Abstract
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection affects about 300 million people worldwide. Although antiviral therapies have improved the long-term outcomes, patients often require life-long treatment and there is no cure for HBV infection. New technologies can help us learn more about the pathogenesis of HBV infection and develop therapeutic agents to reduce its burden. We review recent advances in development of directing-acting antiviral and host-targeting agents, some of which have entered clinical trials. We also discuss strategies for unbiased high-throughput screens to identify compounds that inhibit HBV and for repurposing existing drugs.
Keywords: functional cure, DAA, drug, screening
Despite the availability of effective vaccine, hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a major public health threat, with about 300 million people chronically infected worldwide. These individuals are at high risk for developing liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)1, 2. There are 2 classes of approved treatments for chronic HBV infection: nucleos(t)ide reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), also known as nucleos(t)ide analogs (NUCs), and interferon alpha (IFNA). Both are effective but have limitations3. We review the latest strategies for curing HBV infection, the HBV life cycle, and potential drug targets. These include direct viral targets (by directing-acting antiviral agents) and host factors (by host-targeting agents) that are required for productive HBV infection. For a review of immune modulatory approaches, see XX (insert as new reference #3).
HBV Therapies and Goals
NRTIs target the reverse transcriptase activity of virus polymerase, limiting its replication. However, these drugs do not cure the infection, must be taken life long, and have risks of resistance and toxicity4. IFNA is the only approved treatment for HBV infection that has a distinct duration. IFNA increases the antivirus immune response, inhibits virus entry into cells, induces partial degradation of HBV covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA), epigenetically suppresses cccDNA transcription, and inhibits post-transcription steps and virion secretion5. However, patients have a low rate of response to IFNA and its side effects are often difficult to tolerate4. Second-generation NRTIs, such as entecavir and tenofovir, potently suppress HBV replication but have little effect on the level and activity of cccDNA, which has a long half-life and can persist for decades in the liver despite suppression of viral replication3. This limitation necessitates prolonged (possibly indefinite) treatment with this class of anti-HBV drugs. Derivatives of tenofovir, such as prodrugs with improved pharmacological properties, have been developed and may reduce some side effects6. Despite these limitations, antiviral treatment can reverse liver fibrosis and even cirrhosis, prevent complications, and reduce though not eliminate the risk of HCC7.
Chronic HBV infection might be completely cured by inhibiting the virus replication intermediate—the cccDNA, and blocking reinfection. The goal is to achieve a functional cure—a state that resembles the natural recovery from HBV infection. This is defined as: persistently undetectable HBV DNA in serum, loss of HB surface antigen (HBsAg), preferably with seroconversion (development of anti-HBs), and normal liver enzymes and histology after stopping treatment, which is rarely achieved with treatments that do not directly target cccDNA1.
HBV Life Cycle and Therapeutic Targets
HBV is an enveloped DNA virus that specifically targets human hepatocytes (Figure 2). HBV infects hepatocytes via the low-affinity interaction between determinant(s) of the viral envelope protein and heparan sulfate proteoglycans on hepatocytes. This interaction brings the preS1 protein in proximity to the solute carrier family 10 member 1 (SLC10A1 or NTCP); the resulting high-affinity interaction with the bile acid-binding pocket of NTCP facilitates virus entry8–10. NTCP, responsible for the liver tropism of HBV and hepatitis D virus (HDV), is expressed only on the basolateral and sinusoidal membranes of hepatocytes. However, overexpression of human NTCP by mouse hepatocyte lines does not confer their susceptibility to HBV infection11. Additionally, HepG2-NTCP clones that express similarly high levels of ectopic NTCP have varying efficiencies of HBV infection12. These findings indicate that additional cell factors are required for efficient HBV infection.
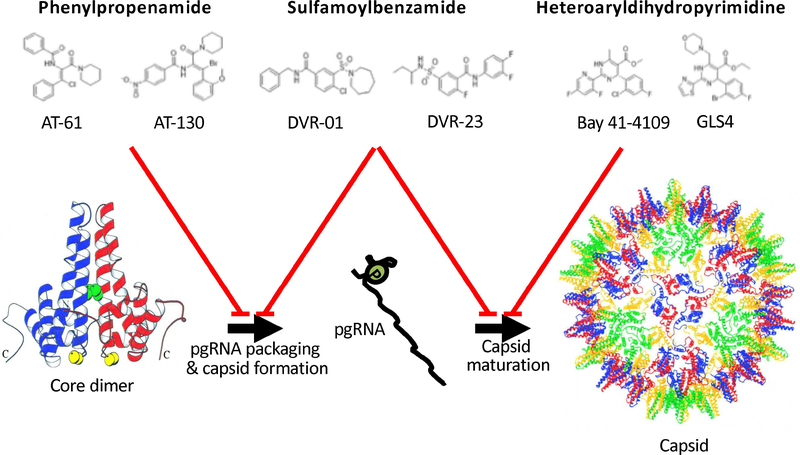
Figure 2. Types and Structures of HBV Capsid Inhibitors.
(A) Representative compounds belong to phenylpropenamide, heteroaryldihydropyrimidine, or sulfamoylbenzamide family. (B) The targets of different compounds are: phenylpropenamide chemicals, which interfere with pgRNA packaging; heteroaryldihydropyrimidine compounds, which induce abnormal assembly of capsid; and sulfamoylbenzamide family serials, which target both. The target side of heteroaryldihydropyrimidine is shown with a black arrow. (Figure adapted from Wynne et al. Mol Cell 1999. with permission from Cell Press)
The process of virus entry into hepatocytes is an attractive target for development of antiviral agents. HBV entry can be inhibited by heparin, small molecule compounds, and IFNA-induced factors that bind heparan sulfate proteoglycans in cell cultures8, 13, 14. Myrcludex-B, a synthetic N-myristoylated lipopeptide derived from HBV preS1 protein, competes with the virus for binding to NTCP. This agent prevents HBV and HDV infection and in cells and animal models15, 16. HBV enters hepatocytes via endocytosis. Caveolin and clathrin participate in HBV entry into HepaRG cells and immortalized primary human hepatocytes17, 18. Viral particles are then transported from early to late endosomes, mediated by RAB5 and RAB7, which are probably required for nucleocapsid release from the envelope19. Chemicals such as chlorpromazine specifically block clathrin-mediated endocytosis to inhibit HBV entry17, 18.
After entry and uncoating, virus capsids migrate along microtubules to the nuclear periphery20. With diameters of 36 nm (below the limit for transport by the nuclear pore complex)21, the HBV can capsids pass through nuclear pores and enter the nuclei. The passage is mediated by interactions among the cellular transport receptors of the importin family22. The capsids are retained on the nuclear side of the nuclear pore complex by strong interaction with nucleoporin 153, a protein in the nuclear basket that participates in nuclear transport via importin beta23. Nocodazole, which depolymerizes microtubules, inhibits nuclear import of capsids and thereby suppresses virus replication20.
Disassembly of capsids at the nuclear pore results in the release of the virus’s relaxed circular DNA (rcDNA) genome into the nucleus, where the partially double-stranded rcDNA is converted into cccDNA. Little is known about the detailed mechanisms of this process. Inhibition of HBV polymerase by nucleos(t)ide analogs does not block cccDNA formation in models of HBV infection, so cellular DNA repair enzymes rather than viral polymerases might responsible for cccDNA formation16. This multi-step process involves the removal of covalently attached viral polymerase and an RNA primer from the positive strand, cleavage of terminally redundant sequences from the negative strand, repair of the incomplete positive strand, and ligation of both DNA strands. A DNA repair enzyme, tyrosyl-DNA-phosphodiesterase 2 (TDP2), removes the covalently bound viral polymerase from HBV and rcDNA in the nucleus 24. However, TDP2-knockout cells can still be infected by human HBV, indicating that other TDP-related proteins contribute to this activity25. Flap-endonuclease 1 (FEN1) can remove the 5’-flap structure from rcDNA and might contribute to cccDNA formation26. DNA polymerase κ (POLK) was found to complete the positive strand DNA synthesis of the rcDNA27, whereas DNA ligase 1 and 3 contribute to formation of cccDNA during de novo HBV infection28. Although POLK is important for maintenance of genomic stability29, DNA ligase inhibitors, which are being developed as anti-cancer agents 30, might be developed for treatment of chronic HBV infection, if the side effects are tolerable.
HBV cccDNA is stable and has a long half-life in infected cells, so its clearance, a marker of a complete cure, has been difficult to achieve. High doses of IFNA or lymphotoxin beta receptor agonists induce non-cytolytic degradation of cccDNA from infected primary human hepatocytes or HepaRG cells, through induction of nuclear deaminase apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme catalytic subunit (APOBEC) 3A or 3B31, 32. The lymphotoxin pathway is active in livers of patients with chronic HBV infection 33. However, increased expression of genes that regulate the lymphotoxin pathway, including APOBEC3 enzymes, are not associated with a lower cccDNA content 33. Interestingly, upregulation of APOBEC3A in the liver correlates with an antiviral response in patients treated with IFNA34. Unfortunately, because of IFNA’s side effects, it may not be feasible to increase the dose to achieve this goal. Recently, overexpression of APOBEC3G in a Cre-mediated HBV recombinant cccDNA cell line resulted in cccDNA loss. This indicates that there could be ways to induce cccDNA degradation without IFNA treatment35.
Although cell proliferation can cause cccDNA loss in animal models36, HBV cccDNA is stably maintained as a mini-chromosome in infected hepatocytes. Loaded with histone and non-histone proteins, cccDNA serves as a template for RNA polymerase 2-mediated transcription of 4 viral RNAs, via the cell’s transcription machinery37. HBV cccDNA transcription is controlled by 4 promoters (the core, pre-S1, pre-S2/S, and × promoters) and 2 enhancers. Enhancer I mediates the activation of an early transcript (HBx mRNA), whereas enhancer II mediates expression of late transcripts 38. IFN-induced tripartite motif 22 (TRIM22) inhibits HBV core promoter activity and thereby HBV gene expression and replication in cells and animal models 39.
Several liver-enriched transcription factors and nuclear receptors bind the HBV promoter or enhancer elements and regulate HBV transcription. PreS1 promoter contains binding sites for hepatocyte nuclear factor (HNF)1 and HNF340–43. Transcription from the pre-S2/S promoter is mediated by transcription factor SP1 and it is also responsive to retinoid × receptor alpha (RXRA), peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor alpha (PPARα), and HNF4A 44, 45. Enhancer 1 contains binding sites for HNF1, HNF3, and CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein (CEBP)46–48. In addition, the pre-C/C promoter and both enhancers contain binding sites for nuclear receptors including HNF4A, RXRS, PPARα, the nuclear receptor subfamily 2 group F member (NR2F2 or COUPTF) 1 and 2, and nuclear receptor subfamily 2 group C member 1 (NR2C1 or TR2) 41, 42, 49. Compounds that target these transcription factors suppress HBV replication16, 50.
Epigenetic modifications to HBV cccDNA mini-chromosomes, such as DNA methylation and histone modifications, affect transcription of HBV cccDNA. HBV can induce methylation of cell and virus DNA, by induction of DNA methyltransferases51. Hypoacetylation of the cccDNA‐associated H3 and H4 histones and recruitment of the cell’s HDAC1 onto cccDNA are associated with low HBV replication in cells and in animal models 52. Cell factors involved in epigenetic modifications, including cAMP responsive element binding protein (CREB), E1A binding protein p300 (p300), lysine acetyltransferase 2B (KAT3B or PCAF), CREB regulated transcription coactivator 1 (CRTC1), lysine acetyltransferase 2A (KAT2A or GCN5), and YY1 transcription factor (YY1) bind to cccDNA and promote its transcription53–55. On the other hand, signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 1 and 2, HDAC1, sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), SIRT3, protein arginine methyltransferase (PRMT) 1 and 5, enhancer of zeste 2 polycomb repressive complex 2 subunit (EZH2), defensin alpha 1 (DEFA1 or HP1), and structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) 5 and 6 interact with cccDNA to inhibit HBV cccDNA transcription53, 56–62.
An important function of HBx is to redirect the damage specific DNA binding protein 1 (DDB1) E3 ubiquitin ligase to SMC5 and SMC6 for degradation and thereby relieve this suppression62. Similarly, HBx counteracts SETDB1-mediated histone 3 di- and tri-methylation (H3K9me3) and HP1 recruitment to activate cccDNA transcription61. HBx is therefore an attractive virus therapeutic target.
IFNA represses HBV by reducing active histone markers on the cccDNA mini-chromosome in HBV-infected primary human hepatocytes 63. The small molecule C646 also achieves this effect, by specifically inhibiting p300 and CBP histone acetyltransferases 63. Drugs that modify epigenetic regulation have also been developed to treat patients with cancer or viral infections64–66. These agents might be used to inactivate cccDNA in infected hepatocytes.
The HBV polymerase is translated from an internal AUG codon on pregenomic RNA (pgRNA), whereas translation of other HBV proteins is controlled by initiation codons located closest to the 5′ end of their mRNA67, 68. In response to binding of the polymerase to the packaging signal epsilon at the 5′ end, core proteins complex with the pgRNA and viral polymerase complex and initiate capsid formation69, 70. The heat shock protein 90 mediates the interaction between pgRNA and polymerase71. Serine arginine protein kinase might bind to the C-terminal domain of core protein and regulate subsequent phosphorylation to prevent self-assembly and nonspecific RNA packaging72. In addition, the human cytidine deaminase APOBEC3G is incorporated into viral particles through binding to the viral reverse transcriptase and might be a negative regulator of virus replication73. Capsid assembly modulators (CAMs), which are small-molecule compounds that target core protein, are under development.
Inside the viral capsid, pgRNA is reverse transcribed into minus-strand DNA by the viral polymerase, with its terminal protein domain acting as a primer for initiation of reverse transcription74. During negative-strand synthesis, degradation of the pgRNA template by the RNase H activity of polymerase occurs concomitantly. When the polymerase reaches the 5’ end of pgRNA, a RNA oligomer remains, and is used as the primer for plus-strand DNA synthesis by the viral polymerase75. For unknown reasons, plus-strand DNA synthesis is incomplete, occurring for approximately half the genome, which results in formation of the partially double-stranded rcDNA viral genome76.
NRTIs, which target viral polymerase for DNA synthesis activity, are highly effective in inhibiting HBV replication. Additionally, entecavir, tenofovir, and clevudine can inhibit polymerase-mediated protein priming 77, 78. RNase H activity is essential and has specific enzymatic activity of viral polymerase, so it could be a good therapeutic target. Recently, several inhibitors of RNase H, including beta-thujaplicinol and hydroxylated tropolones, have been identified79–82. These anti-HBV agents are under development and might be used in combination with existing treatments to achieve higher suppression of virus replication.
The fate of rcDNA-containing capsids varies, which may be regulated by L protein83. They either are transported back to the nucleus to amplify the cccDNA pool or undergo envelopment to be released as progeny virions. HBV virion assembly is initiated with nucleocapsid transportation to the surface of the MVBs, through NEDD4 and adaptor related protein complex 1 subunit gamma 2 (AP1G2), and then buds into MVB through ESCRT complexes on contact with the HBV envelope proteins via endosomal sorting complex84–86. MVB and/or MVB-derived exosomes then fuse with the plasma membrane to release HBV virion.
In addition to secretion of HBV virions (Dane particles), many incomplete subviral particles, including filaments and spheres, are released from infected hepatocytes. Interestingly, filaments and Dane particles share the same secretion pathway, whereas spheres self assemble in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum and are released by the general secretory pathway87, 88. Subviral particles can reach levels 10,000-fold higher than the Dane particles in the serum of HBV carriers, where they can act as immunological decoys89. In addition, secreted particles containing HBV RNA90, 91 or no viral nucleic acid92 have been reported.
Bone marrow stromal cell antigen 2 (BST2 or TETHERIN), expressed by immune cells in response to interferon, blocks the egress of enveloped viruses, including HBV, by tethering budding virions on the cell surface via its membrane anchor domains 93. Inhibitors that target HBV secretion and budding are preclinical studies and clinical trials94, 95. Nucleic acid polymers blocked the release of HBsAg from infected hepatocytes in patients with chronic HBV infection and HBV and HDV coinfection in a phase 2 trial96, 97.
Persistent HBV replication is associated with integration of HBV sequences into the hepatocyte genome. This integration is believed to be caused by non homologous end joining or microhomology-mediated end joining of double-stranded linear HBV DNA (dslDNA)98. Reverse transcription of the pgRNA occasionally forms dslDNA as an aberrant by-product; the dslDNA can be released as defective virions or integrated into host genome98, 99. In most integrated HBV DNA, the HBV core promoter is separated from its open reading frame, resulting in replication-incompetent transcripts. On the other hand, HBV DNA integrated into the genome can still act as a template for HBsAg expression100, 101.
Direct-acting Antivirals
Development of antiviral agents has largely focused on viral targets. The rationale was that these agents would have little or no cross-activity with human cells or proteins, and therefore be non-toxic. NRTIs are the backbone of treatment for chronic HBV infection. Although second-generation NRTIs efficiently suppress viral DNA synthesis, they do not eliminate the virus. There are several NRTIs in development that aim to improve upon existing NRTIs. These include besifovir102, metacavir103, 2 prodrugs of tenofovir CMX157, and DA-2802 (see Table 1). Studies are needed to determine whether these NRTIs provide substantial advantages over current treatments.
Table 1.
Direct-acting Antivirals for HBV in Development
| Compound | Mechanism and Target | Stage of Development | Sponsor | Reference and Clinicaltials.gov no |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Besifovir | Polymerase | Phase 3, Approved in S. Korea | Il Dong Pharmaceutical; South Korea | 102; NCT01937806 |
| DA-2802 (tenofovir disoproxil orotate) | Polymerase | Phase 3 | Dong-A ST Co., Ltd.; South Korea | NCT02967939 |
| Metacavir | Polymerase | Phase 2 | Guangzhou Yipinhong Pharmaceutical, China | 103; NCT02965859 |
| CMX157 (tenofovir Exalidex) | Polymerase | Phase 2 | ContraVir Pharmaceuticals | NCT02710604 |
| RNase H inhibitors | RNaseH | Preclinical | Arbutus | sponsor’s web site |
| JNJ-379 (JNJ-56136379) |
Capsid | Phase 2 | Janssen Sciences, Belgium | NCT03361956 |
| GLS4 | Capsid | Phase2 | HEC Pham, China | 145; sponsor’s web site |
| ABI-H0731 | Capsid | Phase 1b/2a | Assembly | NCT03109730 |
| NVR 3–778 (AL-3778) |
Capsid | Phase 1/2 | Novira |
146; NCT02112799 NCT02401737 |
| Bay 41–4109 | Capsid | Phase 1 | AiCuris, Germany | 147; sponsor’s web site |
| RO7049389 | Capsid | Phase 1 | Roche, Switzerland | NCT02952924 |
| JNJ-440 | Capsid | Phase 1 | Alios Biopharma | NCT03439488 |
| AB-423 | Capsid | Phase 1 | Arbutus | sponsor’s web site |
| QL-007 | Capsid | Phase 1 | Qilu Pharmaceutical, China | NCT03244085 |
| AB-506 | Capsid | Preclinical | Arbutus | sponsor’s web site |
| ABI-H2158 | Capsid | Preclinical | Assembly | sponsor’s web site |
| ARB-1467 (TKM-HBV) |
siRNA | Phase 2 | Arbutus | NCT02631096 |
| ARO-HBV | siRNA | Phase 1/2 | Arrowhead | NCT03365947 |
| ALN-HBV | siRNA | Phase 1/2 | Alnylam | sponsor’s web site |
| LUNAR™-HBV | siRNA | Preclinical | Arcturus | sponsor’s web site |
| Hepbarna (BB-HB-331) | siRNA | Preclinical | Benitec, Australia | sponsor’s web site |
| ARC-520 | siRNA | Terminated | Arrowhead |
NCT02452528 NCT02604212 NCT02604199 NCT02738008 NCT02065336 NCT02577029 |
| ARC-521 | siRNA | Terminated | Arrowhead | NCT02797522 |
| ARB-1740 | siRNA | Terminated | Arbutus | sponsor’s web site |
| IONIS-HBVLRx (GSK3389404) |
Antisense oligonucleotide | Phase 2 | Ionis Pharmaceuticals, with GlaxoSmithKline, United Kingdom | NCT03020745 |
| IONIS-HBVRx (GSK3228836) |
Antisense oligonucleotide | Phase 2 | Ionis Pharmaceuticals, with GlaxoSmithKline, United Kingdom | NCT02981602 |
| RG6004 (RO7062931) |
Locked Nucleic Acid | Phase 1/2 | Roche, Switzerland | 148; NCT03038113 |
| AB-452 | RNA destabilizer | Preclinical | Arbutus | sponsor’s web site |
| EBT106 | CRISPR | Preclinical | Excision BioTherapeutics | sponsor’s web site |
| HBV | CRISPR | Preclinical | Intellia Therapeutics | sponsor’s web site |
Capsid inhibitors
Nucleocapsid formation and pgRNA packaging are critical steps of viral life cycle that might be targeted by antiviral agents. Two main classes of CAMs have been developed according to their mode of action on assembly. The phenylpropenamide and sulfamoylbenzamide chemical series interfere with pgRNA packaging and accelerate formation of immature empty capsid-like particles104–107. Heteroaryldihydropyrimidine compounds induce formation of aggregated and aberrant capsid structures and also disrupt intact capsid 108–112(Figure 1). Clinical studies are underway to test CAMs, including JNJ-379, GLS4, ABI-H0731, NVR 3–778, Bay 41–4109, RO7049389, JNJ-440, AB-423, and QL-007 (see Table 1). AB-506 and ABI-H2158 are in preclinical studies. JNJ-379, administered for 28 days, was generally well tolerated and had potent antiviral activity at the doses evaluated113. ABI-H0731 was safe and well tolerated in a phase 1 trial, and once-daily doses had potent antiviral activity114. Similarly, RO7049389 had robust anti-HBV activity in patients with chronic HBV infection, and was safe and well tolerated115.
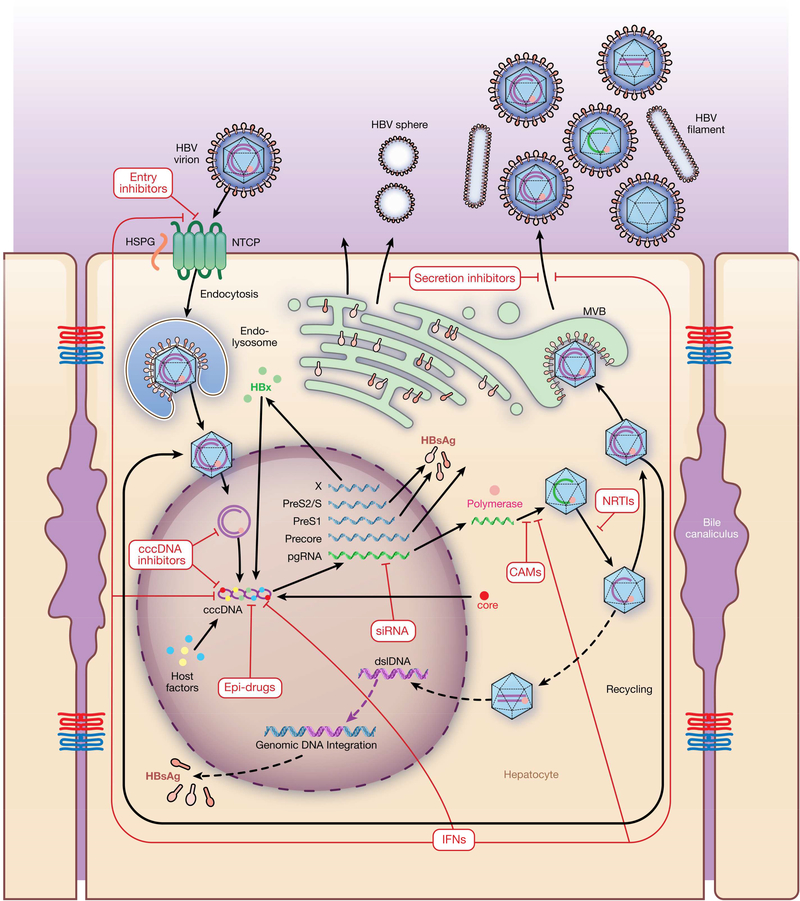
Figure 1. HBV Life Cycle and Therapeutic Targets.
The HBV cycle includes virus attachment, entry, uncoating, trafficking to nucleus, cccDNA formation, transcription, translation, encapsulation, secretion, and integration. HBV infection is initiated via interaction with heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSGP), resulting in a large envelope protein that binds NTCP. After internalization, viral capsids are released and then directed to the nucleus, where the HBV genomes are released. In the nucleus, relaxed circular DNA genomes are converted into cccDNAs, which can persist in the nucleus of infected cells as a mini-chromosome and serve as template for viral RNA transcription. Viral mRNAs are transported to the cytoplasm, where they are translated into viral proteins. Together with the viral polymerase, the pgRNA is encapsulated and reverse transcribed within the nucleocapsid into progeny rcDNA. Mature nucleocapsids are then either directed to the MVB pathway for envelopment with HBV envelope proteins or re-directed to the nucleus to establish a cccDNA pool. dslDNA that contains capsid is also produced that can be integrated into the cellular genome or released as defective virion. Drugs or antiviral agents designed to target different steps of the HBV life cycle are shown in red.
RNA interference
RNA interference (RNAi) technology can be used to manipulate virus gene expression and might be developed for treatment. Briefly, small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) are designed to target specific viral mRNA sequences. After they are delivered into the hepatocytes, the siRNAs hybridize with viral mRNA, and the resulting double‐stranded RNA is degraded116. The first siRNA against HBV to enter development was ARC-520117. Single and multiple doses of ARC-520 reduced HBsAg, HBeAg, HBcAg, and HBV DNA titers in HBV-infected chimpanzees and patients 118, 119. However, the observed HBsAg reductions were significantly lower in HBeAg‐negative than in HBeAg‐positive chimpanzees and patients. This could be because ARC-520 targets cccDNA‐derived, but not integrated, transcripts. The secondgeneration siRNA, ARC-521,120 was therefore developed. However, due to potential safety issue with the delivery platform, trials were terminated.
Using a proprietary, subcutaneously administered delivery vehicle, researchers at Arrowhead developed ARO-HBV, which is currently in a phase 1/2 trial. Other siRNAs, from different companies, are in phase 1 or 2 or preclinical studies (Table 1). Similar strategies include antisense oligonucleotides, locked nucleic acids, and RNA destabilizers, which are in development (Table 1). siRNAs against HBV are still in experimental stages—more studies are necessary to address the efficacy issues and safety concerns.
Gene editing
The genome editing tool, clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats associated nuclease 9 (CRISPR/Cas9), has many innovative applications in different fields because of its potential for gene therapy. The CRISPR/Cas9 system comes from the immune system of bacteria and archaea, which detects and degrades foreign DNA from bacteriophages and plasmids121. Briefly, for gene editing, Cas9 is directed to its DNA target by base pairing between the guide RNA (gRNA) and DNA. A protospacer-adjacent motif (PAM) motif downstream of the gRNA-binding region is required for Cas9 recognition and cleavage. Cas9/gRNA cuts both strands of the target DNA, leading to double-strand DNA break repair. The promise of CRISPR/Cas9 as a tool for the cleavage and elimination, or at least inactivation, of HBV cccDNA and HBV genome integration, has prompted many studies. These have provided a clear proof of concept that this approach has the potential to treat or even cure patients with chronic HBV infection 122–124. Excision BioTherapeutics and Intellia Therapeutics announced their first CRISPR/Cas9 candidates for HBV infection (Table 1). However, off-target effects of the CRISPR/Cas9 system in patients are a concern125. The p53-mediated DNA damage response induced during gene editing might also hamper its clinical applications126.
Agents That Target Host Proteins
Despite the best effort to designing direct acting drugs that are highly virus-specific, off-target effects inevitably occur and cause side effects 127. Many of these can be managed with thorough toxicology, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic studies. Furthermore, drug resistance often emerges when direct antivirals are used for extended time periods, leading to the requirement for combination regimens.
Nontoxic drugs have been developed that are effective in treatment of viral infections, including HBV. However, HBV has a small genome that encodes 4 major gene families, so it does not provide many targets for drug development. It is therefore important to study agents that target non-viral proteins or pathway required for HBV infection and replication (see Table 2). However, toxicity is a concern with this approach. Avoidance of toxicity requires a detailed understanding of the targeted pathways. Redundancy is often the rule rather than the exception in biology. When 1 pathway is inhibited, another often takes its place—either involving other members of the targeted pathway or separate pathways that overlap or converge with the targeted pathway. Differences in sensitivity of a virus vs human cells to disruption of a pathway can exploited to achieve an acceptable therapeutic window. Viruses are less likely to become resistant to agents that target cell functions, although viruses can acquire mutations that reduce dependency on the targeted protein or pathway 128.
Table 2.
Agents that Target Host Factors in Development for Treatment of HBV Infection
| Compound | Mechanism and Target | Stage of Development | Sponsor | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Myrcludex B | entry | phase 2 | Hepatera, Russia |
NCT02888106 NCT02637999 |
| GS-5801 | epidrug | phase 1 | Gilead | sponsor’s web site |
| REP 2139 | HBsAg | phase 2 | Replicor, Canada | 96, 97; NCT02565719 |
| REP 2165 | HBsAg | phase 2 | Replicor, Canada | 97; NCT02565719 |
| RO7020322 (RG7834) |
HBsAg | Terminated | Roche, Switzerland | 149; NCT02604355 |
| EYP001 | FXR agonist | phase 1 | Enyo Pharma, France | NCT03469583 |
| APG-1387 | apoptosis | phase 1 | Asscentage Pharma, China | 150; sponsor’s web site |
| Birinapant | apoptosis | terminated | TetraLogic Pharmaceutical | NCT02288208 |
| CRV431 | cyclophilin inhibitor | preclinical | ContraVir Pharmaceutical | sponsor’s web site |
| GS-9688 | TLR8 agonist | phase 2 | Gilead | NCT03491553 |
| GS-9620 | TLR7 agonist | phase 2 | Gilead, USA | NCT02579382 |
| RO6864018 (RG7795 and ANA773) |
TLR7 agonist | phase 2 | Roche, Switzerland | NCT02391805 |
| RO7020531 | TLR7 agonist | phase 1 | Roche, Switzerland | NCT02956850 |
| AL-034 | TLR7 agonist | phase 1 | Alios Biopharma | NCT03285620 |
| AIC649 | immune modulator | phase 1 | AiCuris, Germany | 151 |
| Inarigivir (GS-999 and SB 9200) |
RIGI and NOD2 agonist | phase 2 | Spring Bank |
NCT02751996 NCT03434353 |
| INO-1800 | therapeutic vaccine | phase 1 | Inovio Pharmaceuticals | NCT02431312 |
| TG1050 | therapeutic vaccine | phase 1 | Transgene, France | NCT02428400 |
| HB-110 | therapeutic vaccine | phase 1 | Genexine, South Korea |
152;NCT01641536 NCT00513968 |
| HepTcell (FP-02.2) |
therapeutic vaccine | phase 1 | Altimmune | NCT02496897 |
| JNJ-64300535 | therapeutic vaccine | phase 1 | Janssen Sciences, Belgium | NCT03463369 |
| TomegaVax HBV | therapeutic vaccine | preclinical | TomegaVax | sponsor’s web site |
| MVA-VLP-HBV | therapeutic vaccine | preclinical | GeoVax and CaroGen | sponsor’s web site |
| GS-4774 | therapeutic vaccine | terminated | Gilead | NCT02258581 |
| LTCR-H2–1 | T-cell receptor | preclinical | Lion TCR, Singapore | sponsor’s web site |
| Thymalfasin | immune modulator | phase 4 | Huashan Hospital, China | NCT03448744 |
One example of a drug designed to target a cellular protein required for viral infection is maraviroc, which blocks CCR5 to prevent cell entry by HIV129. Ribavirin, a broad-spectrum antiviral agent used to treat patients with HCV infection, is believed to potentiate the effects of interferon130. Myrcludex B, which blocks NTCP, just completed a phase 2 trial of patients with HBV and HDV co-infection 131, 132. Cyclosporin A-like compounds, which probably interfere with NTCP-mediated HBV entry, are also in development 133. EYP001, a selective synthetic FXR agonist, prevents HBV infection of HepaRG cells and is in a phase 1 trial 134. GS-5801, a liver-targeted prodrug of a lysine demethylase-5 inhibitor, is in a phase 1 trial—it is one of the first epigenetic modifiers to be tested in patients with HBV infection 135. Glucosidase inhibitors and nucleic acid polymers, which prevent assembly and release of HBV particles, also in development96, 97, 136.
Unbiased High-throughput Screen for Small Molecule HBV Inhibitors
With advances in high-throughput technologies and expansion of small molecule chemical libraries, researchers have begun to perform large-scale unbiased screens to identify compounds that inhibit HBV. Screens for antiviral compounds require a miniaturized platform of an infectious or replicating cell culture system coupled with a high-throughput read-out system needs to be developed first (see Figure 3). The overall system would have identify HBV inhibitors with high levels of sensitivity, with reproducible and robust results. These systems have been developed for many viruses and yielded promising compounds for further development137, 138.
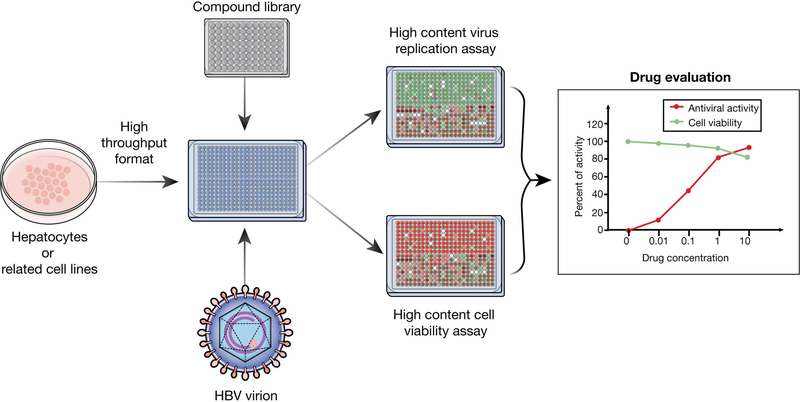
Figure 3. High-throughput Screen for Anti-HBV Compounds.
A high-throughput screen for compounds that inhibit HBV involves culture of HBV-susceptible hepatocytes, followed by infection with HBV and addition of compound library. Compounds found to block HBV entry or replication in this assay can be validated in additional assays and for their effects on cell viability.
For HBV, the building blocks for such a system are available. HBV infectious or replicating cell culture systems are established139. Highly sensitive and specific assays to detect HBV replication are standard tools and can be readily applied to high-throughput screens. Several screens have already been developed and performed to identify HBV inhibitors140.
It could also be possible to repurpose or reposition drugs that have already undergone substantial preclinical or clinical testing141. Drugs developed for a specific disorder can be used to treat other diseases that have overlapping pathogenic mechanisms. However, drugs affect multiple factors and pathways beyond the initial target for which they were developed. An unbiased screen of these drugs for those that inhibit HBV replication nor infection might identify new candidates. Collections of these drugs are currently available for this purpose142. This approach can markedly reduce the duration of drug development, which can last more than 10 years, because many of these drugs have already undergone toxicology and pharmacokinetic analyses. Efforts to repurpose drugs for antiviral development have been under way for viral infections and viral hepatitis143, 144.
Immune-based Approaches
Immune cells and cytokines mediate cytolytic and non-cytolytic clearance of HBV infection5. Therapies that promote cytokine-mediated innate immune control of virus infection and restore adaptive immunity are important to develop. Agonists of toll like receptor 7 (TLR7), TLR8 and DExD/H-box helicase 58 (DDX58 or RIG-I) and therapeutic vaccines are in phase 1 and 2 trials (see Table 2). See ref XX for a detailed review of immune-based therapies for HBV infection (Gehring and Protzer reference).
Future Directions
Strategies to cure HBV infection have been met with renewed interest and energy by pharmaceutical and academic communities, partly because researchers have realized the limitations of treatment options and the unprecedented success of HCV therapy. Although HCV and HBV are different viruses, and challenges to curing their infections are virus are distinct, recent advances in technologies and expanded understanding of HBV infection have paved the way for exciting new directions for development of HBV therapies. Efforts to develop new classes of direct acting antivirals other than the traditional NRTIs are under way and some have entered clinical trials. Innovative approaches that focus on nontraditional viral targets, such as host targeting agents, warrant earnest consideration and should be pursued in parallel. Curing HBV infection is likely to require combination therapies that leverage our knowledge of the Achilles heel of the virus. Armed with new tools and technologies, coupled with increased understanding of HBV’s pathogenic mechanisms, we should be able to cure HBV infection within the next decade.
Acknowledgment
This work was support by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institutes of Health. Yuchen Xia is partly sponsored by ILCA-Bayer fellowship.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- 1.Liang TJ, Block TM, McMahon BJ, et al. Present and future therapies of hepatitis B: From discovery to cure. Hepatology 2015;62:1893–908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Polaris Observatory C. Global prevalence, treatment, and prevention of hepatitis B virus infection in 2016: a modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Tang LSY, Covert E, Wilson E, et al. Chronic Hepatitis B Infection: A Review. JAMA 2018;319:1802–1813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ghany MG. Current treatment guidelines of chronic hepatitis B: The role of nucleos(t)ide analogues and peginterferon. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2017;31:299–309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Xia Y, Protzer U. Control of Hepatitis B Virus by Cytokines. Viruses 2017;9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Buti M, Gane E, Seto WK, et al. Tenofovir alafenamide versus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for the treatment of patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B virus infection: a randomised, double-blind, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016;1:196–206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lin CL, Kao JH. Review article: the prevention of hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Schulze A, Gripon P, Urban S. Hepatitis B virus infection initiates with a large surface protein-dependent binding to heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Hepatology 2007;46:1759–68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Yan H, Zhong G, Xu G, et al. Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus. Elife 2012;1:e00049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Verrier ER, Colpitts CC, Bach C, et al. A targeted functional RNA interference screen uncovers glypican 5 as an entry factor for hepatitis B and D viruses. Hepatology 2016;63:35–48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Yan H, Peng B, He W, et al. Molecular determinants of hepatitis B and D virus entry restriction in mouse sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide. J Virol 2013;87:7977–91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Iwamoto M, Watashi K, Tsukuda S, et al. Evaluation and identification of hepatitis B virus entry inhibitors using HepG2 cells overexpressing a membrane transporter NTCP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2014;443:808–13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Krepstakies M, Lucifora J, Nagel CH, et al. A new class of synthetic peptide inhibitors blocks attachment and entry of human pathogenic viruses. J Infect Dis 2012;205:1654–64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Xia Y, Cheng X, Blossey CK, et al. Secreted Interferon-Inducible Factors Restrict Hepatitis B and C Virus Entry In Vitro. J Immunol Res 2017;2017:4828936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Volz T, Allweiss L, Ben MM, et al. The entry inhibitor Myrcludex-B efficiently blocks intrahepatic virus spreading in humanized mice previously infected with hepatitis B virus. J Hepatol 2013;58:861–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Xia Y, Carpentier A, Cheng X, et al. Human stem cell-derived hepatocytes as a model for hepatitis B virus infection, spreading and virus-host interactions. J Hepatol 2017;66:494–503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Macovei A, Radulescu C, Lazar C, et al. Hepatitis B virus requires intact caveolin-1 function for productive infection in HepaRG cells. J Virol 2010;84:243–53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Huang HC, Chen CC, Chang WC, et al. Entry of hepatitis B virus into immortalized human primary hepatocytes by clathrin-dependent endocytosis. J Virol 2012;86:9443–53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Macovei A, Petrareanu C, Lazar C, et al. Regulation of hepatitis B virus infection by Rab5, Rab7, and the endolysosomal compartment. J Virol 2013;87:6415–27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Rabe B, Glebe D, Kann M. Lipid-mediated introduction of hepatitis B virus capsids into nonsusceptible cells allows highly efficient replication and facilitates the study of early infection events. J Virol 2006;80:5465–73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pante N, Kann M. Nuclear pore complex is able to transport macromolecules with diameters of about 39 nm. Mol Biol Cell 2002;13:425–34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Rabe B, Vlachou A, Pante N, et al. Nuclear import of hepatitis B virus capsids and release of the viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003;100:9849–54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Schmitz A, Schwarz A, Foss M, et al. Nucleoporin 153 arrests the nuclear import of hepatitis B virus capsids in the nuclear basket. PLoS Pathog 2010;6:e1000741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Koniger C, Wingert I, Marsmann M, et al. Involvement of the host DNA-repair enzyme TDP2 in formation of the covalently closed circular DNA persistence reservoir of hepatitis B viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2014;111:E4244–53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Cui X, McAllister R, Boregowda R, et al. Does Tyrosyl DNA Phosphodiesterase-2 Play a Role in Hepatitis B Virus Genome Repair? PLoS One 2015;10:e0128401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kitamura K, Que L, Shimadu M, et al. Flap endonuclease 1 is involved in cccDNA formation in the hepatitis B virus. PLoS Pathog 2018;14:e1007124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Qi Y, Gao Z, Xu G, et al. DNA Polymerase kappa Is a Key Cellular Factor for the Formation of Covalently Closed Circular DNA of Hepatitis B Virus. PLoS Pathog 2016;12:e1005893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Long Q, Yan R, Hu J, et al. The role of host DNA ligases in hepadnavirus covalently closed circular DNA formation. PLoS Pathog 2017;13:e1006784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Pillaire MJ, Betous R, Hoffmann JS. Role of DNA polymerase kappa in the maintenance of genomic stability. Mol Cell Oncol 2014;1:e29902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Tomkinson AE, Howes TR, Wiest NE. DNA ligases as therapeutic targets. Transl Cancer Res 2013;2. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lucifora J, Xia Y, Reisinger F, et al. Specific and nonhepatotoxic degradation of nuclear hepatitis B virus cccDNA. Science 2014;343:1221–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Xia Y, Stadler D, Lucifora J, et al. Interferon-gamma and Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha Produced by T Cells Reduce the HBV Persistence Form, cccDNA, Without Cytolysis. Gastroenterology 2016;150:194–205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Meier MA, Suslov A, Ketterer S, et al. Hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA homeostasis is independent of the lymphotoxin pathway during chronic HBV infection. J Viral Hepat 2017;24:662–671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Li Y, Xia Y, Han M, et al. IFN-alpha-mediated Base Excision Repair Pathway Correlates with Antiviral Response Against Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Sci Rep 2017;7:12715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wu M, Li J, Yue L, et al. Establishment of Cre-mediated HBV recombinant cccDNA (rcccDNA) cell line for cccDNA biology and antiviral screening assays. Antiviral Res 2018;152:45–52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Allweiss L, Volz T, Giersch K, et al. Proliferation of primary human hepatocytes and prevention of hepatitis B virus reinfection efficiently deplete nuclear cccDNA in vivo. Gut 2018;67:542–552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Rall LB, Standring DN, Laub O, et al. Transcription of hepatitis B virus by RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol 1983;3:1766–73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Doitsh G, Shaul Y. Enhancer I predominance in hepatitis B virus gene expression. Mol Cell Biol 2004;24:1799–808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Gao B, Duan Z, Xu W, et al. Tripartite motif-containing 22 inhibits the activity of hepatitis B virus core promoter, which is dependent on nuclear-located RING domain. Hepatology 2009;50:424–33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Courtois G, Baumhueter S, Crabtree GR. Purified hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 interacts with a family of hepatocyte-specific promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1988;85:7937–41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Guo W, Chen M, Yen TS, et al. Hepatocyte-specific expression of the hepatitis B virus core promoter depends on both positive and negative regulation. Mol Cell Biol 1993;13:443–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Lopez-Cabrera M, Letovsky J, Hu KQ, et al. Multiple liver-specific factors bind to the hepatitis B virus core/pregenomic promoter: trans-activation and repression by CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1990;87:5069–73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Raney AK, Zhang P, McLachlan A. Regulation of transcription from the hepatitis B virus large surface antigen promoter by hepatocyte nuclear factor 3. J Virol 1995;69:3265–72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Tang H, McLachlan A. Transcriptional regulation of hepatitis B virus by nuclear hormone receptors is a critical determinant of viral tropism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001;98:1841–6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Raney AK, Le HB, McLachlan A. Regulation of transcription from the hepatitis B virus major surface antigen promoter by the Sp1 transcription factor. J Virol 1992;66:6912–21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Chen M, Hieng S, Qian X, et al. Regulation of hepatitis B virus ENI enhancer activity by hepatocyte-enriched transcription factor HNF3. Virology 1994;205:127–32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Ori A, Shaul Y. Hepatitis B virus enhancer binds and is activated by the Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3. Virology 1995;207:98–106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Trujillo MA, Letovsky J, Maguire HF, et al. Functional analysis of a liver-specific enhancer of the hepatitis B virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1991;88:3797–801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Yu X, Mertz JE. Differential regulation of the pre-C and pregenomic promoters of human hepatitis B virus by members of the nuclear receptor superfamily. J Virol 1997;71:9366–74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.He F, Chen EQ, Liu L, et al. Inhibition of hepatitis B Virus replication by hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha specific short hairpin RNA. Liver Int 2012;32:742–51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Vivekanandan P, Daniel HD, Kannangai R, et al. Hepatitis B virus replication induces methylation of both host and viral DNA. J Virol 2010;84:4321–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Pollicino T, Belloni L, Raffa G, et al. Hepatitis B virus replication is regulated by the acetylation status of hepatitis B virus cccDNA-bound H3 and H4 histones. Gastroenterology 2006;130:823–37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Belloni L, Pollicino T, De Nicola F, et al. Nuclear HBx binds the HBV minichromosome and modifies the epigenetic regulation of cccDNA function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009;106:19975–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Tang HM, Gao WW, Chan CP, et al. Requirement of CRTC1 coactivator for hepatitis B virus transcription. Nucleic Acids Res 2014;42:12455–68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Hayashi Y, Kitamura Y, Nakanishi M, et al. The binding site of transcription factor YY1 is required for intramolecular recombination between terminally repeated sequences of linear replicative hepatitis B virus DNA. J Virol 2000;74:9471–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Belloni L, Allweiss L, Guerrieri F, et al. IFN-alpha inhibits HBV transcription and replication in cell culture and in humanized mice by targeting the epigenetic regulation of the nuclear cccDNA minichromosome. J Clin Invest 2012;122:529–37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Guo YH, Li YN, Zhao JR, et al. HBc binds to the CpG islands of HBV cccDNA and promotes an epigenetic permissive state. Epigenetics 2011;6:720–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Ren JH, Hu JL, Cheng ST, et al. SIRT3 restricts HBV transcription and replication via epigenetic regulation of cccDNA involving SUV39H1 and SETD1A histone methyltransferases. Hepatology 2018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Benhenda S, Ducroux A, Riviere L, et al. Methyltransferase PRMT1 is a binding partner of HBx and a negative regulator of hepatitis B virus transcription. J Virol 2013;87:4360–71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Zhang W, Chen J, Wu M, et al. PRMT5 restricts hepatitis B virus replication through epigenetic repression of covalently closed circular DNA transcription and interference with pregenomic RNA encapsidation. Hepatology 2017;66:398–415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Riviere L, Gerossier L, Ducroux A, et al. HBx relieves chromatin-mediated transcriptional repression of hepatitis B viral cccDNA involving SETDB1 histone methyltransferase. J Hepatol 2015;63:1093–102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Decorsiere A, Mueller H, van Breugel PC, et al. Hepatitis B virus × protein identifies the Smc5/6 complex as a host restriction factor. Nature 2016;531:386–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Tropberger P, Mercier A, Robinson M, et al. Mapping of histone modifications in episomal HBV cccDNA uncovers an unusual chromatin organization amenable to epigenetic manipulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2015;112:E5715–24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Khan S, Iqbal M, Tariq M, et al. Epigenetic regulation of HIV-1 latency: focus on polycomb group (PcG) proteins. Clin Epigenetics 2018;10:14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Gherardini L, Sharma A, Capobianco E, et al. Targeting Cancer with Epi-Drugs: A Precision Medicine Perspective. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 2016;17:856–65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Arbuckle JH, Gardina PJ, Gordon DN, et al. Inhibitors of the Histone Methyltransferases EZH2/1 Induce a Potent Antiviral State and Suppress Infection by Diverse Viral Pathogens. MBio 2017;8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Fouillot N, Tlouzeau S, Rossignol JM, et al. Translation of the hepatitis B virus P gene by ribosomal scanning as an alternative to internal initiation. J Virol 1993;67:4886–95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Chen A, Kao YF, Brown CM. Translation of the first upstream ORF in the hepatitis B virus pregenomic RNA modulates translation at the core and polymerase initiation codons. Nucleic Acids Res 2005;33:1169–81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Bartenschlager R, Schaller H. Hepadnaviral assembly is initiated by polymerase binding to the encapsidation signal in the viral RNA genome. EMBO J 1992;11:3413–20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Hu J, Boyer M. Hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase and epsilon RNA sequences required for specific interaction in vitro. J Virol 2006;80:2141–50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Hu J, Flores D, Toft D, et al. Requirement of heat shock protein 90 for human hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase function. J Virol 2004;78:13122–31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Chen C, Wang JC, Zlotnick A. A kinase chaperones hepatitis B virus capsid assembly and captures capsid dynamics in vitro. PLoS Pathog 2011;7:e1002388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Nguyen DH, Hu J. Reverse transcriptase- and RNA packaging signal-dependent incorporation of APOBEC3G into hepatitis B virus nucleocapsids. J Virol 2008;82:6852–61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Wang GH, Seeger C. The reverse transcriptase of hepatitis B virus acts as a protein primer for viral DNA synthesis. Cell 1992;71:663–70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Will H, Reiser W, Weimer T, et al. Replication strategy of human hepatitis B virus. J Virol 1987;61:904–11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Summers J, Mason WS. Replication of the genome of a hepatitis B--like virus by reverse transcription of an RNA intermediate. Cell 1982;29:403–15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Jones SA, Murakami E, Delaney W, et al. Noncompetitive inhibition of hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase protein priming and DNA synthesis by the nucleoside analog clevudine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2013;57:4181–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Seifer M, Hamatake RK, Colonno RJ, et al. In vitro inhibition of hepadnavirus polymerases by the triphosphates of BMS-200475 and lobucavir. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1998;42:3200–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Tavis JE, Cheng X, Hu Y, et al. The hepatitis B virus ribonuclease H is sensitive to inhibitors of the human immunodeficiency virus ribonuclease H and integrase enzymes. PLoS Pathog 2013;9:e1003125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Hu Y, Cheng X, Cao F, et al. beta-Thujaplicinol inhibits hepatitis B virus replication by blocking the viral ribonuclease H activity. Antiviral Res 2013;99:221–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Cai CW, Lomonosova E, Moran EA, et al. Hepatitis B virus replication is blocked by a 2-hydroxyisoquinoline-1,3(2H,4H)-dione (HID) inhibitor of the viral ribonuclease H activity. Antiviral Res 2014;108:48–55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Lu G, Lomonosova E, Cheng X, et al. Hydroxylated tropolones inhibit hepatitis B virus replication by blocking viral ribonuclease H activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2015;59:1070–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Lentz TB, Loeb DD. Roles of the envelope proteins in the amplification of covalently closed circular DNA and completion of synthesis of the plus-strand DNA in hepatitis B virus. J Virol 2011;85:11916–27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Lambert C, Doring T, Prange R. Hepatitis B virus maturation is sensitive to functional inhibition of ESCRT-III, Vps4, and gamma 2-adaptin. J Virol 2007;81:9050–60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Prange R Host factors involved in hepatitis B virus maturation, assembly, and egress. Med Microbiol Immunol 2012;201:449–61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Watanabe T, Sorensen EM, Naito A, et al. Involvement of host cellular multivesicular body functions in hepatitis B virus budding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007;104:10205–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Jiang B, Himmelsbach K, Ren H, et al. Subviral Hepatitis B Virus Filaments, like Infectious Viral Particles, Are Released via Multivesicular Bodies. J Virol 2015;90:3330–41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Patient R, Hourioux C, Sizaret PY, et al. Hepatitis B virus subviral envelope particle morphogenesis and intracellular trafficking. J Virol 2007;81:3842–51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Gerlich WH, Heermann KH, Lu X. Functions of hepatitis B surface proteins. Arch Virol Suppl 1992;4:129–32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.van Bommel F, Bartens A, Mysickova A, et al. Serum hepatitis B virus RNA levels as an early predictor of hepatitis B envelope antigen seroconversion during treatment with polymerase inhibitors. Hepatology 2015;61:66–76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Wang J, Shen T, Huang X, et al. Serum hepatitis B virus RNA is encapsidated pregenome RNA that may be associated with persistence of viral infection and rebound. J Hepatol 2016;65:700–710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Luckenbaugh L, Kitrinos KM, Delaney Wet, et al. Genome-free hepatitis B virion levels in patient sera as a potential marker to monitor response to antiviral therapy. J Viral Hepat 2015;22:561–70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Yan R, Zhao X, Cai D, et al. The Interferon-Inducible Protein Tetherin Inhibits Hepatitis B Virus Virion Secretion. J Virol 2015;89:9200–12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Xu YB, Yang L, Wang GF, et al. Benzimidazole derivative, BM601, a novel inhibitor of hepatitis B virus and HBsAg secretion. Antiviral Res 2014;107:6–15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Yu W, Goddard C, Clearfield E, et al. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of triazolo-pyrimidine derivatives as novel inhibitors of hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HBsAg) secretion. J Med Chem 2011;54:5660–70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Bazinet M, Pantea V, Cebotarescu V, et al. Safety and efficacy of REP 2139 and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis B virus and hepatitis D virus co-infection (REP 301 and REP 301-LTF): a non-randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017;2:877–889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Roehl I, Seiffert S, Brikh C, et al. Nucleic Acid Polymers with Accelerated Plasma and Tissue Clearance for Chronic Hepatitis B Therapy. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2017;8:1–12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Tu T, Budzinska MA, Shackel NA, et al. HBV DNA Integration: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Viruses 2017;9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Gao W, Hu J. Formation of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA: removal of genome-linked protein. J Virol 2007;81:6164–74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Sung WK, Zheng H, Li S, et al. Genome-wide survey of recurrent HBV integration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Genet 2012;44:765–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Wooddell CI, Yuen MF, Chan HL, et al. RNAi-based treatment of chronically infected patients and chimpanzees reveals that integrated hepatitis B virus DNA is a source of HBsAg. Sci Transl Med 2017;9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Yuen MF, Ahn SH, Lee KS, et al. Two-year treatment outcome of chronic hepatitis B infection treated with besifovir vs. entecavir: results from a multicentre study. J Hepatol 2015;62:526–32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Zhang P, Zhang L, Jiang Z, et al. In vitro mitochondrial toxicity of metacavir, a new nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor for treatment of hepatitis B virus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2010;54:4887–92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Campagna MR, Liu F, Mao R, et al. Sulfamoylbenzamide derivatives inhibit the assembly of hepatitis B virus nucleocapsids. J Virol 2013;87:6931–42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Katen SP, Chirapu SR, Finn MG, et al. Trapping of hepatitis B virus capsid assembly intermediates by phenylpropenamide assembly accelerators. ACS Chem Biol 2010;5:1125–36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Billioud G, Pichoud C, Puerstinger G, et al. The main hepatitis B virus (HBV) mutants resistant to nucleoside analogs are susceptible in vitro to non-nucleoside inhibitors of HBV replication. Antiviral Res 2011;92:271–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Feld JJ, Colledge D, Sozzi V, et al. The phenylpropenamide derivative AT-130 blocks HBV replication at the level of viral RNA packaging. Antiviral Res 2007;76:168–77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Stray SJ, Zlotnick A. BAY 41–4109 has multiple effects on Hepatitis B virus capsid assembly. J Mol Recognit 2006;19:542–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Wang XY, Wei ZM, Wu GY, et al. In vitro inhibition of HBV replication by a novel compound, GLS4, and its efficacy against adefovir-dipivoxil-resistant HBV mutations. Antivir Ther 2012;17:793–803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Deres K, Schroder CH, Paessens A, et al. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication by drug-induced depletion of nucleocapsids. Science 2003;299:893–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Stray SJ, Bourne CR, Punna S, et al. A heteroaryldihydropyrimidine activates and can misdirect hepatitis B virus capsid assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005;102:8138–43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Schlicksup CJ, Wang JC, Francis S, et al. Hepatitis B virus core protein allosteric modulators can distort and disrupt intact capsids. Elife 2018;7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Zoulim F, Yogaratnam JZ, Vandenbossche JJ, et al. Safety, pharmakokinetics and antiviral activity of novel capsid assembly modulator (CAM) JNJ-56136379 (JNJ-6379) in treatmentnaive chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients without cirrhosis. Journal of Hepatology 2018;68 (supplement):102. [Google Scholar]
- 114.Yuen MF, Agarwal K, Gane E, et al. Interim safety, tolerability pharmacokinetics, and antiviral activity of ABI-H0731, a novel core protein allosteric modulator, in healthy volunteers and non-cirrhotic viremic subjects with chronic hepatitis B. Journal of Hepatology 2018;68(supplement):111. [Google Scholar]
- 115.Gane E, Liu A, Yuen MF, et al. RO7049389, a core protein allosteric modulator, demonstrates robust anti-HBV activity in chronic hepatitis B patients and is safe and well tolerated. Journal of Hepatology 2018;68(supplement):101. [Google Scholar]
- 116.Gish RG, Yuen MF, Chan HL, et al. Synthetic RNAi triggers and their use in chronic hepatitis B therapies with curative intent. Antiviral Res 2015;121:97–108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Schluep T, Lickliter J, Hamilton J, et al. Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of ARC-520 Injection, an RNA Interference-Based Therapeutic for the Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection, in Healthy Volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev 2017;6:350–362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Xu Z, Chavez D, Guerra B, et al. Treatment of Chronically HBV-Infected Chimpanzees with RNA Interference Therapeutic ARC-520 LED to Potent Reduction of Viral MRNA, DNA and Proteins without Observed Drug Resistance. Journal of Hepatology 2016;64(Supplement):398. [Google Scholar]
- 119.Yuen MF, Chan HLY, Liu K, et al. Differential Reductions in Viral Antigens Expressed from CCCDNA VS Integrated DNA in Treatment Naïve HBEAG Positive and Negative Patients with Chronic HBV after RNA Interference Therapy with ARC-520. Journal of Hepatology 2016;64(Supplement):391–2. [Google Scholar]
- 120.Gane E, Schwabe C, Given B, et al. A phase 1 study to evaluate safety and tolerability of escalating single doses of the hepatitis B virus RNA interference drug ARC-521 in a healthy volunteer population. Journal of Hepatology 2017;66(Supplement):265. [Google Scholar]
- 121.Fineran PC, Charpentier E. Memory of viral infections by CRISPR-Cas adaptive immune systems: acquisition of new information. Virology 2012;434:202–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Seeger C, Sohn JA. Targeting Hepatitis B Virus With CRISPR/Cas9. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2014;3:e216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Ramanan V, Shlomai A, Cox DB, et al. CRISPR/Cas9 cleavage of viral DNA efficiently suppresses hepatitis B virus. Sci Rep 2015;5:10833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Li H, Sheng C, Wang S, et al. Removal of Integrated Hepatitis B Virus DNA Using CRISPR-Cas9. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2017;7:91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Anderson KR, Haeussler M, Watanabe C, et al. CRISPR off-target analysis in genetically engineered rats and mice. Nat Methods 2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Haapaniemi E, Botla S, Persson J, et al. CRISPR–Cas9 genome editing induces a p53-mediated DNA damage response. Nature Medicine 2018;Published online. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Anighoro A, Bajorath J, Rastelli G. Polypharmacology: challenges and opportunities in drug discovery. J Med Chem 2014;57:7874–87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Garcia-Rivera JA, Bobardt M, Chatterji U, et al. Multiple mutations in hepatitis C virus NS5A domain II are required to confer a significant level of resistance to alisporivir. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2012;56:5113–21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Gulick RM, Lalezari J, Goodrich J, et al. Maraviroc for previously treated patients with R5 HIV-1 infection. N Engl J Med 2008;359:1429–41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Thomas E, Feld JJ, Li Q, et al. Ribavirin potentiates interferon action by augmenting interferon-stimulated gene induction in hepatitis C virus cell culture models. Hepatology 2011;53:32–41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Blank A, Eidam A, Haag M, et al. The NTCP-inhibitor Myrcludex B: Effects on Bile Acid Disposition and Tenofovir Pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2018;103:341–348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Wedemeyer H, Bogomolov P, Blank A, et al. Final results of a multicenter, open-label phase 2b clinical trial to assess safety and efficacy of Myrcludex B in combination with Tenofovir in patients with chronic HBV/HDV co-infection. Journal of Hepatology 2018;68 (Supplement):3. [Google Scholar]
- 133.Watashi K, Sluder A, Daito T, et al. Cyclosporin A and its analogs inhibit hepatitis B virus entry into cultured hepatocytes through targeting a membrane transporter, sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP). Hepatology 2014;59:1726–37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Joly S, Porcherot M, Radreau P, et al. The selective FXR agonist EYP001 is well tolerated in healthy subjects and has additive anti-HBV effect with nucleoside analogues in HepaRG cells. Journal of Hepatology 2017;66 (Supplement). [Google Scholar]
- 135.Gilmore S, Tam D, Dick R, et al. Antiviral activity of GS-5801, a liver-targeted prodrug of a lysine demethylase 5 inhibitor, in a hepatitis B virus primary human hepatocyte infection model. Journal of Hepatology 2017;66(Supplement):690–1. [Google Scholar]
- 136.Durantel D, Alotte C, Zoulim F. Glucosidase inhibitors as antiviral agents for hepatitis B and C. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 2007;8:125–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Hu Z, Hu X, He S, et al. Identification of novel anti-hepatitis C virus agents by a quantitative high throughput screen in a cell-based infection assay. Antiviral Res 2015;124:20–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Beyleveld G, White KM, Ayllon J, et al. New-generation screening assays for the detection of anti-influenza compounds targeting viral and host functions. Antiviral Res 2013;100:120–32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Thomas E, Liang TJ. Experimental models of hepatitis B and C - new insights and progress. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016;13:362–74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Cai D, Mills C, Yu W, et al. Identification of disubstituted sulfonamide compounds as specific inhibitors of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA formation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2012;56:4277–88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Baker NC, Ekins S, Williams AJ, et al. A bibliometric review of drug repurposing. Drug Discov Today 2018;23:661–672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Huang R, Southall N, Wang Y, et al. The NCGC pharmaceutical collection: a comprehensive resource of clinically approved drugs enabling repurposing and chemical genomics. Sci Transl Med 2011;3:80ps16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Schor S, Einav S. Repurposing of Kinase Inhibitors as Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Drugs. DNA Cell Biol 2018;37:63–69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.He S, Lin B, Chu V, et al. Repurposing of the antihistamine chlorcyclizine and related compounds for treatment of hepatitis C virus infection. Sci Transl Med 2015;7:282ra49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Wu G, Liu B, Zhang Y, et al. Preclinical characterization of GLS4, an inhibitor of hepatitis B virus core particle assembly. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2013;57:5344–54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Klumpp K, Shimada T, Allweiss L, et al. Efficacy of NVR 3–778, Alone and In Combination With Pegylated Interferon, vs Entecavir In uPA/SCID Mice With Humanized Livers and HBV Infection. Gastroenterology 2018;154:652–662 e8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Brezillon N, Brunelle MN, Massinet H, et al. Antiviral activity of Bay 41–4109 on hepatitis B virus in humanized Alb-uPA/SCID mice. PLoS One 2011;6:e25096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Javanbakht H, Mueller H, Walther J, et al. Liver-Targeted Anti-HBV Single-Stranded Oligonucleotides with Locked Nucleic Acid Potently Reduce HBV Gene Expression In Vivo. Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids 2018;11:4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Mueller H, Wildum S, Luangsay S, et al. A novel orally available small molecule that inhibits hepatitis B virus expression. J Hepatol 2018;68:412–420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Pan W, Luo Q, Yan X, et al. A novel SMAC mimetic APG-1387 exhibits dual antitumor effect on HBV-positive hepatocellular carcinoma with high expression of cIAP2 by inducing apoptosis and enhancing innate anti-tumor immunity. Biochem Pharmacol 2018;154:127–135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Paulsen D, Weber O, Ruebsamen-Schaeff H, et al. AIC649 Induces a Bi-Phasic Treatment Response in the Woodchuck Model of Chronic Hepatitis B. PLoS One 2015;10:e0144383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Kim CY, Kang ES, Kim SB, et al. Increased in vivo immunological potency of HB-110, a novel therapeutic HBV DNA vaccine, by electroporation. Exp Mol Med 2008;40:669–76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]