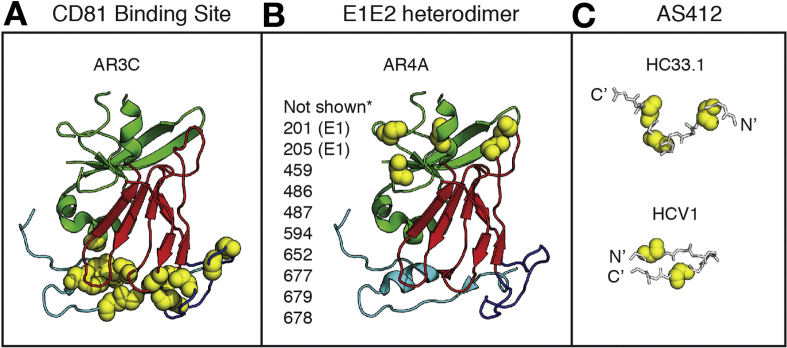
Figure 2.
bNAb epitopes are conformationally complex and flexible. (A, B) The crystallized structure of a truncated HCV E2 protein, strain H77, PDB 4MWF, from Kong et al,119 with E2 domains and bNAb binding residues highlighted in Pymol, v1.8.6.2. The E2 front layer is cyan, central beta sheet is red, and the back layer is green. Binding residues of the CD81 binding site-targeting bNAb AR3C (A) or the E1E2 complex-targeting bNAb AR4A (B), identified by alanine scanning mutagenesis and binding assays, are marked with yellow spheres.116 Amino acid side chains are not shown. *Putative AR4A binding residues not present in the E2 crystal structure are listed next to the structure. Binding residues shown or listed are positions at which mutation to alanine had the greatest effect on AR3C or AR4A binding, but minimal effect on control mAbs. Numbering is relative to the H77 polyprotein sequence. (C) Structures of peptide epitopes crystallized in complex with AS412-targeting bNAbs HC33.1 or HCV1. Fab structures are not shown. HC33.1 binds the peptide in an extended conformation (PDB 4XVJ),127 whereas HCV1 binds the peptide in a hairpin conformation (PDB 4DGY).113 Critical binding residues for each bNAb determined by alanine scanning mutagenesis and binding assays are marked with yellow spheres.110, 120 Amino acid side chains are not shown.