Abstract
A proportion of neoplastic polyps are incompletely resected, resulting in local recurrence, especially after resection of large polyps or piecemeal resection. Local recurrences that develop after endoscopic resection of intramucosal neoplasms that lacked risk factors for lymph node metastasis or positive vertical margins are usually treated endoscopically. Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) is indicated for local residual or recurrent early carcinomas after endoscopic resection. However, ESD for such recurrent lesions is technically difficult and is typically a lengthy procedure. Underwater endoscopic mucosal resection (UEMR), which was developed in 2012, is suitable for recurrent or residual lesions and reportedly achieves superior en bloc resection rates and endoscopic complete resection rates than conventional EMR. However, a large recurrent lesion is a negative independent predictor of successful en bloc resection and of complete endoscopic removal. We therefore perform UEMR for relatively small (≤ 10-15 mm) recurrent lesions and ESD for larger lesions.
Keywords: Recurrence, Endoscopic management, Colon, Endoscopic submucosal dissection, Underwater endoscopic mucosal resection, Polyp, Endoscopic resection, Fibrosis, Non-lifting sign
Core tip: Local recurrences of neoplastic colonic polyps can occur, especially after resection of large polyps or piecemeal resection. Local recurrences that develop after endoscopic resection of intramucosal neoplasms that lacked risk factors for lymph node metastasis or positive vertical margins are usually treated endoscopically. We perform underwater endoscopic mucosal resection for relatively small (≤ 10-15 mm) recurrent lesions and endoscopic submucosal dissection for larger lesions.
INTRODUCTION
Adenomatous polyps are the commonest neoplasms found during colorectal cancer screening[1]. Detection and removal of these cancer precursors may prevent many cancers and reduce mortality[2]. However, a proportion of neoplastic polyps are incompletely resected[3], resulting in local recurrence, especially after resection of large polyps (≥ 20 mm), in 4.3% to 36.7% of cases[4-10]. Not only size[4,6,8-10], but also piecemeal resection[7,9-11], histology of adenoma (compared with serrated polyp)[5,10], and intraprocedural bleeding[6,10] are also reportedly risk factors for local recurrence. A systematic review found that local recurrence after endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) of non-pedunculated colorectal lesions occurs in 3% of en bloc resections and 20% of piecemeal resections; more than 90% of recurrences are detected 6 mo after EMR[12]. Periodic inspection by colonoscopy is desirable for early detection of local residual tumors/recurrences, and endoscopic management measures being suitable for many such lesions that are detected early[13]. The European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy guideline recommends endoscopic follow-up within 6 mo of piecemeal resection of adenomas larger than 10 mm[14]. Local recurrences that develop after endoscopic resection of intramucosal neoplasms that lacked risk factors for lymph node metastasis or positive vertical margins are usually treated endoscopically. Here we review and summarize the management of local recurrence after endoscopic resection.
MANAGEMENT OF LOCAL RECURRENCE AFTER ENDOSCOPIC RESECTION
Several groups have reported their management of local recurrences. Hotta et al[11] reported performing additional endoscopic resection in 32 of 34 recurrent lesions (94%), the remaining two patients (6%) undergoing additional surgery. In a multicenter prospective study of 1000 consecutive wide-field EMRs, 93% (135 of 145) of local recurrences were successfully resected endoscopically, the remaining 10 being referred for surgery[6]. Knabe et al[7] reported a prospective two-center study of 243 consecutive patients with 252 adenomas resected endoscopically. Seventy-seven residual tumors and recurrences were all treated by endoscopic resection and/or argon plasma coagulation. Sakamoto et al[15] have reported a retrospective study of 60 consecutive patients with locally recurrent or residual tumors after endoscopic resection. Of 69 lesions in 60 patients, 67 were treated endoscopically, whereas two required surgical treatment. En bloc resection rates were 39% (23/58) with EMR (39%) and 56% (5/9) with endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD)[15].
According to the Japan Gastroenterological Endoscopy Society guidelines for colorectal ESD/EMR[13], ESD (Figure 1) is indicated for local residual or recurrent early carcinomas after endoscopic resection. Although most local recurrences can be treated endoscopically, additional endoscopic resection is technically challenging because of severe fibrosis at the original resection site because such fibrosis results in the non-lifting sign with submucosal fluid injection. Thus, ESD for such recurrences is technically difficult and typically a lengthy procedure.
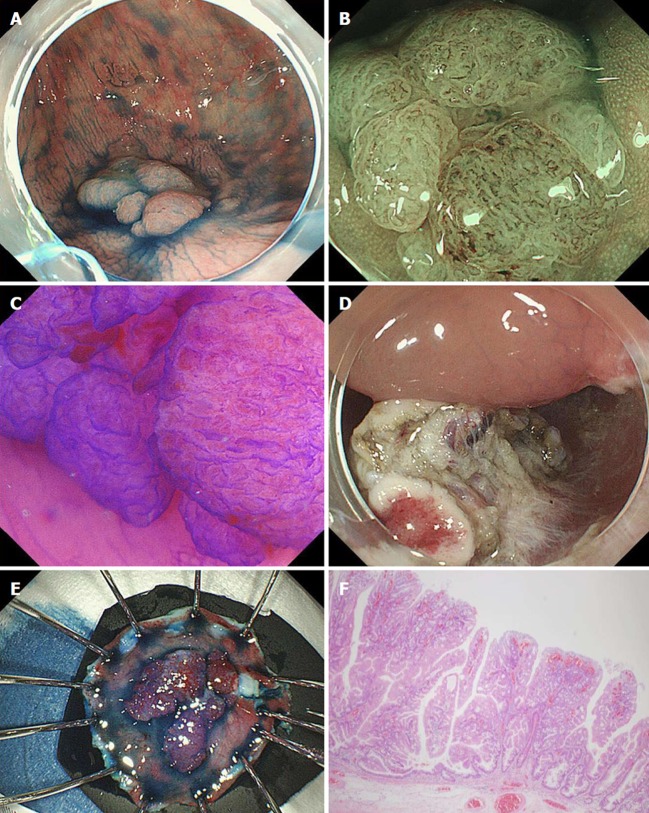
Figure 1.
Endoscopic submucosal dissection of recurrent lesion in the cecum. A: A Local recurrence (laterally spreading tumor, granular type) was identified in the cecum 18 mo after piecemeal endoscopic mucosal resection; B: The Japan Narrow-band imaging Expert Team classification was type 2B[19]; C: Kudo’s pit pattern was VI[20]. The laterally spreading tumor was diagnosed as an intramucosal lesion and ESD performed; D, E: Although there was severe fibrosis in the submucosal layer, en bloc resection was achieved; F: The pathological diagnosis was adenocarcinoma arising from a sessile serrated adenoma/polyp, type 0-IIa, 16 × 15 mm, pTis, pHM0, pVM0; ER0, Cur EA; pap > tub1, ly0, v0.
Underwater EMR (UEMR) was developed and described by Binmoeller et al[16] in 2012. In this procedure, air is evacuated from the affected segment of lumen and water infused until the lumen is complete full, at which stage hot snare polypectomy is performed without submucosal injection. This procedure is reportedly effective for resecting large polyps[16,17]. It is also suitable for recurrent or residual lesions. Kim et al[18] reported a retrospective, cross-sectional study of patients with recurrent adenoma after piecemeal EMR of colorectal laterally spreading tumor (≥ 2 cm). The en bloc resection rate (47% vs 16%, P = 0.002) and complete resection rate (89% vs 32%, P < 0.001) were significantly higher in the UEMR group (n = 36) than that of the conventional EMR (n = 44)[18]. Argon plasma coagulation of visible residual lesions during the salvage procedure was less frequently required in the UEMR than the EMR group (11% vs 66%, P < 0.001). The recurrence rate at follow-up colonoscopy was significantly lower in the UEMR group (10% vs 39%, P = 0.02). In this trial, UEMR was an independent predictor of en bloc resection and complete resection, whereas a large recurrent lesion is a negative independent predictor of successful en bloc resection and complete endoscopic removal. We therefore perform UEMR for relatively small (≤ 10-15 mm) recurrent lesions (Figure 2) and ESD for larger lesions.
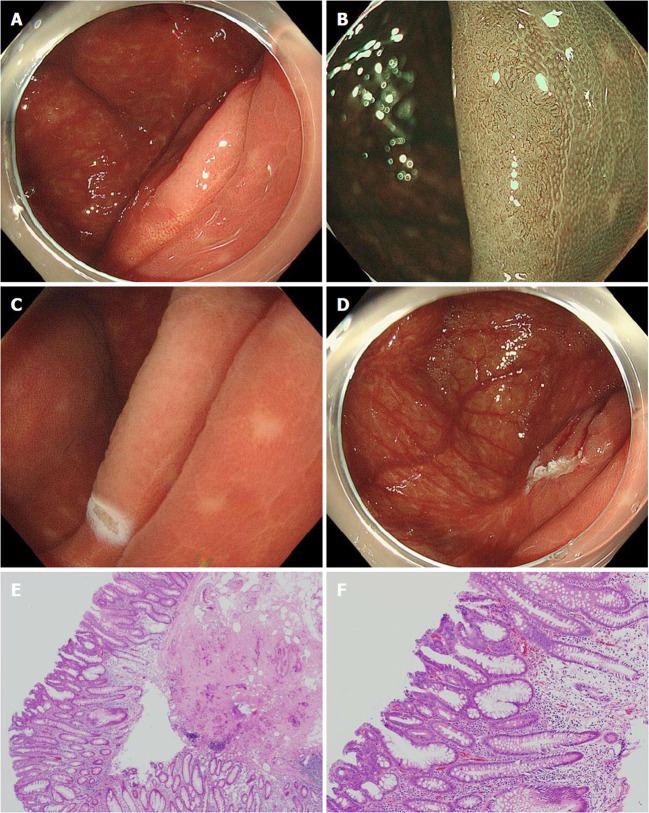
Figure 2.
Underwater endoscopic mucosal resection of a recurrent lesion in the cecum. A: A local recurrence was identified in the cecum 12 mo after en bloc endoscopic mucosal resection; B: Magnified endoscopy with narrow band imaging revealed Japan Narrow-band imaging Expert Team classification type 2A; C: Underwater endoscopic mucosal resection was performed after marking; D: Complete resection was achieved. E, F: The pathological diagnosis was low grade adenoma.
Even with the technical advances of ESD and development of UEMR, endoscopic treatment of recurrent lesions is still challenging. We therefore recommend precise diagnosis of the extent of naïve lesions by careful examination using indigo carmine and/or narrow band imaging endoscopy. We also recommend close follow-up after piecemeal resection or resection of large polyps.
Footnotes
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Manuscript source: Invited manuscript
Peer-review started: August 20, 2018
First decision: October 5, 2018
Article in press: November 8, 2018
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country of origin: Japan
Peer-review report classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P- Reviewer: Mutoh M; Dogan UB S- Editor: Dou Y L- Editor: A E- Editor: Tan WW
Contributor Information
Satoki Shichijo, Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Osaka International Cancer Institute, Osaka 541-8567, Chuo-ku, Japan. shichijiyou-tky@umin.ac.jp.
Yoji Takeuchi, Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Osaka International Cancer Institute, Osaka 541-8567, Chuo-ku, Japan.
Noriya Uedo, Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Osaka International Cancer Institute, Osaka 541-8567, Chuo-ku, Japan.
Ryu Ishihara, Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Osaka International Cancer Institute, Osaka 541-8567, Chuo-ku, Japan.
References
- 1.Lieberman DA, Rex DK, Winawer SJ, Giardiello FM, Johnson DA, Levin TR. Guidelines for colonoscopy surveillance after screening and polypectomy: a consensus update by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2012;143:844–857. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Nishihara R, Wu K, Lochhead P, Morikawa T, Liao X, Qian ZR, Inamura K, Kim SA, Kuchiba A, Yamauchi M, et al. Long-term colorectal-cancer incidence and mortality after lower endoscopy. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:1095–1105. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1301969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pohl H, Srivastava A, Bensen SP, Anderson P, Rothstein RI, Gordon SR, Levy LC, Toor A, Mackenzie TA, Rosch T, et al. Incomplete polyp resection during colonoscopy-results of the complete adenoma resection (CARE) study. Gastroenterology. 2013;144:74–80.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.09.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Khashab M, Eid E, Rusche M, Rex DK. Incidence and predictors of “late” recurrences after endoscopic piecemeal resection of large sessile adenomas. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;70:344–349. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2008.10.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Liang J, Kalady MF, Church J. Snaring large serrated polyps. Surg Endosc. 2013;27:1622–1627. doi: 10.1007/s00464-012-2640-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Moss A, Williams SJ, Hourigan LF, Brown G, Tam W, Singh R, Zanati S, Burgess NG, Sonson R, Byth K, et al. Long-term adenoma recurrence following wide-field endoscopic mucosal resection (WF-EMR) for advanced colonic mucosal neoplasia is infrequent: results and risk factors in 1000 cases from the Australian Colonic EMR (ACE) study. Gut. 2015;64:57–65. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2013-305516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Knabe M, Pohl J, Gerges C, Ell C, Neuhaus H, Schumacher B. Standardized long-term follow-up after endoscopic resection of large, nonpedunculated colorectal lesions: a prospective two-center study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014;109:183–189. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2013.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Rex KD, Vemulapalli KC, Rex DK. Recurrence rates after EMR of large sessile serrated polyps. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;82:538–541. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2015.01.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Oka S, Tanaka S, Saito Y, Iishi H, Kudo SE, Ikematsu H, Igarashi M, Saitoh Y, Inoue Y, Kobayashi K, et al. Local recurrence after endoscopic resection for large colorectal neoplasia: a multicenter prospective study in Japan. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015;110:697–707. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2015.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Pellise M, Burgess NG, Tutticci N, Hourigan LF, Zanati SA, Brown GJ, Singh R, Williams SJ, Raftopoulos SC, Ormonde D, et al. Endoscopic mucosal resection for large serrated lesions in comparison with adenomas: a prospective multicentre study of 2000 lesions. Gut. 2017;66:644–653. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-310249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hotta K, Saito Y, Matsuda T, Shinohara T, Oyama T. Local recurrence and surveillance after endoscopic resection of large colorectal tumors. Dig Endosc. 2010;22 Suppl 1:S63–S68. doi: 10.1111/j.1443-1661.2010.00965.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Belderbos TD, Leenders M, Moons LM, Siersema PD. Local recurrence after endoscopic mucosal resection of nonpedunculated colorectal lesions: systematic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy. 2014;46:388–402. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1364970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Tanaka S, Kashida H, Saito Y, Yahagi N, Yamano H, Saito S, Hisabe T, Yao T, Watanabe M, Yoshida M, et al. JGES guidelines for colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection/endoscopic mucosal resection. Dig Endosc. 2015;27:417–434. doi: 10.1111/den.12456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hassan C, Quintero E, Dumonceau JM, Regula J, Brandão C, Chaussade S, Dekker E, Dinis-Ribeiro M, Ferlitsch M, Gimeno-García A, et al. Post-polypectomy colonoscopy surveillance: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline. Endoscopy. 2013;45:842–851. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1344548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sakamoto T, Saito Y, Matsuda T, Fukunaga S, Nakajima T, Fujii T. Treatment strategy for recurrent or residual colorectal tumors after endoscopic resection. Surg Endosc. 2011;25:255–260. doi: 10.1007/s00464-010-1169-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Binmoeller KF, Weilert F, Shah J, Bhat Y, Kane S. “Underwater” EMR without submucosal injection for large sessile colorectal polyps (with video) Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;75:1086–1091. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2011.12.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Uedo N, Nemeth A, Johansson GW, Toth E, Thorlacius H. Underwater endoscopic mucosal resection of large colorectal lesions. Endoscopy. 2015;47:172–174. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1390749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kim HG, Thosani N, Banerjee S, Chen A, Friedland S. Underwater endoscopic mucosal resection for recurrences after previous piecemeal resection of colorectal polyps (with video) Gastrointest Endosc. 2014;80:1094–1102. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2014.05.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sano Y, Tanaka S, Kudo SE, Saito S, Matsuda T, Wada Y, Fujii T, Ikematsu H, Uraoka T, Kobayashi N, et al. Narrow-band imaging (NBI) magnifying endoscopic classification of colorectal tumors proposed by the Japan NBI Expert Team. Dig Endosc. 2016;28:526–533. doi: 10.1111/den.12644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kudo S, Rubio CA, Teixeira CR, Kashida H, Kogure E. Pit pattern in colorectal neoplasia: endoscopic magnifying view. Endoscopy. 2001;33:367–373. doi: 10.1055/s-2004-826104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]