In the published article “Effect of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress inhibitor treatment during parthenogenetic activation on the apoptosis and in vitro development of parthenogenetic porcine embryos. Dev. Reprod. 2018; 22 (3):235–244. https://doi.org/10.12717/DR.2018.22.3.235,” the Fig. 1 was given incorrectly. The Editorial Office of Korean Society of Developmental Biology would like to correct the Fig.1. In addition, Fig. 1 had some mistakes and the corresponding authors asked change it with correcting one. The Editorial Office apologizes for any inconvenience that it may have caused.
Fig. 1. Xbp1 mRNA expression in porcine parthenogenetic 1-cell embryos. The spliced and unspliced form of XBP1 mRNAs were detected by RT-PCR and band intensity was measured by a densitometer. Data are presented as means±SEM. E, electric stiulus; EC, E+10 μM Ca-ionophore (A23187) treatment; Sal, 200 nM salubrinal; TUD, 100 μM TUDCA; Xbp1s, spliced XBP1; Xbp1u, unspliced XBP1.
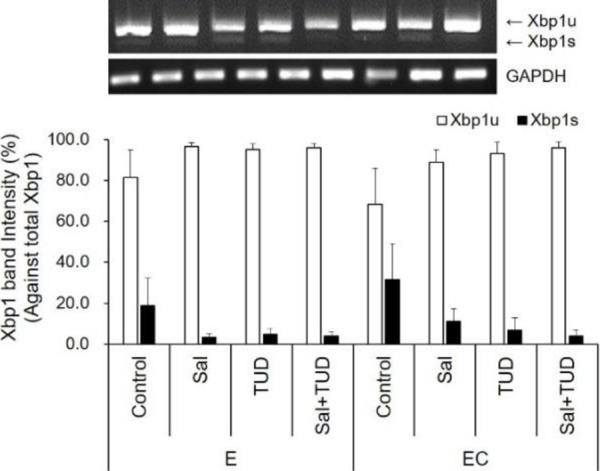
The Fig. 1 should be corrected as follows:
References
- Park HB, Kim MJ, Jung BD, Lee S, Park CK, Yang BK, Cheong HT. Effect of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress inhibitor treatment during parthenogenetic activation on the apoptosis and in vitro development of parthenogenetic porcine embryos. Dev Reprod. 2018;22:235–244. doi: 10.12717/DR.2018.22.3.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


