Figure 2. Chemogenetic activation of DA receptors D1 and D2 in the Sp5C oppositely affects trigeminal neuropathic pain.
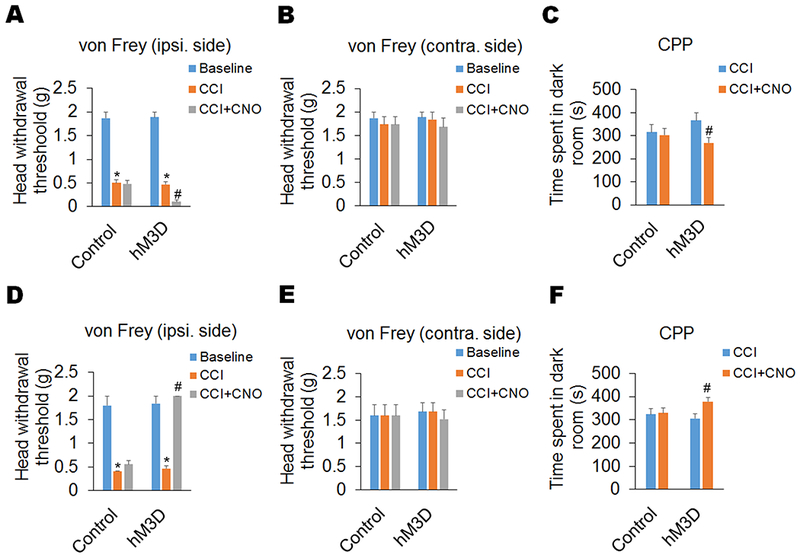
The Cre-inducible excitatory DREADD virus (hM3D) and its control were infused unilaterally (ipsilateral side of CCI-ION) into Sp5C of D1-Cre and D2-Cre mice. (A–C) In D1-Cre mice, chemogenetic activation of the Sp5C D1-expressing neurons with the injection of CNO (1 mg/kg, i.p) significantly enhanced the CCI-ION-induced neuropathic pain on day 14 post-surgery, including a decreased head withdrawal threshold in the ipsilateral side (A), but not contralateral side (B), in the von Frey filament test and decreased time spent in the paired dark room in the CPP test (C). (D–F) In D2-Cre mice, chemogenetic activation of the Sp5C D2-expressing neurons with the injection of CNO (1 mg/kg, i.p) significantly diminished neuropathic pain on day 14 post-surgery in the CCI-ION model, including an increased head withdrawal threshold in the ipsilateral side (D), but not contralateral side (E), in the von Frey filament test and increased time spent in the paired dark room in the CPP test (F). Chemogenetic activation did not significantly affect pain behaviors in the D1/2-Cre mice with the expression of control DREADD virus in the Sp5C. n = 6–7 mice per group. *P < 0.05 vs. the corresponding Baseline values; #P < 0.05 vs. the corresponding CCI group.
