Abstract
Phosphatidylethanolamine N‐methyltransferase (PEMT) is a hepatic integral membrane protein localized to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). PEMT catalyzes approximately 30% of hepatic phosphatidylcholine (PC) biosynthesis. Pemt–/– mice fed a high‐fat diet (HFD) develop steatohepatitis. Interestingly, portions of the ER located close to the canaliculus are enriched in PEMT. Phospholipid balance and asymmetrical distribution by adenosine triphosphatase phospholipid transporting 8B1 (ATP8B1) on the canalicular membrane is required for membrane integrity and biliary processes. We hypothesized that PEMT is an important supplier of PC to the canaliculus and that PEMT activity is critical for the maintenance of canalicular membrane integrity and bile formation following HFD feeding when there is an increase in overall hepatic PC demand. Pemt+/+ and Pemt–/– mice were fed a chow diet, an HFD, or a choline‐supplemented HFD. Plasma and hepatic indices of liver function and parameters of bile formation were determined. Pemt–/– mice developed cholestasis, i.e, elevated plasma bile acid (BA) concentrations and decreased biliary secretion rates of BAs and PC, during HFD feeding. The maximal BA secretory rate was reduced more than 70% in HFD‐fed Pemt–/– mice. Hepatic ABCB11/bile salt export protein, responsible for BA secretion, was decreased in Pemt–/– mice and appeared to be retained intracellularly. Canalicular membranes of HFD‐fed Pemt–/– mice contained fewer invaginations and displayed a smaller surface area than Pemt+/+ mice. Choline supplementation (CS) prevented and reversed the development of HFD‐induced cholestasis. Conclusion: We propose that hepatic PC availability is critical for bile formation. Dietary CS might be a potential noninvasive therapy for a specific subset of patients with cholestasis.
Abbreviations
- Abcb
adenosine triphosphatase binding cassette subfamily B
- ALT
alanine aminotransferase
- ANOVA
analysis of variance
- ATP8B1
adenosine triphosphatase phospholipid transporting 8B1
- BA
bile acid
- BiP
binding immunoglobulin protein
- BRIC
benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis
- BSEP
bile salt export protein (Abcb11)
- CD
clusters of differentiation
- CHOP
CCAAT/‐enhancer‐binding protein homologous protein
- Col1a1
collagen type I alpha 1 chain
- CS
choline supplementation
- CSHFD
choline‐supplemented high‐fat diet
- CYP
cytochrome P450
- ER
endoplasmic reticulum
- FXR
farnesoid X receptor
- GAPDH
glyceraldehyde 3‐phosphate dehydrogenase
- HFD
high‐fat diet
- LSD
least significant difference
- MDR
multidrug resistance
- mRNA
messenger RNA
- MRP
multidrug resistance‐associated protein
- NAFLD
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- NASH
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
- Nox2
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, reduced form oxidase
- NTCP
sodium‐taurocholate co‐transporting polypeptide
- OATP1
organic anion co‐transporting polypeptide
- PC
phosphatidylcholine
- PE
phosphatidylethanolamine
- PEMT
phosphatidylethanolamine N‐methyltransferase
- PFIC
progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis
- SHP
small heterodimer partner
- TG
triacylglycerol
- TUDCA
tauroursodeoxycholic acid
- VLDL
very low‐density lipoprotein
- Zfp36l1
zinc finger protein 36 like 1
Phosphatidylethanolamine N‐methyltransferase (PEMT) converts phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) to phosphatidylcholine (PC) in the liver and accounts for approximately 30% of hepatic PC synthesis.1 The remaining 70% of hepatic PC is synthesized from choline through the cytidine diphosphate choline pathway.1 Our laboratory has previously demonstrated that Pemt–/– mice fed a high‐fat diet (HFD) are protected from diet‐induced obesity and insulin resistance.2 However, HFD‐fed Pemt–/– mice also develop nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), largely due to impairment in very low‐density lipoprotein (VLDL) secretion associated with insufficient availability of PC.2, 3 PEMT deficiency decreases the hepatic PC:PE molar ratio, which impairs membrane integrity and results in endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and liver disease.2, 4, 5, 6, 7 Long‐term HFD feeding in Pemt–/– mice leads to progression of hepatic steatosis into nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and fibrosis.8 Interestingly, these effects can largely be prevented by dietary choline supplementation (CS).2
The equivalent of the entire hepatic pool of PC is secreted into the bile within 24 hours (approximately 23 mg/day/20g mouse) along with bile acids (BAs) and cholesterol.9, 10 Biliary PC is essential for the protection of cells lining the biliary tree from the cytotoxic actions of high concentrations of biliary BA.11 BAs, which are exclusively synthesized from cholesterol in the liver, are secreted into bile by the bile salt export protein (BSEP; also known as adenosine triphosphatase [ATPase] binding cassette subfamily B member 11 [ABCB11]), PC by the flippase ABCB4/multidrug resistance 2 (MDR2), and cholesterol by the ABCG5/ABCG8 heterodimer.11, 12 ATPase phospholipid transporting 8B1 (ATP8B1) maintains phospholipid asymmetry of the canalicular membrane that is essential for hepatobiliary transport. Mutations or defects in the above proteins can result in the development of cholestasis, which is an impairment in secretion of bile and biliary constituents. In humans, mutations in genes encoding ATP8B1, BSEP (ABCB11), or ABCB4 result in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC) types 1, 2, and 3, respectively.9 BAs are effectively maintained in the enterohepatic circulation, with only 5% of BAs lost per cycle in the feces, which is the major pathway for cholesterol elimination.13 BAs can activate the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) in both the intestine and liver to maintain hepatic BA homeostasis, i.e., decrease hepatic BA synthesis and uptake while increasing BA secretion.14, 15
Although PEMT is present throughout the ER, this protein is enriched in portions of the ER that are in proximity to the canalicular membrane.16 We previously observed no differences in bile formation between Pemt+/+ and Pemt–/– mice fed a chow diet.17 However, we hypothesized that HFD feeding, which decreases hepatic PC content and reduces membrane integrity in Pemt–/– mice, might attenuate biliary secretion processes and thereby induce aspects of cholestasis.2, 5 We report that, following HFD feeding, PEMT deficiency indeed leads to hallmarks of cholestasis. Dietary choline was able to moderately increase hepatic PC availability and to both treat and prevent the development of cholestasis in HFD‐fed Pemt–/– mice. Hence, maintaining an adequate supply of hepatic PC is critical for proper biliary secretion.
Materials and Methods
Animals
All procedures were approved by the University of Alberta’s Institutional Animal Care Committee in accordance with guidelines of the Canadian Council on Animal Care. All animals were exposed to a 12‐hour light/dark cycle and had free access to drinking water. Male Pemt+/+ and Pemt–/– mice (backcrossed into C57Bl/6 for seven generations, six animals per group), were 8 to 10 weeks old at the start of the study. For 2 to 10 weeks, they were fed a standard chow diet (No. 5001; LabDiet) or a semisynthetic HFD (catalog No. F3282; Bio‐Serv, Flemington, NJ) that contained 60 kcal% from lard and 1.3 g/kg choline chloride. Some mice were fed the HFD supplemented with choline chloride (4 g/kg diet; Sigma‐Aldrich, St Louis, MO) for 10 weeks. A different set of Pemt+/+ and Pemt–/– mice were placed on the HFD for 6 weeks. At this time, half the animals were either given the choline‐supplemented HFD (CSHFD) or continued on the HFD for an additional 6 weeks. Body weight was monitored weekly during the experiments. Gall bladders were cannulated, and bile was collected for 30 minutes as described.18 Tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA; Calbiochem) infusions were performed on Pemt+/+ and Pemt–/– mice fed the HFD for 10 weeks as described.18 In short, TUDCA was infused into the jugular vein with stepwise increases in infusion rates (0‐600 nmol/minute; 30 minutes per step), during which bile was continuously collected. Animals were not fasted prior to collection of blood by cardiac puncture. Tissues were collected, snap‐frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at −80°C until further analyses. Samples for histologic evaluation were fixed in formalin and subjected to anti‐BSEP antibody (PB9414; BosterBio, Pleasanton, CA) staining. For electron microscopy, samples were preserved in 3% glutaraldehyde and 3% paraformaldehyde in 0.1 M sodium cacodylate buffer, stored overnight at 4°C, and analyzed the following morning.
Analytic Procedures
Hepatic triacyglycerols (TGs) were measured by a commercially available kit from Roche Diagnostics. Hepatic PC and PE were isolated by thin‐layer chromatography and quantified by the phosphorous assay. Plasma alanine aminotransferase (ALT) activity was measured using a commercially available kit from Biotron Diagnostics. For immunoblotting, livers were homogenized in buffer (100 mM Tris‐HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid, 1 mM dithiothreitol, and 0.1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, pH 7.4) containing a protease inhibitor cocktail from Sigma‐Aldrich (P8340). Proteins were transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane. Membranes were probed with CCAAT/‐enhancer‐binding protein homologous protein (CHOP; catalog No. 2895; Cell Signaling, Beverly, MA), binding immunoglobulin protein (BiP)/78 kDa glucose‐regulated protein (GRP78) (catalog No. 3183; Cell Signaling), BSEP (catalog No. PB9414; Boster), glyceraldehyde 3‐phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH; catalog No. AM4300; Ambion), and tubulin (catalog No. T6199; Sigma‐Aldrich). Proteins were visualized by an enhanced chemiluminescence system (Amersham Biosciences, Piscataway, NJ) and quantified using G:Box (Syngene, Cambridge, United Kingdom) software. RNA isolation, complementary DNA synthesis, and real‐time quantitative polymerase chain reaction were performed as described.2 Messenger RNA (mRNA) levels were normalized to cyclophilin. Secretion of biliary components as well as BA pool composition were determined by described methods.18
Statistical Analysis
Data were analyzed with GraphPad Prism software (GraphPad, La Jolla, CA). All values are means ± SEM. For comparison of groups, 2‐way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Fisher’s least significant difference (LSD) post hoc test was used. To compare genotypes on the same feeding regimen, a Student t test was used. Level of significance of differences was set at P < 0.05. All groups were n = 6.
Results
Pemt–/– Mice Fed the HFD Develop NASH
After 10 weeks of HFD feeding, body weight was lower in Pemt–/– mice compared to Pemt+/+ mice (Supporting Fig. S1A). However, liver weight was dramatically elevated in Pemt–/– mice compared to Pemt+/+ mice (liver weight, 2.76 g versus 1.24 g, respectively) due to increased hepatic TG accumulation (Fig. 1A,B). This steatosis in Pemt–/– mice occurred concomitantly with a reduction in the hepatic PC:PE molar ratio arising from decreased PC and increased PE (Fig. 1C,D). Plasma ALT, a marker for liver damage, was significantly elevated in Pemt–/– mice compared to Pemt+/+ mice (Fig. 1E). These changes in hepatic lipids and plasma ALT developed acutely, i.e., within 2 weeks of the Pemt–/– mice being fed the HFD (Supporting Fig. S2A‐E,K).
Figure 1.
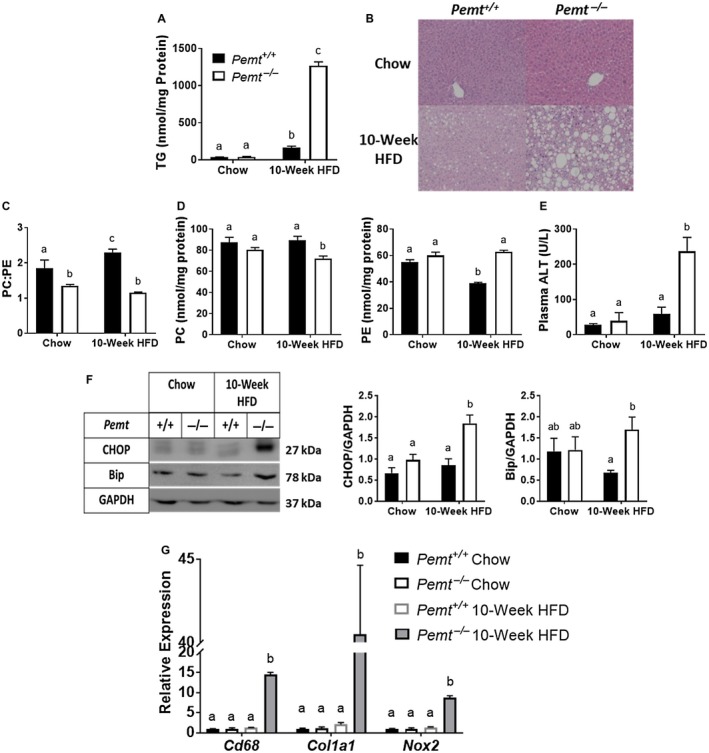
Pemt–/– mice develop NASH when fed the HFD. Pemt+/+ and Pemt–/– mice were fed the chow diet or the HFD for 10 weeks. (A) Hepatic TG mass. (B) Representative hematoxylin and eosin staining of livers of Pemt+/+and Pemt–/– mice fed either the chow diet or the HFD for 10 weeks (magnification ×20). (C) PC:PE molar ratio. (D) Mass of PC and PE. (E) Plasma ALT levels. Values are means ± SEM (n = 6 per group). (F) Bip and ER stress‐responsive CHOP and densitometry. Values are means ± SEM (n = 4 per group). (G) mRNA expression of genes involved in inflammation (Cd68), fibrosis (Col1a1), and oxidative stress (Nox2). Values are means ± SEM (n = 5 per group) and are expressed relative to Pemt+/+ mice fed the chow diet; 2‐way ANOVA, followed by Fisher’s LSD post hoc test. Values that do not share a letter are significantly different (P < 0.05).
The amount of CHOP and BiP, markers for ER stress, were significantly elevated in HFD‐fed Pemt–/– mice compared to Pemt+/+ mice (Fig. 1F; Supporting Fig. S3). Hepatic mRNA levels of clusters of differentiation (CD) 68 (CD68), collagen type I alpha 1 chain (Col1a1), and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, reduced form, oxidase (Nox2), which are markers for inflammation, fibrosis, and oxidative stress, respectively, were all significantly elevated in HFD‐fed Pemt–/– mice compared to Pemt+/+ mice (Fig. 1G). After 2 weeks of the HFD, ER stress, inflammation, and fibrosis were all significantly increased in Pemt–/– mice compared to Pemt+/+ mice (Supporting Figs. S2F‐J and S4A‐C). When the Pemt–/– mice were fed the chow diet, despite a lower hepatic PC:PE molar ratio compared to that in Pemt+/+ mice, there were no differences in hepatic TG content or liver health between genotypes (Fig. 1B).
HFD‐fed Pemt–/– Mice Develop Cholestasis
Previous studies have shown that bile flow and biliary secretion of BAs, PC, and cholesterol are not different between Pemt+/+ mice and Pemt–/– mice fed a chow diet.19 Yet, under HFD‐fed conditions, Pemt–/– mice had a markedly lower rate of bile flow as well as lower biliary secretion rates of BA and PC than Pemt+/+ mice (Fig. 2A,B). This impairment in biliary secretion in Pemt–/– mice resulted in a significant increase in plasma BA concentrations, indicative of cholestasis (Fig. 2C). The impairment in biliary BA and PC secretion was not associated with reduced biliary cholesterol secretion in Pemt–/– mice (Fig. 2B). Although biliary cholesterol secretion is usually coupled to BA and PC secretion, there are conditions under which it can be uncoupled.20, 21, 22 Plasma total bilirubin, a marker for the onset of cholestasis, was significantly higher in Pemt–/– mice than in Pemt+/+ mice (Fig. 2D).23 Pemt–/– mice fed the chow diet or the HFD for 2 weeks did not exhibit a reduced biliary BA secretion rate or an elevation in plasma BA concentration (Fig. 2A‐C; Supporting Fig. S5A‐E). However, plasma total bilirubin was increased in Pemt–/– mice after 2 weeks of HFD feeding (Supporting Fig. S5F). This indicates an early impairment in biliary elimination of bilirubin, which may suggest early signs of the development of cholestasis.
Figure 2.
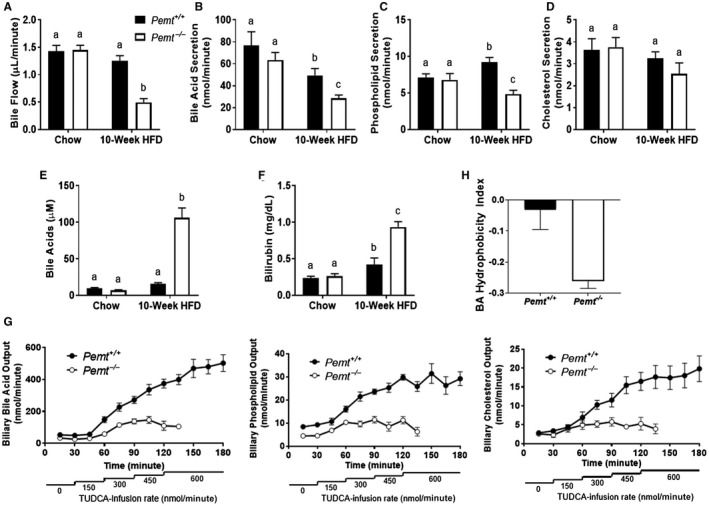
Pemt–/– mice develop diet‐induced cholestasis. Pemt+/+ and Pemt–/– mice were fed the chow diet or the HFD for 10 weeks. (A) Basal biliary bile flow and (B) secretion of BAs, (C) phospholipids, and (D) cholesterol. (E) Plasma BAs and (F) total bilirubin concentration. (G) Maximal biliary secretion of BAs, phospholipids, and cholesterol after TUDCA infusion in mice fed the HFD for 10 weeks. (H) Hydrophobicity of the BA pool after 10 weeks of the HFD. Values are means ± SEM (n = 6 per group); 2‐way ANOVA, followed by Fisher’s LSD post hoc test. Values that do not share a letter are significantly different (P < 0.05).
To determine the maximal secretory rates of BA, we infused increasing amounts of TUDCA into the jugular vein of gallbladder‐cannulated Pemt+/+ and Pemt–/– mice fed the HFD for 10 weeks. As expected, the secretion rates of BAs, PC, and cholesterol were increased following TUDCA infusion in Pemt+/+mice. However, these increases were much less pronounced in the Pemt–/– mice (Fig. 2E). Consequently, Pemt–/– mice were not able to tolerate the highest rate of TUDCA infusion and perished (Fig. 2E).
Decreased Hydrophobicity of the BA Pool in Cholestatic Pemt–/– Mice
We also determined the composition of the BA pool in Pemt+/+ and Pemt–/– mice fed the HFD for 10 weeks. The relative plasma concentrations of tauro‐β muricholic acid, β‐muricholic acid, taurocholic acid, and TUDCA were higher in Pemt–/– mice than in Pemt+/+ mice, whereas the relative amounts of cholic acid and ursodeoxycholic acid were lower (Supporting Table S1; Supporting Fig. S6). These changes resulted in a significant decrease in the hydrophobicity of the plasma BA pool in Pemt–/– mice compared to Pemt+/+ mice (Fig. 2F). Consequently, this shifted the BA pool to a less toxic nature by reducing its detergent potency. These changes may represent a compensatory mechanism to reduce BA‐induced cytotoxicity in Pemt–/– mice.24, 25
Disruption of Genes Involved in BA Homeostasis in Pemt–/– Mice
When fed a chow diet, the only difference in the expression of genes involved in BA homeostasis was a slightly higher level of multidrug resistance‐associated protein 2 (Mrp2) mRNA in Pemt–/– mice compared to Pemt+/+ mice (Fig. 3A). After 10 weeks of HFD feeding, mRNA levels of hepatic genes related to BA synthesis (cytochrome P450 family 8 subfamily B member 1 [Cyp8b1], Cyp27a1, biliary BA secretion (Abcb11), PC secretion (Abcb4), and BA import from the circulation (sodium‐taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide [Ntcp], organic anion cotransporting polypeptide [Oatp1]) were all significantly lower in Pemt–/– mice than in Pemt+/+ mice (Fig. 3B). mRNA levels of Fxr, the “master regulator” of BA homeostasis, and its effector, small heterodimer partner (Shp), were also lower in Pemt–/– mice than in Pemt+/+ mice (Fig. 3B).26 mRNA levels of zinc finger protein 36 like 1 (Zfp36l1), an RNA‐binding protein that induces degradation of Cyp7a1 mRNA, Cyp7a1, and Atp8b1, were not different between genotypes (Fig. 3B).27 Mrp2, Mrp3, and Mrp4 encode proteins that mediate alternative pathways for the secretion of BA metabolites into bile (Mrp2) and blood (Mrp3, Mrp4). Mrp2 and Mrp3 mRNA levels were significantly lower, whereas those of Mrp4 were massively induced in Pemt–/– mice compared to Pemt+/+ mice (Fig. 3B).28 In contrast, the mRNA levels of BA homeostatic genes were not different between Pemt–/– and Pemt+/+ mice fed the HFD for 2 weeks, except for Oatp1 mRNA, which was lower in Pemt–/– mice (Supporting Fig. S7).
Figure 3.
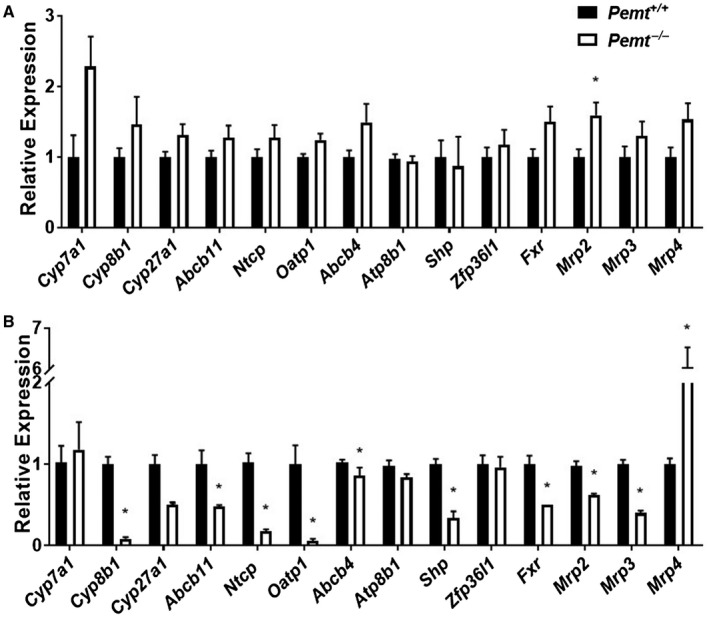
Dysregulation of expression of hepatic genes involved in BA homeostasis in Pemt–/– mice. Hepatic mRNA levels of genes involved in BA synthesis, biliary secretion and basolateral import of BAs, biliary secretion of phospholipids, regulators of BA synthesis, BA homeostasis, and the alternative pathway of BA secretion into bile and circulation were determined in Pemt+/+ and Pemt–/– mice fed (A) chow or (B) the HFD and normalized to cyclophilin mRNA levels. Values are expressed relative to Pemt+/+ mice on the same diet. Values are means ± SEM (n = 5 per group). Student t test; *P < 0.05.
Altered Bile Canaliculus in Pemt–/– Mice on the HFD
In agreement with Abcb11 mRNA levels, protein expression of BSEP was significantly lower in Pemt–/– mice after 10 weeks (Fig. 4A; Supporting Fig. S3D,E) but not 2 weeks of the HFD (Supporting Figs. S4D,E and S8). Representative immunohistochemistry slides confirmed that the canaliculus of Pemt–/– mice contained smaller amounts of BSEP compared to those of Pemt+/+ mice (Fig. 4B). Interestingly, visualization of the canalicular membrane, through transmission electron microscopy, revealed a marked loss of canalicular structure and surface area and widening of the lumen of the HFD‐fed Pemt–/– mice compared to the Pemt+/+ mice (Fig. 4C).
Figure 4.
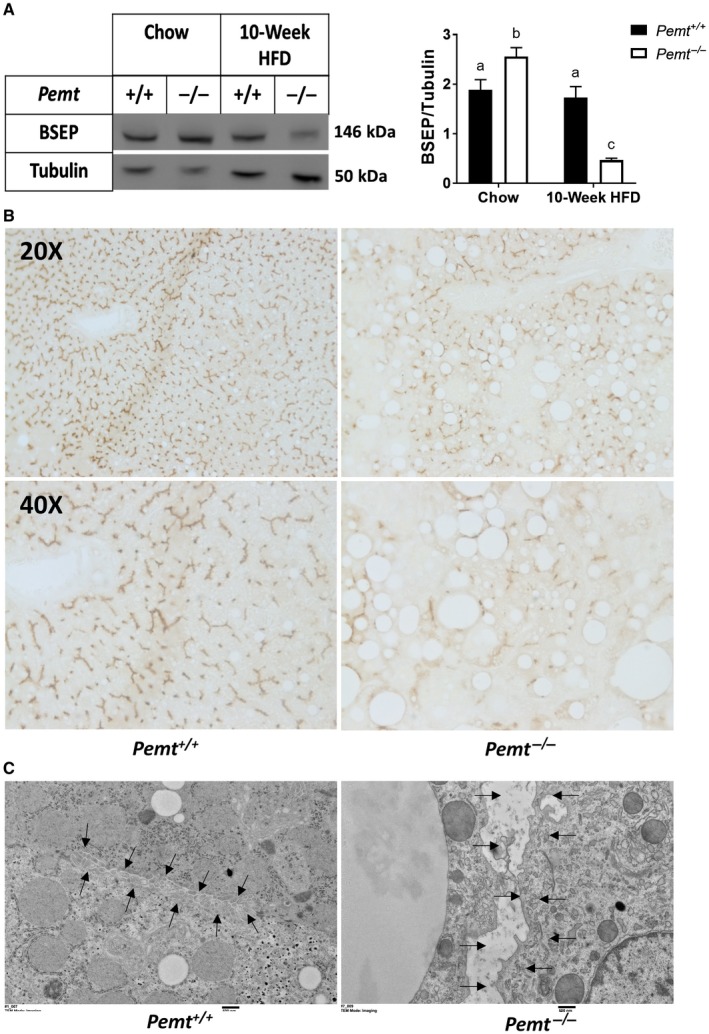
Loss of canalicular structure and BSEP deficiency in Pemt–/– mice. (A) Representative immunoblot of hepatic BSEP protein and quantification in Pemt+/+ and Pemt–/– mice fed the chow diet or the HFD for 10 weeks. Values are means ± SEM (n = 6 per group); 2‐way ANOVA followed by Fisher’s LSD post hoc test. Values that do not share a letter are significantly different (P < 0.05). (B) Representative immunohistochemistry (above, magnification ×20; below, magnification ×40) for BSEP. (C) Electron microscopy of the canalicular membrane (magnification ×6,000) in livers of Pemt+/+ and Pemt–/– mice fed the HFD for 10 weeks. Arrows outline the edge of the canaliculus.
CS Prevents the Development of Cholestasis in Pemt–/– Mice
Dietary CS has been shown to normalize hepatic PC concentrations in Pemt–/– mice to those in wild‐type mice.29 Pemt–/– mice that were fed the CSHFD (3 times normal choline) for 10 weeks did not develop hepatic steatosis, and there was no difference between hepatic PC levels or body weight between genotypes fed the same diet (Supporting Figs. S1B and S9A,B,G). However, hepatic PE levels were higher, and thus the PC:PE ratio was lower in Pemt–/– mice than in Pemt+/+ mice (Supporting Fig. S9C,D). The CSHFD was also unable to normalize plasma ALT levels in Pemt–/– mice to those in Pemt+/+ mice (Supporting Fig. S9E). However, CHOP and Bip levels as well as mRNA levels of Cd68, Col1a1, and Nox2 in Pemt–/– mice were normalized by the CSHFD (Supporting Figs. S10A‐C and S11A‐C).
Dietary supplementation of Pemt–/– mice with choline for 10 weeks normalized plasma BA concentrations, the rate of bile flow, and the amounts of biliary components secreted into bile (Fig. 5A‐C). Prevention of cholestasis occurred concomitant to a normalization of hepatic Bsep protein levels (Fig. 5D; Supporting Fig. S11D,E). When fed the CSHFD, mRNA levels of BA homeostatic genes were also not different between genotypes (Supporting Fig. S10D), which is likely related to improved liver health (Supporting Figs. S9 and S10).
Figure 5.
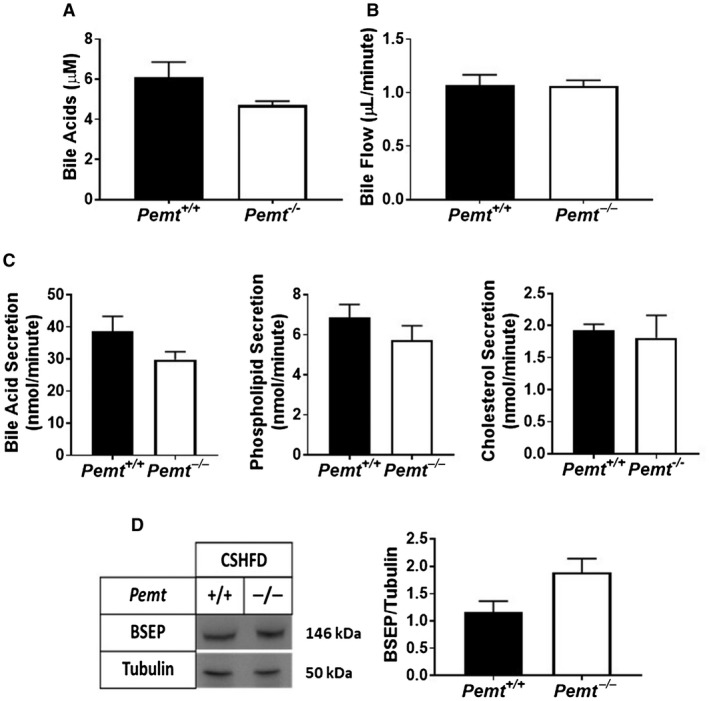
CS prevents cholestasis in Pemt–/– mice. Pemt+/+ and Pemt–/– mice were fed the CSHFD for 10 weeks. (A) Plasma BA concentration. (B) Basal biliary bile flow and (C) BA, phospholipid, and cholesterol secretion. (D) Hepatic BSEP protein and quantification relative to the amount of tubulin. Values are means ± SEM (n = 6 per group); 2‐way ANOVA followed by Fisher’s LSD post hoc test. Values that do not share a letter are significantly different (P < 0.05).
CS Resolves Cholestasis Induced by the HFD in Pemt–/–Mice
Because CS was able to prevent cholestasis, we hypothesized that it might also treat cholestasis induced by the HFD in Pemt–/– mice. Therefore, we fed Pemt+/+ and Pemt–/– mice the HFD for 6 weeks. After 6 weeks on the HFD, mice of each genotype were split into two groups and either continued on the HFD for another 6 weeks or fed the CSHFD for 6 weeks. As anticipated, after 6 and 12 weeks of the HFD, plasma BA concentrations were dramatically higher in the Pemt–/– mice compared to the Pemt+/+ mice (Fig. 6A). However, supplementation of the HFD with choline after 6 weeks of the HFD normalized plasma BA concentrations in Pemt–/– mice (Fig. 6A). Concomitant to resolution of cholestasis was a marked improvement in liver health in Pemt–/– mice. Pemt–/– mice fed the HFD for 12 weeks developed hepatic steatosis, which was improved by CS (Fig. 6B). mRNA levels of Cd68 and Col1a1 were reduced in Pemt–/– mice with CS, and levels of Nox2 were normalized to Pemt+/+ levels in mice with CS (Fig. 6F‐H). There were no significant changes in hepatic concentrations of PC, PE, or the PC:PE molar ratio between the different dietary regimens, although the PC:PE molar ratio trended to be modestly increased following CS (Fig. 6C‐E). Despite the lack of changes in steady‐state levels of hepatic phospholipids, CS restored hepatic BSEP and reduced CHOP levels in Pemt–/– mice (Fig. 6I; Supporting Fig. S12A,C,D). Surprisingly, Bip levels, another marker of ER stress, were not different between genotypes under any dietary condition in this experiment (Fig. 6I; Supporting Fig. S12B,D).
Figure 6.
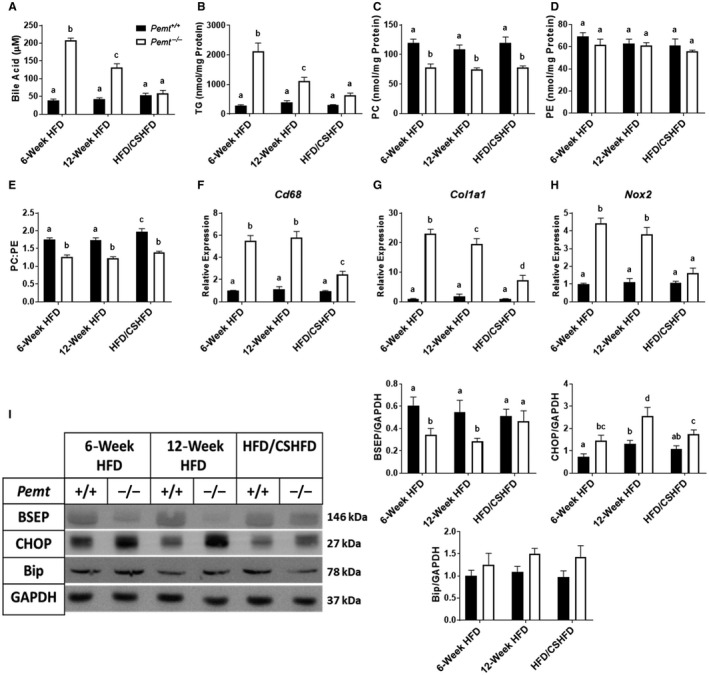
CS improves liver health and treats cholestasis in Pemt–/– mice. Pemt+/+ and Pemt–/– mice were fed the HFD for 6 weeks and either continued on the HFD or the CSHFD for an additional 6 weeks. (A) Plasma BA concentration. (B) Hepatic TG, (C) PC, (D) PE, and (E) PC:PE ratio. Values are means ± SEM (n = 6 per group). mRNA expression of hepatic genes involved in (F) inflammation, (G) fibrosis, and (H) oxidative stress. Values are means ± SEM (n = 5 per group). (I) Hepatic BSEP, CHOP, and Bip and quantification relative to the amount of GAPDH. Values are means ± SEM (n = 6 per group); two‐way ANOVA followed by Fisher’s LSD post‐hoc test. Values that do not share a letter are significantly different (P < 0.05).
Discussion
Pemt–/– mice that are fed the HFD are protected from diet‐induced obesity but develop NAFLD, which can progress to NASH.2, 4, 8 We now show that Pemt–/– mice also develop cholestasis when fed the HFD. This cholestasis can be both prevented and treated by CS. It is interesting to note that the maximal biliary secretory rate is approximately 10‐fold higher than physiologic BA secretion in mice, demonstrating an impressive mechanism to prevent BA accumulation. However, decreasing PC availability or altering the membrane phospholipid ratio leads to a reduction of the BA secretory capacity and leads to accumulation of BAs in plasma and hepatocytes, which might activate hepatic stellate cells, eventually resulting in fibrosis.30
Cholestasis in Pemt–/– Mice Mimics PFIC1 and/or PFIC2
In humans, mutations in the genes encoding BSEP or ATP8B1 can result in PFIC2 and PFIC1, respectively.9 Mutations in either gene can also lead to the development of benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis (BRIC) types 1 and 2.31 Patients with BRIC develop bouts of cholestasis with similar symptoms to their respective PFIC type but are symptomatically normal between recurrences.31 Clinically, patients with PFIC1/2 present with elevated levels of plasma BA and ALT as well as severely diminished biliary BA secretion and increased portal fibrosis.9 Atp8b1–/– and Bsep–/– mice have altered canalicular structure, cholestasis, and elevated plasma BA levels.32, 33, 34 Similar to the Bsep–/– and Atp8b1–/–mice, prolonged HFD feeding of Pemt–/–mice leads to dramatic elevations in plasma BA concentration and impairment of biliary BA secretion, likely due to the 75% decrease in hepatic BSEP protein as well as the loss of canalicular surface area. ATP8B1 is required for maintaining lipid asymmetry and the PC:PE ratio on the canalicular membrane by flipping PE to the inner leaflet of the canalicular membrane. Although the mechanism by which the lack of ATP8B1 induces cholestasis has not been fully elucidated, it has been suggested that loss of lipid asymmetry and PC/PE distribution, similar to HFD‐fed Pemt–/– mice, reduces BA transport across the canalicular membrane and leads to the loss of canalicular structure. Our results suggest that Pemt–/–mice fed the HFD represent a novel model for diet‐induced cholestasis that mimics aspects of both PFIC2/BRIC2 and PFIC1/BRIC1.
Dysregulation of Genes Controlled by FXR
Genes involved in BA homeostasis are tightly regulated by the nuclear receptor FXR in both the liver and the intestine. Under normal conditions, high intrahepatic concentrations of BAs activate FXR, thereby increasing mRNA levels of Shp; decreasing mRNA levels of Cyp7a1, Cyp8b, Ntcp, and Oatp1; and increasing that of Abcb11.15, 36 FXR activation in the intestine also reduces BA synthesis through the secretion of fibroblast growth factor 19.14 FXR activation also increases the mRNA levels of Zfp36l1, thereby inducing degradation of the Cyp7a1 transcript.28 A working model of hepatic physiology in Pemt+/+ mice is illustrated in Fig. 7A. In contrast, Pemt–/– mice fed the HFD for 10 weeks are unable to appropriately regulate the expression of genes responsible for BA synthesis and export. mRNA levels of Abcb11, Shp, and Fxr are lower and Zfp36l1 is unchanged in Pemt–/– mice compared to Pemt+/+ mice, indicating an impairment in FXR signaling (Fig. 3B). In agreement, liver‐specific FXR‐deficient mice have constitutively lower mRNA levels of Abcb11 than wild‐type mice, and these levels are not normalized by treatment with an FXR agonist.28, 35 In addition, ER stress and oxidative stress, both of which are evident in Pemt–/– mice, can negatively impact hepatic FXR signaling.37, 38, 39, 40 Decreased intestinal BA appearance and elevated levels of muricholic acid species, which are known to be antagonists for FXR, may also repress FXR activation.41 Besides the reduction in BA transporters, we also observed a reduction in the phospholipid transporter (Abcb4) in Pemt–/– mice after 10 weeks of the HFD. This could be a mechanism for preventing a further decrease in the hepatic PC:PE molar ratio to less than 1.0, below which liver failure rapidly occurs.5
Figure 7.
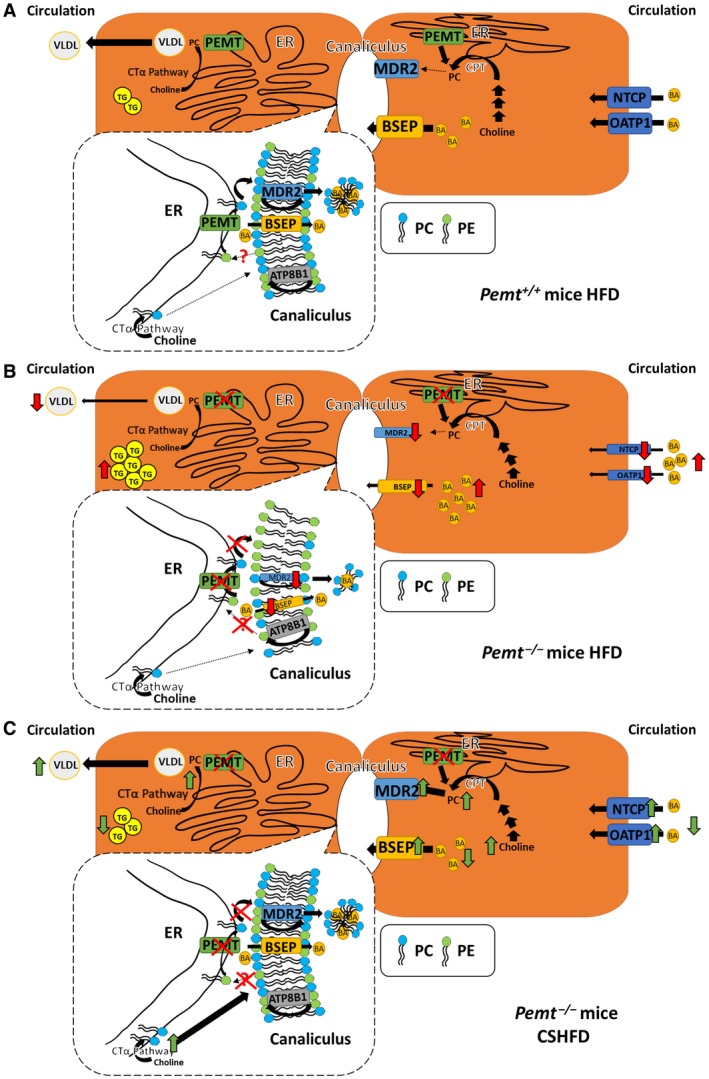
Working model of cholestasis in Pemt+/+ and Pemt–/– mice fed the HFD. (A) When Pemt+/+ mice are fed the HFD, BAs are secreted from the hepatocyte into bile by BSEP and removed from the portal circulation by NTCP and OATP1. Hepatic PC is synthesized either by means of the choline pathway or the PEMT pathway (conversion from PE to PC) in the ER. Hepatic PC and TG are secreted into the circulation as VLDL, and PC is secreted into bile. MDR2 flips PC from the inner to the outer membrane of the canalicular membrane from where the PC is extracted into bile by the BAs. ATP8B1 flips PE from the outer to the inner canalicular membrane. The dotted box represents enlargement of the area of ER close to the canaliculus. ER domains that are close to the canalicular membrane are enriched with PEMT, thereby providing PC directly to the canalicular membrane for biliary secretion. In addition, PEMT might deplete PE from the canaliculus so that an appropriate PC:PE ratio is maintained. Moreover, PC is made in areas of the ER not close to the canaliculus through the choline pathway and might also provide PC for biliary secretion. (B) When Pemt–/– mice are fed the HFD, the amount of mRNAs encoding NTCP, OATP1, and BSEP is decreased (mechanism not known), leading to the accumulation of BAs in plasma and, likely, in the liver/hepatocytes. Moreover, the amount of MDR2 is decreased in an attempt to conserve hepatic PC. Thus, because PC is synthesized only by the choline pathway in Pemt–/– hepatocytes, a reduction in hepatic PC leads to impaired VLDL secretion and consequently hepatic steatosis. The lack of PEMT in the hepatocytes reduces the local supply of PC for the canalicular membrane, which cannot be compensated by PC synthesized in the bulk of the ER by the choline pathway. The deficiency of PC in the canalicular membrane would compromise integrity of the canalicular membrane and change in structure of the canaliculus. Arrows in red indicate differences compared to Pemt+/+ mice. (C) When Pemt–/– mice are fed the CSHFD, the increased supply of dietary choline is likely to increase PC synthesis by means of the choline pathway, thereby increasing the availability of PC at the canalicular membrane and restoring membrane integrity. Consequently, the amounts of mRNAs encoding BSEP, MDR2, NTCP, and OATP1 are increased so that hepatocellular and plasma BA concentrations are reduced. The increased amount of PC in the hepatocyte also enhances VLDL secretion and reduces hepatic steatosis. Arrows in green indicate differences compared to Pemt+/+ mice fed the HFD. Abbreviations: CPT, Choline phosphotransferase; CTα, phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase.
Hepatic Changes Contributing to Cholestasis and BSEP Deficiency
One of the features that is well characterized in HFD‐fed Pemt–/– mice is the lower hepatic PC:PE molar ratio compared to that in Pemt+/+ mice.2, 5, 8 Alterations in the PC:PE ratio are known to negatively impact membrane integrity and liver health.5, 7 Pemt–/– mice fed a chow diet have a mild reduction in the hepatic PC:PE molar ratio but do not develop NAFLD or liver damage (Fig. 1). However, after Pemt–/– mice had been fed the HFD for 2 weeks, the hepatic PC:PE ratio dropped dramatically to approximately 1.05 (approximately 2 in Pemt+/+ mice), and the plasma concentration of ALT, a marker of liver damage, increased 7‐fold compared to that in Pemt+/+ mice (Supporting Fig. S3B,E). This dramatic decrease in the hepatic PC:PE molar ratio results in a loss of membrane integrity and leads to ER stress, which may initiate the onset of cholestasis after 2 weeks of HFD feeding. Cholestasis and ER stress can both aggravate inflammation, fibrosis, and oxidative stress, leading to a further dysregulation of FXR‐controlled genes. Increased BA levels can activate hepatic stellate cells, thereby aggravating fibrosis.30 These changes can promote the severe cholestatic phenotype observed when Pemt–/– mice were fed the HFD for 10 weeks.
Moreover, we hypothesize that PEMT, which localizes close to the canaliculus, is required to maintain the canalicular PC:PE molar ratio and PC availability (Fig. 7B).16 PEMT may remove PE, which is flipped to the inner canalicular membrane by ATP8B1, to offset the continuous loss of PC into bile and also produce PC locally for direct delivery to the canalicular membrane. Recent literature reports that Pemt is a BA‐responsive gene and suggests that PEMT plays an important role in maintenance of biliary secretion capacity.42 Thus, ultimately the decreased PC:PE ratio is likely responsible for the loss of canalicular structure and contributes to hepatic BSEP deficiency in Pemt–/– mice.
Dietary CS Prevents and Treats Cholestasis
Interestingly, dietary CS prevented the development of cholestasis in the HFD‐fed Pemt–/– mice. Although CS did not normalize the hepatic PC:PE ratio to Pemt+/+ levels, the PC:PE ratios were increased to approximately 1.4 after CS compared to approximately 1.1 after the HFD, which may have been sufficient to improve hepatic membrane integrity and function (Fig. 7C). Strikingly, we were also able to effectively treat Pemt–/– mice that developed cholestasis on an HFD with dietary CS (Fig. 6A). Although it was not significant, treatment with dietary choline also increased the PC:PE ratio to approximately 1.4, which was sufficient to restore hepatic BSEP protein levels and improve liver health. This suggests that the canalicular membrane, a major site for phospholipid export, may be sensitive to minute changes in the PC:PE balance. Recently, 4‐phenylbutyric acid, a drug known to alleviate ER stress, has successfully treated a case of BRIC2.43 Interestingly, CS reduced ER stress in Pemt–/– mice, which may be an additional mechanism by which cholestasis is alleviated. Phospholipid imbalance is the major underlying cause in patients with PFIC1 and BRIC1. Because there are limited therapies for cholestasis, CS might prove to be effective as a potential addition to therapy for these patients with cholestasis.
In conclusion, we have established that PEMT is a critical modulator of biliary secretion processes and “canalicular health” in mice fed an HFD by maintaining PC availability. Moreover, the experiments revealed that dietary CS might be a novel adjuvant therapy for the subset of patients with cholestasis who have phospholipid imbalance and/or decreased hepatic PC availability.
Potential conflict of interest
Nothing to report.
Supporting information
Acknowledgment
We thank Susanne Lingrell, Martijn Koehorst, and Randal Nelson for excellent technical assistance and Dr. Jean Vance for the critical reading of our manuscript.
Supported by Canadian Institutes of Health Research (MOP 5182 to D.E.V, R.L.J, and J.N.vd V.).
References
Author names in bold designate shared co‐first authorship.
- 1. DeLong CJ, Shen YJ, Thomas MJ, Cui Z. Molecular distinction of phosphatidylcholine synthesis between the CDP‐choline pathway and phosphatidylethanolamine methylation pathway. J Biol Chem 1999;274:29683‐29688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Jacobs RL, Zhao Y, Koonen DP, Sletten T, Su B, Lingrell S, et al. Impaired de novo choline synthesis explains why phosphatidylethanolamine N‐methyltransferase‐deficient mice are protected from diet‐induced obesity. J Biol Chem 2010;285:22403‐22413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Noga AA, Zhao Y, Vance DE. An unexpected requirement for phosphatidylethanolamine N‐methyltransferase in the secretion of very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem 2002;277:42358‐42365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Ling J, Chaba T, Zhu LF, Jacobs RL, Vance DE. Hepatic ratio of phosphatidylcholine to phosphatidylethanolamine predicts survival after partial hepatectomy in mice. Hepatology 2012;55:1094‐1102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Li Z, Agellon LB, Allen TM, Umeda M, Jewell L, Mason A, et al. The ratio of phosphatidylcholine to phosphatidylethanolamine influences membrane integrity and steatohepatitis. Cell Metab 2006;3:321‐331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Gao X, van der Veen JN, Vance JE, Thiesen A, Vance DE, Jacobs RL. Lack of phosphatidylethanolamine N‐methyltransferase alters hepatic phospholipid composition and induces endoplasmic reticulum stress. Biochim Biophys Acta 2015;1852:2689‐2699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. van der Veen JN, Kennelly JP, Wan S, Vance JE, Vance DE, Jacobs RL. The critical role of phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine metabolism in health and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 2017;1859:1558‐1572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. van der Veen JN, Lingrell S, Gao X, Takawale A, Kassiri Z, Vance DE, et al. Fenofibrate, but not ezetimibe, prevents fatty liver disease in mice lacking phosphatidylethanolamine N‐methyltransferase. J Lipid Res 2017;58:656‐667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Nicolaou M, Andress EJ, Zolnerciks JK, Dixon PH, Williamson C, Linton KJ. Canalicular ABC transporters and liver disease. J Pathol 2012;226:300‐315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Walkey CJ, Yu L, Agellon LB, Vance DE. Biochemical and evolutionary significance of phospholipid methylation. J Biol Chem 1998;273:27043‐27046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Smit JJ, Schinkel AH, Oude Elferink RP, Groen AK, Wagenaar E, van Deemter L, et al. Homozygous disruption of the murine mdr2 P‐glycoprotein gene leads to a complete absence of phospholipid from bile and to liver disease. Cell 1993;75:451‐462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Wang R, Liu L, Sheps JA, Forrest D, Hofmann AF, Hagey LR, et al. Defective canalicular transport and toxicity of dietary ursodeoxycholic acid in the abcb11‐/‐ mouse: transport and gene expression studies. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2013;305:G286‐G294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Ridgway N, McLeod R, eds. Biochemistry of lipids, lipoproteins, and membranes. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Elsevier Science;2016:377‐383. [Google Scholar]
- 14. Inagaki T, Choi M, Moschetta A, Peng L, Cummins CL, McDonald JG, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 15 functions as an enterohepatic signal to regulate bile acid homeostasis. Cell Metab 2005;2:217‐225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Fiorucci S, Distrutti E. Bile acid‐activated receptors, intestinal microbiota, and the treatment of metabolic disorders. Trends Mol Med 2015;21:702‐714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Sehayek E, Wang R, Ono JG, Zinchuk VS, Duncan EM, Shefer S, et al. Localization of the PE methylation pathway and SR‐BI to the canalicular membrane: evidence for apical PC biosynthesis that may promote biliary excretion of phospholipid and cholesterol. J Lipid Res 2003;44:1605‐1613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Agellon LB, Walkey CJ, Vance DE, Kuipers F, Verkade HJ. The unique acyl chain specificity of biliary phosphatidylcholines in mice is independent of their biosynthetic origin in the liver. Hepatology 1999;30:725‐729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Plosch T, van der Veen JN, Havinga R, Huijkman NC, Bloks VW, Kuipers F. Abcg5/Abcg8‐independent pathways contribute to hepatobiliary cholesterol secretion in mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2006;291:G414‐G423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Verkade HJ, Havinga R, Shields DJ, Wolters H, Bloks VW, Kuipers F, et al. The phosphatidylethanolamine N‐methyltransferase pathway is quantitatively not essential for biliary phosphatidylcholine secretion. J Lipid Res 2007;48:2058‐2064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Kosters A, Frijters RJ, Kunne C, Vink E, Schneiders MS, Schaap FG, et al. Diosgenin‐induced biliary cholesterol secretion in mice requires Abcg8. Hepatology 2005;41:141‐150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Morgado N, Rigotti A, Valenzuela A. Comparative effect of fish oil feeding and other dietary fatty acids on plasma lipoproteins, biliary lipids, and hepatic expression of proteins involved in reverse cholesterol transport in the rat. Ann Nutr Metab 2005;49:397‐406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Di Ciaula A, Wang DQ, Garruti G, Wang HH, Grattagliano I, de Bari O, et al. Therapeutic reflections in cholesterol homeostasis and gallstone disease: A review. Curr Med Chem 2014;21:1435‐1447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Mesa VA, De Vos R, Fevery J. Elevation of the serum bilirubin diconjugate fraction provides an early marker for cholestasis in the rat. J Hepatol 1997;27:912‐916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Araki Y, Andoh A, Bamba H, Yoshikawa K, Doi H, Komai Y, et al. The cytotoxicity of hydrophobic bile acids is ameliorated by more hydrophilic bile acids in intestinal cell lines IEC‐6 and Caco‐2. Oncol Rep 2003;10:1931‐1936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Sagawa H, Tazuma S, Kajiyama G. Protection against hydrophobic bile salt‐induced cell membrane damage by liposomes and hydrophilic bile salts. Am J Physiol 1993;264:G835‐G839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Koutsounas I, Theocharis S, Delladetsima I, Patsouris E, Giaginis C. Farnesoid x receptor in human metabolism and disease: the interplay between gene polymorphisms, clinical phenotypes and disease susceptibility. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 2015;11:523‐532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Tarling EJ, Clifford BL, Cheng J, Morand P, Cheng A, Lester E, et al. RNA‐binding protein ZFP36L1 maintains posttranscriptional regulation of bile acid metabolism. J Clin Invest 2017;127:3741‐3754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Akita H, Suzuki H, Ito K, Kinoshita S, Sato N, Takikawa H, et al. Characterization of bile acid transport mediated by multidrug resistance associated protein 2 and bile salt export pump. Biochim Biophys Acta 2001;1511:7‐16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Watkins SM, Zhu X, Zeisel SH. Phosphatidylethanolamine‐N‐methyltransferase activity and dietary choline regulate liver‐plasma lipid flux and essential fatty acid metabolism in mice. J Nutr 2003;133:3386‐3391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Svegliati‐Baroni G, Ridolfi F, Hannivoort R, Saccomanno S, Homan M, De Minicis S, et al. Bile acids induce hepatic stellate cell proliferation via activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Gastroenterology 2005;128:1042‐1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Stapelbroek JM, van Erpecum KJ, Klomp LW, Houwen RH. Liver disease associated with canalicular transport defects: current and future therapies. J Hepatol 2010;52:258‐271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Zhang Y, Li F, Patterson AD, Wang Y, Krausz KW, Neale G, et al. Abcb11 deficiency induces cholestasis coupled to impaired beta‐fatty acid oxidation in mice. J Biol Chem 2012;287:24784‐24794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Wang R, Salem M, Yousef IM, Tuchweber B, Lam P, Childs SJ, et al. Targeted inactivation of sister of P‐glycoprotein gene (spgp) in mice results in nonprogressive but persistent intrahepatic cholestasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001;98:2011‐2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Paulusma CC, Groen A, Kunne C, Ho‐Mok KS, Spijkerboer AL, Rudi de Waart D, et al. Atp8b1 deficiency in mice reduces resistance of the canalicular membrane to hydrophobic bile salts and impairs bile salt transport. Hepatology 2006;44:195‐204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Schmitt J, Kong B, Stieger B, Tschopp O, Schultze SM, Rau M, et al. Protective effects of farnesoid X receptor (FXR) on hepatic lipid accumulation are mediated by hepatic FXR and independent of intestinal FGF15 signal. Liver Int 2015;35:1133‐1144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Goodwin B, Jones SA, Price RR, Watson MA, McKee DD, Moore LB, et al. A regulatory cascade of the nuclear receptors FXR, SHP‐1, and LRH‐1 represses bile acid biosynthesis. Mol Cell 2000;6:517‐526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Kemper JK, Xiao Z, Ponugoti B, Miao J, Fang S, Kanamaluru D, et al. FXR acetylation is normally dynamically regulated by p300 and SIRT1 but constitutively elevated in metabolic disease states. Cell Metab 2009;10:392‐404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Kemper JK. Regulation of FXR transcriptional activity in health and disease: emerging roles of FXR cofactors and post‐translational modifications. Biochim Biophys Acta 2011;1812:842‐850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Balasubramaniyan N, Luo Y, Sun AQ, Suchy FJ. SUMOylation of the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) regulates the expression of FXR target genes. J Biol Chem 2013;288:13850‐13862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Xiong X, Wang X, Lu Y, Wang E, Zhang Z, Yang J, et al. Hepatic steatosis exacerbated by endoplasmic reticulum stress‐mediated downregulation of FXR in aging mice. J Hepatol 2014;60:847‐854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Sayin SI, Wahlstrom A, Felin J, Jantti S, Marschall HU, Bamberg K, et al. Gut microbiota regulates bile acid metabolism by reducing the levels of tauro‐beta‐muricholic acid, a naturally occurring FXR antagonist. Cell Metab 2013;17:225‐235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Kim YC, Seok S, Byun S, Kong B, Zhang Y, Guo G, et al. AhR and SHP regulate phosphatidylcholine and S‐adenosylmethionine levels in the one‐carbon cycle. Nat Commun 2018;9:540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Hayashi H, Naoi S, Hirose Y, Matsuzaka Y, Tanikawa K, Igarashi K, et al. Successful treatment with 4‐phenylbutyrate in a patient with benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis type 2 refractory to biliary drainage and bilirubin absorption. Hepatol Res 2016;46:192‐200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials


