Abstract
Dickeya solani is a recently emerged virulent bacterial potato pathogen that poses a major threat to world agriculture. Because of increasing antibiotic resistance and growing limitations in antibiotic use, alternative antibacterials such as bacteriophages are being developed. Myoviridae bacteriophages recently re-ranked as a separate Ackermannviridae family, such as phage PP35 described in this work, are the attractive candidates for this bacterial biocontrol. PP35 has a very specific host range due to the presence of tail spike protein PP35 gp156, which can depolymerize the O-polysaccharide (OPS) of D. solani. The D. solani OPS structure, →2)-β-D-6-deoxy-D-altrose-(1→, is so far unique among soft-rot Pectobacteriaceae, though it may exist in non-virulent environmental Enterobacteriaceae. The phage tail spike depolymerase degrades the shielding polysaccharide, and launches the cell infection process. We hypothesize that non-pathogenic commensal bacteria may maintain the population of the phage in soil environment.
Keywords: bacteriophage, Dickeya solani, Lelliottia, genomics, tail spike protein, polysaccharide, depolymerase
Introduction
Soft-rot Pectobacteriaceae (SRP) include phytopathogenic bacterial species from the genera Pectobacterium and Dickeya that cause economic losses in potato crops, as well as other vegetables and ornamental plants worldwide (Pérombelon, 2002). Dickeya spp. were mostly associated with plant diseases in tropical climates (Toth et al., 2011). A new virulent species named D. solani emerged in the early 2010s (Laurila et al., 2010; van der Wolf et al., 2014) and rapidly spread throughout Europe, including Russia (Ignatov et al., 2014). No potato cultivars is resistant to D. solani, and the spread of the disease is mostly contained by quarantining and controlling seed stocks (Mansfield et al., 2012). Treating seeds and harvested tubers with bacteriophages – viruses specific to particular bacterial pathogens – is considered a promising and environmentally safe strategy to protect plants and harvested crops from bacterial diseases (Frampton et al., 2012). A number of isolated bacteriophages infect D. solani (Adriaenssens et al., 2012b; Day et al., 2017) and some can also infect other Dickeya spp. (Czajkowski et al., 2014b, 2015). They have been thoroughly characterized and used to protect and control soft rot caused by D. solani. The primary goal of the present study was an investigation of the D. solani – specific bacteriophage newly isolated in Russia and the molecular details of its interaction with the bacterial host.
Materials and Methods
Isolation and Purification of Phage PP35
Bacteriophage PP35 was isolated in 2014 from sewage water near an outbreak of soft rot in harvested potatoes caused by D. solani (Moscow region, Russia). Phage was propagated on D. solani strain F012 in LB at 26°C following a published general protocol (Clokie and Kropinski, 2009). After chloroform treatment, removal of cell debris by centrifugation (8000 g, 20 min), filtration through a 0.22-μm-pore size membrane filter (Millipore), and treatment with DNase I (0.5 mg/mL, 60 min), the phage was purified by ultracentrifugation (22,000 g, 120 min, 4°C, Beckman SW28 rotor) in a CsCl step gradient with densities of 0.5 to 1.7 g/mL. The resulting suspension of PP35 was dialyzed overnight against phage buffer (10 mM Tris–HCl, pH 7.4, 10 mM MgSO4) to remove CsCl. Purified phage was stored at 4°C in phage buffer.
Host Range and General Characterization of Phage PP35
The host range of phage PP35 was tested by standard plaque assays and by spotting phage suspensions (106 pfu/ml) onto a bacterial lawn. Bacterial strains listed in Supplementary Table S1 were grown on LB agar at 26°C. In adsorption experiments, the host strains F012 or F154 were grown to an OD600 ∼ 0.4 and infected with PP35 at a multiplicity of infection of 0.1. Every 3 min after infection, 100 μl aliquots were taken and transferred into 800 μl LB medium supplied with 50 μl chloroform. After bacterial lysis the mixtures were centrifuged and the supernatant was titrated to determine the amount of non-adsorbed or reversibly adsorbed phages. One-step-growth assays were performed according to Adriaenssens et al. (2012b). To assay a lytic activity of phage PP35, an exponentially growing culture of F012 or F154 (106 cfu/ml) was mixed with phage PP35 (MOI of 0.1). The mixture was then incubated with shaking at 26°C. Every 10 min, aliquots were taken, and the appropriate dilutions were spread on LB agar plates, and incubated overnight at 26°C. The next day, colonies were counted. Phage stability was studied by incubating a 107 pfu/ml phage suspension at different temperatures or in a range of buffer solutions (20 mM Tris–HCl/20 mM Na citrate/20 mM Na phosphate) adjusted with NaOH to pH range 4–9. All experiments were performed independently 3–4 times, and the results were averaged. Plots were generated with Microsoft Excel.
Electron Microscopy
Purified phage particles were applied to grids and stained with 1% uranyl acetate aqueous solution (Ackermann, 2009). The specimens were observed in a JEOL JEM-CX100 electron microscope at 100 kV accelerating voltage.
Genome Sequencing and Annotation
Bacterial and phage DNA was extracted using the phenol-chloroform method and fragmented with a Bioruptor sonicator (Diagenode). Paired-end libraries were constructed using Nebnext Ultra DNA library prep kit (New England Biolabs) and sequenced on the Illumina MiSeqTM platform (Illumina) using paired 150 bp reads. After filtering with CLC Genomics Workbench 8.5 (Qiagen), overlapping paired-end library reads were merged with the SeqPrep tool1. Reads from bacteriophage PP35 were assembled in CLC Genomic workbench v. 7.5; reads from F012 and F154 bacterial strains were assembled using SPAdes 3.6.1 (Bankevich et al., 2012). Contig count, assembly length and mean coverage are displayed in Table 1.
Table 1.
Genome assembly properties.
| Genome | Contig (scaffold) count | Assembly length, bp | Mean coverage |
|---|---|---|---|
| PP35 (phage) | 1 (1) | 152 048 | 245 |
| Dickeya F012 | 27 (25) | 4 879 104 | 52.3 |
| Lelliottia F154 | 23 (23) | 4 457 928 | 54.3 |
Bacterial genomes were annotated with the RAST automated pipeline2 (Aziz et al., 2008). Phage genome was annotated by first calling ORFs with GeneMarkS (Besemer et al., 2001). ORF functions were predicted using Psi-BLAST alignment against the NCBI nr database (Altschul et al., 1997) and Pfam domain prediction using HMMER (Finn et al., 2011). tRNA coding regions were identified with tRNAscan-SE (Schattner et al., 2005), search of other non-coding RNA was performed using SEED. Putative phage promoters were predicted by PHIRE (Lavigne et al., 2004) and phiSITE (Klucar et al., 2009). CRISPR arrays were detected using CRISPRfinder3. ANI were calculated using the ani.rb script4. Genome sequences were clustered by ANI value within R.
Phage Genome Comparison and Taxonomy
A phylogeny for the phage was constructed using the VICTOR server (Meier-Kolthoff and Göker, 2017). All pairwise comparisons of the amino acid sequences were conducted using the Genome-BLAST Distance Phylogeny (GBDP) method (Meier-Kolthoff et al., 2013) with settings recommended for prokaryotic viruses (Meier-Kolthoff and Göker, 2017). The resulting intergenomic distances were used to infer a balanced minimum evolution tree with branch support via FASTME including SPR post-processing for each of the formulas D0, D4, and D6, respectively (Lefort et al., 2015). Branch support was inferred from 100 pseudo-bootstrap replicates each. Trees were rooted at the midpoint (Farris, 1972) and visualized with FigTree (Rambaut, 2016). Taxon boundaries at the species, genus, and family level were estimated with the OPTSIL program, the recommended clustering thresholds (Meier-Kolthoff and Göker, 2017) and an F value (fraction of links required for cluster fusion) of 0.5.
Sequences were uploaded into the ANI calculator package5 in order to perform pairwise genome calculations of the ANI using the default conditions. The ANI calculator estimates the average nucleotide identity using reciprocal best hits (two-way ANI) between two genomic datasets.
Tail Spike Protein Cloning, Expression and Purification
Nucleotide sequence representing phage PP35 ORF156 (120600–122246) was PCR-amplified using primers 5′-TATTTCCAGGGCAGCGGATCCAACTCGCAATTCTCACAGCCG (forward) and 5′-GCTCGAGTGCGGCCGCAAGCTTACCCCAATTTGTACCAGG (reverse) bearing BamHI and HindIII restriction sites. An amplicon was cloned to vector pTSL (Taylor et al., 2016) using NEBuilder HiFi DNA Assembly kit (New England Biolabs). Clones with inserts were selected by PCR, restriction analysis, and verified by sequencing. Preparative gene expression was performed in E. coli B834(DE3) by induction with 1 mM IPTG at 16°C overnight. Cells were pelleted at 4,000 g, lysed by sonication in lysis buffer (20 mM Tris–HCl (pH 8.0), 200 mM NaCl), and centrifuged (13,000 g) to remove debris. Recombinant tail spike protein (PP35gp156) was purified on a Ni-NTA Sepharose column (GE Healthcare, 5 mL) by a stepwise gradient from 0 to 200 mM imidazole in 20 mM Tris–HCl (pH 8.0), 200 mM NaCl. Purified fractions were dialyzed against 20 mM Tris–HCl (pH 8.0) to remove imidazole, and treated with TEV protease for 12 h at 20°C. The target protein was purified on a 5 mL SourceQ 15 (GE Healthcare) column by a linear gradient of 0–600 mM NaCl in 20 mM Tris–HCl (pH 8.0). Protein concentration was determined spectrophotometrically at 280 nm using a theoretical absorption coefficient of 65,320 M-1 cm-1. PP35 gp156 oligomeric state was assessed by gel filtration on Superdex 200 10 × 300 column (GE Healthcare).
Isolation of the O-Polysaccharides
Bacterial LPS was isolated by extraction of bacterial cells (∼2 g) with hot phenol-water (Westphal and Jann, 1965) followed by removal of nucleic acids and proteins by precipitation with 50% trichloroacetic acid at 4°C. A LPS sample (70 mg) was hydrolyzed with aqueous 2% HOAc at 100°C for 1 h, a lipid precipitate was removed by centrifugation (13,000 g, 20 min), and the carbohydrate portion was fractionated by gel-permeation chromatography on a Sephadex G-50 Superfine (GE Healthcare) column (56 × 2.6 cm) in 0.05 M pyridinium acetate buffer (pH 4.5) monitored with a Knauer differential refractometer to yield a high-molecular-mass OPS preparation (7 mg).
Treatment of the O-Polysaccharides With Bacteriophage PP35 Recombinant Tail Spike Protein
Dried sample of F012 or F154 O-polysaccharide was solubilized in 20 mM Tris–HCl (pH 8.0), then purified PP35 gp156 recombinant protein was added to 1/100 (w/w), and the reaction mixture was incubated overnight at 20°C.
NMR Spectroscopy of O-Polysaccharides
Samples were deuterium-exchanged by freeze-drying twice from 99.9% D2O and then examined as solutions in 99.9% D2O. 1H and 13C NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker Avance II 600 MHz spectrometer (Germany) at 50°C using sodium 3-trimethylsilylpropanoate-2,2,3,3-d4 (δH 0.0, δC –1.6) as internal reference for calibration. Assignments of the 1H and 13C NMR signals were measured using two-dimensional 1H,1H COSY, 1H,1H TOCSY, and 1H,13C HSQC experiments, which were done by standard Bruker software. The Bruker TopSpin 2.1 program was used to acquire and process the NMR data. Spin-lock time of 60 ms was used in the 1H,1H TOCSY experiment.
Mass Spectrometry of Products of OPS Degradation With Recombinant PP35 gp156
Negative ion mode HR ESI MS was performed on a Bruker micrOTOF II instrument. Interface capillary voltage was 3200 V, mass range from m/z 50 to 3000 Da. Samples were dissolved in a 1:1:0.1 acetonitrile/water/triethylamine mixture, and the solution was injected with a syringe at a flow rate of 3 μL/min. Nitrogen was applied as drying gas; interface temperature was set at 180°C. Internal calibration was done with Electrospray Calibrant Solution (Fluka).
Results
Basic Properties of Phage PP35
Bacteriophage PP35 was isolated in 2014 from sewage water in a potato storage warehouse (Moscow region, Russia) with a soft rot infection caused by D. solani. Pathogenic strain F156 was identified as D. solani by PCR amplification and DNA sequencing of the 16S rRNA region (van Vaerenbergh et al., 2012). The better characterized D. solani lab strain, F012, was used as a host for phage propagation. Phage PP35 forms small clear plaques 1–2 mm in diameter on strains of D. solani including strain F012. We obtained a high phage titer for further purification, genomic DNA extraction, and electron microscopy. Phage PP35 is stable in solution between a pH of 5–10, and temperatures between 4 and 40°C. Freezing without cryoprotectors or heating above 50°C causes phage particles to rapidly lose infectivity.
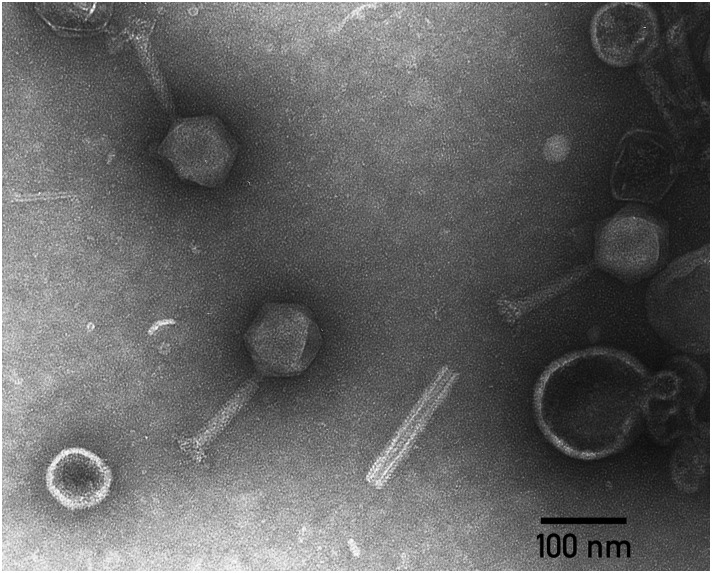
Transmission electron microscopy shows that the phage PP35 particle has a contractile tail (∼ 130 nm long), isometric icosahedral head (∼95 nm in diameter), and a pronounced baseplate complex with approximately 10 nm-long tail spikes (Figure 1). The morphology of PP35 is similar to that of Salmonella phage Vi1 (Pickard et al., 2010) and other phages assigned to the Vi1-like group. This large group of phages was previously referred as the Vi1virus genus of the family Myoviridae (Adriaenssens et al., 2012a). However, Vi1-like viruses were reclassified recently as the taxonomic family Ackermannviridae, where Dickeya viruses related to phage Limestone are grouped as the Limestonevirus genus of subfamily Aglimvirinae (Adriaenssens et al., 2017). Therefore, dependent on the ratification of the proposal, the unified naming of PP35 should be either vB_DsoM_PP35 or vB_DsoA_PP35.
FIGURE 1.
Electron micrograph of PP35 virions. Specimens were stained with 1% uranyl acetate.
Phage Host Range Determination
Among 36 strains representing various Pectobacterium and Dickeya spp. causing black leg and soft rot in potato, phage PP35 only infects nine strains determined as D. solani, and not D. dianthicola, P. atrosepticum, P. parmentieri, P. carotovorum subsp. carotovorum and P.c. subsp. brasilense (Supplementary Table S1). This corresponds to previous observations concerning this phage group: The host range of phages Limestone1 (Adriaenssens et al., 2012b), ϕD3 (Czajkowski et al., 2015), XF4, and JA15 (Day et al., 2017) is also limited to D. solani.
Phage PP35 also can infect at least one non-virulent Enterobacteriaceae isolate associated with soft rot pathogenesis. This strain, F154, yielded a positive signal from the PCR diagnostic test for Pectobacterium based on primer set EXPCC (Kang et al., 2003). Further sequencing and bioinformatic analysis of strain F154 genome referred it as a representative of the genus Lelliottia. The Lelliottia genus was reclassified from Enterobacter spp. and divided into two species, L. nimipressuralis and L. amnigena (previously Enterobacter nimipressuralis and E. amnigenus, respectively) (Brady et al., 2013), based on genomic MLST analysis and biochemical properties. Two other species of Lelliottia were proposed, based on genomic identity and with very slight differences in biochemical properties – L. jeotgali (Yuk et al., 2018) and L. aquatilis (Kämpfer et al., 2018). Lelliottia spp. are environmental bacteria (optimum growth temperature ca. 30°C) that can be isolated from natural water sources, and little is known about their ecological role. They are reportedly associated with food spoilage and phytopathogenesis, including soft rot (Kõiv et al., 2015), and, rarely, with human infections (Kim et al., 2010).
Infectious Properties of PP35 With Respect to Dickeya and Lelliottia Strains
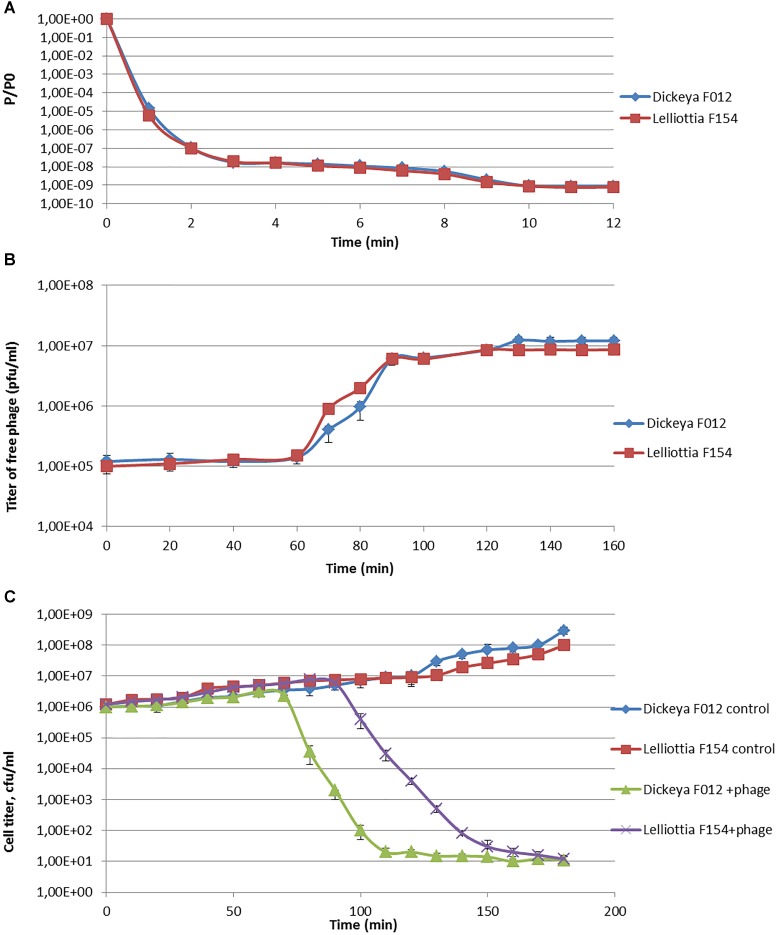
Phage infection parameters were determined with adsorption, one-step-growth, and bacterial elimination assays for phage PP35 on strains D. solani F012 and Lelliottia sp. F154. Infection kinetics were similar in both cases, with fast (∼ 2 min) and complete adsorption of phages to host bacteria with MOI = 0.1 (Figure 2A). One-step-growth assays also shows similar curves, with a somewhat longer latent period (80 vs. 65 min) and smaller burst size (90 vs. 150 released particles per cell) for F154 (Figure 2B). Within 3 h no substantial secondary growth of bacteria was observed (Figure 2C). Therefore, it is possible to conclude that the lytic infection cycle is realized equally effectively in both bacterial hosts.
FIGURE 2.
(A) Adsorption of phage PP35 on host surface. (B) One-step growth curves of PP35 using D. solani F012 and Lelliottia F154 as hosts. (C) Multistep bacterial killing curve in the life cycle of phage PP35. Intact growing D. solani F012 and Lelliottia F154 cells were used as controls. (MOI = 0.1 in all experiments).
Phage Genome Comparison
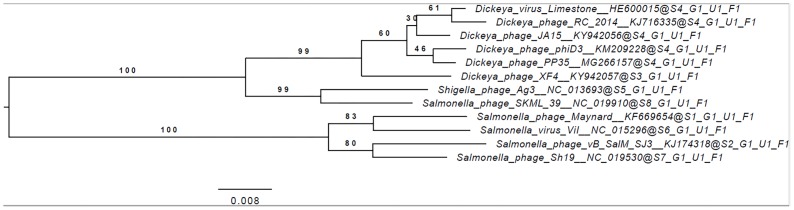
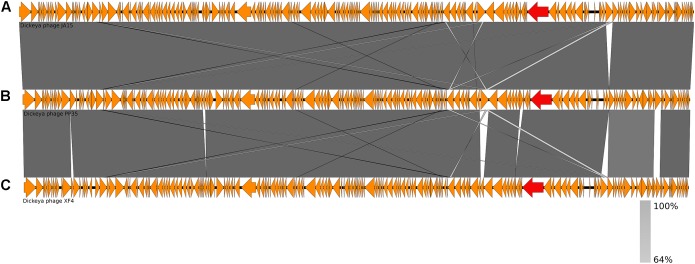
The annotated genome sequence of phage PP35 was deposited in the GenBank database with accession number MG266157.1. Double stranded DNA genome contains 152,048 bp with an average GC content of 49.30%. The genome follows the bidirectional and clustered organization typical for T-even bacteriophages. BLASTN alignment of full-length genomes shows very close relations between PP35 and a number of previously described Dickeya phages: Limestone (HE600015.1) (Adriaenssens et al., 2012b), ϕXF4 (KY942057.1), ϕJA15 (KY942056.1) (Day et al., 2017), RC-2014 (KJ716335.1) (Czajkowski et al., 2014b), ϕD3 (Czajkowski et al., 2015). Sequence similarity (Table 2) identified them as belonging to a single species of the genus Limestonevirus (Adriaenssens et al., 2017). By transferring annotations from the well described genome and proteome of Limestone, the type phage of the genus (Adriaenssens et al., 2012b), we assigned putative functions to ∼30% of 198 predicted ORFs (Supplementary Table S2). Taxonomic analysis using the VICTOR server (Meier-Kolthoff and Göker, 2017) clusters phage PP35 with the newly proposed family Ackermannviridae (Figure 3). Sequences and genome locations of predicted promotors as well as metabolically and structurally essential genes are conserved not only among Dickeya -specific Limestone-like phages, but also throughout the genomes of other phages in this family: Shigella phage Ag3, Salmonella phages SKML-39, Sh19 (Hooton et al., 2011), vB_SalM_SJ3 (Zhang et al., 2014), Vi01 (Pickard et al., 2010), and Maynard (Tatsch et al., 2013) (50–80% pairwise identity) (Table 2). For example, the genome of phage Vi1 was shown to bear hypermodified pyrimidines derived from 5-hydroxymethyl-2’-deoxyuridine (5-hmdU) (Lee et al., 2018). The exact structure of DNA modification in PP35 and the ratio of non-canonical residues are yet to be determined, but the genes responsible for 5-hmdU transformation are conserved in all Ackermannviridae phages, and correspond to ORF43 (dUMP hydroxymethyltransferase), ORF44 and ORF183 (kinases), ORF169 (PLP enzyme), ORF113 and ORF187 (alpha-glutamyl/putrescinyl thymidine pyrophosphorylases) in PP35 genome (Supplementary Table S2). Another example of conserved gene clusters is the region located at bp 114,315–128,300 in the PP35 genome. This operon includes 10 ORFs encoding components of the phage baseplate and the adsorption apparatus (Supplementary Table S2). The predicted tail spike sequence encoded by PP35 ORF 156, is identical to the corresponding tail spike sequences of the Dickeya phages listed above. The N-terminal domain of ORF156 that is responsible for the attachment of the spike to the phage particle is conserved among all Ackermannviridae. Most PP35 genes with unidentified functions are homologous and syntenous with genes in other Limestone-like phages. There are only three unique genes in the PP35 genome, and few indels and duplications (Supplementary Table S2 and Figure 4). Most of these ORFs are hypothetical proteins presumably related to homing endonucleases. No integrases, excisionases, or repressors indicative of lysogenic infection cycle, and no genes encoding toxins or antibiotic resistance mechanisms were detected.
Table 2.
Genome properties of Ackermannviridae phages.
| Phage | NCBI # | Genome (kbp) | GC% | ORFs | tRNA | ANI% | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP35 | MG266157.1 | 152.0 | 49.3 | 198 | 1 | 100 | This work |
| Limestone | HE600015.1 | 152.4 | 49.3 | 201 | 1 | 98.78 | Adriaenssens et al., 2012b |
| ϕD3 | KM209228 | 152.3 | 49.4 | 190 | 1 | 99.09 | Czajkowski et al., 2015 |
| RC2014 | KJ716335.1 | 155.4 | 49.6 | 196 | 1 | 98.28 | Czajkowski et al., 2014b |
| ϕJA15 | KY942056.1 | 153.8 | 49.3 | 198 | 1 | 99.16 | Day et al., 2017 |
| ϕXF4 | KY942057.1 | 151.5 | 49.4 | 195 | 1 | 98.90 | Day et al., 2017 |
| Ag3 | NC_013693.1 | 158.0 | 50.4 | 216 | 4 | 87.67 | Direct submission |
| SKML-39 | NC_019910.1 | 159.6 | 50.2 | 208 | 7 | 87.66 | Hooton et al., 2011 |
| Sh19 | NC_019530.1 | 157.8 | 44.7 | 166 | 5 | 77.45 | Hooton et al., 2011 |
| SJ3 | KJ174318 | 162.9 | 44.4 | 210 | 4 | 77.36 | Zhang et al., 2014 |
| Vi01 | NC_015296.1 | 157.7 | 45.2 | 208 | 6 | 76.45 | Pickard et al., 2010 |
| Maynard | KF669654.1 | 154.7 | 45.6 | 200 | 4 | 79.71 | Tatsch et al., 2013 |
FIGURE 3.
Phylogenomic genome-BLAST distance phylogeny trees inferred using the formula, D4 and yielding average support of 35, 73, and 48%, respectively. The numbers above branches are GBDP pseudo-bootstrap support values from 100 replications.
FIGURE 4.
Genome comparison of Dickeya phages: (A) Limestone, (B) PP35, (C) ϕD3. Genes encoding tail spike proteins are marked red.
Host Genome Comparison
The D. solani strain F012 (the PP35 host) genome (NCBI accession numbers PGOJ00000000.1) is similar to other D. solani genomes deposited in the public nucleotide databases. IPO2222T is the nearest relative of the Dickeya strain F012, with 100% ANI (which is not the same as 100% nucleotide similarity) (Table 3). Homogeneity among D. solani strains is thought to reflect the recent evolution of this species (Pritchard et al., 2013). There are only 17 SNPs and InDels between the F012 and IPO2222T genomes. Two putative small CRISPR arrays in contigs PGOJ01000008.1 and PGOJ01000012.1 were identified. Identical CRISPR spacers from those arrays were also found in Dickeya spp., Pantoea vagans, and Pectobacterium polaris genomes.
Table 3.
Genomic features of Dickeya F012 and type strain IPO2222T.
| Dickeya solani IPO2222T | Dickeya solani F012 | |
|---|---|---|
| Genome, bp | 4919833 | 4878843 |
| #genes | 4208 | 4309 |
| CDS | 4059 | 4234 |
| RNA | 104 | 75 |
| tRNA | 75 | 62 |
| ncRNA | 7 | 7 |
| Pseudogenes | 45 | 110 |
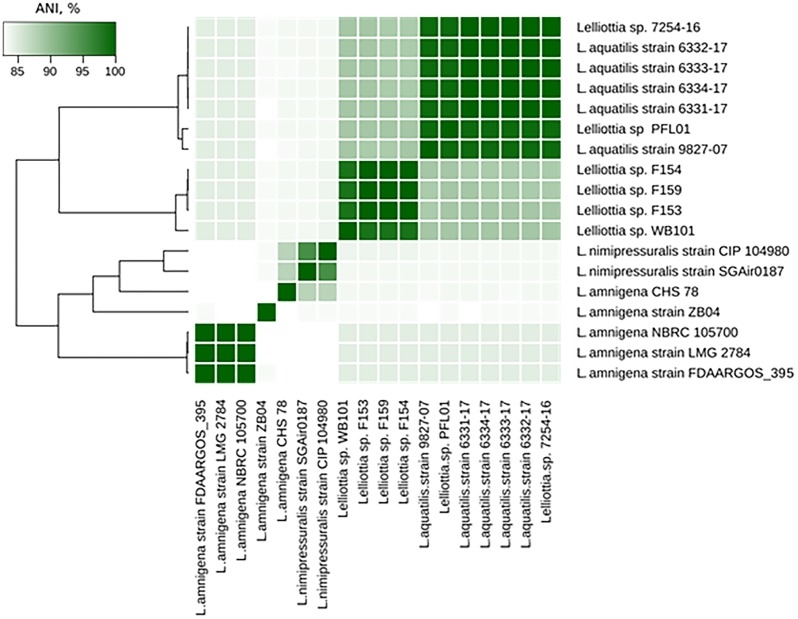
The Lelliottia strain F154 genome (accession number PKFV00000000.1) is most similar to the draft genome of Lelliottia sp. WB101 (GCA_003051885.1) isolated from a denitrifying woodchip bioreactor (98.23% ANI). There is no species designation for F154 and WB101 yet. Genome assemblies of Lelliottia strain F153 (draft genome accession number PKFT00000000.1) and F159 (PKFU00000000.1) are included in the same cluster as genomes of F154 and WB101 (ANI > 98.2%). These strains were also isolated in 2014 in the Moscow region, Russia, and are associated with soft rot pathogenesis in potato, however, they are resistant to phage PP35. ANI values between genome assemblies from this cluster and other Lelliottia assemblies are not greater than 88.6%, suggesting that these four strains form a distinct species of Lelliottia (Figure 5). The newly formed species L. aquatilis (which includes Lelliottia sp. 7254-16) and Lelliottia jeotgalii (PFL01) are most similar to the F154-like cluster, but distinct enough that F154 doesn’t belong to either species (Figure 5). Our findings show the necessity for subsequent phylogenomic research to refine Lelliottia strains taxonomy after a thorough study and comparison of their physiological and biochemical properties.
FIGURE 5.
Lelliottia genome clusters inferred by ANI between genome assemblies.
Properties of the Tail Spike Protein of PP35
Earlier studies suggest that the host range of tailed phages is largely determined by the interaction of their baseplate structures (tail fibers and tail spikes) with molecules on the bacterial surface (Fokine and Rossmann, 2014). Surface polysaccharides, including the O-antigens of lipopolysaccharides (LPS), are obvious candidates for receptor interaction with phages (Steinbacher et al., 1996). Tail spikes contain enzymatic domains (Leiman and Molineux, 2008) that depolymerize (Barbirz et al., 2008) or deacetylate (Prokhorov et al., 2017) OPS to allow a phage to attach to the cell surface. Recombinant tail spike proteins of phages infecting Enterobacteria (Steinbacher et al., 1996; Barbirz et al., 2008), Pseudomonas (Olszak et al., 2017), and Acinetobacter (Lee et al., 2017) have been extensively studied functionally and structurally. They were shown to have uniform trimeric β-helical architecture, and enzymatic active sites are located either on the surface of the resulting trimeric prism or within the loops protruding from the prism (Leiman and Molineux, 2008). Recombinant PP35 gp156 tail spike protein forms trimers spontaneously, and can be purified to electrophoretic homogeneity. The protein tends to aggregate at high concentrations, so its crystallization and further detailed structural investigation is impossible at present. In dilute solution (<2 mg/mL) PP35 gp156 is stable for several weeks at 4°C.
Identification of Surface Polysaccharides of Dickeya F012 and Lelliottia F154
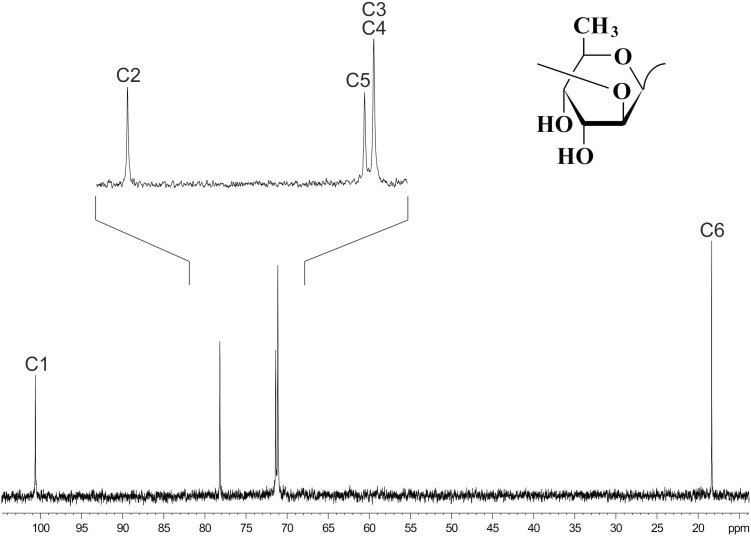
13C NMR spectroscopy (Figure 6) showed that the OPS of D. solani F012 is composed of 6-deoxy-D-altrose repeating units and is identical to the polysaccharides of five other strains of D. solani and D. dadantii 3937 reported previously (Ossowska et al., 2017). Analysis of the OPS of Lelliottia sp. F154 revealed the same structure with the units →2)- 6-deoxy- β-D-altrose-(1→ (Figure 6). Thus, we hypothesize that the indistinguishable OPS homolog on the surface of the bacterial cells susceptible to phage PP35 is the primary receptor for the PP35 tail spike protein.
FIGURE 6.
13C NMR spectrum of the O-polysaccharide of Dickeya solani F012. Structure of the O-polysaccharide is shown in the inset.
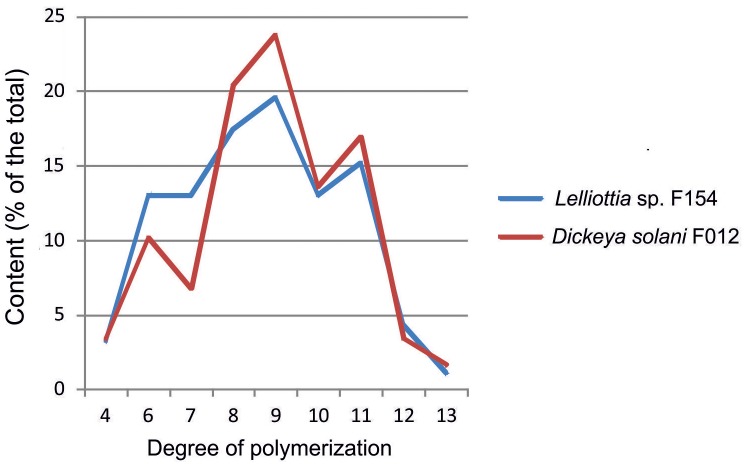
Depolymerization of the O-antigen launches the phage infection process, and the metabolic differences between Dickeya and Lelliottia do not prevent the infection. To test the hypothesis that PP35 tail spike protein depolymerizes the OPS of strains from these genera, we incubated OPS purified from representative strains with recombinant PP35 gp156. We measured the formation of 6-deoxy-D-altrose oligomers in the range of 4–13 monosaccharide units (degradation products) with high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HR ESI MS). The degradation of Dickeya F012 OPS resulted in mostly octa- and nonamers, while the products of Lelliottia F154 OPS degradation are distributed more evenly (Figure 7). Therefore, gp156 can hydrolyze 6-deoxy- β-D-altrose-(1→2)-6-deoxy-D-altrose linkage.
FIGURE 7.
Distribution of oligomers of 6-deoxy-D-altrose derived from the O-polysaccharides of D. solani F012 and Lelliottia sp. F154 by depolymerization with bacteriophage PP35 recombinant tail-spike protein gp156 based on HR ESI MS analysis data.
We sought the genomic loci responsible for the synthesis and secretion of O-antigen. The ORFs involved to lipopolysaccharide synthesis listed in Ossowska et al. (2017) are conserved in Dickeya genomes, and most other enterobacterial genomes. They catalyze the formation of lipid A and the linkage between lipid and sugar moieties common for Enterobacteriaceae (Knirel and Valvano, 2011). We hypothesized that the ABC transporter-dependent OPS biosynthesis pathway was responsible for D. solani OPS production (Greenfield and Whitfield, 2012), because D. solani OPS consists of the single repetitive carbohydrate GDP-6-deoxyaltrose. We identified the operon of eight ORFs that fits this model. The annotated ORFs of this operon include: (i) manC (protein accession number WP_022634985.1 in the case of F012 genome), manB (WP_022634986.1), and GDP-mannose 4,6-dehydratase (WP_022634987.1) that isomerizes and activates mannose substrate; (ii) GDP-fucose synthetase (WP_022634990.1) some alleles of which produce GDP-6-deoxyaltrose (Lau and Tanner, 2008); (iii) wzm (WP_026594546.1) permease and wzt (WP_022634989.1) ATP-binding protein that are responsible for the transport of the nascent polysaccharide chain; and (iv) two glycosyltransferases responsible for GDP-6-deoxyaltrose chain initiation, and subsequent polymerization. Homologs of these genes from all D. solani genomes present in NCBI GenBank are identical. Distant homologs of some of these ORFs can be found in the genome of Lelliottia F154 genome, but they are members of a more complicated cascade of genes. Therefore, we were unable to identify all Lelliottia F154 ORFs involved in the 6-deoxy-D-altrose OPS production. Further research is required to identify and characterize those ORFs.
Discussion
In this work, we characterize the interaction of Dickeya solani bacteriophage PP35 with its host. This interaction is believed to be the same as for sensu stricto Limestone and ϕD3 phages because they share a host range limited to D. solani strains and identical tail spike protein sequences. Attachment of the tail spike to the OPS on the bacterial surface and enzymatic depolymerization of the polysaccharide are key initial events in phage infection. The structure of the OPS is the same for all D. solani strains (Ossowska et al., 2016), as well as some other Pectobacteriaceae and Enterobacteriaceae. We present an example of Enterobacteriaceae phage host Lelliottia F154. This bacterial strain is evolutionarily distantly related to Dickeya sp., shows no virulence to potatoes, and lacks the genetic loci essential for pectate degradation associated with pathogenesis. However, it is infected by phage PP35 effectively, and we’d propose that such a bacterium may be an environmental reservoir for phage PP35.
Investigation of D. solani emergence and spread in Europe suggested that the pathogen arose from a single recent evolutionary event (van der Wolf et al., 2014). D. solani isolates from different locations in Europe (Belgium, Netherlands, Great Britain, Finland, Israel, Poland, and Russia) that are very closely related according to ANI. Attempts to isolate D. solani –specific bacteriophages in samples where the pathogen was detected resulted in the characterization of very similar Myoviruses resembling phage Limestone, the first isolated type representative of the species. Thus, we hypothesize two routes for natural phage infection of the plant pathogen D. solani: (i) Phages travel from a single source together with the bacterial population via transfer of seed potatoes, and (ii) a population of bacteriophages propagating on an endemic non- D. solani bacterium cross-infects D. solani.
There are numerous reports about phages that infect multiple bacterial hosts, especially Enterobacteriaceae (Hyman and Abedon, 2010). However, differences in metabolism between environmental and pathogenic bacteria and, especially, the possibility of generalized transduction reported for Limestone-like phages (Day et al., 2017) should lead to greater genetic diversity than is observed (Table 2). On the other hand, Limestone-like phages isolated in nearby locations and using the same D. solani strain for enrichment are not identical (Adriaenssens et al., 2012b; Czajkowski et al., 2014a; Day et al., 2017). Phages of this type retain viability on the surface of potato tubers for several weeks (Czajkowski et al., 2017), so the distribution of different phages via seed potato distribution is also possible. Further monitoring and assessment of the diversity of SRP-specific phages is necessary to model the geographic distribution and temporal dynamics of these phages more quantitatively.
The discovery of alternative hosts for SRP-specific phages is useful for phage control applications in addition to its ecological implications. It is desirable to use a well characterized non-pathogenic host for large-scale phage production (Gill and Hyman, 2010). Non-virulent Lelliottia strain F154 had similar infection parameters compared to the target pathogenic host and can be a valid choice for industrial propagation of Limestonevirus. Limestone-like phages also were shown to be effective for preventive and curative treatment of D. solani in field applications (Adriaenssens et al., 2012b). The infection properties of phage PP35 are like those previously described for phages belonging to this species. These properties indicate that it is a promising candidate to include in a phage cocktail for soft rot treatment and prevention.
Data Availability Statement
The complete genome sequence of phage PP35 has been deposited in the NCBI database under the GenBank accession number MG266157.1. Draft genome assemblies of strains F012 and F154, and related information can be found in the NCBI database under the GenBank Accession numbers PGOJ00000000.1, and PKFV00000000.1, correspondingly.
Author Contributions
MS, AI, and KAM designed the experiments. APK, MS, AAK, EB, EZ, and EK planned and performed the experiments. AAK, KKM, ST, AI, YK, and KAM performed the data analysis. APK, MS, AI, and KAM wrote the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. A. S. Shashkov and Dr. A. O. Chizhov for help with NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry, respectively. We express our gratitude to Dr. N. M. Brown for thorough proofreading and discussion of the manuscript.
Funding. This research was supported by Russian Science Foundation grant #16-16-00073.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2018.03288/full#supplementary-material
References
- Ackermann H.-W. (2009). Basic phage electron microscopy. Methods Mol. Protocols 501 113–126. 10.1007/978-1-60327-164-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adriaenssens E. M., Ackermann H. W., Anany H., Blasdel B., Connerton I. F., Goulding D., et al. (2012a). A suggested new bacteriophage genus: “Viunalikevirus.”. Arch. Virol. 157 2035–2046. 10.1007/s00705-012-1360-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adriaenssens E. M., Krupovic M., Knezevic P., Ackermann H. W., Barylski J., Brister J. R., et al. (2017). Taxonomy of prokaryotic viruses: 2016 update from the ICTV bacterial and archaeal viruses subcommittee. Arch. Virol. 162 1153–1157. 10.1007/s00705-016-3173-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adriaenssens E. M., van Vaerenbergh J., Vandenheuvel D., Dunon V., Ceyssens P. J., de Proft M., et al. (2012b). T4-related bacteriophage LIMEstone isolates for the control of soft rot on potato caused by “Dickeya solani.”. PLoS One 7:e33227. 10.1371/journal.pone.0033227 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Madden T. L., Schäffer A. A., Zhang J., Zhang Z., Miller W., et al. (1997). Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 25 3389–3402. 10.1093/nar/25.17.3389 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aziz R. K., Bartels D., Best A. A., DeJongh M., Disz T., Edwards R. A., et al. (2008). The RAST Server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genom. 9:75. 10.1186/1471-2164-9-75 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankevich A., Nurk S., Antipov D., Gurevich A. A., Dvorkin M., Kulikov A. S., et al. (2012). SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 19 455–477. 10.1089/cmb.2012.0021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbirz S., Müller J. J., Uetrecht C., Clark A. J., Heinemann U., Seckler R. (2008). Crystal structure of Escherichia coli phage HK620 tailspike: Podoviral tailspike endoglycosidase modules are evolutionarily related. Mol. Microbiol. 69 303–316. 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06311.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besemer J., Lomsadze A., Borodovsky M. (2001). GeneMarkS: a self-training method for prediction of gene starts in microbial genomes. Implications for finding sequence motifs in regulatory regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 29 2607–2618. 10.1093/nar/29.12.2607 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady C., Cleenwerck I., Venter S., Coutinho T., De Vos P. (2013). Taxonomic evaluation of the genus Enterobacter based on multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA): proposal to reclassify E. nimipressuralis and E. amnigenus into Lelliottia gen. nov. as Lelliottia nimipressuralis comb. nov. and Lelliottia amnigena comb. nov.,. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 36 309–319. 10.1016/j.syapm.2013.03.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clokie M. R. J., Kropinski A. M. (2009). Bacteriophages?: Methods and Protocols: Isolation, Characterization, and Interactions, Vol. 1 New York, NY: Humana Press; 10.1007/978-1-60327-164-6 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Czajkowski R., Ozymko Z., Lojkowska E. (2014a). Isolation and characterization of novel soilborne lytic bacteriophages infecting Dickeya spp. biovar 3 (‘ D. solani ’). Plant Pathol. 63 758–772. 10.1111/ppa.12157 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Czajkowski R., Ozymko Z., Siwinska J., Ossowicki A., de Jager V., Narajczyk M., et al. (2015). The complete genome, structural proteome, comparative genomics and phylogenetic analysis of a broad host lytic bacteriophage ϕD3 infecting pectinolytic Dickeya spp. Stand. Genomic Sci. 10:68. 10.1186/s40793-015-0068-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czajkowski R., Ozymko Z., Zwirowski S., Lojkowska E. (2014b). Complete genome sequence of a broad-host-range lytic Dickeya spp. bacteriophage ϕD5. Arch. Virol. 159 3153–3155. 10.1007/s00705-014-2170-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czajkowski R., Smolarska A., Ozymko Z. (2017). The viability of lytic bacteriophage ΦD5 in potato-associated environments and its effect on Dickeya solani in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) plants. PLoS One 12:e0183200. 10.1371/journal.pone.0183200 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day A., Ahn J., Fang X., Salmond G. P. C. (2017). Environmental bacteriophages of the emerging Enterobacterial phytopathogen, Dickeya solani, show genomic conservation and capacity for horizontal gene transfer between their bacterial hosts. Front. Microbiol. 8:1654. 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01654 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farris J. S. (1972). Estimating phylogenetic trees from distance matrices. Am. Nat. 106 645–668. 10.1086/282802 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Finn R. D., Clements J., Eddy S. R. (2011). HMMER web server: interactive sequence similarity searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 39 W29–W37. 10.1093/nar/gkr367 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fokine A., Rossmann M. G. (2014). Molecular architecture of tailed double-stranded DNA phages. Bacteriophage 4:e28281. 10.4161/bact.28281 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frampton R. A., Pitman A. R., Fineran P. C. (2012). Advances in bacteriophage-mediated control of plant pathogens. Int. J. Microbiol. 2012:326452. 10.1155/2012/326452 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill J. J., Hyman P. (2010). Phage choice, isolation, and preparation for phage therapy. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 11 2–14. 10.2174/138920110790725311 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield L. K., Whitfield C. (2012). Synthesis of lipopolysaccharide O-antigens by ABC transporter-dependent pathways. Carbohydr. Res. 356 12–24. 10.1016/j.carres.2012.02.027 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooton S. P. T., Timms A. R., Rowsell J., Wilson R., Connerton I. F. (2011). Salmonella typhimurium-specific bacteriophage ΦSH19 and the origins of species specificity in the Vi01-like phage family. Virol. J. 8:498. 10.1186/1743-422X-8-498 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman P., Abedon S. T. (2010). Bacteriophage host range and bacterial resistance. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 70 217–248. 10.1016/S0065-2164(10)70007-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignatov A. N., Karlov A. N., Dzhalilov F. S. (2014). Spreading of the blackleg of potatoes in Russia caused by bacteria of Dickeya genus. Zaschita Karantin Rastenij 11 41–43. [Google Scholar]
- Kämpfer P., Glaeser S. P., Packroff G., Behringer K., Exner M., Chakraborty T., et al. (2018). Lelliottia aquatilis sp. nov., isolated from drinking water. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 68 2454–2461. 10.1099/ijsem.0.002854 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang H. W., Kwon S. W., Go S. J. (2003). PCR-based specific and sensitive detection of Pectobacterium carotovorum ssp. carotovorum by primers generated from a URP-PCR fingerprinting-derived polymorphic band. Plant Pathol. 52 127–133. 10.1046/j.1365-3059.2003.00822.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kim D. M., Jang S. J., Neupane G. P., Jang M. S., Kwon S. H., Kim S. W., et al. (2010). Enterobacter nimipressuralis as a cause of pseudobacteremia. BMC Infect. Dis. 10:315. 10.1186/1471-2334-10-315 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klucar L., Stano M., Hajduk M. (2009). PhiSITE: database of gene regulation in bacteriophages. Nucleic Acids Res. 38 D366–D370. 10.1093/nar/gkp911 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knirel Y. A., Valvano M. A. (2011). Bacterial Lipopolysaccharides?: Structure, Chemical Synthesis, Biogenesis and Interaction with Host Cells. Berlin: Springer-Verlag; 10.1007/978-3-7091-0733-1 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kõiv V., Roosaare M., Vedler E., Ann Kivistik P., Toppi K., Schryer D. W., et al. (2015). Microbial population dynamics in response to Pectobacterium atrosepticum infection in potato tubers. Sci. Rep. 5:11606. 10.1038/srep11606 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau S. T. B., Tanner M. E. (2008). Mechanism and active site residues of GDP-fucose synthase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130 17593–17602. 10.1021/ja807799k [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurila J., Hannukkala A., Nykyri J., Pasanen M., Hélias V., Garlant L., et al. (2010). Symptoms and yield reduction caused by Dickeya spp. strains isolated from potato and river water in Finland. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 126 249–262. 10.1007/s10658-009-9537-9 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Lavigne R., Sun W. D., Volckaert G. (2004). PHIRE, a deterministic approach to reveal regulatory elements in bacteriophage genomes. Bioinformatics 20 629–635. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btg456 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee I. M., Tu I. F., Yang F. L., Ko T. P., Liao J. H., Lin N. T., et al. (2017). Structural basis for fragmenting the exopolysaccharide of Acinetobacter baumannii by bacteriophage ϕaB6 tailspike protein. Sci. Rep. 7:42711. 10.1038/srep42711 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y.-J., Dai N., Walsh S. E., Müller S., Fraser M. E., Kauffman K. M., et al. (2018). Identification and biosynthesis of thymidine hypermodifications in the genomic DNA of widespread bacterial viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 115 E3116–E3125. 10.1073/pnas.1714812115 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefort V., Desper R., Gascuel O. (2015). FastME 2.0: a comprehensive, accurate, and fast distance-based phylogeny inference program. Mol. Biol. Evol. 32 2798–2800. 10.1093/molbev/msv150 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiman P. G., Molineux I. J. (2008). Evolution of a new enzyme activity from the same motif fold. Mol. Microbiol. 69 287–290. 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06241.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansfield J., Genin S., Magori S., Citovsky V., Sriariyanum M., Ronald P., et al. (2012). Top 10 plant pathogenic bacteria in molecular plant pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 13 614–629. 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2012.00804.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier-Kolthoff J. P., Auch A. F., Klenk H.-P. P., Göker M. (2013). Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinformatics 14:60. 10.1186/1471-2105-14-60 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier-Kolthoff J. P., Göker M. (2017). VICTOR: genome-based phylogeny and classification of prokaryotic viruses. Bioinformatics 33 3396–3404. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx440 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olszak T., Shneider M. M., Latka A., Maciejewska B., Browning C., Sycheva L. V., et al. (2017). The O-specific polysaccharide lyase from the phage LKA1 tailspike reduces Pseudomonas virulence. Sci. Rep. 7:16302. 10.1038/s41598-017-16411-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowska K., Czerwicka M., Sledz W., Zoledowska S., Motyka A., Golanowska M., et al. (2017). The uniform structure of O-polysaccharides isolated from Dickeya solani strains of different origin. Carbohydr. Res. 445 40–43. 10.1016/j.carres.2017.04.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowska K., Czerwicka M., Sledz W., Zoledowska S., Motyka A., Szulta S., et al. (2016). The structure of O-polysaccharides isolated from plant pathogenic bacteria Pectobacterium wasabiae IFB5408 and IFB5427. Carbohydr. Res. 426 46–49. 10.1016/j.carres.2016.03.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérombelon M. C. M. (2002). Potato diseases caused by soft rot erwinias: an overview of pathogenesis. Plant Pathol. 51 1–12. 10.1046/j.0032-0862.2001.Shorttitle.doc.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Pickard D., Toribio A. L., Petty N. K., van Tonder A., Yu L., Goulding D., et al. (2010). A conserved acetyl esterase domain targets diverse bacteriophages to the Vi capsular receptor of Salmonella enterica serovar typhi. J. Bacteriol. 192 5746–5754. 10.1128/JB.00659-10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard L., Humphris S., Saddler G. S., Parkinson N. M., Bertrand V., Elphinstone J. G., et al. (2013). Detection of phytopathogens of the genus Dickeya using a PCR primer prediction pipeline for draft bacterial genome sequences. Plant Pathol. 62 587–596. 10.1111/j.1365-3059.2012.02678.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Prokhorov N. S., Riccio C., Zdorovenko E. L., Shneider M. M., Browning C., Knirel Y. A., et al. (2017). Function of bacteriophage G7C esterase tailspike in host cell adsorption. Mol. Microbiol. 105 385–398. 10.1111/mmi.13710 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rambaut A. (2016). FigTree v1.4.3. Molecular Evolution, Phylogenet ics and Epidemiology. Available at: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ [Google Scholar]
- Schattner P., Brooks A. N., Lowe T. M. (2005). The tRNAscan-SE, snoscan and snoGPS web servers for the detection of tRNAs and snoRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 33 W686–W689. 10.1093/nar/gki366 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbacher S., Baxa U., Miller S., Weintraub A., Seckler R., Huber R. (1996). Crystal structure of phage P22 tailspike protein complexed with Salmonella sp. O-antigen receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93 10584–10588. 10.1073/pnas.93.20.10584 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatsch C. O., Wood T. L., Chamakura K. R., Kuty Everett G. F. (2013). Complete Genome of Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium myophage maynard. Genome Announc. 1:e00866-13. 10.1128/genomeA.00866-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor N. M. I., Prokhorov N. S., Guerrero-Ferreira R. C., Shneider M. M., Browning C., Goldie K. N., et al. (2016). Structure of the T4 baseplate and its function in triggering sheath contraction. Nature 533 346–352. 10.1038/nature17971 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toth I. K., van der Wolf J. M., Saddler G., Lojkowska E., Hélias V., Pirhonen M., et al. (2011). Dickeya species: an emerging problem for potato production in Europe. Plant Pathol. 60 385–399. 10.1111/j.1365-3059.2011.02427.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- van der Wolf J. M., Nijhuis E. H., Kowalewska M. J., Saddler G. S., Parkinson N., Elphinstone J. G., et al. (2014). Dickeya solani sp. nov., a pectinolytic plant-pathogenic bacterium isolated from potato (Solanum tuberosum). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 64 768–774. 10.1099/ijs.0.052944-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Vaerenbergh J., Baeyen S., de Vos P., Maes M. (2012). Sequence diversity in the Dickeya flic gene: phylogeny of the Dickeya genus and taqman PCR for “D. solani”, new biovar 3 variant on potato in Europe. PLoS One 7:e35738. 10.1371/journal.pone.0035738 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westphal O., Jann K. (1965). Bacterial lipopolysaccharides: extraction with phenol-water and further applications of procedure. Methods Carbohydr. Chem. 5 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- Yuk K.-J., Kim Y.-T., Huh C.-S., Lee J.-H. (2018). Lelliottia jeotgali sp. nov., isolated from a traditional Korean fermented clam. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 68 1725–1731. 10.1099/ijsem.0.002737 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Hong Y., Harman N. J., Das A., Ebner P. D. (2014). Genome sequence of a salmonella phage used to control Salmonella transmission in Swine. Genome Announc. 2:e00521-14. 10.1128/genomeA.00521-14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The complete genome sequence of phage PP35 has been deposited in the NCBI database under the GenBank accession number MG266157.1. Draft genome assemblies of strains F012 and F154, and related information can be found in the NCBI database under the GenBank Accession numbers PGOJ00000000.1, and PKFV00000000.1, correspondingly.