Abstract
Background
The purpose of the Aging-ONDUAL-TASK study is to determine if a supervised dual-task program carried out in long-term nursing homes is able to attenuate frailty in a greater extent than the same multicomponent exercise program alone.
Methods
This multicenter randomized controlled trial will include 188 participants who will be randomly allocated to either a multicomponent exercise program or to the same multicomponent program with simultaneous cognitive training (dual-task training). Inclusion criteria are as follows: ≥ 70 years, ≥ 50 on the Barthel Index, ≥ 20 on the Mini Examen Cognoscitivo (MEC-35) who are able to stand up and walk independently for 10 m. Subjects in the multicomponent group will attend a twice-a-week multicomponent exercise program of 1-h duration per session, consisting of strength and balance exercises. Participants in the dual-task group will perform the same multicomponent exercise program with concurrent individually tailored cognitive tasks. Study assessments will be conducted at baseline and at 3 months. The primary outcome measure will be gait speed under dual-task conditions and secondary outcomes will include physical fitness measurements, gait spatiotemporal parameters, cognition and emotional assessments, several frailty scales and objectively measured physical activity.
Discussion
The present research will add valuable information to the knowledge around the effects of the dual-task program in long-term nursing home residents, taking altogether physical, cognitive and emotional variables linked to frailty.
Trial registration
Australian and New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry (ANZCTR) with the identifier: ACTRN12618000536268. Registration date: 11/04/2018.
Keywords: Dual-task, Frailty, Exercise, Physical activity, Long-term nursing home, Cognitive frailty, Dual-task intervention, Older adults, Aging
Introduction
The global increase in life expectancy and consequent aging of the population, leads to estimates that the number of dependent older adults will rise from 350 million in 2010 to 488 million by 2030 [1]. Accordingly, the number of older adults living in long-term nursing homes will also increase considerably. Older adults in long-term nursing homes represent a complex and heterogeneous population with a high prevalence of dependence in the activities of daily living, cognitive impairment, depression, high fall rates, multimorbidity and polymedication [2, 3]. In addition, long-term nursing home residents tend to be extremely inactive, engaging in sedentary activities for most of the day [4]. Thus, providing the best care for this population has become a challenge for both social and health care services [5].
In the last few years, research in aging has focused on frailty syndrome. Frailty is considered a state of vulnerability highly prevalent among the older adult population [6–8]. Although frailty has traditionally been described as a purely physical syndrome, a number of epidemiological studies have reported that frailty increases the risk of future cognitive decline and that cognitive impairment increases the risk of frailty, suggesting that physical frailty and cognitive impairment interact [9]. Cognition declines with age, with normal subtle cognitive changes that may affect everyday life functioning [10] and frail older adults usually perform worse in certain executive function and processing speed tests [11]. Recently, the International Academy on Nutrition and Aging (I.A.N.A) and the International Association of Gerontology and Geriatrics organized an International Consensus Group on “Cognitive Frailty”, which proposed a definition of cognitive frailty [12] and suggested that all frail older adults should undertake a complete cognitive evaluation, including executive function tests [13].
In consonance with this idea, an impaired capacity to perform attention-demanding mobility activities such as carrying out two tasks (physical + cognitive) simultaneously, also known as dual-task, could be a novel marker of physical and cognitive frailty. Many activities of daily life involve the performance of several tasks at a time, creating competing demands for attentional resources that challenge both motor and cognitive functions [14]. Considering that attentional capacity is limited, when demands exceed capacity, performance of dual-tasks can be affected compared to performance of the same tasks in a single-task fashion. Indeed, older adults show greater impairments compared to their younger counterparts in cognitive-motor dual-task performance, such as naming animals while walking or making calculations during balance exercises [15, 16]. Additionally, low dual-task performance capacity is associated with cognitive impairment and with a high risk of falling [17–19].
Previous studies of dual-task as a test of functional performance in older adults have focused on the gait speed test or on the Timed Up and Go test as physical tasks, while introducing semantic fluency or a calculus command as cognitive content. The difference between performance in the dual-task and the single-task tests is known as dual-task interference or dual-task cost [20]; this difference increases with aging [21]. The dual-task cost can be accounted for in both the physical and the cognitive domains. In this regard, the most commonly used formula is: dual-task cost = ((dual task − single task) single-task) × 100% [18]. For the physical dual-task cost calculation, time in seconds is used, whereas for the cognitive dual-task cost, either the number of correct responses or the percent of correct responses can be used to compare between single and dual task performances.
Dual-task performance can be modified with specific dual-task training [22, 23]. In fact, this type of intervention can maintain or even improve cognitive function [24, 25], especially executive function [26]. Two models have been suggested that might explain training-mediated dual-task performance changes [27]. The task-automatization model is based on the assumption that individual tasks can be automatized and predicts similar improvements either with single-task or dual-task training [27]. Alternatively, the task-integration model advocates for the efficient integration of both tasks through dual-task training, resulting in dual-task performance improvements [27]. According to the latter model, dual-task performance would only improve after dual-task but not single-task training. Furthermore, dual-task training may be superior to single-task training [28–30], since dual-task training requires greater cognitive and motor resources and is more complex in terms of control and coordination demands. Pellecchia et al. [31] observed greater improvements in postural sway under dual-task conditions after dual-task training compared to single-task training, supporting the task-integration model and suggesting that both physical and cognitive functions interact in a way still to be revealed.
To our knowledge, no studies have explored the effects of a supervised dual-task multicomponent exercise intervention in long-term nursing home facilities from a broad perspective of frailty, assessing functional capacity under single-task and dual-task conditions, physical activity, cognitive performance and emotional status. Therefore, we designed a randomized multicenter study, the Aging-ONDUAL-TASK study, to test hypothesis that the addition of cognitive training to a supervised multicomponent exercise program can improve gait speed performance under dual-task conditions by, at least 0.08 m/seg in a population of older adults in long-term nursing homes. The major aim of the Aging-ONDUAL-TASK study is to determine if a supervised dual-task program carried out in long-term nursing homes can attenuate frailty to a greater extent than the same multicomponent exercise program without cognitive training.
The Aging-ONDUAL-TASK study is based on a previous study [32, 33] in which feasibility regarding recruitment, adherence and safety of the multicomponent exercise program were successfully ascertained. A pilot study was performed to refine the outcome assessments, establish the progression of the cognitive training, and optimize the organizational infrastructure.
Methods
Study design and participants
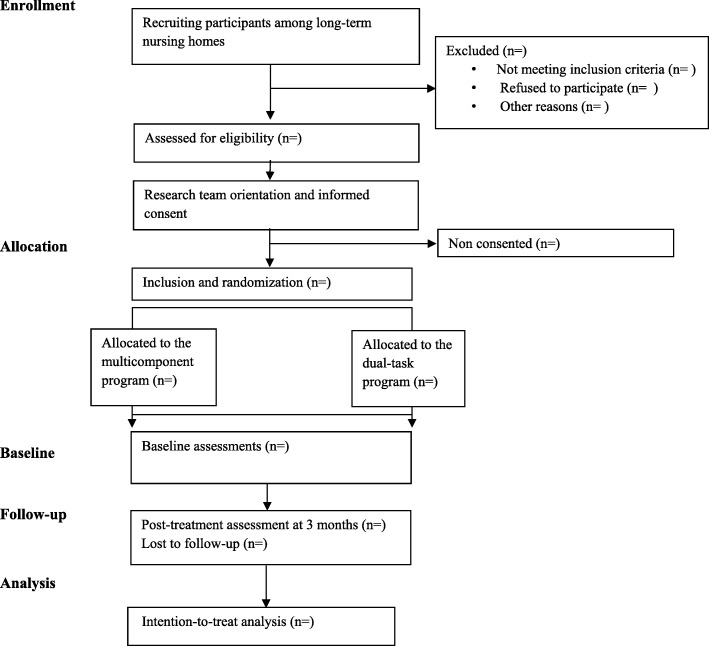
Based on the proposed objective, an experimental multicentre simple randomized study was designed (Aging-ONDUAL-TASK). Participants will be randomly allocated to either a multicomponent exercise program or to the same multicomponent program with simultaneous cognitive training (dual-task program). Participants will be recruited from eight long-term nursing homes in Gipuzkoa, Basque Country, Spain. Each site will enroll a minimum of 16 subjects and interventions will take place between June 2018 and December 2018. Researchers responsible for data gathering will be blinded to group assignment. The assessments will be carried out by research staff at baseline and at 3 months after the beginning of the intervention. The study has been designed and results will be reported following the CONSORT Statement extension for trials of non-pharmacological interventions and pragmatic intervention trials (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
Flow diagram of the study
Inclusion and exclusion criteria, recruitment, and randomization
The inclusion criteria, recruitment, and randomization methodologies in the Aging-ONDUAL-TASK study will be the same as on a previously published protocol [33]. The inclusion criteria will be: age ≥ 70 years old; a Barthel Index [34] score ≥ 50 and score ≥ 20 on the MEC-35 Test [35] [Mini-examen cognoscitivo, an adapted and validated version of Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE) in Spanish]; and capacity to stand up and walk independently for at least 10 m. Participants will not be eligible if they are judged clinically unstable by the medical staff, or have in any other condition in which entering the study would not be in the subject’s best interests.
Identification of individuals that meet the inclusion criteria will be facilitated by the databases of the included long-term nursing homes. The primary recruitment strategy will be information provided to the potential participants by the medical and nursing professionals from each facility. All volunteers will receive detailed study information at their reference sites through the research team: objectives, measurement variables, and other details about the interventions will be explained orally and in writing to both potential participants and their families. After signing the informed consent, the participants within each center will randomly be assigned (in a 1:1 ratio) through sealed opaque envelopes to either the multicomponent or the dual-task group by coin-tossing sequence generation.
Multicomponent exercise program
Feasibility and safety of the multicomponent exercise program were ascertained in a previous study which included full details on volume, intensity, and type of strength and balance exercises [32, 33]. Participants allocated to this group will attend a twice-a-week multicomponent exercise program of one-hour duration per session, consisting of strength and balance exercises conducted by an experienced physical trainer. Participants will also continue attending their usual activities and workshops.
Dual-task program
In the dual-task program, individually tailored cognitive tasks relying predominantly on executive function will be conducted concurrently with approximately four of the multicomponent exercises (Table 1).
Table 1.
Programation of the intervention for the 5th week
| Objective | Sesion 1 | Sesion 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Warm-up 5 min | Range of motion for different joints | Range of motion for different joints |
| Strength training | – | Arm curl 60% 2 sets 8–12 rep + DAT (cog) |
| Chair stand 60% 2 sets 8–12 rep |
Chair stand 60% 2 sets 8–12 rep |
|
| Leg flexion 60% 2 sets 8–12 rep + DAT (cog) |
– | |
| – | Leg extension 60% 2 sets 8–12 rep + Inhibition task |
|
| Leg abduction 60% 2 sets 8–12 rep + Calculus task |
– | |
| – | Hip extensión 60% 2 sets 8–12 rep |
|
| Standing on tips and heels 3 sets 10 rep + SAT |
Standing on tips and heels 3 sets 10 rep + SAT |
|
| Balance training | – | Feet together stance 2 sets 10 s + DAT (physical) |
| One legged stand 2 sets 10 s |
– | |
| Semi-tandem/Tandem 2 sets 10 s + DAT (physical) |
Semi-tandem/Tandem 2 sets 10 s + DAT (cog) |
|
| Circuit training 2 sets |
– | |
| – | Stepping 2 sets 10 rep | |
| Ball reaching 2 sets + Semantic memory |
– | |
| Cool down 5 min | Stretching, breathing, relaxing exercises. | Stretching, breathing, relaxing exercises. |
rep repetitions, DAT divided attention task, cog cognitive, SAT sustained attention task
The challenge of dual-task-s will be increased by augmenting the complexity of motor tasks (progressing from sitting to standing and from static to dynamic exercises, reducing base of support, etc) (Table 2) and/or cognitive tasks (number of stimuli, complexity of word categories, etc.) (Table 3).
Table 2.
Detailed description of the general DT group intervention
| 3 MONTHS | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Objective | 1ST MONTH Familiarisation phase |
2ND MONTH Strength development Static balance DT |
3RD MONTH Strength maintenance Dynamic balance DT |
| Strength | 3–4 ex: 1–2 sets, 8–12 rep at 40–50% of 1RM | 4–5 ex: 2 sets, 8–12 rep at 60% of 1RM | 4–5 ex:1–2 sets, 8–12 rep at 65–70% of 1RM |
| Balance | 2–3 ex, progressive difficulty in sitting position and progressing to standing position. | 4–5 ex, progressive difficulty in standing position with decreasing arm support and increasing instability. | |
| Dual-task | In 3–4 of strength ex | In 2–3 of strength ex and 1–2 of balance ex | In 1–2 of strength ex and 3–4 of balance ex |
ex exercises, rep repetitions
Table 3.
Progression of complexity of secondary tasks by levels of difficulty
| Main cognitive function | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Level 4 | Level 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Attention | Divided (cognitive) CATEGORIES:Buildings/ Dairy products/ colors | The participant will repeat a specific word from a certain category (e.g house) every time the instructor says it | The participant will raise a hand every time the instructor says a specific word from a certain category or when a green card is presented | The participant will raise a hand every time the instructor says two specific words from certain categories or when a green card is presented | The participant will raise a hand every time the instructor says two specific words from certain categories or when a green card is presented or when the instructor claps | The participant will raise a hand and repeat the word every time the instructor says two specific words from certain categories or when a green card is presented or when the instructor claps |
| Divided (physical) | Participants will carry out the physical task whilst maintaining a cup with a ball upright to avoid the ball from falling | |||||
| Sustained | Naming months of the year forward | Naming months of the year forward starting from a random month | Naming even or odd months of the year forward | Naming months of the year backwards | Naming months of the year backwards starting from a random month | |
| Shifting | Participants will be asked to shift focus from a cognitive task to another on some of the dual tasks | |||||
| Semantic fluency | Naming colors/days of the week/names | Naming members of the family/clothes | Naming professions | Naming cooking instruments or general tools | Naming fish, dog or tree types | |
| Inhibition | If the instructor says YES they respond NO and viceversa | Every time the instructor says HEADS they have to answer TAILS and viceversa and Previous entry | If a green card is presented they have to say RED and when a red card is presented they have to say GREEN | Level 2 and level 3 instructions altogether | If the word RED is presented in a green color they have to say GREEN and vice versa and when the word YES in red color or NO in green color, they have to name the color. | |
| Problem solving (calculus) | Counting by twos starting from a number ≥ 30 | Counting by threes from a number ≥ 50 | Substracting by twos from a number ≥ 30 | Substracting by threes from a number ≥ 50 | Substracting by fours from a number ≥ 100 | |
| Movement coordination | Inherent to the muticomponent exercise program | |||||
| Movement learning and sequencing | ||||||
The first week of the intervention will mainly serve to familiarize participants with the strength and balance exercises and adjust the level of difficulty of each cognitive function task to every participant in the group. In the second week, strength tests will be performed to individualize strength training and ensure training intensity. Throughout the following weeks, dual tasking will be applied mostly in strength exercises to train for divided attention allocation and will progressively move to balance exercises to optimize training adaptations and mimic everyday situations that require double tasking and increasing instability.
Cognitive training will be conducted based on six main cognitive functions essential for everyday life activities (Table 3). One of the most important functions to train is attention, which will be applied in form of: 1) divided attention tasks (with a secondary physical or cognitive task) where participants will have to divide their attention to ensure task achievement; 2) sustained attention tasks, in which attention will have to be maintained throughout a certain time period (1–2 min); 3) shifting, where participants will have to shift their focus of attention between cognitive tasks. In addition, semantic fluency will consist of naming words according to different categories with increasing difficulty such as naming animals, professions or even dog breeds. Other executive functions including calculus or inhibitory control will also be trained, the latter consisting of overriding the natural response to certain stimuli. Finally, due to the fact that movement coordination, movement learning and sequencing are inherent to any exercise-based program, these will be present in both the multicomponent exercise program group and in dual-task group.
Outcome measures
The primary outcome measure will be gait speed under dual-task conditions. The distance to be covered will be 9 m on a smooth non-slippery surface with starting and ending points marked on the floor with tape. The cognitive task to be performed will previously be explained to participants. Straight after the explanation, the participant will be asked to walk at a comfortable pace on a straight line while simultaneously performing the cognitive task. Time to perform the test will be measured following the procedure described by Bohannon [36]. Gait speed will be then calculated dividing the covered distance (in meters) by the employed time (in seconds).
In addition, both gait spatiotemporal parameters (cadence, single and double support time, etc.) and cognition (number of correct, incorrect and total responses) will be analyzed, and compared with performance in the single-task modality. This difference is referred to as dual-task cost, and will be calculated using the formula: ((dual task – single-task)/single-task × 100) [18].
Secondary outcome measures will include functional (Table 4), cognitive, and emotional assessments (Table 5). Functional capacity will be determined by the following tests (Table 4): the Short Physical Performance Battery test [37] (SPPB); the Senior Fitness Test [38] (SFT); the instrumented Timed Up and Go test [39] (iTUG; BTS Biomedical G-WALK triaxial accelerometer and gyroscope); usual walking speed [36]; the handgrip strength test [40] (Jamar dynamometer) and Berg balance test [41]. Frailty assessment will include the Tilburg Frailty index [42], the Frailty index [43] and the Rockwood clinical frailty scale [44]. In addition, participants will wear an accelerometer (Actigraph GT3X model (Actigraph LLC, Pensacola, FL, USA)) on the hip with a belt for 7 days to measure active and sedentary periods during everyday life, by daily step quantification. Active-period intensities will be classified as light, moderate or vigorous based on Freedson and colleagues’ criteria [45] and recorded in minutes.
Table 4.
Functional assessment tests
| Test (Reference) | Functions/Parameters | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB) (Guralnik et al., 1994)a | Lower extremity function: static balance, gait speed and getting in and out of a chair | Side-by-side, semi-tandem and tandem stands (10 s); 4 m walk test at comfortable speed and 5 quickly sit to stand from a chair without upper extremity assistance |
| Senior Fitness Test (Rikli & Jones, 2007)a | Upper and lower extremity strength and flexibility, static and dynamic balance and aerobic capacity | Chair-stands in 30 s; 6-min walking test; arm curl test (30 s); chair sit and reach; back scratch and 8 Foot Up and Go test |
| Instrumented Timed Up and Go test (BTS Biomedical G-WALK) (Mathias et al., 1986)a | Dynamic balance | Get up from a chair, walk 3 m at a normal pace, turn and walk back to sit down again |
| Instrumented walking speed (BTS Biomedical G-WALK) (Bohannon et al., 1996)a | Standard gait parameters: speed, step frequency, cadence | Walk for 4 and 9 m at comfortable speed |
| Bilateral handgrip strength test (Jamar dynamometer) (Fess, 1992)a | Hand grip strength | Squeeze the dynamometer with maximum isometric effort for about 5s |
| Berg balance test (Berg et al., 1992)a | Postural stability | Performance of 14 functional tasks |
| Accelerometry [Actigraph GT3X model (Actigraph LLC, Pensacola, FL, USA)] (Freedson et al., 1988)a | Active and sedentary periods during everyday life | 7 days period quantification of the number of steps performed per day and minutes completed at light, moderate or vigorous intensity |
aRodriguez-Larrad et al. [33]
Table 5.
Cognitive and Emotional assessment tests
| Test (Reference) | Functions | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) (Coen et al., 2016)a | Mild Cognitive Impairment, Early Alzheimer’s disease | Covered domains: attention and concentration, executive functions, memory, language, visuoconstructional skills, conceptual thinking, calculations, orientation |
| Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS-IV) (Wechsler et al., 2010) | Cognitive impairment | Covered domains: attention, visual scanning, motor speed |
| Trail Making Test (TMT) (Reitan, 1958) | Cognitive impairment | Assesses: visual-conceptual and visual-motor tracking, sustained attention and task alternation abilities |
| Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test (RAVLT) (Lezak, 1995) | Memory and learning capacity | Evaluates short- and long-term verbal memory assessing the ability to learn a list of 15 common words |
| Anxiety and Depression Goldberg Scale (Goldberg et al., 1988)a | Affective state | Includes nine depression and nine anxiety items from the past month |
| The Jong Gierveld loneliness scale (de Jong-Gierveld, 1987) | Emotional and social loneliness | Includes characteristics of the social network, background variables, personality characteristics, and evaluative aspects |
| Questionnaire QoL-AD (Logsdon et al., 2002) | Perceived quality of life | Self-rated quality of life for people with cognitive impairments |
aRodriguez-Larrad et al. [33]
For cognitive and emotional assessment (Table 5), participants will be assessed through the Montreal Cognitive Assessment [46] (MoCA), the Coding and Symbol Search test (which provide a measure of processing speed) from the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale, Fourth Edition (WAIS-IV) [47], the Trail Making Test part A [48] (TMT), the Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test [49] (RAVLT), the Anxiety and Depression Goldberg Scale [50], the Jong Gierveld loneliness scale [51], and the Quality of Life Alzheimer’s disease scale [52] (QoL-AD).
The following additional variables will also be registered: sociodemographic variables: age, gender, socioeconomic situation, educational level, and marital status; level of independence in activities of daily living: Barthel index [34]; cognitive impairment assessed through MEC-35 [35]; anthropometric measurements: weight, height, body mass index, waist and hip circumferences, and waist-to-hip ratio; and clinical outcomes Charlson comorbidity index [53], number of falls, visits to the emergency service, number and length of hospitalizations, death rates, and medication.
Dual-task assessment
The secondary tasks included in the dual-task evaluation will be of three different natures: 1) semantic fluency: naming animals or fruits and vegetables; 2) backward counting by ones; and 3) inhibition ability through the Go no go test (when the evaluator says ‘one’, the participant has to respond ‘two’ and viceversa). We selected these tasks by the following process: a) a review of the literature, b) expert consultation through interviews and a discussion group, c) final selection.
Cognitive tasks will be applied during two different physical function tests: 9 m usual gait speed and the Timed Up and Go test. In addition, these physical tasks will be performed in a single task mode to allow for dual-task cost calculation. Dual-task gait speed and dual-task Timed Up and Go tests will be performed on two non-consecutive testing days to minimize learning effects and the order of the dual-task and the single-task will be randomized for the same purpose. In addition, participants will wear an accelerometer (BTS Biomedical G-WALK triaxial accelerometer and gyroscope) during the tests to measure gait kinematic parameters such as step number, cadence, step symmetry, and step time variability. The number of total responses, errors, repetitions, and stops will be recorded. No instructions will be given regarding task prioritization.
Safety assessments
All co-existing diseases or conditions related to the intervention will be treated in accordance with prevailing medical practice and will be reported as an adverse event. In cases where the functional and cognitive state of a participant decreases due to an adverse event (e.g. illness, falls, etc.) the program will be individualized and adapted for that person upon her/his return.
Power and sample size
Sample size for the current study was calculated to detect a significant clinical difference on the dual-task gait speed test [54]. Accepting an alpha risk of 0.05 and a beta risk of 0.20 in a bilateral contrast, 141 individuals are required to detect a difference equal to or greater than 0.08 m/seg in the dual-task gait speed test (SD = 0.24). The sample size was increased by 20% to account for losses during follow-up and an additional 5% for mortality. The resulting sample size is 188 individuals, allocating 94 participants to each group.
Statistical considerations
Data analysis will be performed using the IBM SPSS Statistics 24 statistical software package (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL). Intention-to-treat analyses will be performed and the level of statistical significance will be set at p < .05 for all computations. First, all data will be checked for normality of distribution using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Results will be expressed as mean (with standard deviation) for continuous and normally distributed variables and as median (with interquartile range) when normality of data for that variable cannot be assumed. In the case of categorical variables, frequency counts and percentages will be used to describe the results. Tests for baseline comparisons will be selected based on the nature and distribution of the data: Student’s-t test with continuous and normally distributed variables, Mann-Whitney test with non-normally distributed continuous variables, and Chi-squared test with categorical variables.
To test the effects of training interventions, mixed-designed ANCOVA-s or the Friedman test, including baseline measurements, age, or gender as covariates, will be performed for physical, cognitive, and emotional variables. In cases where a significant F value is found, LSD post hoc procedures will be performed for pairwise comparisons.
Discussion
The current trial is a large multi-center randomized study aiming to investigate whether dual-task performance, including gait and cognitive parameters, can be improved by specific dual-task training. So far, guidelines for the geriatric population and professionals working in the field are scarce, despite the exponentially increasing number of people above 65 years old. Older adults in long-term nursing homes are at particular risk of adverse outcomes and have been the focus of interventions aiming to prevent or reverse frailty [55].
The results of the present study will add valuable knowledge about the effects of the dual-task program in long-term nursing home residents, taking together functional, cognitive, and emotional variables linked to frailty. Particularly, analysis of a multicomponent exercise program and the same program with simultaneous cognitive training, or dual-task, will help us to design interventions to improve or at least maintain functionality and cognition in long-term nursing home residents.
One of our main concerns at the time of designing the dual-task intervention was the fact that when performing a dual-task exercise, the execution velocity of the physical task could be reduced when compared with a single task exercise. In addition, movement technique could also be altered if compared to single task training. Consequently, we feared that a dual-task program might affect physical performance and hence not improve physical parameters to the same extent as the multicomponent program. Thus, we conducted a pilot study to ascertain if both the multicomponent and the dual-task programs produce similar training adaptations, in which we successfully observed significant physical improvements in both groups [56].
Methodological strengths of the present study include the fact that the dual-task program here is based on a previously published physical exercise protocol. This protocol was feasible and demonstrated improvements in many functional outcomes [32, 33]. In addition, the proposed interventions are easy to deliver and include exhaustive practical information regarding implementation such as training frequency, volume, intensity, individualization, and resting periods. This will allow an easy and straightforward implementation in long-term nursing homes. The existing literature about exercise protocols for older adults living in long-term care facilities includes few randomized controlled trials and the methodology tends to be heterogeneous. Furthermore, description of the methods used is often not enough to allow for replication.
We also recognize possible limitations to the study. The selected inclusion criteria preclude the majority of long-term nursing home residents, as we will include light to moderately dependent subjects while the prevalent profile in this type of institution is severely dependent. Consequently, we might encounter difficulties reaching the desired sample size. However, the large number of agreements made with long-term care institutions will facilitate the recruitment of enough subjects.
The proposed interventions will help to define the best approach to prevent the functional, cognitive, and emotional decline associated with age in older adults living in long-term nursing homes, considering feasibility and adherence.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all the forthcoming participants and their families for their cooperation and their confidence in the research team. The authors also would like to express their gratitude to all the nursing home staff for their time and assistance during the coming fieldwork process: the Bermingham, Lamourous, Julián Rezola (Matia), Anaka (Caser), Betharram (Caser), Zorroaga, Villa Sacramento (DomusVi), Berra (DomusVi), and San Markosene long-term nursing homes.
Funding
This research is supported by a research grant from the Basque Government (RIS3 316/07; ELKARTEK17/61; N°. EXPT.: KK-2017/00085; “Etorkizuna Erakiz”). This research was partially supported by the University of the Basque Country (UPV/EHU) (PPG17/34) and the Basque Government (IT922–16). Chloe Rezola and Haritz Arrieta are supported by two fellowships from University of the Basque Country (UPV/EHU).
Availability of data and materials
‘Not applicable’.
Abbreviations
- I.A.N.A
International Academy on Nutrition and Aging
- iTUG
instrumented Timed Up and Go test
- MEC-35
Mini Examen Cognoscitivo
- MMSE
Mini Mental State Examination
- MoCA
Montreal Cognitive Assessment
- QoL-AD
Quality of Life Alzheimer’s disease scale
- RAVLT
Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test
- SFT
Senior Fitness Test
- SPPB
Short Physical Performance Battery test
- TMT
Trail Making Test
- WAIS-IV
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale, Fourth Edition
Authors’ contributions
SMG, JI, ARL and JJY conceived and designed the experiments; CR and HA performed the experiments; CR and ARL analyzed and interpreted the data; MI contributed the recruitment of the participants; CR, ARL, SMG, JI and MI wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study has been approved by the Committee on Ethics in Research of the University of the Basque Country (Humans Committee Code M10/2016/105). All participants will provide written informed consent based on documents approved by the University of the Basque Country Institutional Review Board. In addition, the study will be conducted in accordance with Good Clinical Practice, applicable local regulatory requirements, and the guiding principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent for publication
‘Not applicable’.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Chloe Rezola-Pardo, Email: chloe.rezola@ehu.eus.
Haritz Arrieta, Email: haritz.arrieta@ehu.eus.
Susana Maria Gil, Email: susana.gil@ehu.eus.
Jose Javier Yanguas, Email: javiyanguaslezaun@gmail.com.
Miren Iturburu, Email: miren.iturburu@matiainstituto.net.
Jon Irazusta, Email: jon.irazusta@ehu.eus.
Begoña Sanz, Email: mariabegona.sanz@ehu.eus.
Ana Rodriguez-Larrad, Phone: +34-619-12-47-40, Email: ana.rodriguez@ehu.eus.
References
- 1.Prince M, Prina M, Guerchet M. Journey of caring, an analysis of long-term Care for Dementia. World Alzheimer report 2013. London: Alzheimer’s Disease International; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 2.De Souto BP, Morley JE, Chodzko-Zajko W, et al. Recommendations on physical activity and exercise for older adults living in long-term care facilities: a taskforce report. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2016;17(5):381–392. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2016.01.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bercovitz A, Dwyer LL, Jones A, et al. The National Nursing Home Survey 2009; 2004 overview. Vital Health Stat. 2009;13(167):1–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bates-Jensen BM, Alessi CA, Cadogan M, et al. The minimum data set bedfast quality indicator: differences among nursing homes. Nurs Res. 2004;53(4):260–272. doi: 10.1097/00006199-200407000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Pereira C, Rosado H, Cruz-Ferreira A, et al. Effects of a 10-week multimodal exercise program on physical and cognitive function of nursing home residents: a psychomotor intervention pilot study. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2017. 10.1007/s40520-017-0803-y. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 6.Rodriguez-Manas L, Fried LP. Frailty in the clinical scenario. Lancet. 2015;385(9968):e7–e9. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61595-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Collard RM, Boter H, Schoevers RA, et al. Prevalence of frailty in community-dwelling older persons: a systematic review. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2012;60(8):1487–1492. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2012.04054.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Santos-Eggimann B, Cuénoud P, Spagnoli J, et al. Prevalence of frailty in middle-aged and older community-dwelling Europeans living in 10 countries. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2009;64(6):675–681. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glp012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Robertson DA, Savva GM, Kenny RA. Frailty and cognitive impairment—a review of the evidence and causal mechanisms. Ageing Res Rev. 2013;12(4):840–851. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2013.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Harada CN, Love MC, Triebel K. Normal cognitive aging. Clin Geriatr Med. 2013;29(4):737. doi: 10.1016/j.cger.2013.07.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Langlois F, Vu TT, Kergoat MJ, et al. The multiple dimensions of frailty: physical capacity, cognition, and quality of life. Int Psychogeriatr. 2012;24(9):1429–1436. doi: 10.1017/S1041610212000634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kelaiditi E, Cesari M, Canevelli M, et al. Cognitive frailty: rational and definition from an (I.a.N.a./I.a.G.G.) international consensus group. J Nutr Health Aging. 2013;17(9):726–734. doi: 10.1007/s12603-013-0367-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Martínez-Ramírez A, Martinikorena I, Lecumberri P, et al. Dual task gait performance in frail individuals with and without mild cognitive impairment. Dement Geriatr Cogn Dis. 2016;42(1–2):7–16. doi: 10.1159/000447451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Plummer P, Zukowski LA, Giuliani C, et al. Effects of physical exercise interventions on gait-related dual-task interference in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gerontology. 2015;62(1):94–117. doi: 10.1159/000371577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wickens CD. Multiple resource and performance prediction. Theor Issues Ergon Sci. 2002;3:159–177. doi: 10.1080/14639220210123806. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Albinet C, Bernard PL, Palut Y. Attentional control of postural stability in institutionalised elderly people: effects of a physical exercise program. Ann Readapt Med Phys. 2006;49:625–631. doi: 10.1016/j.annrmp.2006.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Beauchet O, Annweiler C, Dubost V, et al. Stops walking when talking: a predictor of falls in older adults? Eur J Neurol. 2009;16:786–795. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-1331.2009.02612.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Plummer-D’Amato P, Brancato B, Dantowitz M, et al. Effects of gait and cognitive task difficulty on cognitive-motor interference in aging. J Aging Res. 2012. 10.1155/2012/583894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 19.Faulkner KA, Redfern MS, Cauley JA, et al. Multitasking: association between poorer performance and a history of recurrent falls. JAGS. 2007;55:570–576. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2007.01147.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Yogev-Seligmann G, Hausdorff JM, Giladi N. The role of executive function and attention in gait. Mov Disord. 2008;23:329–342. doi: 10.1002/mds.21720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Al-Yahya E, Dawes H, Smith L, et al. Cognitive motor interference while walking: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2011;35:715–728. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2010.08.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Falbo S, Condello G, Capranica L, et al. Effects of physical-cognitive dual task training on executive function and gait performance in older adults: a randomized controlled trial. Biomed Res Int. 2016. 10.1155/2016/5812092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 23.Halvarsson A, Franzen E, Stahle A. Balance training with multi-task exercises improves fall-related self-efficacy, gait, balance performance and physical function in older adults with osteoporosis: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil. 2015;29(4):365–375. doi: 10.1177/0269215514544983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Langdon KD, Corbett D. Improved working memory following novel combinations of physical and cognitive activity. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2012;26:523–532. doi: 10.1177/1545968311425919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Schaefer S, Schumacher V. The interplay between cognitive and motor functioning in healthy older adults: findings from dual-task studies and suggestions for intervention. Gerontology. 2011;57(3):239–246. doi: 10.1159/000322197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Prakash RS, Voss MW, Erickson KI, et al. Physical activity and cognitive vitality. Annu Rev Psychol. 2015;66(1):769–797. doi: 10.1146/annurev-psych-010814-015249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Silsupadol P, Siu KC, Shumway-Cook A, et al. Training of balance under single- and dual-task conditions in older adults with balance impairment. Phys Ther. 2006;86(2):269–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Silsupadol P, Shumway-Cook A, Lugade V, et al. Effects of single-task versus dual-task training on balance in older adults: a double-blind, randomized controlled trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2009;90:381–387. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2008.09.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Silsupadol P, Lugade V, Shumway-Cook A, et al. Training-related changes in dual-task walking performance of elderly persons with balance impairment: a double-blind, randomized controlled trial. Gait Posture. 2009;29:634–639. doi: 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2009.01.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wollesen B, Voelcker-Rehage C. Training effects on motor–cognitive dual-task performance in older adults. Eur Rev Aging Phys Act. 2013;11(1):5. doi: 10.1007/s11556-013-0122-z. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Pellecchia GL. Dual-task training reduces impact of cognitive task on postural sway. J Mot Behav. 2005;37(3):239–246. doi: 10.3200/JMBR.37.3.239-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Arrieta H, Rezola-Pardo C, Zarrazquin I, et al. A multicomponent exercise program improves physical function in long-term nursing home residents: a randomized controlled trial. Exp Gerontol. 2018;8(103):94–100. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2018.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Rodriguez-Larrad A, Arrieta H, Rezola C, et al. Effectiveness of a multicomponent exercise program in the attenuation of frailty in long-term nursing home residents: study protocol for a randomized clinical controlled trial. BMC Geriatrics. 2017;17(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s12877-017-0453-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wade DT, Collin C. The Barthel ADL Index: a standard measure of physical disability? Int Disabil Stud. 1988;10(2):64–67. doi: 10.3109/09638288809164105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lobo A, Saz P, Marcos G, et al. Revalidación y normalización del Mini-Examen Cognoscitivo (primera versión en castellano del Mini-Mental Status Examination) en la población general geriátrica. Med Clin (Barc) 1999;112(20):767–774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Bohannon RW, Andrews AW, Thomas MW. Walking speed: reference values and correlates for older adults. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 1996;24(2):86–90. doi: 10.2519/jospt.1996.24.2.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Guralnik JM, Simonsick EM, Ferrucci L, et al. A short physical performance battery assessing lower extremity function: association with self-reported disability and prediction of mortality and nursing home admission. J Gerontol. 1994;49(2):M85–M94. doi: 10.1093/geronj/49.2.M85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Rikli RE, Jones CJ. Senior fitness test. Champaign: Human Kinetics; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Mathias S, Nayak US, Isaacs B. Balance in elderly patients: the “get-up and go” test. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1986;67(6):387–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Fess EE. Grip strength. In: Casanova JS, editor. Clinical assessment recommendations, 2nd ed. Chicago: American Society of Hand Therapists; 1992. pp. 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Berg KO, Wood-Dauphinée SL, Williams JI, et al. Measuring balance in the elderly: validation of an instrument. Can J Publ Health. 1992;83:S7–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Gobbens RJ, van Assen MA, Luijkx KG, et al. The Tilburg frailty Indicator: psychometric properties. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2010;11(5):344–355. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2009.11.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Fried LP, Tangen CM, Walston J, et al. Frailty in older adults: evidence for a phenotype. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2001;56(3):M146–M156. doi: 10.1093/gerona/56.3.M146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Rockwood K, Song X, MacKnight C, et al. A global clinical measure of fitness and frailty in elderly people. CMAJ. 2005;173(5):489–495. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.050051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Freedson PS, Melanson E, Sirard J. Calibration of the computer science and applications, Inc. accelerometer. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1998;30(5):777–781. doi: 10.1097/00005768-199805000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Coen RF, Robertson DA, Kenny RA, et al. Strengths and limitations of the MoCA for assessing cognitive functioning findings from a large representative sample of Irish older adults. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 2016;29(1):18–24. doi: 10.1177/0891988715598236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wechsler D. WAIS-IV UK Administration and scoring manual. London: Pearson; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Reitan RM. Validity of the trail making test as an indicator of organic brain damage. Percep Mot Skills. 1958;8:271–276. doi: 10.2466/pms.1958.8.3.271. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Ponton MO. Research and assessment issues with Hispanic populations. In: Neuropsychology and the Hispanic patient: a clinical handbook. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 2001. p. 39–58.
- 50.Goldberg D, Bridges K, Duncan-Jones P, et al. Detecting anxiety and depression in general medical settings. Br Med J. 1988;297(6653):897–899. doi: 10.1136/bmj.297.6653.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.de Jong-Gierveld J. Developing and testing a model of loneliness. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1987;53(1):119–128. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.53.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Logsdon RG, Gibbons LE, McCurry SM, et al. Assessing quality of life in older adults with cognitive impairment. Psychosom Med. 2002;64:510–519. doi: 10.1097/00006842-200205000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Charlson M, Szatrowski TP, Peterson J, et al. Validation of a combined comorbidity index. J Clin Epidemiol. 1994;47(11):1245–1251. doi: 10.1016/0895-4356(94)90129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Perera S, Mody SH, Woodman RC, et al. Meaningful change and responsiveness in common physical performance measures in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006;54(5):743–749. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2006.00701.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.World Health Organization. Regional Committee for Europe 66th Session. Action plan for the prevention and control of noncommunicable diseases in the WHO European Region. Copenhagen, Denmark, 12–15 September 2016. http://www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0011/315398/66wd11e_NCDActionPlan_160522.pdf?ua=1.
- 56.Rezola-Pardo C, Arrieta H, Vidán A, et al. Comparación de un programa de ejercicio físico multicomponente con un programa de ejercicio multicomponente dual (dual-task) en la función física de personas mayores de centros residenciales: datos preliminares del estudio Aging-ONDUAL-TASK. 2018; XVII Congress of Zahartzaroa.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
‘Not applicable’.