Abstract
Background
Chromosomal translocation-induced expression of the chromatin modifying oncofusion protein MLL-AF9 promotes acute myelocytic leukemia (AML). Whereas WNT/β-catenin signaling has previously been shown to support MLL-AF9-driven leukemogenesis, the mechanism underlying this relationship remains unclear.
Methods
We used two novel small molecules targeting WNT signaling as well as a genetically modified mouse model that allow targeted deletion of the WNT protein chaperone Wntless (WLS) to evaluate the role of WNT signaling in AML progression. ATAC-seq and transcriptome profiling were deployed to understand the cellular consequences of disrupting a WNT signaling in leukemic initiating cells (LICs).
Findings
We identified Six1 to be a WNT-controlled target gene in MLL-AF9-transformed leukemic initiating cells (LICs). MLL-AF9 alters the accessibility of Six1 DNA to the transcriptional effector TCF7L2, a transducer of WNT/β-catenin gene expression changes. Disruption of WNT/SIX1 signaling using inhibitors of the Wnt signaling delays the development of AML.
Interpretation
By rendering TCF/LEF-binding elements controlling Six1 accessible to TCF7L2, MLL-AF9 promotes WNT/β-catenin-dependent growth of LICs. Small molecules disrupting WNT/β-catenin signaling block Six1 expression thereby disrupting leukemia driven by MLL fusion proteins.
Research in the context.
Evidence before this study
MLL-AF9 is an established driver of acute myelocytic leukemia (AML). The transcriptional activator β-catenin previously has been shown to promote MLL-AF9 driven leukemogenesis. Attempts to exploit this observation to achieve therapeutic goals has been stymied by the limited understanding of WNT signaling in this cancer context and the dearth of small molecules targeting WNT signaling.
Added value of this study
We identified the WNT acyltransferase Porcupine (Porcn) and the Tankyrase enzymes as regulators of a WNT-SIX1 signaling axis that promotes cell growth in MLL-AF9-expressing leukemic cells.
Implications of all the available evidence
Targeting the WNT-SIX1 signaling axis may be useful in leukemias driven by MLL oncofusion proteins.
Alt-text: Unlabelled Box
1. Introduction
Exceptional cell fate plasticity is a common feature of transformed cells and contributes to their metastatic potential [1]. Disruptions in epigenetic gene regulation as a consequence of genetic mutations can license transcriptional events not native to the cancer cell of origin thus altering cell fate outcomes [[2], [3], [4]]. Cancers of blood cells are oftentimes associated with mutations in epigenetic regulatory enzymes [5]. For example, fusion of the mixed lineage leukemia (MLL) and myeloid/lymphoid or mixed lineage leukemia; translocation to chromosome 3 (MLLT3, also known as AF9) genes as a consequence of t(9;11)(p22;q23) results in the expression of an oncofusion protein (MLL-AF9) that re-directs the DOTL1 methyltransferase to DNA regions with histone proteins not typically accessible to the enzyme [[6], [7], [8], [9]]. An understanding of the signaling networks that control deviant transcriptional events as a consequence of alterations in chromatin architecture could define novel anti-cancer therapeutic intervention strategies.
The prevalence of mutations in the WNT pathway suppressor gene adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) in colorectal cancer (CRC) has largely driven the search for WNT inhibitors as potential disease management agents in cancer [10]. Thus a preponderance of our understanding of WNT biology is derived from studies focused on stem cells that give rise to epithelial tissue. The assignment of a role for WNT signaling in leukemia and drug resistance blood cancers [[11], [12], [13], [14], [15]] was unexpected given that: a) mutations that directly induce WNT signaling typically found in solid tumors have yet to be discovered in this cancer type, and b) β-catenin (CTNNB1) is not essential for adult myeloid cell production [16].
Palmiteolyation of WNT proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) by the Porcupine (PORCN) acyltransferase licenses WNTs to engage the secretory pathway chaperone Wntless (WLS) and to exit the intracellular milieu [17]. Disruption of WNT acylation either by small molecule inhibitors of PORCN or genetic elimination of PORCN results in the ER entrapment of WNT ligands due to a failure for them to partner with WLS [18]. Similarly, genetic ablation of WLS compromises the production of all 19 WNT ligands [19]. Despite the plethora of WNT genes in mammals, PORCN remains the only characterized WNT fatty acyltransferase [10]. Small molecules targeting PORCN disable the production of all WNT molecules [19] and are currently in clinical testing as anti-cancer drugs in WNT-related cancers [10]. A class of small molecules that cripples β-catenin-dependent transcriptional responses to WNT ligands by inhibiting the Tankyrase (TNKS) enzymes represents another frequently used chemical probe set for WNT signaling [[20], [21], [22]].
To delineate the molecular program that supports deviant WNT signaling in AML, we have used novel tool compounds targeting PORCN and TNKS, and AML cells harboring a floxed WLS allele to understand WNT pathway architecture in MLL-AF9 induced LICs. We provide evidence that tumor-intrinsic WNT ligand-mediated signaling when coupled with MLL-AF9 expression is sufficient to promote AML progression and that the MLL-AF9 protein licenses the expression of the growth-promoting homeobox gene SIX1 by re-directing WNT/β-catenin control of the TCF7L2 transcriptional effector to SIX1 transcriptional regulatory elements. Our findings detail how epigenetic disturbances enable the rewiring of a master cell fate determination pathway to promote tumor progression and how understanding these cellular re-organization phenomena can be exploited for therapeutic ends.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Chemical synthesis and reagent
IWR107 was chemically modified based on the structure of IWR1 [20]. Briefly, to a suspension of 1 (1.0 g, 1.81 mmol, 1.0 equiv.; Chen et al. 2009) in a mixture of methylene chloride (35 mL) and tetrahydrofuran (70 mL) was added Dess-Martin periodinane (1.5 g, 3.62 mmol, 2.0 equiv) followed by water (65 μL, 3.62 mmol, 2.0 equiv) at room temperature. After stirring for 1.5 h, the volatiles were removed under reduced pressure and the residue was partitioned between ethyl acetate (350 mL) and 10% sodium bisulfate in saturated sodium bicarbonate (200 mL). The organic layer was then washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate (200 mL × 2) and brine (200 mL), dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and concentrated to give crude 2 as a yellow solid (783 mg). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 10.7 (s, br, 1H), 10.6 (s, 1H), 9.09 (d, J = 4.2 Hz, 1H), 9.00 (dd, J = 8.0, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 8.66 (dd, J = 8.5, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 8.11 (m, 2H), 7.89 (d, J = 4.3 Hz, 1H), 7.78 (dd, J = 8.5, 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.38 (m, 2H), 6.29 (dd, J = 1.9, 1.9 Hz, 2H), 3.54 (m, 2H), 3.49 (m, 2H), 1.82 (dt, J = 8.9, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 1.65 (m, 1H). MS(ESI)+ calcd for C26H20N3O4 [M + H]+ 438.1, found 438.1.
To a suspension of crude 2 obtained above (387 mg, 0.88 mmol, 1.0 equiv) in anhydrous toluene (8 mL) was added N,N-dimethylethylenediamine (120 μL, 1.06 mmol, 1.2 equiv). After stirring under reflux for 1.5 h, the clear solution was cooled to room temperature and concentrated. The residue was then dissolved in a mixture of methanol (3 mL) and tetrahydrofuran (3 mL). A freshly prepared mixture of sodium borohydride (101 mg, 2.6 mmol, 3.0 equiv) in methanol (3 mL) was subsequently added at 0 °C. After stirring at room temperature overnight, acetone (5 mL) was added and the solution was concentrated. The residue was then dissolved in chloroform (40 mL), washed with water and brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and concentrated. A solution of the crude product in tetrahydrofuran (30 mL) was treated with DIAION WA30 resin (6 mL) at 50 °C for 3 h to give 3 as a white solid after filtration and concentration. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 10.8 (s, 1H), 8.86 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 8.75 (d, J = 4.3 Hz, 1H), 8.02 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 7.73 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 1H), 7.67 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 7.59 (m, 1H), 7.54 (d, J = 4.4 Hz, 1H), 6.23 (dd, J = 5.8, 2.8 Hz, 1H), 6.15 (dd, J = 5.8, 2.9 Hz, 1H), 5.10 (s, 1H), 4.26 (s, 2H), 3.74 (m, 2H), 3.39 (s, 1H), 3.35 (dd, J = 8.6, 4.8 Hz, 1H), 3.29 (s, 1H), 2.80 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 2H), 2.49 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 2H), 2.23 (s, 6H), 1.64 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 1.46 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H). MS(ESI)+ calcd for C30H34N5O3 [M + H]+ 512.3, found 512.2.
IWR1, IWP2 and IWP2G9 were synthesized as described previously [20,23]. LGK974 was purchased from Active Biochem (Hong Kong).
2.2. Cell lines
HEK293T, HeLa, THP1, MV4;11, HL60 and U937 cell lines were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC). The MONO-MAC-6 (MM6) cell line was purchased from DSMZ (Germany). The cells were maintained either in DMEM medium (Sigma, HEK293T and HeLa) or RPMI-1640 medium (Sigma, THP1 and MV4;11) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Sigma) and 1× PSG (Sigma).
2.3. Mice
All animal experiments were performed with the approval of the Institutional Animal Care & Use Committee (IACUC) at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center (UTSWMC). Mice were housed in 12-h light/12-h dark cycles and given ad libitum access to food and water at the UTSWMC animal facility. To obtain a specific deletion of Wls in hematopoietic cells of adult mice, 129 mice strain carrying the loxP-flanked Wls (Wls-fl/fl) [24] were crossed with C57BL/6 mice strain expressing the tamoxifen-inducible CreERT recombinase under the control of stem cell leukemia (Scl) stem-cell enhancer [25] (Scl-Cre-ERT) to produce Scl-CreERT;Wls-fl/fl mice. The Scl-CreERT;Wls-fl/fl mice were backcrossed with Wls-fl/fl mice for at least 4 generations to obtain a 129 background before used for the study. To obtain a specific deletion of Six1 in hematopoietic cells of adult mice, C57BL/6 mice carrying the loxP-flanked Six1 (Six1-fl/fl) [26] were crossed with HSC-Scl-Cre-ERT mice to generate Scl-CreERT;Six1-fl/fl mice. The Scl-CreERT;Six1-fl/fl mice were backcrossed with Six1-fl/fl mice for at least 2 generations before used for the study.
2.4. Murine AML model
We used mouse AML model driven by oncogene MLL-AF9 [27]. For virus transduction and AML transplantation, we followed the protocol described previously [28]. For therapy studies, YFP+ leukemic cells from primary AML were sorted and transplanted into healthy lethally irradiated recipients, to generate secondary AML. 1000 cells per mouse were used to generate AML mouse model with a slower disease progression to allow enough time for compound treatment. One week after the transplantation, mice were orally administered with WNT inhibitors IWR107 and IWP2G9 at a dose of 80 mg/kg and 20 mg/kg, respectively, twice daily for 4 wks. 4 h after the last dosing, bone marrow cells were collected from 2 mice of each group and combined with equal cell number. LICs were sorted for microarray analysis or transplanted into healthy mice (2000 cells/mouse) for survival analysis. For Wls KO studies, GMP cells were sorted from mice with Wls WT or KO background 8 wks after Tmx induction and transduced with retrovirus co-expressing MLLAF9 oncofusion protein and YFP selection marker. 5000 YFP+ GMP cells were transplanted into healthy mice and subjected to survival analysis. Two AML mice were sacrificed on day 28 and LICs sorted for microarray analysis. For Six1 KO studies, Lin− cells were collected from mice with Six1 WT or KO background 8 wks after Tmx induction and transduced with MLLAF9- and YFP-expressing retrovirus. 5000 transduced YFP+ Lin− cells were transplanted into healthy mice to generate primary AML. 2000 LICs were sorted from moribund mice and transplanted into healthy mice for survival analysis. The Kaplan-Meier survival curves were plotted based on the survival data.
2.5. Genotyping
Genotyping was performed to identify positive offsprings or maintain strains using tail tissues, or to verify the targeted excision of genes using whole blood cells of transgenic mice following instructions of REDExtract-N-Amp™ Tissue PCR Kit (Sigma). Primers and PCR conditions were the same as recommended by the creators except for primers used to verify Six1 excision: forward 5’ CAC TCG GAG TCT AGC TCA C 3′ and reverse 5’ CCT TCA GCT TCA CGG TGT TG 3′, and for PCR conditions verifying Wls and Six1 excision: initial denaturation 94 °C 3 min, 34 cycles of 94 °C 30 s, 58 °C 30 s and 72 °C 2 min, and final extension 72 °C 10 min.
2.6. Induction of Cre activity
Tamoxifen (Sigma) was dissolved in Corn oil (Sigma) at a concentration of 20 mg/mL for 6 h at 37 °C with gentle rotation and stored at 4 °C afterwards. 100 μL solution was intraperitoneally administered into 7–9 week old mice for 5 days, once daily. Corn oil was used as the vehicle control. Genotyping on whole blood was used to confirm the knockout efficiency after Tamoxifen induction. All experiments were done on transgenic mice of 8-week induction because this duration is enough to induce gene excision to be maximal.
2.7. Pharmacokinetic analysis
Male C57BL/6 mice received 40 mg/kg IWR107 or IWP2G9 by oral gavage, 0.2 mL/mouse formulated as 5% DMA, 9% cremophor EL, 1% Tween 80, and 85% of 5% carboxymethylcellulose prepared in 5% dextrose in water, pH 7.4 (D5W). Plasma was processed from the collected whole blood by centrifugation for 10 min at 9600 ×g. A two- (IWP2G9) or four-fold (IWR107) volume of acetonitrile containing formic acid and n-benzylbenzamide internal standard was added to 0.1 mL of plasma to precipitate plasma protein and release bound drug. The supernatant was then analyzed by LC-MS/MS using an ABSciex (Framingham, MA) 3200 Qtrap mass spectrometer coupled to a Shimadzu (Columbia, MD) Prominence LC. The compounds were detected with the mass spectrometer in MRM (multiple reaction monitoring) mode by following the precursor to fragment ion transitions optimized for the instrument: IWR107: 512.2 to 202.1; IWP2G9: 521.1 to 303.3; n-benzylbenzamide 212.1 to 91.1. An Agilent (Santa Clara, CA) XDB C18 column (50 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm packing) was used for chromatography with the following conditions: Buffer A: dH20 + 0.1% formic acid, Buffer B: methanol +0.1% formic acid; 0–1 min 100% A, 1–1.5 min gradient to 100% B, 1.5–2.5 min 100% B, 2.6–3.6 min gradient to 100% A. A value of 3-fold above the signal obtained in the blank plasma was designated the limit of detection (LOD). The limit of quantitation (LOQ) was defined as the lowest concentration at which back calculation yielded a concentration within 20% of the theoretical value and above the LOD signal (1 ng/mL for IWR107 and 5 ng/mL for IWP2G9.) Pharmacokinetic parameters were determined using the noncompartmental analysis tool in Phoenix WinNonlin (Certara Corp., Princeton, NJ.)
2.8. Histology
Liver tissues were collected from mice transplanted with YFP+ LICs for 21 days and processed for histology as described previously [29]. Images were acquired with NanoZoomer 2.0-HT (Hamamatsu).
2.9. Flow cytometry
For analysis of hematopoietic lineage markers in the BMs of mice with specific knockout of Wls or Six1 in hematopoietic cells, we follow protocols described previously [30]. Characterization of MLL-AF9 AML and isolation of the enriched LIC population from BMs of AML mice have been described previously [28]. Fluorescein-labeled antibodies used in the study include: Biotin Mouse Lineage Depletion Cocktail (BD Biosciences); Streptavidin-PerCP-Cy5.5, Sca1-FITC, cKit-APC-Cy7, cKit-PE, FcγR-PE-Cy7, CD34-PacificBlue, FLT3-PE, IL7R-APC, Mac1-APC, B220-PE, CD3-APC, Gr1-PE, Mac1-APC, CD16/CD32, all antibodies are anti-mouse and were purchased from eBiosciences.
2.10. Click chemistry
We followed the protocol that has been described previously [31] to measure Wnt lipidation by Porcn inhibitors IWP2 and IWP2G9. The concentration for the indicated compounds used in the study was 10 μM.
2.11. In Vitro TNKS activity analysis
IWR1 and IWR107 were serially diluted at the indicated concentrations and used to inhibit human TNKS1 activity (Trevigen) in vitro following the manufacturer's instruction. Curve fitting was performed and IC50 values calculated with Prism (GraphPad Software).
2.12. RNA isolation
Total RNA was isolated from sorted GMP cells, LICs or human AML cells with RNeasy Plus Mini Kit (Qiagen) following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration was measured on Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometers (Thermo Fisher Scientific).
2.13. Quantitative RT-PCR (qPCR)
First-strand cDNA was synthesized from total RNA using ProtoScript® First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (NEB). Samples were analyzed in triplicate of 15 μL reactions on LightCycle480 (Roche). SYBR Green I Master mix was from Roche. Primers are commercially available at Integrated DNA Technologies for mouse Six1 (Mm.PT.58.13903884) and human Six1 (Hs.PT.58.20841096), and at Qiagen for human Ptch1 (QT00075824) and Actb (QT00095431), and mouse Actb (QT01136772) and Wls (QT00113316). The ΔΔCt method was used to calculate the fold change of gene expression.
2.14. Colony formation assay
500 YFP+ LICs were sorted into 1-mL MethoCult™ GF M3534 medium (STEMCELL Technologies) supplemented with growth factors IL-2, IL-6 and SCF (PeproTech), mixed well and plated into one well of a 12-well plate. Colony numbers were determined on day 6. Mouse bone marrow cells were plated in M3534 medium supplemented with IL-3, IL-6, SCF, Epo and indicated concentration of WNT inhibitors. Colonies were scored on day 3 for CFU-E (colony-forming unit erythroid) and on day 7 for BFU-E (burst-forming unit erythroid), CFU-Mk (megakaryocyte) and myeloid colonies including CFU-G (granulocyte), CFU-M (macrophage) and CFU-GM. Experiments were in triplicate.
2.15. Cell proliferation assay
5000 LICs were seeded in each well of 96-well microtiter plates and cultured for indicated time. BrdU addition, cell fixation and permeabilization, and BrdU visualization were performed using the BrdU Cell Proliferation ELISA Kit (Abcam) according to the manufacturer's protocol. The incubation time for DNA incorporation of BrdU was 4 h.
2.16. Silver staining
Lyophilized human recombinant WNT1 (Abcam) was dissolved in ddH2O. Indicated amounts of proteins were mixed with sample loading buffer and subjected to SDS-PAGE. The gel was washed, fixed, stained and developed using the Pierce Silver Stain Kit (Thermo Scientific) following the manufacturer's protocol. Another identical set of samples on the same gel was used for Western blot analysis.
2.17. Western Blotting
HeLa cells were plated at 1 × 105/well in a 24-well pate and grew overnight. 1 × 106 BM cells or YFP+ LCs from secondary AML were cultured for 6 h in StemSpan™ Serum-free expansion medium (STEMCELL Technologies) supplemented with growth factors IL-2, IL-6 and SCF (PeproTech). Indicated compounds were added onto the cells at a final concentration of 10 μM and allowed to grow for another 24 h. Cell lysate preparation, protein separation and immunoblotting have been described previously [32]. Antibodies used in the study include: β-catenin (BD Pharmagen), TNKS1/2 (Santa Cruz), AXIN1 (Cell signaling), DVL2 (Cell signaling), β-actin (ACTNB, Sigma) and WNT1 (Abcam).
2.18. Microarray analysis
RNA quality was checked on Bioanalyzer Nanochip (Agilent Technologies). Samples with RNA integrity number (RIN) >7 were subjected to microarray analysis. mRNA transcription profiling was performed on the MouseRef-8 v2 Expression Beadchip (Illumina). The experimental procedure and data analysis were described previously [33]. Fold change was calculated as the ratio of normalized intensity of treatment group to that of control group. The cutoff for genes to be considered as differentially expressed is set at 1.5 folds.
2.19. ATAC sequencing
50,000 LSK or LIC cells were sorted and subjected to nuclear lysis, transposition and library amplification following the protocol established by [34]. Duplicate samples were used for each cell type. A total of 11 cycles of PCR was used for LICs and 12 for LSKs to amplify the library. The library was size-selected between the range of 100 bp and 1000 bp with Agencourt AMPure XP (Beckman Coulter). Library quality was determined by Bioanalyzer (Agilent). The library was then quantified by Qubit (Thermo Scientific) and the same amount of DNA was subjected to high-throughput sequencing on HiSEquation 2000 (Illumina) with 2 × 75 bp paired-end at a sequencing depth of ~33 million reads per sample. The ATAC-seq raw reads alignment, trimming, peak calling and normalization were described previously [35]. The data were visualized on the IGV2.3.91 (Broad Institute) with mouse mm9 assembly, along with bed files from ATAC-seq analysis of LSKs and LSKCs.
2.20. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (CHIP) qPCR
Normal mouse BM cells or YFP+ leukemic cells were harvested and subjected to ChIP. ChIP was performed with ChIP-IT® Express kit (ActiveMotif) following the manufacturer's instructions. Antibody against TCF7L2/TCF4 (Cell Signaling) was used to precipitate specific DNA fragments. Eluted DNA fragments were analyzed by qPCR using primers partially covering the proximal and distal regions of Six1 TSS upstream. Primers and amplicon sequences are provided in Supplemental Table 1. Amplicon sequences were also in silico analyzed for TCF/LEF binding motifs using online tool PROMO [36,37]. Conditions used: Factors of eukaryota and sites of eukaryota.
2.21. Human SIX1 expression and TCGA analysis
The analysis of SIX1 expression was done via the web portal BloodSpot [38]. Datasets include GSE42519 of human normal hematopoietic lineage cells, and GSE13159, GSE15434, GSE61804 and GSE14468 of human AML cells. The survival curve was plotted based on the dataset of TCGA [39].
2.22. Statistics
The survival rates of two groups were analyzed using the log-rank test. Cox proportional hazards model were used for multivariate analysis. All other data were expressed as mean ± SD and Student's t-test was used for their statistical analysis. Data were considered statistically significant as P < .05.
2.23. Data availability
All raw and processed microarray and ATAC-seq data are deposited in the Gene Expression Omnibus, GSE: 111278.
3. Results
3.1. WNT/β-catenin signaling is a chemical vulnerability in MLL-AF9-driven AML
The β-catenin transcriptional co-activator is essential for MLL-AF9-induced cellular transformation [14] and promotes resistance to various anti-leukemic agents including bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET) motif inhibitors which disrupt the ability of members of the bromodomain (BRD) protein family to recognize acetylated histone protein [12]. To better understand the contribution of WNT signaling to β-catenin function in leukemic cells, we first evaluated the effects of MLL-AF9 leukemic cells exposed in vivo to a PORCN or TNKS inhibitor (Fig. 1a) on their ability to colonize a secondary recipient. These chemicals are next-generation molecules with improvements in pharmacokinetic properties (Supp. Fig. 1) that are built upon well-validated scaffolds supporting activity against either the presumed active site of PORCN or the adenosine-binding pocket of TNKS1 and TNKS2 [40]. We show that IWR107 and IWP2G9 retain the ability to suppress cytoplasmic and nuclear biochemical markers of WNT signaling in cultured cells (Supp. Fig. 2a), and either inhibits recombinant TNKS activity, or WNT fatty acylation as determined using a click chemistry-based technique (Supp. Fig. 2b,c).
Fig. 1.
WNT/β-catenin signaling is a chemical vulnerability in MLL-AF9-driven AML. (a) Next generation WNT pathway inhibitors based on the IWR1 and IWP2 scaffolds [20]. (b) IWR107 and IWP2G9 exhibit WNT pathway inhibitory activity in murine bone marrow cells and leukemic cells (BM-derived Lin− cells with MLL-AF9 expression identified by sorting for co-expressed YFP signal). Both cell populations were exposed for 24 h to the inhibitors (10 μM) in vitro prior to Western blot analysis. (c) Evaluating the effects of WNT pathway inhibition in a mouse model of AML. Wnt inhibitors were orally administered in AML mice for 4 wks and leukemic initiating cells (LICs, YFP+ Mac1+ cKit+) from treated mice transplanted into healthy mice for survival analysis. (d) Abundance of circulating YFP+ leukemic cells is decreased in mice transplanted with LICs exposed to IWR107 (n = 9) or IWP2G9 (n = 8) compared to the Vehicle control (n = 9). PB = peripheral blood. Data is expressed as mean ± S.D. Error bars represent indicated numbers of biological replicates. **P < .01 [Student's t-test]. (e) Animals transplanted with LICs exposed to WNT inhibitors IWR107 (n = 9) and IWP2G9 (n = 8) exhibit extended survival compared to the Vehicle control (n = 9). Kaplan-Meier curves were plotted and the Log-Rank test used for the statistical analysis. (f) Liver tissues in animals transplanted with LICs previously exposed to systemically delivered WNT inhibitors exhibit less leukemic cell infiltration compared to the Vehicle control. Scale bar: 500 μm.
Fig. 2.
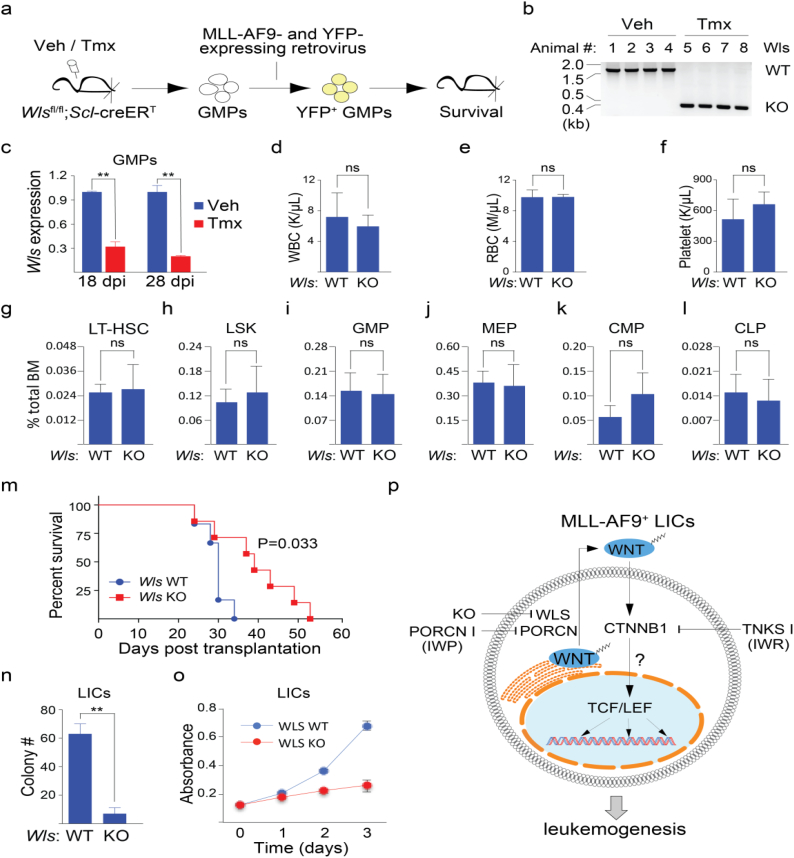
Cell-autonomous WNT signaling contributes to MLL-AF9-induced AML. (a) An experimental approach for evaluating the contribution of cell-autonomous WNT signaling in MLL-AF9-driven AML. GMPs: granulocyte-monocyte progenitors (Lin− Sca1− c-Kit+ FcγR+ CD34+). (b) Tamoxifen (Tmx) induction results in excision of the Wls locus. Genomic DNA was extracted from whole blood of mice induced with Tmx or Vehicle (Veh, corn oil) for 8 wks. (c) Decreased mRNA expression of Wls in bone marrow GMPs derived from Scl-creERT; Wls-flox mice compared with those from WT animals. Dpi = days post Tmx induction. n = 3 per group. (d-l) Loss of Wls does not affect normal adult hematopoiesis as measured using contents of white blood cells (WBC, d), red blood cells (RBC, e) and platelets (f), and the percentage of long-term hematopoietic stem cells (LT-HSC, Lin− Sca1+ cKit+ Flt3− CD34−, g), hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells (LSK, Lin− Sca1+ cKit+, h), GMP (i), megakaryocyte and erythroid progenitors (MEP, Lin− Sca1− c-Kit+ CD34− FcγR−, j), common myeloid progenitors (CMP, Lin− Sca1− c-Kit+ CD34+ FcγR−; k), and common lymphoid progenitors (CLP, Lin− Sca1low c-Kitlow FLT3+ IL7R+; l) in the total BM cell population at week 8 after Tmx induction. n = 4 per group. (m) Animals transplanted with Wls null leukemic cells (n = 7) exhibit extended survival compared with its WT counterparts (n = 6). Kaplan-Meier curves were generated and the Log-Rank test used for statistical analysis. (n) Wls null LICs form significantly less colony formation units (CFU) compared to WT LICs. n = 3 per group. (o) Wls null LICs proliferate more slowly compared to their WT counterparts. BrdU incorporation was used for the measurement of proliferation at the indicated time points. n = 3 per group. (p) Model of cell-autonomous WNT signaling in LICs of AML driven by MLL-AF9. In c-l and n-o, data is expressed as mean ± S.D. Error bars represent indicated numbers of biological replicates. ** P < .01. ns: not significant. [Student's t-test].
We confirmed in MLL-AF9 leukemic cells that these new molecules retain their intended activities using either β-catenin abundance and/or drug-induced TNKS accumulation as biochemical markers of on-target activity (Fig. 1b). These results also demonstrate the expression of TNKS enzymes in WT BM cells and in MLL-AF9 leukemic cells, and the existence of cell-autonomous WNT signaling activity in these populations based on the PORCN inhibitor activity. We also noted the elevated expression of β-catenin in MLL-AF9 leukemic cells compared to WT BM cells that was sensitive to PORCN inhibition suggesting higher levels of WNT-dependent signaling in the transformed cells and the ability to restore to some extent homeostatic levels of β-catenin using a small molecule-based strategy. We noted that WNT inhibitors targeting PORCN or TNKS did not impact the differentiation of blood cells or colony formation ex vivo consistent with previous results demonstrating the absence of effects on blood homeostasis by chemically disabling WNT signaling [18] (Supp. Fig. 2d,e).
To evaluate the effects of a PORCN or TNKS inhibitor on AML disease progression, we turned to a serial leukemic cell transplantation model of AML using secondary recipient and circulating leukemic cell numbers as read-outs [28] (Fig. 1c). Decreased numbers of circulating leukemic cells and increased survival time in animals transplanted with enriched LIC population (YFP+ Mac1+ cKit+) exposed to either IWR107 or IWP2G9 when compared with drug carrier alone in the secondary host were observed (Fig. 1d-e; Supp. Fig. 2f and Supp. Fig. 3). The overall benefit seen with the WNT inhibitors was also evident in decreased presence of AML cells infiltrating the liver in the secondary host (Fig. 1f). Thus, transient systemic suppression of WNT/β-catenin signaling impacts the ability of AML LICs to promote disease.
Fig. 3.
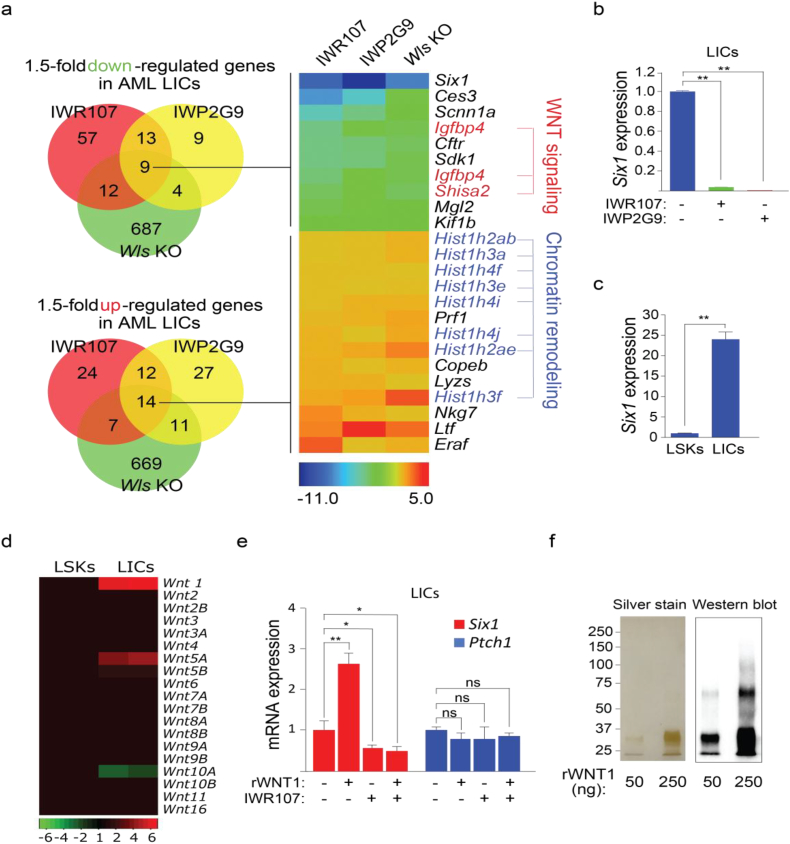
Transcriptional profiling identifies the homeobox gene Six1 as an atypical target of WNT/β-catenin signaling in AML. (a) Heat map revealing a gene signature of LICs perturbed by IWR107 and IWP2G9 and by Wls deletion. Total RNA was extracted from LICs isolated by FACS and subjected to microarray analysis. The cutoff for differentiated gene expression is set at 1.5 folds. Red = WNT signaling regulators, blue = histone genes. (b) Six1 mRNA expression in LICs isolated from animals exposed to IWP2G9 or IWR107 is significantly reduced compared to the Vehicle control. n = 3 per group. (c) MLL-AF9 LICs exhibit elevated Six1 mRNA expression compared to normal LSKs. n = 3 per group. (d) Profiling of mRNA expression of 19 WNT ligands in normal LSKs and enriched LIC population of AML. Fold change of mRNA expression in LICs was normalized to LSKs and used to generate the heat map. (e) Recombinant human WNT1 (rWNT1) induced expression of Six1 in LICs can be countered with IWR107. Cells were incubated with either rWNT (300 ng/ml) or IWR107 (10 μM) or both for 30 h and isolated cDNA subjected to qPCR analysis. The Hedgehog pathway target gene Ptch1 serves as a control. (f) Silver stain and Western blot using a WNT1 antibody of rWNT1 samples used in e. In b, c and f, data is expressed as mean ± S.D. Error bars represent indicated numbers of biological replicates. ** P < .01. * P < .05. ns: not significant. [Student's t-test].
3.2. Cell-autonomous WNT signaling contributes to AML progression
Tumor intrinsic WNT signaling has been previously associated with the ability of cancerous cells to abandon their native niche and to metastasize [41,42]. To determine if cell-autonomous WNT signaling contributes to AML progression, we performed a similar serial transplantation experiment as previously described for evaluating the WNT pathway inhibitors but using instead MLL-AF9 expressing retrovirus (co-expressing YFP marker) transduced granulocyte-monocyte progenitors (GMP, Lin− Sca-1− c-Kit+ FcγR+ CD34+, Supp. Fig. 4) lacking the WNT chaperone Wls in lieu of WT cells (Fig. 2a). We used a Wls floxed animal and tamoxifen-inducible Cre expression driven by the stem cell leukemia (Scl) promoter [30] to achieve targeted deletion of Wls in hematopoietic cells. Consistent with the absence of impact of a PORCN inhibitor or genetic elimination of PORCN on normal hematopoiesis [18], elimination of Wls (Fig. 2b-c) had little effect on normal hematopoiesis as determined using counts of differentiated blood cells (Fig. 2d-f) and hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (Fig. 2g-l; Supp. Fig. 4). Similar to the observations that stem from our chemically based experiments (see Fig. 1e), we observed a significant life extension in animals implanted with Wls null leukemic cells compared to Wls WT leukemic cells suggesting cell-autonomous WNT signaling contributes to the pathogenesis of AML (Fig. 2m). Supporting this hypothesis, LICs lacking Wls expression grew more slowly in culture compared to those with Wls expression (Fig. 2n). Decreased levels of BrdU incorporation suggest a slower rate of proliferation in the Wls null LICs compared with those expressing Wls mRNA (Fig. 2o). Our chemical and genetic observations when taken together delineate a mechanistic understanding of PORCN and TNKS inhibitor responses in animals harboring AML leukemic cells and reveal a contribution of tumor-intrinsic WNT/β-catenin signaling in AML progression (Fig. 2p).
Fig. 4.
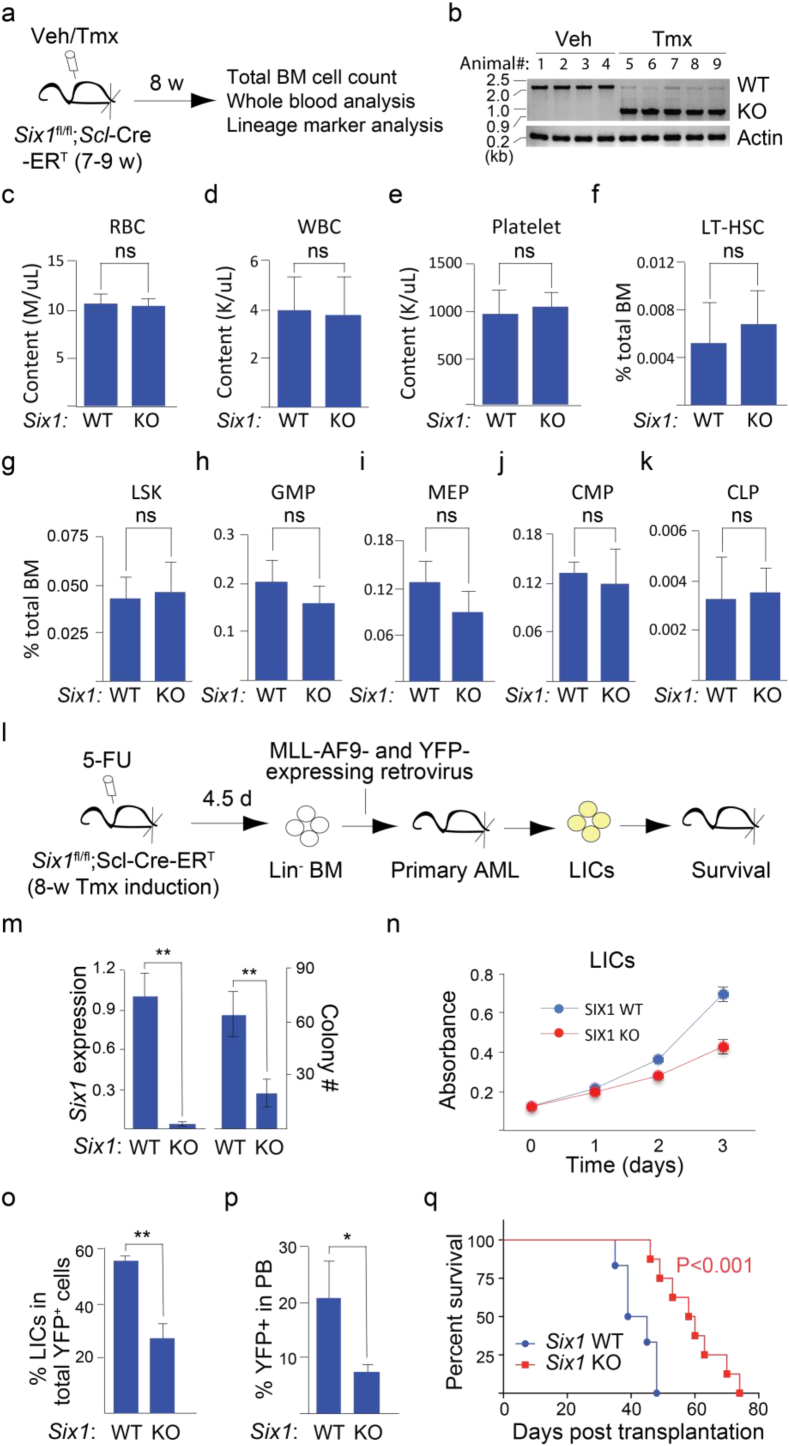
The homeobox gene Six1 is essential for the development of MLL-AF9-driven AML but not normal adult hematopoiesis. (a) Experimental approach for evaluating the role of SIX1 in normal hematopoiesis of adult mice. (b) Tmx induction results in excision of the Six1 locus. Genomic DNA was extracted from whole blood of mice induced with Tmx or Veh for 8 wks. (c-k) Loss of Six1 does not affect mouse normal adult hematopoiesis as measured using contents of RBC (c), WBC (d) and platelets (e) from whole blood; and percentage of BM cells that are LT-HSC (f), LSK (g), GMP (h), MEP (i), CMP (j) and CLP (k) at week 8 after Tmx induction. n = 4 per group. (l) Experimental approach for evaluating the role of SIX1 in MLL-AF9-dependent leukemogenesis. (m) Significant reduction of Six1 mRNA levels and CFU counts were observed in Tmx-exposed MLL-AF9-transformed Six1-fl/fl;Scl-creERT LICs compared to WT controls. n = 3 per group. (n) Six1 null LICs proliferate more slowly compared to WT control cells. BrdU incorporation was used for the measurement of proliferation at the indicated time points. n = 3 per group. (o) Six1 null AML mice exhibit decreased LICs in total YFP+ leukemic cells of BM than WT controls. n = 4 per group. (p) Abundance of circulating YFP+ leukemic cells is decreased in mice transplanted with Six1 null LICs (n = 8) compared to WT controls (n = 6). (q) Loss of Six1 in LICs (n = 8) slows disease progression in animals engrafted with AML LICs as compared with WT controls (n = 6). Log-Rank test is used for statistical analysis. In c-k and m-p, data is expressed as mean ± S.D. Error bars represent indicated numbers of biological replicates. ** P < .01. * P < .05. ns: not significant. [Student's t-test].
3.3. Transcriptional profiling identifies the six1 homeobox gene as an atypical target of WNT/β-catenin signaling in AML
In response to certain Wnt ligands, nuclear accumulation coupled with biochemical changes in β-catenin induces activation of the TCF/LEF family of DNA binding proteins [43]. To determine if PORCN, TNKS, and WLS regulate transcriptional output in AML LICs we performed transcriptome profiling in LICs isolated from animals treated with either IWP2G9 or IWR107, or that lack Wls expression (Fig. 3a; Supp. Table 1). The superimposition of genes with shared responses to these perturbations returned down-regulated genes known to suppress WNT-mediated signaling (Igfbp4 and Shisa2) [44,45], suggesting the presence of WNT pathway feed-forward signaling mechanisms in LICs akin to those seen in other tissues [43]. At the same time, the induction of many histone genes coupled with the decrease in circulating leukemic cells in peripheral blood observed with loss of WNT signaling suggests a stalling in the LIC cell cycle [46].
The most extensive gene expression change was associated with the DNA binding protein SIX1. SIX1 along with its binding partner Eyes absent (EYA) and the other SIX and EYA family members play pivotal roles in metazoan organogenesis [47,48]. Mutations in either SIX1 or EYA1 result in branchio-oto-renal (BOR) syndrome which is associated with several developmental defects including those of the heart, ear, and kidney [49]. We confirmed that Six1 mRNA expression indeed is reduced in LICs following exposure to a PORCN or TNKS inhibitor using quantitative RT-PCR (qPCR) analysis (Fig. 3b). Furthermore, we observed a nearly 20-fold increase in Six1 mRNA expression in MLL-AF9 expressing LICs compared to WT hematopoietic stem/progenitor population LSKs (Lin− Sca1+ cKit+; Fig. 3c) suggesting that WNT/β-catenin signaling controls a developmental program not typically found in hematopoietic cells. Increased expression of SIX1 and EYA1 has also been previously reported in MLL-AF9 transformed leukemic cells [50,51].
3.4. WNT1 regulates Six1 expression in LICs
Disruption of WNT signaling by either chemical or genetic attack of PORCN reduces Six1 expression in MLL-AF9 transformed LICs. We profiled the mRNAs encoding any of the 19 WNT proteins in MLL-AF9 LICs and normal LSKs in order to identify changes in Wnt gene expression that may contribute to the induction of Six1 expression in MLL-AF9 cells (Fig. 3d). We identified four mRNAs encoding WNT proteins to be altered by expression of MLL-AF9: Wnt1, Wnt5a and Wnt5b were induced whereas Wnt10a was reduced. We selected WNT1 for further evaluation given the abundance of its mRNA was the most altered among WNT family member mRNAs associated with MLL-AF9 expression. Exposure of LICs to recombinant WNT1 induced expression of Six1 mRNA in a TNKS-dependent fashion (Fig. 3e-f) suggesting WNT1 promotes β-catenin-dependent expression of Six1 in MLL-AF9 transformed cells and that both IWP2G9 and IWR107 at least in part counteract WNT1 signaling.
3.5. SIX1 is essential for MLL-AF9-driven AML but not normal adult hematopoiesis
We directly tested the role of SIX1 in adult blood cell formation with the targeted deletion of Six1 in the hematopoietic system using the strategy employed to evaluate the role of Wls on hematopoiesis (Fig. 4a-b). A survey of cell numbers for differentiated and stem/progenitor blood cell types revealed no discernible difference in blood cell development in animals with WT or Six1 null background (Fig. 4c-k). In support of these observations, hematopoietic defects have not been reported in BOR syndrome patients harboring autosomal dominant mutations in either SIX1 or EYA1 [52].
We next evaluated the role of SIX1 in AML progression using targeted deletion of Six1 in hematopoietic cells followed by transformation of isolated Lin− cells with MLL-AF9 expressing retrovirus (Fig. 4l). Compared with WT LICs, Six1 null LICs had little/no detectable Six1 expression and reduced ability to form colonies when cultured in vitro (Fig. 4m). Decreased levels of BrdU incorporation suggest a slower rate of proliferation in the Six1 null LICs compared with those expressing Six1 mRNA (Fig. 4n). When transplanted into secondary hosts, the percent of LICs isolated from the bone marrow of Six1 null animals was ~2-fold less than those observed with WT cells (Fig. 4o). Consistent with this observation, Six1 null leukemic cells were less frequently observed in circulating blood compared with WT leukemic cells (Fig. 4p). Overall, the diminished ability of the Six1 null LICs to populate the secondary host likely accounts for the extension in life span seen in these animals compared with those inoculated with Six1 WT LICs (Fig. 4q).
3.6. Chromatin remodeling by MLL-AF9 installs a WNT/SIX1 signaling apparatus in LICs
Much of our understanding of how MLL-AF9 promotes tumorigenesis is inferred from MLL-AF9-associated gene expression changes, or the identification of genomic loci potentially subject to MLL-AF9-induced chromatin remodeling using ChIP-seq analysis [6,14,27,50,53,54]. We used assay for transposase-accessible chromatin using sequencing (ATAC-seq) to better understand the contribution of MLL-AF9 induced chromatin changes to the assembly of a WNT/SIX1 signaling axis (Fig. 5a; Supp. Fig. 5; Supp. Table 2). Among the genes we have identified with chromatin accessibility changes using this approach that were previously shown to be bound by MLL-AF9 [6] were several that are essential for AML development (Hoxa9, Meis1, Jmjd1c) in addition to Six1 and Eya1 (Fig. 5b). Co-expression of the HOXA9 and MEIS1 homeobox proteins is sufficient to induce AML in mice [14] whereas the histone demethylase JMJD1C is required for disease progression [55,56]. MLL-AF9 altered transposase accessibility of two genomic regions within 10 kb of the Six1 transcriptional start site (Fig. 5c). Using ChIP-qPCR, we demonstrated that DNA sequences containing consensus TCF/LEF binding motifs within these Six1 proximal genomic regions were associated with TCF7L2 binding in an MLL-AF9-dependent manner (Fig. 5d; Supp. Table 3). TCF7L2 is one of four TCF/LEF gene family members and has been associated with β-catenin-dependent transcriptional responses that promote resistance to inhibitors targeting the chromatin reader BRD4 in MLL-AF9 leukemic cells [57]. These observations taken together suggest MLL-AF9 alters the accessibility of TCF/LEF transcriptional regulatory elements controlling SIX1 expression thus placing SIX1 under WNT-mediated control in LICs.
Fig. 5.
Chromatin remodeling by MLL-AF9 confers WNT-dependent regulation of Six1 expression in LICs. (a) Assay for Transposase Accessible Chromatin with high-throughput sequencing (ATAC-Seq) was used to identify shared and unique chromatin regions (peaks) accessible to transposase activity in MLL-AF9 AML LICs vs. WT LSKs. Numbers of mapped genes from identified peaks are shown in the inset. Two biological replicates were used in the assay. (b) Putative direct target genes of MLL-AF9 identified by superimposing genes associated with regions of chromatin change induced by MLL-AF9 and previously identified by ChIP-Seq analysis using MLL-AF9 pull-down [6]. Six1 and its binding partner gene Eya1 (in bold) are among them. (c) Normalized ATAC-Seq profiles at Six1 locus. Signals of AML LICs and normal LSKs are depicted in red and blue, respectively. Two elevated peaks are observed: one immediately upstream of the transcriptional start site (TSS) and another ~8 K further upstream of TSS. (d) TCF7L2 (TCF4) binding to DNA regions within each peak was determined by ChIP-qPCR. Amplicons used in the analysis and whether or not they harbor putative TCF/LEF binding sites are outlined. Data is expressed as means ± S.D. Error bars represent three biological replicates. * P < .05, ** P < .01, ns: not significant. [Student's t-test].
3.7. Six1 is a potential biomarker for targeting WNT signaling in some forms of human MLL rearranged AML
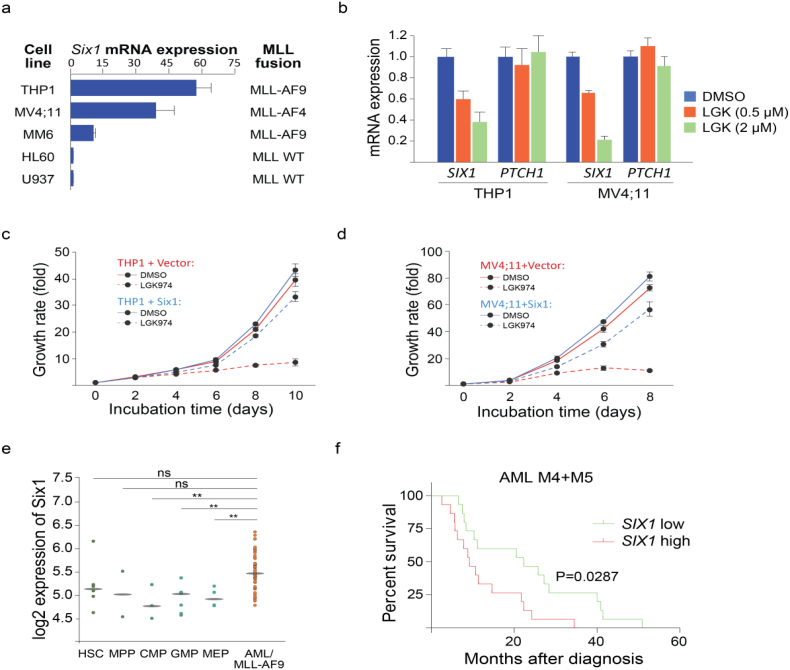
Our studies in mice have revealed a role for a WNT/SIX1 signaling axis in AML progression. To investigate if this signaling axis plays roles in human leukemia, we profiled a panel of human AML cell lines for their Six1 mRNA expression (Fig. 6a). Among these cell lines, THP1 (MLL-AF9 re-arrangement) and MV4;11 (MLL-AF4 re-arrangement) cells manifest higher Six1 expression. We next tested the impact of the PORCN inhibitor LGK974 on Six1 expression in both cell lines. Similar to the effects seen with our compound IWP2G9, LGK974 was found to target the WNT acyltransferase PORCN and is currently in clinic testing. LGK974 inhibits Six1 expression (Fig. 6b) and reduces cell growth of both cell lines (Fig. 6c-d). To test if the growth inhibition is Six1-dependent, we established stable cell lines expressing Six1 in both cell lines. As expected, Six1 overexpression partially rescued the growth inhibition by LGK974 in THP1 (Fig. 6c) and MV4;11 cells (Fig. 6d). To further investigate the broader relevance of Six1 in human leukemogenesis, we explored publically available datasets and provide two lines of evidence to support the role of Six1 in AML. First, primary AML cells that harbor MLL-AF9 gene re-arrangements exhibit elevated SIX1 expression level when compared with that found in normal hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell types (Fig. 6e). Second, we observed a significant increase in mortality ~5 years after diagnosis in M4 and M5 AML subtype patients with elevated SIX1 expression (Fig. 6f). Notably, MLL-AF9 AML is most commonly associated with these subtypes of AML [58]. In addition, age and the FAB subtype M5 are risk factors when analyzed with the multivariate Cox proportional hazards model (Supp. Table 4).
Fig. 6.
Six1 is a potential biomarker for targeting WNT signaling in some forms of human MLL rearranged AML. (a) Profiling of Six1 mRNA expression in a panel of human AML lines. Expression levels are normalized to U937 cells (lowest expression) and rank ordered. THP1 (MLL-AF9 re-arrangement) and MV4;11 (MLL-AF4 re-arrangement) cells have higher Six1 mRNA expression among 6 cell lines tested. n = 3 technical replicates. (b) The PORCN inhibitor LGK974 dose-dependently inhibits Six1 mRNA expression in THP1 and MV4;11 cells. Cells were incubated with LGK974 for 30 h at the indicated doses. PTCH1 was used as a control for evaluating the on-target effect of the compound. (c-d) The growth of THP1 (c) or MV4;11 (d) cells is inhibited by LGK974 (2 μM) in the indicated time course. Stably expressing Six1 in THP1 (c) or MV4;11 (d) cells partially rescues the growth inhibition by LGK974. (e) SIX1 expression in human normal hematopoietic lineage cells (GSE42519) vs. human AML cells [GSE13159, GSE15434, GSE61804, GSE14468, The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA)]. ** P < .01. ns: not significant. [Student's t-test] AML/MLL-AF9: AML with t(11q23)/MLL-AF9 rearrangement. (f) High SIX1 expression is correlated with poor survival in AML subtype M4 and M5 patients [based on the French-American-British (FAB) classification system]. The Kaplan-Meier plots were generated using gene expression data of 183 AML patient samples from TCGA [39]. High and low SIX1 expression is defined as above and below the median of expression values across all patient samples, respectively.
4. Discussion
The ease in which the forced expression of only four proteins (Yamanaka factors) can transform differentiated cells into those with pluripotent properties reveals a previously unimaginable level of plasticity in adult cells [59]. Cancerous cells to different degrees emerge from this inherent cellular plasticity. Whereas anti-cancer strategies premised upon directly targeting the epigenetic machinery are in development and have seen some initial responses [3], the rewiring of well-established signaling programs by epigenetic alterations that ultimately fuel tumor growth as described here offers unanticipated therapeutic opportunities with potentially robust companion biomarkers (Fig. 7). The non-essentiality of WNT/β-catenin signaling to adult hematopoiesis also contributes to the potential of PORCN inhibitors as a point of intervention in MLL-AF9-driven tumors [16,18].
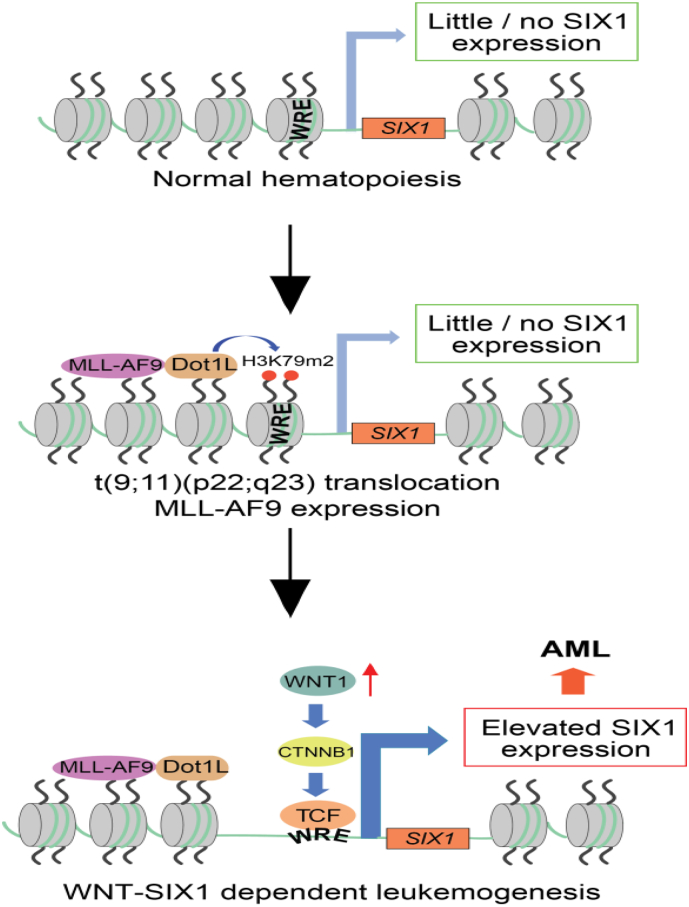
Fig. 7.
Model of WNT/SIX1 signaling promoting AML. MLL-AF9 recruits the histone methyltransferase Dot1L to TCF/LEF binding sites proximal to SIX1 thus installing a LIC-intrinsic WNT/SIX1 signaling axis that promotes leukemogenesis. WRE = WNT Responsive Element.
Persistent exposure of some adult stem cells to WNT ligands, such as those in the gut and liver, is required to prevent their differentiation and premature loss of tissue renewal capacity [43]. Our results reveal two types of WNT pathway alterations introduced by MLL-AF9 expression in LICs. First, changes in chromatin accessibility are observed in several WNT genes (Wnt1, 2B, 3A, 6, 9B, and 11) with one of these (Wnt1) also shown to be transcriptionally altered (see Fig. 3 and Supp. Table 2). Although the chemical and genetic evidence presented here suggest that LIC-intrinsic WNT signaling is critical in experimental models of AML, they clearly do not eliminate a disease-supporting role for WNT ligands produced from other cells in the niche [60]. Indeed, we note that loss of Wls in the LICs only delays disease progression. It is also conceivable that the contribution of non-canonical WNT signaling to the development of AML was not illuminated by our focus on molecular changes as a consequence of disabling WNT/β-catenin signaling using both PORCN and TNKS inhibitors. Second, chromatin changes to DNA proximal to Six1 that harbor TCF/LEF binding elements license WNT/β-catenin-dependent regulation of SIX1 expression (see Fig. 7). We speculate that WNT-dependent regulation of SIX1 expression albeit foreign in the context of hematopoiesis, is not an innovation of disease-promoting cells but rather a mechanism used in embryonic development, adult tissue maintenance, or both. Indeed, some observations indirectly linking WNT signaling and SIX1 expression in developmental processes suggest this could be the case [61,62].
Whereas our studies have focused on MLL-AF9-driven tumors primarily given the reliability of MLL-AF9 for delivering a pre-clinical model of AML in mice, translocations that give rise to MLL-AF9 represent only a minor percentage of all AML (2–5%) [63]. However, a greater portion of childhood AMLs (25%) are associated with MLL-AF9 expression thus warranting additional resources to evaluate the role of WNT signaling in these pediatric cancers [63]. Indeed, a broader role of WNT signaling in AML is implicated from the results of DNA methylation analysis in pediatric AML cases where the majority is associated with one or more changes in well-established WNT pathway suppressors such as AXIN2 or DKK1 [11].
A more general role of SIX1 in hematological malignancies is also inferred from its induced expression in MLL-ENL AML and in Hodgkin lymphoma [51,64]. In addition to other proteins, SIX1 is also known to directly regulate the cell cycle machinery by transcriptional control of several of its components thus potentially providing a mechanistic account of SIX1 function in AML [65,66]. Conversion of SIX1 from a transcriptional suppressor to an activator is dependent upon the phosphatase activity of EYA1 [67]. This activity is necessary for the recruitment of transcriptional co-factors such as CREB-binding protein (CBP) [67]. Indeed, the ability of EYA1 overexpression to immortalize hematopoietic progenitor cells suggests that it plays an important role in cellular transformation [51].
Our studies identify two chemically actionable targets – PORCN and the TNKS enzymes – that regulate a WNT-SIX1 oncogenic pathway in leukemogenesis. Whereas LGK974 has progressed to clinical testing, the TNKS inhibitors have yet to see human experience [68]. Thus, PORCN inhibitors may afford a path to targeting a subset of AMLs. Although not yet formally established in the context of AML that EYA1 is required for SIX1 activity, previous observations that support the concomitant induction of SIX1 and EYA1 by MLL-AF9 [50,51], and the evidence provided here that implicate a direct effect of MLL-AF9 activity on SIX1 and EYA1 expression (see Fig. 5B) suggests that small molecules that target EYA1 should also be investigated for therapeutic utility in hematological malignancies [69].
Acknowledgments
Acknowledgements
The Six1-floxed mouse strain was kindly provided by Dr. Carmen J. Williams at National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences and Dr. Pin-Xian Xu at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
Sources of funding
This work was supported by the Welch Foundation (I-1665 to LL; I-1834 to CCZ), CPRIT (RP130212 to LL and CC; and RP180435 to CCZ), and the National Cancer Institute (1R01 CA168761 to JK; P50-CA70907). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Declaration of interests
L. Lum, C. Chen, and L.S. Zhang are named inventors on patents covering various WNT inhibitors including those targeting PORCN. C.C. Zhang reports grants and other from Immune-Onc Therapeutics, outside the submitted work.
Author contributions
LSZ and LL conceived the study and wrote the paper. LSZ, XK, XW, GW, JZ, RT and HY performed experiments. JL, HS, and QW performed the chemical synthesis of Wnt inhibitors. YZ performed the ATAC-Seq data analysis. LSZ performed all other data analysis. LM performed the PK study of WNT inhibitors. PM constructed Six1-floxed mouse line. LJH, JK, NW, JX, CC, CCZ and LL provided technical support and conceptual input. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Footnotes
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.11.039.
Appendix A. Supplementary data
Supplementary material 1
Supplementary material 2
Supplementary material 3
References
- 1.Hanahan D., Weinberg R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144(5):646–674. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bennett R.L., Licht J.D. Targeting epigenetics in cancer. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018;58:187–207. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010716-105106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Brien G.L., Valerio D.G., Armstrong S.A. Exploiting the epigenome to control cancer-promoting gene-expression programs. Cancer Cell. 2016;29(4):464–476. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.03.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Jones P.A., Issa J.P., Baylin S. Targeting the cancer epigenome for therapy. Nat Rev Genet. 2016;17(10):630–641. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2016.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hu D., Shilatifard A. Epigenetics of hematopoiesis and hematological malignancies. Genes Dev. 2016;30(18):2021–2041. doi: 10.1101/gad.284109.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bernt K.M., Zhu N., Sinha A.U., Vempati S., Faber J., Krivtsov A.V. MLL-rearranged leukemia is dependent on aberrant H3K79 methylation by DOT1L. Cancer Cell. 2011;20(1):66–78. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.06.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chang M.J., Wu H., Achille N.J., Reisenauer M.R., Chou C.W., Zeleznik-Le N.J. Histone H3 lysine 79 methyltransferase Dot1 is required for immortalization by MLL oncogenes. Cancer Res. 2010;70(24):10234–10242. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Jo S.Y., Granowicz E.M., Maillard I., Thomas D., Hess J.L. Requirement for Dot1l in murine postnatal hematopoiesis and leukemogenesis by MLL translocation. Blood. 2011;117(18):4759–4768. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-12-327668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Nguyen A.T., Taranova O., He J., Zhang Y. DOT1L, the H3K79 methyltransferase, is required for MLL-AF9-mediated leukemogenesis. Blood. 2011;117(25):6912–6922. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-02-334359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lum L., Chen C. Chemical disruption of wnt-dependent cell fate decision-making mechanisms in cancer and regenerative medicine. Curr Med Chem. 2015;22(35):4091–4103. doi: 10.2174/0929867322666150827094015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bolouri H., Farrar J.E., Triche T., Jr., Ries R.E., Lim E.L., Alonzo T.A. The molecular landscape of pediatric acute myeloid leukemia reveals recurrent structural alterations and age-specific mutational interactions. Nat. Med. 2018;24(1):103–112. doi: 10.1038/nm.4439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fong C.Y., Gilan O., Lam E.Y., Rubin A.F., Ftouni S., Tyler D. BET inhibitor resistance emerges from leukaemia stem cells. Nature. 2015;525(7570):538–542. doi: 10.1038/nature14888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Heidel F.H., Bullinger L., Feng Z., Wang Z., Neff T.A., Stein L. Genetic and pharmacologic inhibition of beta-catenin targets imatinib-resistant leukemia stem cells in CML. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;10(4):412–424. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2012.02.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wang Y, Krivtsov AV, Sinha AU, North TE, Goessling W, Feng Z, et al. The Wnt/beta-catenin pathway is required for the development of 1leukemia stem cells in AML. Science.327(5973):1650–3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 15.Yeung J., Esposito M.T., Gandillet A., Zeisig B.B., Griessinger E., Bonnet D. Beta-Catenin mediates the establishment and drug resistance of MLL leukemic stem cells. Cancer Cell. 2010;18(6):606–618. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2010.10.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cobas M., Wilson A., Ernst B., Mancini S.J., MacDonald H.R., Kemler R. Beta-catenin is dispensable for hematopoiesis and lymphopoiesis. J Exp Med. 2004;199(2):221–229. doi: 10.1084/jem.20031615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gross J.C., Boutros M. Secretion and extracellular space travel of Wnt proteins. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2013;23(4):385–390. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2013.02.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kabiri Z., Numata A., Kawasaki A., Blank E., Tenen D.G., Virshup D.M. Wnts are dispensable for differentiation and self-renewal of adult murine hematopoietic stem cells. Blood. 2015;126(9):1086–1094. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-09-598540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Najdi R., Proffitt K., Sprowl S., Kaur S., Yu J., Covey T.M. A uniform human Wnt expression library reveals a shared secretory pathway and unique signaling activities. Differentiation. 2012;84(2):203–213. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2012.06.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chen B., Dodge M.E., Tang W., Lu J., Ma Z., Fan C.W. Small molecule-mediated disruption of Wnt-dependent signaling in tissue regeneration and cancer. Nat Chem Biol. 2009;5(2):100–107. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Huang S.M., Mishina Y.M., Liu S., Cheung A., Stegmeier F., Michaud G.A. Tankyrase inhibition stabilizes axin and antagonizes Wnt signalling. Nature. 2009;461(7264):614–620. doi: 10.1038/nature08356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Waaler J., Machon O., Tumova L., Dinh H., Korinek V., Wilson S.R. A novel tankyrase inhibitor decreases canonical Wnt signaling in colon carcinoma cells and reduces tumor growth in conditional APC mutant mice. Cancer Res. 2012;72(11):2822–2832. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wang X., Moon J., Dodge M.E., Pan X., Zhang L., Hanson J.M. The development of highly potent inhibitors for porcupine. J Med Chem. 2013;56(6):2700–2704. doi: 10.1021/jm400159c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Carpenter A.C., Rao S., Wells J.M., Campbell K., Lang R.A. Generation of mice with a conditional null allele for Wntless. Genesis. 2010;48(9):554–558. doi: 10.1002/dvg.20651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gothert J.R., Gustin S.E., Hall M.A., Green A.R., Gottgens B., Izon D.J. In vivo fate-tracing studies using the Scl stem cell enhancer: embryonic hematopoietic stem cells significantly contribute to adult hematopoiesis. Blood. 2005;105(7):2724–2732. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-08-3037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Le Grand F., Grifone R., Mourikis P., Houbron C., Gigaud C., Pujol J. Six1 regulates stem cell repair potential and self-renewal during skeletal muscle regeneration. J Cell Biol. 2012;198(5):815–832. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201201050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Krivtsov A.V., Twomey D., Feng Z., Stubbs M.C., Wang Y., Faber J. Transformation from committed progenitor to leukaemia stem cell initiated by MLL-AF9. Nature. 2006;442(7104):818–822. doi: 10.1038/nature04980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kang X., Lu Z., Cui C., Deng M., Fan Y., Dong B. The ITIM-containing receptor LAIR1 is essential for acute myeloid leukaemia development. Nat Cell Biol. 2015;17(5):665–677. doi: 10.1038/ncb3158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Moon J., Zhou H., Zhang L.S., Tan W., Liu Y., Zhang S. Blockade to pathological remodeling of infarcted heart tissue using a porcupine antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114(7):1649–1654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1621346114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zheng J., Lu Z., Kocabas F., Bottcher R.T., Costell M., Kang X. Profilin 1 is essential for retention and metabolism of mouse hematopoietic stem cells in bone marrow. Blood. 2014;123(7):992–1001. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-04-498469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Dodge M.E., Moon J., Tuladhar R., Lu J., Jacob L.S., Zhang L.S. Diverse chemical scaffolds support direct inhibition of the membrane-bound O-acyltransferase porcupine. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(27):23246–23254. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.372029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wu X., Zhang L.S., Toombs J., Kuo Y.C., Piazza J.T., Tuladhar R. Extra-mitochondrial prosurvival BCL-2 proteins regulate gene transcription by inhibiting the SUFU tumour suppressor. Nat Cell Biol. 2017;19(10):1226–1236. doi: 10.1038/ncb3616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zhu H., Mi W., Luo H., Chen T., Liu S., Raman I. Whole-genome transcription and DNA methylation analysis of peripheral blood mononuclear cells identified aberrant gene regulation pathways in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016;18:162. doi: 10.1186/s13075-016-1050-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Buenrostro J.D., Wu B., Chang H.Y., Greenleaf W.J. ATAC-seq: a method for assaying chromatin accessibility genome-wide. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2015;109:1–9. doi: 10.1002/0471142727.mb2129s109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Liu X., Zhang Y., Chen Y., Li M., Zhou F., Li K. In Situ Capture of Chromatin Interactions by Biotinylated dCas9. Cell. 2017;170(5):1028–1043. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.08.003. [e19] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Farre D., Roset R., Huerta M., Adsuara J.E., Rosello L., Alba M.M. Identification of patterns in biological sequences at the ALGGEN server: PROMO and MALGEN. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31(13):3651–3653. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Messeguer X., Escudero R., Farre D., Nunez O., Martinez J., Alba M.M. PROMO: detection of known transcription regulatory elements using species-tailored searches. Bioinformatics. 2002;18(2):333–334. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/18.2.333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bagger F.O., Sasivarevic D., Sohi S.H., Laursen L.G., Pundhir S., Sonderby C.K. BloodSpot: a database of gene expression profiles and transcriptional programs for healthy and malignant haematopoiesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44(D1):D917–D924. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Cancer Genome Atlas Research N., Ley T.J., Miller C., Ding L., Raphael B.J., Mungall A.J. Genomic and epigenomic landscapes of adult de novo acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(22):2059–2074. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1301689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Dodge M.E., Lum L. Drugging the cancer stem cell compartment: lessons learned from the hedgehog and Wnt signal transduction pathways. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2011;51:289–310. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010510-100558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Nguyen D.X., Chiang A.C., Zhang X.H., Kim J.Y., Kris M.G., Ladanyi M. WNT/TCF signaling through LEF1 and HOXB9 mediates lung adenocarcinoma metastasis. Cell. 2009;138(1):51–62. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.04.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Scheel C., Eaton E.N., Li S.H., Chaffer C.L., Reinhardt F., Kah K.J. Paracrine and autocrine signals induce and maintain mesenchymal and stem cell states in the breast. Cell. 2011;145(6):926–940. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.04.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Nusse R., Clevers H. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling, disease, and emerging therapeutic modalities. Cell. 2017;169(6):985–999. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Yamamoto A., Nagano T., Takehara S., Hibi M., Aizawa S. Shisa promotes head formation through the inhibition of receptor protein maturation for the caudalizing factors. Wnt and FGF Cell. 2005;120(2):223–235. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.11.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Zhu W., Shiojima I., Ito Y., Li Z., Ikeda H., Yoshida M. IGFBP-4 is an inhibitor of canonical Wnt signalling required for cardiogenesis. Nature. 2008;454(7202):345–349. doi: 10.1038/nature07027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Ewen M.E. Where the cell cycle and histones meet. Genes Dev. 2000;14(18):2265–2270. doi: 10.1101/gad.842100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Christensen K.L., Patrick A.N., McCoy E.L., Ford H.L. The six family of homeobox genes in development and cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 2008;101:93–126. doi: 10.1016/S0065-230X(08)00405-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Xu P.X. The EYA-SO/SIX complex in development and disease. Pediatric Nephrology (Berlin, Germany) 2013;28(6):843–854. doi: 10.1007/s00467-012-2246-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Kochhar A., Fischer S.M., Kimberling W.J., Smith R.J. Branchio-oto-renal syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2007;143A(14):1671–1678. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.31561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Stavropoulou V., Kaspar S., Brault L., Sanders M.A., Juge S., Morettini S. MLL-AF9 expression in hematopoietic stem cells drives a highly invasive AML expressing EMT-related genes linked to poor outcome. Cancer Cell. 2016;30(1):43–58. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.05.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Wang Q.F., Wu G., Mi S., He F., Wu J., Dong J. MLL fusion proteins preferentially regulate a subset of wild-type MLL target genes in the leukemic genome. Blood. 2011;117(25):6895–6905. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-12-324699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Smith R.J.H. Branchiootorenal Spectrum Disorders. In: Adam M.P., Ardinger H.H., Pagon R.A., Wallace S.E., LJH Bean, Mefford H.C., editors. GeneReviews((R)) 1993. Seattle (WA) [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kuntimaddi A., Achille N.J., Thorpe J., Lokken A.A., Singh R., Hemenway C.S. Degree of recruitment of DOT1L to MLL-AF9 defines level of H3K79 Di- and tri-methylation on target genes and transformation potential. Cell Rep. 2015;11(5):808–820. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.04.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Wei J., Wunderlich M., Fox C., Alvarez S., Cigudosa J.C., Wilhelm J.S. Microenvironment determines lineage fate in a human model of MLL-AF9 leukemia. Cancer Cell. 2008;13(6):483–495. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.04.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Chen M., Zhu N., Liu X., Laurent B., Tang Z., Eng R. JMJD1C is required for the survival of acute myeloid leukemia by functioning as a coactivator for key transcription factors. Genes Dev. 2015;29(20):2123–2139. doi: 10.1101/gad.267278.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Sroczynska P., Cruickshank V.A., Bukowski J.P., Miyagi S., Bagger F.O., Walfridsson J. shRNA screening identifies JMJD1C as being required for leukemia maintenance. Blood. 2014;123(12):1870–1882. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-08-522094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Rathert P., Roth M., Neumann T., Muerdter F., Roe J.S., Muhar M. Transcriptional plasticity promotes primary and acquired resistance to BET inhibition. Nature. 2015;525(7570):543–547. doi: 10.1038/nature14898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Swansbury G.J., Slater R., Bain B.J., Moorman A.V., Secker-Walker L.M. Hematological malignancies with t(9;11)(p21-22;q23)--a laboratory and clinical study of 125 cases. European 11q23 Workshop participants. Leukemia. 1998;12(5):792–800. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2401014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Takahashi K., Yamanaka S. A decade of transcription factor-mediated reprogramming to pluripotency. Nature Reviews. 2016;17(3):183–193. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Lane S.W., Wang Y.J., Lo Celso C., Ragu C., Bullinger L., Sykes S.M. Differential niche and Wnt requirements during acute myeloid leukemia progression. Blood. 2011;118(10):2849–2856. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-03-345165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Freyer L., Morrow B.E. Canonical Wnt signaling modulates Tbx1, Eya1, and Six1 expression, restricting neurogenesis in the otic vesicle. Dev Dyn. 2010;239(6):1708–1722. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.22308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Petropoulos H., Skerjanc I.S. Beta-catenin is essential and sufficient for skeletal myogenesis in P19 cells. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(18):15393–15399. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112141200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Muntean A.G., Hess J.L. The pathogenesis of mixed-lineage leukemia. Annu Rev Pathol. 2012;7:283–301. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-011811-132434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Nagel S., Meyer C., Kaufmann M., Drexler H.G., MacLeod R.A. Aberrant expression of homeobox gene SIX1 in Hodgkin lymphoma. Oncotarget. 2015;6(37):40112–40126. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Coletta R.D., Christensen K., Reichenberger K.J., Lamb J., Micomonaco D., Huang L. The Six1 homeoprotein stimulates tumorigenesis by reactivation of cyclin A1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(17):6478–6483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0401139101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Ford H.L., Kabingu E.N., Bump E.A., Mutter G.L., Pardee A.B. Abrogation of the G2 cell cycle checkpoint associated with overexpression of HSIX1: a possible mechanism of breast carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95(21):12608–12613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.21.12608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Li X., Oghi K.A., Zhang J., Krones A., Bush K.T., Glass C.K. Eya protein phosphatase activity regulates Six1-Dach-Eya transcriptional effects in mammalian organogenesis. Nature. 2003;426(6964):247–254. doi: 10.1038/nature02083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Sheridan C. Wnt is back in drugmakers' sights, but is it druggable? Nat Biotechnol. 2018;36(11):1028–1029. doi: 10.1038/nbt1118-1028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Krueger A.B., Drasin D.J., Lea W.A., Patrick A.N., Patnaik S., Backos D.S. Allosteric inhibitors of the Eya2 phosphatase are selective and inhibit Eya2-mediated cell migration. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(23):16349–16361. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.566729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary material 1
Supplementary material 2
Supplementary material 3
Data Availability Statement
All raw and processed microarray and ATAC-seq data are deposited in the Gene Expression Omnibus, GSE: 111278.