FIG 2.
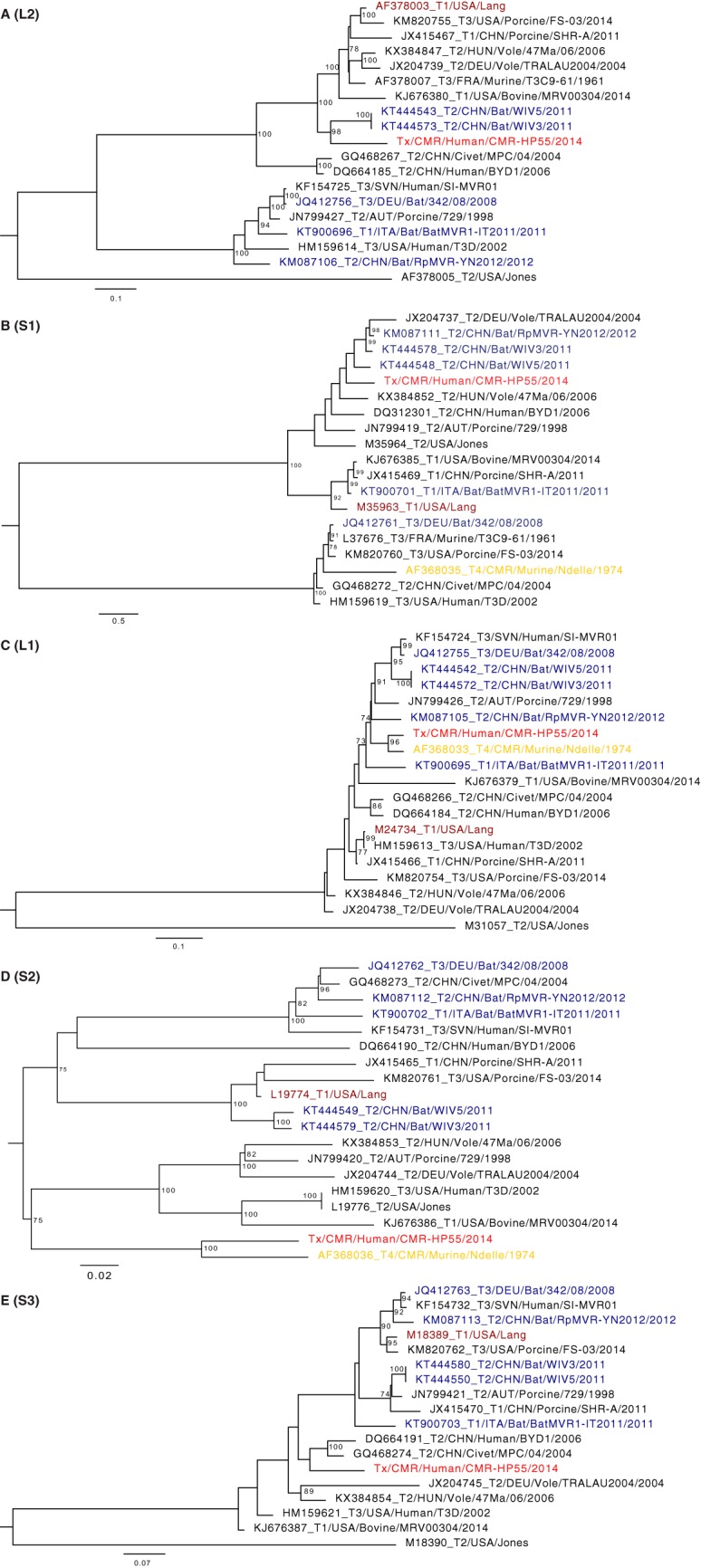
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic trees based on the nucleotide sequences of the L2, S1, L1, S2, and S3 coding segments of the novel MORV (indicated in red) and representative strains from GenBank showing 3 patterns of clustering with respect to the novel strain: A and B, clustering of novel strain with bat strains from China; C and D, clustering of novel strain with murine strain from Cameroon; and E, clustering of novel strain with human and civet strains from China. Trees were constructed using the GTR+G+I nucleotide substitution model using RAxML, with the autoMRE flag, which enables a posteriori bootstrapping analysis. Only bootstrap values greater than 70% are shown. Bars indicate nucleotide substitutions per site.
