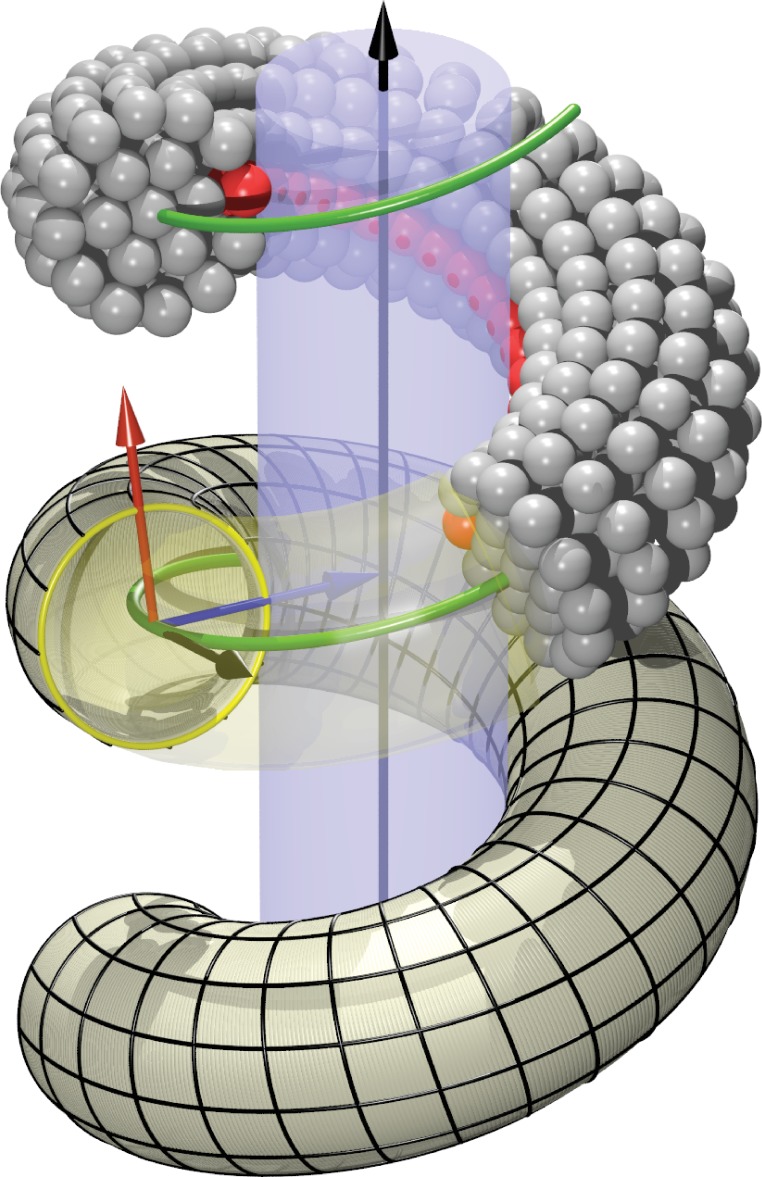
Figure 5. Definition of helicoidal coordinate system.
The black vertical -axis is surrounded by a cylinder, around which a helical dynamin tube winds. Its green center line with radius and pitch is given by (Equation 1). On this space curve we define the (right-handed) Darboux-frame , consisting of a tangent vector (black), normal vector (blue) and co-normal vector (red), which are given by (Equation 2). In the --plane we can then define the circular cross-section of the filament and place rings of CG beads at the correct distance from the green filament axis. The direction along points towards the enclosed cylinder, but it is easy to rotate it by an angle around the axis. This is how one may rotate the beads representing the PH domain (red) off the underlying substrate.