Fig. 2.
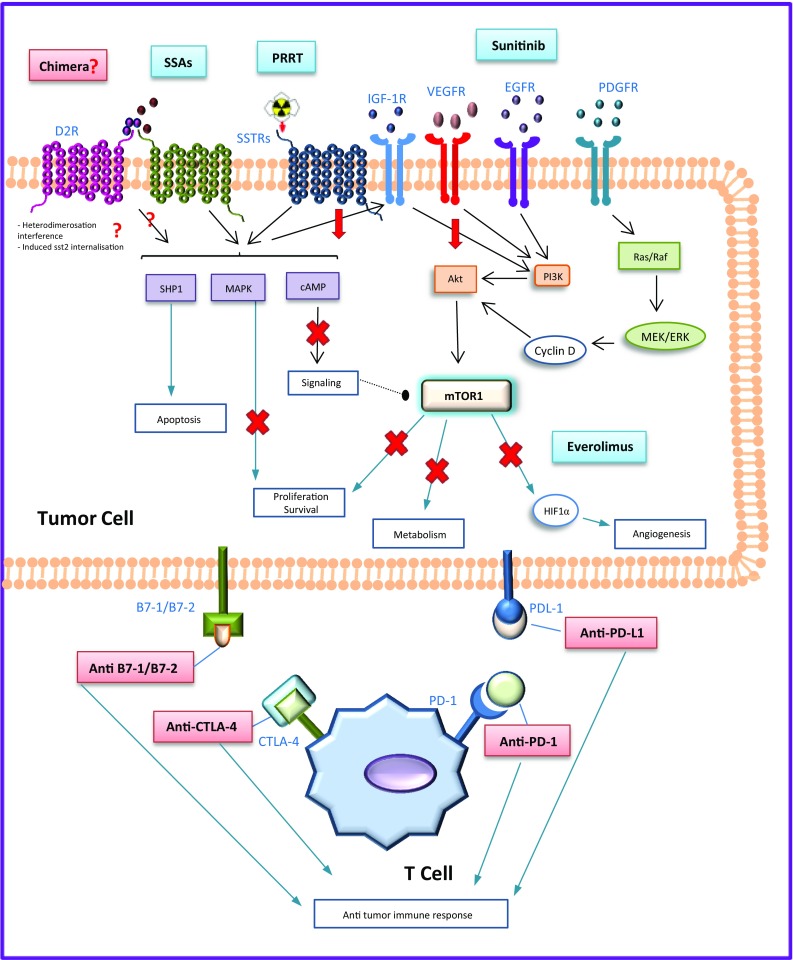
Current and future medical options for tumor control in neuroendocrine tumors. Current therapeutic options are presented in blue, possible novel therapeutic options are presented in red. SSAs and PRRT: increase apoptosis by activating the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP1; decrease cell proliferation and survival through the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP); and inhibit the signaling of the insulin-like growth factor receptor type 1 (IGFR-1); additionally, PRRT produces DNA double strand breaks induced by β-irradiation, consequently leading to apoptosis. Sunitinib is a multikinase inhibitor that modulates the phosphoinositate-3-kinase/Akt pathway (it blocks the vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFR) 1-3, the platelet-derived growth factor receptors (PDGFR) α and β, and the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)). Everolimus decreases tumor cell proliferation, metabolism, survival, and angiogenesis through the mammalian target of rapamycin complex-1. The indirect inhibition of mTOR through the phosphoinositate-3-kinase/Akt produced by the SSAs seems to increase sensitivity to mTOR inhibition. Multi-receptor chimeras may bind SSTR and D2R, and may enhance the signaling of the cAMP and JNK pathways; induced SST2R internalization and SST2R/D2R heterodimerisation interference have also been hypothesized. The interaction between some receptors expressed on the surface of cytotoxic T-cells (PD-1, CTLA-4) with ligands expressed on the tumor cells (PDL-1, B7-1/B7-2) downregulates the immune response to tumor cells; novel drugs that target these specific immune checkpoints inhibit this interaction allowing the immune system to maximize an efficient antitumor response. SSAs somatostatin analogs, PRRT peptide receptor radionuclide therapy, IGF-1R insulin-growth factor receptor type 1, VEGFR vascular endothelial growth factor, EGFR epidermal growth factor receptor, PDGFR platelet-derived growth factor receptors, mTOR mammalian Target of Rapamycin, CTL4 cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4, PDL-1 Programmed death-ligand 1
