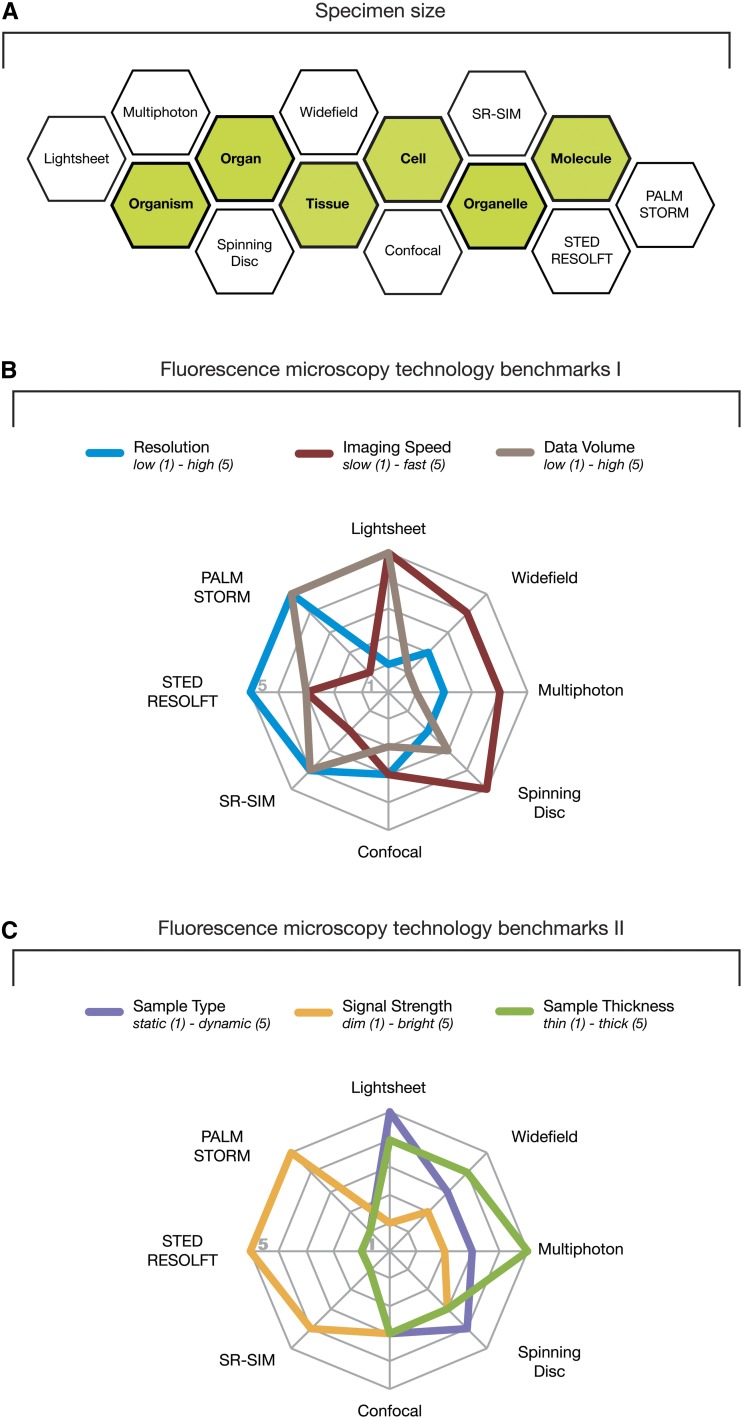
Figure 5.
Capabilities and limitations of fluorescence microscopy technologies. (A) A comprehensive set of fluorescence imaging technologies allow the visualization of specimens across multiple orders of magnitude in size, ranging from molecules to entire organisms. (B and C) Each individual fluorescence microscopy technology has its inherent capabilities and limitations with regard to the resolution of the final image, the imaging speed, the volume of generated data, the type and thickness of the sample, and the strength of the signal. For each fluorescence microscopy technology, these benchmark criteria are illustrated in two radar diagrams ranging from 1 (center) to 5 (margin) to facilitate comparison between imaging technologies and aid the selection of a suitable imaging technology that fulfills the experimental needs. PALM, Photo-Activated Localization Microscopy; RESOLFT, REversible Saturable Optical Linear Fluorescence Transitions; SR-SIM, Superresolution Structured Illumination Microscopy; STED, STimulated Emission Depletion; STORM, STochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy.