Abstract
Dendritic cells (DC) are professional antigen presenting cells, uniquely able to induce naïve T cell activation and effector differentiation. They are, likewise, involved in the induction and maintenance of immune tolerance in homeostatic conditions. Their phenotypic and functional heterogeneity points to their great plasticity and ability to modulate, according to their microenvironment, the acquired immune response and, at the same time, makes their precise classification complex and frequently subject to reviews and improvement. This review will present general aspects of the DC physiology and classification and will address their potential and actual uses in the management of human disease, more specifically cancer, as therapeutic and monitoring tools. New combination treatments with the participation of DC will be also discussed.
Keywords: human dendritic cells, DC, monocyte-derived dendritic cells, mo-DC, cancer vaccines, cancer combination therapies
Introduction
Identified in mouse spleen for their peculiar shape and capacity to activate naïve lymphocytes (1–3), dendritic cells (DC) are considered the most efficient antigen presenting cells (APC) (3, 4), uniquely able to initiate, coordinate, and regulate adaptive immune responses. Though their ability to capture, process and present antigens is considered their main characteristic, their phenotypic heterogeneity is striking and very different consequences can come from their action. This review will present an overview of the main subpopulations of human DC described and will focus on their potential translational use.
Overview of Dendritic Cells in the Immune System Physiology
Human DC are identified by their high expression of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules (MHC-II) and of CD11c, both of which are found on other cells, like lymphocytes, monocytes and macrophages (5–12). DC express many other molecules which allow their classification into various subtypes (Table 1). Although some of the DC subtypes were originally described as macrophages, DC and macrophages have distinct characteristics (13–15) and ontogeny, so that, currently, little doubt remains that they belong to distinct lineages (16–24).
Table 1.
Main surface markers of human and mouse DC subtypes.
| DC subtype | Human | Mouse |
|---|---|---|
| cDC1 | CD141/CLEC9A/XCR1 | CD8a/CD103/XCR1 |
| cDC2 | CD1c/CD172a | CD11b/CD172a |
| pDC | CD123/CD303/CD304 | B220/SiglecH |
| LC | Langerin/CD1a | Langerin/CD24 |
DC can be found in practically all tissues, where they detect homeostatic imbalances and process antigens for presentation to T cells, establishing a link between innate and adaptive immune responses. Furthermore, DC can secrete cytokines and growth factors (25) that modify ongoing immune responses, and are influenced by their interactions with other immune cells, like natural killer (26–28) and innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) (29).
DC are found in two different functional states, “mature” and “immature”. These are distinguished by many features, but the ability to activate antigen-specific naïve T cells in secondary lymphoid organs is the hallmark of mature DC (30–32). DC maturation is triggered by tissue homeostasis disturbances, detected by the recognition of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMP) or damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMP) (33, 34) (Figure 1). Maturation turns on metabolic, cellular, and gene transcription programs allowing DC to migrate from peripheral tissues to T-dependent areas in secondary lymphoid organs, where T lymphocyte-activating antigen presentation may occur (35–40).
Figure 1.
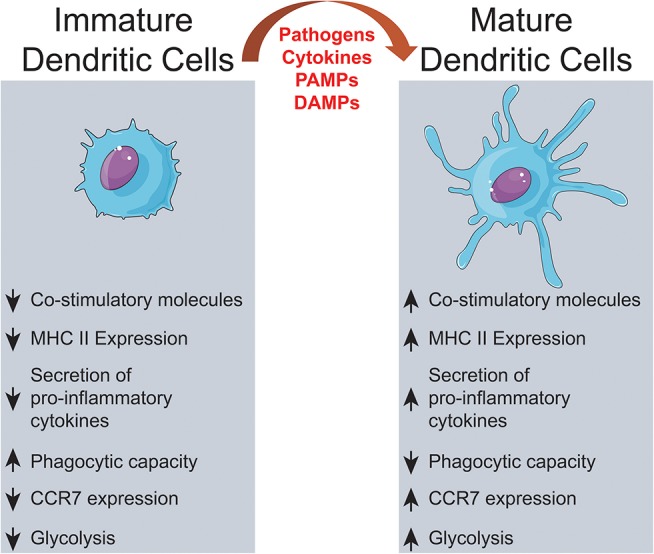
Dendritic cells activation. Extracellular signals, such as PAMPs or DAMPs, trigger alterations on immature DCs culminating on significant changes on surface proteins, intracellular pathways and metabolic activity.
During maturation, DC lose adhesive structures, reorganize the cytoskeleton and increase their motility (41). DC maturation also leads to a decrease in their endocytic activity but increased expression of MHC-II and co-stimulatory molecules (42–44). Mature DC express higher levels of the chemokine receptor, CCR7 (45–48) and secrete cytokines, essential for T-cell activation (42, 49–52). Thus, the interaction between mature DC and antigen-specific T cells is the trigger of antigen-specific immune responses (53, 54). When interacting with CD4+ T cells, DC may induce their differentiation into different T helper (Th) subsets (52) such as Th1 (55–60), Th2 (56, 57, 61, 62), Th17 (63–65), or other CD4+ T cell subtypes (66) (Figure 2). T cell differentiation in each subtype is a complex phenomenon, that can be influenced by the cytokines in the DC tissue of origin (67), their maturation state (42) and cause of tissue imbalance (68). However, this process is not completely elucidated, as, for example, the source of IL-4 during Th2 responses, which is discussed extensively elsewhere (69).
Figure 2.
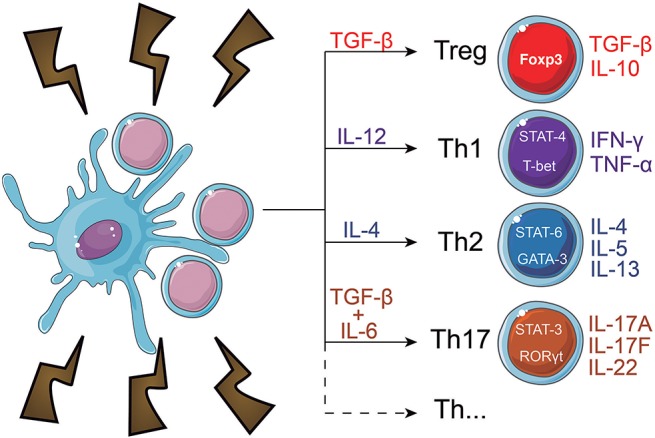
CD4+ T cell fate induced by dendritic cells. When in contact with DC, naïve CD4+ T cells can differentiate into a number of subtypes. Among them, are regulatory T cells (Treg) and T helper (Th) subsets, which include Th1, Th2, and Th17 cells. Each subtype expresses different transcription factors, which regulate the function and cytokine secretion pattern of the cells. The T cell fate decision is a complex phenomenon that heavily depends on the interaction of DC with the T cells and the cytokines present in the microenvironment.
DC present a unique characteristic: the ability to perform cross-presentation (70–74). This phenomenon was described in 1976, by Bevan (75) and is defined as the presentation, in the context of class I MHC molecules (MHC-I), of antigens captured from the extracellular milieu. This feature allows DC to trigger responses against intracellular antigens from other cell types, thus providing means for the system to deal with threats that avoid professional APC (70, 76, 77) and, even, to prime CD8+ lymphocytes in the absence of CD4+ T cells (78, 79). Cross-presentation is involved also in the induction of tolerance to intracellular self-antigens that are not expressed by APC and, then, called, cross-tolerance (80, 81).
Before receiving maturation stimuli, DC are said to be in an “immature state.” Immature DC are poor inducers of naïve lymphocyte effector responses, since they have low surface expression of co-stimulatory molecules, low expression of chemokine receptors, and do not release immunostimulatory cytokines (44, 82). These “immature” cells, though, are very efficient in antigen capture due to their high endocytic capacity, via receptor-mediated endocytosis, including lectin- (83–85); Toll-like- (86–88), FC- and complement receptors (89) and macropinocytosis (84). Thus, immature DC act, indeed, as sentinels against invading pathogens (32, 90), but also as tissue scavengers, capturing apoptotic and necrotic cells (91).
This latter feature confers to immature DC an essential role in the induction and maintenance of immune tolerance (31, 92–95). Apoptotic cells that arise in consequence of natural tissue turnover (96, 97) are internalized by DC but do not induce their maturation (31, 98–100). Thus, their antigens are presented to T cells without the activating co-stimulatory signals that a mature DC would deliver, resulting in T cell apoptosis (80, 101), anergy (102, 103) or development into regulatory T cells (104, 105).
These “tolerogenic DC” express less co-stimulatory molecules and proinflammatory cytokines, but upregulate the expression of inhibitory molecules (like PD-L1 and CTLA-4), secrete anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10, for example) (102, 106–108) and are essential to prevent responses against healthy tissues (30, 31, 109–112). However, in some contexts, immature DC can be harmful to the body. It is known that DC that are unable to induce lymphocyte effector responses may contribute to the immune system's failure to fight infections (113, 114) or tumors (115–120). In these situations, DC, even after recognition of pathogens or other changes in microenvironment, fail to increase the co-stimulatory molecules required to activate T cells, thus allowing the disease to “escape” immune control.
Although many factors are recognized as contributing to drive DC maturation (100, 121, 122), the full set of such factors is not precisely defined, but involves a long series of transcriptional adaptations (119, 121, 123–125). The complexity and heterogeneity of these adaptations allows DC to translate effectively (most of the times) the pattern of homeostatic disturbance to interacting T lymphocytes, thus establishing DC as the main connector between innate and acquired mechanisms of immunity (43, 126).
Human Dendritic Cell Subpopulations and Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells
Dendritic cells can be divided into resident lymphoid tissue DC and migratory non-lymphoid tissue DC (16). Both are heterogeneous cell populations with different subsets that can be distinguished by phenotypic markers and genetic profile. The first identification of different DC subsets arose from the observation that CD8 expression occurred on some, but not all, mouse resident splenic and thymic DCs (127). While the identification of mouse DC subpopulations is well advanced (128, 129), mostly due to tissue accessibility, the same is not true for human DC, where most studies were performed only in peripheral blood or skin, in spite of recent data characterizing DC subpopulations in human lung (130) and intestine (131).
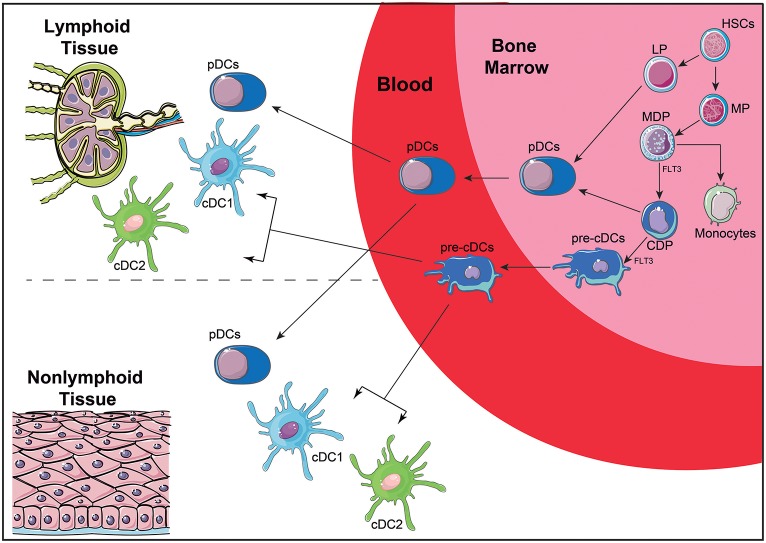
Recent efforts have been addressed to understand the ontogeny and function of human DC subsets, attempting to correlate well-defined murine subpopulations with those found in human peripheral blood (16, 128, 132). DC arise from a CD34+ hematopoietic precursor that gives rise to myeloid (MP) and lymphoid (LP) precursors (Figure 3). MP differentiate into monocyte, macrophage and DC precursors (MDP), which will give rise to monocytes and to the common DC precursors (CDP). CDP can differentiate into plasmacytoid DC (pDC) or the preclassical DC (pre-cDC). Pre-cDC are the progenitors of the two major cDC subpopulations named cDC1 and cDC2 (14), which will be further discussed latter. Recent technologies, such as single cell RNAseq, are allowing a better characterization of DC ontogeny and the identification of DC subset precursors in peripheral blood (133), demonstrating that the commitment with a DC subset may be an early event, both in mice (134) and humans (135).
Figure 3.
Simplified scheme of DC ontogeny. DC arise from HSC that give rise to MP and LP. MP are further differentiated into MDP that can differentiate into CDP and monocytes. CDP differentiate further into pDC or pre-cDC. LP can also give rise to pDC, although this ontogenic pathway is not completely elucidated. Once in the blood, pre-cDC give rise to two of the main DC subtypes: cDC1 and cDC2. Both pDC and cDC can migrate from the blood to lymphoid and non-lymphoid tissues. HSC, hematopoietic stem cell; MP, myeloid precursors; LP, lymphoid precursors; MDP, macrophage-DC precursors; CDP, common DC precursors; pre-cDC, pre-classical dendritic cells; pDC, plasmacytoid dendritic cells; cDCs, conventional dendritic cells; FLT3, Fms-Related Tyrosine Kinase 3.
Curiously, in lymphohematopoietic tissue, such as spleen, thymus and blood, DC commitment to a subpopulation is mainly defined by ontogeny, while in non-lymphohematopoietic tissue, such as lung and skin, DC subpopulations are more influenced by signals derived from the microenvironment. This, once again, confirms that DC are a very plastic cell population that can shape its phenotype to the microenvironment and to homeostatic state of the tissue where it is located (136).
In blood, DC constitute a rare cell population that can be broadly divided into two subtypes (Figure 4): CD123+CD11c− DC, called plasmacytoid DC (pDC), and CD123−CD11c+ cells, called classical DC or myeloid DC (cDC) (25, 128, 137). Dzionek et al. (138) identified three antigens called BDCA-2, BDCA-3, and BDCA-4 (Blood Dendritic Cell Antigens), which, together with BDCA-1 (CD1c), allowed the further discrimination of human blood DC subsets. cDC can be separated into cDC1 and cDC2 (139): cDC1 are characterized by the expression of BDCA-3 (CD141) and Clec9A, while cDC2 express CD1c. BDCA-2 (CD303) and−4 (CD304), on the other hand, together with CD123, characterize pDC.
Figure 4.
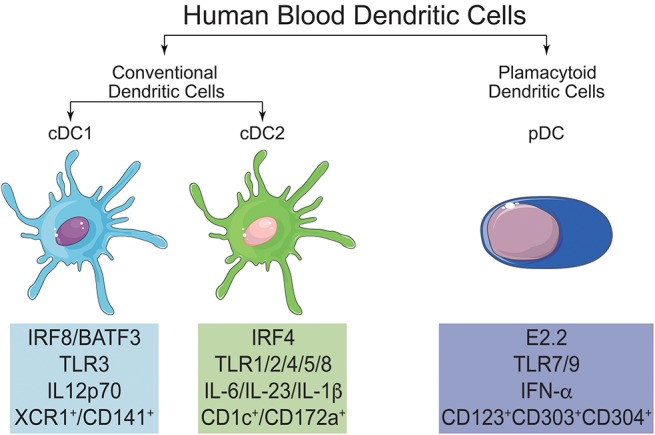
Main characteristics and differences of cDC1, cDC2, and pDC. In human blood, it is possible to find two main populations of DC, named conventional DC (cDC) and plasmacytoid DC (pDC). cDC can be further subdivided in cDC1 and cDC2. All three subtypes of DC can be differentiated by their signature transcription factors and also by the expression of specific surface markers.
It is noteworthy that recent genomic studies, with emphasis on the subpopulations of monocytes and DC, made it possible to align CD141+ DC (cDC1) and CD1c+ (cDC2) from human peripheral blood with the mouse CD8α+/CD103+ and CD11b+DC, respectively (140, 141). This will allow the confirmation, or not, of the roles played by these subsets in murine immune responses also in humans.
cDC1
The human cDC1 subpopulation is present in blood and in lymphoid and non-lymphoid tissues (142). This subpopulation is characterized by the expression of CD141, the chemokine receptor XCR1, C-type lectin CLEC9A, the cell adhesion molecule CADM1, and is the counterpart of mouse CD8α+/CD103+ cross-presenting DC subset (132, 142). cDC1 can be generated in vitro from CD34+ progenitors after 21 days of culture with fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 ligand (Flt3L) and thrombopoietin (TPO) (143) or with Flt3L and murine bone marrow stromal cell lines (144). As mentioned above, this subpopulation of DC seems to be specially adapted to perform cross-presentation, a phenomenon that is associated with the expression of the chemokine receptor XCR1 (145). The main transcription factors (TF) shown to be essential for the generation of cDC1 are the basic leucine zipper transcriptional factor ATF-like 3 (BATF3) (146) and IFN-regulatory factor 8 (IRF8) (130). In mice, besides BATF3 (147) and IRF8 (148), gene knockout models pointed out to the role of two other TF: DNA binding protein inhibitor ID2 (149) and nuclear factor interleukin-3-regulated protein (NFIL3) (150), whose participation in the generation of human cDC1 needs yet to be demonstrated.
cDC1 prime CD8+ T cells efficiently, what is important in anti-tumor and anti-virus immunity. However, the induction and modulation of an immune response is a very complex phenomenon that involves many cell interactions, including interactions among different DC subsets, as recently demonstrated in mice infected with modified vaccinia virus Ankara (MVA) (151). In this model, activated CD8+ T cells recruit both pDC (via CCL3/CCL4) and cDC1 (via XCL1); type I interferons, (IFN-I) produced by pDC, act on cDC1 optimizing their maturation, costimulatory capacity and ability to cross-present viral antigens, thus leading to an effective anti-virus response. cDC1 were also shown to be important for the antitumor activity induced by heat-inactivated MVA in murine melanoma and colon cancer models (152). Furthermore, both in mice and humans, cDC1 are found sparsely distributed along tumor margins (competing with tumor associated macrophages–TAM-for tumor antigens?) and their presence was important for the success of adoptively transferred cytotoxic T cells (CTL) (153) and for the delivery of tumor antigens to the draining lymph nodes, in a CCR7 dependent manner (154).
cDC2
cDC2 constitute a heterogeneous subset of DC that can be found in blood, lymphoid and non-lymphoid tissue (16, 142). SIRPα (CD172a) is expressed by cDC2 (both in humans and mice) (130) and, along with CD1c (humans) and CD11b (mice), characterizes this subpopulation (25, 132). Coherently with its heterogeneity, other markers are expressed by cDC2, according to their localization, as for example, CD1a in dermal and CD103 in gut cDC2 (25, 141). Like cDC1, cDC2 can also be differentiated from CD34+ progenitors, after 21 days of culture with Flt3L and TPO (143) or with Flt3L and murine bone marrow stromal cell lines (144). More than one transcription factor is involved in cDC2 differentiation and IRF4 seems to be the master transcription factor (155), but other transcription factors are required. In mice, PU.1 (156), RelB (157) and recombining binding protein suppressor of hairless (RBP/J) (158) were shown to be associated with the differentiation of cDC2, and in humans, IRF8 (159).
Again, in accordance with their heterogeneity and innate plasticity (132), cDC2 have been show to induce Th1, Th2, and Th17 responses (160, 161). The puzzling heterogeneity of these cells is further illustrated by the recent description of two novel DC subtypes within the CD1c+ subpopulation: DC2 and DC3. These two subpopulations diverged by the expression of CD32B and CD163/CD36. Functional experiments showed that both these cDC2 subtypes were potent stimulators of naïve T cell proliferation, but show a different pattern of cytokine secretion after stimulation with a series of toll like receptors (TLR) agonists (162).
In the immune system physiology, cDC2 seem to have many, but frequently, regulatory roles. These cells have been described as potent inducers of regulatory T cells in intestine (141), and as responsible for maintaining tolerance in the liver (163). Also, cDC2 have been described as the only DC subset able to produce retinoic acid upon stimulation with vitamin D3, thus stimulating CD4+ naïve T cells to express gut-homing molecules and to produce Th2 cytokines (164).
Plasmacytoid DC (pDC)
The pDC subpopulation is a subset of DC distinct from cDC, that arises directly from the CDP (while cDC arise from pre-DC precursor) (14). These cells are characterized by the secretion of high levels of IFN-α/β upon TLR7/9 stimulation, and are extremely important in viral infections (165). This subset of DC is phenotypically distinct in mice and humans. In mice, it is characterized as CD11cintCD11b−B220+SiglecH+CD317+ while in humans it is characterized by the absence of expression of CD11c and the expression of CD123, CD303, and CD304 (25, 128, 132). In terms of transcription factors, on the other hand, both mouse and human pDC seem to depend on the same master transcription factor, E2.2 (25, 132, 166).
Since the secretion of IFN-α/β is the main feature of pDC, their association with viral infections is not surprising. The secretion of IFN-α/β by pDCs can be a consequence of direct viral infection [like in HIV infection, where the virus infects pDC via CD4, CCR5 and CXCR4 (167)], or from external stimuli. Indeed, human pDC were shown to secrete high levels of IFN-α/β in Aspergilus fumigatus infection in a Dectin-2-dependent manner (168).
In keeping with the other DC subpopulations heterogeneity, human pDC may be subdivided into two subpopulations, distinguished by the expression of CD2 (169). Both pDC subsets secrete IFN-α/β efficiently, but only the CD2hi subset secretes IL-12p40 and induces CD4+ T cell proliferation. These data, however, may be in need of a second look. As mentioned before, single cell RNAseq analysis is providing new data and allowing better characterization of DC subpopulations. When this approach was used to study pDC subpopulations, a “contaminant” putative precursor of cDC (pre-cDC), characterized as CD123+CD33+CD303+CD304+CD2+, was identified. When these putative pre-cDC and “pure” pDC populations (characterized by the absence of CD2 and CD33 expression) were separated and stimulated, only pre-cDC were able to induce CD4+ T cell proliferation and secrete IL-12p40 (135). This raises the possibility that many of the observed attributes of pDC, such as their ability to induce Th1 responses (170), to perform cross-presentation (171), to exhibit naïve T cell allostimulatory capacity (169) and expression of co-stimulatory (172) molecules might reflect the activity of this contaminating pre-cDC population.
Puzzling, as these data may seem, they illustrate quite well the plasticity of the cells “clustered” under the name of DC. They further suggest that attempts to classify strictly these cells may lead to more confusion than it is necessary to understand their role in responding to microenvironmental challenges, in shaping immune response patterns in the body and, eventually, in driving the immune response toward therapeutic goals in humans.
Monocyte-Derived DC (mo-DC)
Much of the knowledge acquired in the past years about human DC biology was possible due to the methodology of in vitro deriving DC from CD34+ precursors (stimulated with GM-CSF and TNF-α) (173) or from monocytes (stimulated with GM-CSF and IL-4) (174). Like cDC2, mo-DC depend on IRF4 for their differentiation (175). However, they do not seem to be an equivalent population, since they arise from different precursors (14).
In mice, the precursors used for in vitro generation of DC are extracted from the bone marrow. In the presence of GM-CSF, these precursors give rise to large number of cells that resemble tissue DC and are called bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDC) (176). Helft et al. showed that BMDC comprise a heterogeneous population expressing both CD11c and MHCII. A CD11c+MHCIIint population seems to be more closely related to macrophages (hence, called GM-Macs), while the CD11c+MHCIIhigh population resembles DC and is, thus, called GM-DC. Addition of IL-4 to these cultures limits, but does not eliminate, the generation of GM-Macs (177). The heterogeneity of precursors and cell populations obtained in vitro fuels a vivid and complex discussion about the biological relevance of these cells (178–180).
It is still unclear to which subpopulation of DC, mo-DC are more closely related, but DC ontogeny data suggest that mo-DC are similar to the inflammatory DC (132). Not surprisingly, inflammatory DC is the designation of another heterogeneous subpopulation of DC, typically CD11chiMHCIIhi. One of the first reports of inflammatory DCs described a population of DC characterized by the production of TNF and iNOS, named Tip-DCs (181). Another study identified inflammatory DC in the skin of atopic dermatitis patients and named these cells inflammatory epidermal dendritic cells (IDECs), which were characterized by the expression of CD11c, CD206, CD1a, CD11b, CD209, FcεRI (182). Recently, another inflammatory DC population was described in the synovial fluid of rheumatoid arthritis patients and in the inflammatory ascites of untreated cancer patients. In this study, inflammatory DC were characterized as CD14+CD1c+SIRPα+CD206+FcεRI+ and their gene signature (when compared to in vitro generated mo-DC, macrophages, cDC2, CD16+ monocytes and CD14+ monocytes) was more closely related to that of mo-DC, suggesting that inflammatory DC could be, indeed, the in vivo counterparts of mo-DC (183).
Mo-DC as a “Window” to Immune System Evaluation in Cancer Patients
It has been known for a while that established tumors affect their microenvironment in ways that facilitate their persistence and progression. These local modifications include zones of hypoxia, altered pH, induction of angiogenesis (184), alterations of pre-mRNA splicing in surrounding cells (185) and the recruitment of cells that facilitate tumor progression, such as tumor-associated macrophages (TAM) (186), immature DC (115), myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) (187) and regulatory T cells (188). However, mechanisms to avoid immune system surveillance and tumor progression (189) are not limited to the tumor site and, today, it is recognized that individuals with cancer present also systemic modifications to that effect as well (190). As discussed before, DC are a plastic and heterogeneous population and it should be expected that, among these systemic adaptations, some affect the various DC subpopulations, including mo-DC.
Described Alterations in mo-DC of Cancer Patients
Various publications have described phenotypic and functional alterations in mo-DC from patients with different tumors (191–193). Our group demonstrated that mo-DC from breast cancer patients are poor stimulators of allogeneic T lymphocytes proliferation but are good inducers of regulatory T cells. These characteristics were observed both in immature and mature mo-DC and the regulatory T cell bias, though decreased by blocking of TGF-β, was not completely inhibited (192). Similar phenomena were also observed in patients with CLL, whose mo-DC expressed reduced levels of important molecules involved in antigen presentation and lymphocyte activation, such as HLA-DR, CD80, CD86, CD83, and CD40, and, coherently, were less effective in inducing proliferation of both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Furthermore, CD4+ T lymphocytes co-cultivated with mo-DC from CLL patients presented reduced IFN-γ and IL-4 production, when compared to healthy donors (193). Further similar results were also observed in chronic myeloid leukemia (194), colorectal cancer (195), and cervical neoplasia (196). It is worth noting that dysfunctional and apoptosis prone mo-DC were also obtained from healthy donors, when their monocytes were exposed to tumor culture supernatants (197).
Although detected in cancer patients, the altered phenotype and functions of mo-DC could precede the emergence of the tumor and reflect an individual constitutional characteristic of the patients, which might be related or not to their disease. The follow up of cancer patients that present such alterations, however, suggests otherwise and indicate that, indeed, it is the presence of the tumor that affects the cells.
In a study of a chromophobe renal carcinoma patient, mo-DC obtained before surgery induced less allogeneic T cell proliferation and more regulatory T cells when compared to cells from healthy donors. Three months after surgery, yet, mo-DC from the patient exhibited functional properties similar to that of healthy controls, suggesting that the presence of the tumor was the cause of the biased mo-DC function in the patient (198). Another example of the transitory and, possibly, in this case, tumor-dependent functional bias of circulating cells has been described in a study with patients with obstructive jaundice. Monocytes from 53 patients with obstructive jaundice (44 due to cancer and 9 due to non-neoplastic diseases) were obtained before surgery and found unable to release H2O2 upon stimulation, but this was progressively reversed after surgery (199). Yet, in another paper we described a patient with type 2-papillary renal cell carcinoma, whose mo-DC also presented functional biases. Though after the tumor was surgically removed, the patient's mo-DC already regained some activity, their T lymphocyte-stimulating activity reached healthy controls' levels only after the patient was submitted to treatment with a dendritic cell-based cancer vaccine (200).
Altogether, these data point out to the fact that circulating monocytes may reflect systemic effects of tumors in such a manner that their functional evaluation could become an effective tool to monitor disease progression and/or response to therapy.
Alterations in Circulating Subpopulations of DC in Cancer Patients
Circulating subsets of DC are also affected in cancer patients. Diminished numbers of total DC have been observed in melanoma patients; this was more intense in stage IV patients and, though it was more pronounced in the pDCs, it also occurred among cDC (201). In breast cancer patients, reductions in total circulating DC and in DC IL-12 production was also described. However, in these patients cDC were the culprit and not pDC (117). Circulating DC isolated from patients with CLL showed decreased expression of co-stimulatory molecules, lower ability to stimulate allogeneic T lymphocytes and did not secrete IL-12, but retained the ability to secrete IL-10 (202). A recent publication, evaluating the effects of different TLR-L in cDC1, cDC2, pDC, and monocytes from breast cancer patients showed that, upon stimulation with IFN-α, cDC2 and non-classical monocytes (CD14−CD16+) exhibited reduced secretion of TNF-α (203).
These observations point out to systemic effects induced by tumors upon the immune-hematopoietic system and suggest that circulating cells are influenced and, possibly functionally handicapped to fight the tumor, even before actually infiltrating the tumor mass. These phenomena, added to our view and understanding of tumor biology, should allow the design of improved therapeutic approaches, even for those that do not specifically target the immune system.
Possible Mechanisms
It is quite evident, thus, that tumors promote local and systemic alterations in immune cells and substantial efforts have been made to identify possible mechanisms of how tumors promote these alterations and, most importantly, how to correct them.
Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 6 (STAT6) is an important molecule, induced by IL-4, in the process of mo-DC differentiation. STAT6 is naturally inhibited by the Suppressor Of Cytokine Signaling 5 (SOCS5), which, in turn, is up regulated by phosphorylated STAT3 in monocytes. In CLL patients, IL-10 induces the phosphorylation of STAT3, thus up regulating the expression of SOCS5. As a consequence, monocytes of CLL patients have impaired phosphorylation of STAT6 and its downstream genes, blocking their differentiation and maturation into functional mo-DC (193). However, mo-DC from healthy donors differentiated in the presence of lung cancer patients' sera, showed decreased STAT3 phosphorylation (204). Although apparently contradictory, these findings might reflect a difference in the monocytes of patients and healthy donors or a difference in the moment of analysis. If monocytes from patients and healthy donors differ, it would not be surprising that they would respond differently to the same stimuli. Likewise, the moment when STAT3 phosphorylation is analyzed may show quite different results. When monocytes from healthy donors were pre-treated with IL-10 and then stimulated with IL-4, an initial increase in STAT3 phosphorylation occurred during the first 72 h, but with the increasing SOCS5 expression, STAT3 (and STAT6) phosphorylation was downregulated (193).
The STAT3 pathway is activated also by IL-6, which, like IL-10, is found in higher concentration in patients sera (205). The impaired functions of DC have been, thus, also attributed to upregulation of IL-6-induced STAT3 activity, both in animal models (206) and humans (207)- these data were recently reviewed by Kitamura et al. (208). Offering a potential solution to these hard to reconcile data is the fact that STAT3 signaling induced by IL-6 seems to be modulated by SOCS in a different way than the IL-10-induced signaling, at least in human macrophages (209).
Undeniably, the available data, though suggesting possible pathways are not enough to elucidate the complex molecular mechanisms underlying DC dysfunction in patients.
Dendritic Cells as Therapeutic Instruments
The key concept of the cancer immunotherapy is that the manipulation of the immune system can achieve cancer control and, ideally, cure. The possibility of cancer immunotherapy was first shown by Coley, who used a mixture of bacterial toxins to treat patients with inoperable sarcomas (210). Since then, many studies have shown clinical benefit when using general immune system activators, such as bacterial products (211) and TLR agonists (212). The antitumor activity of these approaches, when it occurs, is attributed to the ability of these compounds to activate the immune system that, in turn, acquires the ability to kill tumor cells. Much of this effect was shown to be due to DC activation followed by the generation of T cell responses (213). Dendritic cells, as key activators of the adaptive immune response, would be expected to have a central role in inducing antitumor immune responses and the many functional deviations these cells show in cancer patients emphasize the relevant role they may, indeed, play in anti-tumor immune responses. In face of these data, it would be intuitive to exploit the immune activating potential of DC to induce antitumor responses in cancer patients. However, because of the difficulty of obtaining large numbers of these cells by non-invasive methods, therapeutic approaches using DC became possible only after methods for the in vitro generation of these cells were described (174).
Use of Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells
mo-DC are able to present antigens in the context of both MHC class I (91) and class II molecules (214) and, hence, can be used to generate therapeutic cancer vaccines. When injected in humans, mo-DC can prime CD4+ and CD8+ T cells (215) and expand antigen-specific cytotoxic T cells, which can lead to regression of metastatic lesions in patients (216). Nevertheless, some argue that mo-DC, possibly due to a limited migration potential, might be insufficient to consistently induce effective immune responses in vivo (217). Contrastingly, Kuhn and co-workers have shown that successful therapy using immune-activating compounds was followed by the appearance of mo-DC in the draining lymph nodes of treated mice (218) and these cells were essential for the priming of CD8+ T cells and antitumor immunity (219).
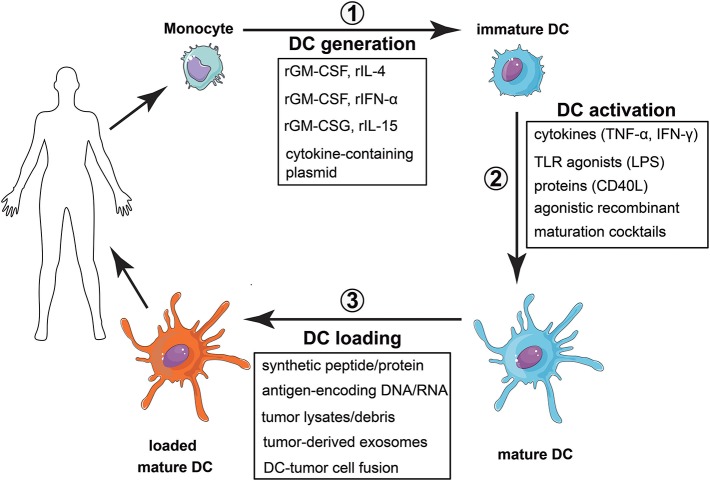
Nonetheless, to be used as therapeutic instruments, mo-DC must be properly differentiated in vitro, induced to mature, loaded with tumor antigens, and, finally, administered to the patient (Figure 5). It is easy, thus, to realize the challenges that face the development of mo-DC-based vaccines. What are the markers of a “properly activated” DC? What is the “proper” response to be induced? What are the relevant tumor antigens? What is the best pathway for these cells to reach secondary lymphoid organs, where they should encounter tumor-specific T lymphocytes? Not surprisingly, each of the aforementioned steps diverges among the various clinical reported protocols, adding much complexity to the evaluation of the approach, but also a possible explanation for the large diversity in the reported efficiencies of such treatments.
Figure 5.
Vaccination strategy with monocyte derived dendritic cells. (1) Monocytes are obtained from peripheral blood and differentiated into dendritic cells. This differentiation can be achieved by using different recombinant cytokines, with rGMCSF + rIL-4 as the most common combination, or by transfecting monocytes with plasmids encoding the cytokines. (2) Once differentiated, DC activation can be accomplished by using different stimuli, most of them associated with tissue damage, inflammation or the presence of a pathogen. (3) The last step is to load the DC with selected or total tumor antigens. Finally, the cells are injected in the patient, expecting them to induce a tumor-specific adaptive immune response able to eradicate the tumor.
To differentiate monocytes into dendritic cells, the cytokines IL-4 and GM-CSF are classically used (174). Most approaches use this protocol to obtain mo-DC, but other ways to differentiate monocytes into dendritic cells have been described and tested. mo-DC differentiated in the presence of GM-CSF and IFN-α, for example, secrete large amounts of pro-inflammatory cytokines, induce a IL-12p70-independent Th1 response (220) and have given rise to cancer-specific CD8 responses, in phase I/II clinical trials (221). mo-DC differentiated in the presence of GM-CSF and IL-15, on the other hand, were better inducers of Th17 responses (222).
The lengthy culture time to achieve the differentiation of mo-DC (usually 5–7 days) is a limitation of the wide clinical use of these protocols. Thus, alternative protocols for mo-DC differentiation were developed. Dauer et al. have shown that monocytes cultured for 48-hours with IL-4 and GM-CSF already have characteristics of immature DC (223) and these, so called FastDC, prime tumor-antigen specific CD8 T cells as efficiently as conventional mo-DC (224). Another strategy is the transduction of monocytes with plasmids containing the genes of the cytokines, which, constitutively expressed, will lead to their differentiation into DC (225). The FDA-approved cancer vaccine, Sipuleucel-T (PROVENGE®) uses a similar approach for mo-DC generation, in a protocol that only requires 3 days for manufacturing (226). This vaccine is approved for castration-resistant prostate cancer and consists of autologous PBMC incubated with a fusion protein containing both GM-CSF and PAP, a prostate-specific cancer-associated antigen (227).
The second step in vaccines generation consists of mo-DC activation, since differentiation generates immature cells. The maturation stimulus can come from a variety of molecules, including cytokines (TNF-α, IFN-γ), TLR agonists (LPS), agonistic recombinant proteins (CD40L) or maturation cocktails (228). However, the best conditions for mo-DC activation are still unclear. Activation with TNF-α, for example, has been implicated in the induction of mo-DC with impaired ability to secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines, which could even protect mice from autoimmunity (229). On the other hand, combinations of TLR agonists synergize to promote Th1 responses (230). Vopenkova et al. made a direct in vitro comparison of different maturation stimuli to induce tumor-specific T cells, showing that the highest response was achieved with the combination of IFN-γ and LPS (231). However, clinical effectiveness comparisons of different mo-DC formulations are still lacking.
Next, mo-DC need to be loaded with tumor antigens. For this, bulk tumor products or selected tumor antigens have been used. Tumor associated antigens (TAAs), recognized by T cells, are found in several tumors (232). Immunodominant synthetic peptides derived from TAAs have been tested and were able to induce clinical and immunological responses of the vaccinated patients (233). Also DNA molecules encoding TAA genes can be employed to load mo-DC, in which case, viral vectors, intrinsically able to activate DC (234), bring further advantage. It is noteworthy that, for all these methods, there is no need of tumor samples from the patient, which may be scarce. However, the use of single antigens has its drawback. Due to the cellular heterogeneity of tumors, they can escape from the immune response generated by the vaccine, through the selection of cells that do not express the immunizing antigens (235). Strategies that involve the induction of a poly-antigenic response can be used to avoid this resistance, especially in melanoma, where this effect is frequently observed. Bulk tumor products may be used as a broad source of tumor antigens.
In addition to tumor lysates, living tumor cells, necrotic debris, apoptotic bodies and tumor-derived exosomes have been used (236). The type of antigenic source used, however, can interfere with the type of immune response obtained and it is impossible, today, to predict which would be the most appropriate antigenic source. For example, in mice, dendritic cells loaded with apoptotic tumor cells were show to induce better responses than tumor lysates, peptides or RNA (237), a finding that contradicts the many data showing that apoptotic cells captured by DC constitute a mechanism of immune tolerance induction.
Although several protocols of vaccination with mo-DC have been tested in clinical trials, only a few obtained relevant clinical responses, and most of them failed to reach the expected results (238). The lack of success in these approaches could be attributed to the functional alterations found in cancer patients mo-DC (239). The use of allogeneic mo-DC obtained from healthy histocompatible donors would be a strategy to bypass this problem, although limited by the need of a MHC-matched donor. Another approach is the use of dendritic cell-tumor cell hybrids. These fused cells express MHC molecules from both tumor and DC origin, forsaking the need of a MHC-matched donor to generate the mo-DC (240). They are also superior than the mixture of these cells, induce antitumor responses and clinical response in patients with advanced metastatic tumors (241). Regardless of the strategy, however, clinical responses to mo-DC-based vaccines are still beyond the desired. This suggests that it may be not enough to have an efficient antigen presentation to induce tumor regression, once it is established. Other compromises between the tumor and the immune system might still prevent an effective tumor-clearing immune response requiring the design of new approaches and, very likely, the combined targeting of different immunological pathways.
Targeting DC Subsets in vivo
More recently, a new modality of DC-based immunotherapy strategy is under development. With the better DC subsets characterization and the identification of specific surface markers for these subsets, it became possible to design strategies to deliver different molecules or “packages” to these cells in vivo (242). This would allow the selective delivery of antigens and/or immunostimulatory molecules to defined cell subtypes in vivo, preventing the costly and laborious ex vivo mo-DC generation.
Among the most studied DC-targeting antibodies are those specific for DEC205, CLEC9A, and CLEC12A. These C-type lectin receptors are expressed, in mice, by cDC1 and, the last two, also by pDC (243). Due to their cross-presentation ability, targeting to cDC1 seems to be a reasonable choice, which would favor a higher CD8+ T cell response.
Indeed, experimental settings targeting these molecules were able to induce T cell responses (244, 245) and regression of metastatic melanoma in mice (246). Interesting and well designed as this strategy may be, in humans this strategy is still restricted to in vitro studies (247) and awaits, urgently, translational research.
Strategies to Improve the Clinical Effectiveness of mo-DC-Based Therapies
Before specifically addressing the many current pathways for the improved translation of our knowledge of DC biology into clinical applications, it is worth mentioning that, though most of this effort is concentrated into the use of these cells to induce effector immune responses, it is only a matter of time till it becomes feasible to delineate DC-based strategies to treat conditions where the immune system went rogue and is causing autoimmunity, or where medical interventions require the limitation of immune responses, like organ transplantations.
That said, let us consider the strategies that may lead to enhanced immunogenic effects of mo-DC-based treatments.
Approaches for the Improvement of DC-Based Treatments
Since mo-DC show deviant phenotypes in cancer (192) and are susceptible to negative modulation by different drugs, for example STAT5 inhibitors (248), the converse is also true and various approaches are under development to achieve the generation of “better” mo-DC.
The chemokine CXCL-4 is a powerful chemoattractant to monocytes and an important immunoregulator that has been shown to enhance the expression of MHC, CD86, and CD83 molecules by mo-DC of healthy donors, leading to more efficient antigen presentation, induction of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells proliferation and production of IFN-γ (249).
As mentioned before, IL-6 through the activation of STAT3 interferes with proper DC maturation and, indeed, in patients with colorectal cancer has been associated with poor CD4+ T cells responses (207). Coherently, a phase-I study in ovarian cancer patients showed that, combined with chemotherapy, IL-6 blockade was safe and induced a series of positive modifications in immune parameters of the treated patients, including increases in IL-12, IL-1β, TNF-α, and IFN-γ secretion (250).
Besides targeting the negative regulators of DC activation, it is possible to overcome this phenomenon by changing the activating signals delivered to these cells. Following this line of research, a cocktail of inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, poly I:C, IFN-α, and IFN-γ) has been tested for mo-DC maturation and was shown to increase their IL-12 production and their ability to prime melanoma-antigens-specific T cells in vitro (251). This mo-DC activating cocktail, in a vaccination study of 22 recurrent glioma patients, was associated with increases in serum type 1 cytokines and chemokines, tumor-associated antigens-specific T cell responses and clinical benefit in 9 patients (252).
Another approach is based on the use of adjuvants to boost the immune response. Among these, GM-CSF used in vaccines as GVAX (253) and STINGVAX (254) and, even TLR agonists (255), may be more effective for cell maturation. Other adjuvants could be listed, as for example, aluminum salts (256) (an inflammasome activator), and montanide (257) (an equivalent to incomplete Freund's adjuvant). Those adjuvants may boost responses due to physical effects upon antigens and cells, but also enhance DC activation. Nonetheless, the consideration of such a heterogeneous group of substances is enough to realize that adjuvant research is a rich field that may broaden the applicability and enhance the effectiveness of DC-based vaccination (258).
A different pathway to improve the effectiveness of DC-based therapy focuses on the selection of the immunizing antigens. In cancer, the mapping of a patient's set of neoantigens and use thereof would represent the epitome of personalized medicine. Though very tempting, this approach would still have its drawbacks, a significant one being the fact that not all tumors express immunogenic neoantigens (259), not to mention the cost that such strategy would impose on any health care system. Nevertheless, its feasibility and efficacy has already been demonstrated in an elegant study (260) where personalized vaccines were prepared for 6 melanoma patients. Whole-exome sequencing of their tumors allowed the identification of the mutated antigens from which a set of peptides was selected and synthesized so that they would be presented in the context of MHC-I. Four patients presented complete clinical responses to the vaccine alone and the other two, who had progressive disease after the vaccination, experienced complete responses after treatment with anti-PD-1. Curiously, in spite of the selection of MHC-I selective peptides, both CD4+ and CD8+ antigen-specific T cells were stimulated, with a predominance of CD4+ T cell responses. This observation illustrates very well how much “real life” immune responses still differ from our predictions.
Another ingenious strategy bypasses many of the known hurdles to exploit the immunogenic potential of DC. This approach aims to deliver RNA-containing nanoparticles systemically, which due to their lipid composition would be preferentially captured by DC and, then, release the RNA encoding the selected antigen(s) to be synthesized and presented. In a murine model, this approach lead, indeed, to DC maturation, IFN-α production and strong antigen-specific immune responses, which were effective in a series of tumor models (261). Accordingly, this strategy is under investigation in a clinical trial (NCT02410733) for patients with advanced melanoma.
Combination Treatments Including mo-DC
Chemotherapy and radiotherapy, together with surgery, still remain as the main pillars of cancer therapy. Since chemotherapy in general was formerly considered immunosuppressive, little attention was given to the fact that this is not always true. Indeed, some drugs might potentiate the anti-tumor immune response, by inducing the now recognized “immunogenic cell death” (262, 263). However, due to the frequently observed cancer patients' DC dysfunctions, the simple immunogenic death may not be enough to disrupt the tumor-favoring status of the immune response in patients. To achieve that, active immune interventions may be necessary to take advantage of the phenomenon. Indeed, a series of studies, both experimental and in humans, has been addressing this issue with promising results (264–266).
Radiation may also favor the induction of anti-tumor immune responses and, as with chemotherapy, there are plenty of data indicating a beneficial effect of its combination with cancer vaccines or other immune-stimulating strategies in different settings, including hepatocellular carcinoma (267), prostate cancer (268), lymphoma (269), and glioblastoma (270). Currently, the potential of such combinations are under scrutiny in a series of clinical trials for patients with such disparate diseases as anal (NCT01671488), lung (NCT01579188) and pancreatic cancer (NCT01072981) (271).
The disparity of the diseases mentioned at the previous paragraphs is a good indicator of the contrast between therapeutic strategies directed against the tumor cell and those targeting the immune system. Those that aim at the tumor cell will differ significantly from one tumor to the other, since each tumor has its own set of genetic changes and will respond differently to a given treatment. On the other hand, strategies that target the immune system, though still dealing with a very complex set of interactions, will face, very frequently, standard responses of the immune system to the perturbations caused by the presence of the tumor, regardless of the tumor's set of genetic mutations.
Actually, the realization of this scenario and the better understanding of the immune system and its interactions with tumors opened the way to a very attractive and successful approach for cancer immunotherapy: instead of targeting directly the tumor, one could target the immune regulatory mechanisms that allow a frequently immunogenic tumor to grow in an otherwise immunocompetent host. With this, the “checkpoint inhibitors era” started and achieved unprecedented good clinical results (272), leading to this 2018's award of the Nobel Prize in Medicine for James Allison and Tasuku Honjo for their work in this area.
However, after the initial excitement and even after the inclusion of other checkpoint inhibitors among the available armamentarium against cancer, it is necessary to appreciate that not all patients will respond to this approach, since it needs an existing response, kept in check and “waiting” to be released by the treatment. On the other hand, it is quite possible that the frequently unsatisfactory response to cancer vaccines is caused by the pre-existence or vaccine-induced activation of these same regulatory circuits. Hence, a coherent path to achieve better clinical results would be the combination of both immune modulating strategies. Indeed, experimental (273) and clinical data (274) suggest that this may be true. In the aforementioned clinical study, patients with advanced melanoma were treated with a combination of MART-1-peptide pulsed-DC and anti-CTLA-4 and the results indicated that the combination might be, indeed, more effective than either approach alone. Likewise, also in the PD-1/PD-L1-PD-L2 pathway (275, 276) the combination of DC vaccination with checkpoint inhibition may offer, at least theoretical, advantages.
A different set of combination treatments has been targeting immune modulatory enzymes. The enzyme indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) catalyzes the degradation of tryptophan contributing to tolerance induction by favoring regulatory T cell differentiation and reducing DC activity (277). IDO expression by DC is induced by inflammatory stimuli (278), but also by CTLA-4 and PD-1 (279). Accordingly, IDO inhibition has shown positive effects in murine models of pancreatic cancer (280) and a study combining IDO inhibitors with DC vaccines for breast cancer patients has completed recruitment (NCT01042535). Similarly, an inhibitor of BCR-ABL, SRC, c-KIT, PDGFR, and ephrin tyrosine kinases has shown synergistic effects with a DC vaccine in a mouse melanoma model (281) and this combination is the object of ongoing clinical trials in patients with melanoma (NCT01876212) and metastatic renal cells carcinoma (NCT02432846 phase II e NCT01582672 phase III). Arginase-1, an enzyme that regulates cell proliferation and is constitutively expressed by myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) (282) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX2), are other two enzyme whose inhibition might have positive interactions with immunotherapeutic approaches, including those that exploit DC.
Concluding Remarks
Dendritic cells have a central role in the immune system homeostasis and are directly involved in defining the patterns of response the system develops when facing an antigenic challenge. Their normal function warrants protection against infections, possibly cancer, but also against autoimmunity and hypersensitivity reactions. The more is uncovered of the mechanisms that drive these cells to modulate the response in one way or another, the more tools will be available to direct the immune system to desired therapeutic outcomes. Today, much of the efforts and clinical results are focused into harnessing these cells to induce effector responses, mainly, but not only, in cancer. With the advancement of the understanding of their physiology and regulatory pathways, it is possible to predict their effective use in such opposing conditions as cancer and diabetes, with less untoward and more durable effects.
Author Contributions
TP, MP, AO, and GE reviewed the literature and wrote the manuscript. PB-S revised the literature and the manuscript and JB designed, wrote and revised the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Funding. This work had the support of grants from the Sao Paulo Research Foundation-FAPESP (2014/25988-1; 2014/26437-9; 2105/03314-1; 2016/01137-8), the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel-CAPES, and from National Council for Scientific and Technological Development-CNPq (308053/2017-6).
References
- 1.Steinman RM, Cohn ZA. Identification of a novel cell type in peripheral lymphoid organs of mice. I. Morphology, quantitation, tissue distribution. J Exp Med. (1973) 137:1142–62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Steinman RM, Idoyaga J. Features of the dendritic cell lineage. Immunol Rev. (2010) 234:5–17. 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2009.00888.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Steinman RM, Witmer MD. Lymphoid dendritic cells are potent stimulators of the primary mixed leukocyte reaction in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (1978) 75:5132–6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Banchereau J, Briere F, Caux C, Davoust J, Lebecque S, Liu YJ, et al. Immunobiology of dendritic cells. Annu Rev Immunol. (2000) 18:767–811. 10.1146/annurev.immunol.18.1.767 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Carlens J, Wahl B, Ballmaier M, Bulfone-Paus S, Förster R, Pabst O. Common γ-chain-dependent signals confer selective survival of eosinophils in the murine small intestine. J Immunol. (2009) 183:5600–7. 10.4049/jimmunol.0801581 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Drutman SB, Kendall JC, Trombetta ES. Inflammatory spleen monocytes can upregulate CD11c expression without converting into dendritic cells. J Immunol. (2012) 188:3603–10. 10.4049/jimmunol.1102741 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hebel K, Griewank K, Inamine A, Chang HD, Hilke BM, Fillatreau S, et al. Plasma cell differentiation in T-independent type 2 immune responses is independent of CD11chigh dendritic cells. Eur J Immunol. (2006) 36:2912–9. 10.1002/eji.200636356 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hochweller K, Striegler J, Hämmerling GJ, Garbi N. A novel CD11c. DTR transgenic mouse for depletion of dendritic cells reveals their requirement for homeostatic proliferation of natural killer cells. Eur J Immunol. (2008) 38:2776–83. 10.1002/eji.200838659 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Huleatt JW, Lefrançois L. Antigen-driven induction of CD11c on intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes and CD8+ T cells in vivo. J Immunol. (1995) 154:5684–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rubtsov AV, Rubtsova K, Fischer A, Meehan RT, Gillis JZ, Kappler JW, et al. Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7)–driven accumulation of a novel CD11c+ B-cell population is important for the development of autoimmunity. Blood (2011) 118:1305–15. 10.1182/blood-2011-01-331462 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Probst HC, Tschannen K, Odermatt B, Schwendener R, Zinkernagel RM, Van Den Broek M. Histological analysis of CD11c-DTR/GFP mice after in vivo depletion of dendritic cells. Clin Exp Immunol. (2005) 141:398–404. 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02868.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Vermaelen K, Pauwels R. Accurate and simple discrimination of mouse pulmonary dendritic cell and macrophage populations by flow cytometry: methodology and new insights. Cytometry (2004) 61A:170–7. 10.1002/cyto.a.20064 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Delamarre L, Pack M, Chang H, Mellman I, Trombetta ES. Differential lysosomal proteolysis in antigen-presenting cells determines antigen fate. Science (2005) 307:1630–4. 10.1126/science.1108003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Geissmann F, Manz MG, Jung S, Sieweke MH. Development of monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. Science (2010) 327:656–61. 10.1126/science.1178331 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.van Montfoort N, Camps MG, Khan S, Filippov DV, Weterings JJ, Griffith JM, et al. Antigen storage compartments in mature dendritic cells facilitate prolonged cytotoxic T lymphocyte cross-priming capacity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2009) 106:6730–5. 10.1073/pnas.0900969106 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Haniffa M, Collin M, Ginhoux F. Ontogeny and functional specialization of dendritic cells in human and mouse. (2013) 120:1–49. 10.1016/B978-0-12-417028-5.00001-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hashimoto D, Chow A, Noizat C, Teo P, Beasley MB, Leboeuf M, et al. Tissue-resident macrophages self-maintain locally throughout adult life with minimal contribution from circulating monocytes. Immunity (2013) 38:792–804. 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.04.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hettinger J, Richards DM, Hansson J, Barra MM, Joschko A-C, Krijgsveld J, et al. Origin of monocytes and macrophages in a committed progenitor. Nat Immunol. (2013) 14:821–30. 10.1038/ni.2638 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.McGovern N, Schlitzer A, Gunawan M, Jardine L, Shin A, Poyner E, et al. Human dermal CD14? cells are a transient population of monocyte-derived macrophages. Immunity (2014) 41:465–77. 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.08.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Naik SH, Perié L, Swart E, Gerlach C, van Rooij N, de Boer RJ, et al. Diverse and heritable lineage imprinting of early haematopoietic progenitors. Nature Publish Group (2013) 496:229–32. 10.1038/nature12013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Schulz C, Gomez Perdiguero E, Chorro L, Szabo-Rogers H, Cagnard N, Kierdorf K, et al. A lineage of myeloid cells independent of Myb and hematopoietic stem cells. Science (2012) 336:86–90. 10.1126/science.1219179 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Schraml BU, van Blijswijk J, Zelenay S, Whitney PG, Filby A, Acton SE, et al. Genetic tracing via DNGR-1 expression history defines dendritic cells as a hematopoietic lineage. Cell (2013) 154:843–58. 10.1016/j.cell.2013.07.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wang J, Dai X, Hsu C, Ming C, He Y, Zhang J, Wei L, et al. Discrimination of the heterogeneity of bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. Mol Med Rep. (2017) 16:6787–93. 10.3892/mmr.2017.7448 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yona S, Kim K-W, Wolf Y, Mildner A, Varol D, Breker M, et al. Fate mapping reveals origins and dynamics of monocytes and tissue macrophages under homeostasis. Immunity (2013) 38:79–91. 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.12.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.O'Keeffe M, Mok WH, Radford KJ. Human dendritic cell subsets and function in health and disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2015) 72:1–17. 10.1007/s00018-015-2005-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hermans IF, Silk JD, Gileadi U, Salio M, Mathew B, Ritter G, et al. NKT cells enhance CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses to soluble antigen in vivo through direct interaction with dendritic cells. J Immunol. (2003) 171:5140–7. 10.4049/jimmunol.171.10.5140 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Münz C, Steinman RM, Fujii S-I. Dendritic cell maturation by innate lymphocytes: coordinated stimulation of innate and adaptive immunity. J Exp Med. (2005) 202:203–7. 10.1084/jem.20050810 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Smyth MJ, Crowe NY, Hayakawa Y, Takeda K, Yagita H, Godfrey DI. NKT cells - conductors of tumor immunity? Curr Opin Immunol. (2002) 14:165–71. 10.1016/S0952-7915(02)00316-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Halim TYF, Hwang YY, Scanlon ST, Zaghouani H, Garbi N, Fallon PG, et al. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells license dendritic cells to potentiate memory TH2 cell responses. Nat Immunol. (2016) 17:57–64. 10.1038/ni.3294 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hawiger D, Inaba K, Dorsett Y, Guo M, Mahnke K, Rivera M, et al. Dendritic cells induce peripheral T cell unresponsiveness under steady state conditions in vivo. J Exp Med. (2001) 194:769–79. 10.1084/jem.194.6.769 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Steinman RM, Hawiger D, Liu K, Bonifaz L, Bonnyay D, Mahnke K, et al. Dendritic cell function in vivo during the steady state: a role in peripheral tolerance. Ann NY Acad Sci. (2003) 987:15–25. 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb06029.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Worbs T, Hammerschmidt SI, Förster R. Dendritic cell migration in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. (2017) 17:30–48. 10.1038/nri.2016.116 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hemmi H, Akira S. TLR signalling and the function of dendritic cells. Chem Immunol Aller. (2005) 86:120–135. 10.1159/000086657 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Cerboni S, Gentili M, Manel N. Diversity of pathogen sensors in dendritic cells. Adv Immunol. (2013) 120:211–237. 10.1016/B978-0-12-417028-5.00008-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Alvarez D, Vollmann EH, Andrian von UH. Mechanisms and consequences of dendritic cell migration. Immunity (2008) 29:325–42. 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.08.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Dong H, Bullock TNJ. Metabolic influences that regulate dendritic cell function in tumors. Front Immunol. (2014) 5:24. 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00024 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Friedl P, Gunzer M. Interaction of T cells with APCs: the serial encounter model. Trends Immunol. (2001) 22:187–91. 10.1016/S1471-4906(01)01869-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Henderson RA, Watkins SC, Flynn JL. Activation of human dendritic cells following infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol. (1997) 159:635–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Randolph GJ, Angeli V, Swartz MA. Dendritic-cell trafficking to lymph nodes through lymphatic vessels. Nature Rev Immunol. (2005) 5:617–28. 10.1038/nri1670 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Imai Y, Yamakawa M, Kasajima T. The lymphocyte-dendritic cell system. Histol Histopathol. (1998) 13:469–510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Winzler C, Rovere P, Rescigno M, Granucci F, Penna G, Adorini L, et al. Maturation stages of mouse dendritic cells in growth factor-dependent long-term cultures. J Exp Med. (1997) 185:317–28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Reis e Sousa C. Dendritic cells in a mature age. Nature Rev Immunol. (2006) 6:476–83. 10.1038/nri1845 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Steinman RM. Decisions about dendritic cells: past, present, and future. Annu Rev Immunol. (2012) 30:1–22. 10.1146/annurev-immunol-100311-102839 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Trombetta ES, Mellman I. Cell biology of antigen processing in vitro and in vivo. Annu Rev Immunol. (2005) 23:975–1028. 10.1146/annurev.immunol.22.012703.104538 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Förster R, Schubel A, Breitfeld D, Kremmer E, Renner-Müller I, Wolf E, et al. CCR7 coordinates the primary immune response by establishing functional microenvironments in secondary lymphoid organs. Cell (1999) 99:23–33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Ohl L, Mohaupt M, Czeloth N, Hintzen G, Kiafard Z, Zwirner J, et al. CCR7 governs skin dendritic cell migration under inflammatory and steady-state conditions. Immunity (2004) 21:279–88. 10.1016/j.immuni.2004.06.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Sallusto F, Schaerli P, Loetscher P, Schaniel C, Lenig D, Mackay CR, et al. Rapid and coordinated switch in chemokine receptor expression during dendritic cell maturation. Eur J Immunol. (1998) 28:2760–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Steinman RM. The control of immunity and tolerance by dendritic cell. Pathol Biol. (2003) 51:59–60. 10.1016/S0369-8114(03)00096-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Caux C, Massacrier C, Vanbervliet B, Dubois B, Van Kooten C, Durand I, et al. Activation of human dendritic cells through CD40 cross-linking. J Exp Med. (1994) 180:1263–72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Jensen SS, Gad M. Differential induction of inflammatory cytokines by dendritic cells treated with novel TLR-agonist and cytokine based cocktails: targeting dendritic cells in autoimmunity. J Inflamm (Lond) (2010) 7:37. 10.1186/1476-9255-7-37 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Tan JKH, O'Neill HC. Maturation requirements for dendritic cells in T cell stimulation leading to tolerance versus immunity. J Leukocyte Biol. (2005) 78:319–324. 10.1189/jlb.1104664 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Iwasaki A, Medzhitov R. Control of adaptive immunity by the innate immune system. Nat Immunol. (2015) 16:343–353. 10.1038/ni.3123 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Luft T, Rodionova E, Maraskovsky E, Kirsch M, Hess M, Buchholtz C, et al. Adaptive functional differentiation of dendritic cells: integrating the network of extra- and intracellular signals. Blood (2006) 107:4763–9. 10.1182/blood-2005-04-1501 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Jonuleit H, Knop J, Enk AH. Cytokines and their effects on maturation, differentiation and migration of dendritic cells. Arch Dermatol Res. (1996) 289:1–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Amsen D, Blander JM, Lee GR, Tanigaki K, Honjo T, Flavell RA. Instruction of distinct CD4 T helper cell fates by different notch ligands on antigen-presenting cells. Cell (2004) 117:515–26. 10.1038/nri1402 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Constant S, Pfeiffer C, Woodard A, Pasqualini T, Bottomly K. Extent of T cell receptor ligation can determine the functional differentiation of naive CD4+ T cells. J Exp Med (1995) 182:1591–6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Hosken NA, Shibuya K, Heath AW, Murphy KM, O'Garra A. The effect of antigen dose on CD4+ T helper cell phenotype development in a T cell receptor-alpha beta-transgenic model. J Exp Med. (1995) 182:1579–84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Kadowaki N. Dendritic cells: a conductor of T cell differentiation. Allergol Int. (2007) 56:193–9. 10.2332/allergolint.R-07-146 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Maekawa Y, Tsukumo S-I, Chiba S, Hirai H, Hayashi Y, Okada H, et al. Delta1-Notch3 interactions bias the functional differentiation of activated CD4+ T cells. Immunity (2003) 19:549–59. 10.1016/S1074-7613(03)00270-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Pulendran B, Smith JL, Caspary G, Brasel K, Pettit D, Maraskovsky E, et al. Distinct dendritic cell subsets differentially regulate the class of immune response in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (1999) 96:1036–41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Jenkins SJ, Perona-Wright G, Worsley AGF, Ishii N, MacDonald AS. Dendritic cell expression of OX40 ligand acts as a costimulatory, not polarizing, signal for optimal Th2 priming and memory induction in vivo. J Immunol. (2007) 179:3515–23. 10.4049/jimmunol.179.6.3515 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Soumelis V, Reche PA, Kanzler H, Yuan W, Edward G, Homey B, et al. Human epithelial cells trigger dendritic cell mediated allergic inflammation by producing TSLP. Nat Immunol. (2002) 3:673–680. 10.1038/ni805 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Bailey SL, Schreiner B, McMahon EJ, Miller SD. CNS myeloid DCs presenting endogenous myelin peptides “preferentially” polarize CD4+ T(H)-17 cells in relapsing EAE. Nat Immunol. (2007) 8:172–80. 10.1038/ni1430 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Iezzi G, Sonderegger I, Ampenberger F, Schmitz N, Marsland BJ, Kopf M. CD40-CD40L cross-talk integrates strong antigenic signals and microbial stimuli to induce development of IL-17-producing CD4+ T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2009) 106:876–81. 10.1073/pnas.0810769106 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Huang G, Wang Y, Chi H. Regulation of TH17 cell differentiation by innate immune signals. Cell Mol Immunol. (2012) 9:287–95. 10.1038/cmi.2012.10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Levings MK, Gregori S, Tresoldi E, Cazzaniga S, Bonini C, Roncarolo MG. Differentiation of Tr1 cells by immature dendritic cells requires IL-10 but not CD25+CD4+ Tr cells. Blood (2005) 105:1162–9. 10.1182/blood-2004-03-1211 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Rescigno M. Dendritic cell-epithelial cell crosstalk in the gut. Immunol Rev. (2014) 260:118–28. 10.1111/imr.12181 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Vega-Ramos J, Roquilly A, Asehnoune K, Villadangos JA. Modulation of dendritic cell antigen presentation by pathogens, tissue damage and secondary inflammatory signals. Curr Opin Pharmacol. (2014) 17:64–70. 10.1016/j.coph.2014.07.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Na H, Cho M, Chung Y. Regulation of Th2 cell immunity by dendritic cells. Immune Netw. (2016) 16:1–12. 10.4110/in.2016.16.1.1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Coulon P-G, Richetta C, Rouers A, Blanchet FP, Urrutia A, Guerbois M, et al. HIV-infected dendritic cells present endogenous MHC class II-restricted antigens to HIV-specific CD4+ T cells. J Immunol. (2016) 197:517–32. 10.4049/jimmunol.1600286 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Delamarre L, Mellman I. Harnessing dendritic cells for immunotherapy. Semin Immunol. (2011) 23:2–11. 10.1016/j.smim.2011.02.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Jung S, Unutmaz D, Wong P, Sano G-I, De los Santos K, Sparwasser T, et al. In vivo depletion of CD11c+ dendritic cells abrogates priming of CD8+ T cells by exogenous cell-associated antigens. Immunity (2002) 17:211–20. 10.1016/S1074-7613(02)00365-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Segura E, Amigorena S. Cross-presentation in mouse and human dendritic cells. Adv Immunol. (2015) 127:1–31. 10.1016/bs.ai.2015.03.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Segura E, Villadangos JA. Antigen presentation by dendritic cells in vivo. Curr Opin Immunol. (2009) 21:105–110. 10.1016/j.coi.2009.03.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Bevan MJ. Cross-priming for a secondary cytotoxic response to minor H antigens with H-2 congenic cells which do not cross-react in the cytotoxic assay. J Exp Med. (1976) 143:1283–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Bevan MJ. Cross-priming for a secondary cytotoxic response to minor H antigens with H-2 congenic cells which do not cross-react in the cytotoxic assay. J Exp Med. (1976) 143:1283–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Sánchez-Paulete AR, Teijeira A, Cueto FJ, Garasa S, Pérez-Gracia JL, et al. Antigen cross-presentation and T-cell cross-priming in cancer immunology and immunotherapy. Ann Oncol. (2017) 28:xii74 10.1093/annonc/mdx727 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.McCoy KD, Hermans IF, Fraser JH, Le Gros G, Ronchese F. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) can regulate dendritic cell-induced activation and cytotoxicity of CD8(+) T cells independently of CD4(+) T cell help. J Exp Med. (1999) 189:1157–62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Young JW, Steinman RM. Dendritic cells stimulate primary human cytolytic lymphocyte responses in the absence of CD4+ helper T cells. J Exp Med. (1990) 171:1315–32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Kurts C, Kosaka H, Carbone FR, Miller JF, Heath WR. Class I-restricted cross-presentation of exogenous self-antigens leads to deletion of autoreactive CD8(+) T cells. J Exp Med. (1997) 186:239–45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Rock KL, Shen L. Cross-presentation: underlying mechanisms and role in immune surveillance. Immunol Rev. (2005) 207:166–83. 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2005.00301.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Steinman RM, Swanson J. The endocytic activity of dendritic cells. J Exp Med. (1995) 182:283–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Geijtenbeek TB, Torensma R, van Vliet SJ, van Duijnhoven GC, Adema GJ, van Kooyk Y, et al. Identification of DC-SIGN, a novel dendritic cell-specific ICAM-3 receptor that supports primary immune responses. Cell (2000) 100:575–585. 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80693-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Sallusto F, Cella M, Danieli C, Lanzavecchia A. Dendritic cells use macropinocytosis and the mannose receptor to concentrate macromolecules in the major histocompatibility complex class II compartment: downregulation by cytokines and bacterial products. J Exp Med. (1995) 182:389–400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Valladeau J, Ravel O, Dezutter-Dambuyant C, Moore K, Kleijmeer M, Liu Y, et al. Langerin, a novel C-type lectin specific to Langerhans cells, is an endocytic receptor that induces the formation of Birbeck granules. Immunity (2000) 12:71–81. 10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80160-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Keller R, Gehri R, Keist R. Macrophage response to viruses, protozoa, and fungi: secretory and cellular activities induced in resting unprimed bone marrow-derived mononuclear phagocytes. Cell Immunol. (1994) 159:323–30. 10.1006/cimm.1994.1318 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Medzhitov R, Preston-Hurlburt P, Janeway CA. A human homologue of the Drosophila Toll protein signals activation of adaptive immunity. Nature (1997) 388:394–7. 10.1038/41131 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Muzio M, Bosisio D, Polentarutti N, D'amico G, Stoppacciaro A, Mancinelli R, et al. Differential expression and regulation of toll-like receptors (TLR) in human leukocytes: selective expression of TLR3 in dendritic cells. J Immunol. (2000) 164:5998–6004. 10.4049/jimmunol.164.11.5998 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Rescigno M, Granucci F, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P. Molecular events of bacterial-induced maturation of dendritic cells. J Clin Immunol (2000) 20:161–166. 10.1023/A:1006629328178 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Wilson NS, El-Sukkari D, Villadangos JA. Dendritic cells constitutively present self antigens in their immature state in vivo and regulate antigen presentation by controlling the rates of MHC class II synthesis and endocytosis. Blood (2004) 103:2187–95. 10.1182/blood-2003-08-2729 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Albert ML, Sauter B, Bhardwaj N. Dendritic cells acquire antigen from apoptotic cells and induce class I-restricted CTLs. Nature (1998) 392:86–9. 10.1038/32183 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Castellano G, Woltman AM, Schena FP, Roos A, Daha MR, van Kooten C. Dendritic cells and complement: at the cross road of innate and adaptive immunity. Mol Immunol. (2004) 41:133–40. 10.1016/j.molimm.2004.03.018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Deluce-Kakwata-Nkor N, Lamendour L, Chabot V, Héraud A, Ivanovic Z, Halary F, et al. Differentiation of human dendritic cell subsets for immune tolerance induction. Transfus Clin Biol. (2018) 25:90–5. 10.1016/j.tracli.2017.08.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Liu J, Cao X. Regulatory dendritic cells in autoimmunity: a comprehensive review. J Autoimmun. (2015) 63:1–12. 10.1016/j.jaut.2015.07.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Shiokawa A, Kotaki R, Takano T, Nakajima-Adachi H, Hachimura S. Mesenteric lymph node CD11b- CD103+ PD-L1High dendritic cells highly induce regulatory T cells. Immunology (2017) 152:52–64. 10.1111/imm.12747 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Huang FP, Platt N, Wykes M, Major JR, Powell TJ, Jenkins CD, et al. A discrete subpopulation of dendritic cells transports apoptotic intestinal epithelial cells to T cell areas of mesenteric lymph nodes. J Exp Med. (2000) 191:435–44. 10.1084/jem.191.3.435 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Steinman RM, Turley S, Mellman I, Inaba K. The induction of tolerance by dendritic cells that have captured apoptotic cells. J Exp Med. (2000) 191:411–416. 10.1084/jem.191.3.411 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Liu K, Iyoda T, Saternus M, Kimura Y, Inaba K, Steinman RM. Immune tolerance after delivery of dying cells to dendritic cells in situ. J Exp Med. (2002) 196:1091–1097. 10.1084/jem.20021215 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Stuart LM, Lucas M, Simpson C, Lamb J, Savill J, Lacy-Hulbert A. Inhibitory effects of apoptotic cell ingestion upon endotoxin-driven myeloid dendritic cell maturation. J Immunol. (2002) 168:1627–35. 10.4049/jimmunol.168.4.1627 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Wallet MA, Sen P, Flores RR, Wang Y, Yi Z, Huang Y, et al. MerTK is required for apoptotic cell-induced T cell tolerance. J Exper Med. (2008) 205:219–32. 10.1084/jem.20062293 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Hong J, Gu X-D, Xiang J-B, Zhang Z, Zang Y-W, Zhang Q-H, et al. Recipient dendritic cells modified by RNA interference targeting CD80 and CD86 elicit T cell hyporesponsiveness via enhanced T cell apoptosis. Chin Med J. (2013) 126:2139–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Manicassamy S, Pulendran B. Dendritic cell control of tolerogenic responses. Immunol Rev. (2011) 241:206–27. 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01015.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Zhu H-C, Qiu T, Liu X-H, Dong W-C, Weng X-D, Hu C-H, et al. Tolerogenic dendritic cells generated by RelB silencing using shRNA prevent acute rejection. Cell Immunol. (2012) 274:12–8. 10.1016/j.cellimm.2012.02.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Saito M, Nagasawa M, Takada H, Hara T, Tsuchiya S, Agematsu K, et al. Defective IL-10 signaling in hyper-IgE syndrome results in impaired generation of tolerogenic dendritic cells and induced regulatory T cells. J Exper Med. (2011) 208:235–49. 10.1084/jem.20100799 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Sela U, Park CG, Park A, Olds P, Wang S, Steinman RM, et al. Dendritic cells induce a subpopulation of IL-12Rβ2-Expressing treg that specifically consumes IL-12 to control Th1 responses. PLoS ONE (2016) 11:e0146412. 10.1371/journal.pone.0146412 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Grohmann U, Orabona C, Fallarino F, Vacca C, Calcinaro F, Falorni A, et al. CTLA-4-Ig regulates tryptophan catabolism in vivo. Nat Immunol. (2002) 3:1097–101. 10.1038/ni846 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Morelli AE, Thomson AW. Tolerogenic dendritic cells and the quest for transplant tolerance. Nature Rev Immunol. (2007) 7:610–21. 10.1038/nri2132 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Sakaguchi S, Miyara M, Costantino CM, Hafler DA. FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in the human immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. (2010) 10:490–500. 10.1038/nri2785 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Idoyaga J, Fiorese C, Zbytnuik L, Lubkin A, Miller J, Malissen B, et al. Specialized role of migratory dendritic cells in peripheral tolerance induction. J Clin Invest. (2013) 123:844–54. 10.1172/JCI65260 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Mahnke K, Qian Y, Knop J, Enk AH. Induction of CD4+/CD25+ regulatory T cells by targeting of antigens to immature dendritic cells. Blood (2003) 101:4862–9. 10.1182/blood-2002-10-3229 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Yates SF, Paterson AM, Nolan KF, Cobbold SP, Saunders NJ, Waldmann H, et al. Induction of regulatory T cells and dominant tolerance by dendritic cells incapable of full activation. J Immunol (2007) 179:967–76. 10.4049/jimmunol.179.2.967 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Yogev N, Frommer F, Lukas D, Kautz-Neu K, Karram K, Ielo D, et al. Dendritic cells ameliorate autoimmunity in the CNS by controlling the homeostasis of PD-1 receptor(+) regulatory T cells. Immunity (2012) 37:264–75. 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.05.025 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Campanelli AP, Roselino AM, Cavassani KA, Pereira MSF, Mortara RA, Brodskyn CI, et al. CD4+CD25+ T cells in skin lesions of patients with cutaneous leishmaniasis exhibit phenotypic and functional characteristics of natural regulatory T cells. J Infect Dis. (2006) 193:1313–22. 10.1086/502980 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Montagnoli C, Bacci A, Bozza S, Gaziano R, Mosci P, Sharpe AH, et al. B7/CD28-dependent CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells are essential components of the memory-protective immunity to Candida albicans. J Immunol. (2002) 169:6298–308. 10.4049/jimmunol.169.11.6298 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Baleeiro RB, Anselmo LB, Soares FA, Pinto CAL, Ramos O, Gross JL, et al. High frequency of immature dendritic cells and altered in situ production of interleukin-4 and tumor necrosis factor-α in lung cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother (2008) 57:1335–45. 10.1007/s00262-008-0468-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Almand B, Resser JR, Lindman B, Nadaf S, Clark JI, Kwon ED, et al. Clinical significance of defective dendritic cell differentiation in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. (2000) 6:1755–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Bella SD, Gennaro M, Vaccari M, Ferraris C, Nicola S, Riva A, et al. Altered maturation of peripheral blood dendritic cells in patients with breast cancer. Br J Cancer (2003) 89:1463–72. 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601243 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Dunn GP, Old LJ, Schreiber RD. The immunobiology of cancer immunosurveillance and immunoediting. Immunity (2004) 21:137–48. 10.1016/j.immuni.2004.07.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Johnson DJ, Ohashi PS. Molecular programming of steady-state dendritic cells: impact on autoimmunity and tumor immune surveillance. Anna NY Acad Sci. (2013) 1284:46–51. 10.1111/nyas.12114 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Vicari AP, Caux C, Trinchieri G. Tumour escape from immune surveillance through dendritic cell inactivation. Semin Cancer Biol. (2002) 12:33–42. 10.1006/scbi.2001.0400 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Ardouin L, Luche H, Chelbi R, Carpentier S, Shawket A, Montanana Sanchis F, et al. Broad and largely concordant molecular changes characterize tolerogenic and immunogenic dendritic cell maturation in thymus and periphery. Immunity (2016) 45:305–18. 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.07.019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.George TC, Bilsborough J, Viney JL, Norment AM. High antigen dose and activated dendritic cells enable Th cells to escape regulatory T cell-mediated suppression in vitro. Eur J Immunol. (2003) 33:502–11. 10.1002/immu.200310026 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Gon Y, Asai Y, Hashimoto S, Mizumura K, Jibiki I, Machino T, et al. A20 inhibits toll-like receptor 2- and 4-mediated interleukin-8 synthesis in airway epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2004) 31:330–6. 10.1165/rcmb.2003-0438OC [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Hammer GE, Turer EE, Taylor KE, Fang CJ, Advincula R, Oshima S, et al. Expression of A20 by dendritic cells preserves immune homeostasis and prevents colitis and spondyloarthritis. Nat Immunol. (2011) 12:1184–93. 10.1038/ni.2135 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Kool M, van Loo G, Waelput W, De Prijck S, Muskens F, Sze M, et al. The ubiquitin-editing protein A20 prevents dendritic cell activation, recognition of apoptotic cells, and systemic autoimmunity. Immunity (2011) 35:82–96. 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.05.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Steinman RM. Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature (1998) 392:245–52. 10.1038/32588 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Vremec D. The surface phenotype of dendritic cells purified from mouse thymus and spleen: investigation of the CD8 expression by a subpopulation of dendritic cells. J Exp Med. (1992) 176:47–58. 10.1084/jem.176.1.47 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Merad M, Sathe P, Helft J, Miller J, Mortha A. The dendritic cell lineage: ontogeny and function of dendritic cells and their subsets in the steady state and the inflamed setting. Annu Rev Immunol. (2013) 31:563–604. 10.1146/annurev-immunol-020711-074950 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Mildner A, Jung S. Development and function of dendritic cell subsets. Immunity (2014) 40:642–56. 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.04.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Guilliams M, Dutertre C-A, Scott CL, McGovern N, Sichien D, Chakarov S, et al. Unsupervised high-dimensional analysis aligns dendritic cells across tissues and species. Immunity (2016) 45:669–84. 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.08.015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Granot T, Senda T, Carpenter DJ, Matsuoka N, Weiner J, Gordon CL, et al. Dendritic cells display subset and tissue-specific maturation dynamics over human life. Immunity (2017) 46:504–15. 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.02.019 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Reynolds G, Haniffa M. Human and mouse mononuclear phagocyte networks: a tale of two species? Front Immunol. (2015) 6:330. 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00330 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Breton G, Lee J, Zhou YJ, Schreiber JJ, Keler T, Puhr S, et al. Circulating precursors of human CD1c+ and CD141+ dendritic cells. J Exp Med. (2015) 212:401–13. 10.1084/jem.20141441 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Schlitzer A, Sivakamasundari V, Chen J, Bin Sumatoh HR, Schreuder J, Lum J, et al. Identification of cDC1- and cDC2-committed DC progenitors reveals early lineage priming at the common DC progenitor stage in the bone marrow. Nat Immunol. (2015) 16:1–13. 10.1038/ni.3200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.See P, Dutertre C-A, Chen J, Günther P, McGovern N, Irac SE, et al. Mapping the human DC lineage through the integration of high-dimensional techniques. Science (2017) 66:eaag3009 10.1126/science.aag3009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Heidkamp GF, Sander J, Lehmann CHK, Heger L, Eissing N, Baranska A, et al. Human lymphoid organ dendritic cell identity is predominantly dictated by ontogeny, not tissue microenvironment. Sci Immunol. (2016) 1:eaai7677 10.1126/sciimmunol.aai7677 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Boltjes A, van Wijk F. Human dendritic cell functional specialization in steady-state and inflammation. Front Immunol. (2014) 5:131. 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00131 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Dzionek A, Fuchs A, Schmidt P, Cremer S, Zysk M, Miltenyi S, et al. BDCA-2, BDCA-3, and BDCA-4: three markers for distinct subsets of dendritic cells in human peripheral blood. J Immunol. (2000) 165:6037–46. 10.4049/jimmunol.165.11.6037 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Guilliams M, Ginhoux F, Jakubzick C, Naik SH, Onai N, Schraml BU, et al. Dendritic cells, monocytes and macrophages: a unified nomenclature based on ontogeny. Nat Rev Immunol. (2014) 14:571–8. 10.1038/nri3712 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Robbins SH, Walzer T, Dembélé D, Thibault C, Defays A, Bessou G, et al. Novel insights into the relationships between dendritic cell subsets in human and mouse revealed by genome-wide expression profiling. Genome Biol. (2008) 9:R17. 10.1186/gb-2008-9-1-r17 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Watchmaker PB, Lahl K, Lee M, Baumjohann D, Morton J, Kim SJ, et al. Comparative transcriptional and functional profiling defines conserved programs of intestinal DC differentiation in humans and mice. Nat Immunol. (2013) 15:98–108. 10.1038/ni.2768 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Haniffa M, Shin A, Bigley V, McGovern N, Teo P, See P, et al. Human tissues contain CD141hi cross-presenting dendritic cells with functional homology to mouse CD103+ nonlymphoid dendritic cells. Immunity (2012) 37:60–73. 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.04.012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Proietto AI, Mittag D, Roberts AW, Sprigg N, Wu L. The equivalents of human blood and spleen dendritic cell subtypes can be generated in vitro from human CD34+ stem cells in the presence of fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 ligand and thrombopoietin. Cell Mol Immunol. (2012) 9:446–54. 10.1038/cmi.2012.48 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Lee J, Breton G, Aljoufi A, Zhou YJ, Puhr S, Nussenzweig MC, et al. Clonal analysis of human dendritic cell progenitor using a stromal cell culture. J Immunol Methods (2015) 425:21–6. 10.1016/j.jim.2015.06.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Bachem A, Güttler S, Hartung E, Ebstein F, Schaefer M, Tannert A, et al. Superior antigen cross-presentation and XCR1 expression define human CD11c +CD141 +cells as homologues of mouse CD8 +dendritic cells. J Exp Med. (2010) 207:1273–81. 10.1084/jem.20100348 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Poulin LF, Reyal Y, Uronen-Hansson H, Schraml BU, Sancho D, Murphy KM, et al. DNGR-1 is a specific and universal marker of mouse and human Batf3-dependent dendritic cells in lymphoid and nonlymphoid tissues. Blood (2012) 119:6052–62. 10.1182/blood-2012-01-406967 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Hildner K, Edelson BT, Purtha WE, Diamond M, Matsushita H, Kohyama M, et al. Batf3 deficiency reveals a critical role for CD8alpha+ dendritic cells in cytotoxic T cell immunity. Science (2008) 322:1097–100. 10.1126/science.1164206 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Schiavoni G, Mattei F, Sestili P, Borghi P, Venditti M, Morse HC, III, et al. ICSBP is essential for the development of mouse Type I interferon-producing cells and for the generation and activation of CD8α +Dendritic Cells. J Exp Med. (2002) 196:1415–25. 10.1084/jem.20021263 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Hacker C, Kirsch RD, Ju X-S, Hieronymus T, Gust TC, Kuhl C, et al. Transcriptional profiling identifies Id2 function in dendritic cell development. Nat Immunol. (2003) 4:380–6. 10.1038/ni903 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Kashiwada M, Pham N-LL, Pewe LL, Harty JT, Rothman PB. NFIL3/E4BP4 is a key transcription factor for CD8α? dendritic cell development. Blood (2011) 117:6193–97. 10.1182/blood-2010-07-295873 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Brewitz A, Eickhoff S, Dähling S, Quast T, Bedoui S, Kroczek RA, et al. CD8+ T cells orchestrate pDC-XCR1+ dendritic cell spatial and functional cooperativity to optimize priming. Immunity (2017) 46:205–19. 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.01.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Dai P, Wang W, Yang N, Serna-Tamayo C, Ricca JM, Zamarin D, et al. Intratumoral delivery of inactivated modified vaccinia virus Ankara (iMVA) induces systemic antitumor immunity via STING and Batf3-dependent dendritic cells. Sci Immunol. (2017) 2:eaal1713. 10.1126/sciimmunol.aal1713 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Broz ML, Binnewies M, Boldajipour B, Nelson AE, Pollack JL, Erle DJ, et al. Dissecting the tumor myeloid compartment reveals rare activating antigen-presenting cells critical for T cell immunity. Cancer Cell (2014) 26:638–52. 10.1016/j.ccell.2014.09.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Roberts EW, Broz ML, Binnewies M, Headley MB, Nelson AE, Wolf DM, et al. Critical Role for CD103+/CD141+ Dendritic Cells Bearing CCR7 for Tumor Antigen Trafficking and Priming of T Cell Immunity in Melanoma. Cancer Cell (2016) 30:324–36. 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.06.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Schlitzer A, McGovern N, Teo P, Zelante T, Atarashi K, Low D, et al. IRF4 Transcription factor-dependent CD11b+ dendritic cells in human and mouse control mucosal IL-17 cytokine responses. Immunity (2013) 38:970–83. 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.04.011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Guerriero A, Langmuir PB, Spain LM, Scott EW. PU.1 is required for myeloid-derived but not lymphoid-derived dendritic cells. Blood (2000) 95:879–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Wu L, D'Amico A, Winkel KD, Suter M, Lo D, Shortman K. RelB is essential for the development of myeloid-related CD8alpha- dendritic cells but not of lymphoid-related CD8alpha+ dendritic cells. Immunity (1998) 9:839–47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Caton ML, Smith-Raska MR, Reizis B. Notch–RBP-J signaling controls the homeostasis of CD8 –dendritic cells in the spleen. J Exp Med. (2007) 204:1653–64. 10.1084/jem.20062648 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Hambleton S, Salem S, Bustamante J, Bigley V, Boisson-Dupuis S, Azevedo J, et al. IRF8 mutations and human dendritic-cell immunodeficiency. N Engl J Med. (2011) 365:127–38. 10.1056/NEJMoa1100066 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Segura E, Valladeau-Guilemond J, Donnadieu M-H, Sastre-Garau X, Soumelis V, Amigorena S. Characterization of resident and migratory dendritic cells in human lymph nodes. J Exp Med. (2012) 209:653–60. 10.1084/jem.20111457 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Leal Rojas IM, Mok WH, Pearson FE, Minoda Y, Kenna TJ, Barnard RT, et al. Human blood CD1c+ dendritic cells promote Th1 and Th17 effector function in memory CD4+ T Cells. Front Immunol. (2017) 8:563–11. 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00971 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Villani A-C, Satija R, Reynolds G, Sarkizova S, Shekhar K, Fletcher J, et al. Single-cell RNA-seq reveals new types of human blood dendritic cells, monocytes, and progenitors. Science (2017) 356:eaah4573–14. 10.1126/science.aah4573 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Bamboat ZM, Stableford JA, Plitas G, Burt BM, Nguyen HM, Welles AP, et al. Human Liver Dendritic Cells Promote T Cell Hyporesponsiveness. J Immunol. (2009) 182:1901–11. 10.4049/jimmunol.0803404 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Sato T, Kitawaki T, Fujita H, Iwata M, Iyoda T, Inaba K, et al. Human CD1c+ myeloid dendritic cells acquire a high level of retinoic acid-producing capacity in response to vitamin D3. J Immunol. (2013) 191:3152–60. 10.4049/jimmunol.1203517 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Reizis B, Bunin A, Ghosh HS, Lewis KL, Sisirak V. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells: recent progress and open questions. Annu Rev Immunol. (2011) 29:163–83. 10.1146/annurev-immunol-031210-101345 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Swiecki M, Colonna M. The multifaceted biology of plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Nat Rev Immunol. (2015) 15:471–85. 10.1038/nri3865 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Evans VA, Lal L, Akkina R, Solomon A, Wright E, Lewin SR, et al. Thymic plasmacytoid dendritic cells are susceptible to productive HIV-1 infection and efficiently transfer R5 HIV-1 to thymocytes in vitro. Retrovirology (2011) 8:43. 10.1186/1742-4690-8-43 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Loures FV, Röhm M, Lee CK, Santos E, Wang JP, Specht CA, et al. Recognition of Aspergillus fumigatus hyphae by human plasmacytoid dendritic cells is mediated by dectin-2 and results in formation of extracellular traps. PLoS Pathog. (2015) 11:e1004643–23. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004643 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Matsui T, Connolly JE, Michnevitz M, Chaussabel D, Yu CI, Glaser C, et al. CD2 distinguishes two subsets of human plasmacytoid dendritic cells with distinct phenotype and functions. J Immunol. (2009) 182:6815–23. 10.4049/jimmunol.0802008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Cella M, Facchetti F, Lanzavecchia A, Colonna M. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells activated by influenza virus and CD40L drive a potent TH1 polarization. Nat Immunol. (2000) 1:305–10. 10.1038/79747 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Hoeffel G, Ripoche A-C, Matheoud D, Nascimbeni M, Escriou N, Lebon P, et al. Antigen crosspresentation by human plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Immunity (2007) 27:481–92. 10.1016/j.immuni.2007.07.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Krug A, Towarowski A, Britsch S, Rothenfusser S, Hornung V, Bals R, et al. Toll-like receptor expression reveals CpG DNA as a unique microbial stimulus for plasmacytoid dendritic cells which synergizes with CD40 ligand to induce high amounts of IL-12. Eur J Immunol. (2001) 31:3026–37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Caux C, Dezutter-Dambuyant C, Schmitt D. GM-CSF and TNF- cooperate in the generation of dendritic Langerhans cells. Nature (1992) 360:258–61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Sallusto F, Lanzavecchia A. Efficient presentation of soluble antigen by cultured human dendritic cells is maintained by granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor plus interleukin 4 and downregulated by tumor necrosis factor alpha. J Exp Med. (1994) 179:1109–18. 10.1084/jem.179.4.1109 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Lehtonen A, Veckman V, Nikula T, Lahesmaa R, Kinnunen L, Matikainen S, et al. Differential expression of IFN regulatory factor 4 gene in human monocyte-derived dendritic cells and macrophages. J Immunol. (2005) 175:6570–9. 10.4049/jimmunol.175.10.6570 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Inaba K, Inaba M, Romani N, Aya H, Deguchi M, Ikehara S, et al. Generation of large numbers of dendritic cells from mouse bone marrow cultures supplemented with granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Exp Med. (1992) 176:1693–702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Helft J, Böttcher J, Chakravarty P, Zelenay S, Huotari J, Schraml BU, et al. GM-CSF mouse bone marrow cultures comprise a heterogeneous population of CD11c(+)MHCII(+) macrophages and dendritic cells. Immunity (2015) 42:1197–211. 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.05.018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Guilliams M, Malissen B. A death notice for in-vitro-Generated GM-CSF dendritic cells? Immunity (2015) 42:988–90. 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.05.020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Lutz MB, Inaba K, Schuler G, Romani N. Still alive and kicking: in-vitro-generated GM-CSF dendritic cells! Immunity (2016) 44:1–2. 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.12.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Helft J, Böttcher JP, Chakravarty P, Zelenay S, Huotari J, Schraml BU, et al. Alive but confused: heterogeneity of CD11c+ MHC class II+ cells in GM-CSF mouse bone marrow cultures. Immunity (2016) 44:3–4. 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.12.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Serbina NV, Salazar-Mather TP, Biron CA, Kuziel WA, Pamer EG. TNF/iNOS-producing dendritic cells mediate innate immune defense against bacterial infection. Immunity (2003) 19:59–70. 10.1016/S1074-7613(03)00171-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Wollenberg A, Kraft S, Hanau D, Bieber T. Immunomorphological and ultrastructural characterization of langerhans cells and a novel, inflammatory dendritic epidermal cell (IDEC) population in lesional skin of atopic eczema. J Invest Dermatol. (1996) 106:446–53. 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12343596 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Segura E, Touzot M, Bohineust A, Cappuccio A, Chiocchia G, Hosmalin A, et al. Human inflammatory dendritic cells induce Th17 cell differentiation. Immunity (2013) 38:336–48. 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.10.018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Quail DF, Joyce JA. Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat Med. (2013) 19:1423–37. 10.1038/nm.3394 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Brosseau JP, Lucier JF, Nwilati H, Thibault P, Garneau D, Gendron D, et al. Tumor microenvironment-associated modifications of alternative splicing. RNA (2014) 20:189–201. 10.1261/rna.042168.113 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Bingle L, Brown NJ, Lewis CE. The role of tumour-associated macrophages in tumour progression: implications for new anticancer therapies. J Pathol. (2002) 196:254–65. 10.1002/path.1027 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Nagaraj S, Gabrilovich DI. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in human cancer. Cancer J. (2010) 16:348–53. 10.1097/PPO.0b013e3181eb3358 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Ichihara F, Kono K, Takahashi A, Kawaida H, Sugai H, Fujii H. Increased populations of regulatory T cells in peripheral blood and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in patients with gastric and esophageal cancers. Clin Cancer Res. (2003) 9:4404–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of Cancer: the next generation. Cell (2011) 144:646–74. 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.McAllister SS, Weinberg RA. The tumour-induced systemic environment as a critical regulator of cancer progression and metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. (2014) 16:717–27. 10.1038/ncb3015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Alvarez KLF, Beldi M, Sarmanho F, Rossetti RAM, Silveira CRF, Mota GR, et al. Local and systemic immunomodulatory mechanisms triggered by Human Papillomavirus transformed cells: a potential role for G-CSF and neutrophils. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:1–16. 10.1038/s41598-017-09079-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Ramos RN, Chin LS, Santos Dos APSA, Bergami-Santos PC, Laginha F, Barbuto JAM. Monocyte-derived dendritic cells from breast cancer patients are biased to induce CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells. J Leukoc Biol. (2012) 92:673–82. 10.1189/jlb.0112048 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Toniolo PA, Liu S, Yeh JE, Ye DQ, Barbuto JAM, Frank DA. Deregulation of SOCS5 suppresses dendritic cell function in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Oncotarget (2016) 7:46301–14. 10.18632/oncotarget.10093 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Brown S, Hutchinson CV, Aspinall-O'Dea M, Whetton AD, Johnson SM, Rees-Unwin K, et al. Monocyte-derived dendritic cells from chronic myeloid leukaemia have abnormal maturation and cytoskeletal function that is associated with defective localisation and signalling by normal ABL1 protein. Eur J Haematol. (2014) 93:96–102. 10.1111/ejh.12306 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Orsini G, Legitimo A, Failli A, Ferrari P, Nicolini A, Spisni R, et al. Defective generation and maturation of dendritic cells from monocytes in colorectal cancer patients during the course of disease. IJMS (2013) 14:22022–41. 10.3390/ijms141122022 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Lopes A, Michelin MR, Murta E. Monocyte-derived dendritic cells from patients with cervical intraepithelial lesions. Oncol Lett. (2017) 13:1456–62. 10.3892/ol.2017.5595 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Kiertscher SM, Luo J, Dubinett SM, Roth MD. Tumors promote altered maturation and early apoptosis of monocyte-derived dendritic cells. J Immunol. (2000) 164:1269–76. 10.4049/jimmunol.164.3.1269 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Clavijo-Salomon MA, Ramos RN, Crippa A, Pizzo CR, Bergami-Santos PC, Barbuto JAM. Monocyte-derived dendritic cells reflect the immune functional status of a chromophobe renal cell carcinoma patient: could it be a general phenomenon? Cancer Immunol Immunother (2015) 64:161–71. 10.1007/s00262-014-1625-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Lago MT-D, Jukemura J, Machado MCC, Da Cunha JEM, Barbuto JAM. Phagocytosis and production of H2O2 by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with obstructive jaundice. Pancreatology (2006) 6:273–8. 10.1159/000092688 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Clavijo-Salomon MA, Bergami-Santos PC, M Barbuto JA. Immunomonitoring reveals interruption of anergy after vaccination in a case of type-2-papillary renal cell carcinoma. Immunotherapy (2017) 9:319–29. 10.2217/imt-2016-0145 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Failli A, Legitimo A, Orsini G, Romanini A, Consolini R. Numerical defect of circulating dendritic cell subsets and defective dendritic cell generation from monocytes of patients with advanced melanoma. Cancer Lett. (2013) 337:1–9. 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.05.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Orsini E, Guarini A, Chiaretti S, Mauro FR, Foa R. The circulating dendritic cell compartment in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia is severely defective and unable to stimulate an effective T-cell response. Cancer Res. (2003) 63:4497–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Verronèse E, Delgado A, Valladeau-Guilemond J, Garin G, Guillemaut S, Tredan O, et al. Immune cell dysfunctions in breast cancer patients detected through whole blood multi- parametric flow cytometry assay. OncoImmunology (2016) 5:1–15. 10.1080/2162402X.2015.1100791 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Li R, Fang F, Jiang M, Wang C, Ma J, Kang W, et al. STAT3 and NF-κB are simultaneously suppressed in dendritic cells in lung cancer. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:1–11. 10.1038/srep45395 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Fayad L, Keating MJ, Reuben JM, O'Brien S, Lee BN, Lerner S, et al. Interleukin-6 and interleukin-10 levels in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: correlation with phenotypic characteristics and outcome. Blood (2001) 97:256–63. 10.1182/blood.V97.1.256 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Park SJ, Nakagawa T, Kitamura H, Atsumi T, Kamon H, Sawa SI, et al. IL-6 Regulates in vivo dendritic cell differentiation through STAT3 activation. J Immunol. (2004) 173:3844–54. 10.4049/jimmunol.173.6.3844 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Ohno Y, Kitamura H, Takahashi N, Ohtake J, Kaneumi S, Sumida K, et al. IL-6 down-regulates HLA class II expression and IL-12 production of human dendritic cells to impair activation of antigen-specific CD4+ T cells. Cancer Immunol. Immunother (2016) 65:1–12. 10.1007/s00262-015-1791-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Kitamura H, Ohno Y, Toyoshima Y, Ohtake J, Homma S, Kawamura H, et al. Interleukin-6/STAT3 signaling as a promising target to improve the efficacy of cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Sci. (2017) 108:1947–52. 10.1111/cas.13332 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Niemand C, Nimmesgern A, Haan S, Fischer P, Schaper F, Rossaint R, et al. Activation of STAT3 by IL-6 and IL-10 in primary human macrophages is differentially modulated by suppressor of cytokine signaling 3. J Immunol. (2003) 170:3263–72. 10.4049/jimmunol.170.6.3263 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 210.Coley WB. The Treatment of inoperable sarcoma by bacterial toxins (the mixed toxins of the Streptococcus erysipelas and the Bacillus prodigiosus). Proc R Soc Med. (1910) 3:1–48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211.Bernardes N, Seruca R, Chakrabarty AM, Fialho AM. Microbial-based therapy of cancer: current progress and future prospects. Bioeng. Bugs (2010) 1:178–90. 10.4161/bbug.1.3.10903 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212.Adams S. Toll-like receptor agonists in cancer therapy. Immunotherapy (2009) 1:949–64. 10.2217/imt.09.70 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 213.Burns EM, Yusuf N. Toll-like receptors and skin cancer. Front Immunol. (2014) 5:135. 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00135 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 214.Tanaka H, Demeure CE, Rubio M, Delespesse G, Sarfati M. Human monocyte-derived dendritic cells induce naive T cell differentiation into T helper cell type 2 (Th2) or Th1/Th2 effectors. Role of stimulator/responder ratio. J Exp Med. (2000) 192:405–12. 10.1084/jem.192.3.405 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 215.Dhodapkar MV, Steinman RM, Sapp M, Desai H, Fossella C, Krasovsky J, et al. Rapid generation of broad T-cell immunity in humans after a single injection of mature dendritic cells. J Clin Invest. (1999) 104:173–80. 10.1172/JCI6909 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 216.Thurner B, Haendle I, Röder C, Dieckmann D, Keikavoussi P, Jonuleit H, et al. Vaccination with mage-3A1 peptide-pulsed mature, monocyte-derived dendritic cells expands specific cytotoxic T cells and induces regression of some metastases in advanced stage IV melanoma. J Exp Med. (1999) 190:1669–78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 217.Soruri A, Zwirner J. Dendritic cells: limited potential in immunotherapy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. (2005) 37:241–5. 10.1016/j.biocel.2004.07.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 218.Kuhn S, Hyde EJ, Yang J, Rich FJ, Harper JL, Kirman JR, et al. Increased numbers of monocyte-derived dendritic cells during successful tumor immunotherapy with immune-activating agents. J Immunol. (2013) 191:1984–92. 10.4049/jimmunol.1301135 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 219.Kuhn S, Yang J, Ronchese F. Monocyte-derived dendritic cells are essential for CD8(+) T cell activation and antitumor responses after local immunotherapy. Front Immunol. (2015) 6:584. 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00584 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 220.Mohty M, Vialle-Castellano A, Nunes JA, Isnardon D, Olive D, Gaugler B. IFN-alpha skews monocyte differentiation into Toll-like receptor 7-expressing dendritic cells with potent functional activities. J Immunol. (2003) 171:3385–93. 10.4049/jimmunol.171.7.3385 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 221.Farkas A, Kemény L. Interferon-α in the generation of monocyte-derived dendritic cells: recent advances and implications for dermatology. Br J Dermatol. (2011) 165:247–54. 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2011.10301.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 222.Harris KM. Monocytes differentiated with GM-CSF and IL-15 initiate Th17 and Th1 responses that are contact-dependent and mediated by IL-15. J Leukoc Biol. (2011) 90:727–34. 10.1189/jlb.0311132 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 223.Dauer M, Obermaier B, Herten J, Haerle C, Pohl K, Rothenfusser S, et al. Mature dendritic cells derived from human monocytes within 48 hours: a novel strategy for dendritic cell differentiation from blood precursors. J Immunol (2003) 170:4069–76. 10.4049/jimmunol.170.8.4069 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 224.Dauer M, Schad K, Herten J, Junkmann J, Bauer C, Kiefl R, et al. FastDC derived from human monocytes within 48 h effectively prime tumor antigen-specific cytotoxic T cells. J Immunol Methods (2005) 302:145–55. 10.1016/j.jim.2005.05.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 225.Sundarasetty BS, Singh VK, Salguero G, Geffers R, Rickmann M, Macke L, et al. Lentivirus-induced dendritic cells for immunization against high-risk WT1(+) acute myeloid leukemia. Hum Gene Ther. (2013) 24:220–37. 10.1089/hum.2012.128 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 226.Anassi E, Ndefo UA. Sipuleucel-T (provenge) injection: the first immunotherapy agent (vaccine) for hormone-refractory prostate cancer. PT (2011) 36:197–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 227.Sims RB. Development of sipuleucel-T: autologous cellular immunotherapy for the treatment of metastatic castrate resistant prostate cancer. Vaccine (2012) 30:4394–7. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.11.058 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 228.Castiello L, Sabatino M, Jin P, Clayberger C, Marincola FM, Krensky AM, et al. Monocyte-derived DC maturation strategies and related pathways: a transcriptional view. Cancer Immunol Immunother (2011) 60:457–66. 10.1007/s00262-010-0954-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 229.Menges M, Rößner S, Voigtländer C, Schindler H, Kukutsch NA, Bogdan C, et al. Repetitive injections of dendritic cells matured with tumor necrosis factor alpha induce antigen-specific protection of mice from autoimmunity. J Exp Med. (2002) 195:15–21. 10.1084/jem.20011341 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 230.Napolitani G, Rinaldi A, Bertoni F, Sallusto F, Lanzavecchia A. Selected Toll-like receptor agonist combinations synergistically trigger a T helper type 1-polarizing program in dendritic cells. Nat Immunol. (2005) 6:769–76. 10.1038/ni1223 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 231.Vopenkova K, Mollova K, Buresova I, Michalek J. Complex evaluation of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells for cancer immunotherapy. J Cell Mol Med. (2012) 16:2827–37. 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2012.01614.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 232.Coulie PG, Van den Eynde BJ, van der Bruggen P, Boon T. Tumour antigens recognized by T lymphocytes: at the core of cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer (2014) 14:135–46. 10.1038/nrc3670 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 233.Brossart P, Wirths S, Stuhler G, Reichardt VL, Kanz L, Brugger W. Induction of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses in vivo after vaccinations with peptide-pulsed dendritic cells. Blood (2000) 96:3102–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 234.Jenne L, Schuler G, Steinkasserer A. Viral vectors for dendritic cell-based immunotherapy. Trends Immunol. (2001) 22:102–7. 10.1016/S1471-4906(00)01813-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 235.Slingluff CL. The present and future of peptide vaccines for cancer: single or multiple, long or short, alone or in combination? Cancer J. (2011) 17:343–50. 10.1097/PPO.0b013e318233e5b2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 236.Mosca PJ, Clay TM, Morse MA, Lyerly HK. Dendritic cell vaccines. Front Biosci. (2007) 12:4050–60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 237.Fry TJ, Shand JL, Milliron M, Tasian SK, Mackall CL. Antigen loading of DCs with irradiated apoptotic tumor cells induces improved anti-tumor immunity compared to other approaches. Cancer Immunol Immunother (2009) 58:1257–64. 10.1007/s00262-008-0638-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 238.Kalinski P, Urban J, Narang R, Berk E, Wieckowski E, Muthuswamy R. Dendritic cell-based therapeutic cancer vaccines: what we have and what we need. Future Oncol. (2009) 5:379–90. 10.2217/fon.09.6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 239.Barbuto JAM. Are dysfunctional monocyte-derived dendritic cells in cancer an explanation for cancer vaccine failures? Immunotherapy (2013) 5:105–7. 10.2217/imt.12.153 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 240.Pinho MP, Sundarasetty BS, Bergami-Santos PC, Steponavicius-Cruz K, Ferreira AK, Stripecke R, et al. Dendritic-tumor cell hybrids induce tumor-specific immune responses more effectively than the simple mixture of dendritic and tumor cells. Cytotherapy (2016) 18:570–80. 10.1016/j.jcyt.2016.01.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 241.Barbuto JAM, Ensina LFC, Neves AR, Bergami-Santos P, Leite KRM, Marques R, et al. Dendritic cell-tumor cell hybrid vaccination for metastatic cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother (2004) 53:1111–8. 10.1007/s00262-004-0551-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 242.Tacken PJ, de Vries IJM, Torensma R, Figdor CG. Dendritic-cell immunotherapy: from ex vivo loading to in vivo targeting. Nat Rev Immunol. (2007) 7:790–802. 10.1038/nri2173 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 243.van Dinther D, Stolk DA, van de Ven R, van Kooyk Y, de Gruijl TD, Haan den JMM. Targeting C-type lectin receptors: a high-carbohydrate diet for dendritic cells to improve cancer vaccines. J Leukoc Biol. (2017) 102:1017–34. 10.1189/jlb.5MR0217-059RR [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 244.Caminschi I, Maraskovsky E, Heath WR. Targeting Dendritic Cells in vivo for cancer therapy. Front Immunol. (2012) 3:13. 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 245.Macri C, Dumont C, Johnston AP, Mintern JD. Targeting dendritic cells: a promising strategy to improve vaccine effectiveness. Clin Trans Immunol. (2016) 5:e66. 10.1038/cti.2016.6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 246.Mahnke K, Qian Y, Fondel S, Brueck J, Becker C, Enk AH. Targeting of antigens to activated dendritic cells in vivo cures metastatic melanoma in mice. Cancer Res. (2005) 65:7007–12. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-0938 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 247.Tullett KM, Leal Rojas IM, Minoda Y, Tan PS, Zhang J-G, Smith C, et al. Targeting CLEC9A delivers antigen to human CD141+ DC for CD4+ and CD8+T cell recognition. JCI Insight (2016) 1:e87102. 10.1172/jci.insight.87102 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 248.Toniolo PA, Liu S, Yeh JE, Moraes-Vieira PM, Walker SR, Vafaizadeh V, et al. Inhibiting STAT5 by the BET bromodomain inhibitor JQ1 disrupts human dendritic cell maturation. J Immunol. (2015) 194:3180–90. 10.4049/jimmunol.1401635 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 249.Silva-Cardoso SC, Affandi AJ, Spel L, Cossu M, van Roon JAG, Boes M, et al. CXCL4 Exposure Potentiates TLR-Driven polarization of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells and increases stimulation of T Cells. J Immunol. (2017) 199:253–62. 10.4049/jimmunol.1602020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 250.Dijkgraaf EM, Santegoets SJAM, Reyners AKL, Goedemans R, Wouters MCA, Kenter GG, et al. A phase I trial combining carboplatin/doxorubicin with tocilizumab, an anti-IL-6R monoclonal antibody, and interferon-α2b in patients with recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer. Ann Oncol. (2015) 26:2141–9. 10.1093/annonc/mdv309 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 251.Mailliard RB, Wankowicz-Kalinska A, Cai Q, Wesa A, Hilkens CM, Kapsenberg ML, et al. alpha-type-1 polarized dendritic cells: a novel immunization tool with optimized CTL-inducing activity. Cancer Res. (2004) 64:5934–7. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1261 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 252.Okada H, Kalinski P, Ueda R, Hoji A, Kohanbash G, Donegan TE, et al. Induction of CD8+ T-cell responses against novel glioma-associated antigen peptides and clinical activity by vaccinations with {alpha}-type 1 polarized dendritic cells and polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid stabilized by lysine and carboxymethylcellulose in patients with recurrent malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol. (2011) 29:330–6. 10.1200/JCO.2010.30.7744 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 253.Sakamoto C, Kohara H, Inoue H, Narusawa M, Ogawa Y, Hirose-Yotsuya L, et al. Therapeutic vaccination based on side population cells transduced by the granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor gene elicits potent antitumor immunity. Cancer Gene Ther. (2017) 24:165–74. 10.1038/cgt.2016.80 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 254.Fu J, Kanne DB, Leong M, Glickman LH, McWhirter SM, Lemmens E, et al. STING agonist formulated cancer vaccines can cure established tumors resistant to PD-1 blockade. Sci Transl Med. (2015) 7:283ra52. 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaa4306 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 255.Gonzalez-Gugel E, Saxena M, Bhardwaj N. Modulation of innate immunity in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Immunol Immunother (2016) 65:1261–8. 10.1007/s00262-016-1859-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 256.Oleszycka E, Lavelle EC. Immunomodulatory properties of the vaccine adjuvant alum. Curr Opin Immunol. (2014) 28:1–5. 10.1016/j.coi.2013.12.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 257.van Doorn E, Liu H, Huckriede A, Hak E. Safety and tolerability evaluation of the use of Montanide ISA™51 as vaccine adjuvant: a systematic review. Hum Vaccin Immunotherapeut. (2016) 12:159–69. 10.1080/21645515.2015.1071455 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 258.Saxena M, Bhardwaj N. ScienceDirect Turbocharging vaccines: emerging adjuvants for dendritic cell based therapeutic cancer vaccines. Curr Opin Immunol. (2017) 47:35–43. 10.1016/j.coi.2017.06.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 259.Yarchoan M, Johnson BA, Lutz ER, Laheru DA, Jaffee EM. Targeting neoantigens to augment antitumour immunity. Nat Rev Cancer (2017) 17:209–222. 10.1038/nrc.2016.154 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 260.Ott PA, Hu Z, Keskin DB, Shukla SA, Sun J, Bozym DJ, et al. An immunogenic personal neoantigen vaccine for patients with melanoma. Nature Publish. Group (2017) 547:217–21. 10.1038/nature22991 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 261.Kranz LM, Diken M, Haas H, Kreiter S, Loquai C, Reuter KC, et al. Systemic RNA delivery to dendritic cells exploits antiviral defence for cancer immunotherapy. Nature (2016) 534:1–16. 10.1038/nature18300 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 262.Marzbani E, Inatsuka C, Lu H, Disis ML. The invisible arm of immunity in common cancer chemoprevention agents. Cancer Prev Res. (2013) 6:764–73. 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-13-0036 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 263.Fecek RJ, Storkus WJ. Combination strategies to enhance the potency of monocyte-derived dendritic cell-based cancer vaccines. Immunotherapy (2016) 8:1205–18. 10.2217/imt-2016-0071 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 264.Ouyang M, White EE, Ren H, Guo Q, Zhang I, Gao H, et al. Metronomic doses of temozolomide enhance the efficacy of carbon nanotube CpG immunotherapy in an invasive glioma model. PLoS ONE (2016) 11:e0148139. 10.1371/journal.pone.0148139 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 265.Noguchi M, Moriya F, Koga N, Matsueda S, Sasada T, Yamada A, et al. A randomized phase II clinical trial of personalized peptide vaccination with metronomic low-dose cyclophosphamide in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother (2016) 65:151–60. 10.1007/s00262-015-1781-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 266.Tseng C-W, Hung C-F, Alvarez RD, Trimble C, Huh WK, Kim D, et al. Pretreatment with cisplatin enhances E7-specific CD8+ T-Cell-mediated antitumor immunity induced by DNA vaccination. Clin Cancer Res. (2008) 14:3185–92. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0037 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 267.Shen J, Wang L-F, Zou Z-Y, Kong W-W, Yan J, Meng F-Y, et al. Phase I clinical study of personalized peptide vaccination combined with radiotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. (2017) 23:5395–404. 10.3748/wjg.v23.i29.5395 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 268.Gulley JL, Arlen PM, Bastian A, Morin S, Marte J, Beetham P, et al. Combining a recombinant cancer vaccine with standard definitive radiotherapy in patients with localized prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. (2005) 11:3353–62. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-2062 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 269.Brody JD, Ai WZ, Czerwinski DK, Torchia JA, Levy M, Advani RH, et al. In situ vaccination with a TLR9 agonist induces systemic lymphoma regression: a phase I/II study. J Clin Oncol. (2010) 28:4324–32. 10.1200/JCO.2010.28.9793 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 270.Inogés S, Tejada S, de Cerio AL-D, Gállego Pérez-Larraya J, Espinós J, Idoate MA, et al. A phase II trial of autologous dendritic cell vaccination and radiochemotherapy following fluorescence-guided surgery in newly diagnosed glioblastoma patients. J Transl Med. (2017) 15:104. 10.1186/s12967-017-1202-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 271.Loi M, Desideri I, Greto D, Mangoni M, Sottili M, Meattini I, et al. Radiotherapy in the age of cancer immunology: Current concepts and future developments. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. (2017) 112:1–10. 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2017.02.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 272.Raval RR, Sharabi AB, Walker AJ, Drake CG, Sharma P. Tumor immunology and cancer immunotherapy: summary of the 2013 SITC primer. J Immunother Cancer (2014) 2:14. 10.1186/2051-1426-2-14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 273.Son C-H, Bae J-H, Shin D-Y, Lee H-R, Choi Y-J, Jo W-S. CTLA-4 blockade enhances antitumor immunity of intratumoral injection of immature dendritic cells into irradiated tumor in a mouse colon cancer model. J Immunother (2014) 37:1–7. 10.1097/CJI.0000000000000007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 274.Ribas A, Comin-Anduix B, Chmielowski B, Jalil J, la Rocha de P, McCannel TA, et al. Dendritic cell vaccination combined with CTLA4 blockade in patients with metastatic melanoma. Clin Cancer Res. (2009) 15:6267–76. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1254 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 275.Freeman GJ, Long AJ, Iwai Y, Bourque K, Chernova T, Nishimura H, et al. Engagement of the PD-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a novel B7 family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte activation. J Exp Med. (2000) 192:1027–34. 10.1084/jem.192.7.1027 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 276.Latchman Y, Wood CR, Chernova T, Chaudhary D, Borde M, Chernova I, et al. PD-L2 is a second ligand for PD-1 and inhibits T cell activation. Nat Immunol. (2001) 2:261–8. 10.1038/85330 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 277.Munn DH, Mellor AL. Indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase and metabolic control of immune responses. Trends Immunol. (2013) 34:137–43. 10.1016/j.it.2012.10.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 278.Grohmann U, Fallarino F, Bianchi R, Orabona C, Vacca C, Fioretti MC, et al. A Defect in tryptophan catabolism impairs tolerance in nonobese diabetic mice. J Exp Med. (2003) 198:153–60. 10.1084/jem.20030633 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 279.Baban B, Chandler PR, Johnson BA, Huang L, Li M, Sharpe ML, et al. Physiologic Control of IDO Competence in Splenic Dendritic Cells. J Immunol. (2011) 187:2329–35. 10.4049/jimmunol.1100276 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 280.Liu X, Shin N, Koblish HK, Yang G, Wang Q, Wang K, et al. Selective inhibition of IDO1 effectively regulates mediators of antitumor immunity. Blood (2010) 115:3520–30. 10.1182/blood-2009-09-246124 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 281.Lowe DB, Bose A, Taylor JL, Tawbi H, Lin Y, Kirkwood JM, et al. Dasatinib promotes the expansion of a therapeutically superior T-cell repertoire in response to dendritic cell vaccination against melanoma. OncoImmunology (2014) 3:e27589. 10.4161/onci.27589 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 282.Bronte V, Zanovello P. Regulation of immune responses by L-arginine metabolism. Nature Rev Immunol. (2005) 5:641–654. 10.1038/nri1668 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]