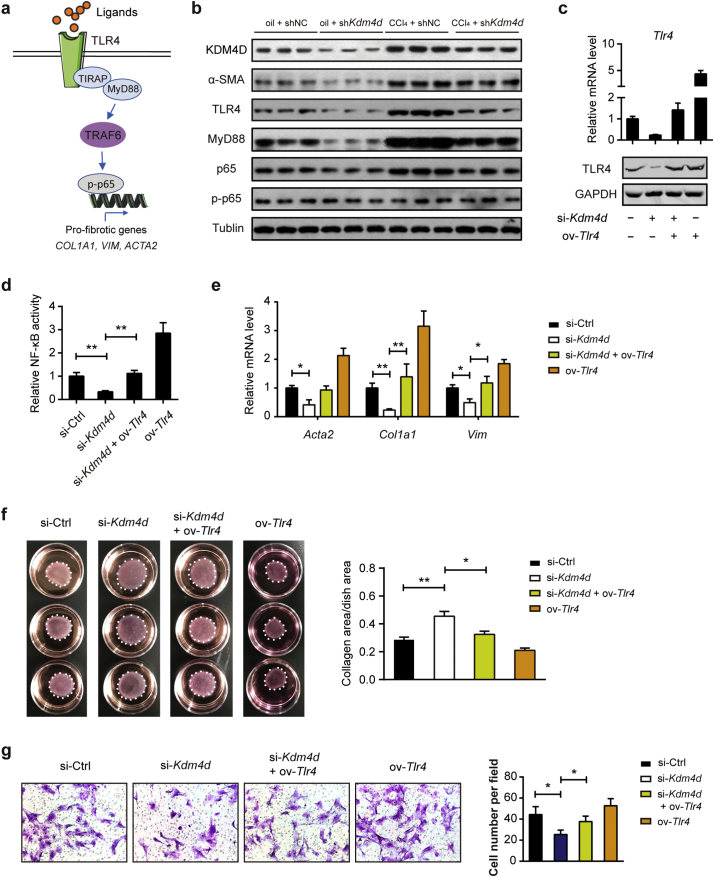
Fig. 6.
KDM4D promotes liver fibrosis by activating TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathways. (a) Schematic depicting TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. (b) Proteins from primary HSCs in oil + shNC, oil + shKdm4d, CCl4 + shNC, and CCl4 + shKdm4d groups were harvested and assayed by western blotting (n = 3 representative mice for each group) with indicated antibodies. Tubulin was used as the loading control. (c) Certification of Kdm4d and Tlr4 expression at both mRNA and protein level in the presence of Kdm4d knockdown and/or Tlr4 overexpression in primary isolated HSCs. (d–g) The effects of Tlr4 overexpression on the NF-κB transcriptional activity, expression of pro-fibrotic genes, and contractile and migratory capacities in Kdm4d knockdown primary HSCs. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. *p < .05, **p < .01.