ABSTRACT
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) progression and chemotherapy insensitivity have been associated with aberrant PI3K/mTOR/MEK signalling. However, cell death responses activated by inhibitors of these pathways can differ – contextually varying with tumour genetic background. Here, we demonstrate that combining the dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor PF5212384 (PF384) and MEK inhibitor PD325901 (PD901) more effectively induces apoptosis compared with either agent alone, independent of KRAS mutational status in PDAC cell lines. Additionally, a non-caspase dependent decrease in cell viability upon PF384 treatment was observed, and may be attributed to autophagy and G0/G1 cell cycle arrest. Using reverse phase protein arrays, we identify key molecular events associated with the conversion of cytostatic responses (elicited by single inhibitor treatments) into a complete cell death response when PF384 and PD901 are combined. This response was also independent of KRAS mutation, occurring in both BxPC3 (KRAS wildtype) and MIA-PaCa-2 (KRASG12C mutated) cells. In both cell lines, Bim expression increased in response to PF384/PD901 treatment (by 60% and 48%, respectively), while siRNA-mediated silencing of Bim attenuated the apoptosis induced by combination treatment. In parallel, Mcl-1 levels decreased by 36% in BxPC3, and 30% in MIA-PaCa-2 cells. This is consistent with a functional role for Mcl-1, and siRNA-mediated silencing enhanced apoptosis in PF384/PD901-treated MIA-PaCa-2 cells, whilst Mcl-1 overexpression decreased apoptosis induction by 24%. Moreover, a novel role was identified for PDCD4 loss in driving the apoptotic response to PF384/PD901 in BxPC3 and MIA-PaCa-2 cell lines. Overall, our data indicates PF384/PD901 co-treatment activates the same apoptotic mechanism in wild-type or KRAS mutant PDAC cells.
KEYWORDS: pancreatic cancer, PI3K, mTOR, MEK, combination chemotherapy, Bim, Mcl-1, PDCD4
Introduction
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) has a global incidence of > 85,000 cases yearly and has one of the poorest prognoses, with an age-standardised 5-year survival of 3.7%.1,2 The lack of efficacy of current chemotherapy options (gemcitabine, FOLFIRINOX and Nab-paclitaxel), and the rapid emergence of resistance to these regimens, highlights the need for developing targeted therapeutic strategies for this malignancy. Although this has largely been hampered by the lack of identification of key actionable pathogenic drivers in PDAC, there has recently been progress in understanding the genetic signature of PDAC, which should lead to new therapies.3-7 It is well documented that the KRAS gene is mutated in ~ 90% of PDAC and is thought to be an early and initiating event, which in combination with cooperative genetic alterations (TP53, CDKN2A and SMAD4) is sufficient to drive the formation of premalignant lesions into PDAC.8 Ras pathway alterations are common in most cancers and have been identified as important drivers of oncogenesis, for example in high-grade serous ovarian cancers.9 While a number of pharmacological approaches have sought to block Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK signalling, direct inhibition of the K-Ras protein has been unsuccessful clinically and efforts have instead focused on targeting downstream signalling proteins, such as Raf, MEK and Akt.10
Targeting Ras signalling via MEK inhibition is a logical strategy but trials have demonstrated no clinical benefit as monotherapy.11-16 Many PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibitors are undergoing clinical development, but their efficacy may be limited by the induction of compensatory pro-oncogenic MEK signalling.17-19 Therefore there is a strong rationale for combining inhibitors of both pathways, and a number of preclinical studies have demonstrated improved efficacy by combining either PI3K and/or mTOR inhibitors with a MEK inhibitor in various tumour types.20-22 Studies to identify potential molecular biomarkers of response to these agents have largely focused on genomic aberrations in KRAS and PIK3CA. However, these alone do not appear to be absolute predictive markers of response.23-29 Defining the cell death pathways activated by these inhibitors may suggest additional response biomarkers. There is preliminary but equivocal evidence that PI3K/mTOR/MEK inhibitor-induced changes in the expression of Bim and Mcl-1 proteins are related to KRAS mutational status. In part the ambiguity surrounding this may relate to specific cancer types. For example, mTOR inhibition has been found to decrease expression of Mcl-1 in colorectal cancer cells, but only when KRAS mutations were present.30 In comparison, the dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor BEZ235 had no effect on Mcl-1 expression in PDAC cell lines irrespective of KRAS status,31 but reduced expression in ovarian cancer cell lines.32 Additionally, while MEK inhibition is more commonly reported to increase or stabilise expression of Bim, it has also been reported by some to modulate Mcl-1 stability.30,32–35 The synergy observed when PI3K/mTOR/MEK inhibitors are combined may stem from Bim induction alongside Mcl-1 decrease, but the primary regulators of these alterations may differ due to the cancer type and the inhibitor used. Therefore it is important to understand how specific agents contribute to the induction of cell death in individual cancer types.
Despite clinical evaluation and phase I trial activity, there are currently no licensed indications for dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors. The induction of compensatory MEK signalling following PI3K/mTOR inhibition provides a strong rationale for combining with MEK inhibitors to enhance therapeutic efficacy. Indeed, a phase 1 trial combining PF5212384 (PF-584, dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor36,37) with PD325901 (PD901, non-ATP competitive MEK inhibitor38) has been completed (NCT01347866), although results have not been published thus far. In the present study, we use reverse phase protein array (RPPA) analysis to compare the differential effects, with respect to response and apoptotic signatures, of PF384 and PD901 combination treatment between KRAS mutant and wild-type PDAC cell lines.
Results
We have previously used RPPA analysis to define a biomarker signature for clinical response to AKT inhibition in the context of platinum re-sensitisation.39 Here, we apply this technology to investigate the response of PDAC cell lines to PF384 and PD901, alone and in combination. BxPC-3 and MIA-PaCa-2 cells were treated for 6 hours with vehicle control (DMSO), 1 μM PF384, 0.1 μM PD901 or both drugs in combination, after which whole cell lysates were subject to expression analysis of 214 proteins (Table S1). As shown in Figure 1a, the response of a panel of PI3K/mTOR/MEK signalling components to these inhibitors is consistent with their on-target effects, although some cross-regulation of these pathways by these agents was observed. Indicative of PI3K inhibition, treatment with PF384 abrogated phospho-S473AKT (pS473AKT) expression by 80% in BxPC3 cells. Expression of phospho-S2448mTOR (pS2448mTOR) and phospho-T389p70-S6K (pT389p70-S6K) were also decreased by 60% and 90%, respectively, indicating mTOR inhibition. In comparison, PD901 did not affect expression of pS473AKT in this cell line and decreased the expression of pS2448mTOR and pT389p70-S6K to much lesser extents (20% and 50%, respectively). MEK signalling, as indicated by phospho-T202/Y204MAPK (pT202/Y204MAPK) expression was decreased by 30% in response to PF384, but by 60% following treatment with PD901. In MIA-PaCa-2 cells, treatment with PF384 had a reduced inhibitory effect on PI3K signalling (compared with BxPC3 cells) with pS473AKT levels decreasing by 40% – and they remained unaffected by PD901 treatment. Levels of pS2448mTOR and pT389p70-S6K were decreased in response to PF384 to similar extents as in BxPC3 cells, with reductions of 50% and 90%, respectively. Again, PD901 had a reduced effect on these signalling components with observed reductions of 20% and 40%, respectively. With respect to inhibition of MEK signalling in MIA-PaCa-2 cells, pT202/Y204MAPK expression was found to be decreased by 40% following treatment with PD901, but increased 2-fold in response to PF384. Although our data indicates successful inhibition of PI3K/mTOR by PF384 and MEK signalling by PD901 in BxPC3 and MIA-PaCa-2 cell lines, treatment for 6 hours with these agents induced minimal apoptosis in either cell line (Figure 1b). By comparison, when PF384 and PD901 were combined, apoptosis was significantly increased compared with single agent responses, to 6.6-fold in BxPC3 cells (p < 0.0001) for which a combination index (CI) of 0.55, indicating synergy, was calculated. In MIA-PaCa-2 cells, the 4.3-fold apoptosis induction measured following co-treatment with PF384 and PD901 was twice that induced by PF384 alone, and significantly higher compared to that induced by PD901 single treatment (p < 0.05) with a CI of 0.86 again indicating synergy. Extending the time of treatment to 24 hours and to additional cell lines, a similar response profile was observed: as shown in Figure 2, the combination of PF384 and PD901 induced the highest level of apoptosis in a panel of PDAC cell lines (BxPC3, MIA-PaCa-2, Panc-1, and Panc05.04). Relative to that induced by single agent treatments, apoptosis in response to this combination treatment was significantly higher and synergistic (BxPC3 CI = 0.3; MIA-PaCa-2 CI = 0.88; Panc05.04 CI = 0.62) in all but the Panc-1 cell line (CI = 1.17).
Figure 1.
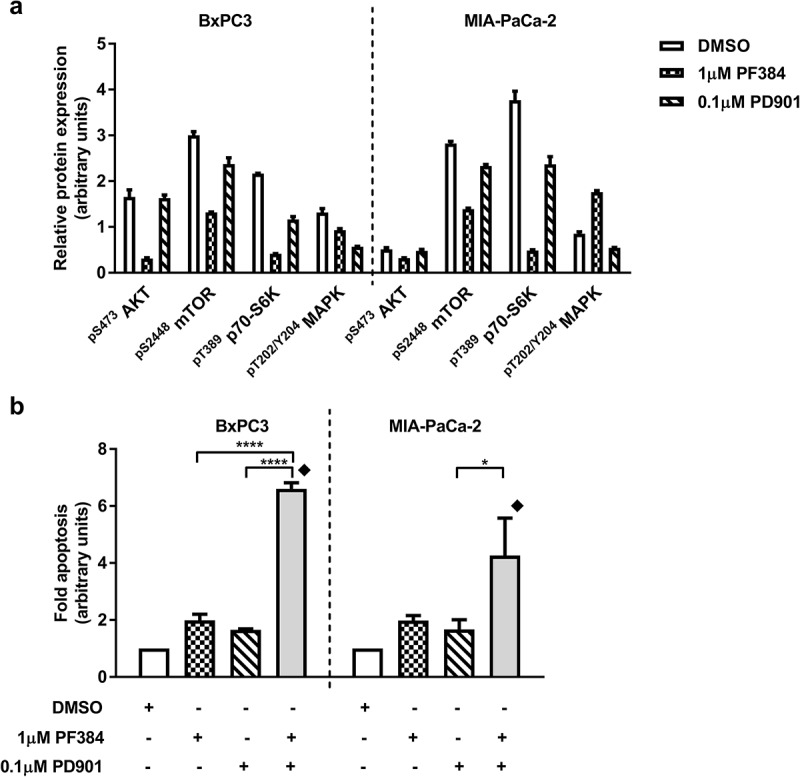
PF384 and PD901 effectively target PI3K and MEK signalling pathways and enhance apoptotic induction when combined. BxPC-3 and MIA-Pa-Ca-2 cells were treated as indicated for 6 hours after which whole cell lysates were processed for a) RPPA analysis, and normalised Log2 median-centred values used to calculate relative expression of PI3K/mTOR/MEK signalling pathway components and b) fold-apoptosis was determined as caspase-3/7 activity normalised to MTT cell viability data. All data shown are the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) for 3 independent experiments. *p ≤ 0.05, ****p ≤ 0.0001, one-way ANOVA.  CI < 1.
CI < 1.
Figure 2.
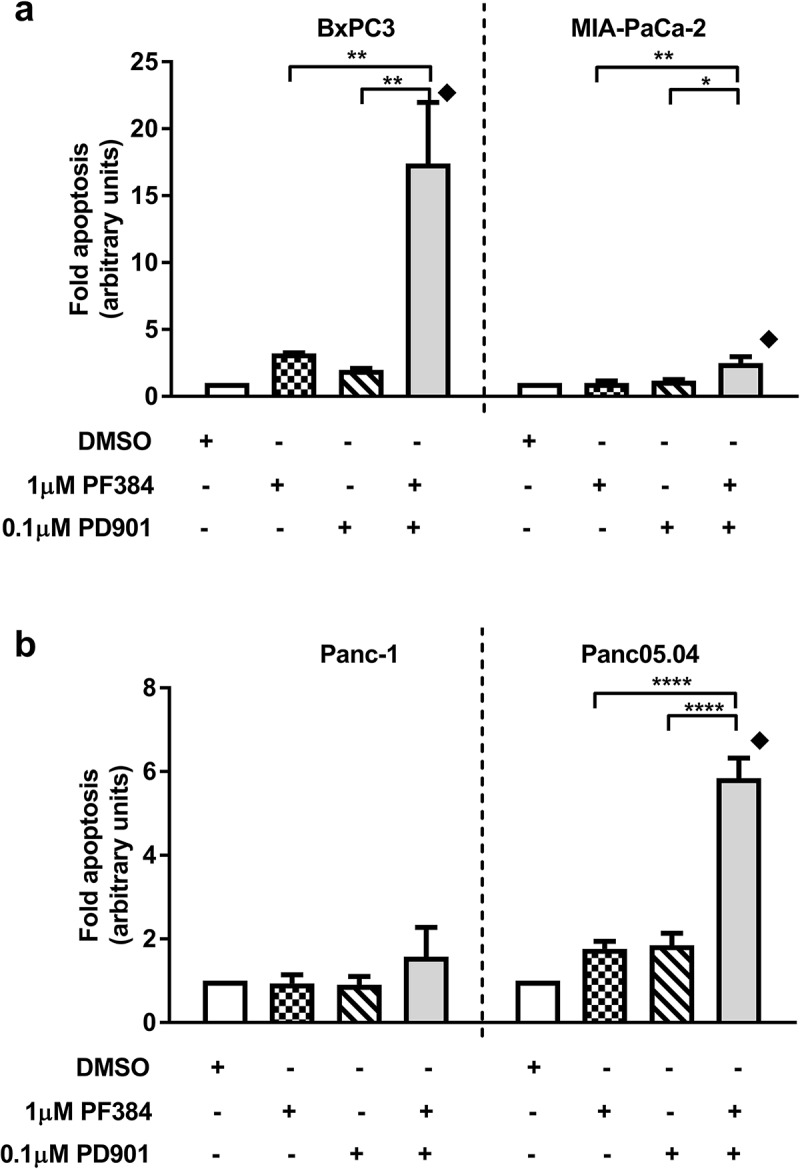
PF384 and PD901 in combination induces apoptosis in PDAC cell lines. a) BxPC-3, MIA-Pa-Ca-2, b) Panc-1 and Panc05.04 cells were treated as indicated for 24 hours after which fold-apoptosis was determined as caspase-3/7 activity normalised to MTT cell viability data. All data shown are the mean ± SEM for 3 independent experiments. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ****p ≤ 0.0001, one-way ANOVA.  CI < 1.
CI < 1.
In addition to apoptosis, we hypothesised whether the inhibitors used may also affect cell viability or growth via other mechanisms. As shown in Figure 3a, both BxPC3 and MIA-PaCa-2 cells were found to arrest in the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle in response to 24 hours treatment with PF384, and this was accompanied by a reduction in the S- and G2M-phase populations. In response to PD901 treatment for the same time, G0/G1 arrest was also observed in both cell lines, although to a slightly greater extent in MIA-PaCa-2 cells. Following co-treatment with PF384 and PD901, the cell cycle populations showed a distribution similar to those obtained following single agent PF384 treatment. Consistent with these findings, reduced BxPC3 (14%) and MIA-PaCa-2 (17%) cell viability was observed after treatment with PF384 for 6 hours (Figure 3b). This was decreased by a further 8% when PF384 was combined with PD901. In comparison, PD901 treatment alone minimally affected cell viability. Together this data suggested that growth arrest or non-caspase-associated cell death might result from PF384 treatment. In support of a contribution of non-caspase-associated cell death to PDAC cell line response to PF384 treatment, the decrease in BxPC3 and MIA-PaCa-2 cell viability induced by PF384 or PF384/PD901 was not restored to that of control levels when the cells were pre-treated with the pan-caspase inhibitor z.VAD.fmk (100 μM). In fact, when compared to non-caspase inhibited cells, the viability decrease was enhanced – by an average of 19% in BxPC3 cells and 13% in MIA-PaCa-2 cells in the presence of z.VAD.mk (Figure 3b). Due to the established role of mTOR in autophagy, we investigated whether activation of this process may account for the above observation. In support of this, the autophagy marker LC3A/B-II was found to be increased in response to the 6 hour treatment with PF384, either alone or in combination with PD901 (Figure 3c), and this was accompanied by a concomitant reduction in LC3A/B-1 expression.
Figure 3.
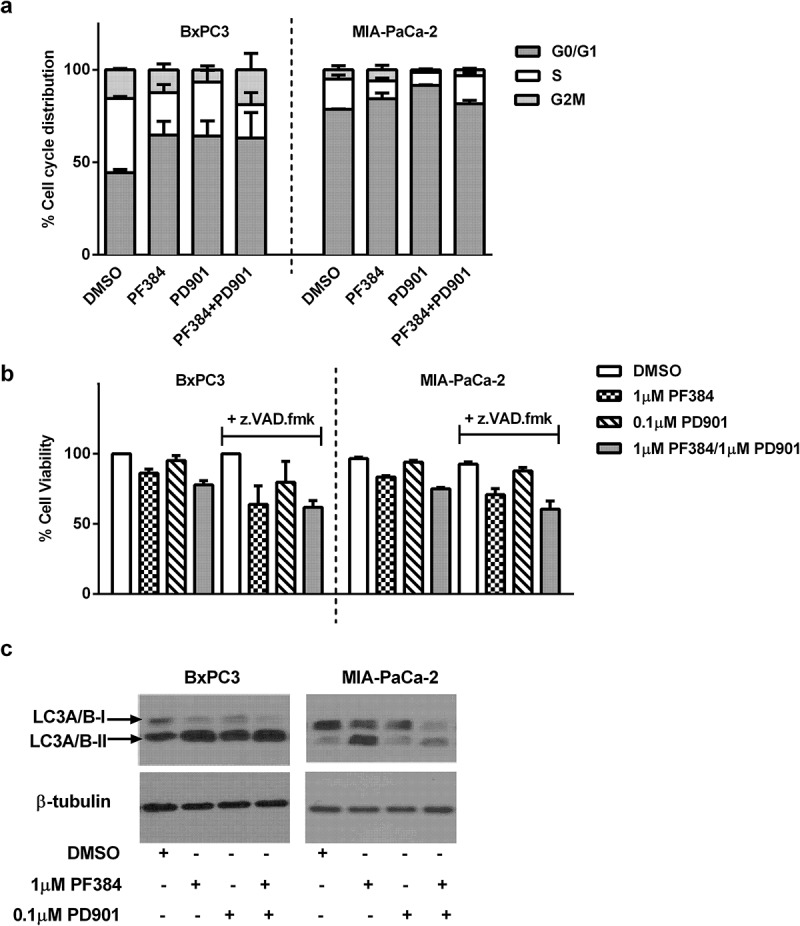
PF384 induces G1/G0 cell cycle arrest and decreases cell viability in a non-caspase dependent manner in association with the induction of autophagy. a) BxPC-3 and MIA-Pa-Ca-2 cells were treated as indicated for 24 hours after which they were labelled with propidium iodide and the percentage of cells in each stage of the cell cycle determined by flow cytometry. b) Cells were treated as indicated for 6 hours after which cell viability was determined by MTT assay. Where z.VAD.fmk (100 μM) was used, cells were pre-incubated with this for 1 hour before the addition of other drugs. c) Cells were treated as indicated for 24 hours after which whole cell lysates were assessed for expression of LC3A/B and β-tubulin by western blotting. All data shown are the mean ± SEM for 3 independent experiments. Blots are representative of two biological repeats.
To identify mechanistic drivers of response to combination PI3K/mTOR and MEK inhibition, we mined our proteomic data for alterations, which may account for the apparent synergistic apoptotic phenotype observed on combining PF384 and PD901. For this we also included data from an ovarian cancer cell line, PEA2 (Fig S1, Table S1), for comparison between cancer types. The majority of proteins with significantly altered expression under combination treatment conditions were, unsurprisingly, related to PI3K/mTOR/MEK signalling. Excluding these, the pro-apoptotic protein Bim was found to be among the top 5 proteins whose expression was significantly increased in all cell lines in response to PF384/PD901 (relative to DMSO treated cells). As shown in Figure 4a, Bim expression increased in BxPC3 cells by 56% (p ≤ 0.0001) after treatment with this combination, and although also significantly increased by single agents, this was not by more than 28% (p ≤ 0.0001) for either drug. For MIA-PaCa-2 cells, Bim expression increased by 48% (p ≤ 0.001) after PF384/PD901 treatment, whilst a 38% increase (p ≤ 0.01) was noted in response to PD901 alone. Consistent with this, western blotting found levels of Bim (BimEL, the predominant isoform was detected using this antibody) to be increased on treatment with PD901 alone or in combination with PF384 in these cell lines (Figure S1). Also noted was a mobility shift of Bim in MIA-Pa-Ca-2, which may represent a change in phosphorylation status. In PEA2 cells, a significant increase in Bim expression of 36% (p ≤ 0.01) was also detected in response to PF384/PD901 co-treatment from the RPPA data. Confirmation of a role for Bim in driving PF384/PD901-induced apoptosis was assessed using siRNA in MIA-PaCa-2 cells as a representative model. As shown in Figure 4b, the silencing of Bim attenuated the apoptosis induced in response to PF384/PD901 co-treatment, albeit not significantly.
Figure 4.
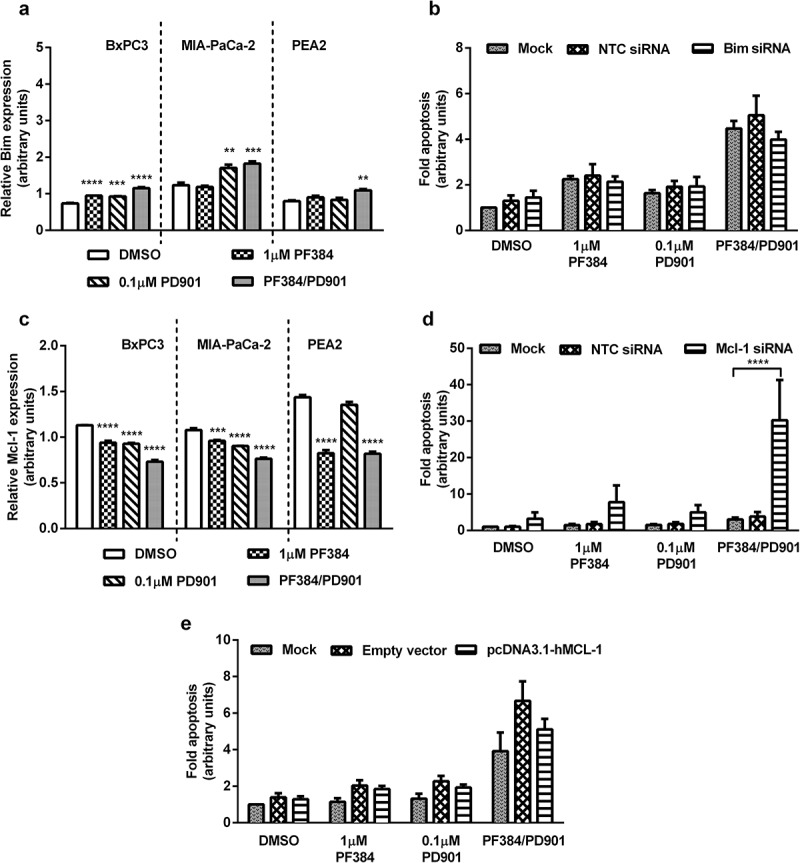
Expression of Bim increases and Mcl-1 decreases in response to PF384/PD901 treatment, and gene modulation studies (siRNA, overexpression) confirm roles for these proteins in apoptosis induced by this combination.
BxPC3, MIA-PaCa-2 and PEA2 were treated as indicated for 6 hours after which whole cell lysates were processed for RPPA analysis, and normalised Log2 median-centred values used to calculate relative expression of a) pro-apoptotic Bim and c) anti-apoptotic Mcl-1. All data shown are the mean ± SEM for 3 independent experiments. **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, ****p ≤ 0.0001, one-way ANOVA. MIA-PaCa-2 cells were transfected with b) non-targeting control (NTC) and Bim siRNA or d) NTC and Mcl-1 siRNA or e) pcDNA3.1-hMCL-1, empty vector and mock transfected for 48 hours, after which they were re-seeded and treated as indicated for 24 hours. Fold-apoptosis was determined as caspase-3/7 activity normalised to MTT cell viability data. All data shown are the mean ± SEM for 3 independent experiments. ****p ≤ 0.0001, one-way ANOVA.
Bim-induced apoptosis is often associated with a reduction in levels of the anti-apoptotic protein Mcl-1, including in response to PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibition,32 and indeed our RPPA data (Figure 4c) indicated a significant decrease (p ≤ 0.0001) in Mcl-1 expression in all assessed cell lines (BxPC3 36%, MIA-PaCa-2 30% and PEA2 43%) following PF384/PD901 co-treatment. These decreases were also observed in response to single agent treatment (except for PD901 in PEA2 cells). Confirmation of these responses in PDAC cells by western blotting confirmed this reduction of Mcl-1, with the greatest decrease observed in response to PF384/PD901 co-treatment (Figure S2). We also note an additional band, possibly corresponding to the short 32kDa form of Mcl-1 in MIA-PaCa-2 cells only, and this followed a similar pattern of regulation in response to PF384/PD901 treatment. However, siRNA-mediated silencing of Mcl-1 was found to only enhance the apoptotic response of MIA-PaCa-2 cells to the combination treatment (Figure 4d). Conversely, overexpression of Mcl-1 in this cell line (Figure 4e) resulted in a 24% decrease in apoptosis induction, relative to vector control, in response to the combination treatment. These results are consistent with a functional role for Mcl-1 in the apoptotic phenotype observed on combination of PI3K/mTOR and MEK inhibitors.
In comparison to previous reports showing that the tumour suppressor PDCD4 is negatively regulated by PI3K and mTOR signalling,40,41 our RPPA analysis indicated a down-regulation of ~ 50% (p ≤ 0.001; for all cell lines) in its expression in response to PF384/PD901 co-treatment (Figure 5a). Although this was not validated by immunoblotting, with levels remaining unchanged in BxPC-3 and MIA-Pa-Ca-2 under all treatment conditions (Figure S2). Despite the paradox, as shown in Figure 5b, siRNA-mediated silencing of PDCD4 significantly increased PF384/PD901-induced apoptosis in MIA-PaCa-2 cells 1.8-fold (p ≤ 0.001), relative to that measured in PF384/PD901-treated mock-transfected cells.
Figure 5.
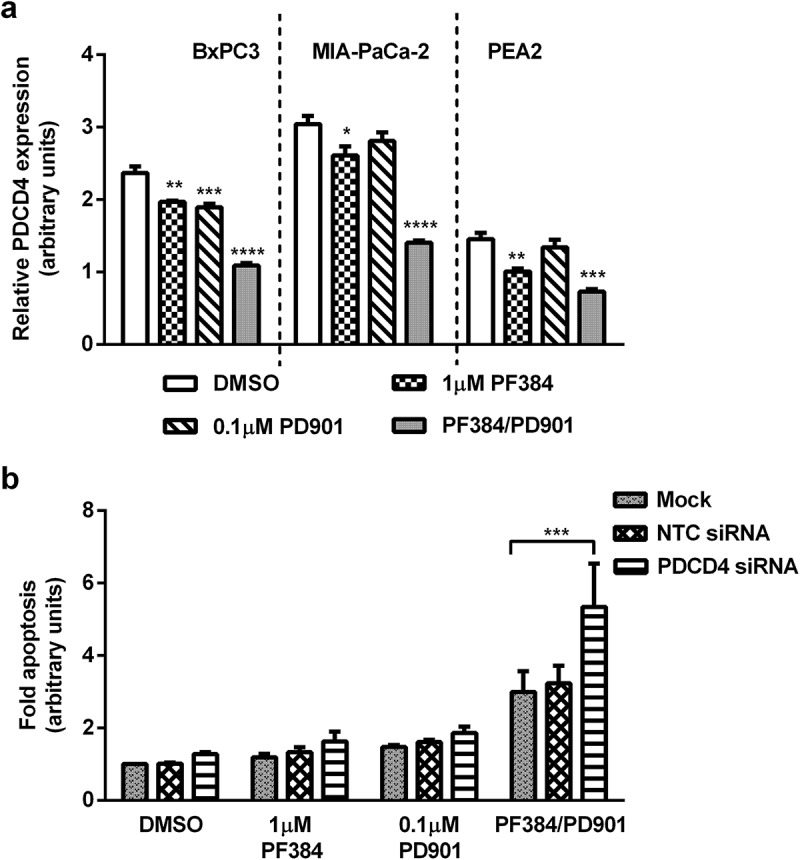
PDCD4 expression decreases in response to PF384/PD901 treatment, and siRNA-mediated silencing identifies a role for it in apoptosis induced by this combination. a) BxPC3, MIA-PaCa-2 and PEA2 cells were treated as indicated for 6 hours after which whole cell lysates were processed for RPPA analysis, and normalised Log2 median-centred values used to calculate relative expression of PDCD4. b) MIA-PaCa-2 cells were transfected with NTC or PDCD4 siRNA, or mock transfected for 48 hours, after which they were re-seeded and treated as indicated for 24 hours. Fold-apoptosis was determined as caspase-3/7 activity normalised to MTT cell viability data. All data shown are the mean ± SEM for 3 independent experiments. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, ****p ≤ 0.0001, one-way ANOVA.
Discussion
In this study we identify a novel role for PDCD4 in the cell death mechanism activated when PDAC cells are co-treated with the PI3K/mTOR inhibitor PF384 and the MEK inhibitor PD901. Additionally, our data indicates roles for Bim and Mcl-1 in regulating PDAC response to this combination irrespective of KRAS mutation status. Due to the complexity and co-dependency of cancer cell survival networks, it is not surprising that combining inhibitors of these critical signalling nodes achieved a far greater level of tumour cell kill than single agent treatments. While this is reflective of preclinical and clinical studies demonstrating the improved efficacy of combining PI3K and/or mTOR inhibitors with a MEK inhibitor in PDAC,20-22 and other cancer types, our study indicates that the mechanism(s) underpinning this may be inhibitor-specific. Defining these may assist in developing theranostic biomarkers for future development of such inhibitors for treating PDAC.
In line with previous studies, our RPPA data confirms a role for Bim and Mcl-1 in the apoptotic pathway induced in response to PI3K/mTOR/MEK co-inhibition.30-35 Although in our study this did not differ between KRAS mutant and wild-type PDAC cell lines (and was also the same in the KRAS wild-type ovarian cancer PEA2 cell line), we note some differences with other studies regarding the extent to which each inhibitor affects each protein. Reports of MEK inhibition leading to increased expression and stabilisation of Bim have generally been consistent, across various tumour and inhibitor types, regardless of KRAS mutation status.30,32,34,35 Consistent with this, we found expression of pro-apoptotic Bim to be increased in both BxPC3 and MIA-PaCa-2 cells in response to PD901. By comparison, the effect of the dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor on Bim expression can vary between cell types, although this is reportedly not KRAS related.31,32 Of interest however, while Venkannagari et al., reported that BEZ235 (another dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor) treatment increased Bim expression in both KRAS mutant (Panc-1) and wild-type (HS766T) PDAC cell lines,31 our study found an increase in Bim expression following PF384 treatment only in BxPC3 (KRAS wild-type) cells. This could be extended to a larger panel of cell lines to determine if this is an inhibitor-specific effect, or related to KRAS status.
With regards to Mcl-1 expression, we found it to be decreased in response to PI3K/mTOR inhibition in all cell lines. This is in contrast to studies using other inhibitors which found no effect,31 or a decrease only in KRAS mutant cells.30 Although anti-apoptotic Mcl-1 is highly expressed in many cancers including pancreatic tumours42 and therefore an attractive therapeutic target, it appears that strategies to decrease/inhibit it are cell-type specific, highlighting the importance of defining molecular mechanisms specific to both individual inhibitor and tumour type. Our present study suggests that PF384 may be a useful agent to achieve this in a broad spectrum of PDAC cases. Additionally, our RPPA data also hints that PF384/PD901-induced cell cycle arrest may be related to Mcl-1 downregulation as both KRAS mutant and wild-type PDAC cell lines p27 levels were found to be increased (Table S1) and this may parallel a study in colorectal cancer cells in which cell cycle arrest has been associated with elevated p27 levels following Mcl-1 loss.43 Our RPPA analysis also suggests STAT3, whose inhibition has previously been shown to reduce Mcl-1 levels and induce apoptosis in PDAC cells in vitro,44 as a possible effector of PI3K/mTOR/MEK-mediated Mcl-1 regulation as in MIA-Pa-Ca-2 cells levels of STAT3 were significantly reduced in response to all treatments (Table S1).
Contrary to its role as a tumour suppressor, we found expression of PDCD4 to be downregulated in response to PF384/PD901 treatment. Decreased expression of this protein has widely been correlated with tumour progression and poor outcomes in a range of cancer types, including pancreatic and ovarian, with its tumour suppressive effect being largely attributed to regulating cell cycle progression past G1, as well as apoptosis and autophagy.41,45–48 However, in response to mitogenic signals, PDCD4 can undergo PI3K/Akt/mTOR driven proteasomal degradation49-51 and decreased expression of this protein has been associated with chemoresistance.52 Therefore our data indicating that the siRNA-mediated suppression of PDCD4 increases apoptotic response to PF384/PD901 treatment was surprising and we speculate this is related to a PI3K-independent and lesser known role for PDCD4 in suppressing pro-caspase-3 translation.53 Such a role for PDCD4 in driving PI3K/mTOR/MEK inhibitor-induced apoptosis has not previously been reported, and additional studies to establish this role of PDCD4 in our system may clarify its potential as a novel therapeutic target or biomarker in PDAC. For example, the function of PDCD4 may be dependent on levels of interacting proteins such as PRMT5.54 Alternatively, it is possible that the decreased PDCD4 expression in our RPPA data is the result of increased mir-21 expression: mir-21, an established PDCD4 repressor,55 can be upregulated by COX-256 which we found to be significantly increased in BxPC3 and PEA2 cells treated with PF384 (Table S1).
In addition to confirming that a greater apoptotic response is elicited in PDAC cells when the PI3K/mTOR inhibitor PF384 and the MEK inhibitor PD901 are used simultaneously, compared with inhibition of either pathway in isolation, we found that single agent PF384 or PD901 treatment results in G0/G1 cell cycle arrest. This is consistent with previous reports indicating a mechanism of cytostatic response in PDAC cells following PI3K/mTOR or MEK inhibition.26,29,31,57,58 Although this may account for the lack of cell death induced by these agents, our data also suggests autophagy induction in BxPC3 and MIA-PaCa-2 cells following PI3K/mTOR inhibition with PF384. The presence of autophagy in pancreatic malignancies has been investigated, although its role in promoting or suppressing tumour cell survival appears to be context dependent.59 Autophagic responses have previously been associated with PDAC resistance to PI3K/mTOR inhibitors,60,61 and our data supports this correlation: the increase in LC3A/B-II observed in response to PF384 was more pronounced in MIA-PaCa-2 cells which showed no apoptotic response to this drug, compared with BxPC3 cells in which a 3-fold increase in apoptosis was measured after 24 hour treatment. Interestingly however, our RPPA data indicated that mTOR expression was reduced by similar levels in both cell lines following PF384 treatment. One possible explanation for this could be the inhibition of an mTOR-independent, PI3K-driven autophagy pathway62 in BxPC3 cells. Given that viability in both cell lines decreased to similar extents in response to PF384, this appears unlikely however. Alternatively this may be the result of increased FOXO3a levels in PF384 treated-MIA-PaCa-2 cells (Table S1), which have been shown to drive LC3 expression,63 or may be related to the incompletely understood association of KRAS mutational status with autophagy induction.59 However, regardless of differences in autophagic molecular responses, our data indicates activation of this process in both KRAS mutant and wild-type PDAC cell lines in response to PF384.
Although there are important roles for PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Ras/MEK signalling pathways in PDAC progression and chemosensitivity, the most effective method of exploiting these for therapeutic gain remains unclear. A myriad of inhibitors targeting these pathways are available and their efficacy and mechanism of action are likely linked to structure and tumour type.19,64 Additionally, the compensatory cross-regulation of these pathways highlights the importance of selecting the right combination, and possibly right sequence, for the right tumour. Our data indicates that in PDAC cell lines, the response to PF384 and PD901 is independent of KRAS status. Although G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and autophagy are induced following PI3K/mTOR inhibition, the conversion of these to a complete cell death response is greatest when both inhibitors are combined and involves the modulation of the Bim/Mcl-1 apoptotic axis. Additionally we suggest a new role for PDCD4 in eliciting cell death in response to this combination of agents.
Materials and methods
Cell lines and reagents
BxPC-3 (93120816; KRAS wild-type), MiaPaCa-2 (85062806; KRASG12C mutated) and Panc-1 (87092802; KRASG12D mutated) cells lines were purchased from the Health Protection Agency Culture Collections and Panc05.04 cells (CRL-2557; KRASG12D mutated) were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection. PEA2 cells65 (KRAS wild-type) were obtained from Dr. Simon Langdon (University of Edinburgh, UK). BxPC-3 and PEA2 cells were maintained in RPMI-1640 (Sigma, R5886), and Mia-Pa-Ca-2 and Panc-1 in DMEM (Sigma, D5546), supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum (First Link UK, 02–00–850), 2 mM L-glutamine (Thermo Fisher, 25030–024) and penicillin/streptomycin (50 units/ml and 50 μg/ml respectively; Thermo Fisher, 15070–063). Panc05.04 cells were maintained in RPMI-1640 supplemented with 15% fetal calf serum, plus 2 mM L-glutamine and penicillin/streptomycin. Cells were routinely tested for mycoplasma, and their authenticity confirmed by STR analysis. The PI3K/mTOR inhibitor PF5212384 (PF384) was a gift from Pfizer (UK), the MEK inhibitor PD325901 (PD901) was purchased from Selleck Chemicals (S1036), and the caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK was from R&D (FMK001). All inhibitors were reconstituted in DMSO (Sigma, 276855) and stored at −20°C. Primary antibodies were used according to manufacturers’ instructions and their Antibody Registry IDs are as follows: from Cell Signaling Technology anti-LC3-A/B (AB_2137703), anti-Mcl-1 (AB_2281980), anti-Bim (AB_659953) and anti-PDCD4 (AB_2162318); from Sigma anti-β-tubulin (AB_477577). For cell cycle analysis, propidium iodide was purchased from Sigma (P4170) and RNase A was from Qiagen (19101).
RPPA analysis
Cells were seeded to 70% confluency and allowed to adhere overnight before being treated with either 1 μM PF384 alone or in combination with 0.1 μM PD901 for 6 hours. Cells were then washed in PBS and RPPA lysis buffer added (1% Triton X-100, 50 mM HEPES pH 7.4, 150 mM NaCl, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EGTA, 100 mM NaF, 10 mM sodium pyrophosphate, 1 mM Na3VO4, 10% glycerol, containing freshly added protease (Roche Applied Science, 04693159001) and phosphatase inhibitors (VWR, EM524628)). Cells were incubated on ice with the buffer for 20 minutes before scraping and centrifuged (14,000 rpm, 10 minutes, 4°C) and the supernatant collected. RPPA assay was performed at the Functional Proteomics RPPA Core Facility at MD Anderson, as previously described.66 Data provided from the RPPA facility consisted of protein intensity values normalised to the loading control and transformed to linear values (normalised linear) which were used to calculate relative significant fold expression.
Apoptosis and cell viability assays
Cells were seeded at a density of 5000 cells/well in a 96 well plate and allowed to adhere overnight before being treated with inhibitors. When required, cells were treated with the caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK one hour prior to co-treatment with other agents. All treatments were performed at 37°C 5% CO2 for the durations indicated. Apoptosis was measured by detection of active caspase-3/7 using the Caspase Glo 3/7 assay (Promega, G8090) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Cell viability was determined using 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assays (Sigma, M5655) and as previously described, caspase activity was normalised to viability data for each treatment to correct for cell density and to determine overall apoptosis levels.67
Cell cycle analysis
Cells were seeded in 6 well plates to 70% confluency and allowed to adhere overnight before being treated as required. After trypsinisation and harvesting, cells were resuspended in PBS before being fixed in ice cold 90% ethanol. Cells were stored at 4°C overnight or until required. For DNA staining, cells were pelleted and resuspended in 25 μg/ml propidium iodide solution containing 0.4 μg/ml RNase A and incubated at 37°C for 1.5 hours. Analysis was performed using a FACSCalibur Flow Cytometer (BD Biosciences) and data processed using FlowJo software (FlowJo, LLC).
Immunoblotting
Cells were seeded in 6 well plates to approximately 70% confluency and allowed to adhere overnight before being subject to the appropriate treatment for the indicated duration. Cells were then trypsinised and together with the residual medium were pelleted before being washed in ice cold PBS, and final cell pellet resuspended in RIPA Lysis buffer (Santa Cruz, sc-24948) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. An equal quantity of the cleared protein lysate was then subject to western blotting as described previously.67
siRNA-mediated gene silencing
Cells were seeded in 6 well plates to 50–60% confluency and allowed to adhere overnight before being transfected with 100 nM final concentration siRNA (GE Healthcare, L-004383–00, L-004501–00, L-004438–00, equivalent non-targeting siRNA control (GE Healthcare, D-001810–10-05) or transfection reagent alone. Transfections were carried out using DharmaFECT1 (GE Healthcare, T-2001) as per manufacturer instructions. 48 hours post-transfection, cells were trypsinised and reseeded into 96 well plates and left to adhere overnight prior to inhibitor treatment and subsequent apoptosis and viability assays.
Mcl-1 overexpression
The vector pcDNA3.1 containing the MCL1 gene (pcDNA3.1-hMCL-1 Addgene plasmid #25375) and control vector pcDNA3.1: hygro(+) (Thermo Fisher, V87020) were amplified in bacterial cells (Bioline, BIO-85027) and purified using a plasmid purification kit (Qiagen, 12162). These were then transfected into cells, seeded in 6 well plates to 50–60% confluency and allowed to adhere overnight, using Effectene transfection reagent (Qiagen, 301425), according to manufacturer instructions. 24 hours post-transfection, cells were trypsinised and reseeded into 96 well plates for inhibitor treatment and subsequent apoptosis and viability assays.
Statistical and combination index analysis
Statistical analysis and data visualisation were performed using GraphPad Prism 6 (GraphPad). Combination indices (CI) were calculated using the response additivity model68 with CI = (effect of drug A + effect of drug B)/(effect of combination treatment). Where CI< 1, a greater effect than an expected additive effect is indicated.
Funding Statement
This work was supported by funding from Plum’s Fund, The Jacqueline Land Pancreatic Cancer Research Fund, Imperial College Healthcare Charity, and Ovarian Cancer Action. We also thank Pfizer for providing PF5212384 for unrestricted research.
Supplemental Material
Supplemental data for this article can be accessedhere
References
- 1.Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F.. GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0, cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 11 [Internet]. Lyon (France): International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2013. accessed on 22/09/2017 Available from http://globocan.iarc.fr [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cancer Research UK Available from: http://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/statistics-by-cancer-type/pancreatic-cancer/survival#heading-Zero. Accessed 13/09/2017.
- 3.Waddell N, Pajic M, Patch AM, Chang DK, Kassahn KS, Bailey P, Johns AL, Miller D, Nones K, Quek K, et al. Whole genomes redefine the mutational landscape of pancreatic cancer. Nature. 2015;518(7540):495–501. doi: 10.1038/nature14169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bailey P, Chang DK, Nones K, Johns AL, Patch AM, Gingras MC, Miller DK, Christ AN, Bruxner TJ, Quinn MC, et al. Genomic analyses identify molecular subtypes of pancreatic cancer. Nature. 2016;531(7592):47–52. doi: 10.1038/nature16965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network Integrated genomic characterization of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2017;32(2):185–203.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.07.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Feigin ME, Garvin T, Bailey P, Waddell N, Chang DK, Kelley DR, Shuai S, Gallinger S, McPherson JD, Grimmond SM, et al. Recurrent noncoding regulatory mutations in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Nat Genet. 2017;49(6):825–833. doi: 10.1038/ng.3861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Humphris JL, Patch AM, Nones K, Bailey PJ, Johns AL, McKay S, Chang DK, Miller DK, Pajic M, Kassahn KS, et al. Hypermutation in pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology. 2017;152(1):68–74.e2. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.09.060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Cowan RW, Maitra A. Genetic progression of pancreatic cancer. Cancer J. 2014;20(1):80–84. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0000000000000011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network Integrated genomic analyses of ovarian carcinoma. Nature. 2011;474(7353):609–615. doi: 10.1038/nature10166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cox AD, Fesik SW, Kimmelman AC, Luo J, Der CJ. Drugging the undruggable RAS: mission possible? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014;13(11):828–851. doi: 10.1038/nrd4389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Rinehart J, Adjei AA, Lorusso PM, Waterhouse D, Hecht JR, Natale RB, Hamid O, Varterasian M, Asbury P, Kaldjian EP, et al. Multicenter phase II study of the oral MEK inhibitor, CI-1040, in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung, breast, colon, and pancreatic cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22(22):4456–4462. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2004.01.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hainsworth JD, Cebotaru CL, Kanarev V, Ciuleanu TE, Damyanov D, Stella P, Ganchev H, Pover G, Morris C, Tzekova V. A phase II, open-label, randomized study to assess the efficacy and safety of AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) versus pemetrexed in patients with non-small cell lung cancer who have failed one or two prior chemotherapeutic regimens. J Thorac Oncol. 2010;5(10):1630–1636. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181e8b3a3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Haura EB, Ricart AD, Larson TG, Stella PJ, Bazhenova L, Miller VA, Cohen RB, Eisenberg PD, Selaru P, Wilner KD, et al. A phase II study of PD-0325901, an oral MEK inhibitor, in previously treated patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16(8):2450–2457. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.O’Neil BH, Goff LW, Kauh JSW, Strosberg JR, Bekaii-Saab TS, Lee R-M, Kazi A, Moore DT, Learoyd M, Lush RM, et al. Phase II study of the mitogen-activated protein kinase 1/2 inhibitor selumetinib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(17):2350–2356. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.33.9432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bodoky G, Timcheva C, Spigel DR, La Stella PJ, Ciuleanu TE, Pover G, Tebbutt NC. A phase II open-label randomized study to assess the efficacy and safety of selumetinib (AZD6244 [ARRY-142886]) versus capecitabine in patients with advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer who have failed first-line gemcitabine therapy. Invest New Drugs. 2012;30(3):1216–1223. doi: 10.1007/s10637-011-9687-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kirkwood JM, Bastholt L, Robert C, Sosman J, Larkin J, Hersey P, Middleton M, Cantarini M, Zazulina V, Kemsley K, et al. Phase II, open-label, randomized trial of the MEK1/2 inhibitor selumetinib as monotherapy versus temozolomide in patients with advanced melanoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(2):555–567. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Polivka J Jr, Janku F. Molecular targets for cancer therapy in the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Pharmacol Ther. 2014;142(2):164–175. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Soares HP, Ming M, Mellon M, Young SH, Han L, Sinnet-Smith J, Rozengurt E. Dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors induce rapid overactivation of the MEK/ERK pathway in human pancreatic cancer cells through suppression of mTORC2. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015;14(4):1014–1023. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Asati V, Mahapatra DK, Bharti SK. PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathways inhibitors as anticancer agents: structural and pharmacological perspectives. Eur J Med Chem. 2016;109:314–341. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Collisson EA, Trejo CL, Silva JM, Gu S, Korkola JE, Heiser LM, Charles RP, Rabinovich BA, Hann B, Dankort D, et al. A central role for RAF→MEK→ERK signaling in the genesis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2012;2(8):685–693. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-11-0347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Britten CD. PI3K and MEK inhibitor combinations: examining the evidence in selected tumor types. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013;71(6):1395–1409. doi: 10.1007/s00280-013-2121-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Jokinen E, Koivunen JP. MEK and PI3K inhibition in solid tumors: rationale and evidence to date. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2015;7(3):170–180. doi: 10.1177/1758834015571111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wee S, Jagani Z, Xiang KX, Loo A, Dorsch M, Yao YM, Sellers WR, Lengauer C, Stegmeier F. PI3K pathway activation mediates resistance to MEK inhibitors in KRAS mutant cancers. Cancer Res. 2009;69(10):4286–4293. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sheppard KE, Cullinane C, Hannan KM, Wall M, Chan J, Barber F, Foo J, Cameron D, Neilsen A, Ng P, et al. Synergistic inhibition of ovarian cancer cell growth by combining selective PI3K/mTOR and RAS/ERK pathway inhibitors. Eur J Cancer. 2013;49(18):3936–3944. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2013.08.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zhong H, Sanchez C, Spitzer D, Plambeck-Suess S, Gibbs J, Hawkins WG, Denardo D, Gao F, Pufahl RA, Lockhart AC, et al. Synergistic effects of concurrent blockade of PI3K and MEK pathways in pancreatic cancer preclinical models. PLoS One. 2013;8(10):e77243. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hamidi H, Lu M, Chau K, Anderson L, Fejzo M, Ginther C, Linnartz R, Zubel A, Slamon DJ, Finn RS. KRAS mutational subtype and copy number predict in vitro response of human pancreatic cancer cell lines to MEK inhibition. Br J Cancer. 2014;111(9):1788–1801. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2014.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Pitts TM, Newton TP, Bradshaw-Pierce EL, Addison R, Arcaroli JJ, Klauck PJ, Bagby SM, Hyatt SL, Purkey A, Tentler JJ, et al. Dual pharmacological targeting of the MAP kinase and PI3K/mTOR pathway in preclinical models of colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 2014;9(11):e113037. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Haagensen EJ, Thomas HD, Mudd C, Tsonou E, Wiggins CM, Maxwell RJ, Moore JD, Newell DR. Pre-clinical use of isogenic cell lines and tumours in vitro and in vivo for predictive biomarker discovery; impact of KRAS and PI3KCA mutation status on MEK inhibitor activity is model dependent. Eur J Cancer. 2016;56:.69–76. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2015.12.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ning C, Liang M, Liu S, Wang G, Edwards H, Xia Y, Polin L, Dyson G, Taub JW, Mohammad RM, et al. Targeting ERK enhances the cytotoxic effect of the novel PI3K and mTOR dual inhibitor VS-5584 in preclinical models of pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(27):44295–44311. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Faber AC, Coffee EM, Costa C, Dastur A, Ebi H, Hata AN, Yeo AT, Edelman EJ, Song Y, Tam AT, et al. mTOR inhibition specifically sensitizes colorectal cancers with KRAS or BRAF mutations to BCL-2/BCL-XL inhibition by suppressing MCL-1. Cancer Discov. 2014;4(1):42–52. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Venkannagari S, Fiskus W, Peth K, Atadja P, Hidalgo M, Maitra A, Bhalla KN. Superior efficacy of co-treatment with dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 and pan-histone deacetylase inhibitor against human pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget. 2012;3(11):1416–1427. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Jebahi A, Villedieu M, Pétigny-Lechartier C, Brotin E, Louis MH, Abeilard E, Giffard F, Guercio M, Briand M, Gauduchon P, et al. PI3K/mTOR dual inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 decreases Mcl-1 expression and sensitizes ovarian carcinoma cells to Bcl-xL-targeting strategies, provided that Bim expression is induced. Cancer Lett. 2014;348(1–2):38–49. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Boucher MJ, Morisset J, Vachon PH, Reed JC, Lainé J, Rivard N. MEK/ERK signaling pathway regulates the expression of Bcl-2, Bcl-X(L), and Mcl-1 and promotes survival of human pancreatic cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 2000;79(3):355–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Corcoran RB, Cheng KA, Hata AN, Faber AC, Ebi H, Coffee EM, Greninger P, Brown RD, Godfrey JT, Cohoon TJ, et al. Synthetic lethal interaction of combined BCL-XL and MEK inhibition promotes tumor regressions in KRAS mutant cancer models. Cancer Cell. 2013;23(1):121–128. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.11.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Tan N, Wong M, Nannini MA, Hong R, Lee LB, Price S, Williams K, Savy PP, Yue P, Sampath D, et al. Bcl-2/Bcl-xL inhibition increases the efficacy of MEK inhibition alone and in combination with PI3 kinase inhibition in lung and pancreatic tumor models. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013;12(6):853–864. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Venkatesan AM, Dehnhardt CM, Delos Santos E, Chen Z, Dos Santos O, Ayral-Kaloustian S, Khafizova G, Brooijmans N, Mallon R, Hollander I, et al. Bis(morpholino-1,3,5-triazine) derivatives: potent adenosine 5’-triphosphate competitive phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors: discovery of compound 26 (PKI-587), a highly efficacious dual inhibitor. J Med Chem. 2010;53(6):2636–2645. doi: 10.1021/jm901830p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Shapiro GI, Bell-McGuinn KM, Molina JR, Bendell J, Spicer J, Kwak EL, Pandya SS, Millham R, Borzillo G, Pierce KJ, et al. First-in-Human Study of PF-05212384 (PKI-587), a small-molecule, intravenous, dual inhibitor of PI3K and mTOR in patients with advanced cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21(8):1888–1895. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-1306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Barrett SD, Bridges AJ, Dudley DT, Saltiel AR, Fergus JH, Flamme CM, Delaney AM, Kaufman M, LePage S, Leopold WR, et al. The discovery of the benzhydroxamate MEK inhibitors CI-1040 and PD 0325901. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008;18(24):6501–6504. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2008.10.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Cheraghchi-Bashi A, Parker CA, Curry E, Salazar JF, Gungor H, Saleem A, Cunnea P, Rama N, Salinas C, Mills GB, et al. A putative biomarker signature for clinically effective AKT inhibition: correlation of in vitro, in vivo and clinical data identifies the importance of modulation of the mTORC1 pathway. Oncotarget. 2015;6(39):41736–41749. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Carlson CB, Robers MB, Vogel KW, Machleidt T. Development of LanthaScreen cellular assays for key components within the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. J Biomol Screen. 2009;14(2):121–132. doi: 10.1177/1087057108328132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wei N, Liu SS, Chan KK, Ngan HY. Tumour suppressive function and modulation of programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) in ovarian cancer. PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30311. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Abulwerdi F, Liao C, Liu M, Azmi AS, Aboukameel A, Mady AS, Gulappa T, Cierpicki T, Owens S, Zhang T, et al. A novel small-molecule inhibitor of mcl-1 blocks pancreatic cancer growth in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014;13(3):565–575. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Lee WS, Park YL, Kim N, Oh HH, Son DJ, Kim MY, Oak CY, Chung CY, Park HC, Kim JS, et al. Myeloid cell leukemia-1 is associated with tumor progression by inhibiting apoptosis and enhancing angiogenesis in colorectal cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 2014;5(1):101–113. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Huang S, Sinicrope FA. Sorafenib inhibits STAT3 activation to enhance TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010;9(3):742–750. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wei NA, Liu SS, Leung TH, Tam KF, Liao XY, Cheung AN, Chan KK, Ngan HY. Loss of Programmed cell death 4 (Pdcd4) associates with the progression of ovarian cancer. Mol Cancer. 2009;8:.70. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-8-70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Ma G, Zhang H, Dong M, Zheng X, Ozaki I, Matsuhashi S, Guo K. Downregulation of programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) in tumorigenesis and progression of human digestive tract cancers. Tumour Biol. 2013;34(6):3879–3885. doi: 10.1007/s13277-013-0975-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Song X, Zhang X, Wang X, Zhu F, Guo C, Wang Q, Shi Y, Wang J, Chen Y, Zhang L. Tumor suppressor gene PDCD4 negatively regulates autophagy by inhibiting the expression of autophagy-related gene ATG5. Autophagy. 2013;9(5):743–755. doi: 10.4161/auto.24069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Zhen Y, Li D, Li W, Yao W, Wu A, Huang J, Gu H, Huang Y, Wang Y, Wu J, et al. Reduced PDCD4 expression promotes cell growth through PI3K/Akt signaling in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Res. 2016;23(1–2):61–68. doi: 10.3727/096504015X14478843952861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Dorrello NV, Peschiaroli A, Guardavaccaro D, Colburn NH, Sherman NE, Pagano M. S6K1- and betaTRCP-mediated degradation of PDCD4 promotes protein translation and cell growth. Science. 2006;314(5798):467–471. doi: 10.1126/science.1130276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Matsuhashi S, Hamajima H, Xia J, Zhang H, Mizuta T, Anzai K, Ozaki I. Control of a tumor suppressor PDCD4: degradation mechanisms of the protein in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Signal. 2014;26(3):603–610. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.11.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Vikhreva PN, Shepelev MV, Korobko IV. mTOR-dependent transcriptional repression of Pdcd4 tumor suppressor in lung cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1839(1):43–49. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Xu H, Dephoure N, Sun H, Zhang H, Fan F, Liu J, Ning X, Dai S, Liu B, Gao M, et al. Proteomic profiling of paclitaxel treated cells identifies a novel mechanism of drug resistance mediated by PDCD4. J Proteome Res. 2015;14(6):2480–2491. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.5b00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Eto K, Goto S, Nakashima W, Ura Y, Abe SI. Loss of programmed cell death 4 induces apoptosis by promoting the translation of procaspase-3 mRNA. Cell Death Differ. 2012;19(4):573–581. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2011.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Powers MA, Fay MM, Factor RE, Welm AL, Ullman KS. Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 accelerates tumor growth by arginine methylation of the tumor suppressor programmed cell death 4. Cancer Res. 2011;71(16):5579–5587. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-0458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Nagao Y, Hisaoka M, Matsuyama A, Kanemitsu S, Hamada T, Fukuyama T, Nakano R, Uchiyama A, Kawamoto M, Yamaguchi K, et al. Association of microRNA-21 expression with its targets, PDCD4 and TIMP3, in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Mod Pathol. 2012;25(1):112–121. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Peacock O, Lee AC, Cameron F, Tarbox R, Vafadar-Isfahani N, Tufarelli C, Lund JN. Inflammation and MiR-21 pathways functionally interact to downregulate PDCD4 in colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e110267. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Gysin S, Lee SH, Dean NM, McMahon M. Pharmacologic inhibition of RAF–>MEK–>ERK signaling elicits pancreatic cancer cell cycle arrest through induced expression of p27Kip1. Cancer Res. 2005;65(11):4870–4880. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Glienke W, Maute L, Wicht J, Bergmann L. The dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor NVP-BGT226 induces cell cycle arrest and regulates Survivin gene expression in human pancreatic cancer cell lines. Tumour Biol. 2012;33(3):757–765. doi: 10.1007/s13277-011-0290-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.New M, Van Acker T, Long JS, Sakamaki JI, Ryan KM, Tooze SA. Molecular pathways controlling autophagy in pancreatic cancer. Front Oncol. 2017;7:.28. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Mirzoeva OK, Hann B, Hom YK, Debnath J, Aftab D, Shokat K, Korn WM. Autophagy suppression promotes apoptotic cell death in response to inhibition of the PI3K-mTOR pathway in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Mol Med (Berl). 2011;89(9):877–889. doi: 10.1007/s00109-011-0774-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Tang JY, Dai T, Zhang H, Xiong WJ, Xu MZ, Wang XJ, Tang QH, Chen B, Xu M. GDC-0980-induced apoptosis is enhanced by autophagy inhibition in human pancreatic cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;453(3):533–538. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.09.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Sarkar S. Regulation of autophagy by mTOR-dependent and mTOR-independent pathways: autophagy dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases and therapeutic application of autophagy enhancers. Biochem Soc Trans. 2013;41(5):1103–1130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Mammucari C, Milan G, Romanello V, Masiero E, Rudolf R, Del Piccolo P, Burden SJ, Di Lisi R, Sandri C, Zhao J, et al. FoxO3 controls autophagy in skeletal muscle in vivo. Cell Metab. 2007;6(6):458–471. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2007.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Dienstmann R, Rodon J, Serra V, Tabernero J. Picking the point of inhibition: a comparative review of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway inhibitors. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014;13(5):1021–1031. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Langdon SP, Lawrie SS, Hay FG, Hawkes MM, McDonald A, Hayward IP, Schol DJ, Hilgers J, Leonard RC, Smyth JF. Characterization and properties of nine human ovarian adenocarcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1988;48(21):6166–6172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Tibes R, Qiu Y, Lu Y, Hennessy B, Andreeff M, Mills GB, Kornblau SM. Reverse phase protein array: validation of a novel proteomic technology and utility for analysis of primary leukemia specimens and hematopoietic stem cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006;5(10):2512–2521. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Stronach EA, Chen M, Maginn EN, Agarwal R, Mills GB, Wasan H, Gabra H. DNA-PK mediates AKT activation and apoptosis inhibition in clinically acquired platinum resistance. Neoplasia. 2011;13(11):1069–1080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Foucquier J, Guedj M. Analysis of drug combinations: current methodological landscape. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2015;3(3):e00149. doi: 10.1002/prp2.149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


