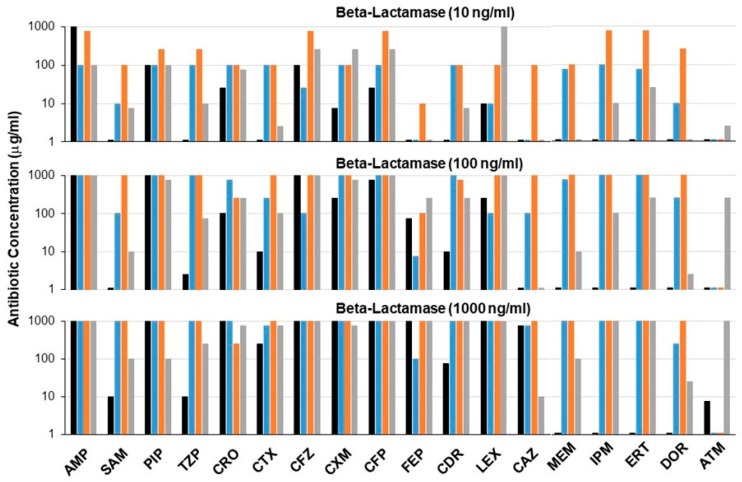
Figure 1.
Antibiotic degradation profiles of beta-lactamase enzymes. Antibiotic degradation was assessed using an E. coli growth assay. Purified beta-lactamases (10, 100, or 1000 ng/mL) were added to wells of a microtiter plate containing high antibiotic concentrations (10, 100, or 1000 µg/mL) after which E. coli were added immediately. Bacterial growth, an indication of antibiotic inactivation, was measured the next day (OD625). The data represent the highest concentration of antibiotic that was inactivated by the beta-lactamase. Ribaxamase: black, P2A: blue, New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase (NDM): orange, Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC): gray. AMP: ampicillin, SAM: ampicillin/sulbactam, PIP: piperacillin, TZP: piperacillin/tazobactam, CRO: ceftriaxone, CTX: cefotaxime, CFZ: cefazolin, CXM: cefuroxime, CFP: cefoperazone, FEP: cefepime, CDR: cefdinir, LEX: cephalexin, CAZ: ceftazidime, MEM: meropenem, IPM: imipenem, ERT: ertapenem, DOR: doripenem, ATM: aztreonam.