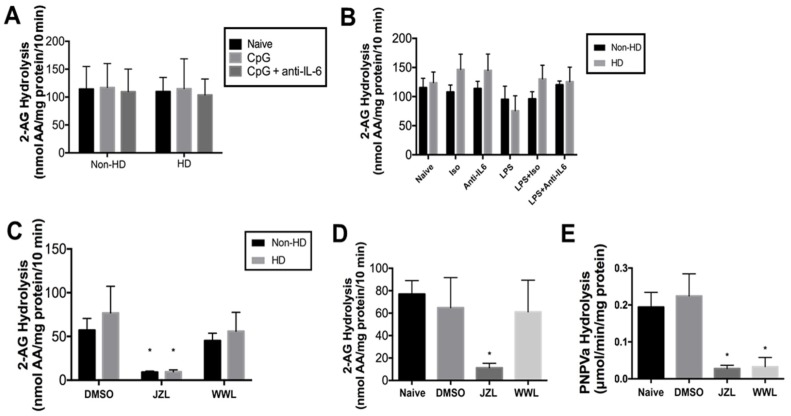
Figure 2.
2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) hydrolytic activity and carboxylesterase (CES) activity in human PBMCs. Cell lysates were pre-incubated for 5 min at 37 °C, then supplemented with 2-AG (final concentration, 50 µM). Incubation proceeded for 10 min before quenching the reaction, and arachidonic acid (AA) levels were quantified by LC/MS-MS using AA-d8 as internal standard. PBMCs treated with CpG (1 µM) or CpG with an IL-6 neutralizing antibody were utilized (A; n = 6) or PBMCs treated with LPS, an IL-6 neutralizing antibody, or an isotype control were utilized (B; n = 5 for all groups except the group treated with LPS alone, n = 2). (C) Cell lysates from non-HD and HD individuals (n = 5) were pretreated with inhibitors of CES1 (WWL113) and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) (JZL184) (final concentration, 1 µM) or 0.1% DMSO for 30 min at 37 °C prior to adding 2-AG. (D) Cell lysates from commercially obtained healthy PBMCs (n = 5 individuals) confirmed the results observed with non-HD and HD individuals. (E) CES activity of commercially obtained PBMCs (n = 5 individuals) was determined by measuring the hydrolysis of the pan-CES substrate pNPVa (final concentration, 500 µM). JZL184 or WWL113 (final concentration, 1 µM) was utilized in some experiments to inhibit CES activity. Three technical replicates were run for each individual. * p < 0.05 as compared to DMSO of same treatment group. Differences between groups and treatments were assessed by one-way analysis of variance (D,E) and two-way analysis of variance (A–C).