Abstract
The mesenchymal chondrosarcoma (MC) is a rare malignant tumour and accounts for less than 3% of primary chondrosarcomas. Mostly MC arises from the craniofacial bones, the ribs, the ilium, the femur and the vertebrae. A 54-year-old man was treated due to an icterus of unknown origin. The medical history of the patient consists of a multimodal treated MC of the thoracic vertebrae. A CT imaging identified a 2×4 cm sized mass of the pancreatic head. Suspecting a pancreatic head carcinoma surgical removal was performed. Histopathological a metastasis of MC was diagnosed. Our patient left the hospital after 17 days and died 23 month after surgery. Metastases of MC to the pancreas are rare. When detecting a mass of the pancreas in patients with a medical history of an MC, a metastasis of these tumour should be taken in consideration.
Keywords: pancreas and biliary tract, cardiothoracic surgery, surgical oncology, orthopaedic and trauma surgery
Background
The mesenchymal chondrosarcoma (MC) is a rare malignant tumour and was first described by Lightenstein and Bernstein in 1959.1 Macroscopically, this rare variant of a chondrosarcoma usually appears as a grey, well-defined, circumscribed mass with a diameter of up to 30 cm.2 Microscopically, the tumour is characterised by poorly differentiated small round cells and areas of well-differentiated hyaline cartilage.2 The small round cell components are immunhistochemically positive for SOX9, CD 99 and desmin.2 3
Case presentation
In February 2017, a 54-year-old man was treated in our hospital due to an icterus of unknown origin.
His medical history includes multimodal therapy of a rectal carcinoma in 2004. The patient had a palsy of the plexus brachialis with Horner’s syndrome following a motorcycle accident. Furthermore, in March 2015, he suffered from an acute spinal ataxia with paraparesis.
Differential diagnosis
A MRI revealed a tumour infiltration of the third thoracic vertebrae with compression of the spinal canal. A laminectomy with dorsal spondylodesis and marginal tumour resection was performed. The histopathological examination revealed an MC. The patient subsequently underwent adjuvant radiotherapy, chemotherapy and had no further tumour progress for 12 months.
In December 2016, the patient was referred to our hospital due to an icterus of unknown origin. We performed an endoscopic retrograde cholangiography with implantation of a bile duct-stent due to a stenosis of the ductus choledochus. A CT imaging identified a 2×4 cm sized ill-defined hypodense mass of the pancreatic head (figure 1), an 8 cm sized soft tissue tumour of the left proximal thigh and a disseminated bone metastasis of the sacral bone, the right ilium and the ribs.
Figure 1.
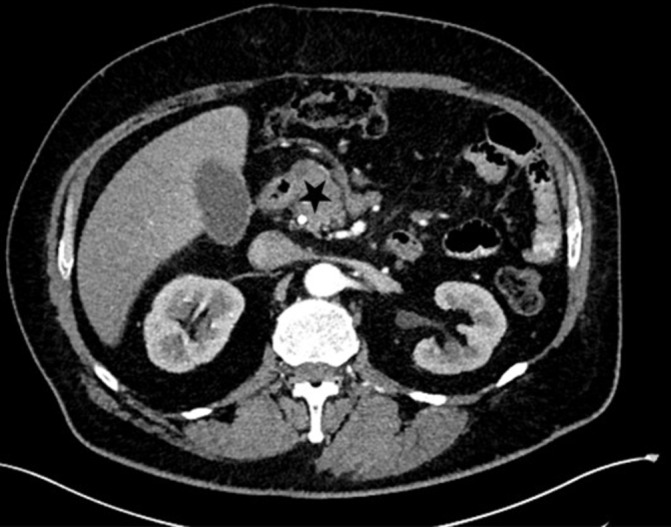
The CT imaging detected a 2×4 cm sized tumour of the pancreas head (marked by black star).
Following an interdisciplinary case discussion at our sarcoma board, we suspected a prognosis-determining pancreatic head carcinoma. We assigned the soft tissue tumour of the left proximal thigh and the bone metastasis to the known chondrosarcoma.
Treatment
An explorative laparotomy was indicated and performed. Intraoperatively, a tumour of the pancreas head without any evidence of macroscopic peripancreatic infiltration was detected. We performed a pylorus-preserving pancreatic head resection. The postinterventional course was prolonged due to a wound infection and a cholangitis. After wound revision and negative pressure wound therapy, we performed a secondary wound closure. The cholangitis was treated with antibiotics. The patient left the hospital after 17 days of treatment. The histopathological examination diagnosed surprisingly a 40 mm sized metastasis of the known extraskeletal MC of the pancreatic head. A lymphangioinvasion and hemangioinvasion, cone-shaped extension in the ductus choledochus, and another peripancreatic lymph node metastasis in one of 17 resected lymph nodes was revealed (figure 2). Immunohistochemically the tumour expressed S100.
Figure 2.
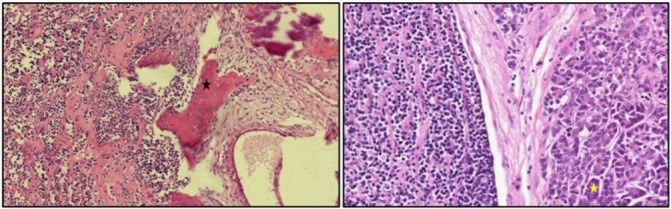
Histopathological examination revealed a mesenchymal chondrosarcoma. The left picture shows an abrupt transition between cartilaginous islands marked by black star and small blue cell components (HE staining, magnification ×10). The right picture shows the small cell proliferation on the left side surrounded by a myopericytomatous pattern in HE staining. The pancreatic tissue is marked by a yellow star (magnification ×20).
Outcome and follow-up
After a case discussion in our sarcoma board we recommended a palliative chemotherapy with epirubicine and ifosfamide. As follow-up MRI 6 month after chemotherapy was advised. The patient died 23 months after surgery.
Discussion
The aetiology of MC is unclear, however, in some cases various abnormalities on chromosome 8 eight have been described in literature.2 4 MC accounts for less than 3% of primary chondrosarcomas. Men and women are considered to be affected equally. The peak incidence is in the second and third decade of life.2 5 MC most commonly arises from the craniofacial bones, the ribs, the ilium, the femur and the vertebrae.5 The primary MC rarely arises from extraskeletal, as the most common extraosseous involvement MC can be determinated in the somatic soft tissue and the meninges.1 Also, intra-abdominal occurrences of MC are described in literature.5
Clinically, patients with MC very often suffer from pain due to the space-occupying effect caused by the growing tumour.2 6
The Ewing sarcoma and the enchondroma are described as the main differential diagnosis.2
To diagnose MC, a CT or an MRI is advised.2 The skeletal lesions appear mostly lytic and destructive with poor margins. Nevertheless, in comparison with conventional chondrosarcoma, the radiological features are unspecific. Chondroid-type calcification with contrast medium uptake may be revealed.2 Moreover, a fine-needle aspiration has been described as a sufficient diagnostic approach.7
This tumour entity is very rare and therefore, randomised clinical trials examining the effect of chemotherapy are lacking. A clear treatment strategy has not yet been defined. Generally, the therapy of MC consists of radical surgery and chemotherapy (methotrexate, doxorubicin, cisplatin and ifosfamide). But also neoadjuvant therapy in a non-metastatic stage and radiotherapy as a therapeutic approach have been published.6 After interdisciplinary case discussion at our sarcoma board an exploratory laparotomy was indicated. Not suspecting a metastasis of MC we made this decision. And to prevent local complications we did not conduct a fine needle aspiration according to our German guidelines.8 With the knowledge of a possible survival for years even in a metastatic stage, we wanted to surgical treat the suspected pancreas carcinoma.
The prognosis is poor and distant metastasis may occur much later on. The majority of metastasis of MC is skeletal. But also the intra-abdominal appearance of MC like in the case report at hand has been described in literature. To that some case reports were published concerning the primary and secondary occurrence of MC in the kidney as a rare extraperitoneal manifestation.9 10 Moreover, Suzuki et al treated a patient suffering from MC of the uterus.11 To our knowledge, only one case report of MC in the spleen was described in literature.12
Secondary tumours of the pancreas have been published to compose approximately 4% of pancreatic masses.13 Metastasis of MC to the pancreas is rare. Local recurrence may occur.14 We reviewed the literature using Pubmed and Google Scholar (table 1). The search yielded 12 relevant publications containing 14 cases (nine women, five men) of MC of the pancreas.7 14–24 The mean age was 34 years (range, 24–44). In most of the cases, the pancreas tail was affected (n=7). Only one patient suffered from MC of the pancreas head such as in the case report at hand. In two cases, MC primary appeared and in 11 cases, MC appeared secondary in the pancreas. With one exception MCs were surgical resected. Six patients underwent pancreatic surgery and had metastases of other sites. Most likely these authors did not expect a metastasis of MC either. The survival after surgery ranged in these cases between 15 and 120 months.14 17 19 20 24 To that Schneiderman et al conducted a survival analysis of MCs. Describing metastases as independent predictor of death a 44% 10-year-overall survival rate of patients suffering from extraskeletal MC has been described.25
Table 1.
Publications on mesenchymal chondrosarcoma (MC) of the pancreas
| Author | Year of publication | Gender | Age | Location | Size | Pathological findings | Treatment | Outcome |
| Years | Head/corpus/tail | cm | Secondary/primary MC | Month of survival after surgery | ||||
| Byun et al 15 | 1995 | Female | 36 | Tail | 7,7×4,3 | Secondary | Distal pancreatectomy, CT | NR |
| Komatsu et al 16 | 1999 | Female | 28 | Tail | 5,5 | Secondary | Distal pancreatectomy | NR |
| Yamamoto et al 17 | 2001 | Male | 29 | Corpus, Head | NR | Secondary | Enucleation (pancreas head) Distal pancreatectomy |
>120 |
| Yamamoto et al 17 | 2001 | Female | 40 | Head | NR | Secondary | pylorus-preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy | >72 |
| Naumann et al 18 | 2002 | Female | 24 | NR | NR | Secondary | RT, CT | >84* |
| Trembath et al 19 | 2003 | Female | 27 | NR | 9,5 | Secondary | CT, partial pancreatectomy | NR |
| Chatzipantelis et al 20 | 2006 | Male | 26 | Tail | 3,8×3,5 | Secondary | Distal pancreatectomy | NR |
| Oh et al 21 | 2007 | Male | 41 | Corpus, Tail | 13×12 x7 | Primary | Enucleation | NR |
| Bu and Dai22 | 2010 | Female | 34 | Corpus, Tail | 18×16 | Primary | Surgical resection of pancreas body and tail | >52 |
| Tsukamoto et al 23 | 2014 | Male | 39 | Corpus, Tail | 5×6 | Secondary | Distal pancreatectomy, CT | 34 |
| Guo et al 24 | 2015 | Male | 40 | Corpus | 2×3×2 | Secondary | Distal pancreatectomy | >108 |
| Smith et al 7 | 2015 | Female | 44 | Corpus | NR | Secondary | Distal pancreatectomy, CT | >24 |
| Cohen et al 14 | 2016 | Female | 32 | Tail | 2,9 | Secondary | Laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy, CT | 15 |
| Cohen et al 14 | 2016 | Female | 38 | Tail | 9,5 | Unknown | Distal pancreatectomy, systemic neoadjuvant CT | 40 |
*Month of survival after diagnosis of MC.
CT, chemotherapy; MC, mesenchymal chondrosarcoma; NR, not recorded; RT, radiotherapy.
Learning points.
Metastases of mesenchymal chondrosarcoma to the pancreas are rare. To our knowledge only 14 cases are published.
When detecting a mass of the pancreas in patients with medical history of MC, a metastasis of this tumour entity should be taken in consideration.
Acknowledgments
Mrs Dr Caroline Blind (histopathological examination).
Footnotes
Contributors: CP, GDS, KRB and MWS took care of the patient. CP, GDS, KRB wrote the report. MWS evaluated the draft and suggested revisions. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding: The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests: None declared.
Patient consent: Obtained.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
References
- 1. Lightenstein L, Bernstein D. Unusual benign and malignant chondroid tumors of bone. A survey of some mesenchymal cartilage tumors and malignant chondroblastic tumors, including a few multicentric ones, as well as many atypical benign chondroblastomas and chondromyxoid fibromas. Cancer 1959;12:1142–57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Fletcher C, Bridge JA, Hogendoorn P FM. WHO ClAssification of tumours of soft tissue and bone. 5 4th edn, 2013:72–3. [Google Scholar]
- 3. Fanburg-Smith JC, Auerbach A, Marwaha JS, et al. Immunoprofile of mesenchymal chondrosarcoma: aberrant desmin and EMA expression, retention of INI1, and negative estrogen receptor in 22 female-predominant central nervous system and musculoskeletal cases. Ann Diagn Pathol 2010;14:8–14. 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2009.09.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Gatter KM, Olson S, Lawce H, et al. Trisomy 8 as the sole cytogenetic abnormality in a case of extraskeletal mesenchymal chondrosarcoma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2005;159:151–4. 10.1016/j.cancergencyto.2004.10.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Nakashima Y, Unni KK, Shives TC, et al. Mesenchymal chondrosarcoma of bone and soft tissue. A review of 111 cases. Cancer 1986;57:2444–53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Cesari M, Bertoni F, Bacchini P, et al. Mesenchymal chondrosarcoma. An analysis of patients treated at a single institution. Tumori 2007;93:423–7. 10.1177/030089160709300503 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Smith AL, Odronic SI, Springer BS, et al. Solid tumor metastases to the pancreas diagnosed by FNA: a single-institution experience and review of the literature. Cancer Cytopathol 2015;123:347–55. 10.1002/cncy.21541 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Leitlinienprogramm Onkologie (Deutsche Krebsgesellschaft, Deutsche Krebshilfe, AWMF): S3-Leitlinie Exokrines Pankreaskarzinom, Langversion 1.0, 2013, AWMF Registernummer: 032-010OL. http://leitlinienprogramm-onkologie.de/Leitlinien.7.0.html.
- 9. Kaneko T, Suzuki Y, Takata R, et al. Extraskeletal mesenchymal chondrosarcoma of the kidney. Int J Urol 2006;13:285–6. 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2006.01293.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Rothberg MB, Bhalodi AA, Reda EF, et al. Primary renal mesenchymal chondrosarcoma: a case report. Urology 2015;85:676–8. 10.1016/j.urology.2014.11.032 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Suzuki Y, Todo Y, Okamoto K, et al. Mesenchymal chondrosarcoma of the uterus. Pathol Int 2014;64:45–7. 10.1111/pin.12130 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Rossetto A, Saccomano E, Zompicchiatti A, et al. Mesenchymal chondrosarcoma of the spleen: report of a case. Tumori 2011;97:e10–15. 10.1177/030089161109700423 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Adsay NV, Andea A, Basturk O, et al. Secondary tumors of the pancreas: an analysis of a surgical and autopsy database and review of the literature. Virchows Arch 2004;444:527–35. 10.1007/s00428-004-0987-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Cohen JN, Solomon DA, Horvai AE, et al. Pancreatic involvement by mesenchymal chondrosarcoma harboring the HEY1-NCOA2 gene fusion. Hum Pathol 2016;58:35–40. 10.1016/j.humpath.2016.07.026 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Hun Byun JHK, Kim JA, Kim HK, et al. Extraskeletal Mesenchymal Chondrosarcoma of Thigh with Metastasis to Pancreas: A case report and literature review. Journal of the Korean Cancer Association 1995;27:1070–7. [Google Scholar]
- 16. Komatsu T, Taira S, Matsui O, et al. A case of ruptured mesenchymal chondrosarcoma of the pancreas. Radiat Med 1999;17:239–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Yamamoto H, Watanabe K, Nagata M, et al. Surgical treatment for pancreatic metastasis from soft-tissue sarcoma: report of two cases. Am J Clin Oncol 2001;24:198–200. 10.1097/00000421-200104000-00019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Naumann S, Krallman PA, Unni KK, et al. Translocation der(13;21)(q10;q10) in skeletal and extraskeletal mesenchymal chondrosarcoma. Mod Pathol 2002;15:572–6. 10.1038/modpathol.3880565 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Trembath DG, Dash R, Major NM, et al. Cytopathology of mesenchymal chondrosarcomas: a report and comparison of four patients. Cancer 2003;99:211–6. 10.1002/cncr.11300 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Chatzipantelis P, Karvouni E, Fragoulidis GP, et al. Clinicopathologic features of two rare cases of mesenchymal metastatic tumors in the pancreas: review of the literature. Pancreas 2006;33:301–3. 10.1097/01.mpa.0000234075.53630.2f [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Oh BG, Han YH, Lee BH, et al. Primary extraskeletal mesenchymal chondrosarcoma arising from the pancreas. Korean J Radiol 2007;8:541–4. 10.3348/kjr.2007.8.6.541 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Bu X, Dai X. Primary mesenchymal chondrosarcoma of the pancreas. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 2010;92:e10–12. 10.1308/147870810X12659688851672 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Tsukamoto S, Honoki K, Kido A, et al. Chemotherapy improved prognosis of mesenchymal chondrosarcoma with rare metastasis to the pancreas. Case Rep Oncol Med 2014;2014:1–5. 10.1155/2014/249757 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Guo J, Gu Y, Guo L, et al. A Case of mesenchymal chondrosarcoma arising from the femoral vein with 8 years of follow-up. Ann Vasc Surg 2015;29:1455.e1–5. 10.1016/j.avsg.2015.04.086 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Schneiderman BA, Kliethermes SA, Nystrom LM. Survival in mesenchymal chondrosarcoma varies based on age and tumor location: a survival analysis of the SEER database. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2017;475:799–805. 10.1007/s11999-016-4779-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


