using Flowing version (v.)2.5.1 (http://flowingsoftware.btk.fi). Only batches with ≥80% γδ-positive CD3+ cells were used for further experiments (≥95% for in vivo experiments). MDA-MB-231.hNIS-GFP cells27 were grown in DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), penicillin, streptomycin, and l-glutamine (2 mM), and they were tested for mycoplasma contamination (e-Myco PCR detection kit, Bulldog Bio).
PET Tracer Synthesis
[89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4 was synthesized as previously described.23 Full details are provided in the Supplemental Materials and Methods.
Cell Labeling
γδ-T cells expanded in vitro12 were washed with PBS (Ca2+/Mg2+ free) and re-suspended at 5 × 106/mL in PBS at RT. [89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4 (6−600 mBq/cell) in aqueous DMSO was added to the cell suspension, keeping DMSO concentrations ≤0.7%. Neutralized [89Zr]Zr(oxalate)4 with an equivalent amount of DMSO was used as a control. After 10−30 min of incubation, cells were pelleted and the supernatants kept aside. The cells were washed with PBS, centrifuged, and the washings combined with the previous supernatants. The cells were suspended in growth medium or PBS for further experiments. Viability was assessed using the trypan blue dye exclusion method. Radioactivity in re-suspended cells and combined supernatants was measured in a gamma-counter. Cell-labeling efficiency (LE[%]) was calculated as follows.
For radiotracer retention and cell proliferation studies, radiolabeled (or vehicle-treated) γδ-T cells were cultured as described above, and they were analyzed at various time points for viability (using trypan blue), determination of cell-associated radioactivity (by γ-counting), and cell death (by flow cytometry using propidium iodide [PI]; Thermo Scientific). Further details are provided in the Supplemental Materials and Methods.
Cancer Cell-Killing Assay
MDA-MB-231.hNIS-GFP cells seeded in a 96-well plate at 104 cells/well and incubated overnight were treated with 3 μM zoledronate or vehicle for 24 hr. The cells were washed and the medium was replaced with γδ-T cells in growth medium. As a control for radiolabeled γδ-T cells, an equal amount of 89Zr in medium was added to some wells. After 48 hr, γδ-T cells were removed by washing with PBS, and cancer cell viability was evaluated using the alamarBlue assay (Thermo Scientific), reading plates in a GloMax (Promega) reader (530 nm excitation and 590 nm emission filters).
Determination of DNA Double-Strand Breaks
Radiolabeled γδ-T cells in medium were seeded onto poly-l-lysine-coated coverslips and incubated for 1 hr. After centrifugation and gentle rinsing with PBS, the cells were fixed and permeabilized with 3.7% formalin, 0.5% Triton X-100, and 0.5% IGEPAL CA-630 in PBS, then blocked with 2% BSA and 1% goat serum. γH2AX foci were detected with an anti-γH2AX (Ser139) mouse monoclonal antibody (mAb) (1:1,600; JBW301, Merck 05-636) and goat anti-mouse AF488-immunoglobulin G (IgG) (1:500; Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories 115-545-062). Nuclei were detected with Hoechst 33342. Images were acquired on a TCS SP5 II confocal microscope (Leica) with a 100×/1.40 HCX PL Apochromat objective (Leica) and Leica Application Suite Advanced Fluorescence (LAS-AF) control software. Ten sections (0.4-μm thickness) were imaged. At least 30 nuclei/slide were imaged (2 slides/treatment). Maximal intensity projections of z stacks were made using ImageJ v.1.51p (https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/). Nuclei and γH2AX foci were counted using CellProfiler v.2.2.0 (http://cellprofiler.org), calculating average numbers of γH2AX foci per nucleus in each image. Full details are provided in the Supplemental Materials and Methods.
Animals, Tumor Model, and Tumor Sensitization with Liposomal Alendronate
Approximately 1.5 × 106 MDA-MB-231.hNIS-GFP cells were injected subcutaneously in the mammary fat pad between the fourth and fifth nipples in the left flank; tumors were grown over 3 weeks. Animals were randomly assigned to experimental groups, and investigators were not blinded to cohort allocation when assessing outcomes. Cohort sizes were chosen based on prior experience,44, 50 in compliance with local regulations concerning animal experiments. Liposomal formulations were prepared at Shaare Zedek MC as previously described.13 Alendronate-loaded liposomes (PLA) contained 1.5−5.4 mg/mL alendronate and 36−40 μmol/mL phospholipids. Placebo liposomes contained 20−50 μmol/mL phospholipids. PLA was co-injected with placebo liposomes for a total dose of 5 mg/kg alendronate and 4 μmol phospholipids per mouse in PLA-treated animals. Placebo-treated animals received empty liposomes corresponding to 4 μmol phospholipids per mouse. Another control group received 5 mg/kg alendronate (ALD). Formulations were injected intravenously (i.v.) 4 days before the administration of radiolabeled γδ-T cells.
In Vivo PET and SPECT Imaging of γδ-T Cells, Tumors, and PLA
89Zr-radiolabeled γδ-T cells (107 cells/animal in 100 μL, 0.3−3 MBq 89Zr, single γδ-T donor per experiment) were injected i.v. at t = 0 hr and imaged by PET/CT within 30 min. PET/CT imaging was performed for 30−240 min (as indicated) on a nanoScan PET-CT scanner (Mediso). For tumor imaging, 100 μL 99mTcO4− (15−25 MBq) in saline was injected i.v., and SPECT-CT was performed 40 min thereafter in a NanoSPECT/CT scanner (Mediso; 1-mm collimators, 30-min scan). PET-CT and SPECT-CT were repeated at t = 48 and 168 hr. For PLA imaging by SPECT-CT, PLA was radiolabeled with [111In]In(oxinate)3 and administered i.v. (7 MBq 111In/mouse) to NSG mice. PET- and SPECT-CT datasets were reconstructed using a Monte Carlo-based full-3D iterative algorithm (Tera-Tomo, Mediso). Images were co-registered and analyzed using VivoQuant v.2.50 (Invicro). Regions of interest (ROIs) were delineated for PET activity quantification in specific organs. Uptake in each ROI was expressed as a percentage of injected dose per volume (% ID/mL).
Ex Vivo Bio-distribution Studies
Mice from imaging studies were used for bio-distribution studies on day 2 or 7. After culling, organs were dissected, weighed, and γ-counted together with standards prepared from a sample of injected material. The percentage of injected dose per gram (% ID/g) of tissue was calculated. Organs were cryopreserved in optimal cutting temperature (OCT) compound (VWR) for autoradiography and/or formalin fixed and paraffin embedded (FFPE) for histologic analysis.
Autoradiography
Cryopreserved tissues were cut (50 μm), mounted on poly-l-lysine-coated slides (VWR), fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA), mounted in Mowiol, and exposed to a storage phosphor screen for 20 min at 3 hr post-dissection to obtain the 99mTc signal, then for 48 hr at 4 days post-dissection to obtain the 89Zr signal. The storage phosphor screen was read using a Cyclone Plus imager (PerkinElmer), and images were processed with ImageJ.
Immunohistochemistry
Briefly, FFPE organ blocks were sliced and stained using a Discovery XT system (Ventana Medical Systems) using the DAB Map detection kit (Ventana 760-124). For pre-treatment, CC1 (Ventana 950-124) was used. Sections were stained with anti-GFP (1/1,000; Abcam ab290, UK) or anti-CD3 (LN10, Leica CD3-565-L-CE) primary antibodies, followed by biotinylated anti-rabbit or anti-mouse IgG (1/200; Dako) secondary antibodies, as appropriate. Full details are provided in the Supplemental Materials and Methods.
Statistics
Independent experiments were performed on different days with γδ-T cell batches from different donors. Data were plotted using Prism v.7.01 (GraphPad). Differences between 2 groups were evaluated by Student’s two-tailed t test. To account for repeated measurements in a same animal or cell batch and multiple treatments tested on a same cell batch, analysis was performed using 2-way repeated-measures ANOVA in GraphPad Prism or a repeated-measures Mixed Model (MM)51 in InVivoStat v.3.7 (http://invivostat.co.uk/), as indicated. Dunnett’s post hoc test was applied for comparisons back to a control group, or Bonferroni correction for multiple pairwise comparisons, unless otherwise specified. Exact significance values are reported in each figure.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.M., L.L., G.O.F., and R.T.M.d.R.; Methodology, F.M., L.L., A.G., G.O.F., and R.T.M.d.R.; Investigation, F.M., L.L., A.V., B.D., A.C.P.-P., and R.T.M.d.R.; Writing – Original Draft, F.M.; Writing – Review and Editing, F.M., L.L., A.G., J.M., P.J.B., G.O.F., and R.T.M.d.R.; Funding Acquisition, G.O.F., R.T.M.d.R., P.J.B., and J.M.; Resources, F.M., L.L., A.G., H.S., and R.T.M.d.R.; Supervision, R.T.M.d.R., G.O.F., and P.J.B.
Conflicts of Interest
J.M. is chief scientific officer of Leucid Bio, a company dedicated to the commercial development of CAR-T cells for solid tumors. The authors declare no other potential conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank J. Bartnicka, Dr. J. Bordoloi, A. Dzhatdoeva, P. Gawne, I. Hungnes, M. Iafrate, and G. Keeling for technical assistance. This work was supported by a Cancer Research UK (CRUK) Multidisciplinary Project Award (grant C48390/A21153), the KCL/UCL Comprehensive Cancer Imaging Centre funded by CRUK and EPSRC in association with the MRC and DoH (England), the Wellcome EPSRC Centre for Medical Engineering at KCL (grant WT 203148/Z/16/Z), the Medical Research Council Confidence in Concepts scheme, the Experimental Cancer Medicine Centre at KCL, the KHP/KCL CRUK Cancer Centre and the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Biomedical Research Centre based at Guy’s and St Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust and KCL (grant IS-BRC-1215-20006). The views expressed are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR, or the Department of Health.
Footnotes
Supplemental Information includes eight figures, three tables, and Supplemental Materials and Methods and can be found with this article online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.10.006.
Supplemental Information
References
- 1.Turtle C.J., Hay K.A., Hanafi L.-A., Li D., Cherian S., Chen X., Wood B., Lozanski A., Byrd J.C., Heimfeld S. Durable molecular remissions in chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with CD19-specific chimeric antigen receptor–modified T cells after failure of ibrutinib. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017;35:3010–3020. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.72.8519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chandran S.S., Somerville R.P.T., Yang J.C., Sherry R.M., Klebanoff C.A., Goff S.L., Wunderlich J.R., Danforth D.N., Zlott D., Paria B.C. Treatment of metastatic uveal melanoma with adoptive transfer of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes: a single-centre, two-stage, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18:792–802. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30251-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Rosenberg S.A., Restifo N.P. Adoptive cell transfer as personalized immunotherapy for human cancer. Science. 2015;348:62–68. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa4967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gentles A.J., Newman A.M., Liu C.L., Bratman S.V., Feng W., Kim D., Nair V.S., Xu Y., Khuong A., Hoang C.D. The prognostic landscape of genes and infiltrating immune cells across human cancers. Nat. Med. 2015;21:938–945. doi: 10.1038/nm.3909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tyler C.J., Doherty D.G., Moser B., Eberl M. Human Vγ9/Vδ2 T cells: Innate adaptors of the immune system. Cell. Immunol. 2015;296:10–21. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2015.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Vantourout P., Hayday A. Six-of-the-best: unique contributions of γδ T cells to immunology. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013;13:88–100. doi: 10.1038/nri3384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bouet-Toussaint F., Cabillic F., Toutirais O., Le Gallo M., Thomas de la Pintière C., Daniel P., Genetet N., Meunier B., Dupont-Bierre E., Boudjema K., Catros V. Vgamma9Vdelta2 T cell-mediated recognition of human solid tumors. Potential for immunotherapy of hepatocellular and colorectal carcinomas. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2008;57:531–539. doi: 10.1007/s00262-007-0391-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gu S., Sachleben J.R., Boughter C.T., Nawrocka W.I., Borowska M.T., Tarrasch J.T., Skiniotis G., Roux B., Adams E.J. Phosphoantigen-induced conformational change of butyrophilin 3A1 (BTN3A1) and its implication on Vγ9Vδ2 T cell activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2017;114:E7311–E7320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1707547114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Vavassori S., Kumar A., Wan G.S., Ramanjaneyulu G.S., Cavallari M., El Daker S., Beddoe T., Theodossis A., Williams N.K., Gostick E. Butyrophilin 3A1 binds phosphorylated antigens and stimulates human γδ T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2013;14:908–916. doi: 10.1038/ni.2665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.De Rosa G., Misso G., Salzano G., Caraglia M. Bisphosphonates and cancer: what opportunities from nanotechnology? J. Drug Deliv. 2013;2013:637976. doi: 10.1155/2013/637976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kunzmann V., Bauer E., Feurle J., Weissinger F., Tony H.P., Wilhelm M. Stimulation of gammadelta T cells by aminobisphosphonates and induction of antiplasma cell activity in multiple myeloma. Blood. 2000;96:384–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Parente-Pereira A.C., Shmeeda H., Whilding L.M., Zambirinis C.P., Foster J., van der Stegen S.J.C., Beatson R., Zabinski T., Brewig N., Sosabowski J.K. Adoptive immunotherapy of epithelial ovarian cancer with Vγ9Vδ2 T cells, potentiated by liposomal alendronic acid. J. Immunol. 2014;193:5557–5566. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Shmeeda H., Amitay Y., Gorin J., Tzemach D., Mak L., Stern S.T., Barenholz Y., Gabizon A. Coencapsulation of alendronate and doxorubicin in pegylated liposomes: a novel formulation for chemoimmunotherapy of cancer. J. Drug Target. 2016;24:878–889. doi: 10.1080/1061186X.2016.1191081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kobayashi H., Tanaka Y. γδ T cell immunotherapy—A review. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2015;8:40–61. doi: 10.3390/ph8010040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fisher J.P., Heuijerjans J., Yan M., Gustafsson K., Anderson J. γδ T cells for cancer immunotherapy: A systematic review of clinical trials. OncoImmunology. 2014;3:e27572. doi: 10.4161/onci.27572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.James M.L., Gambhir S.S. A molecular imaging primer: modalities, imaging agents, and applications. Physiol. Rev. 2012;92:897–965. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00049.2010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ponomarev V. Advancing immune and cell-based therapies through imaging. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2017;19:379–384. doi: 10.1007/s11307-017-1069-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Volpe A., Kurtys E., Fruhwirth G.O. Cousins at work: How combining medical with optical imaging enhances in vivo cell tracking. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018;102:40–50. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2018.06.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kircher M.F., Gambhir S.S., Grimm J. Noninvasive cell-tracking methods. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011;8:677–688. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2011.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Tavaré R., McCracken M.N., Zettlitz K.A., Knowles S.M., Salazar F.B., Olafsen T., Witte O.N., Wu A.M. Engineered antibody fragments for immuno-PET imaging of endogenous CD8+ T cells in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111:1108–1113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1316922111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mall S., Yusufi N., Wagner R., Klar R., Bianchi H., Steiger K., Straub M., Audehm S., Laitinen I., Aichler M. Immuno-PET imaging of engineered human T cells in tumors. Cancer Res. 2016;76:4113–4123. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-2784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Jurgielewicz P., Harmsen S., Wei E., Bachmann M.H., Ting R., Aras O. New imaging probes to track cell fate: reporter genes in stem cell research. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017;74:4455–4469. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2584-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Charoenphun P., Meszaros L.K., Chuamsaamarkkee K., Sharif-Paghaleh E., Ballinger J.R., Ferris T.J., Went M.J., Mullen G.E., Blower P.J. [(89)Zr]oxinate4 for long-term in vivo cell tracking by positron emission tomography. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 2015;42:278–287. doi: 10.1007/s00259-014-2945-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sato N., Wu H., Asiedu K.O., Szajek L.P., Griffiths G.L., Choyke P.L. 89Zr-oxine complex PET cell imaging in monitoring cell-based therapies. Radiology. 2015;275:490–500. doi: 10.1148/radiol.15142849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Weist M.R., Starr R., Aguilar B., Chea J., Miles J.K., Poku E., Gerdts E., Yang X., Priceman S.J., Forman S.J. PET of adoptively transferred chimeric antigen receptor T cells with 89Zr-oxine. J. Nucl. Med. 2018;59:1531–1537. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.117.206714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bonner W.M., Redon C.E., Dickey J.S., Nakamura A.J., Sedelnikova O.A., Solier S., Pommier Y. GammaH2AX and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2008;8:957–967. doi: 10.1038/nrc2523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Volpe A., Man F., Lim L., Khoshnevisan A., Blower J., Blower P.J., Fruhwirth G.O. Radionuclide-fluorescence Reporter Gene Imaging to Track Tumor Progression in Rodent Tumor Models. J. Vis. Exp. 2018;(133) doi: 10.3791/57088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Abou D.S., Ku T., Smith-Jones P.M. In vivo biodistribution and accumulation of 89Zr in mice. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2011;38:675–681. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2010.12.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.ten Berge R.J., Natarajan A.T., Hardeman M.R., van Royen E.A., Schellekens P.T. Labeling with indium-111 has detrimental effects on human lymphocytes: concise communication. J. Nucl. Med. 1983;24:615–620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kuyama J., McCormack A., George A.J., Heelan B.T., Osman S., Batchelor J.R., Peters A.M. Indium-111 labelled lymphocytes: isotope distribution and cell division. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 1997;24:488–496. doi: 10.1007/BF01267679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Jauw Y.W.S., Menke-van der Houven van Oordt C.W., Hoekstra O.S., Hendrikse N.H., Vugts D.J., Zijlstra J.M., Huisman M.C., van Dongen G.A. Immuno-Positron Emission Tomography with Zirconium-89-Labeled Monoclonal Antibodies in Oncology: What Can We Learn from Initial Clinical Trials? Front. Pharmacol. 2016;7:131. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Zhang X., Zhou J., Cherry S.R., Badawi R.D., Qi J. Quantitative image reconstruction for total-body PET imaging using the 2-meter long EXPLORER scanner. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017;62:2465–2485. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/aa5e46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hodgins N.O., Al-Jamal W.T., Wang J.T.-W., Klippstein R., Costa P.M., Sosabowski J.K., Marshall J.F., Maher J., Al-Jamal K.T. Investigating in vitro and in vivo αvβ6 integrin receptor-targeting liposomal alendronate for combinatory γδ T cell immunotherapy. J. Control. Release. 2017;256:141–152. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.04.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Pang D.J., Neves J.F., Sumaria N., Pennington D.J. Understanding the complexity of γδ T-cell subsets in mouse and human. Immunology. 2012;136:283–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2012.03582.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Beck B.H., Kim H.-G., Kim H., Samuel S., Liu Z., Shrestha R., Haines H., Zinn K., Lopez R.D. Adoptively transferred ex vivo expanded gammadelta-T cells mediate in vivo antitumor activity in preclinical mouse models of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010;122:135–144. doi: 10.1007/s10549-009-0527-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Nicol A.J., Tokuyama H., Mattarollo S.R., Hagi T., Suzuki K., Yokokawa K., Nieda M. Clinical evaluation of autologous gamma delta T cell-based immunotherapy for metastatic solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer. 2011;105:778–786. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2011.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Meidenbauer N., Marienhagen J., Laumer M., Vogl S., Heymann J., Andreesen R., Mackensen A. Survival and tumor localization of adoptively transferred Melan-A-specific T cells in melanoma patients. J. Immunol. 2003;170:2161–2169. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.4.2161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bobisse S., Rondina M., Merlo A., Tisato V., Mandruzzato S., Amendola M., Naldini L., Willemsen R.A., Debets R., Zanovello P., Rosato A. Reprogramming T lymphocytes for melanoma adoptive immunotherapy by T-cell receptor gene transfer with lentiviral vectors. Cancer Res. 2009;69:9385–9394. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ma M.T., Meszaros L.K., Paterson B.M., Berry D.J., Cooper M.S., Ma Y., Hider R.C., Blower P.J. Tripodal tris(hydroxypyridinone) ligands for immunoconjugate PET imaging with (89)Zr(4+): comparison with desferrioxamine-B. Dalton Trans. 2015;44:4884–4900. doi: 10.1039/c4dt02978j. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Roullet M., Gheith S.M.F., Mauger J., Junkins-Hopkins J.M., Choi J.K. Percentage of γδ T cells in panniculitis by paraffin immunohistochemical analysis. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2009;131:820–826. doi: 10.1309/AJCPMG37MXKYPUBE. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Van Acker H.H., Anguille S., Willemen Y., Smits E.L., Van Tendeloo V.F. Bisphosphonates for cancer treatment: Mechanisms of action and lessons from clinical trials. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016;158:24–40. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2015.11.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Prabhakar U., Maeda H., Jain R.K., Sevick-Muraca E.M., Zamboni W., Farokhzad O.C., Barry S.T., Gabizon A., Grodzinski P., Blakey D.C. Challenges and key considerations of the enhanced permeability and retention effect for nanomedicine drug delivery in oncology. Cancer Res. 2013;73:2412–2417. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Hodgins N.O., Al-Jamal W.T., Wang J.T.-W., Parente-Pereira A.C., Liu M., Maher J., Al-Jamal K.T. In vitro potency, in vitro and in vivo efficacy of liposomal alendronate in combination with γδ T cell immunotherapy in mice. J. Control. Release. 2016;241:229–241. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.09.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Edmonds S., Volpe A., Shmeeda H., Parente-Pereira A.C., Radia R., Baguña-Torres J., Szanda I., Severin G.W., Livieratos L., Blower P.J. Exploiting the Metal-Chelating Properties of the Drug Cargo for In Vivo Positron Emission Tomography Imaging of Liposomal Nanomedicines. ACS Nano. 2016;10:10294–10307. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.6b05935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Dillman R.O., Hurwitz S.R., Schiltz P.M., Barth N.M., Beutel L.D., Nayak S.K., O’Connor A.A. Tumor localization by tumor infiltrating lymphocytes labeled with indium-111 in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma, melanoma, and colorectal cancer. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 1997;12:65–71. doi: 10.1089/cbr.1997.12.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kershaw M.H., Westwood J.A., Parker L.L., Wang G., Eshhar Z., Mavroukakis S.A., White D.E., Wunderlich J.R., Canevari S., Rogers-Freezer L. A phase I study on adoptive immunotherapy using gene-modified T cells for ovarian cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006;12:6106–6115. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Ritchie D.S., Neeson P.J., Khot A., Peinert S., Tai T., Tainton K., Chen K., Shin M., Wall D.M., Hönemann D. Persistence and efficacy of second generation CAR T cell against the LeY antigen in acute myeloid leukemia. Mol. Ther. 2013;21:2122–2129. doi: 10.1038/mt.2013.154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Botti C., Negri D.R., Seregni E., Ramakrishna V., Arienti F., Maffioli L., Lombardo C., Bogni A., Pascali C., Crippa F. Comparison of three different methods for radiolabelling human activated T lymphocytes. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 1997;24:497–504. doi: 10.1007/BF01267680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Griffith K.D., Read E.J., Carrasquillo J.A., Carter C.S., Yang J.C., Fisher B., Aebersold P., Packard B.S., Yu M.Y., Rosenberg S.A. In vivo distribution of adoptively transferred indium-111-labeled tumor infiltrating lymphocytes and peripheral blood lymphocytes in patients with metastatic melanoma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1989;81:1709–1717. doi: 10.1093/jnci/81.22.1709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Fruhwirth G.O., Diocou S., Blower P.J., Ng T., Mullen G.E.D. A whole-body dual-modality radionuclide optical strategy for preclinical imaging of metastasis and heterogeneous treatment response in different microenvironments. J. Nucl. Med. 2014;55:686–694. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.113.127480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Wang Z., Goonewardene L.A. The use of MIXED models in the analysis of animal experiments with repeated measures data. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2004;84:1–11. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.