Figure 2.
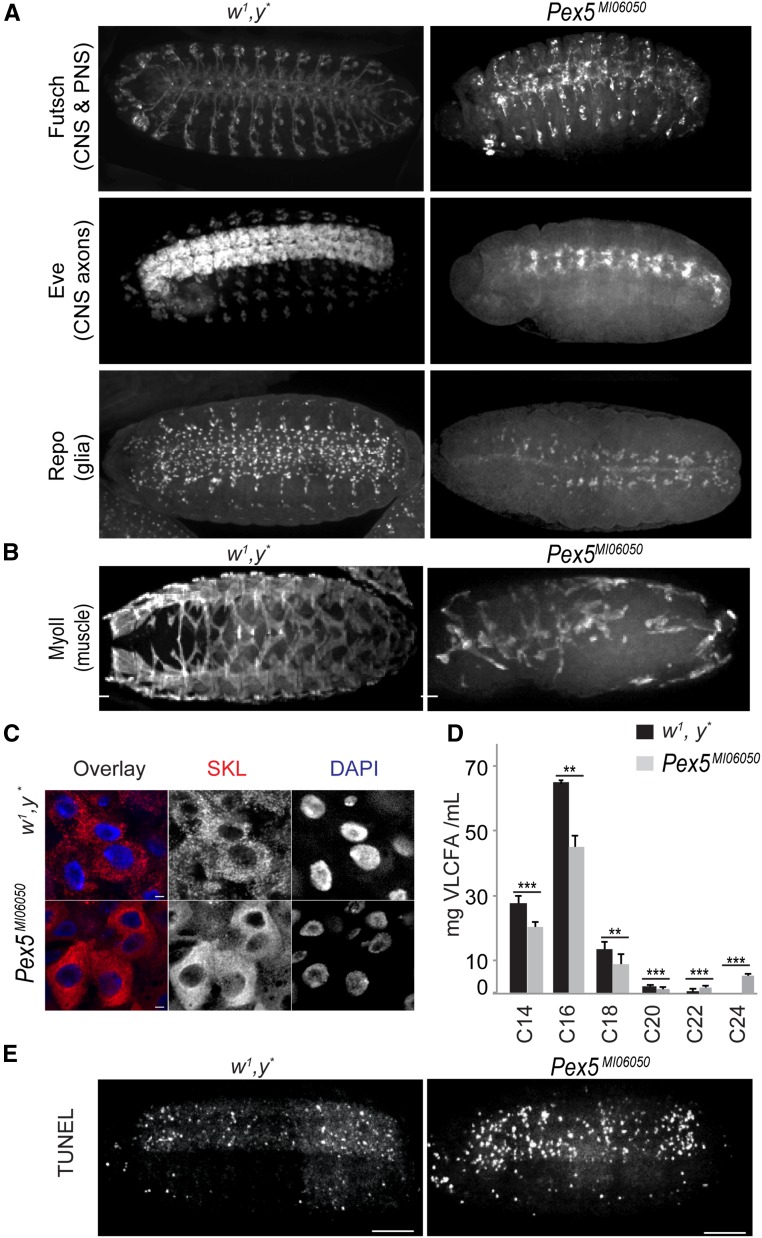
The Pex5MI06050 mutation affects CNS, PNS, and muscle structure. (A) The repeated segmental patterns of neurons of the CNS and PNS marked by anti-Futsch, CNS axons marked by anti-Even-skipped, and glial cells (except midline glia) marked by anti-Repo in control embryos (stage 15) were disrupted in Pex5MI06050/Pex5MI06050 embryos. Bar, 10 μm. (B) The repeated segmental pattern of developing muscles marked by anti-myosin II (MyoII) in control embryos was disrupted in Pex5MI06050/Pex5MI06050 embryos (stage 15). Bar, 10 μm. (C) Mature peroxisomes (punctate anti-SKL signal, red) are observed in the larval midgut. In Pex5MI06050/Pex5MI060 mutants, diffuse cytosolic anti-SKL staining and anti-SKL–positive aggregates indicate PTS1 import was impaired. DAPI-labeled nuclei are in blue. Bar, 2 μm. (D) Pex5MI06050/Pex5MI06050 mutants have lower amounts of C14, C16, C18, and C20 fatty acids and greater amounts of C22 and C24 fatty acids compared to control animals. Values are averages of four independent experiments ± SD; 1000 larvae per sample per each genotype were used in each replicate (4000 larvae total). Significance was determined using Student’s t-test; *** P < 0.001; ** P < 0.01. (E) Pex5MI06050/Pex5MI06050 embryos exhibit greater numbers of TUNEL-positive cells than control embryos. Images are representative of five independent experiments. N = 20 per experiment per genotype. Bar, 10 μm.