Key Clinical Message
Empyema caused by transdiaphragmatic extension of pyogenic liver abscess is a very rare complication of liver abscess. Empyema patients with unclear respiratory symptoms should be evaluated for the presence of underlying liver abscess. Effective drainage with appropriate antibiotic use is an essential part of successful treatment.
Keywords: diaphragm, empyema, liver abscess, Streptococcus constellatus
A 47‐year‐old man visited the hospital, manifesting dyspnea with right chest pain. He had intermittent fever with right upper abdominal pain for four weeks before admission. Vital signs and physical examination were as follows: blood pressure, 92/70 mm Hg; pulse, 120 beats/min; respiration, 22 breaths/min; and temperature, 38.2°C. Decreased breath sounds in the right chest and tenderness over the liver were observed. Blood tests revealed leukocytosis 20,680/mm3 (neutrophil 85.9%), aspartate aminotransferase 42 IU/L, alanine aminotransferase 62 IU/L, and total bilirubin 1.08 mg/dL. An initial chest computed tomography (CT) scan was performed (Figure 1A,B).
Figure 1.
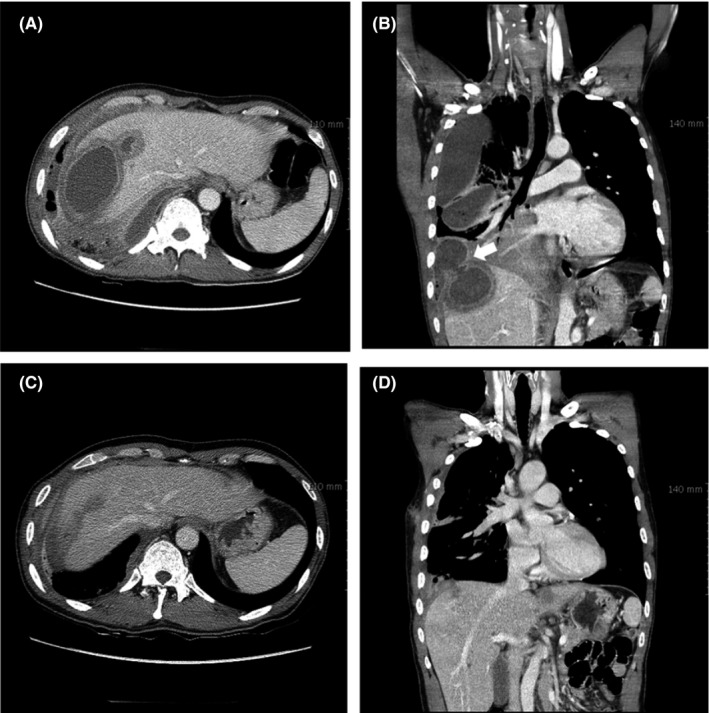
A, A contrast‐enhanced computed tomography scan (CT) of the chest showing about 11.3 cm sized large abscess in the right lobe of liver and loculated pleural effusion with multifocal air‐bubbles in the right hemithorax in axial view. B, Coronal reconstruction view showing a continuous track (arrows) suggestive of hepato‐pleural fistula from the liver abscess extending across the diaphragm and in continuity with the pleural cavity. C and D, Chest CT scan obtained after six weeks of antibiotic treatment showing much decreased size of liver abscess and the amount of loculated pleural effusion
What's your diagnosis?
Liver abscess with empyema connected through hepato‐pleural fistula.
Empirical antibiotics (ceftriaxone, ciprofloxacin, and metronidazole) were administered and pig‐tail catheters were inserted to effectively drain empyema and liver abscess. Streptococcus constellatus was isolated as a causative organism. His symptoms improved after eight weeks of antibiotic treatment (Figure 1C,D) without recurrence before follow‐up at six months. Transdiaphragmatic extension of pyogenic liver abscess is a very rare cause of empyema.1 Although pathogenic potential of S. constellatus remains controversial due to its commensal nature, cases of liver abscess by this organism have been increasingly reported.2 Effective drainage with proper antibiotic is essential for successful treatment.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
None declared.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTION
DHK: contributed to treat the patient and wrote the manuscript.
Kim DH. Empyema caused by transdiaphragmatic extension of pyogenic liver abscess. Clin Case Rep. 2019;7:240–241. 10.1002/ccr3.1950
REFERENCES
- 1. Cho E, Park SW, Jun CH, et al. A rare case of pericarditis and pleural empyema secondary to transdiaphragmatic extension of pyogenic liver abscess. BMC Infect Dis. 2018;18(1):40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Akuzawa N, Hatori T, Kitahara Y, et al. Multiple liver abscesses and bacteremia caused by Streptococcus constellatus infection: a case report. Clin Case Rep. 2017;5(1):69‐74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


