Abstract
Cellular senescence is a typical tumor‐suppressive mechanism that restricts the proliferation of premalignant cells. However, mounting evidence suggests that senescent cells, which also persist in vivo, can promote the incidence of aging‐related disorders principally via the senescence‐associated secretory phenotype (SASP), among which cancer is particularly devastating. Despite the beneficial effects of the SASP on certain physiological events such as wound healing and tissue repair, more studies have demonstrated that senescent cells can substantially contribute to pathological conditions and accelerate disease exacerbation, particularly cancer resistance, relapse and metastasis. To limit the detrimental properties while retaining the beneficial aspects of senescent cells, research advancements that support screening, design and optimization of anti‐aging therapeutic agents are in rapid progress in the setting of prospective development of clinical strategies, which together represent a new wave of efforts to control human malignancies or mitigate degenerative complications.
Keywords: aging‐related diseases, cancer, cellular senescence, clinical trial, senescence‐associated secretory phenotype, senolytics
1.
In response to various intrinsic and/or extrinsic stimuli, cells enter an essentially irreversible senescent state, which is regulated and maintained by the p53/p21CIP1 and p16INK4a/pRB pathways to prevent the occurrence of sporadic events, particularly transformation. Senescent cells display several distinct features including a flattened and enlarged morphology, DNA segments with chromatin alterations reinforcing senescence (DNA SCARS), nuclear heterochromatin foci and senescence‐associated β‐galactosidase (SA‐β‐Gal) activity (Ozcan et al., 2016). However, senescent cells are frequently implicated in multiple disorders, mainly through secretion of numerous bioactive molecules, a distinctive phenomenon found a decade ago and termed as the senescence‐associated secretory phenotype (SASP; Acosta et al., 2008; Coppe et al., 2008; Kuilman et al., 2008). The full SASP spectrum comprises a myriad of soluble factors including pro‐inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, growth factors and proteases, whose functional involvement can be classified into several aspects including but not limited to extracellular matrix formation, metabolic processes, ox‐redox events and gene expression regulation (Ozcan et al., 2016). The SASP promotes embryonic development, tissue repair and wound healing, serving as an evolutionarily adapted mechanism in maintaining tissue and/or organ homeostasis (Davaapil, Brockes, & Yun, 2017; Demaria et al., 2014; Jun & Lau, 2010; Munoz‐Espin et al., 2013; Storer et al., 2013). Senescent cells communicate with their surrounding environment by expressing the SASP, with the potential to boost immune surveillance by mounting specific inflammatory responses including those mediated by CD4+ T cells against antigens expressed in senescent cells, particularly those observed in premalignant lesions (Georgilis et al., 2018; Kang et al., 2011; Toso et al., 2014). Although the SASP is beneficial to several health‐associated events, more evidence has showed that it actively contributes to the formation of a pro‐carcinogenic tumor microenvironment (TME). Long‐term secretion of the SASP factors by senescent cells can impair the functional integrity of adjacent normal cells in the local tissue, serving as a major cause of chronic inflammation which drives aging‐related degeneration of multiple organs (He & Sharpless, 2017). Thus, senescent cells and their unique phenotype, the SASP, can be defined as a form of antagonistic pleiotropy, a property that is beneficial in early life and during tissue turnover, but deleterious over time with advanced age, making both mechanistic investigation and therapeutic intervention of paramount significance in current era of precision medicine.
As the SASP can generate contrasting pathophysiological consequences, substantial interest has been sparked in recent years to achieve an accurate and thorough understanding of this cell‐non‐autonomous phenotype. In cancer patients, the most frequently observed formats of cellular senescence encompass oncogene‐induced senescence (OIS) and therapy‐induced senescence (TIS) (Sieben, Sturmlechner, Sluis, & Deursen, 2018) (Figure 1). Indeed, both modalities are initially tumor suppressive, but later tend to manifest a pro‐tumorigenic capacity by substantially activating the DNA damage response (DDR), which once perceived irreparable by the damaged cells can potently induce the SASP (Rodier et al., 2011). It is now clear that regulation of the initiation and development of the SASP involves multiple signaling pathways, including those mediated by p38MAPK, Jak2/Stat3, the inflammasome, mTOR, GATA4, macroH2A1, ATM and mitochondrial sirtuins (Ito, Hoare, & Narita, 2017). Although some SASP effectors appear to act post transcriptionally, most SASP regulators converge on two transcription factors, NF‐кB and C/EBPβ, which co‐regulate many SASP components (Di Mitri & Alimonti, 2016). Furthermore, some interleukins (ILs) are encoded by the SASP but can reciprocally modulate the SASP by feedback mechanisms, such as IL6, IL‐8 and IL‐1α (Di Mitri & Alimonti, 2016). Although activation of DNA damage response (DDR) is essential for the induction and maintenance of senescence (Rodier et al., 2009, 2011 ), the precise regulatory mechanism directly linking the DDR events to the SASP development remains largely unclear until emergence of recent data, which revealed the implication of a cGAS‐STING (cGMP‐AMP synthase‐stimulator of interferon genes) pathway. Briefly, cGAS is a highly conserved cytosolic DNA sensor, which can be activated once bound by double‐stranded DNA released from genome instability‐induced micronuclei, a process that engages a second messenger cGMP‐AMP (cGAMP), which subsequently triggers the adaptor protein STING to recruit TANK‐binding kinase 1 (TBK1) and IκB kinase to activate IFN regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) and NF‐κB, respectively, causing the production of type I interferons and expression of numerous SASP factors (Dou et al., 2017; Gluck et al., 2017; Mackenzie et al., 2017; Yang, Wang, Ren, Chen, & Chen, 2017). However, how the cGAS‐STING pathway is functionally connected with other SASP modulators including but not limited to p38MAPK, Jak2/Stat3 and GATA4, remains an open question that merits future exploration. Given the remarkable complexity of the SASP signaling, further experimental inputs are essential to achieve new insights and to present optimal molecules for therapeutic targeting of such a distinctive phenotype.
Figure 1.
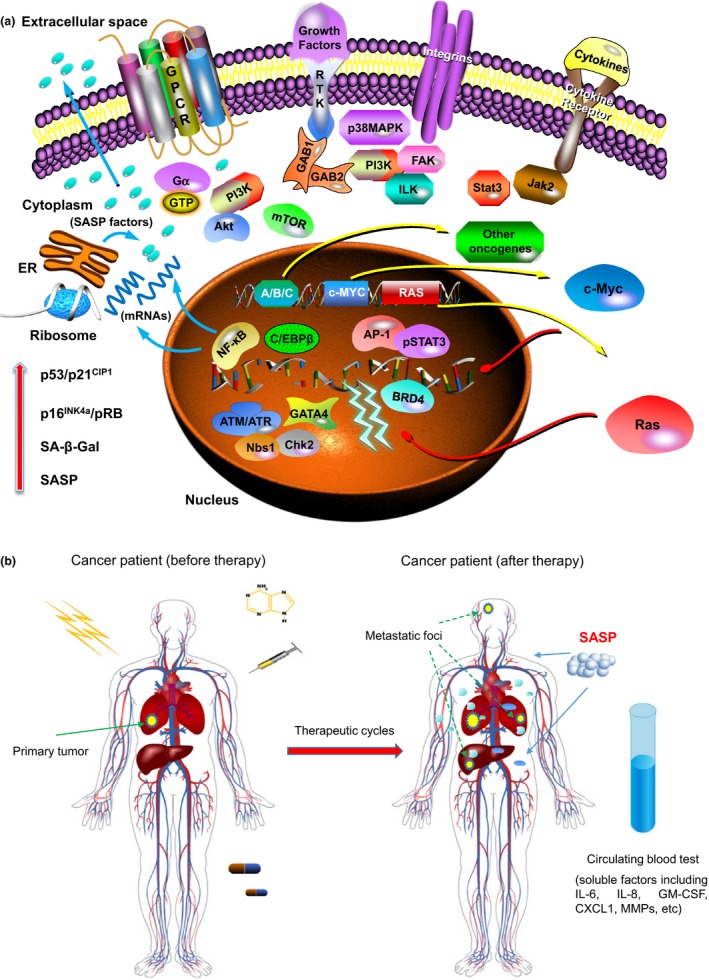
Oncogene‐ and therapy‐induced cellular senescence. (a) oncogene‐induced senescence (OIS) represents a cell responsive program provoked upon aberrant activation of specific oncogenes such as Ras, Raf, Akt, Cyclin E and c‐Myc (Acosta & Gil, 2012; Ko et al., 2018; Warnier et al., 2018). OIS results from the enforcement of a DDR triggered by DNA hyper‐replication induced by oncogene expression, a process that is initially transient but ultimately ends with the permanent establishment of cellular senescence (Di Micco et al., 2006). In such a case, persistent DDR events are observed in senescent cells, and molecules such as ATM/ATR, Nbs1 and Chk2 are actively engaged in DDR‐associated signaling. Regulation of the SASP is subject to multiple intracellular pathways including but not limited to p38MAPK, Jak2/Stat3 and mTOR (Freund, Patil, & Campisi, 2011; Laberge et al., 2015; Toso et al., 2014), which inevitably converge on transcription factors such as NF‐кB, C/EBPβ and AP‐1 (Han et al., 2018; Ito et al., 2017). Recent studies revealed that GATA4 is an upstream modulator of NF‐кB signaling in senescent cells, while the chromatin reader protein BRD4 dynamically binds to super‐enhancer elements adjacent to the genes encoding SASP factors (Kang et al., 2015; Tasdemir et al., 2016). As different cell types show different responses to oncogenic stress, the relevant mechanisms dictating the sensitivity or resistance to a specific oncogene remain to be elucidated by future investigations. (b) Therapy‐induced senescence (TIS) can be typically induced in normal, immortal or transformed, and cancer cells by anticancer compounds or ionizing radiation. Although generally considered tumor suppressive, TIS has recently been demonstrated by multiple studies to be able to enhance cancer resistance, relapse and metastasis by causing diverse cytotoxicity‐related side effects including an in vivo form of the SASP (Chen et al., 2018; Kim et al., 2017; Mikula‐Pietrasik et al., 2016; Wieland et al., 2017; Zhang et al., 2018). Furthermore, experimental data suggested that TIS induced by genotoxic chemotherapy promotes cancer metastasis from primary sites to distant organs (Demaria et al., 2017). It is imaginable that similar consequences could be observed in cancer clinics, a process driven by senescent cells with the tendency to promote malignant progression in the post‐treatment stage, particularly cancer metastasis. We also raise the possibility of assaying typical SASP factors in peripheral blood of cancer patients for appraisal of treatment outcome and prognosis of disease exacerbation, a significant and innovative strategy of the SASP‐based pathological assessment that may be realized in future medicine. Abbreviations and notes: A/B/C, oncogenes alternative to those exemplified (c‐Myc and Ras) in (a); ER, endoplasmic reticulum; SASP, senescence‐associated secretory phenotype; SA‐β‐Gal, senescence‐associated β galactosidase; DDR, DNA damage response; TME, tumor microenvironment; GATA4, GATA binding protein 4; BRD4, bromodomain containing 4; dashed lines in (b), potential metastatic sites of disseminating cancer cells driven by the impact of TIS in patients that have undergone anticancer therapy
In clinical medicine, anticancer agents not only triggers significant apoptosis of cancer cells but also causes substantial damage in the TME and induces typical TIS of the resident stromal cells, which cause therapeutic resistance via secretion of the SASP factors (Chen et al., 2018; Sun et al., 2012, 2016 ). Interestingly, damage‐provoked SASP can also be restrained to preserve tissue homeostasis and prevent chronic inflammation, as suggested by recent study that revealed PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway as a molecular rheostat to control the SASP progression (Bent, Gilbert, & Hemann, 2016). Indeed, a TME‐specific stress response is engaged promptly upon cellular damage particularly those induced by genotoxic insults, and stromal cells exhibit an acute stress‐associated phenotype (ASAP) characterized by subsequent secretion of a small handful of soluble factors including IL‐6 and Timp 1 (Gilbert & Hemann, 2010). In contrast to the ASAP as a rapid response mainly involving the ATM‐TRAF6‐TAK1 axis, the SASP is a relatively chronic process governed by key signaling nodes such as TAK1, a central kinase that functionally mediates phenotypic transition from the ASAP to the SASP and holds remarkable potential as an optimal therapeutic target to manipulate the SASP with a higher efficacy than that of p38‐ or mTOR‐oriented suppression (Zhang et al., 2018).
A new function of the SASP was recently discovered, which is linked with increased expression of stem cell markers and keratinocyte plasticity upon short term exposure of cells to the SASP in vitro and liver regeneration of a treatment‐inducible OIS mouse model in vivo, thus raising the possibility that transient therapeutic delivery of senescent cells could be harnessed to promote tissue regeneration (Ritschka et al., 2017). Interestingly, another study used agent‐inducible senescence animal models targeting trimethylation of lysine 9 at histone H3 (H3K9me3) or p53 to simulate spontaneous escape from cellular senescence, and found that cells released from senescence can re‐enter cell cycle with pronouncedly enhanced stemness and Wnt‐dependent growth potential compared to identical cell populations exposed to same chemotherapy but without experiencing senescence (Milanovic et al., 2018). Thus, senescence‐associated reprogramming promotes cancer stemness (senescence‐associated stemness, or SAS), a distinct property that has profound implications for cancer therapy and presents new mechanistic insights into cancer cell plasticity. Partially resembling cancer cells which pose substantial threat to human lifespan, senescent cells are functionally involved in tumor progression and can be viable targets for some reasons. First, senescent cells share common biochemical features, allowing use of a single therapeutic agent to eliminate them from the tissue microenvironment. Second, new protocols targeting senescent cells could practically synergize with hitherto established or proposed anticancer programs, which are frequently based on a presenescence scenario (Acosta & Gil, 2012). Given that many chemotherapeutics induces collateral senescence in the TME, pharmaceutical agents targeting senescent cells can be a key component of advanced anticancer arsenal (Childs et al., 2017). However, is there a way to radically remove senescent cells in the damaged or aged tissue rather than merely inhibition of the SASP, so that long‐term drug administration can be circumvented?
Several recent studies provided a series of pilot evidence in specific clearing senescent cells, including single or dual treatment of senescent cells with quercetin/dasatinib, and pan‐BCL inhibition with ABT‐263/ABT‐737 (Chang et al., 2016; Yosef et al., 2016; Zhu et al., 2015). Frequently detected in fruits and vegetables, quercetin is natural product and beneficial against aging, as evidenced by its capacity in attenuating premature senescence of human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) in Hutchinson‐Gilford progeria syndrome and postponing physiological‐aging of hMSCs in Werner syndrome (Geng et al., 2018). Dasatinib is a suppressor of Src kinase family and has showed prominent efficacy for some cancer types including chronic myeloid leukemia and colon cancer (Benthani et al., 2018; Naqvi et al., 2018). The senolytic cocktail consisting of dasatinib and quercetin reduces the number of naturally occurring senescent cells in explants of human adipose tissue, while intermittent oral administration of senolytics to either senescent cell‐implanted young animals or naturally aged mice can alleviate physical dysfunction and extend post‐treatment survival (Xu et al., 2018). However, both compounds (dasatinib and quercetin) were considered to be nonspecific among types of senescent cells and can display cell type‐dependent effects (Zhu et al., 2015). Given the prominent efficacy of the senolytic cocktail in controlling aging‐related symptoms as demonstrated in multiple lines of experimental mice including those of an immunodeficient or immunocompetent background, and in human adipose tissue explants (Ogrodnik et al., 2017; Schafer et al., 2017; Xu et al., 2018), a comprehensive and practical use of these compounds as clinical senolytics upon systemic evaluation is intriguing for future medicine. In addition, BCL inhibitors or BH3 mimetic drugs appeared to be an alternative group of agents against senescent cells by specifically targeting multiple BCL family members including BCl‐2, BCL‐xl, and BCL‐w (Chang et al., 2016; Yosef et al., 2016). Specifically, ABT263 (also navitoclax) reduces viability of senescent human lung fibroblasts (IMR90), human umbilical vein epithelial cells (HUVECs) and murine embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs), but not human primary preadipocytes, thus is senolytic in some, but not all types of senescent cells (Zhu et al., 2016). ABT263 has been extensively applied with success in treatment of human malignancies including lymphoma and multiple solid tumors; while another BCL inhibitor ABT737 has experienced an ex vivo evaluation in ovarian tumor samples (Lheureux et al., 2015). Unfortunately, a major drawback of BCL‐targeting agents merits attention, which predominantly results from their pronounced cytotoxicity, especially BCL‐2 inhibitors such as ABT263 and ABT199 (also venetoclax), the strong apoptosis inducers that pose a substantial risk to most cell types. Although applicable for immediate life‐threatening conditions including advanced malignancies, off‐target damage should be avoided intentionally for cancer patients and those at high age. Despite the antisenescence potential of these agents, future studies should be able to address whether further optimization is technically feasible or more selective agents can be designed, the latter ideally targeting intracellular molecules/pathways that are specifically up‐ or down‐regulated in senescent cells and are inherently correlated with their survival. To date, several senolytic molecules have been identified that show promising potency and selectivity such as a D‐retro inverso (DRI) peptide that perturbs FOXO4 interaction with p53 and causes pronounced apoptosis of senescent cells (Baar et al., 2017). Furthermore, utilization of these “first‐generation” senolytic strategies in preclinical models is disease‐minimizing, presumably through attenuation of the SASP. This implies that diseases associated with senescent cells, such as cancer, may be amenable to senotherapy mediated by agents that are in currently ongoing clinical trials but have the potential to be exploited as modulators or eliminators of senescent cells (Table 1).
Table 1.
Small molecule agents that hold potential as SASP inhibitors or senolytics in cancer clinics
| Agent | Target (s) | Target class | Development status | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABT‐263 | BCL‐2/BCL‐XL | Pro‐survival or anti‐apoptotic factors | Preclinical animal models/Clinical trials (phase I/II (NCT00406809 for leukemia and lymphoma/NCT00445198 for lung cancer), phase I (NCT00743028 for leukemia and lymphoma/NCT00982566 for lymphoma and solid tumors), and phase II (NCT02591095 for ovarian cancer/NCT01557777 for leukemia)) | Chang et al. (2016) | |
| ABT‐737 | BCL‐w/BCL‐XL | Pro‐survival or anti‐apoptotic factors | Preclinical animal models/Ex vivo evaluation of ovarian tumor (NCT01440504) | Yosef et al. (2016) | |
| Dasatinib | Pan‐receptor tyrosine kinases | Receptor tyrosine kinases | Clinical trials (Phase I/II (NCT00597038 for melanoma/NCT00550615 for lymphoma), Phase I (NCT00652574 for mesothelioma/NCT01744652 for advanced cancers), Phase II (NCT02744768 for leukemia/NCT00429949 for myeloma), Phase III (NCT02013648 for leukemia), Phase IV (NCT03216070 for leukemia)) | Xu et al. (2018) and Zhu et al. (2015) | |
| Metformin | The IKK complex and/or NF‐κB | The SASP | Approved for type II diabetes/Clinical trials for cancer (Phase I/II (NCT02949700 for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma), Phase II (NCT03137186 for prostate cancer/NCT03398824 for Fanconi Anemia/NCT02506777 for breast cancer)), clinical trials for aging (Phase IV (NCT02745886 for aging/NCT02432287 for aging)) | Oubaha et al. (2016) | |
| Rapamycin | Mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase (mTOR) | The SASP | Approved for immunosuppression/Clinical trials for cancer (Phase I (NCT02724332 for liver cancer/NCT03014297 for neuroendorine tumors)) | Herranz et al. (2015) and Laberge et al. (2015) | |
| RAD001 | Mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase (mTOR) | The SASP | Approved for immunosuppression, clinical trials for cancer (Phase I/II (NCT00516165 for liver cancer/), Phase II (NCT00782626 for glioma and astrocytoma/NCT01051791 for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma/NCT01152840 for adenoid cystic cancer)) | Zhang et al. (2018) | |
| LY2228820 | p38MAPK | The SASP | Clinical trials for cancer (Phase I (NCT01393990 for advanced cancer), Phase I/II (NCT01663857 for ovarian cancer, NCT02364206 for glioblastoma) | Freund et al. (2011) | |
| LY3007113 | fp38MAPK | The SASP | Clinical trials for cancer (Phase I (NCT01463631 for advanced cancer)) | Freund et al. (2011) | |
| Quercetin | Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) and potassium voltage‐gated channel subfamily E regulatory subunit 2 (KCNE2) | Antioxidant enzymes | Phase II clinical trial (NCT02848131) for chronic kidney disease | Zhu et al. (2015) | |
| FOXO4‐DRI | Interaction between FOXO4 and p53 | Pro‐survival or anti‐apoptotic factors | Preclinical animal models | Baar et al, (2017) | |
| 5Z‐7‐Oxozeaenol | Transforming growth factor‐β1‐activated kinase‐1 (TAK1) | The SASP | Preclinical animal models | Zhang et al, (2018) | |
Cellular senescence occurs throughout lifespan, and senescent cells are beneficial to certain physiological and pathological processes including embryonic patterning, tissue repair, wound healing and immune surveillance. However, as address above, a steady accumulation of senescent cells in the tissue has adverse consequences, ultimately enhancing clinical morbidity. Thus, the abundance of senescent cells in vivo may serve as a “molecular” marker for disease occurrence and guide patient stratification (Demaria et al., 2017), a novel approach for clinical advancement which can be correlated with benefit of senotherapy.
Despite all the recent findings from senescence and cancer research, there are several caveats before we move forward. Agents targeting senescent cells, especially SASP inhibitors, should be investigated meticulously to ensure continued maintenance of cell cycle arrest, as bypassing the crisis can inevitably promote carcinogenesis. As senescent cells also have certain health‐promoting functions, identification of the beneficial components of the SASP could lead to development of optimal strategies that preserve vital factors while depleting their detrimental counterparts derived from senescent cells. As a technical issue, achieving the balance between deleterious and beneficial impact of senolytics in cancer patients requires careful and rational design of administration regimens such as classic chemotherapy followed by senolytic treatment, each provided in metronomic cycles to minimize in vivo toxicity but enhancing overall efficacy. Such a therapeutic modality is desirable and holds the potential to enhance patient treatment efficacy while reducing adverse side effects that can be observed upon administration of each agent in a single dose. Finally, targeting senescent cells while simultaneously promoting tissue regeneration represents an optimal solution to remove senescent cells from individuals particularly those with advanced diseases or at later stage in life. In doing so, we are getting even closer to achieving the goal of a real “healthy” therapy against human cancer and aging.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
None Declared.
Zhang B, Lam EW‐F, Sun Y. Senescent cells: A new Achilles’ heel to exploit for cancer medicine? Aging Cell. 2019;18:e12875 10.1111/acel.12875
Funding information
The authors apologize for not being able to cite the publications of many scientists who made substantial contributions to the current topic due to space limitation. This work is supported by grants from National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC1302400), National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (81472709, 31671425 and 31871380), the National 1000 Young Talents Research Program of China and the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) Prostate Cancer Research Program (PCRP) (Idea Development Award PC111703) to YS; and CRUK (A12011), Breast Cancer Now (2012MayPR070; 2012NovPhD016), the Medical Research Council of the United Kingdom (MR/N012097/1), Cancer Research UK Imperial Centre, Imperial ECMC and NIHR Imperial BRC to E.W.‐F.L.
REFERENCES
- Acosta, J. C. , & Gil, J. (2012). Senescence: A new weapon for cancer therapy. Trends in Cell Biology, 22, 211–219. 10.1016/j.tcb.2011.11.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acosta, J. C. , O’Loghlen, A. , Banito, A. , Guijarro, M. V. , Augert, A. , Raguz, S. , … Gil, J. (2008). Chemokine signaling via the CXCR2 receptor reinforces senescence. Cell, 133, 1006–1018. 10.1016/j.cell.2008.03.038 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baar, M. P. , Brandt, R. M. C. , Putavet, D. A. , Klein, J. D. D. , Derks, K. W. J. , Bourgeois, B. R. M. , ... de Keizer, P. L. J. (2017). Targeted apoptosis of senescent cells restores tissue homeostasis in response to chemotoxicity and aging. Cell, 169(1), 132–147.e16. 10.1016/j.cell.2017.02.031 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bent, E. H. , Gilbert, L. A. , & Hemann, M. T. (2016). A senescence secretory switch mediated by PI3K/AKT/mTOR activation controls chemoprotective endothelial secretory responses. Genes & Development, 30, 1811–1821. 10.1101/gad.284851.116 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benthani, F. A. , Herrmann, D. , Tran, P. N. , Pangon, L. , Lucas, M. C. , Allam, A. H. , … Kohonen‐Corish, M. R. J. (2018). ‘MCC’ protein interacts with E‐cadherin and beta‐catenin strengthening cell‐cell adhesion of HCT116 colon cancer cells. Oncogene, 37, 663–672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J. , Wang, Y. , Shao, L. , Laberge, R. M. , Demaria, M. , Campisi, J. , … Zhou, D. (2016). Clearance of senescent cells by ABT263 rejuvenates aged hematopoietic stem cells in mice. Nature Medicine, 22, 78–83. 10.1038/nm.4010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F. , Long, Q. , Fu, D. , Zhu, D. , Ji, Y. , Han, L. , … Sun, Y. (2018). Targeting SPINK1 in the damaged tumour microenvironment alleviates therapeutic resistance. Nature Communications, 9, 4315 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs, B. G. , Gluscevic, M. , Baker, D. J. , Laberge, R. M. , Marquess, D. , Dananberg, J. , & van Deursen, J. M. (2017). Senescent cells: An emerging target for diseases of ageing. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 16, 718–735. 10.1038/nrd.2017.116 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppe, J. P. , Patil, C. K. , Rodier, F. , Sun, Y. , Munoz, D. P. , Goldstein, J. , … Campisi, J. (2008). Senescence‐associated secretory phenotypes reveal cell‐nonautonomous functions of oncogenic RAS and the p53 tumor suppressor. PLoS Biology, 6, 2853–2868. 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060301 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davaapil, H. , Brockes, J. P. , & Yun, M. H. (2017). Conserved and novel functions of programmed cellular senescence during vertebrate development. Development, 144, 106–114. 10.1242/dev.138222 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demaria, M. , O’Leary, M. N. , Chang, J. , Shao, L. , Liu, S. , Alimirah, F. , … Campisi, J. (2017). Cellular senescence promotes adverse effects of chemotherapy and cancer relapse. Cancer Discovery, 7, 165–176. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0241 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demaria, M. , Ohtani, N. , Youssef, S. A. , Rodier, F. , Toussaint, W. , Mitchell, J. R. , … Campisi, J. (2014). An essential role for senescent cells in optimal wound healing through secretion of PDGF‐AA. Developmental Cell, 31, 722–733. 10.1016/j.devcel.2014.11.012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Micco, R. , Fumagalli, M. , Cicalese, A. , Piccinin, S. , Gasparini, P. , Luise, C. , … di Fagagna, F. D. (2006). Oncogene‐induced senescence is a DNA damage response triggered by DNA hyper‐replication. Nature, 444, 638–642. 10.1038/nature05327 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Mitri, D. , & Alimonti, A. (2016). Non‐cell‐autonomous regulation of cellular senescence in cancer. Trends in Cell Biology, 26, 215–226. 10.1016/j.tcb.2015.10.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dou, Z. X. , Ghosh, K. , Vizioli, M. G. , Zhu, J. J. , Sen, P. , Wangensteen, K. J. , … Berger, S. L. (2017). Cytoplasmic chromatin triggers inflammation in senescence and cancer. Nature, 550, 402–406. 10.1038/nature24050 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund, A. , Patil, C. K. , & Campisi, J. (2011). p38MAPK is a novel DNA damage response‐independent regulator of the senescence‐associated secretory phenotype. EMBO Journal, 30, 1536–1548. 10.1038/emboj.2011.69 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geng, L. , Liu, Z. , Zhang, W. , Li, W. , Wu, Z. , Wang, W. , … Liu, G. H. (2018). Chemical screen identifies a geroprotective role of quercetin in premature aging. Protein & Cell. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgilis, A. , Klotz, S. , Hanley, C. J. , Herranz, N. , Weirich, B. , Morancho, B. , … Gil, J. (2018). PTBP1‐mediated alternative splicing regulates the inflammatory secretome and the pro‐tumorigenic effects of senescent cells. Cancer Cell, 34(1), 85–102.e9. 10.1016/j.ccell.2018.06.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, L. A. , & Hemann, M. T. (2010). DNA damage‐mediated induction of a chemoresistant niche. Cell, 143, 355–366. 10.1016/j.cell.2010.09.043 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluck, S. , Guey, B. , Gulen, M. F. , Wolter, K. , Kang, T. W. , Schmacke, N. A. , … Ablasser, A. (2017). Innate immune sensing of cytosolic chromatin fragments through cGAS promotes senescence. Nature Cell Biology, 19, 1061–1070. 10.1038/ncb3586 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han, R. , Li, L. , Ugalde, A. P. , Tal, A. , Manber, Z. , Barbera, E. P. , … Agami, R. (2018). Functional CRISPR screen identifies AP1‐associated enhancer regulating FOXF1 to modulate oncogene‐induced senescence. Genome Biology, 19, 118 10.1186/s13059-018-1494-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He, S. , & Sharpless, N. E. (2017). Senescence in Health and Disease. Cell, 169, 1000–1011. 10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herranz, N. , Gallage, S. , Mellone, M. , Wuestefeld, T. , Klotz, S. , Hanley, C. J. , Gil, J. (2015). mTOR regulates MAPKAPK2 translation to control the senescence‐associated secretory phenotype. Nature Cell Biology, 17, 1205–1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito, Y. , Hoare, M. , & Narita, M. (2017). Spatial and Temporal Control of Senescence. Trends in Cell Biology, 27, 820–832. 10.1016/j.tcb.2017.07.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jun, J. I. , & Lau, L. F. (2010). The matricellular protein CCN1 induces fibroblast senescence and restricts fibrosis in cutaneous wound healing. Nature Cell Biology, 12, 676–U106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang, C. , Xu, Q. , Martin, T. D. , Li, M. Z. , Demaria, M. , Aron, L. , … Elledge, S. J. (2015). The DNA damage response induces inflammation and senescence by inhibiting autophagy of GATA4. Science, 349, aaa5612 10.1126/science.aaa5612 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang, T. W. , Yevsa, T. , Woller, N. , Hoenicke, L. , Wuestefeld, T. , Dauch, D. , … Zender, L. (2011). Senescence surveillance of pre‐malignant hepatocytes limits liver cancer development. Nature, 479, 547–551. 10.1038/nature10599 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y. H. , Choi, Y. W. , Lee, J. , Soh, E. Y. , Kim, J. H. , & Park, T. J. (2017). Senescent tumor cells lead the collective invasion in thyroid cancer. Nature Communications, 8, 15208 10.1038/ncomms15208 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko, A. , Han, S. Y. , Choi, C. H. , Cho, H. , Lee, M. S. , Kim, S. Y. , … Song, J. (2018). Oncogene‐induced senescence mediated by c‐Myc requires USP10 dependent deubiquitination and stabilization of p14ARF. Cell Death and Differentiation, 25(6), 1050–1062. 10.1038/s41418-018-0072-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuilman, T. , Michaloglou, C. , Vredeveld, L. C. W. , Douma, S. , van Doom, R. , Desmet, C. J. , … Peeper, D. S. (2008). Oncogene‐induced senescence relayed by an interleukin‐dependent inflammatory network. Cell, 133, 1019–1031. 10.1016/j.cell.2008.03.039 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laberge, R. M. , Sun, Y. , Orjalo, A. V. , Patil, C. K. , Freund, A. , Zhou, L. , … Campisi, J. (2015). MTOR regulates the pro‐tumorigenic senescence‐associated secretory phenotype by promoting IL1A translation. Nature Cell Biology, 17, 1049–1061. 10.1038/ncb3195 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lheureux, S. , N’Diaye, M. , Blanc‐Fournier, C. , Dugue, A. E. , Clarisse, B. , Dutoit, S. , … Poulain, L. (2015). Identification of predictive factors of response to the BH3‐mimetic molecule ABT‐737: An ex vivo experiment in human serous ovarian carcinoma. International Journal of Cancer, 136, E340–E350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie, K. J. , Carroll, P. , Martin, C. A. , Murina, O. , Fluteau, A. , Impson, D. J. S. , … Jackson, A. P. (2017). cGAS surveillance of micronuclei links genome instability to innate immunity. Nature, 548, 461–465. 10.1038/nature23449 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikula‐Pietrasik, J. , Uruski, P. , Sosinska, P. , Maksin, K. , Piotrowska‐Kempisty, H. , Kucinska, M. , … Ksiazek, K. (2016). Senescent peritoneal mesothelium creates a niche for ovarian cancer metastases. Cell Death & Disease, 7, e2565 10.1038/cddis.2016.417 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milanovic, M. , Fan, D. N. Y. , Belenki, D. , Dabritz, J. H. M. , Zhao, Z. , Yu, Y. , … Schmitt, C. A. (2018). Senescence‐associated reprogramming promotes cancer stemness. Nature, 553, 96–100. 10.1038/nature25167 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz‐Espin, D. , Canamero, M. , Maraver, A. , Gomez‐Lopez, G. , Contreras, J. , Murillo‐Cuesta, S. , … Serrano, M. (2013). Programmed cell senescence during mammalian embryonic development. Cell, 155, 1104–1118. 10.1016/j.cell.2013.10.019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naqvi, K. , Jabbour, E. , Skinner, J. , Yilmaz, M. , Ferrajoli, A. , Bose, P. , … Kantarjian, H. M. (2018). Early results of lower dose dasatinib (50 mg daily) as frontline therapy for newly diagnosed chronic‐phase chronic myeloid leukemia. Cancer, 124, 2740–2747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogrodnik, M. , Miwa, S. , Tchkonia, T. , Tiniakos, D. , Wilson, C. L. , Lahat, A. , … Jurk, D. (2017). Cellular senescence drives age‐dependent hepatic steatosis. Nature Communications, 8, 15691 10.1038/ncomms15691 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oubaha, M. , Miloudi, K. , Dejda, A. , Guber, V. , Mawambo, G. , Germain, M. A. , … Sapieha, P. (2016). Senescence‐associated secretory phenotype contributes to pathological angiogenesis in retinopathy. Science Translational Medicine, 8, 362ra144 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaf9440 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozcan, S. , Alessio, N. , Acar, M. B. , Mert, E. , Omerli, F. , Peluso, G. , & Galderisi, U. (2016). Unbiased analysis of senescence associated secretory phenotype (SASP) to identify common components following different genotoxic stresses. Aging (Albany NY), 8, 1316–1329. 10.18632/aging.100971 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritschka, B. , Storer, M. , Mas, A. , Heinzmann, F. , Ortells, M. C. , Morton, J. P. , … Keyes, W. M. (2017). The senescence‐associated secretory phenotype induces cellular plasticity and tissue regeneration. Genes & Development, 31, 172–183. 10.1101/gad.290635.116 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodier, F. , Coppe, J. P. , Patil, C. K. , Hoeijmakers, W. A. , Munoz, D. P. , Raza, S. R. , … Campisi, J. (2009). Persistent DNA damage signalling triggers senescence‐associated inflammatory cytokine secretion. Nature Cell Biology, 11, 973–979. 10.1038/ncb1909 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodier, F. , Munoz, D. P. , Teachenor, R. , Chu, V. , Le, O. , Bhaumik, D. , … Campisi, J. (2011). DNA‐SCARS: Distinct nuclear structures that sustain damage‐induced senescence growth arrest and inflammatory cytokine secretion. Journal of Cell Science, 124, 68–81. 10.1242/jcs.071340 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer, M. J. , White, T. A. , Iijima, K. , Haak, A. J. , Ligresti, G. , Atkinson, E. J. , … LeBrasseur, N. K. (2017). Cellular senescence mediates fibrotic pulmonary disease. Nature Communications, 8, 14532 10.1038/ncomms14532 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieben, C. J. , Sturmlechner, I. , van de Sluis, B. , & van Deursen, J. M. (2018). Two‐Step Senescence‐Focused Cancer Therapies. Trends in Cell Biology, 28(9), 723–737. 10.1016/j.tcb.2018.04.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storer, M. , Mas, A. , Robert‐Moreno, A. , Pecoraro, M. , Ortells, M. C. , Di Giacomo, V. , … Keyes, W. M. (2013). Senescence is a developmental mechanism that contributes to embryonic growth and patterning. Cell, 155, 1119–1130. 10.1016/j.cell.2013.10.041 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y. , Campisi, J. , Higano, C. , Beer, T. M. , Porter, P. , Coleman, I. , … Nelson, P. S. (2012). Treatment‐induced damage to the tumor microenvironment promotes prostate cancer therapy resistance through WNT16B. Nature Medicine, 18, 1359–1368. 10.1038/nm.2890 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y. , Zhu, D. , Chen, F. , Qian, M. , Wei, H. , Chen, W. , & Xu, J. (2016). SFRP2 augments WNT16B signaling to promote therapeutic resistance in the damaged tumor microenvironment. Oncogene, 35, 4321–4334. 10.1038/onc.2015.494 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Tasdemir, N. , Banito, A. , Roe, J. S. , Alonso‐Curbelo, D. , Camiolo, M. , Tschaharganeh, D. F. , … Lowe, S. W. (2016). BRD4 connects enhancer remodeling to senescence immune surveillance. Cancer Discovery, 6, 612–629. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0217 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toso, A. , Revandkar, A. , Di Mitri, D. , Guccini, I. , Proietti, M. , Sarti, M. , … Alimonti, A. (2014). Enhancing chemotherapy efficacy in Pten‐deficient prostate tumors by activating the senescence‐associated antitumor immunity. Cell Reports, 9, 75–89. 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.08.044 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnier, M. , Flaman, J. M. , Chouabe, C. , Wiel, C. , Gras, B. , Griveau, A. , … Bernard, D. (2018). The SCN9A channel and plasma membrane depolarization promote cellular senescence through Rb pathway. Aging Cell, 17, e12736 10.1111/acel.12736 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland, E. , Rodriguez‐Vita, J. , Liebler, S. S. , Mogler, C. , Moll, I. , Herberich, S. E. , … Fischer, A. (2017). Endothelial Notch1 activity facilitates metastasis. Cancer Cell, 31, 355–367. 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.01.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M. , Pirtskhalava, T. , Farr, J. N. , Weigand, B. M. , Palmer, A. K. , Weivoda, M. M. , … Kirkland, J. L. (2018). Senolytics improve physical function and increase lifespan in old age. Nature Medicine, 24, 1246–1256. 10.1038/s41591-018-0092-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H. , Wang, H. Z. , Ren, J. Y. , Chen, Q. , & Chen, Z. J. J. (2017). cGAS is essential for cellular senescence. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of USA, 114, E4612–E4620. 10.1073/pnas.1705499114 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yosef, R. , Pilpel, N. , Tokarsky‐Amiel, R. , Biran, A. , Ovadya, Y. , Cohen, S. , … Krizhanovsky, V. (2016). Directed elimination of senescent cells by inhibition of BCL‐W and BCL‐XL. Nature Communications, 7, 11190 10.1038/ncomms11190 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B. Y. , Fu, D. , Xu, Q. X. , Cong, X. L. , Wu, C. Y. , Zhong, X. M. , … Sun, Y. (2018). The senescence‐associated secretory phenotype is potentiated by feedforward regulatory mechanisms involving Zscan4 and TAK1. Nature Communications, 9, 1723 10.1038/s41467-018-04010-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y. , Tchkonia, T. , Fuhrmann‐Stroissnigg, H. , Dai, H. M. M. , Ling, Y. Y. Y. , Stout, M. B. , … Kirkland, J. L. (2016). Identification of a novel senolytic agent, navitoclax, targeting the Bcl‐2 family of anti‐apoptotic factors. Aging Cell, 15, 428–435. 10.1111/acel.12445 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y. , Tchkonia, T. , Pirtskhalava, T. , Gower, A. C. , Ding, H. , Giorgadze, N. , … Kirkland, J. L. (2015). The Achilles’ heel of senescent cells: From transcriptome to senolytic drugs. Aging Cell, 14, 644–658. 10.1111/acel.12344 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


