Abstract
Background
Giant cell tumor of bone (GCTB) is a locally aggressive tumor, and its postoperative recurrence remains a problem. The present meta-analysis aimed to analyze the effect of bisphosphonates (BPs) on local recurrence of GCTB.
Methods
Seven case–control studies were included by computerized searches of bibliographic databases (PubMed, AMED, EMBASE, the Cochrane library, ISI Web of Science, and China National Knowledge Infrastructure). The pooled adjusted ORs were calculated to evaluate the local recurrence of GCTB.
Results
The BP group presented significantly lower total local recurrence rate than the control group in GCTB (P<0.01). Subgroup analysis shows BP group presented significantly lower local recurrence than the control group in GCTB with different tumor grades (P<0.05). In patients who underwent intralesional curettage, a significantly lower local recurrence rate was found in the BP group compared with the control group (P<0.01), but no significance was found for patients who underwent wide resection (P=0.16). None of the included studies described severe adverse effects related to BPs.
Conclusion
The results confirmed the effect of BPs on reducing the local recurrence of GCTB, and the effect is not influenced by the tumor grades. BPs are benefit for the patients who underwent intralesional curettage but not recommended for those who underwent wide resection.
Keywords: bisphosphonates, giant cell tumor of bone, local recurrence, meta-analysis
Background
Giant cell tumor of bone (GCTB) is a common and locally aggressive bone tumor in East and Southeast Asian patients, which usually involves the end of long bones and comprises approximately one-fifth of all benign and potentially malignant bone tumors.1 Although surgery remains the preferred treatment for GCTB, it is limited by a high recurrence rate regardless of wide resection or intralesional curettage. GCTBs are classified by Campanacci et al into three grades: stage I, latent; stage II, active; and stage III, aggressive according to their radiological appearance.2 Wide resection may lead to severe restricted movement which is usually performed in stage III patient.3 For tumors classified as stage I or II, intralesional curettage is often performed first. It was reported that the local recurrence rates range from 19% to 50% in the first 2 years for both surgical procedures.4–7
A multitude of studies revealed that chemical cauterization, such as hypertonic saline, phenol, alcohol, and liquid nitrogen, and other physical treatments, such as blurring, cryotherapy, and argon laser after intralesional curettage may reduce the risk of recurrence.8–11 These methods could cause many complications, such as infections, pathologic fractures, and damage to soft tissues. Recent studies reported the potential of bone metabolism drugs for GCTB, including bisphosphonates (BPs) and denosumab.12–14 Recent studies reveal that denosumab failed to show a benefit on local recurrence in the adjuvant setting in patients with GCTB treated with surgery.15–18 BPs are inhibitors of bone resorption, which promote bone mineralization and inhibit farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase.19 Some studies showed that BPs could promote apoptosis of the stromal cell component, and reduce the recurrence rate after surgery in GCT.20–22
Recently, there were some studies evaluating the effect of BPs on preventing postoperative recurrence of GCTB.23–29 However, to the best of our knowledge, there is no definite direction or consensus on the application of BPs in GCTB. The present meta-analysis of six case–control trials aimed to confirm the effect of BPs on the local recurrence of GCTB and analyze the influence of different tumor stages and different procedures of surgery on this effect.
Methods
Study registration
The present meta-analysis was conducted according to the PRISMA (Table S1).30 The protocol was registered in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO).31
Literature search
The literature search was conducted in duplicate by two independent investigators. An electronic systematic search of four databases including PubMed, AMED, EMBASE, the Cochrane Library, ISI Web of Science, and China National Knowledge Infrastructure was performed for relevant articles from the inception dates to October 28, 2018. The search consisted of the following keywords and Boolean operators: (alendronate OR pamidronate OR etidronate OR zoledronate OR clodronate OR bisphosphonate) AND (giant cell tumor). To include more additional eligible studies, a manual search was carried out on the bibliographies of related reviews and reference lists of all selected articles. If necessary, the authors of studies were contacted to provide additional information.
Selection criteria
The studies selected for inclusion were required to contain the following criteria: 1) the participants were diagnosed as GCTB and underwent surgical treatment; 2) the intervention was oral, intramuscular, or intravenous BPs after surgery; 3) the outcomes must include the local recurrence rate of GCTB; and 4) the design was case–control study. The exclusion criteria were as follows: 1) studies with no reported follow-up time or those with <6 months of follow-up time, 2) data of local recurrence were unavailable, and 3) the same participants reported in a previous article with a short follow-up.
Data extraction
The data were extracted by two independent investigators. If any disagreement was found, a third reviewer was consulted. For each eligible study, basic information was extracted onto a data collection form including the following parameters: the first author name, publication year, sample size, intervention protocol, control protocol, similarities between BP group and control group, surgical procedures, follow-up duration, and outcome measurements. If outcome data were not described as text, it was extrapolated from the accompanying figures, tables, or other supplementary material. Finally, the characteristics of the seven included studies were shown in Table 1. The primary outcome measurement was the local recurrence rate of GCTB. And the second measurement was the local recurrence rate in different subgroups, including different tumor grades (stage I–II and stage III) and different surgical procedures (intralesional curettage and wide resection). A sensitivity analysis was performed for the effect size by omitting the studies for which risk of bias and heterogeneity was imputed.
Table 1.
Characteristics of the included studies
| Study | Sample size, I/C | Intervention | Control | Similarities | Surgical procedures (BP group) | Surgical procedures (control group) | Average follow- up after surgery (months) | Outcome measures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tse et al (2008)23 | 44 (24/20) | Seven received pamidronate 90 mg, and 17 received zoledronic acid 4 mg twice before surgery and three times after surgery | No placebo | Not mentioned | IC: 21 WR: 3 | IC: 15 WR: 4 | 115.4 (control group) 48 (BP group) | Local recurrence rate, local BMD |
| Zheng et al (2009)24 | 39 (19/20) | Zoledronic acid 4 mg or incadronate disodium 10 mg twice before surgery and three times after surgery | No placebo | Not mentioned | IC: 16 WR: 3 | IC: 15 WR: 5 | 43.6 | Local recurrence rate, pain VAS, swelling relief |
| Fan (2013)25 | 55 (29/26) | Zoledronic acid 4 mg three times after surgery | No placebo | Calcium | IC: 17 WR: 12 | IC: 15 WR: 11 | 45 | Local recurrence rate, Enneking postoperative functional score, local BMD |
| Xu et al (2014)26 | 85 (32/53) | Zoledronic acid 4 mg once before surgery and monthly after surgery for 2 years | No placebo | Postoperative adjuvant radiotherapy | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | 54.7 | Local recurrence rate |
| Ding et al (2016)27 | 37 (22/15) | Zoledronic acid 4 mg one to three times before surgery and once every 6 months after surgery for 2 years | No placebo | Not mentioned | IC: 15 WR: 7 | IC: 10 WR: 5 | 24 | Local recurrence rate, pain VAS |
| Xu et al (2017)28 | 35 (19/16) | Seven received zoledronic acid 4 mg, and 12 received incadronate disodium 10 mg once before surgery and monthly after surgery for 2 years | No placebo | Postoperative adjuvant radiotherapy | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | 47.2 | Local recurrence rate, nerve function |
| Kundu et al (2018)29 | 37 (18/19) | Zoledronic acid 4 mg three times 2 weeks before surgery | No placebo | Not mentioned | IC: 18 WR: 0 | IC: 19 WR: 0 | 32 | Local recurrence rate, functional scores |
Abbreviations: BMD, bone mineral density; BPs, bisphosphonates; I/C, intervention/control groups; IC, intralesional curettage; WR, wide resection.
Methodological quality assessment
In the included studies, the methodological quality was independently assessed by two reviewers with the New-castle–Ottawa scale for risk of bias, in which assessing factors included selection, comparability, and exposure. The weighted kappa for the agreement on the trial quality between reviewers was 0.86 (95% CI, 0.80–0.92). The criteria of the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) system were used to evaluate the quality of evidence.
Statistical analysis
Extracted results were pooled in a meta-analysis. The meta-analysis was performed by computing ORs and their 95% CIs weighted by the inverse of a variance in Review Manager 5.3.5 software (The Cochrane Collaboration, Oxford, UK). The statistical heterogeneity was tested with I2 and the chi-squared test.32 The value of I2 >50% was considered as high statistical heterogeneity and <50% as low statistical heterogeneity, respectively.33 When there was no statistical evidence of heterogeneity, a fixed effects model was used; otherwise, a random-effect model was chosen.
Sensitivity analyses were performed by omitting each of the individual study. The heterogeneity P-value <0.05 was considered as statistically significant. The sensitivity analysis was performed only if there were three or more studies in comparison. Publication bias was assessed by visually inspecting the funnel plot asymmetry.
Results
Studies selection
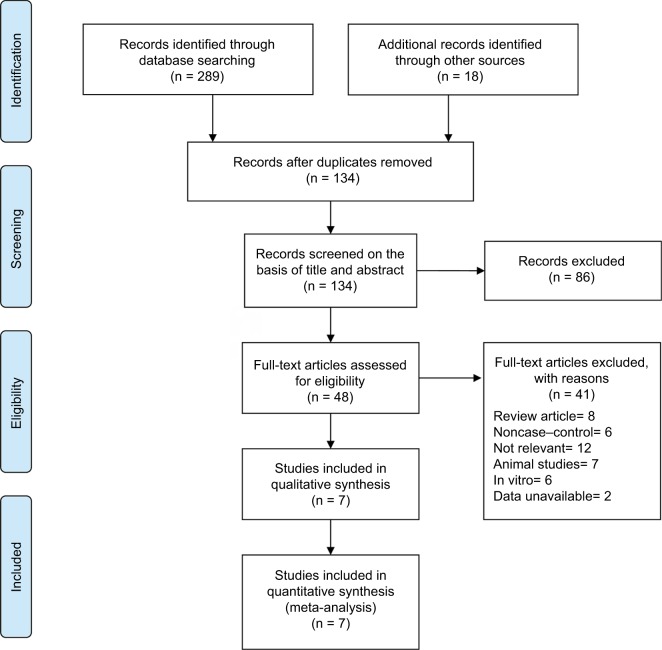
A flow diagram illustrating the study identification is shown in Figure 1. Literature search initially yielded 307 relevant articles, and 173 articles were excluded because they were duplicated. Of the 134 remaining articles, 86 articles were excluded by screening the title and abstract. Another 41 of the qualifying studies were excluded after their full texts were retrieved because they were laboratory studies, non-case–control study, reviews, unavailable data, or not relevant to the topic.
Figure 1.
Flowchart of the selection strategy and inclusion/exclusion criteria for the present meta-analysis.
Finally, seven case–control studies involving 332 participants were included in our meta-analysis.23–29 The weighted kappa for agreement on eligibility between reviewers was 0.87 (95% CI, 0.79–0.95). The characteristics of the included trials are summarized in Table 1.
Methodological quality
The quality of included studies was assessed according to the Newcastle–Ottawa scale (Table 2).34,35 According to the Newcastle–Ottawa scale, the risk of bias within the included studies reached 6.43 stars on average, which is also acceptable as there is no study with a high risk of bias. Three studies were judged to have a low risk of bias (more than seven stars),24,26,27 and three studies were found to have a moderate risk of bias (five or six stars).23,25,28,29 The reviewers achieved excellent agreement in the quality assessment of studies (intraclass correlation: 0.88; 95% CI, 0.84–0.92).
Table 2.
Newcastle–Ottawa scale assessment of the quality of the studies
| Study | Selection | Comparability based on design or analysis | Exposure | Total scores | Qualitya | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case definition adequate | Representativeness of the cases | Selection of controls | Definition of controls | Ascertainment of exposure | Same method of ascertainment for cases and controls | Nonresponse rate | ||||
| Tse et al (2008)23 | ⋆b | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ✰ | 7 | High |
| Zheng et al (2009)24 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆⋆ | ✰ | ✰ | ✰ | 6 | Medium |
| Fan (2013)25 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ✰ | 8 | High |
| Xu et al (2014)26 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ✰ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ✰ | 5 | Medium |
| Ding et al (2016)27 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ✰ | ⋆⋆ | ⋆ | ✰ | ✰ | 6 | Medium |
| Xu et al (2017)28 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ✰ | ⋆⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ✰ | 7 | High |
| Kundu et al (2018)29 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ✰ | ✰ | ⋆⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ✰ | 6 | Medium |
Notes:
The quality is assessed by the score as follows: ≥7, high quality; ≥5 to <7, medium quality; <5, low quality.
Cells with a star indicate that the corresponding item is addressed satisfactorily in the publication in question.
Recurrence rate of GCTB
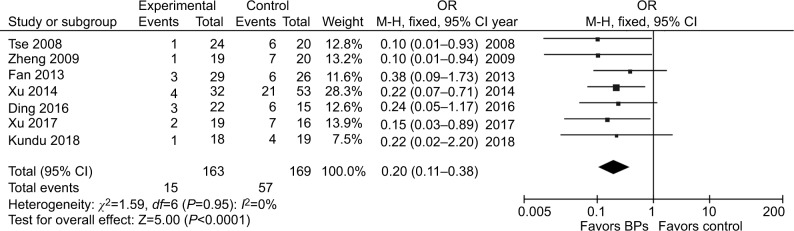
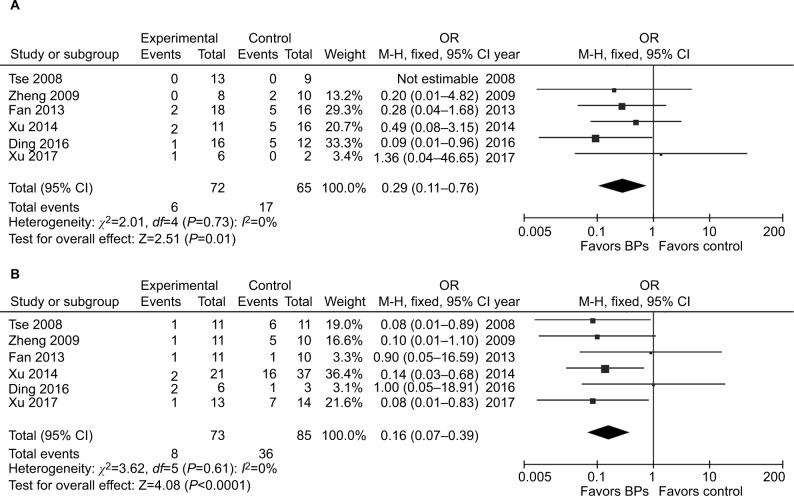
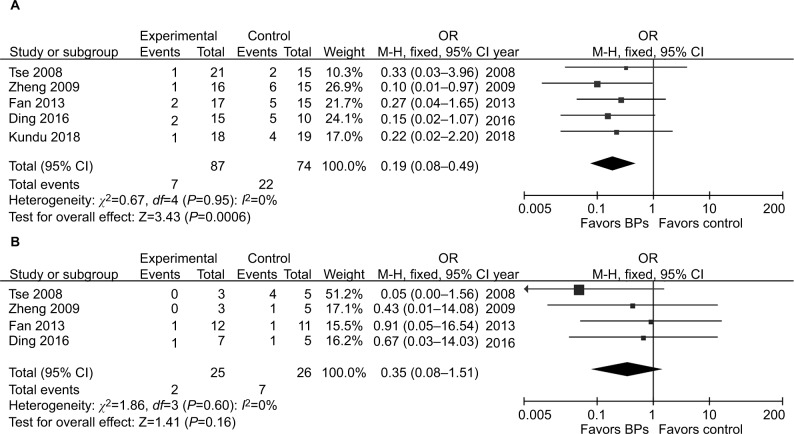
It was illustrated that the BP group presented significantly lower local recurrence rate than the control group in GCTB (seven studies, OR, 0.20; 95% CI, 0.11–0.38; P<0.01) (Figure 2). The BP group presented significantly lower local recurrence rate than the control group in GCTB in both of the subgroups with different tumor grades. For patients with stage I–II GCTB, a significant difference in local recurrence rate was found between the BP group and the control group (six studies, OR, 0.29; 95% CI, 0.11–0.76; P<0.05) (Figure 3A). In patients with stage III GCTB, a significant difference in local recurrence rate was found between the BP group and the control group (six studies, OR, 0.16; 95% CI, 0.07–0.39; P<0.01) (Figure 3B). Subgroup analysis based on different surgical procedures reveals a different result. In patients who underwent intralesional curettage, a significant difference in local recurrence rate was found between the BP group and the control group (five studies, OR, 0.19; 95% CI, 0.08–0.49; P<0.01) (Figure 4A). In patients who underwent wide resection, there was no significant difference in local recurrence rate between the BP group and the control group (four studies, OR, 0.35; 95% CI, 0.08–0.1.51; P=0.16) (Figure 4B).
Figure 2.
Forest plots for the effect of BPs on total postoperative recurrence in patients with GCTB.
Abbreviations: BPs, bisphosphonates; GCTB, giant cell tumor of bone.
Figure 3.
Forest plots for subgroup analysis for the effect of BPs on postoperative recurrence in patients with GCTB with different tumor grades.
Notes: (A) For patients with stage I–II GCTB, a significant difference in local recurrence rate was found between the BP group and the control group (P<0.05). (B) For patients with stage III GCTB, a significant difference in local recurrence rate was found between the BP group and the control group.
Abbreviations: BPs, bisphosphonates; GCTB, giant cell tumor of bone.
Figure 4.
Forest plots for subgroup analysis for the effect of BPs on postoperative recurrence in patients with GCTB with different surgical procedures.
Notes: (A) For patients who underwent intralesional curettage, a significant difference in local recurrence rate was found between the BP group and the control group (P<0.01). (B) For patients who underwent wide resection, there was no significant difference in local recurrence rate between the BP group and the control group (P=0.16).
Abbreviations: BPs, bisphosphonates; GCTB, giant cell tumor of bone.
Risk of bias across studies
Publication bias assessments using funnel plots (Figure S1) indicated that there was no significant asymmetry and no significant evidence of bias among the included studies of the five meta-analyses.
Heterogeneity and sensitivity analysis
There was no statistical heterogeneity in these five analyses (total recurrence: χ2=1.59, P=0.95, I2=0%; subgroup of stage I–II GCTB: χ2=2.01, P=0.73, I2=0%; subgroup of stage III GCTB: χ2=3.62, P=0.61, I2=0%; subgroup of intralesional curettage: χ2=0.67, P=0.95, I2=0%; subgroup of wide resection: χ2=1.86, P=0.60, I2=0%). The heterogeneity and overall effect were not significantly altered by omitting any study.
Strength of evidence
According to the criteria of the GRADE system for evidence quality,36 all the included trials in the present meta-analysis began as high-quality or moderate-quality evidence, which was downgraded by five categories of limitations (Table S2). Inadequate case definition, substantial loss to follow-up, and inconsistent reporting of outcomes in some studies might raise the risk of bias. The number of included patients <150 is considered to be small and may cause imprecision and effect size >0.05 is considered to be large and strengthen the evidence.
Adverse acute reaction
No serious or fatal acute adverse effect was reported related to BPs in all the included studies. The most common acute side effects were fever and gastric dyspepsia mentioned in three studies: 15 patients in Zheng et al;24 six patients in Fan;25 seven patients in Ding et al.27 There was no major adverse effect on renal function or stress fractures.
Discussion
GCTB usually does not remain latent and tends to develop progressive destruction of the affected bone.37 Therefore, surgical treatment should be performed as early as possible. Wide resection has an advantage of lower recurrence rate which is 0%–12%,38,39 as it removes the tumor entirely. Wide resection has been used in Campanacci stage III tumors or some cases without marked functional impairment, such as the ulna, fibula, and other small bones.40,41 However, wide resection may lead to restricting movement. Intralesional curettage with adjuvant methods is the preferred treatment for most cases of GCTB. This surgical procedure shows a better functional outcome but is associated with a higher risk of local recurrence.42,43 With developed surgical procedures and local adjuvants, the local recurrence rate of GCTB remains to be >20% in the recent studies.4–7,43
Nowadays denosumab, a monoclonal antibody to RANK ligand, is approved for the most common use for this type of pathology. Due to its efficacy, denosumab is recommended as the first option in inoperable or metastatic GCT. However, some clinical studies showed that denosumab might have no effect on reducing the risk of recurrence in patients with GCTB following curettage17,18 or even might increase the risk of recurrence.15,16 In vitro studies found that the inhibitory effect of denosumab on neoplastic cells and osteoclast survival were not observed, whereas BPs inhibited the growth of neoplastic cells and osteoclast survival.
Experimental studies confirmed the cytotoxic effect of BPs on neoplastic stromal cells of GCTB, and clinical studies showed that administration of BPs could reduce the recurrence rate of GCTB after surgery. The present meta-analysis of case–control studies verifies that BPs could reduce the postoperative recurrence of GCTB from 33.7% to 9.2% (57 of 169 vs 15 of 163), with no statistical heterogeneity. Subgroup analysis showed that BP group presented significantly lower local recurrence rate than the control group, regardless of the tumors’ Campanacci stages. The antitumor mechanism of BPs is not clear. It was reported that BPs could induce the apoptosis of neoplastic stromal cells by blocking the mevalonate pathway. Moreover, BPs have been proved to inhibit the proteolytic activity of tumor cell-derived matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and MMP-9 by inhibiting the zinc-dependent proteolytic activity of matrix MMPs, which are essential for the degradation of extracellular matrix proteins, invasion, and migration.44
Subgroup analysis of different surgical procedures showed that the recurrence of GCTB was significantly lower in BP group for patients who underwent intralesional curettage, but there was no difference between BP group and control group for patients who underwent wide resection. One possible interpretation of the different result is that wide resection avoids the marginal positive of bone in curettage and decreases the recurrence rate to a low level. Another interpretation is that recurrence is associated with soft tissue infiltration and wide resection removes all the infiltrate soft tissue.45 These results suggest that BPs are benefit for the patients who underwent intralesional curettage but not necessary for those who underwent wide resection.
In this meta-analysis, six of the seven included studies reported preoperative application of BPs. Preoperative application of BPs could reduce tumor size and prevent surgical dissemination, but the frequency should be restricted because delayed surgery may lead to progression of tumor lesions. The duration of postoperative application of BPs was from 3 months to 2 years. Prolonged postoperative application of BPs was considered important because most instances of recurrence occur in the first 2 years after surgery.46 In these studies, the main adverse reactions of BPs are mild and nonfatal in patients without renal dysfunction or stress fractures and include fever and digestive upset. However, some studies found that long-term and large-dose systemic administration of BPs might induce osteonecrosis of the jaw and atypical fracture of long bones.47,48 Above all, this meta-analysis confirmed the effect of BPs on local recurrence of GCTB but did not conclude that BPs can substitute the role of denosumab. It is reported that denosumab is very efficient in unresectable or metastatic GCTB as a neoadjuvant setting.49 In fact, denosumab was associated with tumor responses and reduced the need for morbid surgery in patients with GCTB.50 In the present meta-analysis, no evidence showed the role of BPs on these two parameters, tumor responses and the need for morbid surgery in patients with GCTB.
The strength of the present meta-analysis consists of being rigorously conducted according to PRISMA guidelines and using a robust systematic review and meta-analysis procedures. Moreover, the advantage of this meta-analysis over individual studies is a convincing clinical recommendation of postoperative application of BPs for GCTB to practitioners.
The present meta-analysis has several limitations. First, the limited number of studies and the small sample size in some studies might reduce the precision of the pooled estimates. For subgroup analysis, the total number of patients who underwent wide resection was only 51, which would lead to large bias in the overall effect. Further investigation with big sample size is required to confirm the different effect of BPs on the recurrence of GCTB in patient who underwent different surgical procedures. Second, all the included studies were case–control, which would downgrade the strength of evidence. Finally, the presented study analyzed the middle-term effect of BPs on local recurrence of GCTB, and the long-term effect remained unknown and required more clinical studies.
Conclusion
In the present meta-analysis of case–control, comparing controlled treatment, the use of BPs as an adjuvant therapy decrease the local recurrence rate of GCTB. This effect is not influenced by different Campanacci stages of GCTB. BPs are benefit for the patients who underwent intralesional curettage but not recommended for those who underwent wide resection.
Supplementary materials
The funnel plots asymmetry for the outcome showed the evidence of publication bias on the meta-analyses for (A) total postoperative recurrence, (B) subgroup of stage I–II GCTB, (C) subgroup of stage III GCTB, (D) subgroup of intralesional curettage, and (E) subgroup of wide resection.
Abbreviation: GCTB, giant cell tumor of bone.
Table S1.
PRISMA 2009 checklist
| Section/topic | # | Checklist item | Reported on page # |
|---|---|---|---|
| TITLE | |||
| Title | 1 | Identify the report as a systematic review, meta-analysis, or both. | 1 |
| ABSTRACT | |||
| Structured summary | 2 | Provide a structured summary including, as applicable: background; objectives; data sources; study eligibility criteria, participants, and interventions; study appraisal and synthesis methods; results; limitations; conclusions and implications of key findings; systematic review registration number. | 3 |
| INTRODUCTION | |||
| Rationale | 3 | Describe the rationale for the review in the context of what is already known. | 4 |
| Objectives | 4 | Provide an explicit statement of questions being addressed with reference to participants, interventions, comparisons, outcomes, and study design (PICOS). | 4 |
| METHODS | |||
| Protocol and registration | 5 | Indicate if a review protocol exists, if and where it can be accessed (eg, Web address) and, if available, provide registration information including registration number. | 5 |
| Eligibility criteria | 6 | Specify study characteristics (eg, PICOS, length of follow-up) and report characteristics (eg, years considered, language, publication status) used as criteria for eligibility, giving rationale. | 5 |
| Information sources | 7 | Describe all information sources (eg, databases with dates of coverage, contact with study authors to identify additional studies) in the search and date last searched. | 5 |
| Search | 8 | Present full electronic search strategy for at least one database, including any limits used, such that it could be repeated. | 5 |
| Study selection | 9 | State the process for selecting studies (ie, screening, eligibility, included in systematic review, and, if applicable, included in the meta-analysis). | 5 |
| Data collection process | 10 | Describe method of data extraction from reports (eg, piloted forms, independently, in duplicate) and any processes for obtaining and confirming data from investigators. | 5 |
| Data items | 11 | List and define all variables for which data were sought (eg, PICOS, funding sources) and any assumptions and simplifications made. | 5 |
| Risk of bias in individual studies | 12 | Describe methods used for assessing risk of bias of individual studies (including specification of whether this was done at the study or outcome level), and how this information is to be used in any data synthesis. | 6 |
| Summary measures | 13 | State the principal summary measures (eg, risk ratio, difference in means). | 6 |
| Synthesis of results | 14 | Describe the methods of handling data and combining results of studies, if done, including measures of consistency (eg, I2) for each meta-analysis. | 6 |
| Risk of bias across studies | 15 | Specify any assessment of risk of bias that may affect the cumulative evidence (eg, publication bias, selective reporting within studies). | 6 |
| Additional analyses | 16 | Describe methods of additional analyses (eg, sensitivity or subgroup analyses, meta-regression), if done, indicating which were prespecified. | 6 |
| RESULTS | |||
| Study selection | 17 | Give numbers of studies screened, assessed for eligibility, and included in the review, with reasons for exclusions at each stage, ideally with a flow diagram. | 6 |
| Study characteristics | 18 | For each study, present characteristics for which data were extracted (eg, study size, PICOS, follow-up period) and provide the citations. | 7 |
| Risk of bias within studies | 19 | Present data on risk of bias of each study and, if available, any outcome level assessment (see Item 12). | 7 |
| Results of individual studies | 20 | For all outcomes considered (benefits or harms), present, for each study: a) simple summary data for each intervention group, b) effect estimates and confidence intervals, ideally with a forest plot. | 7 |
| Synthesis of results | 21 | Present results of each meta-analysis done, including CIs and measures of consistency. | 7 |
| Risk of bias across studies | 22 | Present results of any assessment of risk of bias across studies (see Item 15). | 8 |
| Additional analysis | 23 | Give results of additional analyses, if done (eg, sensitivity or subgroup analyses, meta-regression [see Item 16]). | 8 |
| DISCUSSION | |||
| Summary of evidence | 24 | Summarize the main findings including the strength of evidence for each main outcome; consider their relevance to key groups (eg, health care providers, users, and policy makers). | 8–10 |
| Limitations | 25 | Discuss limitations at study and outcome level (eg, risk of bias) and at review-level (eg, incomplete retrieval of identified research, reporting bias). | 10 |
| Conclusions | 26 | Provide a general interpretation of the results in the context of other evidence and implications for future research. | 11 |
| FUNDING | |||
| Funding | 27 | Describe sources of funding for the systematic review and other support (eg, supply of data); role of funders for the systematic review. | 11 |
Table S2.
GRADE evidence profile for effect of BPs on recurrence giant cell tumor of bone
| Summary of findings | Quality assessment | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (I/C) | OR (95% CI) | Limitationsa | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | Others | Quality | |
| Total | 6 (145/150) | 0.20 (0.10–0.38) | No serious | No serious | No serious | No serious | Strong associationb | High |
| Stage I–II | 6 (72/65) | 0.29 (0.11–0.76) | No serious | No serious | No serious | No serious | Strong association | High |
| Stage III | 6 (73/85) | 0.16 (0.07–0.39) | No serious | No serious | No serious | No serious | Strong association | High |
| Intralesional curettage | 4 (69/55) | 0.19 (0.07–0.52) | No serious | No serious | No serious | Seriousc | Strong association | Moderate |
| Wide resection | 4 (25/26) | 0.35 (0.08–0.51) | No serious | Seriousd | No serious | Serious | Strong association | Moderate |
Notes:
The inadequate case definition and substantial loss follow-up in some studies may raise the risk of bias.
Effect size >0.05 is considered to be large and strengthen the evidence.
The number of included patients <150 is considered to be small and may cause imprecision.
Inconsistent report of outcomes may raise the risk of bias.
Abbreviations: GRADE, Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation; I/C: intervention/control groups.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Zhejiang Province Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. LQ16H060002, Medical and Health Science and Technology Project of Zhejiang Province under Grant No. 2016KYB120, and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under Grant No. 2017M612012.
Footnotes
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
- 1.Thangaraj R, Grimer RJ, Carter SR, Stirling AJ, Spilsbury J, Spooner D. Giant cell tumour of the sacrum: a suggested algorithm for treatment. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(7):1189–1194. doi: 10.1007/s00586-009-1270-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Campanacci M, Baldini N, Boriani S, Sudanese A. Giant-cell tumor of bone. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987;69(1):106–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kamal AF, Simbolon EL, Prabowo Y, Hutagalung EU. Wide resection versus curettage with adjuvant therapy for giant cell tumour of bone. J Orthop Surg. 2016;24(2):228–231. doi: 10.1177/1602400221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gaston CL, Bhumbra R, Watanuki M, et al. Does the addition of cement improve the rate of local recurrence after curettage of giant cell tumours in bone? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93-B(12):1665–1669. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.93B12.27663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Balke M, Schremper L, Gebert C, et al. Giant cell tumor of bone: treatment and outcome of 214 cases. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2008;134(9):969–978. doi: 10.1007/s00432-008-0370-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Benevenia J, Rivero SM, Moore J, et al. Supplemental bone grafting in giant cell tumor of the extremity reduces nononcologic complications. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017;475(3):776–783. doi: 10.1007/s11999-016-4755-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chan CM, Adler Z, Reith JD, Gibbs CP. Risk factors for pulmonary metastases from giant cell tumor of bone. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(5):420–428. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.N.00678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.van der Heijden L, Dijkstra PD, van de Sande MA, et al. The clinical approach toward giant cell tumor of bone. Oncologist. 2014;19(5):550–561. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2013-0432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Nithyananth M, Priscilla AJ, Boopalan PV, Titus VT, Lee VN. Time required for effective action of phenol against giant cell tumour cells. J Orthop Surg. 2014;22(1):104–107. doi: 10.1177/230949901402200126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.van der Heijden L, van der Geest IC, Schreuder HW, van de Sande MA, Dijkstra PD. Liquid nitrogen or phenolization for giant cell tumor of bone? A comparative cohort study of various standard treatments at two tertiary referral centers. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(5):e35. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.M.00516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chaudhary P, Khadim H, Gajra A, Damron T, Shah C. Bisphosphonate therapy is effective in the treatment of sacral giant cell tumor. Onkologie. 2011;34(12):702–704. doi: 10.1159/000334549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Borkowska A, Goryń T, Pieńkowski A, et al. Denosumab treatment of inoperable or locally advanced giant cell tumor of bone. Oncol Lett. 2016;12(6):4312–4318. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.5246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Balke M, Campanacci L, Gebert C, et al. Bisphosphonate treatment of aggressive primary, recurrent and metastatic giant cell tumour of bone. BMC Cancer. 2010;10(1):462. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lau CP, Huang L, Wong KC, Kumta SM. Comparison of the anti-tumor effects of denosumab and zoledronic acid on the neoplastic stromal cells of giant cell tumor of bone. Connect Tissue Res. 2013;54(6):439–449. doi: 10.3109/03008207.2013.848202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Müller DA, Beltrami G, Scoccianti G, Campanacci DA, Franchi A, Capanna R. Risks and benefits of combining denosumab and surgery in giant cell tumor of bone – a case series. World J Surg Oncol. 2016;14(1):281. doi: 10.1186/s12957-016-1034-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Errani C, Tsukamoto S, Leone G, et al. Denosumab may increase the risk of local recurrence in patients with giant-cell tumor of bone treated with curettage. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018;100(6):496–504. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.17.00057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mak IW, Evaniew N, Popovic S, Tozer R, Ghert M. A translational study of the neoplastic cells of giant cell tumor of bone following neoadjuvant denosumab. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(15):e127. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.M.01332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Shibuya I, Takami M, Miyamoto A, et al. In vitro study of the effects of denosumab on giant cell tumor of bone: comparison with zoledronic acid. Pathol Oncol Res. 2017 Nov 20; doi: 10.1007/s12253-017-0362-8. Epub. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yokoyama T, Mizuguchi M, Ostermann A, et al. Protonation state and hydration of bisphosphonate bound to farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase. J Med Chem. 2015;58(18):7549–7556. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b01147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Cheng YY, Huang L, Kumta SM, Lee KM, Lai FM, Tam JS. Cytochemical and ultrastructural changes in the osteoclast-like giant cells of giant cell tumor of bone following bisphosphonate administration. Ultrastruct Pathol. 2003;27(6):385–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chang SS, Suratwala SJ, Jung KM, et al. Bisphosphonates may reduce recurrence in giant cell tumor by inducing apoptosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;426:103–109. doi: 10.1097/01.blo.0000141372.54456.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Chen KH, Wu PK, Chen CF, Chen WM. Zoledronic acid-loaded bone cement as a local adjuvant therapy for giant cell tumor of the sacrum after intralesional curettage. Eur Spine J. 2015;24(10):2182–2188. doi: 10.1007/s00586-015-3978-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Tse LF, Wong KC, Kumta SM, Huang L, Chow TC, Griffith JF. Bisphosphonates reduce local recurrence in extremity giant cell tumor of bone: a case-control study. Bone. 2008;42(1):68–73. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2007.08.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zheng X, Yin Q, Kumta SM, Huang H, Zhang Y, Zhang T. Clinical study of bisphosphonates reducing local recurrence in extremity giant cell tumor of bone. Chinese Clin Oncol. 2009;14:1100–1104. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Fan J. Analysis of Zoledronic Acid to Assist Clinical Effect Surgical Treatment for Giant Cell Tumor of Bone [master thesis] Changsha, Hunan, China: Central South University; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Xu W, Xu L, Li L. Prognostic factors of giant cell tumor in mobile spine. Chin J Orthop. 2014;34:487–493. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ding L, Han X, Huang T, Zhang H. Adjuvant administration of bisphosphonates decreases local recurrence rate of extremity giant cell tumor of bone. Chin J Heal Care Med. 2016;18:67–69. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Xu W, Wang Y, Wang J, et al. Long-term administration of bisphosphonate to reduce local recurrence of sacral giant cell tumor after nerve-sparing surgery. J Neurosurg Spine. 2017;82(204):716–721. doi: 10.3171/2016.10.SPINE151197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kundu ZS, Sen R, Dhiman A, Sharma P, Siwach R, Rana P. Effect of intravenous zoledronic acid on histopathology and recurrence after extended curettage in giant cell tumors of bone: a comparative prospective study. Indian J Orthop. 2018;52(1):45–50. doi: 10.4103/ortho.IJOrtho_216_17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ. 2009;339(jul21 1):b2700. doi: 10.1136/bmj.b2700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Shi M, Chen L, Wang Y, Wang W, Yan S. Effect of bisphosphonates on local recurrence of giant cell tumor. PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews web. [Accessed September 8, 2018]. Available from: http://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/display_record.php?ID=CRD42018087636.
- 32.Becker L. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.4. Chichester, England: Wiley-Blackwell; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Higgins JPT, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327(7414):557–560. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wells G, Shea B, O’Connell D, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomised Studies in Meta-Analyses. Ottawa, Ontario, Canada: Ottawa Hospital Research Institute; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010;25(9):603–605. doi: 10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Brozek J, et al. Grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations for diagnostic tests and strategies. BMJ. 2008;336(7653):1106–1110. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39500.677199.AE. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Mcgough RL, Rutledge J, Lewis VO, Lin PP, Yasko AW. Impact severity of local recurrence in giant cell tumor of bone. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;438:116–122. doi: 10.1097/01.blo.0000180055.76969.08. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Arbeitsgemeinschaft Knochentumoren. Becker WT, Dohle J, et al. Local recurrence of giant cell tumor of bone after intralesional treatment with and without adjuvant therapy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(5):1060–1067. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.D.02771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Errani C, Ruggieri P, Asenzio MA, et al. Giant cell tumor of the extremity: a review of 349 cases from a single institution. Cancer Treat Rev. 2010;36(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2009.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Klenke FM, Wenger DE, Inwards CY, Rose PS, Sim FH. Giant cell tumor of bone: risk factors for recurrence. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(2):591–599. doi: 10.1007/s11999-010-1501-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Mozaffarian K, Modjallal M, Vosoughi AR. Treatment of giant cell tumor of distal radius with limited soft tissue invasion: curettage and cementing versus wide excision. J Orthop Sci. 2018;23(1):174–179. doi: 10.1016/j.jos.2017.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Pazionis TJ, Alradwan H, Deheshi BM, Turcotte R, Farrokhyar F, Ghert M. A systematic review and meta-analysis of en-bloc vs intralesional resection for giant cell tumor of bone of the distal radius. Open Orthop J. 2013;7(1):103–108. doi: 10.2174/1874325001307010103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Gortzak Y, Kandel R, Deheshi B, et al. The efficacy of chemical adjuvants on giant-cell tumour of bone. An in vitro study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(10):1475–1479. doi: 10.1302/0301-620x.92b10.23495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Boissier S, Ferreras M, Peyruchaud O, et al. Bisphosphonates inhibit breast and prostate carcinoma cell invasion, an early event in the formation of bone metastases. Cancer Res. 2000;60(11):2949–2954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Xu L, Jin J, Hu A, et al. Soft tissue recurrence of giant cell tumor of the bone: prevalence and radiographic features. J Bone Oncol. 2017;9:10–14. doi: 10.1016/j.jbo.2017.09.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Karpik M. Giant cell tumor (tumor gigantocellularis, osteoclastoma)--epidemiology, diagnosis, treatment. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. 2010;12(3):207–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Migliorati CA, Woo SB, Hewson I, et al. A systematic review of bisphosphonate osteonecrosis (BON) in cancer. Support Care Cancer. 2010;18(8):1099–1106. doi: 10.1007/s00520-010-0882-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Sellmeyer DE. Atypical fractures as a potential complication of long-term bisphosphonate therapy. JAMA. 2010;304(13):1480–1484. doi: 10.1001/jama.2010.1360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Rutkowski P, Gaston L, Borkowska A, et al. Denosumab treatment of inoperable or locally advanced giant cell tumor of bone--Multicenter analysis outside clinical trial. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2018;44(9):1384–1390. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2018.03.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Chawla S, Henshaw R, Seeger L, et al. Safety and efficacy of denosumab for adults and skeletally mature adolescents with giant cell tumour of bone: interim analysis of an open-label, parallel-group, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14(9):901–908. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70277-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
The funnel plots asymmetry for the outcome showed the evidence of publication bias on the meta-analyses for (A) total postoperative recurrence, (B) subgroup of stage I–II GCTB, (C) subgroup of stage III GCTB, (D) subgroup of intralesional curettage, and (E) subgroup of wide resection.
Abbreviation: GCTB, giant cell tumor of bone.
Table S1.
PRISMA 2009 checklist
| Section/topic | # | Checklist item | Reported on page # |
|---|---|---|---|
| TITLE | |||
| Title | 1 | Identify the report as a systematic review, meta-analysis, or both. | 1 |
| ABSTRACT | |||
| Structured summary | 2 | Provide a structured summary including, as applicable: background; objectives; data sources; study eligibility criteria, participants, and interventions; study appraisal and synthesis methods; results; limitations; conclusions and implications of key findings; systematic review registration number. | 3 |
| INTRODUCTION | |||
| Rationale | 3 | Describe the rationale for the review in the context of what is already known. | 4 |
| Objectives | 4 | Provide an explicit statement of questions being addressed with reference to participants, interventions, comparisons, outcomes, and study design (PICOS). | 4 |
| METHODS | |||
| Protocol and registration | 5 | Indicate if a review protocol exists, if and where it can be accessed (eg, Web address) and, if available, provide registration information including registration number. | 5 |
| Eligibility criteria | 6 | Specify study characteristics (eg, PICOS, length of follow-up) and report characteristics (eg, years considered, language, publication status) used as criteria for eligibility, giving rationale. | 5 |
| Information sources | 7 | Describe all information sources (eg, databases with dates of coverage, contact with study authors to identify additional studies) in the search and date last searched. | 5 |
| Search | 8 | Present full electronic search strategy for at least one database, including any limits used, such that it could be repeated. | 5 |
| Study selection | 9 | State the process for selecting studies (ie, screening, eligibility, included in systematic review, and, if applicable, included in the meta-analysis). | 5 |
| Data collection process | 10 | Describe method of data extraction from reports (eg, piloted forms, independently, in duplicate) and any processes for obtaining and confirming data from investigators. | 5 |
| Data items | 11 | List and define all variables for which data were sought (eg, PICOS, funding sources) and any assumptions and simplifications made. | 5 |
| Risk of bias in individual studies | 12 | Describe methods used for assessing risk of bias of individual studies (including specification of whether this was done at the study or outcome level), and how this information is to be used in any data synthesis. | 6 |
| Summary measures | 13 | State the principal summary measures (eg, risk ratio, difference in means). | 6 |
| Synthesis of results | 14 | Describe the methods of handling data and combining results of studies, if done, including measures of consistency (eg, I2) for each meta-analysis. | 6 |
| Risk of bias across studies | 15 | Specify any assessment of risk of bias that may affect the cumulative evidence (eg, publication bias, selective reporting within studies). | 6 |
| Additional analyses | 16 | Describe methods of additional analyses (eg, sensitivity or subgroup analyses, meta-regression), if done, indicating which were prespecified. | 6 |
| RESULTS | |||
| Study selection | 17 | Give numbers of studies screened, assessed for eligibility, and included in the review, with reasons for exclusions at each stage, ideally with a flow diagram. | 6 |
| Study characteristics | 18 | For each study, present characteristics for which data were extracted (eg, study size, PICOS, follow-up period) and provide the citations. | 7 |
| Risk of bias within studies | 19 | Present data on risk of bias of each study and, if available, any outcome level assessment (see Item 12). | 7 |
| Results of individual studies | 20 | For all outcomes considered (benefits or harms), present, for each study: a) simple summary data for each intervention group, b) effect estimates and confidence intervals, ideally with a forest plot. | 7 |
| Synthesis of results | 21 | Present results of each meta-analysis done, including CIs and measures of consistency. | 7 |
| Risk of bias across studies | 22 | Present results of any assessment of risk of bias across studies (see Item 15). | 8 |
| Additional analysis | 23 | Give results of additional analyses, if done (eg, sensitivity or subgroup analyses, meta-regression [see Item 16]). | 8 |
| DISCUSSION | |||
| Summary of evidence | 24 | Summarize the main findings including the strength of evidence for each main outcome; consider their relevance to key groups (eg, health care providers, users, and policy makers). | 8–10 |
| Limitations | 25 | Discuss limitations at study and outcome level (eg, risk of bias) and at review-level (eg, incomplete retrieval of identified research, reporting bias). | 10 |
| Conclusions | 26 | Provide a general interpretation of the results in the context of other evidence and implications for future research. | 11 |
| FUNDING | |||
| Funding | 27 | Describe sources of funding for the systematic review and other support (eg, supply of data); role of funders for the systematic review. | 11 |
Table S2.
GRADE evidence profile for effect of BPs on recurrence giant cell tumor of bone
| Summary of findings | Quality assessment | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (I/C) | OR (95% CI) | Limitationsa | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | Others | Quality | |
| Total | 6 (145/150) | 0.20 (0.10–0.38) | No serious | No serious | No serious | No serious | Strong associationb | High |
| Stage I–II | 6 (72/65) | 0.29 (0.11–0.76) | No serious | No serious | No serious | No serious | Strong association | High |
| Stage III | 6 (73/85) | 0.16 (0.07–0.39) | No serious | No serious | No serious | No serious | Strong association | High |
| Intralesional curettage | 4 (69/55) | 0.19 (0.07–0.52) | No serious | No serious | No serious | Seriousc | Strong association | Moderate |
| Wide resection | 4 (25/26) | 0.35 (0.08–0.51) | No serious | Seriousd | No serious | Serious | Strong association | Moderate |
Notes:
The inadequate case definition and substantial loss follow-up in some studies may raise the risk of bias.
Effect size >0.05 is considered to be large and strengthen the evidence.
The number of included patients <150 is considered to be small and may cause imprecision.
Inconsistent report of outcomes may raise the risk of bias.
Abbreviations: GRADE, Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation; I/C: intervention/control groups.