Abstract
The trans-crustal magma system paradigm is forcing us to re-think processes responsible for magma evolution and eruption. A key concept in petrology is the liquid line of descent (LLD), which relates a series of liquids derived from a single parent, and therefore tracks the inverse of the crystallization path. It is common practice to attribute multiple magma compositions, and/or multiple melt compositions (from melt inclusions and matrix glass), to a single LLD. However, growing evidence for rapid, and often syn-eruptive, assembly of multiple magma components (crystals and melts) from different parts of a magmatic system suggests that erupted magma and melt compositions will not necessarily represent a single LLD, but instead may reflect the multiple paths in pressure–temperature space. Here, we use examples from mafic magmatic systems in both ocean island and arc settings to illustrate the range of melt compositions present in erupted samples, and to explore how they are generated, and how they interact. We highlight processes that may be deduced from mafic melt compositions, including the mixing of heterogeneous primitive liquids from the mantle, pre-eruptive magma storage at a range of crustal and sub-Moho depths, and syn-eruptive mixing of melts generated from these storage regions. The relative dominance of these signatures in the glasses depends largely on the water content of the melts. We conclude that preserved melt compositions provide information that is complementary to that recorded by the volatile contents of crystal-hosted melt inclusions and coexisting mineral compositions, which together can be used to address questions about both the pre- and syn-eruptive state of volcanic systems.
This article is part of the Theo Murphy meeting issue ‘Magma reservoir architecture and dynamics’.
Keywords: melt, mixing, degassing, gas fluxing, trans-crustal, magma reservoir
1. Introduction
Recent reviews of magmatic systems (e.g. [1–6]) emphasize their spatial extent, dynamic nature and rheological complexity. This view of magmatic systems has evolved over the past decades, driven by the accumulation of geophysical, petrological and geochemical evidence that active magmatic systems are vertically and/or laterally extensive and are dominated by crystal mush, with only transient accumulations of crystal-poor melt. Recognition of the transience and the mobility of the melt, combined with the high inferred crystallinity of most sub-volcanic systems, is prompting the community to re-think processes responsible for both magma evolution and volcanic eruptions, particularly related to redistribution of melt and crystals within magma storage regions.
Petrology has contributed to the paradigm of trans-crustal magmatic systems (TCMS) by improving constraints on the pressure (P) and temperature (T) of magma storage using experimentally derived phase relations and thermobarometric models [7–10]. At the same time, direct measurements of dissolved volatile components in crystal-hosted melt inclusions and quenched matrix glass can be used to track the movement of volatile phases through the system [11–13]. Thermodynamic models used to reconstruct crystallization paths, including MELTS [14] and Petrolog [15], and degassing paths, e.g. VolatileCalc [16] and D-Compress [17], extend experimental constraints and allow construction of melt evolution paths for changing conditions of pressure, temperature and composition. New microanalytical techniques permit detailed studies of the entrained crystal populations. Diffusion profiles measured across internal boundaries within crystals are now routinely used to estimate residence times of crystals within the transporting melt and, by extension, time scales of pre-eruptive magma accumulation (e.g. [18–20]). In combination, these approaches have shown that any single batch of erupted magma may combine crystals and melt from a range of P–T conditions within a given magmatic system [21–23].
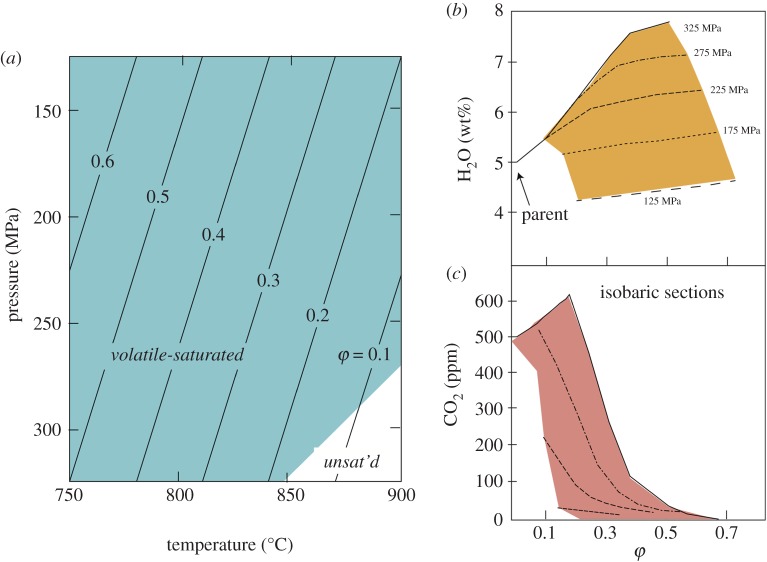
A schematic magma storage system is shown in figure 1a, which spans a range of pressure (P), temperature (T) and crystallinity (φ). As a result, the hypothetical resident magma can be vapour-undersaturated (at high P and T) or vapour-saturated, and ranges from pure melt (also at high P and T) to ‘non-eruptible’ (φ > 0.6) crystal mush [24]. Such a model system has the potential to trap melt inclusions (MIs) with a wide range of H2O and CO2; this forms the basis of using crystal-hosted MIs to infer conditions of magma storage (figure 1b,c) [16]. The same system will have a large range of melt compositions that also reflect the P–T–φ conditions of magma storage; it is this melt compositional range that we explore in this paper. Melt may be trapped as inclusions within crystals, preserved as a matrix phase of the transporting magma and is also commonly preserved as a matrix phase within glomerocrysts and cumulate nodules, or surrounding antecrysts (antemelt) [25,26]. Glass compositions can provide a detailed record of the heterogeneity of ‘primary’ melts [27], magma recharge and mixing [28,29], ascent rate [30] and syn-eruptive mixing [31,32], particularly in hydrous mafic magmas that crystallize rapidly during decompression. Here we explore glass compositions of both relatively dry ocean island tholeiites and hydrous arc basalts to examine the types of processes they record, and discuss their utility for understanding magmatic storage and transport processes in a range of tectonic settings. We focus on basaltic magmas because they occur in most tectonic settings, represent the less evolved input to magmatic systems, and vary widely in H2O content, and therefore in conditions of crystallization.
Figure 1.
Evolution of a model intermediate-composition magma chamber. (a) Model magma chamber set-up in P–T space; blue region indicates volatile saturation, contours are lines of equal crystal volume fraction (φ). Isobaric sections show variations in (b) H2O and crystallinity and (c) CO2 and crystallinity. Reproduced with permission from [24].
2. Exploring melt evolution over P–T space
(a). Model mafic magmatic systems
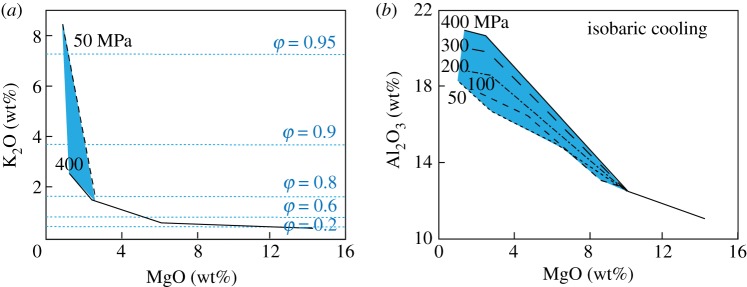
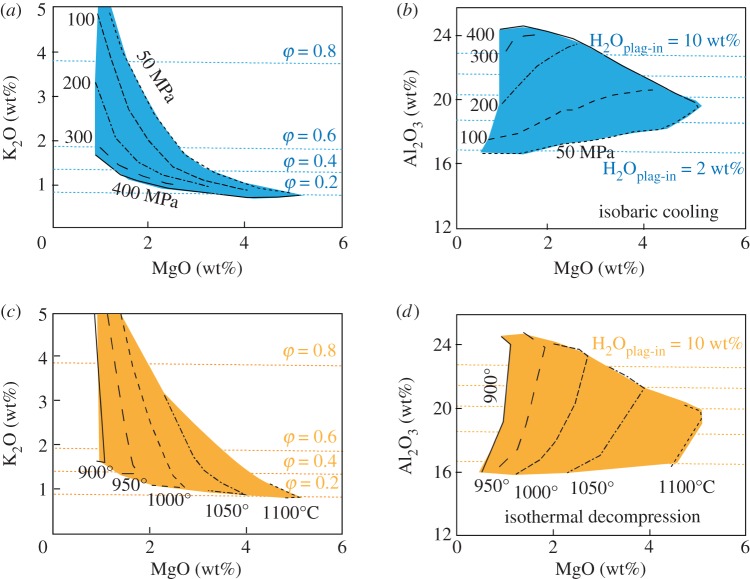
To develop a framework for examining melt compositions, we first develop simple model systems similar to that shown schematically in figure 1. As analogue systems we have chosen Kīlauea volcano, which erupts tholeiitic basalt with approximately 0.7 wt% H2O [33,34], and Fuego volcano, Guatemala, a frequently active and well-studied volcano with a hydrous high-alumina basalt composition [35–37]. For the Kīlauea model, we use MELTS to model equilibrium crystallization at a range of pressures, using a starting composition equivalent to the most primitive post-entrapment crystallization (PEC) corrected melt inclusion from [34] which is similar in composition to the primitive glasses from the Puna Ridge [38], and an fO2 of FMQ (fayalite–magnetite–quartz) [39]. For the Fuego model, we use MELTS and a starting composition appropriate for the bulk Fuego 1974 magma (from [37]). To reduce the number of variables, we use an initial H2O content of 4.5 wt% (from [40]) and assume that fO2 is buffered at NNO (nickel–nickel oxide) (e.g. [41]). For simplicity, we assume equilibrium crystallization paths; fractional crystallization would further enhance the modelled trends. The model space ranges from 1100 to 900°C and from 400 to 50 MPa. We examine end member paths of isobaric cooling (IBC; figures 2 and 3a,b) and isothermal decompression (ITD; figure 3c,d) as illustrated by plots of MgO (to track crystallization of mafic phases) versus K2O to track total crystallinity (assuming that it behaves incompatibly) and Al2O3 to indicate the onset of feldspar crystallization, which is particularly sensitive to .
Figure 2.
Evolution of melt composition during isobaric cooling for a H2O-poor tholeiite. (a) K2O versus MgO, with crystallinity (φ) and pressure marked. (b) MgO versus Al2O3, with pressures marked. Melt compositions from rhyolite-MELTS [14]. (Online version in colour.)
Figure 3.
Evolution of melt composition during IBC (a,b) and ITD (c,d) for an H2O-rich arc basalt. (a,c) K2O versus MgO, with crystallinity (φ) and pressure marked. (b,d) MgO versus Al2O3, with pressures marked. The starting composition was an estimate of the bulk composition for the 1974 Fuego eruption (from [37]) with 4.5 wt% H2O and fO2 of NNO. Compositional paths determined from rhyolite-MELTS [14] run from 400 to 50 MPa and 1100 to 900°C. The compositional space covers most of the observed range of melt compositions at Fuego, and illustrates the compositional spectrum that may arise when magmas are tapped during a single eruption from a range of P–T space within a complex magmatic system. (Online version in colour.)
The Kīlauea model (figure 2) shows that in H2O-poor ocean island tholeiites, the major element composition of the melt is not sensitive to the pressure of crystallization for much of the cooling history; for this reason, IBC trends form a single liquid line of descent (LLD) until the melt MgO content reaches approximately 7–9 wt%, when plagioclase and pyroxene appear on the liquidus. At this point, the influence of plagioclase crystallization on Al2O3 increases as the pressure of crystallization decreases, leading to 2–4 wt% differences in Al2O3 content at a MgO content of 6 wt%. This model system shows that, in low-H2O basaltic magmas, the melt compositions are relatively insensitive to dP/dT paths and instead are much more likely to preserve heterogeneity in major and trace elements (and in isotopic composition) that may be linked back to a variable mantle source composition and degree of melting [42–45].
For more hydrous melts in arc settings, in contrast, the evolution of the melt phase is strongly controlled by pressure, as illustrated by the Fuego model (figure 3). Compositional trends produced by IBC at high pressure are controlled by crystallization of mafic phases, with accompanying strong decreases in MgO and associated increases in Al2O3, with only minor increases in K2O (total crystallinity; figure 3a,b). The MgO content at which plagioclase saturation occurs varies strongly with the crystallization pressure, and is marked by the maximum Al2O3 content of the melt (Al2O3max) [46]. Al2O3 then decreases with decreasing pressure as plagioclase crystallizes. Associated increases in bulk crystallinity are indicated by a rapid steepening of the MgO–K2O curves. During early phases of IBC crystallization, these feldspar-driven MgO–K2O trends are more pronounced at lower pressures because plagioclase crystallization starts earlier in the crystallization sequence, as illustrated by the changing location of Al2O3max. The reverse is true of MgO–K2O curves in the later stages of crystallization, which are steepest at the highest pressure and represent rapid feldspar crystallization once H2O saturation is reached. Compositional trends produced by ITD, in contrast, start with decompression-driven melting of clinopyroxene, which causes an initial increase in MgO. This is followed by rapid decreases in Al2O3 and increases in K2O that record extensive decompression-driven plagioclase crystallization (figure 3c,d). Both curves are steepest at the lowest temperatures. Although not shown, combined decompression and cooling produce melt evolution paths that traverse the same compositional space covered by the end member cases shown in figure 3. Taken together, these model curves provide an heuristic framework for examining the melt evolution paths preserved in the eruptive products of mafic volcanoes in ocean island and arc settings.
(b). Experimental constraints on melt compositional paths
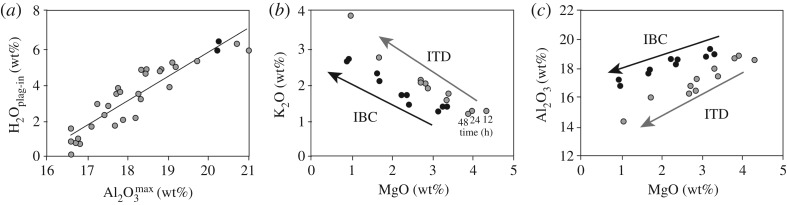
Changes in melt composition related to cooling and changes in PH2O can be calibrated experimentally. For example, variations in MgO caused by olivine crystallization (figure 2) form the basis of an experimentally calibrated glass geothermometer that was first developed for Kīlauea basalt compositions at 1 bar [47] and later extended to Mauna Loa [48] and Columbia River basalt [49] compositions. A generalized form of the MgO-glass geothermometer [50] is T(°C) = 26.3MgOliq + 994.4°C, which has a standard error estimate of ±71°C, although the error can be reduced by adding compositional and pressure-dependent terms. Another example is calibration of a melt-based hygrometer [46], which is based on the relation between H2O saturation and plagioclase crystallization, as illustrated in figure 3b. The calibrated relationship between the H2O content of basaltic melts at plagioclase saturation (H2Oplag-in) and Al2O3max is H2Oplag-in = 1.34Al2O3max − 21.05, as shown in figure 4a. Although the original calibration points were based on moderately low-pressure experiments (100–200 MPa, [46]), data from additional experiments at mid- to lower-crustal pressures [51] suggest that the calibration can also be extended to higher pressures. Together, these examples illustrate the potential of melt compositions to record both pre- and syn-eruptive histories.
Figure 4.
Experimental constraints. (a) Development of an Al2O3 hygrometer. Experimental data from [46] at 200 MPa with best-fit line (equation provided in text); additional data points from higher-pressure experiments of [51]. Standard error is 0.76 wt% H2O. (b,c) Dynamic experiments on H2O-saturated basaltic andesite starting at 1025°C and 150 MPa and with cooling to 925°C or decompressing to 10 MPa. End member effective supercooling (ΔTeff) values for feldspar are labelled. Data from [52].
Experimental data can also be used to compare IBC and ITD crystallization paths, as illustrated by the experiments of [52] on a hydrous basaltic andesite. Here, a melt equilibrated under H2O-saturated conditions at 150 MPa and 1025°C was subsequently (a) cooled to temperatures of 995, 965, 935, 915 and 892°C at a constant pressure of 150 MPa (IBC) and (b) decompressed to 100, 65, 42, 21 and 10 MPa at a constant temperature of 1025°C (ITD). The initial condition of H2O saturation means that we capture only part of the composition space spanned in figure 3, but the crystallization paths are directly comparable in that experimental conditions were chosen to achieve the same effective supersaturations for plagioclase crystallization (the target of these kinetic experiments), and were either cooled or decompressed over the same time intervals. The resulting melt compositions vary with the P–T path, as illustrated by plots of Al2O3, K2O and MgO (figure 4b,c). Specifically, the ITD experiments show a more rapid decrease in Al2O3 and a more rapid increase in K2O than equivalent IBC experiments, consistent with the expected enhanced crystallization of plagioclase relative to mafic phases during decompression. The kinetic effects of varying experimental time scales, in contrast, are small.
In summary, both the model and experimental data illustrate the range of composition space that can be experienced by variably hydrous mafic melts that follow different P–T paths in a single magmatic system. These data have important implications for interpreting the range of melt compositions preserved in erupted material. Here we explore this approach using several rich datasets from mafic eruptions.
3. Melt compositions in mafic ocean island volcanoes
Mafic magmas in ocean island settings typically contain less than 1 wt% H2O [33,53,54], which means that they are not very susceptible to decompression-driven crystallization, and indeed are often erupted near their liquidus. Erupted magmas are therefore characterized by a low phenocryst content and a glassy groundmass. Geobarometric studies that have compared the compositions of coexisting glass and pyroxene [7,10] have shown that eruptions of ocean island volcanoes are supplied by melts that have been stored, prior to eruption, over a wide range of pressures [7,55,56], perhaps extending past the petrologic Moho into the upper mantle for some settings. Beneath Mauna Kea, Hawai‘i, which is in its post-shield phase, fractionation of clinopyroxene occurs during magma storage in the uppermost mantle (800 MPa) to yield hawaiitic magmas [57]. Post-shield magmas from Haleakala volcano, on the island of Maui, Hawai‘i, show evidence for magma storage at pressures up to 950 MPa [10,58]. At many ocean island volcanoes, there is little evidence of long-lived, shallow ‘magma chambers’ [59]. It has been proposed that magma reservoirs beneath Hawai‘i, for example, may develop through a cycle, whereby the early, pre-shield alkalic phase of activity is characterized by multi-stage magma storage, eventually forming long-lived magma reservoirs as the magma supply rate increases [59]. During the tholeiitic stage of volcanism, the dominant zone of magma storage becomes shallower, within a few kilometres of the surface. During this phase, the shallow magma chamber may fill and drain repeatedly; rapid drainage may be associated with caldera collapse. During the post-shield phase, when magma supply wanes, only the deep reservoir survives. The geometry and depth of magma reservoirs beneath ocean islands are not well resolved, however, and we must typically rely on a combination of petrology and geophysics to unravel their form and extent. Importantly, samples of quenched ‘carrier liquid’, which represents the melt phase, provide valuable clues about the depth of storage, fractionation, degassing and mixing of magmas. Here, we examine what the major and trace element composition of the melt for ocean island basalts can tell us about mantle source, mixing and the magmatic plumbing system, before we contrast it, in §4, with the case of more hydrous, mafic arc magmas.
(a). Kīlauea volcano, Hawai‘i
Kīlauea volcano, Hawai‘i, is in its shield-building phase, with large magma fluxes and frequent eruptions. A dominant summit reservoir exists at 2–4 km depth [60,61] and a shallower one at approximately 1 km [62], both of which are well constrained by geophysical data. The rift and summit zones of magma storage may extend vertically downwards, perhaps to the inward-dipping decollement at approximately 10 km depth [63] where the edifice sits on the top of the pre-volcano crust. Magma ascends sub-vertically from the zone of melting at depths of greater than 40 km [64]. P-wave tomography reveals high-velocity regions beneath the summit and rift zones inferred to represent dense cumulates, as well as low-velocity regions that may represent melt beneath the summit of Kīlauea [65,66]. The detailed structure of the plumbing system beneath the summit magma reservoir, however, is very poorly known, and topics for debate include the extent to which magmas may ‘bypass’ the summit reservoir, the depth of lateral transport in the rift zones, and the extent of rift zone storage [63].
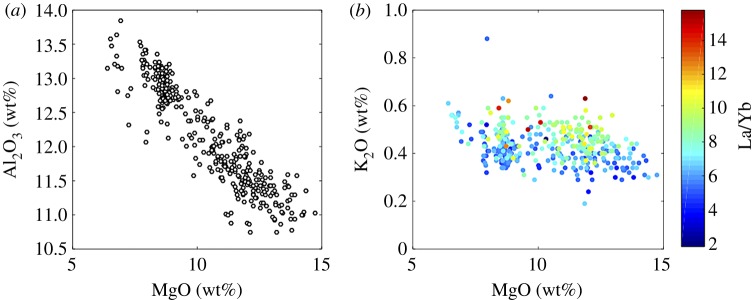
The magmas erupted at Kīlauea volcano are relatively simple petrographically, offering scant opportunity for barometric reconstructions of magma storage, as many melts erupt with only olivine on the liquidus. Olivine control dominates the LLD, with plagioclase and augite appearing on the liquidus at MgO contents of less than 7 wt%. Whole-rock compositions often exhibit signs of olivine accumulation [67,68]. Primary melts have approximately 16 wt% MgO [38] and fractionate approximately 30% of their mass as olivine to reach approximately 7 wt% MgO. Picritic glasses erupt exceedingly rarely, if at all, and are recorded only in dredged samples from the submarine portion of the Puna Ridge [38]. Figure 5 shows matrix glass and melt inclusion compositions for tephras erupted during 25 summit and upper East Rift Zone eruptions over the last 600 years of Kīlauea's activity [34]. Melt inclusions corrected for PEC reach almost 15 wt% MgO [34] while matrix glasses reach up to approximately 10 wt% MgO [69]. However, the relative insensitivity of basaltic glass composition to the pressure of crystallization (figure 2) means that the depth at which these olivines crystallize is very poorly constrained. The melt water content and fO2 also affect the timing of plagioclase and clinopyroxene fractionation with respect to temperature.
Figure 5.
Olivine-hosted melt inclusion compositions in tephra erupted during 25 eruptions over the past 400 years at Kīlauea volcano, Hawai‘i, from [34]. (a) Al2O3 versus MgO and (b) K2O versus MgO colour-coded for La/Yb to show that some of the scatter in major element compositions is inherited from the heterogeneity of melts that came out of the mantle and mixed together in crustal magma reservoirs.
The simple petrographic relationships observed in Kīlauea magmas belie considerable complexity, however, related to mixing of heterogeneous melts and accumulation of antecrystic olivines. Together, these phases provide information about the thermal structure of the magma reservoir system (owing to the simple relationship between glass MgO content and temperature [47]; figure 2) and its physical arrangement. Matrix glass compositions overlap with melt inclusion compositions, and while their overall trends are related to olivine fractionation, they exhibit considerable variability in major (and trace) elements for a fixed MgO content. This variability in major element composition correlates with indices of mantle source variability, e.g. La/Yb (figure 5b) and Pb isotopic composition [43,70], which may reflect melt fraction ratios and/or lithology of the mantle source [43,71]. The heterogeneous melts present in the mantle beneath Kīlauea may also have different volatile contents. For example, it has been suggested that the ‘Loa’ trend may be associated with recycled dehydrated oceanic crust, and that the lower H2O and CO2 contents [34,72] may affect phase equilibria during fractionation in the crust. Thus, although they form a broad trend in compositional space, the data in figure 5 are clearly not described well by a single LLD; instead, it is likely that fractionation takes place from a range of primary melt compositions.
Matrix glass compositions also show considerable variability in MgO content and hence temperature (from 4.4 to 10.3 wt%; 1102–1221°C; figure 5) through space and time, even within individual eruptions [34,69]. This requires syn-eruptive mixing of liquids. In particular, extra-caldera eruptions of Kīlauea in 1959, 1971 and 1974 produced matrix glasses ranging from 6.5 to 9.0 wt% within the same deposit [69]. Explosive ash-rich summit eruptions show even wider ranges, producing tephra with 6.5–11.0 wt% (Keanakāko‘i; 1500–1800 AD) and less than or equal to 12.5 wt% (Kulanaokuaiki; ca 400–1000 AD). The widespread Pāhala ash (25–10 ka) includes rare shards with 13–14.5% MgO [73]. Intra-caldera glasses, in contrast, contain only 6.4–7.6 wt% MgO, reflecting compositions that are buffered at the peritectic, probably because of thermal constraints [74]. The extra-caldera eruptions also commonly produce tephra that contains more primitive olivines [34]. Comparison of the matrix glass composition of Kīlauea tephras with the compositions of the cores of their olivine cargoes (figure 6) reveals that the vast majority of the olivine crystals are not in equilibrium with their ‘carrier liquid’ [34,77], a feature earlier highlighted by a comparison between whole rocks and olivine compositions [68,78]. It is worth noting that olivines in the range Fo86–87 would be in equilibrium with melts of MgO content 10.5–11.0 wt%, which is only erupted at Kīlauea in ‘unmixed’ form during the most explosive eruptions (e.g. the Keanakāko‘i and Kulanaokuaiki eruptions). Evidence for magma mixing is pervasive in these olivine crystals, which show resorption and normal and reverse zoning [18,79]; additional evidence for mixing lies in the heterogeneity of melt compositions. The 1959 Kīlauea Iki eruption, for example, involved mixing of an invading high-temperature magma into a cooler, shallower stored magma [47,80–83].
Figure 6.
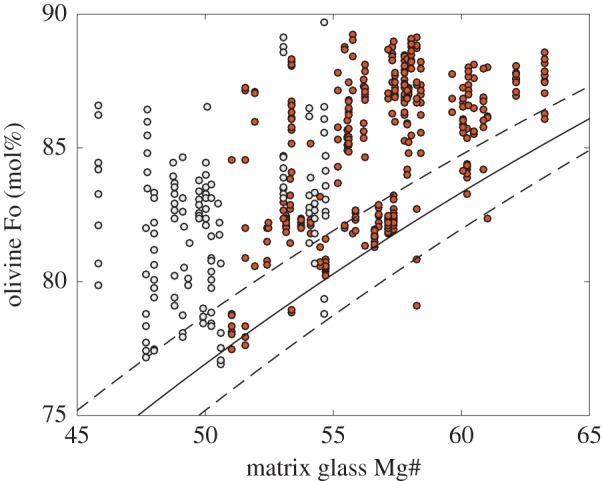
The antecrystic nature of olivines in ocean island basalts. Olivine core compositions plotted against the Mg# of the carrier liquid, for 25 eruptions of Kīlauea volcano over the past 400 years [34] (red) and morphologically young submarine cones from El Hierro (Canary islands) [75] (grey). The solid and dashed lines indicates crystal–melt equilibrium (where KD = (XFeO/XMgO)olivine/(XFeO/XMgO)melt) of 0.3 ± 0.05 for olivine/liquid [76].
These observations have prompted a model of a vertically zoned shallow magma reservoir beneath the summit, with more primitive melt (and olivines) being sourced from deeper in the system (greater than 2–3 km) and erupted only during (1) explosive eruptions from the summit, (2) extra-caldera eruptions during which magma may bypass the shallowest magma storage area [34] and/or mix with shallower stored melts [69] and (3) prolonged rift eruptions which may empty the summit reservoir. The lower and more homogeneous MgO contents of most summit eruptions, in contrast, are sourced from the well-mixed shallowest portion of the reservoir, which may change in composition over decades as the reservoir is recharged by melts from the mantle.
(b). Volcanoes in the Canary Islands, Iceland and the Galapagos
The Canary Islands provide a contrasting view of ocean island magmatic systems and are associated with a lower magma flux. The resulting infrequent eruptions do not allow collation of detailed geodetic or volcano-seismicity datasets over long time scales, but instead require petrological techniques to reconstruct magma storage depths. Unlike Kīlauean magmas, Canarian magmas contain abundant clinopyroxene, reflecting the dominance of clinopyroxene over olivine fractionation at high pressures [84,85]. Barometry using clinopyroxene-melt compositions [7,9,10] for basalts erupted from the shield volcano Teno, on the island of Tenerife, suggests magma storage depths of 20–45 km [86]. Clinopyroxene-melt barometry for basalts on other Canary Islands also suggests the existence of sub-Moho magma reservoirs, which perhaps occur as a plexus of dykes and sills [75,87]. On La Palma, clinopyroxene-melt barometry indicates last equilibration pressures of about 400–700 MPa for magmas erupted from Cumbre Vieja volcano [88]; for El Hierro, 500–710 MPa [75]; and for magmas erupted on the Madeira archipelago, 400–1050 MPa [89,90]. Independent methods to estimate pressures produce similar results: the density of CO2-dominated fluid inclusions in olivines in xenoliths suggests magma storage depths of 650–950 MPa for El Hierro, 600–680 MPa for La Palma and 550–750 MPa for Lanzarote [56]. For many of the volcanic centres, the fluid inclusion systematics also highlight a shallower crustal magma staging area [56], similar to many volcanic systems in Iceland [7,91]. There is evidence for some shallow fractionation of magmas in the Canary Islands to form phonolites, and evolved plutonic nodules are erupted on, for example, Tenerife [92].
Like basalts from Hawai‘i, Canarian magmas often exhibit clear signs of mixing [86]. Here, however, mixing appears to take place in the deep, vertically disseminated, ephemeral magma reservoirs that straddle the (seismic) Moho. In El Hierro lavas [75], olivine cores are frequently not in equilibrium with their carrier liquid (figure 6). By comparing the least and most primitive olivine compositions, one might speculate that a crystal-rich, more evolved magma (and its crystal cargo) mixed with a picritic magma (carrying primitive olivines), or that invading melt disrupted a crystal-rich, compositionally zoned mush, picking up a range of olivine crystals shortly before erupting.
In summary, the structure of magmatic storage systems beneath ocean island volcanoes depends primarily on magma flux from the mantle, such that high fluxes allow development of shallow storage systems while low fluxes promote magma storage in lower-crustal sills. Early crystallized olivine that is physically removed from the melt can be re-incorporated by an intruding carrier liquid; the result is a mafic crystal cargo that is more primitive than the melt that transports it to the surface during eruption. Melt compositions provide evidence of extensive mixing of both deep and shallow magmas, but also of different melt batches from the mantle source. Matrix glass compositions erupted during different styles of eruption hint at a vertically zoned magma storage system beneath the summit of Kīlauea. Finally, variations in the spatial distribution of matrix glass compositions at Kīlauea demonstrate the utility of using a wide range of eruptive products to fully probe the subsurface magmatic system.
4. Melt compositions in mafic arc magmas
Mafic arc magmas are typically hydrous [93] and often high in alumina, which, when combined with the relatively low viscosity of the melts, makes them particularly susceptible to plagioclase-dominated decompression-driven crystallization. For this reason, typical erupted magmas have both a moderate to high phenocryst content and a moderately to highly crystalline groundmass. Geobarometry based on both mineral phases and crystal-hosted melt inclusions suggests that eruptions are typically fed from mid- to upper-crustal depths, rather than directly from the lower crust, although there are exceptions (e.g. [94]). Magmatic systems tend to be vertically extensive, with the deeper parts sampled only during the highest-energy eruptions [95,96]. Pre- and syn-eruptive entrainment of antecrysts is common [97,98], and isotopic data can record entrainment of antemelt [25]. Below we examine processes of recharge, storage and eruption through the lens of melt composition, which provides a complementary record to that of the volatile and crystal phases. Only a limited number of mafic arc volcanoes have extensive published melt compositional data. We have chosen to compare four such volcanoes: (1) Stromboli volcano, Italy, is best known for its eponymous frequent, shallow and low-level activity, which is punctuated by energetic paroxysms; (2) Etna volcano, Italy, is frequently active with recent eruptive styles that range from effusive to violent Strombolian; (3) Llaima volcano, Chile, is sporadically active, with the most recent eruptive phase in 2008–2009 characterized by both violent Strombolian and Strombolian eruptions as well as effusive activity; and (4) Fuego, Guatemala, is frequently active with eruptive styles that range from Strombolian to paroxysmal to, rarely, subPlinian. The range in activity exhibited by these volcanoes, from persistent to intermittent, and from effusive to explosive, provides a volcanological context for examining preserved melt compositions.
(a). Stromboli and Etna, Italy
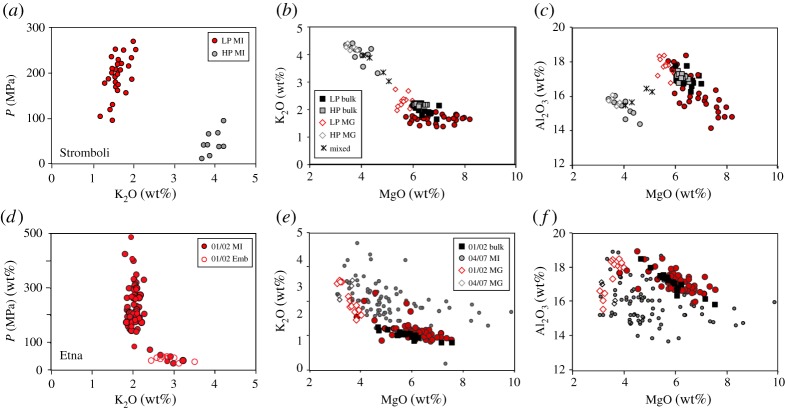
Stromboli volcano is well instrumented and has a long history of petrologic studies, including extensive analysis and interpretation of quenched melt compositions (e.g. [95,99–102]). These data show that the eponymous activity involves frequent low-energy explosions that emit crystal-rich (HP or high-porphyricity) magma from storage regions located at less than 100 MPa (approx. 3 km below the summit). ‘Normal’ Strombolian activity is punctuated by occasional paroxysmal eruptions that erupt crystal-poor (LP or low-porphyricity) magma, with olivine-hosted melt inclusions that record magma storage at temperatures of 1140–1200°C, minimum pressures of 150–280 MPa (figure 7a), and periodic recharge of the deep storage system with CO2-rich basalt. Importantly, separate HP and LP magma storage regions have been maintained over time, with the deep magma erupted only during paroxysmal activity. Suggested triggers for paroxysms include (1) rapid rise of volatile-rich magma [95,103], (2) collapse of a CO2-rich bubble layer [108] or (3) depressurization of the magmatic system during episodes of lava effusion (e.g. [96,109]).
Figure 7.
Melt compositions from Stromboli volcano, Italy (a–c) and Etna volcano, Italy (d–f). Stromboli shows LP data from paroxysmal eruptions (red) and HP data from normal Strombolian eruptions (grey). Bulk-rock data shown as squares (black for LP and grey for HP), melt inclusions as circles and matrix glass as open diamonds, except for mixed/mingled glasses, which are shown as (*). (a) Pressure versus K2O; (b) MgO versus K2O; (c) MgO versus Al2O3. Data from [31,95,99–101,103,104]. The same symbol shapes are used for Etna data, with red symbols for 2001–2002 data (black for bulk rock) and grey symbols for low-level activity of 2004–2007. (d) Pressure versus K2O; (e) MgO versus K2O; (f) MgO versus Al2O3. Data from [105–107].
The melt compositional characteristics of the HP (shallow Strombolian) and LP (deep paroxysmal) storage regions have been characterized [95,100,101,103]. Although the two magma types have similar bulk compositions (figure 7b,c), contrasting storage conditions are evident in both melt inclusion and matrix glass compositions. LP melt inclusions record crystallization between 300 and 100 MPa (minimum pressures; figure 7a) of olivine and, primarily, clinopyroxene [95]; the trend of increasing Al2O3 with decreasing MgO shows that plagioclase was not part of the crystallizing assemblage. Additionally, extension of melt inclusion compositions to higher MgO than the bulk compositions indicates initial crystallization from a more Mg-rich melt. The total amount of crystallization is modest, however, as indicated by the limited variation in incompatible element K2O. LP matrix glass compositions sit at the evolved end of the melt inclusion trend; Al2O3max suggests H2Oplag-in at approximately 3.6 wt% (figure 4a), which is within error of the maximum measured H2O contents in Stromboli melt inclusions (3.8 wt% [95]). High-Al2O3 matrix glass compositions suggest that the upper part of the LP magma storage region is close to H2O-saturated. Olivine-hosted melt inclusions in HP magmas, in contrast, have lower MgO and Al2O3, and higher K2O, consistent with extensive shallow crystallization of plagioclase [95,110]. The host olivines are also more evolved than those in the LP magma. Matrix glass compositions sit at the evolved end of the HP melt inclusion trend, with K2O contents that require an additional approximately 50% crystallization of the average LP matrix glass. Critically, intermediate melt compositions are absent, except when produced by mingling of HP and LP magma during paroxysmal eruptions (figure 7b,c). The lack of intermediate compositions requires isolation of the two magma storage regions, as well as rapid magma transfer from deep storage regions to the surface during paroxysmal activity [95].
Etna volcano is characterized by eruptive activity that is more varied in style and frequency than Stromboli, ranging from effusive to Strombolian, violent Strombolian and, in the past, Plinian. Although primary magma compositions have varied in time, including during recent activity, there are also numerous examples of the same bulk composition recording different trajectories in P–T–φ space, often in association with changes in eruptive style. Here, we compare melt inclusion and matrix glass data from highly explosive eruptive episodes in 2001–2002 [105,106] with similar data from effusive and low-level explosive eruptions in 2004, 2006 and 2007 [107]. The former included violent Strombolian eruptions from different vents; we use data from only the lower 2001 vents, which record the introduction of new magma into the system [105], as well as data from activity in October to November 2002 [106]. The latter were degassed and comprised mostly lava flows [107]; elevated measurement of CO2/SO2 ratios prior to individual effusion events, however, suggests that these flows were fed by ascent of different magma batches from depth [111,112].
Bulk-rock compositions from 2001 to 2002 are somewhat more variable that those of Stromboli LP magma, although estimated magma temperatures of 1125–1160°C are more restricted [106]. Olivine-hosted melt inclusions from these highly explosive eruptions track crystallization of mafic phases over a minimum pressure range of 500 MPa to near-surface values (figure 7d). Variations in K2O are limited except in the few low-pressure melt inclusions (less than 100 MPa) from eruptive activity in late 2002 (figure 7d,e). The maximum Al2O3 values are found at MgO of approximately 4.5 wt%, concurrent with the most evolved higher-pressure MI compositions (figure 7f). Application of the Al2O3 hygrometer (figure 4a) suggests H2Oplag-in less than or equal to 4 wt%, again within error of the maximum measured H2O in melt inclusions. Variations in matrix glass compositions require approximately up to 40% syn-eruptive decompression-driven crystallization, consistent with observed moderate to highly crystalline groundmass textures. In summary, melt compositions from the 2001 to 2002 activity, like the volatile data, provide evidence of magma extraction from a storage region that spanned a substantial P range, and extracted bulk magma compositions that define a near-continuous LLD trend with the melt inclusion and matrix compositions. This continuous trend contrasts with the compositional gaps in melt compositions observed at Stromboli, suggesting that a more vertically continuous magmatic system was required to maintain the sustained activity observed during the 2001–2002 eruptive episode at Etna.
Melt inclusion data from the mostly effusive 2004–2007 samples, in contrast, form a diffuse trend in K2O–MgO space that is parallel to, but elevated above, the 2001–2002 data and also extends to higher MgO (figure 7e,f, grey symbols). Although high K2O could reflect extensive PEC, this does not explain the high-MgO end of the trend, which instead suggests at least limited input of more primitive magma [112]. The host olivine compositions overlap with the olivine hosts of the 2001–2002 sequence, but extend to substantially lower forsterite contents [106]. The melt inclusion data also have highly variable Al2O3, although they reach an Al2O3max that is similar to that of the earlier explosive sequence. Matrix glass compositions are similar to those of 2001–2002 and less evolved than some melt inclusions, which requires entrainment of crystals from shallower, cooler and/or more H2O-poor regions of the magmatic system.
Melt inclusion volatile contents are low in H2O but maintain substantial CO2 [107]; these data led Collins et al. [107] to suggest that the melt had equilibrated with fluxing CO2-rich fluids prior to eruption, consistent with the observations of CO2-rich gas emissions that preceded effusive events [111]. A potential problem with this interpretation is the nature of the samples, which include (slow-cooling) lava, where MIs are prone to diffusive H2O loss [40]. That said, the glass data require a range of storage conditions for the late-erupted lavas, as well as extensive plagioclase crystallization that is consistent with, but does not require, gas fluxing (or ‘flushing’). Arguments for the importance of CO2 flushing at Etna are also provided by Caricchi et al. [113].
(b). LLaima, Chile
Llaima volcano is located in the Southern Volcanic Zone of Chile. Although not persistently active, the volcano has had several historic eruptive episodes, most recently in 1955–1957 and 2008–2009. Detailed studies of the eruptive products of these violent Strombolian paroxysms, as well as those of fissure-fed eruptions in 1850, suggest that, in contrast to Etna and Stromboli, the magmatic system beneath Llaima comprises a relatively shallow complex network of dykes/sills that feeds individual eruptions; the extent to which individual melt bodies are isolated except during periods of eruptive activity is a topic of discussion [114–117]. The dominant crystal phases are plagioclase and olivine. Zoning in both phases preserves evidence of frequent recharge by volatile-rich mafic magma; the recharge and resident magmas are ‘broadly co-genetic’ and linked via variations in the extent of olivine crystallization [114,115].
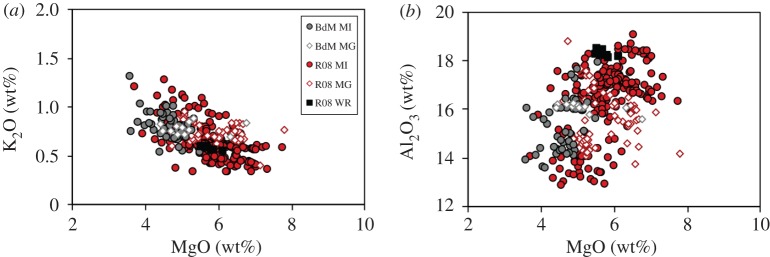
The most extensive documentation of melt compositions exists for the most recent eruption of Llaima (2008–2009) [114–117]. The bulk composition of the erupted samples shows only a limited range, which lies within the compositional range of olivine-hosted melt inclusions (figure 8). Melt inclusion compositions are similar to those of Stromboli and Etna, although they extend to both lower K2O and Al2O3 values, and the crude positive correlation of Al2O3 and MgO records the co-crystallization of olivine and plagioclase phenocrysts, the main phenocryst phases. Melt inclusion trace element measurements show typical arc signatures with moderate enrichment of light rare-earth elements, and overlap with bulk compositions [116]. In detail, they show a negative correlation of Sr/Zr and Al2O3, which can be reproduced by models with less than or equal to 55% crystallization, or close to the nominal ‘eruptible’ limit [114]. We note, however, that the compositional variation shown in figure 8 is difficult to reconcile with a simple LLD, given the variation in both K2O and Al2O3 at a single MgO, and the associated lack of apparent pressure dependence of the Sr/Zr ratio [114], which makes it difficult to place magma evolution within P–T space.
Figure 8.
Melt compositions from Llaima volcano, Chile (BdM from [114]; R08 from [116]). Black squares show bulk composition, circles show melt inclusion data from the 2008 eruptive activity, open diamonds are matrix glass. (a) MgO versus K2O; (b) MgO versus Al2O3.
Further insight is provided by the matrix glass compositions, which are unusual in that they lie within the much larger compositional range of the melt inclusions, rather than at the evolved end of this range. Similarly, the average matrix glass temperature (1140°C; range 1114–1183°C) is higher than the average melt inclusion glass temperature (1118°C; range 1013–1198°C) [118], and olivine compositions are both more and less evolved than expected for equilibrium with associated melt inclusions. Evolved melt inclusion compositions may reflect either PEC or crystal entrainment from more solidified portions of the magmatic system (e.g. [97]). The latter interpretation is supported by the same trend in PEC-corrected melt inclusions and the numerous glomerocrysts observed within the 2008 scoria, which are inferred to be samples of erupted crystal mush [114,116]. There is also evidence of both assimilation (low TiO2, K2O and high Al2O3) and fractionation at a high modal abundance of plagioclase (high TiO2, P2O5, K2O and low Al2O3, CaO). Taken together, the preserved melt compositions in Llaima samples support interpretations [114,116,117] of relatively shallow magma storage, rapid syn-eruptive evacuation of the volcanic conduit, and entrainment of crystals from parts of the system that have experienced different amounts of fractionation and assimilation.
(c). Fuego, Guatemala
Fuego volcano erupts frequently in styles that range from Strombolian to paroxysmal to, on rare occasions, subPlinian [37,119]. Strombolian eruptive products are difficult, if not impossible, to sample directly because of their limited dispersion outside of the vent region. Paroxysmal eruptions, in contrast, vary in size and energy, with the largest generating substantial pyroclastic density currents (PDCs) in addition to widespread ashfall (e.g. 3 and 5 June 2018). The most recent very large (subPlinian) eruption occurred in 1974; it lasted from 14 to 23 October and comprised several explosive events, the largest of which was on 17 October. All eruptive phases were well documented and many were sampled [37]. Here, we examine the compositional data of glass phases from both the 1974 subPlinian eruptions and later paroxysmal eruptions; to the published data we add matrix glass analyses from one 1974 ash sample, two clasts from 1974 PDCs, and three PDC clasts from a paroxysmal eruption in 2012 (see the electronic supplementary material for sample descriptions, analysis methods and data table).
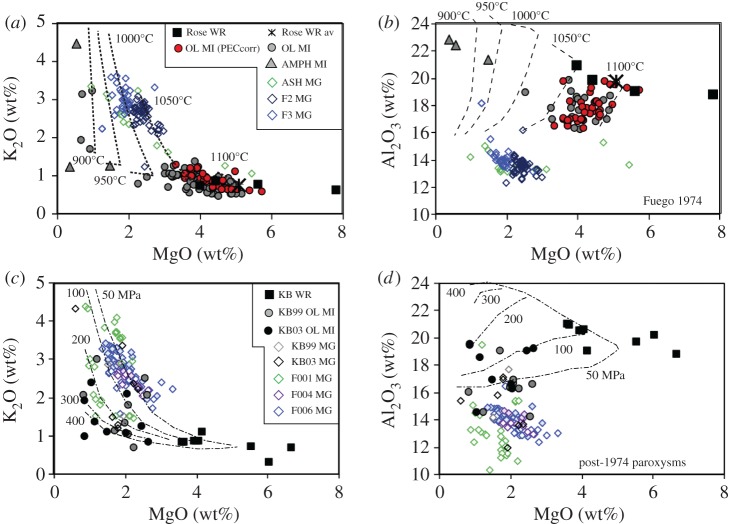
The products of the 1974 eruption have been the subject of numerous studies, starting with a detailed analysis of both the physical and compositional characteristics of deposits from the four main eruptive phases (10–24 October [35]). Important observations from this study include variations in the abundance of olivine and plagioclase through time, with corresponding variations in the bulk compositions of ash samples (figure 9), as well as a wide compositional range of melt inclusions in olivine (K2O = 0.57–1.32 wt%), plagioclase (K2O = 0.5–1.58 wt%) and magnetite (K2O = 0.84–1.01 wt%). Calculated olivine-melt temperatures of the erupted magma ranged from 1010°C to 1130°C, and an inverse relation between S and K2O suggested crystallization over a pressure range. Finally, Anderson [35] demonstrated that, although the eruption tapped material from a range of depths and temperatures, the overall trend was of that of tapping an increasingly deeper source through time. Subsequent petrologic studies have focused primarily on olivine-hosted melt inclusions (e.g. [36,40,120,121]) and have confirmed the variability of both melt inclusion and matrix glass compositions in addition to showing that the volatile contents (H2O ≤ 6.5 wt% and CO2 ≤ 4500 ppm [120,121]) require pre-eruptive storage in a magma reservoir that probably extended to the mid-crust (greater than 500 MPa [123]). The temperatures of melt inclusion entrapment in olivine [36] overlap early estimates (1020–1100°C); rare amphibole inclusions in approximately An91 plagioclase megacrysts, however, suggest lower equilibration temperatures (approx. 988 ± 22°C using the formulation of [36,124]) and confirm early crystallization at high pressures (greater than 500 MPa).
Figure 9.
Melt compositions from Fuego volcano, Guatemala. Data are plotted separately for the 1974 subPlinian eruptions (a,b) and the sub-1974 paroxyms (c,d). (a,c) MgO versus K2O; (b,d) MgO versus Al2O3. Data from [36,120–122]. Also marked are the trends from figure 3 for ITD at a range of temperatures (as labelled). (a,b) Whole-rock data from Rose ([37]; WR); olivine-melt inclusions (OL MI, from [36,120,121]); red circles represent the largest explosion on 17 October 1974 and have been corrected for PEC (from [40]); grey triangles are amphibole melt inclusions (AMPH MI) from [36]; ash matrix glass (MG) from samples described in electronic supplementary material. (c,d) Whole-rock data (KB WR) from [36]; melt inclusion data plotted separately for paroxysms from 1999 (KB99) and 2003 (KB03; both from [36]); diamonds are matrix glass data from 1999 and 2003 (KB99, KB03) and from 2012 (from samples described in the electronic supplementary material).
In detail, olivine-hosted melt inclusions from 1974 samples show a compositional range dominated by variations in MgO, but with increases in K2O that require approximately 50% crystallization (figure 9a). Al2O3 is variable, but generally decreases with decreasing MgO (figure 9b), consistent with crystallization of olivine, clinopyroxene and plagioclase over a range of pressure and temperature (e.g. [40]). Rare amphibole-hosted MIs [36] show strong depletions in MgO and elevated Al2O3, suggesting extensive crystallization of mafic phases prior to feldspar saturation. Although Al2O3max values lie outside the calibration range of the hygrometer (figure 4a), a linear extrapolation of the calibration suggests H2Oplag-in = 7.6–9.6 wt%. These values are similar to H2O contents of high-Al basalts from the Lesser Antilles, which are also characterized by deep-crystallizing amphibole [125]. Amphibole crystallization prior to plagioclase crystallization is also consistent with the low K2O of two melt inclusions, although in this context the high reported K2O of one inclusion is puzzling. Predictably, matrix glass compositions record decompression-driven crystallization of plagioclase and pyroxene (the dominant groundmass phases) that form a broad LLD trend in MgO–K2O space. Close examination, however, shows differences among samples. The ash sample (red open diamonds) preserves a nearly continuous compositional range from the most evolved olivine-hosted melt inclusions to a highly evolved end member, while matrix glass data from PDC samples (black and grey open diamonds) are more restricted in range and generally higher in MgO for the same K2O. Matrix glass data thus confirm extensive late-stage plagioclase crystallization, possibly over slightly different decompression paths.
Data from post-1974 paroxysmal eruptions, in contrast, show a range in bulk compositions, most probably the result of variable abundance of glomerocrysts, which are common in these samples [36]. Olivine-hosted melt inclusions have K2O contents that vary by a factor of six, indicating highly variable crystallization histories (figure 9c). Al2O3max is comparable to that of olivine-hosted MIs from 1974 (approx. 19.8, or H2Oplag-in ≈ 5.5 wt%), but is achieved at lower MgO (figure 9d). Glass compositions of both the matrix and interstitial melt from glomerocrysts track a broad decompression-driven crystallization path, although the inter-sample variability, particularly at low MgO, suggests that individual samples may preserve magma aliquots that have ascended via different dP/dT paths. More curious is the apparent trend in the matrix glass compositions of increasing Al2O3 with decreasing MgO, which is not anticipated given the high plagioclase content of Fuego pyroclasts.
The data shown in figure 9 can be compared with the model data shown in figure 3, with the important caveat that MELTS runs were designed to examine trends but not to reproduce, exactly, the Fuego system (for example, they do not include CO2 or other volatiles, nor do they include deep amphibole crystallization). For clarity, we show model trends for ITD in figure 9a,b, and model trends for IBC in figure 9c,d. Most of the 1974 MI data are bracketed by decompression–crystallization trends at approximately 1050–1100°C, consistent with geothermometry estimates. Matrix glass compositions follow the same trend, although at slightly lower temperatures (1000–1050°C). Exceptions include a few olivine-hosted MIs and the amphibole-hosted MIs, which suggest early IBC at high pressure prior to rapid decompression, as also indicated by thermobarometric evidence for early and deep amphibole crystallization [36]. Melt inclusion data from post-1974 paroxysms, in contrast, follow IBC trends on the plot of K2O versus MgO, while matrix glass compositions from two samples record decompression paths that are similar to 1974. A third sample (F001) preserves glass compositions that overlap with the olivine-hosted melt inclusion glass compositions of [36]. We note that the Al2O3–MgO trends are not well matched by our MELTS model, which probably reflects the open system behaviour of Fuego with respect to volatiles (which we did not attempt to model in MELTS). This mismatch notwithstanding, the data show that paroxysmal eruptions extract magma from a large P–T range, which is recorded in the melt compositions in addition to the phenocryst assemblage and volatile content of melt inclusions. Rapid magma extraction from a range of pressures and temperatures may also help to explain the apparent trend of increasing Al2O3 with decreasing MgO, which could represent magma aliquots that track parallel dP/dT trends.
In summary, melt inclusion data from mafic arc volcanoes record the P–T conditions in the magma storage region, while matrix glass data preserve information on magma ascent paths. All examples record pre-eruptive magma storage over a range of pressures and temperatures, and contribute to the view of arc magmatic systems as primarily vertically, rather than laterally, extensive. Olivine-hosted melt inclusion data differ, however, in the extent to which they record crystallization of mafic phases alone (explosive eruptions of Etna and Stromboli) or co-crystallization of mafic phases and plagioclase (Llaima and Fuego), which in turn records the depth of magma storage relative to the pressure of H2O saturation. Comparison of melt inclusion and matrix glass compositions could further be used to calculate the rate of syn-eruptive magma ascent, if the kinetics of decompression-induced crystallization were well constrained [30]. For example, individual paroxysmal eruptions of Stromboli typically last less than 60 s, and as a result the LP matrix glass shows little evidence of syn-eruptive crystallization (e.g. [126]). Explosive eruptions from Etna, in contrast, are more protracted, and matrix glass compositions record more of the decompression history. The magma storage location and resulting extent of (relatively shallow) plagioclase crystallization may also affect eruption style, as indicated by the difference in matrix glass compositions in explosive and effusive phases of recent Etna eruptions. Finally, the variability of melt inclusion and matrix glass compositions within samples requires that individual clasts, and individual crystals within those clasts, be assembled syn-eruptively from discrete parts of the magmatic system. The insight provided by melt compositions into the physical nature of both the magma storage region and the eruptive process is thus complementary to evidence provided by the crystal cargo and volatile contents of crystal-hosted melt inclusions.
5. Discussion and conclusion
The review of mafic melt compositions provided above illustrates the variability of melt compositional data, and the insight it provides into the structure and dynamics of TCMS. The overarching conclusion is that the products of individual eruptions commonly include melt (± crystals) drawn from an extensive pressure (and sometimes temperature) range. These different components may be intimately mixed, or rapidly mingled, during eruption. Critically, even when these melts are derived from the same starting composition, they cannot necessarily be related by simple LLD models, but instead may reflect rapid assembly from a range of P–T space, and corresponding range of dP/dT paths. Our review also highlights differences in conditions of magma storage and ascent between low-H2O (ocean island) and high-H2O (arc) magmas [93].
Melt compositions erupted from high-flux magmatic systems such as Kīlauea, Hawai‘i, record variations in initial melt inputs from mantle sources, can be used to reconstruct the volume of magma reservoirs, and reveal complex mixing and mingling of melts with a wide compositional range that reflect an equally large temperature range. What emerges is a picture of a shallow magma reservoir that is continually resupplied from depth, and which is underlain by a crystal-rich reservoir of primitive melt (and olivine) that is tapped only during unusually explosive eruptions, or by flank eruptions where magma has circumvented the shallow summit reservoir. Low-flux ocean island systems, in contrast, show little evidence for shallow magma storage but instead erupt magma that is sourced at, or below, the Moho. This is true of both alkalic (pre- and post-shield) stages of Hawaiian volcanism and in low-flux hotspot environments such as the Canaries.
Mafic arc magmas are distinct from ocean island magmas in their high H2O contents; as a result, melt compositions are strongly affected by dP/dT path. Similarities with Kīlauea include the common association of high-intensity eruptions with magma sourced from a wide pressure range (vertical extent) and the rapid ascent of deep-sourced magma, which seems most easily explained by a downward-propagating decompression wave (e.g. [96,109]). Also similar are accumulations of shallow-sourced magma in frequently active volcanic systems, where melt compositions are buffered either at a peritectic composition (e.g. for differentiated Kīlauea magmas [127]) or by mafic recharge (including volatiles; e.g. [113]).
A final question relates to the stability of different melt–mush configurations and their relation to local fluxes of magma and volatiles. Ocean island volcanoes show a direct relation between magma flux and depth of melt accumulation, with low-flux systems sourced from at or beneath the Moho; the same may be true for mid-ocean ridge systems [128]. Melts erupted from arc volcanoes, in contrast, are commonly sourced from mid- to upper-crustal levels. The extent to which mid-crustal magma accumulation regions are connected permanently, or only transiently, to shallower storage regions is not known. Stromboli presents an interesting example, in that it appears to be a long-lived system that maintains discrete deep and shallow magma reservoirs, which communicate only during paroxysmal eruptions.
In conclusion, we demonstrate that melt compositions provide a comprehensive record of magma evolution, accumulation, decompression and mixing that cannot be explained by simple LLD trends. Instead, observed compositional variations contain important information about the physical nature of TCMS across a range of tectonic settings, as well as paths of magma transport to the surface during eruption. Importantly, these compositional variations are supported by both experimental data and thermodynamic models, which are used to simulate fractionation at a range of pressures, thermal conditions and volatile contents. Finally, we note that detailed analyses of rhyolitic melts used to assess the chemical and physical nature of melt bodies that supply very large eruptions are providing evidence for equally diverse melt sources (e.g. [4,118,129,130]), and further illustrate the importance of combining melt and crystal analyses to fully characterize magmatic systems.
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
This work arose from a Royal Society discussion meeting in November 2017, which the authors helped to organize. We thank all attendees at that meeting for stimulating views on magmatic systems, which stimulated us to put together this story of the melt, as a complement to all of the work that has gone into the study of crystals.
Data accessibility
The datasets supporting this article have been uploaded as part of the electronic supplementary material.
Authors' contributions
K.V.C. conceived of the review topic. K.V.C. and M.E. together wrote the introductory and concluding material. M.E. was primarily responsible for the section on ocean island volcanism, while K.V.C. was responsible for the sections on mafic arc volcanism.
Competing interests
We declare we have no competing interests.
Funding
K.V.C. was supported by funding from the AXA Research Fund and the Royal Society (Wolfson Merit Award).
References
- 1.Sparks RSJ, Annen C, Blundy JD, Cashman KV, Rust AC, Jackson MD. 2019. Formation and dynamics of magma reservoirs. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 377, 20180019 ( 10.1098/rsta.2018.0019) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cashman KV, Sparks RSJ, Blundy JD. 2017. Vertically extensive and unstable magmatic systems: a unified view of igneous processes. Science 355, eaag3055 ( 10.1126/science.aag3055) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cooper KM. 2017. What does a magma reservoir look like? The ‘crystal's-eye’ view. Elements 13, 23–28. ( 10.2113/gselements.13.1.23) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cooper KM, Kent AJ. 2014. Rapid remobilization of magmatic crystals kept in cold storage. Nature 506, 480–483. ( 10.1038/nature12991) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ganne J, Bachmann O, Feng X. 2018. Deep into magma plumbing systems: interrogating the crystal cargo of volcanic deposits. Geology 46, 415–418. ( 10.1130/G39857.1) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Putirka KD. 2017. Down the crater: where magmas are stored and why they erupt. Elements 13, 11–16. ( 10.2113/gselements.13.1.11) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Neave DA, Putirka KD. 2017. A new clinopyroxene–liquid barometer, and implications for magma storage pressures under Icelandic rift zones. Am. Mineral. 102, 777–794. ( 10.2138/am-2017-5968) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Putirka K. (ed.) 2014. Amphibole–liquid equilibria: barometers and thermometers for volcanic systems. In 2014 GSA Annual Meeting, Vancouver, British Columbia.
- 9.Putirka KD. 2005. Igneous thermometers and barometers based on plagioclase + liquid equilibria: tests of some existing models and new calibrations. Am. Mineral. 90, 336–346. ( 10.2138/am.2005.1449) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Putirka K, Johnson M, Kinzler R, Longhi J, Walker D. 1996. Thermobarometry of mafic igneous rocks based on clinopyroxene–liquid equilibria, 0–30 kbar. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 123, 92–108. ( 10.1007/s004100050145) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cervantes P, Wallace PJ. 2003. Role of H2O in subduction-zone magmatism: new insights from melt inclusions in high-Mg basalts from central Mexico. Geology 31, 235–238. ( 10.1130/0091-7613(2003)031%3C0235:ROHOIS%3E2.0.CO;2) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Métrich N, Wallace PJ. 2008. Volatile abundances in basaltic magmas and their degassing paths tracked by melt inclusions. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 69, 363–402. ( 10.2138/rmg.2008.69.10) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hartley ME, Bali E, Maclennan J, Neave DA, Halldórsson SA. 2018. Melt inclusion constraints on petrogenesis of the 2014–2015 Holuhraun eruption, Iceland. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 173, 10 ( 10.1007/s00410-017-1435-0) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ghiorso MS, Gualda GA. 2015. An H2O–CO2 mixed fluid saturation model compatible with rhyolite-MELTS. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 169, 53 ( 10.1007/s00410-015-1141-8) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Danyushevsky LV, Plechov P. 2011. Petrolog3: Integrated software for modeling crystallization processes. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 12, Q07021 ( 10.1029/2011GC003516) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Newman S, Lowenstern JB. 2002. VolatileCalc: a silicate melt–H2O–CO2 solution model written in Visual Basic for Excel. Comput. Geosci. 28, 597–604. ( 10.1016/S0098-3004(01)00081-4) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Burgisser A, Alletti M, Scaillet B. 2015. Simulating the behavior of volatiles belonging to the C–O–H–S system in silicate melts under magmatic conditions with the software D-Compress. Comput. Geosci. 79, 1–14. ( 10.1016/j.cageo.2015.03.002) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Rae A, Edmonds M, Morgan DJ, Kahl M, Houghton BF, Maclennan J. 2016. Timescales of magma mixing prior to and during the 1959 Kilauea Iki eruption. Geology 44, 463–466. ( 10.1130/G37800.1) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Costa F, Dungan M. 2005. Short time scales of magmatic assimilation from diffusion modeling of multiple elements in olivine. Geology 33, 837–840. ( 10.1130/G21675.1) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Morgan DJ, Blake S. 2006. Magmatic residence times of zoned phenocrysts: introduction and application of the binary element diffusion modelling (BEDM) technique. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 151, 58–70. ( 10.1007/s00410-005-0045-4) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ruprecht P, Bergantz GW, Dufek J. 2008. Modeling of gas-driven magmatic overturn: tracking of phenocryst dispersal and gathering during magma mixing. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 9, Q07017 ( 10.1029/2008GC002022) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Davidson JP, Hora JM, Garrison JM, Dungan MA. 2005. Crustal forensics in arc magmas. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 140, 157–170. ( 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2004.07.019) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Charlier BLA, Morgan DJ, Wilson CJN, Wooden JL, Allan ASR, Baker JA. 2012. Lithium concentration gradients in feldspar and quartz record the final minutes of magma ascent in an explosive supereruption. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 319 218–227. ( 10.1016/j.epsl.2011.12.016) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Blundy J, Cashman K. 2008. Petrologic reconstruction of magmatic system variables and processes. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 69, 179–239. ( 10.2138/rmg.2008.69.6) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bragagni A, Avanzinelli R, Freymuth H, Francalanci L. 2014. Recycling of crystal mush-derived melts and short magma residence times revealed by U-series disequilibria at Stromboli volcano. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 404, 206–219. ( 10.1016/j.epsl.2014.07.028) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Czuppon G, Lukács R, Harangi S, Mason PR, Ntaflos T. 2012. Mixing of crystal mushes and melts in the genesis of the Bogács ignimbrite suite, northern Hungary: an integrated geochemical investigation of mineral phases and glasses. Lithos 148, 71–85. ( 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.06.009) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Maclennan J, McKenzie D, Hilton F, Gronvöld K, Shimizu N. 2003. Geochemical variability in a single flow from northern Iceland. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 108(B1), 2007 ( 10.1029/2000JB000142) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Davidson JP, Tepley FJ. 1997. Recharge in volcanic systems: evidence from isotope profiles of phenocrysts. Science 275, 826–829. ( 10.1126/science.275.5301.826) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Cassidy M, Edmonds M, Watt SF, Palmer MR, Gernon TM. 2015. Origin of basalts by hybridization in andesite-dominated arcs. J. Petrol. 56, 325–346. ( 10.1093/petrology/egv002) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wright HM, Cashman KV, Mothes PA, Hall ML, Ruiz AG, Le Pennec JL. 2012. Estimating rates of decompression from textures of erupted ash particles produced by 1999–2006 eruptions of Tungurahua volcano, Ecuador. Geology 40, 619–22. ( 10.1130/G32948.1) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Landi P, et al. 2009. Magma dynamics during the 2007 Stromboli eruption (Aeolian Islands, Italy): mineralogical, geochemical and isotopic data. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 182, 255–268. ( 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2008.11.010) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Landi P, Marchetti E, La Felice S, Ripepe M, Rosi M. 2011. Integrated petrochemical and geophysical data reveals thermal distribution of the feeding conduits at Stromboli volcano, Italy. Geophys. Res. Lett. 38, L08305 ( 10.1029/2010GL046296) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wallace PJ. 1998. Water and partial melting in mantle plumes: inferences from the dissolved H2O concentrations of Hawaiian basaltic magmas. Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 3639–3642. ( 10.1029/98GL02805) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sides IR, Edmonds M, Maclennan J, Swanson DA, Houghton BF. 2014. Eruption style at Kīlauea volcano in Hawai'i linked to primary melt composition. Nat. Geosci. 7, 464–469. ( 10.1038/ngeo2140) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Anderson AT. 1984. Probable relations between plagioclase zoning and magma dynamics, Fuego volcano, Guatemala. Am. Mineral. 69, 660–676. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Berlo K, Stix J, Roggensack K, Ghaleb B. 2012. A tale of two magmas, Fuego, Guatemala. Bull. Volcanol. 74, 377–390. ( 10.1007/s00445-011-0530-8) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Rose WI Jr, Anderson AT Jr, Woodruff LG, Bonis SB. 1978. The October 1974 basaltic tephra from Fuego volcano: description and history of the magma body. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 4, 3–53. ( 10.1016/0377-0273(78)90027-6) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Clague DA, Weber WS, Dixon JE. 1991. Picritic glasses from Hawaii. Nature 353, 553–556. ( 10.1038/353553a0) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Rhodes JM, Vollinger MJ. 2005. Ferric/ferrous ratios in 1984 Mauna Loa lavas: a contribution to understanding the oxidation state of Hawaiian magmas. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 149, 666–674. ( 10.1007/s00410-005-0662-y) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lloyd AS, Plank T, Ruprecht P, Hauri EH, Rose W. 2013. Volatile loss from melt inclusions in pyroclasts of differing sizes. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 165, 129–153. ( 10.1007/s00410-012-0800-2) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lloyd A, Plank T, Ruprecht P, Hauri E, Rose W (eds). 2013. Timescales of magma ascent recorded by H2O zonation in clinopyroxene. In AGU Fall Meeting, Abstracts.
- 42.Hauri EH. 1996. Major-element variability in the Hawaiian mantle plume. Nature 382, 415–419. ( 10.1038/382415a0) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Pietruszka AJ, Garcia MO. 1999. A rapid fluctuation in the mantle source and melting history of Kīlauea volcano inferred from the geochemistry of its historical summit lavas (1790–1982). J. Petrol. 40, 1321–1342. ( 10.1093/petroj/40.8.1321) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Maclennan J. 2008. Concurrent mixing and cooling of melts under Iceland. J. Petrol. 49, 1931–1953. ( 10.1093/petrology/egn052) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Kent AJR. 2008. Melt inclusions in basaltic and related volcanic rocks. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 69, 273–331. ( 10.2138/rmg.2008.69.8) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Parman S, Grove T, Kelley K, Plank T. 2010. Along-arc variations in the pre-eruptive H2O contents of Mariana arc magmas inferred from fractionation paths. J. Petrol. 52, 257–278. ( 10.1093/petrology/egq079) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Helz RT, Thornber CR. 1987. Geothermometry of Kilauea Iki lava lake, Hawaii. Bull. Volcanol. 49, 651–668. ( 10.1007/BF01080357) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Montierth C, Johnston AD, Cashman KV. 1995. An empirical glass-composition-based geothermometer for Mauna Loa lavas. In Mauna Loa revealed: structure, composition, history, and hazards (eds JM Rhodes, JP Lockwood), Geophysical Monograph Series, vol. 92, pp. 207–217. Washington, DC: American Geophysical Union ( 10.1029/GM092p0207) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Ho AM, Cashman KV. 1997. Temperature constraints on the Ginkgo flow of the Columbia River Basalt Group. Geology 25, 403–406. ( 10.1130/0091-7613(1997)025%3C0403:TCOTGF%3E2.3.CO;2) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Putirka KD. 2008. Introduction to minerals, inclusions and volcanic processes. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 69, 1–8. ( 10.2138/rmg.2008.69.1) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Melekhova E, Blundy J, Robertson R, Humphreys MC. 2015. Experimental evidence for polybaric differentiation of primitive arc basalt beneath St. Vincent, Lesser Antilles. J. Petrol. 56, 161–192. ( 10.1093/petrology/egu074) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Shea T, Hammer JE. 2013. Kinetics of cooling- and decompression-induced crystallization in hydrous mafic--intermediate magmas. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 260, 127–145. ( 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2013.04.018) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Longpré M-A, Stix J, Klügel A, Shimizu N. 2017. Mantle to surface degassing of carbon- and sulphur-rich alkaline magma at El Hierro, Canary Islands. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 460, 268–280. ( 10.1016/j.epsl.2016.11.043) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Hartley ME, Maclennan J, Edmonds M, Thordarson T. 2014. Reconstructing the deep CO2 degassing behaviour of large basaltic fissure eruptions. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 393, 120–131. ( 10.1016/j.epsl.2014.02.031) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 55.White RS, Edmonds M, Maclennan J, Greenfield T, Agustsdottir T. 2019. Melt movement through the Icelandic crust. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 377, 20180010 ( 10.1098/rsta.2018.0010) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Hansteen TH, Klügel A, Schmincke H-U. 1998. Multi-stage magma ascent beneath the Canary Islands: evidence from fluid inclusions. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 132, 48–64. ( 10.1007/s004100050404) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Frey FA, Wise WS, Garcia MO, West H, Kwon ST, Kennedy A. 1990. Evolution of Mauna Kea volcano, Hawaii: petrologic and geochemical constraints on postshield volcanism. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 95, 1271–1300. ( 10.1029/JB095iB02p01271) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Hammer J, Jacob S, Welsch B, Hellebrand E, Sinton J. 2016. Clinopyroxene in postshield Haleakala ankaramite: 1. Efficacy of thermobarometry. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 171, 7 ( 10.1007/s00410-015-1212-x) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Clague DA, Dixon JE. 2000. Extrinsic controls on the evolution of Hawaiian ocean island volcanoes. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 1, 1010 ( 10.1029/1999GC000023) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Ryan MP. 1988. The mechanics and three-dimensional internal structure of active magmatic systems: Kīlauea volcano, Hawaii. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 93(B5), 4213–4248. ( 10.1029/JB093iB05p04213) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Poland MP, Miklius A, Sutton AJ, Thornber CR. 2012. A mantle-driven surge in magma supply to Kīlauea volcano during 2003–2007. Nat. Geosci. 5, 295–300. ( 10.1038/ngeo1426) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Cervelli PF, Miklius A. 2003. The shallow magmatic system of Kīlauea volcano. In The Pu'u 'O'o-Kupaianaha eruption of Kilauea volcano, Hawai'i: the first 20 years (eds C Heliker, DA Swanson, TJ Takahashi), USGS Professional Paper 1676, pp. 149–163. Reston, VA: US Geological Survey. See https://pubs.usgs.gov/pp/pp1676/pp1676_09.pdf. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Lin G, Amelung F, Lavallée Y, Okubo PG. 2014. Seismic evidence for a crustal magma reservoir beneath the upper east rift zone of Kilauea volcano, Hawaii. Geology 42, 187–190. ( 10.1130/G35001.1) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Wright TL, Klein FW. 2006. Deep magma transport at Kīlauea volcano, Hawaii. Lithos 87, 50–79. ( 10.1016/j.lithos.2005.05.004) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Lin G, Shearer PM, Matoza RS, Okubo PG, Amelung F. 2014. Three-dimensional seismic velocity structure of Mauna Loa and Kilauea volcanoes in Hawaii from local seismic tomography. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 119, 4377–4392. ( 10.1002/2013JB010820) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Okubo PG, Benz HM, Chouet BA. 1997. Imaging the crustal magma sources beneath Mauna Loa and Kilauea volcanoes, Hawaii. Geology 25, 867–870. ( 10.1130/0091-7613(1997)025%3C0867:ITCMSB%3E2.3.CO;2) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Clague DA, Denlinger RP. 1994. Role of olivine cumulates in destabilizing the flanks of Hawaiian volcanoes. Bull. Volcanol. 56, 425–434. ( 10.1007/BF00302824) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Garcia MO, Pietruszka AJ, Rhodes JM, Swanson K. 2000. Magmatic processes during the prolonged Pu'u’O'o eruption of Kilauea volcano, Hawaii. J. Petrol. 41, 967–990. ( 10.1093/petrology/41.7.967) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Helz RT, Clague DA, Mastin LG, Rose TR. 2015. Evidence for large compositional ranges in coeval melts erupted from Kīlauea's summit reservoir. In Hawaiian volcanoes: from source to surface (eds R Carey, V Cayol, M Poland, D Weis), Geophysical Monograph Series, vol. 208, pp. 125–145. Washington, DC: American Geophysical Union; and Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons. ( 10.1002/9781118872079.ch7) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Pietruszka AJ, Garcia MO. 1999. The size and shape of Kīlauea volcano's summit magma storage reservoir: a geochemical probe. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 167, 311–320. ( 10.1016/S0012-821X(99)00036-9) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Pietruszka AJ, Norman MD, Garcia MO, Marske JP, Burns DH. 2012. Chemical heterogeneity in the Hawaiian mantle plume from the alteration and dehydration of recycled oceanic crust. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 361, 298–309. ( 10.1016/j.epsl.2012.10.030) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Marske J, Hauri E, Trusdell F, Garcia M, Pietruszka A. 2015. Major, trace, and volatile (CO2, H2O, S, F, and Cl) elements from 1000+ Hawaiian olivine-hosted melt inclusions reveal the dynamics of crustal recycling. In AGU Fall Meeting, Abstracts.
- 73.Helz RL, Clague DA, Sisson TW, Thornber CR. 2014. Petrologic insights into basaltic volcanism at historically active Hawaiian volcanoes. In Characteristics of Hawaiian volcanoes (eds MP Poland, TJ Takahashi, CM Landowski), USGS Professional Paper 1801, pp. 237–292. Reston, VA: US Geological Survey. See https://pubs.usgs.gov/pp/1801/downloads/pp1801_Chap6_Helz.pdf. [Google Scholar]
- 74.Marsh B. 1981. On the crystallinity, probability of occurrence, and rheology of lava and magma. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 78, 85–98. ( 10.1007/BF00371146) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Stroncik NA, Klügel A, Hansteen TH. 2009. The magmatic plumbing system beneath El Hierro (Canary Islands): constraints from phenocrysts and naturally quenched basaltic glasses in submarine rocks. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 157, 593 ( 10.1007/s00410-008-0354-5) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Roeder PL, Emslie RF. 1970. Olivine–liquid equilibrium. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 29, 275–289. ( 10.1007/BF00371276) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Edmonds M, Sides IR, Maclennan J.. 2015. Insights into mixing, fractionation and degassing of primitive melts at Kīlauea volcano, Hawai'i. In Hawaiian volcanoes: from source to surface (eds R Carey, V Cayol, M Poland, D Weis), Geophysical Monograph Series, vol. 208, pp. 323–349. Washington, DC: American Geophysical Union; and Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons. ( 10.1002/9781118872079.ch15) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Garcia MO, Pietruszka AJ, Rhodes JM. 2003. A petrologic perspective of Kīlauea volcano's summit magma reservoir. J. Petrol. 44, 2313–2339. ( 10.1093/petrology/egg079) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Lynn KJ, Garcia MO, Shea T, Costa F, Swanson DA. 2017. Timescales of mixing and storage for Keanakāko ‘i tephra magmas (1500–1820 CE), Kīlauea volcano, Hawai‘i. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 172, 76 ( 10.1007/s00410-017-1395-4) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Helz RT. 1987. Differentiation behavior of Kīlauea Iki lava lake, Kīlauea volcano, Hawaii: an overview of past and current work. In Magmatic processes: physicochemical principles (ed. BO Mysen), Geochemical Society Special Publication no. 1, pp. 241–258. Washington, DC: Geochemical Society. See https://www.geochemsoc.org/index.php/download_file/view/1001/376. [Google Scholar]
- 81.Wallace PJ, Anderson AT. 1998. Effects of eruption and lava drainback on the H2O contents of basaltic magmas at Kīlauea volcano. Bull. Volcanol. 59, 327–344. ( 10.1007/s004450050195) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Sides I, Edmonds M, Maclennan J, Houghton B, Swanson D, Steele-MacInnis M. 2014. Magma mixing and high fountaining during the 1959 Kīlauea Iki eruption, Hawai‘i. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 400, 102–112. ( 10.1016/j.epsl.2014.05.024) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Eaton J, Richter D, Krivoy H. 1987. Cycling of magma between the summit reservoir and Kīlauea Iki lava lake during the 1959 eruption of Kīlauea volcano. In Volcanism in Hawaii (eds RW Decker, TL Wright, PH Stauffer), USGS Professional Paper 1350, vol. 2, pp. 1307–1335. Reston, VA: US Geological Survey. See https://pubs.usgs.gov/pp/1987/1350/pdf/chapters/pp1350_ch48.pdf. [Google Scholar]
- 84.Lowenstern JB, Mahood GA, Rivers ML, Sutton SR. 1991. Evidence for extreme partitioning of copper into a magmatic vapor phase. Science 252, 1405–1409. ( 10.1126/science.252.5011.1405) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Yoder H Jr, Tilley CE. 1962. Origin of basalt magmas: an experimental study of natural and synthetic rock systems. J. Petrol. 3, 342–532. ( 10.1093/petrology/3.3.342) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Longpré M-A, Klügel A, Diehl A, Stix J. 2014. Mixing in mantle magma reservoirs prior to and during the 2011–2012 eruption at El Hierro, Canary Islands. Geology 42, 315–318. ( 10.1130/G35165.1) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Klügel A, Longpré M-A, Stix J. 2015. Deep intrusions, lateral magma transport and related uplift at ocean island volcanoes. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 431, 140–149. ( 10.1016/j.epsl.2015.09.031) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Klügel A, Hansteen TH, Galipp K. 2005. Magma storage and underplating beneath Cumbre Vieja volcano, La Palma (Canary Islands). Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 236, 211–226. ( 10.1016/j.epsl.2005.04.006) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Schwarz S, Klügel A, Wohlgemuth-Ueberwasser C. 2004. Melt extraction pathways and stagnation depths beneath the Madeira and Desertas rift zones (NE Atlantic) inferred from barometric studies. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 147, 228–240. ( 10.1007/s00410-004-0556-4) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Klügel A, Klein F. 2006. Complex magma storage and ascent at embryonic submarine volcanoes from the Madeira archipelago. Geology 34, 337–340. ( 10.1130/G22077.1) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Neave DA, Passmore E, Maclennan J, Fitton G, Thordarson T. 2013. Crystal–melt relationships and the record of deep mixing and crystallization in the AD 1783 Laki eruption, Iceland. J. Petrol. 2013, egt027 ( 10.1093/petrology/egt027) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Edgar C, Wolff J, Olin P, Nichols H, Pittari A, Cas R, Reiners PW, Marti J, Spell TL. 2007. The late Quaternary Diego Hernandez Formation, Tenerife: volcanology of a complex cycle of voluminous explosive phonolitic eruptions. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 160, 59–85. ( 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2006.06.001) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Edmonds M, Cashman KV, Holness M, Jackson M. 2019. Architecture and dynamics of magma reservoirs. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 377, 20180298 ( 10.1098/rsta.2018.0298) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Ruprecht P, Plank T. 2013. Feeding andesitic eruptions with a high-speed connection from the mantle. Nature 500, 68–72. ( 10.1038/nature12342) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Métrich N, Bertagnini A, Di Muro A. 2009. Conditions of magma storage, degassing and ascent at Stromboli: new insights into the volcano plumbing system with inferences on the eruptive dynamics. J. Petrol. 51, 603–626. ( 10.1093/petrology/egp083) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Ripepe M, et al. 2015. Volcano seismicity and ground deformation unveil the gravity-driven magma discharge dynamics of a volcanic eruption. Nat. Commun. 6, 6998 ( 10.1038/ncomms7998) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Kilgour G, Saunders K, Blundy J, Cashman K, Scott B, Miller C. 2014. Timescales of magmatic processes at Ruapehu volcano from diffusion chronometry and their comparison to monitoring data. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 288, 62–75. ( 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2014.09.010) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Humphreys MC, Christopher T, Hards V. 2009. Microlite transfer by disaggregation of mafic inclusions following magma mixing at Soufrière Hills volcano, Montserrat. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 157, 609–624. ( 10.1007/s00410-008-0356-3) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Métrich N, Bertagnini A, Landi P, Rosi M, Belhadj O. 2005. Triggering mechanism at the origin of paroxysms at Stromboli (Aeolian archipelago, Italy): the 5 April 2003 eruption. Geophys. Res. Lett. 32, L10305 ( 10.1029/2004GL022257) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 100.La Felice S, Landi P. 2011. The 2009 paroxysmal explosions at Stromboli (Italy): magma mixing and eruption dynamics. Bull. Volcanol. 73, 1147–1154. ( 10.1007/s00445-011-0502-z) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 101.La Felice S, Landi P. 2011. A spatter-forming, large-scale paroxysm at Stromboli volcano (Aeolian Islands, Italy): insight into magma evolution and eruption dynamics. Bull. Volcanol. 73, 1393–1406. ( 10.1007/s00445-011-0476-x) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Pichavant M, Pompilio M, D'Oriano C, Di Carlo I. 2011. Petrography, mineralogy and geochemistry of a primitive pumice from Stromboli: implications for the deep feeding system. Eur. J. Mineral. 23, 499–517. ( 10.1127/0935-1221/2011/0023-2109) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Bertagnini A, Métrich N, Landi P, Rosi M. 2003. Stromboli volcano (Aeolian archipelago, Italy): an open window on the deep-feeding system of a steady state basaltic volcano. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 108(B7), 2336 ( 10.1029/2002JB002146) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Landi P, et al. 2006. The December 2002–July 2003 effusive event at Stromboli volcano, Italy: insights into the shallow plumbing system by petrochemical studies. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 155, 263–284. ( 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2006.03.032) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Métrich N, Allard P, Spilliaert N, Andronico D, Burton M. 2004. Flank eruption of the alkali-and volatile-rich primitive basalt responsible for Mount Etna's evolution in the last three decades. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 228, 1–17. ( 10.1016/j.epsl.2004.09.036) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Spilliaert N, Allard P, Métrich N, Sobolev A. 2006. Melt inclusion record of the conditions of ascent, degassing, and extrusion of volatile-rich alkali basalt during the powerful 2002 flank eruption of Mount Etna (Italy). J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 111, B04203 ( 10.1029/2005JB003934) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Collins SJ, Pyle DM, Maclennan J. 2009. Melt inclusions track pre-eruption storage and dehydration of magmas at Etna. Geology 37, 571–574. ( 10.1130/G30040A.1) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Allard P. 2010. A CO2-rich gas trigger of explosive paroxysms at Stromboli basaltic volcano, Italy. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 189, 363–374. ( 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2009.11.018) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Aiuppa A, Bertagnini A, Métrich N, Moretti R, Di Muro A, Liuzzo M, Tamburella G. 2010. A model of degassing for Stromboli volcano. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 295, 195–204. ( 10.1016/j.epsl.2010.03.040) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Métrich N, Rutherford MJ. 1998. Low pressure crystallization paths of H2O-saturated basaltic–hawaiitic melts from Mt Etna: implications for open-system degassing of basaltic volcanoes. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 62, 1195–1205. ( 10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00048-9) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Aiuppa A, Moretti R, Federico C, Giudice G, Gurrieri S, Liuzzo M, Papale P, Shinohara H, Valenza M. 2017. Forecasting Etna eruptions by real-time observation of volcanic gas composition. Geology 35, 1115–1118. ( 10.1130/G24149A.1) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Kahl M, Chakraborty S, Costa F, Pompilio M, Liuzzo M, Viccaro M. 2013. Compositionally zoned crystals and real-time degassing data reveal changes in magma transfer dynamics during the 2006 summit eruptive episodes of Mt. Etna. Bull. Volcanol. 75, 1–14. ( 10.1007/s00445-013-0692-7) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Caricchi L, Sheldrake TE, Blundy J. 2018. Modulation of magmatic processes by CO2 flushing. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 491, 160–171. ( 10.1016/j.epsl.2018.03.042) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 114.De Maisonneuve CB, Dungan M, Bachmann O, Burgisser A. 2012. Insights into shallow magma storage and crystallization at Volcán Llaima (Andean Southern Volcanic Zone, Chile). J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 211, 76–91. ( 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2011.09.010) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 115.de Maisonneuve CB, Costa F, Huber C, Vonlanthen P, Bachmann O, Dungan MA. 2016. How do olivines record magmatic events? Insights from major and trace element zoning. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 171, 56 ( 10.1007/s00410-016-1264-6) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Ruth DC, Cottrell E, Cortés JA, Kelley KA, Calder ES. 2016. From passive degassing to violent Strombolian eruption: the case of the 2008 eruption of Llaima volcano, Chile. J. Petrol. 57, 1833–1864. ( 10.1093/petrology/egw063) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Ruth DC, Costa F, de Maisonneuve CB, Franco L, Cortés JA, Calder ES. 2018. Crystal and melt inclusion timescales reveal the evolution of magma migration before eruption. Nat. Commun. 9, 2657 ( 10.1038/s41467-018-05086-8) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Gualda GA, Ghiorso MS. 2013. Low-pressure origin of high-silica rhyolites and granites. J. Geol. 121, 537–545. ( 10.1086/671395) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Lyons JJ, Waite GP, Rose WI, Chigna G. 2010. Patterns in open vent, Strombolian behavior at Fuego volcano, Guatemala, 2005–2007. Bull. Volcanol. 72, 1 ( 10.1007/s00445-009-0305-7) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Sisson T, Layne G. 1993. H2O in basalt and basaltic andesite glass inclusions from four subduction-related volcanoes. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 117, 619–635. ( 10.1016/0012-821X(93)90107-K) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Roggensack K. 2001. Unraveling the 1974 eruption of Fuego volcano (Guatemala) with small crystals and their young melt inclusions. Geology 29, 911–914. ( 10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029%3C0911:UTEOFV%3E2.0.CO;2) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Lloyd AS, Ferriss E, Ruprecht P, Hauri EH, Jicha BR, Plank T. 2016. An assessment of clinopyroxene as a recorder of magmatic water and magma ascent rate. J. Petrol. 57, 1865–1886. ( 10.1093/petrology/egw058) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Moore LR, et al. 2015. Bubbles matter: an assessment of the contribution of vapor bubbles to melt inclusion volatile budgets. Am. Mineral. 100, 806–823. ( 10.2138/am-2015-5036) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Ridolfi F, Renzulli A, Puerini M. 2010. Stability and chemical equilibrium of amphibole in calc-alkaline magmas: an overview, new thermobarometric formulations and application to subduction-related volcanoes. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 160, 45–66. ( 10.1007/s00410-009-0465-7) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Melekhova E, Blundy J, Martin R, Arculus R, Pichavant M. 2017. Petrological and experimental evidence for differentiation of water-rich magmas beneath St. Kitts, Lesser Antilles. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 172, 98 ( 10.1007/s00410-017-1416-3) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Rosi M, Bertagnini A, Harris A, Pioli L, Pistolesi M, Ripepe M. 2006. A case history of paroxysmal explosion at Stromboli: timing and dynamics of the April 5, 2003 event. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 243, 594–606. ( 10.1016/j.epsl.2006.01.035) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Wright TL, Fiske RS. 1971. Origin of the differentiated and hybrid lavas of Kilauea volcano, Hawaii. J. Petrol. 12, 1–65. ( 10.1093/petrology/12.1.1) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Canales JP, Dunn RA, Ito G, Detrick RS, Sallarès V. 2014. Effect of variations in magma supply on the crustal structure of mid-ocean ridges: insights from the western Galápagos Spreading Center. In The Galapagos: a natural laboratory for the Earth sciences (eds KS Harpp, E Mittelstaedt, N d'Ozouville, DW Graham), Geophysical Monograph Series, vol. 204, pp. 363–389. Washington, DC: American Geophysical Union; and Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons ( 10.1002/9781118852538.ch17) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Cashman KV, Giordano G. 2014. Calderas and magma reservoirs. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 288, 28–45. ( 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2014.09.007) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Swallow EJ, Wilson CJ, Myers ML, Wallace PJ, Collins KS, Smith EG. 2018. Evacuation of multiple magma bodies and the onset of caldera collapse in a supereruption, captured in glass and mineral compositions. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 173, 33 ( 10.1007/s00410-018-1459-0) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The datasets supporting this article have been uploaded as part of the electronic supplementary material.