Abstract
Type 2 immunity participates in the pathogeneses of helminth infection and allergic diseases. Emerging evidence indicates that the components of type 2 immunity are also involved in maintaining metabolic hemostasis and facilitating the healing process after tissue injury. Numerous preclinical studies have suggested regulation of type 2 immunity-related cytokines, such as interleukin-4, -13, and -33, and cell types, such as M2 macrophages, mast cells, and eosinophils, affects cardiac functions after myocardial infarction (MI), providing new insights into the importance of immune modulation in the infarcted heart. This review provides an overview of the functions of these cytokines and cells in the setting of MI as well as their potential to predict the severity and prognosis of MI.
Keywords: myocardial infarction, type 2 immunity, interleukin, M2 macrophages, mast cells, eosinophils, immune modulation
Introduction
Type 2 immunity is characterized by the production of interleukin (IL)-4, IL-5, IL-9, IL-13, IL-25, IL-33, and thymic stromal lymphopoietin, as well as specific cell types including mast cells, eosinophils, basophils, alternatively activated M2 macrophages, type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2), and T-helper (Th) 2 cells. It has mainly been considered to participate in the pathogeneses of helminth infection and allergic diseases. However, growing evidence suggests that these cell types and related cytokines are also involved in maintaining metabolic homeostasis and facilitating the healing process after tissue injury (1). Studies in experimental models and serum biomarker data from humans have proven the participation of type 2 immunity in the progression of myocardial infarction (MI). In this review, we will discuss several pivotal type 2 immunity-associated cytokines and cell types that modulate cardiac functions, following MI and their potential value as biomarkers of MI.
Cytokines
Activation of innate immunity and extensive inflammation are the typical pathological features of MI. Accumulating evidence suggests type 2 cytokines are critical participants in tissue repair and regeneration owing to their ability to regulate the functions of nearby cells and immunomodulation. Moreover, they may serve as ideal biomarkers to predict the severity and clinical outcomes of MI.
IL-4
IL-4 is an important Th2 cytokine with multiple biological functions, which mainly has an anti-inflammatory effect. Previous studies have demonstrated an association of elevated serum IL-4 with a reduced risk of cardiovascular diseases (2). Furthermore, the IL-4 level is lower in MI patients who later develop left ventricular dysfunction (3), indicating its cardioprotective properties.
One of the well-clarified mechanisms of IL-4 is in mediating myocardial repair via converting macrophages to the M2 phenotype. Administration of a long-acting IL-4 complex at 1 h after MI increases the proportion of cardiac M2 macrophages in both the infarct and border myocardium, along with increased tissue repair-related gene expression in M2 macrophages, and an improved cardiac structure (more connective tissue in the infarct zone) and functions. Further experiments suggested that IL-4 promotes fibrotic tissue formation via M2 macrophages rather than a direct interaction with cardiac fibroblasts. However, these effects are not observed when administrated at a late phase (7 or 28 days after MI), implying that IL-4 affects the early recruitment and polarization of M2 macrophages in the acute phase after MI (4). Similarly, injection of IL-4 plasmid DNA (carried by graphene oxide) around the border zone after coronary artery ligation largely reduces the number of inflammatory M1 macrophages, and polarizes macrophages to the reparative M2 phenotype in the mouse heart, leading to enhancement of cardiac functions (5).
IL-4 may also affect the functions of cardiac fibroblasts, thus participating in the profibrotic process directly. In the Ang II-induced hypertension model, wild-type (WT) mice exhibit higher cardiac fibrosis compared with IL-4−/− mice, as indicated by the increase in the interstitial collagen fraction and mRNA levels of procollagen type-I α1 and procollagen type-III α1. In vitro experiments have demonstrated that IL-4 promotes the expression of procollagen type-I α1 and procollagen type-III α1 in mouse cardiac fibroblasts via binding to IL-4Rα, and consequently increasing the production of collagen (6). Treatment of anti-IL-4 neutralizing antibodies reduces both the number and proliferation of fibroblasts as well as infiltration of CD68+ macrophages (7). These findings suggest the sophisticated interaction between IL-4 and various cell types in the heart, which may lead to opposing outcomes under different pathological conditions.
IL-13
IL-13 also polarizes macrophages to the M2 phenotype through binding to IL-4Rα and activating the subsequent signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) 6 signaling pathway (8). In a mouse model of MI, IL-13 significantly increases in the myocardium with a peak on day 3. Further experiments in IL-13−/− mice suggested that IL-13 enhances cardiac functions by recruiting more monocytes/macrophages to the infarct and border area and inducing M2 macrophages. Interestingly, in contrast to the IL-13−/− female mice, IL-13−/− male mice exhibit a significant higher mortality and increased left ventricular dilation compared with WT mice after MI (9).
Recently, IL-13 was also found to induce mitosis of isolated cardiomyocytes when bound to IL-13Rα1. Through activation of the STAT3/periostin signaling pathway, IL-13 facilitates cardiac regeneration (10). Intraperitoneal administration of IL-13 significantly reduces the scar area and increases cardiomyocyte cell cycle activity/mitosis in a cardiomyocyte-specific Gata4 knockout neonatal mouse after cryoinfarction (11). However, whether the salutary effects of IL-13 on the injured myocardium in the adult mouse model of MI are also partially related to its underlying regeneration property needs to be examined further.
IL-33
IL-33, a member of the IL-1 family, has an important role in adaptive and innate immunities (12). After tissue injury, IL-33 released by the damaged endothelial or epithelial cells promotes immune cell recruitment and tissue repair (13, 14). In the heart, IL-33 is mainly released by cardiac fibroblasts responding to biomechanical stress (15). The cognate receptors of IL-33 have two isoforms: transmembrane ST2 (ST2L) and soluble ST2 (sST2) (16). The long form ST2L is expressed on various kinds of immune cells such as macrophages, mast cells, basophils, Th2 cells, regulatory T cells, and ILC2 (17–22). Gene ablation of IL-33 or ST2 has demonstrated that the IL-33/ST2 signaling pathway is crucial for reducing cardiac hypertrophy, ventricular chamber dilation, and cardiac fibrosis under mechanical stress (15, 23). However, the soluble form sST2, which serves as a decoy receptor, may impede the cardioprotective effects by neutralizing IL-33 (24). Accumulating evidence suggests that the IL-33/ST2 system has a profound effect on cardiac functions and potential value to predict the severity and prognosis of acute coronary syndrome (ACS).
In rats, IL-33 is elevated significantly within the first 12 weeks after MI. However, the mRNA level of sST2 shows a similar pattern to inflammatory and fibrosis markers with a peak at 1 week, suggesting that sST2 impairs the cardioprotective effects at an early stage post-MI (25). Preclinical studies have demonstrated that early pharmacological treatment targeting the IL-33/ST2 system promotes cardiac functions in MI rats. Through downregulating and upregulating gene expression of sST2 and IL-33, respectively, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists reduce cardiac fibrosis and mitigate inflammation responses in the infarcted myocardium (26). Furthermore, β-blocker significantly decreases the infarct size and promote cardiac functions by reducing the sST2 level (27).
Further experiments showed that IL-33 reduces hypoxia-induced apoptosis of cardiomyocytes in vitro through suppressing caspase-3 activity and increasing anti-apoptotic protein expression (cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein 1, X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein, survivin, B-cell lymphoma 2, and B-cell lymphoma-extra large). In a rat model of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury, subcutaneous injection of IL-33 significantly reduces the infarct size and myocardial fibrosis. The benefits of IL-33 on cardiac functions were then abolished by ST2 gene deletion, indicating that IL-33 exerts cardioprotective effects through combination with the ST2 receptor (28). In the diabetic myocardium, a low level of IL-33 is associated with chronic activation of protein kinase (PK) CβII that increases the vulnerability of the myocardium to IR injury. Exogenous IL-33 supplementation reduces the phosphorylation of PKCβII, cardiomyocyte apoptosis, and infarct size after cardiac IR injury. In addition, anoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis of high glucose preconditioned cardiomyocytes and activation of PKCβII are alleviated by IL-33 in vitro (29). IL-33 treatment also significantly suppresses proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression, including IL-1β, IL-6, IL-17, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1, and interferon-γ (IFN-γ)-induced protein 10, and reduces macrophage infiltration after MI. These effects are mediated by inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells pathways (30).
Human studies have demonstrated that the circulating levels of IL-33 and sST2 are associated with the severity of ACS patients, and may thus serve as potential biomarkers. The serum level of IL-33 is significantly lower in patients with ACS compared with stable angina pectoris patients and control individuals (31, 32). Similarly, another study showed that the circulating level of IL-33 is significantly lower in ACS patients than in patients with coronary artery disease (33). In contrast, sST2 is negatively correlated with the outcomes of MI patients. For MI patients, serum sST2 immediately elevated on day 1 after MI and correlates positively with peak creatine kinase and negatively with the left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) (34). In addition, a higher sST2 level is observed in patients with a larger infarct size, lower LVEF, transmural infarction, and microvascular obstruction (35). These findings indicate that the sST2 level well-reflects the severity of myocardial injury. Moreover, sST2 can predict both short term (36–39) and long term (39–43) cardiac adverse events and mortality in ACS patients.
Cell Types
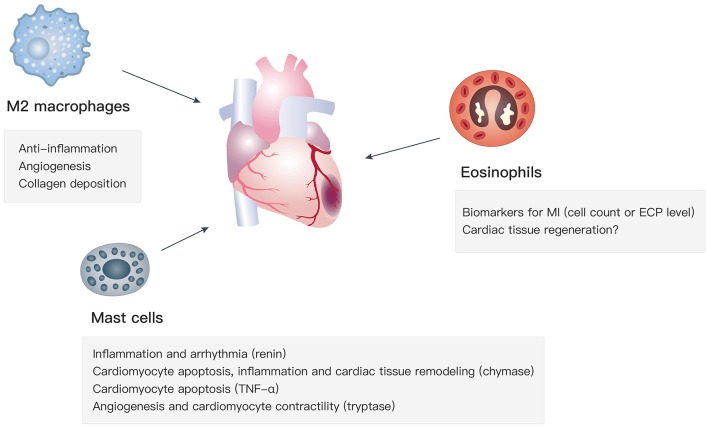
Apart from type 2 cytokines, the recruitment and activation of M2 macrophages, mast cells, and eosinophils, which are key type 2 immunity-related cell types, affect cardiac functions in the progression of MI via various mechanisms (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Functions of M2 macrophages, mast cells, and eosinophils in MI.
M2 Macrophages
So far, two subsets of macrophages have been identified in the heart, according to their different origins: (1) resident cardiac macrophages derived from the yolk sac and fetal liver during embryonic development and (2) macrophages differentiated from circulating monocytes when they migrate into hearts (44, 45). Although there are less macrophages in the myocardium compared with cardiomyocytes, endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and smooth muscle cells (46), they are indispensable for both cardiac homeostasis and myocardial repair. Based on surface markers and gene expression profiles, macrophages are generally divided into classically activated M1 and alternatively activated M2 macrophages, although their phenotypes and functions might be more complex in vivo (47, 48). After MI, the injured myocardium sequentially mobilizes Ly-6Chigh monocytes and Ly-6Clow monocytes via C-C chemokine receptor type 2 and CX3C chemokine receptor 1, respectively (49). Ly-6Chigh monocytes differentiate into M1 macrophages, which dominate in the heart before day 3 post-MI and are responsible for degradation of the extracellular matrix and clearance of cellular debris; whereas Ly-6Clow monocytes differentiate into M2 macrophages that are the prominent subset during day 4–7 post-MI and mainly involved in the healing process (50). Accumulating evidence suggests that M2 macrophages participate in the resolution of inflammation and cardiac repair, which benefits cardiac functions after MI. In the next sections, we will summarize their subpopulations, biological functions, modulation methods, and polarization mechanisms.
Subpopulations
In response to different stimuli or pathological stresses, M2 macrophages polarize into distinctive phenotypes, namely M2a, M2b, and M2c (51, 52). M2a macrophages can be elicited by IL-4 or IL-13 with increased levels of CD206 (53) and arginase 1 (54), which support cell growth, collagen formation, and tissue repair by promoting the biosynthesis of polyamine and proline (55). Chemokines, such as C-C motif chemokine ligand (CCL) 2 (56), CCL17 (57), CCL22 (58), and CCL24 (59), are overexpressed in M2a macrophages, contributing to the recruitment of eosinophils, basophils, and Th2 cells. In addition, fibronectin, β IG-H3, and factor VIII subunit A are overexpressed in M2a macrophages, which are associated with extracellular matrix deposition and tissue remodeling (60, 61). However, the production of proinflammatory cytokines, including IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α, is low in M2a macrophages (62), whereas the level of anti-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-10 and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), is high (63). M2b macrophages (elicited by immune complexes or Toll-like receptor ligands) are characterized by a low level of IL-12 and high level of IL-10. In contrast to elevated anti-inflammatory cytokines in M2a and M2c macrophages, M2b macrophages exhibit increased proinflammatory cytokines including IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α (64, 65). Another obvious distinction between M2b and M2a is that M2b cells have higher expression of sphingosine kinase 1 enzyme (66). They similarly regulate the recruitment of immune cells (eosinophils, Th2 cells, and regulatory T cells) by selective production of CCL1 (67). In terms of M2c macrophages, they are induced by IL-10, TGF-β, or glucocorticoid stimulation and express a high level of the surface marker CD163 (68) with decreased proinflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-12, and TNF-α) and proinflammatory mediators (inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase) (69). Previous studies have shown high quantities of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP)-7, MMP-8, MMP-9, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 in M2c macrophages, suggesting their potential to regulate fibrosis after MI (68, 70, 71). M2c macrophages also express high levels of chemokines CCL16 and CCL18 that attract naïve T cells and eosinophils (51).
Biological Functions: Anti-inflammation, Angiogenesis, and Collagen Deposition
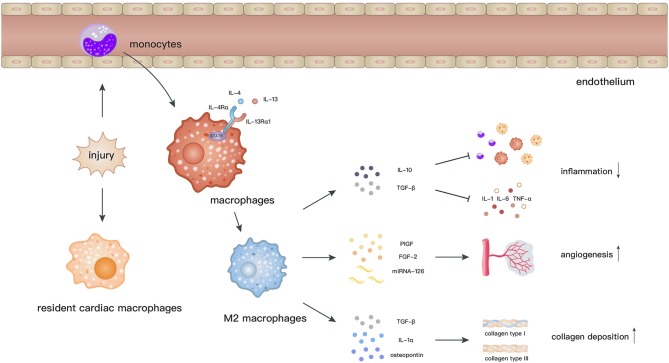
Macrophages are related to the processes of initiation, maintenance, and resolution of the inflammatory response and myocardial repair after MI (72, 73). Cardiac resident macrophages begin to apoptose by 2 h and almost vanish within 24 h after MI. In contrast, a considerable number of monocytes are recruited into the myocardium and then differentiate into macrophages, which peak at day 6 after MI (74). M2 macrophages, which dominate the infiltration during day 4–7 post-MI, facilitate the recovery of cardiac functions via secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines, neovascularization, and collagen deposition (72) (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
After myocardial ischemic attack, resident cardiac macrophages begin to develop apoptose by 2 h and circulating monocytes infiltrate into the injury site and differentiate into macrophages. Elicited by IL-4 and IL-13, macrophages polarize toward the M2 phenotype through activation of STAT6. M2 macrophages facilitate the recovery of cardiac functions via secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines, promoting angiogenesis and collagen deposition.
Anti-inflammation
Previous studies have demonstrated that an exaggerated inflammatory response increases ventricular dilatation and cardiac dysfunction after MI (75), whereas attenuated inflammation suppresses scar formation (76), and increases the risk of cardiac rupture (77). Hence, timely resolution of inflammation is crucial for myocardial repair.
Owing to the ability to secrete pro/anti-inflammatory cytokines, macrophages are essential modulators of the inflammatory process after MI. In apoE−/− atherosclerotic mice, prolonged presence of Ly-6Chigh monocytes and higher proinflammatory gene expression in the infarcted myocardium hamper inflammation resolution and infarct healing (78), indicating the importance of timely infiltration by reparative M2 macrophages. Indeed, M2 macrophages restrict the expansion of inflammation through the release of anti-inflammatory cytokines including IL-10 and TGF-β. Further experiments demonstrated that IL-10 suppresses inflammation by restraining infiltration of inflammatory cells and the synthesis of inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α) in vivo (79). Early inhibition of TGF-β leads to increased infiltration of neutrophils and gene expression of IL-1β, TNF-α, and MCP-1, along with left ventricular dilation and decreased cardiac contractility, indicating that TGF-β protects the myocardium by regulating the inflammatory process (80).
Angiogenesis
Angiogenesis increases cardiac tissue perfusion, which makes it critical to salvage an infarcted myocardium. The beneficial effects of macrophages on cardiac functions are mediated partially by facilitating angiogenesis. Compared with WT mice, macrophage-deficient mice exhibit impaired angiogenesis and infarct healing (72). To further clarify the specific subtypes of macrophages that induce angiogenesis, circulating macrophages were depleted in the inflammatory phase (M1 macrophages) and healing phase (M2 macrophages), respectively. Consequently, there was a decline in quantity of microvascular α-actin+ smooth muscle cells and CD31+ endothelial cells in the infarcted myocardium when M2 macrophages were depleted (49). In addition, increased infiltration of M2 macrophages into myocardium after fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-2/hepatocyte growth factor administration is accompanied by enhanced angiogenesis (81). Simultaneously, M1, M2a, and M2c macrophages were injected subcutaneously into mice to determine their specific roles. In accordance with the above findings, compared with M1 macrophages, M2 macrophages had a higher angiogenic potential. When FGF-2 was neutralized in M2a or placental growth factor (PlGF) was blocked in M2c macrophages, angiogenesis and tube formation were reduced significantly, indicating that FGF signaling in M2a macrophages and PlGF signaling in M2c macrophages might be possible mechanisms of angiogenesis following MI (82). Apart from the release of angiogenic cytokines, M2 macrophages may regulate angiogenesis by transferring miRNAs. Angiogenic early outgrowth cells (EOCs), which are largely positive for M2 macrophage markers, were extracted from humans. Intramyocardial transplantation of EOCs from healthy donors into MI mice improved neovascularization in the infarct border zone and promoted cardiac repair. However, EOCs extracted from patients with chronic heart failure had loss of miRNA-126 and miRNA-130a and showed impaired cardiac neovascularization. Anti-miRNA-126 transfection decreased the angiogenic capacity of EOCs from healthy donors, whereas miRNA-126 mimic transfection increased the angiogenic capacity of EOCs from patients with chronic heart failure (83).
Collagen deposition
During the reparative phase after MI, collagen deposition in the infarcted myocardium stabilizes the damaged tissue and prevents infarct expansion and ventricular dysfunction. Depletion of macrophages decreases collagen deposition and wall thickness, increases left ventricular dilation, and leads to a high mortality after MI (72, 84). In contrast, injection of activated macrophages (73) or macrophage colony-stimulating factor (85) facilitates collagen deposition and myocardial repair.
M2 macrophage-depleted Trib1−/− mice were used to identify the contribution of M2 macrophages to cardiac repair. Trib1−/− mice exhibit decreased collagen fibril formation and more frequent cardiac rapture, whereas exogenous administration of IL-4, which promoted M2 macrophage polarization, increases the collagen volume in the infarct zone (86). Coculture with M2 macrophages isolated from the infarcted myocardium (86) or their secretome (87) enhances activation of cardiac fibroblasts in vitro. These effects might be ascribed to IL-1α and osteopontin, because gene expression of Il1α and Spp1 is increased in M2 macrophages at 7 days after MI, and neutralization of IL-1α or osteopontin significantly reduces the fibroblast-myofibroblast transition when cocultured with M2 macrophages (86). Additionally, TGF-β released by M2 macrophages promotes synthesis of collagen type I and III (88, 89) through activation of Smad3 signaling in cardiac fibroblasts (90).
Modulation Methods and Polarization Mechanisms
Although numerous methods have been applied to promote the shift from M1 macrophages toward M2 macrophages after MI, the precise mechanisms of M1/M2 polarization have not been fully investigated in most studies (Table 1).
Table 1.
Modulation methods and mechanisms of macrophage polarization.
| Modulation methods | Approaches | Animal strains | Pathological status | Polarization mechanisms | Biological effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DRUG TREATMENT | ||||||
| BIO | Intraperitoneal | SD rats | MI | Not investigated | Cardiac fibrosis↓ Cardiac function↑ |
(91) |
| N-propargyl caffeamide | Intraperitoneal | SD rats | MI | Not investigated | Infarct size↓ | (92) |
| DAPT | Intravenous | SD rats | MI | Not investigated | Arrhythmia↓ Sympathetic hyperinnervation↓ |
(93) |
| Pyridostigmine | Contained in water | Wistar rats | MI | Not investigated | Anti-oxidant enzyme activity↓ Cytokine production↓ |
(94) |
| Pyridostigmine | Contained in water | Wistar rats | MI | Not investigated | LV diastolic function↑ Parasympathetic modulation↑ Sympathetic modulation↑ |
(95) |
| Eplerenone | Intracerebroventricular | Wistar rats | MI | Not investigated | Cardiomyocyte apoptosis↓ LVEF↑ |
(96) |
| Atorvastatin | Intragastric | Wistar rats | MI | Not investigated | Arrhythmia↓ Sympathetic hyperinnervation↓ |
(97) |
| Dapagliflozin | Intragastric | Wistar rats | MI | STAT3 signaling pathway | Cardiac contractility and relaxation↑ Cardiac fibrosis↓ Oxidative and nitrosative stress↓ |
(98) |
| Nicorandil | Intragastric | Wistar rats | MI | RhoA/Rho-kinase signaling↓ | Cardiac contractility and relaxation↑ Cardiac fibrosis↓ |
(99) |
| HGF and FGF-2 contained microparticle | Intramyocardial | Wistar rats | MI | Not investigated | Angiogenesis↑ | (81) |
| Telmisartan | Intragastric | Zucker diabetic fatty rats | IR injury | Ubiquitin-proteasome system↓ | Cardiac function↑ Infarct size↓ |
(100) |
| Sitagliptin + G-CSF | Contained in food and intraperitoneal, respectively | C57/BL6 mice | MI | Not investigated | Cardiomyocyte hypertrophy↓ LV dilatation↓ |
(101) |
| Niacin | Intragastric | C57BL/6 mice | MI | PGD2/DP1 axis↑ | Cardiac function↑ | (102) |
| Hydrogen sulfide | Intraperitoneal | C57BL/6 mice | MI | Lipolysis↑fatty acid oxidation↑ | Cardiac function↑ Survival↑ |
(103) |
| IL-2/Anti-IL-2 immune complex | Intraperitoneal | C57BL/6 mice | MI | Not investigated | Cardiomyocyte apoptosis↓ Infarct size↓ LV function↑ |
(104) |
| Long-acting IL-4 complex | Intraperitoneal | C57BL/6 mice | MI | Not investigated | Angiogenesis↑ Cardiomyocyte hypertrophy↓ Connective tissue formation↑ Infarct size↓ |
(4) |
| Topiramate | Intraperitoneal | C57BL/6 mice | MI | Not investigated | Cardiac rupture↓ Collagen density↑ Infarct size↓ Survival↑ |
(105) |
| BAY 60-6583 | Intravenous | C57BL/6 mice | IR injury | PI3K/PKB pathway↑ | Infarct size↓ Inflammation↓ |
(106) |
| Suppressing IRF5 by siRNA | Intravenous | C57BL/6 mice | MI | IRF5 | Infarct healing↑ | (107) |
| IL-10 | Subcutaneous | C57BL/6J mice | MI | Not investigated | ECM deposition↓ Inflammation↓ LV function↑ |
(87) |
| Ω-Alkynyl arachidonic acid | Intraperitoneal | C57BL/6N mice | MI | Regulating cross-talk between PKM2, HIF-1α and iNOS | CK-MB↓ Infarct size↓ |
(108) |
| CRMP2 siRNA | Intravenous | ApoE−/− mice | MI | IRF5↓ | Cardiac fibrosis↓ Inflammation↓ LVEF↑ Scar size↓ Survival↑ |
(109) |
| Graphene oxide-carried IL-4 plasmid DNA | Intramyocardial | Balb/C mice | MI | Not investigated | Angiogenesis↑ Cardiac fibrosis↓ Inflammatory cell infiltration↓ LV function↑ Survival↑ |
(5) |
| Hemin formulated in designed lipid-based particles | Intravenous | Balb/C mice | MI | Not investigated | Angiogenesis↑ Infarct-related regional function↑ Scar tissue↓ |
(110) |
| Histone deacetylase inhibitor | Intraperitoneal | CD1 mice | MI | Not investigated | Angiogenesis↑ LV dilation↓ LVEF↑ |
(111) |
| FGF-9 | Intramyocardial | Db/db diabetic mice | MI | Not investigated | Cardiac function↑ Infarct size↓ Inflammation↓ |
(112) |
| Ac-SDKP | Intraperitoneal | Mice | MI | Not investigated | Cardiac function↑ Collagen deposition↓ |
(113) |
| HBSP | Subcutaneous injection | Rabbits | MI | Not investigated | Coronary atherosclerosis↓ | (114) |
| GENE MODIFICATION | ||||||
| Depletion of Caveolin-1 | Gene modification | Cav1−/− mice | MI | TGF-β/Smad2↑ | Cardiac fibrosis↑ Inflammatory cell infiltration↑ Survival↓ |
(115) |
| Depletion of Lp-PLA2 | Gene modification | BmLp-PLA−/− mice | MI | Not investigated | Angiogenesis↑ Collagen deposition↑ Infarct size↓ LVEF↑ |
(116) |
| Depletion of Wnt | Gene modification | Cfms-icre;Wlsfl/fl mice | MI | Not investigated | Angiogenesis↑ Infarct-related regional function↑ |
(117) |
| Inhibition of PTP1B | Gene modification | PTP1B−/− mice | MI | Not investigated | Angiogenesis↑ LV Diastolic function↑ Myocardial perfusion↑ |
(118) |
| MIF deficiency | Gene modification | MIF deficient mice | MI | Not investigated | Cardiac remodeling↓ Cardiac rupture↓ |
(119) |
| Urokinase plasminogen activator overexpression | Gene modification | SR-uPA mice | MI | Not investigated | Cardiac fibrosis↑ | (120) |
| CELL TRANSPLANTATION AND TISSUE ENGINEERING | ||||||
| MSCs | Intramyocardial | SD rats | MI | Not investigated | Cardiac fibrosis↓ LVEF↑ |
(121) |
| MSCs | Intramyocardial | Macrophage depletion mice | MI | Not investigated | Infarct healing↑ | (84) |
| BM-MSCs | Intravenous | NOD/SCID γ null mice | MI | IL-10 mediated | Cardiac function↑ Cardiac remodeling↓ |
(122) |
| FM-MSCs | Cell sheets | Lewis rats | MI | Not investigated | Angiogensis↑ Cardiac fibrosis↓ Cardiac function↑ |
(123) |
| Bone marrow transplantation | Intravenous | C57BL/6 mice | MI | Not investigated | Cardiac function↑ Cardiac remodeling↓ Survival↑ Wall thickness↑ |
(124) |
| Myocardial ECM patch | Sutured onto infarct area | Wistar rats | MI | Not investigated | Cardiac function↑ | (125) |
| PHB patch | Patched on epicardial | Wistar rats | MI | Not investigated | Angiogenesis↑ | (126) |
BIO, (2'Z,3'E)-6-Bromoindirubin-3'-oxime; DAPT, N-N-(3,5-difluorophenacetylL-alanyl)-S-phenylglycine-t-butyl ester; LV, left ventricular; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; G-CSF, granulocyte-colony stimulating factor; PI3K/PKB, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/ protein kinase B; ECM, extracellular matrix; PKM2, pyruvate kinase isozymes M2; HIF, hypoxia-inducible factor; Inos, inducible nitric oxide synthase; CRMP2, collapsin response mediator protein 2; Ac-SDKP, N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline; HBSP, helix B surface peptide; Smad, mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 2; Lp-PLA2, lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2; PTP1B, protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B; MIF, macrophage migration inhibitory factor; SR-uPA, overexpression of urokinase plasminogen activator; MSCs, mesenchymal stem cells; FM-MSCs, fetal membrane-derived mesenchymal stem cells; BM-MSCs, bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells; PHB, poly(3-hydroxybutyrate).
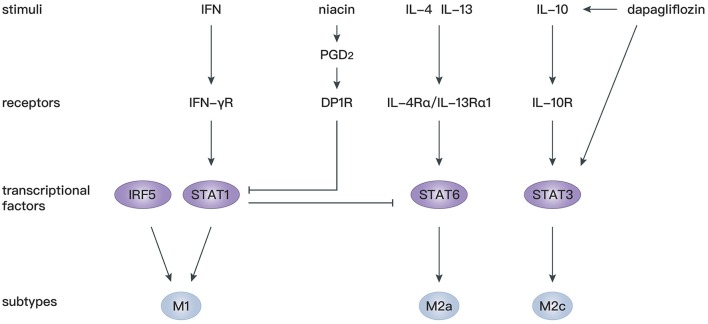
STAT proteins play an essential role in the immune response, inflammation, as well as cell growth and differentiation (127), and participate in various cardiovascular diseases (128, 129). It has been confirmed that IL-4 and IL-13 mediate macrophage polarization toward M2a macrophages depending on STAT6 signaling (130), whereas IFN-γ mediates macrophage polarization toward M1 macrophages depending on STAT1 signaling (131, 132). There is antagonism between STAT1 in M1 macrophages and STAT6 in M2 macrophages (133). Therefore, regulation of STAT1 and STAT6 axes is critical for the shift from M1 to M2 macrophages. Prostaglandin D2 (PGD2) participates in the resolution of inflammation (134) through binding to D prostanoid (DP1 and DP2) receptors (135). Macrophages express high levels of DP1 and DP2 (136), and activation of the DP1 receptor regulates macrophage infiltration and promotes inflammation resolution (137). In mice with macrophage-specific genetic deletion of DP1, macrophages are largely polarized to M1 phenotypes, leading to an extended inflammation period after MI with decreased myocardial repair. In vitro experiments showed that a DP1 receptor agonist inhibits Janus kinase 2/STAT1 phosphorylation by facilitating combination of the separated PKA regulatory IIα subunit and the transmembrane domain of IFN-γ receptor, which in turn induces STAT6 phosphorylation in macrophages (138). Similarly, another study confirmed that niacin activates the PGD2/DP1 axis to polarize macrophages toward the M2 subtype and promotes cardiac healing post-MI (102). In addition, STAT3 is widely recognized as the primary transcription factor modulating IL-10 signaling in macrophages, and activation of the STAT3 pathway is a potential mechanism for polarization toward M2c macrophages (139, 140). Dapagliflozin, a selective sodium-dependent glucose transporter inhibitor, acts as an antioxidant and enhances STAT3 activity during myocardial ischemia. Simultaneously, dapagliflozin preferentially activates M2c macrophages by increasing IL-10 expression and attenuating myofibroblast infiltration during post-infarction remodeling (98).
Apart from STAT, interferon regulatory factor (IRF) 5 has been identified as another transcription factor modulating M1 macrophage polarization (141). In IRF5-silenced mice, expression of a M1 macrophage marker decreases, and the resolution of inflammation and infarct healing are augmented (107). By silencing upstream gene expression of collapsin response mediator protein-2, the level of IRF-5 decreases, which is accompanied by an increase of M2 macrophages. Such an M1/M2 switch is reversed by overexpression of IRF5 (109). These studies provide novel gene modification strategies to modulate M2 macrophage polarization.
Overall, targeting STAT and IRF signaling might be effective approaches to facilitate differentiation of macrophages toward the M2 phenotype, which is beneficial for cardiac repair after MI. More studies should be performed to investigate the precise mechanism of M2 polarization following MI (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
Mechanisms of macrophage polarization after MI.
Mast Cells
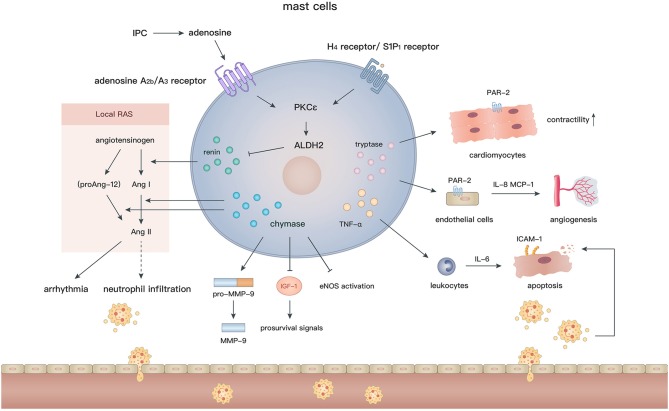
Mast cells arise from hematopoietic pluripotent precursors in bone marrow and then mature in response to proper stimuli such as stem cell factor (c-kit ligand) and IL-3 (142). In contrast to the various phenotypes of macrophages, mast cells appear to be simpler and their effects are largely mediated by degranulation. With regard to their perivascular location and abundant bioactive granules, such as chymases, tryptases, histamine, renin, and cathepsins (143), mast cells are assumed to actively participate in cardiovascular diseases. Cardiac mast cells exist in both the hearts of humans (144) and animals (145, 146), and are essential to maintain aminopeptidase activity in the normal heart (147). In addition, many mast cells accumulate in the subepicardial layer of the infarct zone after MI (148, 149), indicating their involvement in the pathological process. Although numerous studies have been conducted to elucidate the role of mast cells after MI, the effects of mast cells on the ischemic or infarcted myocardium are still controversial (Figure 4).
Figure 4.
In the setting of MI, the diverse biological effects of mast cells are largely mediated by their granules containing renin, chymase, tryptase, and TNF-α. Degranulation of mast cells induces activation of local RAS, inflammatory cell recruitment, angiogenesis, and regulation of cardiomyocyte contractility and apoptosis.
Ischemia-Reperfusion (IR) Injury and Ischemic Preconditioning (IPC)
Although timely and efficient reperfusion is the most critical therapy for MI, it may also induce continuing necrosis of cardiomyocytes and exacerbate inflammation because of IR injury. IPC is an effective approach to reduce myocardial IR injury and improve cardiac functions (150). It has been demonstrated that mast cells contribute to the protective effects of IPC against IR injury in the small intestines (151) and cerebrum (152). However, in the setting of myocardial IR injury, current evidence indicates that mast cell granules are generally deleterious and might augment myocardial injury.
Earlier studies did not find any association between mast cells and IR injury or IPC after MI, because their numbers and granular content are not affected after IPC (153), and neither a mast cell stabilizer nor mast cell degranulating compound 48/80 influence the antiarrhythmic effects of IPC (154, 155). Nevertheless, mast cell peroxidase, which is a marker of mast cell degranulation, exhibits a remarkable increase in the coronary perfusate after IPC or compound 48/80 pretreatment, indicating the potential involvement of mast cell degranulation in IPC (156). Further experiments demonstrated that norepinephrine preconditioning reduces myocardial injury by promoting degranulation (157, 158), whereas adrenoceptor blocker (158) or mast cell stabilizer (159) treatments during IPC largely decrease the degranulation of mast cells, and thus mitigate the salutary effects of IPC. These findings imply that IPC facilitates discharge of toxic substances via premature mast cell degranulation and consequently alleviate detrimental effects during the following prolonged ischemia. Additionally, inhibition of mast cell degranulation by an adenosine A2a receptor agonist (160) or relaxin (161, 162) at the reperfusion phase reduces the oxidative injury, infarct size, and ventricular arrhythmia in an IR model.
More recently, mast cells have been reported to be a crucial source of renin in the myocardium (163) and thus elicit post-IR arrhythmia by activating the local renin angiotensin (Ang) system (RAS) (164, 165). After IPC, the level of adenosine elevates rapidly in the myocardium (166). Ex vivo experiments showed that adenosine further activates the PKCε/aldehyde dehydrogenase type 2 (ALDH2) pathway in cardiac mast cells via combination with adenosine A2b/A3 receptors, in turn, reduces the local secretion of renin and biosynthesis of Ang II, which induces arrhythmia by modulating sympathetic nerve endings (167). In accordance with the above findings, activation of Gi-coupled receptors, such as histamine-H4 and sphingosine-1-phosphate-S1P1 receptors on mast cells, also reduce the infarct size and the occurrence of arrhythmia through triggering the PKCε/ALDH2 pathway. In contrast, pharmacological inhibition of ALDH2 by glyceryl trinitrate treatment or gene modification (ALDH2*2 knock-in mice) abolishes the cardioprotective effects in IR models (168–170).
In addition to renin, IR injury can be caused by other granules in mast cells. Chymases effectively facilitate the conversion of Ang I (171, 172)/proAng-12 (173) (a proteolytic product of angiotensinogen) to Ang II, which may contribute to neutrophil infiltration via CXC chemokines (174) and cardiac tissue remodeling after IR injury. Interestingly, Ang II production is blocked by inhibition of chymases, but not Ang I-converting enzyme, suggesting that local chymase-induced Ang II production is independent from classic RAS activation. In fact, inhibition of chymases protects cardiomyocytes from apoptosis after IR injury by reducing the level of pro-MMP-9, cleaved MMP-9, and neutrophil infiltration, and increasing activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (175). Moreover, mouse mast cell protease 4 (a homolog of human chymase) depletion significantly reduces the late, but not early, infarct area and improves left ventricular functions by ameliorating insulin-like growth factor-1 degradation and activating subsequent prosurvival signals (176). In addition, under oxidative stress, TNF-α, which is released during mast cell degranulation, is recognized as a crucial substance that induces cardiomyocyte apoptosis after IR. TNF-α upregulates transcription of IL-6 in recruited leukocytes and subsequent induction of intracellular adhesion molecule-1 in cardiomyocytes, which mediates neutrophil adherence to cardiomyocytes and neutrophil-mediated cardiomyocyte injury (177, 178). Mast cell stabilizers (ketotifen and cromoglycate) inhibit TNF-α secretion (179) and may attenuate myocardial injury after IR. These findings indicate that inhibition of mast cell degranulation or the release of specific granules may be a promising strategy to alleviate IR injury.
Cardiac Fibrosis
Studies have demonstrated the profibrotic properties of mast cells under various pathological conditions, such as atrial fibrillation (180), valvular heart disease (181, 182), and heart failure (183, 184). However, in MI, credible evidence is lacking for the correlation between mast cells and cardiac fibrosis, except for some indirect observations. Mast cell precursors are recruited in the area of collagen deposition at 2–3 days after reperfusion, which is mediated by macrophage-derived stem cell factor (185). In the chronic phase of MI, in situ hybridization demonstrated that plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, which induces tissue fibrosis by inhibiting MMPs, mainly lies in cardiomyocytes and perivascular mast cells around the infarction border zone (186). In a rat model of MI, inhibition of chymases significantly reduces the fibrotic area and mRNA levels of collagen I, collagen III, and TGF-β, which is important for the growth of fibroblasts (187). In addition, chymases facilitate the proliferation of fibroblasts in a dose-dependent manner in vitro (175). Additionally, bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist (Hoe140) administration reduces the number of myofibroblasts and attenuates interstitial fibrosis post-MI, in accordance with the reduction in mast cell infiltration (188). More studies are needed to ascertain the functions of mast cells in cardiac fibrosis and their underlying mechanisms in MI.
Protective Properties
Despite the long-held view that mast cells and their degranulation are detrimental to myocardial repair, studies continue to uncover their favorable effects. Clinical studies have shown that a high level of baseline serum immunoglobulin E (>200 IU/ml) is associated with less cardiac arrest or cardiogenic shock events in MI patients. It was speculated that immunoglobulin E facilitates mast cell infiltration and degranulation in the ischemic myocardium and thus improves the prognosis (189). Indeed, in a canine model of myocardial IR injury, mast cells accumulate along the cardiac vasculature for 4 weeks or longer and exhibit a defect in granular content (tryptases and chymases). In vitro experiments demonstrated that mast cell tryptases upregulate the expression of angiogenic cytokines by endothelial cells, including IL-8 and MCP-1, which might be mediated by protease-activated receptor 2 (PAR2) activation (149). In addition, mast cell-deficient rats (c-kit deficiency) exhibit a decreased coronary microvessel density around the infarct zone, a larger infarct core, and poorer left ventricular functions compared with WT rats (190). Hence, the infiltration of mast cells might promote the angiogenic activity of cardiac endothelial cells and subsequent healing process in the infarcted myocardium via tryptase secretion. However, c-kit deficiency affects the functions of mast cells as well as other immune cells. Models of specific depletion of tryptases, such as Mcpt6−/− mice (191), are necessary to verify the effects of tryptases in vivo. Recently, a more reliable c-kit-independent mast cell-deficient (Cpa3cre/+) mouse was used to investigate the role of mast cells. Similarly, a large amount of mast cell progenitors, which mainly originated from white adipose tissue, were aggregated in the heart and differentiated into mature mast cells after MI. Although no differences were found in the capillary density, collagen deposition and the infarct size between Cpa3cre/+ and WT mice, it demonstrated that mast cell-derived tryptases inhibit PKA activation and subsequent troponin I and myosin-binding protein C phosphorylation by promoting PAR-2 activation and, in turn, increase the Ca+ sensitivity and contractility of cardiomyocytes (192).
The underlying cardioprotective abilities of mast cells have also been illustrated by direct transplantation (mast cells or their granular components). Mast cell granules (MCGs) obtained by collecting a cell suspension after compound 48/80 stimulation has been proven to be therapeutic in MI. Early MCG injection at the infarct site augments myocardial angiogenesis and reduces cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Treatment with MCGs enhances endothelial cell migration, tube formation, and hypoxic resistance of cardiomyocytes in vitro (193). In addition, intracoronary functional mast cell implantation promotes cardiac fibroblast-to-myofibroblast conversion and angiogenesis compared with non-functional mast cells (KitW/W−V mouse-derived mast cells), thereby preserving cardiac functions. However, these effects cannot be sustained long term (194). In addition, mast cells enhance cardiac functions by supporting the growth of stem cells. Mast cells or MCGs (extracted by freeze-thaw cycles and filtration) promote the migration and proliferation, but not myogenic differentiation, of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) via activation of the platelet-derived growth factor pathway in the early phase of MI. These effects may retain a sufficient number of MSCs for further myofibroblast differentiation in the healing phase (195).
Taken together, mast cell granules are very likely the main determinants in mediating beneficial effects after MI, including angiogenesis, cardiomyocyte contractility regulation, anti-apoptosis, hypoxia resistance, fibroblast-to-myofibroblast conversion, and the survival of stem cells. However, concerning the sophisticated composition of MCGs and different extraction methods, more studies are required to identify the key regulatory factors in their granules and to address the mechanisms using specific animal models.
Eosinophils
Eosinophils differentiate from multipotent progenitors in bone marrow and are then released into peripheral blood. They contain various kinds of specific granular contents including eosinophil cationic protein (ECP), eosinophil peroxidase, major basic protein, eosinophil-derived neurotoxin, cytokines, growth factors, chemokines, and enzymes (196). As an indispensable component of type 2 immunity, eosinophils comprehensively interact with other immune cells and participate in the process of helminth infection and allergic diseases through degranulation activity. Recent data suggest that eosinophils are also involved in the progression of MI owing to their proinflammatory and prothrombotic properties.
Biomarkers for ACS
In MI patients, serum ECP elevates significantly during the initial 2–3 days, whereas the number of eosinophils in peripheral blood decreases, indicating that eosinophils probably infiltrate into the infarcted myocardium and participate in the acute inflammatory process after MI (197). The activation and degranulation of eosinophils in the infarcted myocardium may affect the structure of heart and lead to cardiac rupture (198).
Many studies have investigated the relationship between eosinophils or ECP and clinical outcomes of MI patients. Patients with a higher eosinophil-to-leukocyte ratio at 24 h after admission have significantly higher occurrence of major adverse cardiovascular events (199). Similarly, baseline ECP levels before stent implantation are higher in patients who suffer major adverse cardiac events such as cardiac death, recurrent MI, and clinically driven target lesion revascularization (200, 201). However, it was also reported that a high level of eosinophils (blood samples collected within 72 h after admission) is associated with a lower 1-year risk of death after multivariate adjustment (202). In addition, severe ACS patients have lower blood eosinophils compared with less severe ACS patients (203, 204). The inconsistent results of the relationship between eosinophil numbers and clinical outcomes of MI patients may due to the timing of blood sample collection or different patient cohorts.
By analyzing thrombus aspiration samples during emergency coronary angiography, eosinophils were found to be largely contained in the coronary thrombus of ACS patients and associated with a larger thrombus area, indicated that eosinophils caused the occurrence of MI by facilitating thrombus growth in the coronary artery (204, 205). In accordance with the above results, eosinophil degranulation, ECP levels, and the thrombus score were higher in ST-segment elevation MI patients with major adverse cardiac events at the 1-year follow-up (206).
Potential Mediator of Tissue Repair
Growing evidence has demonstrated that eosinophils also induce tissue repair. In a mouse model of cardiotoxin-induced tibialis anterior muscle injury, eosinophils largely aggregate in the injured site and activate the IL-4/IL-13 signaling pathway in fibro/adipogenic progenitors via secretion of IL-4. Consequently, the proliferation of fibro/adipogenic progenitors facilitate myogenesis. The regeneration ability is impaired in ΔdblGATA mice (unique loss of eosinophil lineage) (207). Similarly, eosinophils are recruited into the liver after hepatic injury and release IL-4 that directly promotes hepatocyte proliferation via blinding to IL-4Rα on these cells (208). However, studies concerning the role of eosinophils in the injured myocardium are lacking. It will be intriguing to further clarify the role of eosinophils in MI with regard to their specific abilities.
Conclusion
Type 2 immunity-related cell types and cytokines participate in various physiological and pathological processes after MI. M2 macrophages inhibit the inflammatory response and promote angiogenesis and collagen deposition, thereby conferring benefits to the infarcted myocardium. Modulation of the macrophage polarization status is critical for myocardial repair. Although mast cells and their granules have been regarded as detrimental to myocardial healing, recent studies using more reliable mouse models have indicated that mast cell-derived tryptases actively regulate contractility of cardiomyocytes. Additionally, injection of MCGs preserves cardiac functions after MI by promoting angiogenesis, fibroblast-to-myofibroblast conversion, migration and proliferation of MSCs, and reducing cardiomyocyte apoptosis. In terms of eosinophils, the serum level of eosinophils and their granules, especially ECP, are closely related to the severity and clinical outcomes of ACS patients. Interestingly, two studies have revealed their underlying ability to activate intrinsic tissue repair of both muscular and hepatic injuries. However, these properties have not been tested in the setting of MI. Owing to the comprehensive interactions with immune and myocardial cells, type 2 cytokines have been proven to facilitate the recovery of cardiac functions after MI and serve as potential biomarkers to evaluate the severity and prognosis of MI. Nevertheless, the roles of basophils, ILC2, Th2 cells, and other type 2 cytokines in MI remain obscure. More studies are needed to further clarify the role of type 2 immunity in MI.
Author Contributions
All authors made substantial contributions to the concept and interpretation of available evidence. J-YX, Y-YX, and X-TL drafted the manuscript and critically revised the manuscript for important intellectual content. All authors gave final approval of the manuscript for publication. All authors agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work and for ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Funding. This review was supported by grants from the CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (2016-I2M-1-009) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81573957 and 81874461).
References
- 1.Wynn TA. Type 2 cytokines: mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Nat Rev Immunol. (2015) 15:271–82. 10.1038/nri3831 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Engelbertsen D, Andersson L, Ljungcrantz I, Wigren M, Hedblad B, Nilsson J, et al. T-helper 2 immunity is associated with reduced risk of myocardial infarction and stroke. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2013) 33:637–44. 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300871 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Szkodzinski J, Hudzik B, Osuch M, Romanowski W, Szygula-Jurkiewicz B, Polonski L, et al. Serum concentrations of interleukin-4 and interferon-gamma in relation to severe left ventricular dysfunction in patients with acute myocardial infarction undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Heart Vessels (2011) 26:399–407. 10.1007/s00380-010-0076-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Shintani Y, Ito T, Fields L, Shiraishi M, Ichihara Y, Sato N, et al. IL-4 as a Repurposed biological drug for myocardial infarction through augmentation of reparative cardiac macrophages: proof-of-concept data in mice. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:6877. 10.1038/s41598-017-07328-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Han J, Kim YS, Lim MY, Kim HY, Kong S, Kang M, et al. Dual roles of graphene oxide to attenuate inflammation and elicit timely polarization of macrophage phenotypes for cardiac repair. ACS Nano (2018) 12:1959–77. 10.1021/acsnano.7b09107 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Peng H, Sarwar Z, Yang XP, Peterson EL, Xu J, Janic B, et al. Profibrotic role for interleukin-4 in cardiac remodeling and dysfunction. Hypertension (2015) 66:582–9. 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.05627 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kanellakis P, Ditiatkovski M, Kostolias G, Bobik A. A pro-fibrotic role for interleukin-4 in cardiac pressure overload. Cardiovasc Res. (2012) 95:77–85. 10.1093/cvr/cvs142 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hershey GK. IL-13 receptors and signaling pathways: an evolving web. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2003) 111:677–90; quiz: 91. 10.1067/mai.2003.1333 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hofmann U, Knorr S, Vogel B, Weirather J, Frey A, Ertl G, et al. Interleukin-13 deficiency aggravates healing and remodeling in male mice after experimental myocardial infarction. Circ Heart Fail. (2014) 7:822–30. 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.113.001020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.O'Meara CC, Wamstad JA, Gladstone RA, Fomovsky GM, Butty VL, Shrikumar A, et al. Transcriptional reversion of cardiac myocyte fate during mammalian cardiac regeneration. Circ Res. (2015) 116:804–15. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.304269 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Malek Mohammadi M, Kattih B, Grund A, Froese N, Korf-Klingebiel M, Gigina A, et al. The transcription factor GATA4 promotes myocardial regeneration in neonatal mice. EMBO Mol Med. (2017) 9:265–79. 10.15252/emmm.201606602 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Schmitz J, Owyang A, Oldham E, Song Y, Murphy E, McClanahan TK, et al. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity (2005) 23:479–90. 10.1016/j.immuni.2005.09.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Baekkevold ES, Roussigne M, Yamanaka T, Johansen FE, Jahnsen FL, Amalric F, et al. Molecular characterization of NF-HEV, a nuclear factor preferentially expressed in human high endothelial venules. Am J Pathol. (2003) 163:69–79. 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63631-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Li J, Razumilava N, Gores GJ, Walters S, Mizuochi T, Mourya R, et al. Biliary repair and carcinogenesis are mediated by IL-33-dependent cholangiocyte proliferation. J Clin Invest. (2014) 124:3241–51. 10.1172/JCI73742 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sanada S, Hakuno D, Higgins LJ, Schreiter ER, McKenzie AN, Lee RT. IL-33 and ST2 comprise a critical biomechanically induced and cardioprotective signaling system. J Clin Invest. (2007) 117:1538–49. 10.1172/JCI30634 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bergers G, Reikerstorfer A, Braselmann S, Graninger P, Busslinger M. Alternative promoter usage of the Fos-responsive gene Fit-1 generates mRNA isoforms coding for either secreted or membrane-bound proteins related to the IL-1 receptor. EMBO J. (1994) 13:1176–88. 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06367.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wang M, Shen G, Xu L, Liu X, Brown JM, Feng D, et al. IL-1 receptor like 1 protects against alcoholic liver injury by limiting NF-κB activation in hepatic macrophages. J Hepatol. (2018) 68:109–17. 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.08.023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Moritz DR, Rodewald HR, Gheyselinck J, Klemenz R. The IL-1 receptor-related T1 antigen is expressed on immature and mature mast cells and on fetal blood mast cell progenitors. J Immunol. (1998) 161:4866–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Tare N, Li H, Morschauser A, Cote-Sierra J, Ju G, Renzetti L, et al. KU812 cells provide a novel in vitro model of the human IL-33/ST2L axis: functional responses and identification of signaling pathways. Exp Cell Res. (2010) 316:2527–37. 10.1016/j.yexcr.2010.04.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Minutti CM, Drube S, Blair N, Schwartz C, McCrae JC, McKenzie AN, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor expression licenses type-2 helper T cells to function in a T cell receptor-independent fashion. Immunity (2017) 47:710–22 e6. 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.09.013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Biton J, Khaleghparast Athari S, Thiolat A, Santinon F, Lemeiter D, Herve R, et al. In vivo expansion of activated Foxp3+ regulatory T cells and establishment of a type 2 immune response upon IL-33 treatment protect against experimental arthritis. J Immunol. (2016) 197:1708–19. 10.4049/jimmunol.1502124 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Monticelli LA, Sonnenberg GF, Abt MC, Alenghat T, Ziegler CG, Doering TA, et al. Innate lymphoid cells promote lung-tissue homeostasis after infection with influenza virus. Nat Immunol. (2011) 12:1045–54. 10.1038/ni.2131 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Veeraveedu PT, Sanada S, Okuda K, Fu HY, Matsuzaki T, Araki R, et al. Ablation of IL-33 gene exacerbate myocardial remodeling in mice with heart failure induced by mechanical stress. Biochem Pharmacol. (2017) 138:73–80. 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.04.022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kakkar R, Lee RT. The IL-33/ST2 pathway: therapeutic target and novel biomarker. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2008) 7:827–40. 10.1038/nrd2660 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Sanchez-Mas J, Lax A, Asensio-Lopez Mdel C, Fernandez-Del Palacio MJ, Caballero L, Santarelli G, et al. Modulation of IL-33/ST2 system in postinfarction heart failure: correlation with cardiac remodelling markers. Eur J Clin Invest. (2014) 44:643–51. 10.1111/eci.12282 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lax A, Sanchez-Mas J, Asensio-Lopez MC, Fernandez-Del Palacio MJ, Caballero L, Garrido IP, et al. Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists modulate galectin-3 and interleukin-33/ST2 signaling in left ventricular systolic dysfunction after acute myocardial infarction. JACC Heart Fail (2015) 3:50–8. 10.1016/j.jchf.2014.07.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Xia J, Qu Y, Yin C, Xu D. Preliminary study of beta-blocker therapy on modulation of interleukin-33/ST2 signaling during ventricular remodeling after acute myocardial infarction. Cardiol J. (2017) 24:188–94. 10.5603/CJ.a2016.0096 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Seki K, Sanada S, Kudinova AY, Steinhauser ML, Handa V, Gannon J, et al. Interleukin-33 prevents apoptosis and improves survival after experimental myocardial infarction through ST2 signaling. Circ Heart Fail (2009) 2:684–91. 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.109.873240 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Rui T, Zhang J, Xu X, Yao Y, Kao R, Martin CM. Reduction in IL-33 expression exaggerates ischaemia/reperfusion-induced myocardial injury in mice with diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc Res. (2012) 94:370–8. 10.1093/cvr/cvs015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Yin H, Li P, Hu F, Wang Y, Chai X, Zhang Y. IL-33 attenuates cardiac remodeling following myocardial infarction via inhibition of the p38 MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways. Mol Med Rep. (2014) 9:1834–8. 10.3892/mmr.2014.2051 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Liu CL, Shen DL, Zhu K, Tang JN, Wang XF, Zhang L, et al. Characterization of interleukin-33 and matrix metalloproteinase-28 in serum and their association with disease severity in patients with coronary heart disease. Coron Artery Dis. (2014) 25:498–504. 10.1097/MCA.0000000000000117 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Liu CL, Shen DL, Zhu K, Tang JN, Hai QM, Zhang JY. Levels of interleukin-33 and interleukin-6 in patients with acute coronary syndrome or stable angina. Clin Invest Med. (2013) 36:E234–41. 10.25011/cim.v36i4.19957 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Al Shahi H, Shimada K, Miyauchi K, Yoshihara T, Sai E, Shiozawa T, et al. Elevated circulating levels of inflammatory markers in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Int J Vasc Med. (2015) 2015:805375. 10.1155/2015/805375 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Weinberg EO, Shimpo M, De Keulenaer GW, MacGillivray C, Tominaga S, Solomon SD, et al. Expression and regulation of ST2, an interleukin-1 receptor family member, in cardiomyocytes and myocardial infarction. Circulation (2002) 106:2961–6. 10.1161/01.CIR.0000038705.69871.D9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Weir RA, Miller AM, Murphy GE, Clements S, Steedman T, Connell JM, et al. Serum soluble ST2: a potential novel mediator in left ventricular and infarct remodeling after acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2010) 55:243–50. 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.08.047 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Shimpo M, Morrow DA, Weinberg EO, Sabatine MS, Murphy SA, Antman EM, et al. Serum levels of the interleukin-1 receptor family member ST2 predict mortality and clinical outcome in acute myocardial infarction. Circulation (2004) 109:2186–90. 10.1161/01.CIR.0000127958.21003.5A [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.O'Donoghue ML, Morrow DA, Cannon CP, Jarolim P, Desai NR, Sherwood MW, et al. Multimarker risk stratification in patients with acute myocardial infarction. J Am Heart Assoc. (2016) 5:e002586. 10.1161/JAHA.115.002586 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Marino R, Magrini L, Orsini F, Russo V, Cardelli P, Salerno G, et al. Comparison between soluble ST2 and high-sensitivity troponin I in predicting short-term mortality for patients presenting to the emergency department with chest pain. Ann Lab Med. (2017) 37:137–46. 10.3343/alm.2017.37.2.137 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kohli P, Bonaca MP, Kakkar R, Kudinova AY, Scirica BM, Sabatine MS, et al. Role of ST2 in non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome in the MERLIN-TIMI 36 trial. Clin Chem. (2012) 58:257–66. 10.1373/clinchem.2011.173369 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Dhillon OS, Narayan HK, Khan SQ, Kelly D, Quinn PA, Squire IB, et al. Pre-discharge risk stratification in unselected STEMI: is there a role for ST2 or its natural ligand IL-33 when compared with contemporary risk markers? Int J Cardiol. (2013) 167:2182–8. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2012.05.073 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Dhillon OS, Narayan HK, Quinn PA, Squire IB, Davies JE, Ng LL. Interleukin 33 and ST2 in non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction: comparison with Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events Risk Scoring and NT-proBNP. Am Heart J. (2011) 161:1163–70. 10.1016/j.ahj.2011.03.025 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Jenkins WS, Roger VL, Jaffe AS, Weston SA, AbouEzzeddine OF, Jiang R, et al. Prognostic value of soluble ST2 after myocardial infarction: a community perspective. Am J Med. (2017) 130:1112 e9–e15. 10.1016/j.amjmed.2017.02.034 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Eggers KM, Armstrong PW, Califf RM, Simoons ML, Venge P, Wallentin L, et al. ST2 and mortality in non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome. Am Heart J. (2010) 159:788–94. 10.1016/j.ahj.2010.02.022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Gomez Perdiguero E, Klapproth K, Schulz C, Busch K, Azzoni E, Crozet L, et al. Tissue-resident macrophages originate from yolk-sac-derived erythro-myeloid progenitors. Nature (2015) 518:547–51. 10.1038/nature13989 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hoeffel G, Wang Y, Greter M, See P, Teo P, Malleret B, et al. Adult Langerhans cells derive predominantly from embryonic fetal liver monocytes with a minor contribution of yolk sac-derived macrophages. J Exp Med. (2012) 209:1167–81. 10.1084/jem.20120340 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Pinto AR, Ilinykh A, Ivey MJ, Kuwabara JT, D'Antoni ML, Debuque R, et al. Revisiting cardiac cellular composition. Circ Res. (2016) 118:400–9. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.307778 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Gleissner CA, Shaked I, Little KM, Ley K. CXC chemokine ligand 4 induces a unique transcriptome in monocyte-derived macrophages. J Immunol. (2010) 184:4810–8. 10.4049/jimmunol.0901368 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Mosser DM, Edwards JP. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. (2008) 8:958–69. 10.1038/nri2448 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Nahrendorf M, Swirski FK, Aikawa E, Stangenberg L, Wurdinger T, Figueiredo JL, et al. The healing myocardium sequentially mobilizes two monocyte subsets with divergent and complementary functions. J Exp Med. (2007) 204:3037–47. 10.1084/jem.20070885 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Yan X, Anzai A, Katsumata Y, Matsuhashi T, Ito K, Endo J, et al. Temporal dynamics of cardiac immune cell accumulation following acute myocardial infarction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2013) 62:24–35. 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.04.023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Mantovani A, Sica A, Sozzani S, Allavena P, Vecchi A, Locati M. The chemokine system in diverse forms of macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. (2004) 25:677–86. 10.1016/j.it.2004.09.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Colin S, Chinetti-Gbaguidi G, Staels B. Macrophage phenotypes in atherosclerosis. Immunol Rev. (2014) 262:153–66. 10.1111/imr.12218 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Stein M, Keshav S, Harris N, Gordon S. Interleukin 4 potently enhances murine macrophage mannose receptor activity: a marker of alternative immunologic macrophage activation. J Exp Med. (1992) 176:287–92. 10.1084/jem.176.1.287 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Modolell M, Corraliza IM, Link F, Soler G, Eichmann K. Reciprocal regulation of the nitric oxide synthase/arginase balance in mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages by TH1 and TH2 cytokines. Eur J Immunol. (1995) 25:1101–4. 10.1002/eji.1830250436 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Hesse M, Modolell M, La Flamme AC, Schito M, Fuentes JM, Cheever AW, et al. Differential regulation of nitric oxide synthase-2 and arginase-1 by type 1/type 2 cytokines in vivo: granulomatous pathology is shaped by the pattern of L-arginine metabolism. J Immunol. (2001) 167:6533–44. 10.4049/jimmunol.167.11.6533 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Gu L, Tseng S, Horner RM, Tam C, Loda M, Rollins BJ. Control of TH2 polarization by the chemokine monocyte chemoattractant protein-1. Nature (2000) 404:407–11. 10.1038/35006097 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Katakura T, Miyazaki M, Kobayashi M, Herndon DN, Suzuki F. CCL17 and IL-10 as effectors that enable alternatively activated macrophages to inhibit the generation of classically activated macrophages. J Immunol. (2004) 172:1407–13. 10.4049/jimmunol.172.3.1407 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Andrew DP, Chang MS, McNinch J, Wathen ST, Rihanek M, Tseng J, et al. STCP-1 (MDC) CC chemokine acts specifically on chronically activated Th2 lymphocytes and is produced by monocytes on stimulation with Th2 cytokines IL-4 and IL-13. J Immunol. (1998) 161:5027–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Watanabe K, Jose PJ, Rankin SM. Eotaxin-2 generation is differentially regulated by lipopolysaccharide and IL-4 in monocytes and macrophages. J Immunol. (2002) 168:1911–8. 10.4049/jimmunol.168.4.1911 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Gratchev A, Guillot P, Hakiy N, Politz O, Orfanos CE, Schledzewski K, et al. Alternatively activated macrophages differentially express fibronectin and its splice variants and the extracellular matrix protein betaIG-H3. Scand J Immunol. (2001) 53:386–92. 10.1046/j.1365-3083.2001.00885.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Torocsik D, Bardos H, Nagy L, Adany R. Identification of factor XIII-A as a marker of alternative macrophage activation. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2005) 62:2132–9. 10.1007/s00018-005-5242-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Mantovani A, Locati M, Vecchi A, Sozzani S, Allavena P. Decoy receptors: a strategy to regulate inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. Trends Immunol. (2001) 22:328–36. 10.1016/S1471-4906(01)01941-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Gordon S. Alternative activation of macrophages. Nat Rev Immunol. (2003) 3:23–35. 10.1038/nri978 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Mantovani A, Sozzani S, Locati M, Allavena P, Sica A. Macrophage polarization: tumor-associated macrophages as a paradigm for polarized M2 mononuclear phagocytes. Trends Immunol. (2002) 23:549–55. 10.1016/S1471-4906(02)02302-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Anderson CF, Mosser DM. A novel phenotype for an activated macrophage: the type 2 activated macrophage. J Leukoc Biol. (2002) 72:101–6. 10.1189/jlb.72.1.101 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Edwards JP, Zhang X, Frauwirth KA, Mosser DM. Biochemical and functional characterization of three activated macrophage populations. J Leukoc Biol. (2006) 80:1298–307. 10.1189/jlb.0406249 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Sironi M, Martinez FO, D'Ambrosio D, Gattorno M, Polentarutti N, Locati M, et al. Differential regulation of chemokine production by Fcgamma receptor engagement in human monocytes: association of CCL1 with a distinct form of M2 monocyte activation (M2b, Type 2). J Leukoc Biol. (2006) 80:342–9. 10.1189/jlb.1005586 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Lurier EB, Dalton D, Dampier W, Raman P, Nassiri S, Ferraro NM, et al. Transcriptome analysis of IL-10-stimulated (M2c) macrophages by next-generation sequencing. Immunobiology (2017) 222:847–56. 10.1016/j.imbio.2017.02.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Valledor AF, Ricote M. Nuclear receptor signaling in macrophages. Biochem Pharmacol. (2004) 67:201–12. 10.1016/j.bcp.2003.10.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Spiller KL, Anfang RR, Spiller KJ, Ng J, Nakazawa KR, Daulton JW, et al. The role of macrophage phenotype in vascularization of tissue engineering scaffolds. Biomaterials (2014) 35:4477–88. 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.02.012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Lolmede K, Campana L, Vezzoli M, Bosurgi L, Tonlorenzi R, Clementi E, et al. Inflammatory and alternatively activated human macrophages attract vessel-associated stem cells, relying on separate HMGB1- and MMP-9-dependent pathways. J Leukoc Biol. (2009) 85:779–87. 10.1189/jlb.0908579 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.van Amerongen MJ, Harmsen MC, van Rooijen N, Petersen AH, van Luyn MJ. Macrophage depletion impairs wound healing and increases left ventricular remodeling after myocardial injury in mice. Am J Pathol. (2007) 170:818–29. 10.2353/ajpath.2007.060547 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Leor J, Rozen L, Zuloff-Shani A, Feinberg MS, Amsalem Y, Barbash IM, et al. Ex vivo activated human macrophages improve healing, remodeling, and function of the infarcted heart. Circulation (2006) 114(Suppl. 1):I94–100. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.000331 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Nahrendorf M, Sosnovik DE, Waterman P, Swirski FK, Pande AN, Aikawa E, et al. Dual channel optical tomographic imaging of leukocyte recruitment and protease activity in the healing myocardial infarct. Circ Res. (2007) 100:1218–25. 10.1161/01.RES.0000265064.46075.31 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Soehnlein O, Lindbom L. Phagocyte partnership during the onset and resolution of inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. (2010) 10:427–39. 10.1038/nri2779 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Heymans S, Luttun A, Nuyens D, Theilmeier G, Creemers E, Moons L, et al. Inhibition of plasminogen activators or matrix metalloproteinases prevents cardiac rupture but impairs therapeutic angiogenesis and causes cardiac failure. Nat Med. (1999) 5:1135–42. 10.1038/13459 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Matsui Y, Ikesue M, Danzaki K, Morimoto J, Sato M, Tanaka S, et al. Syndecan-4 prevents cardiac rupture and dysfunction after myocardial infarction. Circ Res. (2011) 108:1328–39. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.235689 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Panizzi P, Swirski FK, Figueiredo JL, Waterman P, Sosnovik DE, Aikawa E, et al. Impaired infarct healing in atherosclerotic mice with Ly-6C(hi) monocytosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2010) 55:1629–38. 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.08.089 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Krishnamurthy P, Rajasingh J, Lambers E, Qin G, Losordo DW, Kishore R. IL-10 inhibits inflammation and attenuates left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction via activation of STAT3 and suppression of HuR. Circ Res. (2009) 104:e9–18. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.188243 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Ikeuchi M, Tsutsui H, Shiomi T, Matsusaka H, Matsushima S, Wen J, et al. Inhibition of TGF-beta signaling exacerbates early cardiac dysfunction but prevents late remodeling after infarction. Cardiovasc Res. (2004) 64:526–35. 10.1016/j.cardiores.2004.07.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Barbay V, Houssari M, Mekki M, Banquet S, Edwards-Levy F, Henry JP, et al. Role of M2-like macrophage recruitment during angiogenic growth factor therapy. Angiogenesis (2015) 18:191–200. 10.1007/s10456-014-9456-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Jetten N, Verbruggen S, Gijbels MJ, Post MJ, De Winther MP, Donners MM. Anti-inflammatory M2, but not pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages promote angiogenesis in vivo. Angiogenesis (2014) 17:109–18. 10.1007/s10456-013-9381-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Jakob P, Doerries C, Briand S, Mocharla P, Krankel N, Besler C, et al. Loss of angiomiR-126 and 130a in angiogenic early outgrowth cells from patients with chronic heart failure: role for impaired in vivo neovascularization and cardiac repair capacity. Circulation (2012) 126:2962–75. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.093906 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Ben-Mordechai T, Holbova R, Landa-Rouben N, Harel-Adar T, Feinberg MS, Abd Elrahman I, et al. Macrophage subpopulations are essential for infarct repair with and without stem cell therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2013) 62:1890–901. 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.07.057 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Yano T, Miura T, Whittaker P, Miki T, Sakamoto J, Nakamura Y, et al. Macrophage colony-stimulating factor treatment after myocardial infarction attenuates left ventricular dysfunction by accelerating infarct repair. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2006) 47:626–34. 10.1016/j.jacc.2005.09.037 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Shiraishi M, Shintani Y, Shintani Y, Ishida H, Saba R, Yamaguchi A, et al. Alternatively activated macrophages determine repair of the infarcted adult murine heart. J Clin Invest. (2016) 126:2151–66. 10.1172/JCI85782 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Jung M, Ma Y, Iyer RP, DeLeon-Pennell KY, Yabluchanskiy A, Garrett MR, et al. IL-10 improves cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction by stimulating M2 macrophage polarization and fibroblast activation. Basic Res Cardiol. (2017) 112:33. 10.1007/s00395-017-0622-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Eghbali M, Tomek R, Sukhatme VP, Woods C, Bhambi B. Differential effects of transforming growth factor-beta 1 and phorbol myristate acetate on cardiac fibroblasts. Regulation of fibrillar collagen mRNAs and expression of early transcription factors. Circ Res. (1991) 69:483–90. 10.1161/01.RES.69.2.483 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Chua CC, Chua BH, Zhao ZY, Krebs C, Diglio C, Perrin E. Effect of growth factors on collagen metabolism in cultured human heart fibroblasts. Connect Tissue Res. (1991) 26:271–81. 10.3109/03008209109152444 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Bujak M, Ren G, Kweon HJ, Dobaczewski M, Reddy A, Taffet G, et al. Essential role of Smad3 in infarct healing and in the pathogenesis of cardiac remodeling. Circulation (2007) 116:2127–38. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.704197 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Kim YS, Jeong H-Y, Kim AR, Kim W-H, Cho H, Um J, et al. Natural product derivative BIO promotes recovery after myocardial infarction via unique modulation of the cardiac microenvironment. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:30726. 10.1038/srep30726 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Cheng Y, Yang C, Luo D, Li X, Le XC, Rong J. N-Propargyl caffeamide skews macrophages towards a resolving M2-like phenotype against myocardial ischemic injury via activating Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and inhibiting NF-kB pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2018) 47(6):2544–57. 10.1159/000491651 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Yin J, Hu H, Li X, Xue M, Cheng W, Wang Y, et al. Inhibition of Notch signaling pathway attenuates sympathetic hyperinnervation together with the augmentation of M2 macrophages in rats post-myocardial infarction. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2016) 310:C41–53. 10.1152/ajpcell.00163.2015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Bezerra OC, França CM, Rocha JA, Neves GA, Souza PRM, Teixeira Gomes M, et al. Cholinergic stimulation improves oxidative stress and inflammation in experimental myocardial infarction. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:13687. 10.1038/s41598-017-14021-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Rocha JA, Ribeiro SP, França CM, Coelho O, Alves G, Lacchini S, et al. Increase in cholinergic modulation with pyridostigmine induces anti-inflammatory cell recruitment soon after acute myocardial infarction in rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. (2016) 310:R697–706. 10.1152/ajpregu.00328.2015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Rafatian N, Westcott KV, White RA, Leenen FHH. Cardiac macrophages and apoptosis after myocardial infarction: effects of central MR blockade. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. (2014) 307:R879–87. 10.1152/ajpregu.00075.2014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Yang N, Cheng W, Hu H, Xue M, Li X, Wang Y, et al. Atorvastatin attenuates sympathetic hyperinnervation together with the augmentation of M2 macrophages in rats postmyocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Ther. (2016) 34:234–44. 10.1111/1755-5922.12193 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Lee TM, Chang NC, Lin SZ. Dapagliflozin, a selective SGLT2 Inhibitor, attenuated cardiac fibrosis by regulating the macrophage polarization via STAT3 signaling in infarcted rat hearts. Free Radic Biol Med. (2017) 104:298–310. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.01.035 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Lee T-M, Lin S-Z, Chang N-C. Nicorandil regulates the macrophage skewing and ameliorates myofibroblasts by inhibition of RhoA/Rho-kinase signalling in infarcted rats. J Cell Mol Med. (2018) 22:1056–69. 10.1111/jcmm.13130 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Di Filippo C, Rossi C, Ferraro B, Maisto R, De Angelis A, Ferraraccio F, et al. Involvement of proteasome and macrophages M2 in the protection afforded by telmisartan against the acute myocardial infarction in Zucker diabetic fatty rats with metabolic syndrome. Mediators Inflamm. (2014) 2014:972761. 10.1155/2014/972761 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Gross L, Paintmayer L, Lehner S, Brandl L, Brenner C, Grabmaier U, et al. FDG-PET reveals improved cardiac regeneration and attenuated adverse remodelling following Sitagliptin + G-CSF therapy after acute myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging (2016) 17:136–45. 10.1093/ehjci/jev237 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Kong D, Li J, Shen Y, Liu G, Zuo S, Tao B, et al. Niacin promotes cardiac healing after myocardial infarction through activation of the myeloid prostaglandin D2 receptor subtype 1. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. (2017) 360:435–44. 10.1124/jpet.116.238261 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Miao L, Shen X, Whiteman M, Xin H, Shen Y, Xin X, et al. Hydrogen sulfide mitigates myocardial infarction via promotion of mitochondrial biogenesis-dependent M2 polarization of macrophages. Antioxid Redox Signal (2016) 25:268–81. 10.1089/ars.2015.6577 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Zeng Z, Yu K, Chen L, Li W, Xiao H, Huang Z. Interleukin-2/Anti-Interleukin-2 immune complex attenuates cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction through expansion of regulatory T cells. J Immunol Res. (2016) 2016:8493767. 10.1155/2016/8493767 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Wang Z, Huang S, Sheng Y, Peng X, Liu H, Jin N, et al. Topiramate modulates post-infarction inflammation primarily by targeting monocytes or macrophages. Cardiovasc Res. (2017) 113:475–87. 10.1093/cvr/cvx027 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Tian Y, Piras BA, Kron IL, French BA, Yang Z. Adenosine 2B receptor activation reduces myocardial reperfusion injury by promoting anti-inflammatory macrophages differentiation via PI3K/Akt pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2015) 2015:585297. 10.1155/2015/585297 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Courties G, Heidt T, Sebas M, Iwamoto Y, Jeon D, Truelove J, et al. In vivo silencing of the transcription factor IRF5 reprograms the macrophage phenotype and improves infarct healing. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2014) 63:1556–66. 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.11.023 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Cheng Y, Feng Y, Xia Z, Li X, Rong J. ω-Alkynyl arachidonic acid promotes anti-inflammatory macrophage M2 polarization against acute myocardial infarction via regulating the cross-talk between PKM2, HIF-1α and iNOS. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids (2017) 1862:1595–605. 10.1016/j.bbalip.2017.09.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Zhou L-S, Zhao G-L, Liu Q, Jiang S-C, Wang Y, Zhang D-M. Silencing collapsin response mediator protein-2 reprograms macrophage phenotype and improves infarct healing in experimental myocardial infarction model. J Inflamm (Lond) (2015) 12:11. 10.1186/s12950-015-0053-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Ben-Mordechai T, Kain D, Holbova R, Landa N, Levin L-P, Elron-Gross I, et al. Targeting and modulating infarct macrophages with hemin formulated in designed lipid-based particles improves cardiac remodeling and function. J Control Release (2017) 257:21–31. 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.01.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Kimbrough D, Wang SH, Wright LH, Mani SK, Kasiganesan H, LaRue AC, et al. HDAC inhibition helps post-MI healing by modulating macrophage polarization. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2018) 119:51–63. 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2018.04.011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Singla DK, Singla RD, Abdelli LS, Glass C. Fibroblast growth factor-9 enhances M2 macrophage differentiation and attenuates adverse cardiac remodeling in the infarcted diabetic heart. PLoS ONE (2015) 10:e0120739. 10.1371/journal.pone.0120739 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Ma X, Yuan Y, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Li M. An analog of Ac-SDKP improves heart functions after myocardial infarction by suppressing alternative activation (M2) of macrophages. Int J Cardiol. (2014) 175:376–8. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.05.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Ueba H, Shiomi M, Brines M, Yamin M, Kobayashi T, Ako J, et al. Suppression of coronary atherosclerosis by helix B surface Peptide, a nonerythropoietic, tissue-protective compound derived from erythropoietin. Mol Med. (2013) 19:195–202. 10.2119/molmed.2013.00037 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Shivshankar P, Halade GV, Calhoun C, Escobar GP, Mehr AJ, Jimenez F, et al. Caveolin-1 deletion exacerbates cardiac interstitial fibrosis by promoting M2 macrophage activation in mice after myocardial infarction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2014) 76:84–93. 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2014.07.020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.He S, Chousterman BG, Fenn A, Anzai A, Nairz M, Brandt M, et al. Lp-PLA2 antagonizes left ventricular healing after myocardial infarction by impairing the appearance of reparative macrophages. Circ Heart Fail (2015) 8:980–7. 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.115.002334 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Palevski D, Levin-Kotler L-P, Kain D, Naftali-Shani N, Landa N, Ben-Mordechai T, et al. Loss of macrophage wnt secretion improves remodeling and function after myocardial infarction in mice. J Am Heart Assoc. (2017) 6:e004387. 10.1161/JAHA.116.004387 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Besnier M, Galaup A, Nicol L, Henry J-P, Coquerel D, Gueret A, et al. Enhanced angiogenesis and increased cardiac perfusion after myocardial infarction in protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B-deficient mice. FASEB J. (2014) 28:3351–61. 10.1096/fj.13-245753 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.White DA, Su Y, Kanellakis P, Kiriazis H, Morand EF, Bucala R, et al. Differential roles of cardiac and leukocyte derived macrophage migration inhibitory factor in inflammatory responses and cardiac remodelling post myocardial infarction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2014) 69:32–42. 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2014.01.015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Carlson S, Helterline D, Asbe L, Dupras S, Minami E, Farris S, et al. Cardiac macrophages adopt profibrotic/M2 phenotype in infarcted hearts: Role of urokinase plasminogen activator. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2017) 108:42–49. 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.05.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Cho D-I, Kim MR, Jeong H-y, Jeong HC, Jeong MH, Yoon SH, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells reciprocally regulate the M1/M2 balance in mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages. Exp Mol Med. (2014) 46:e70. 10.1038/emm.2013.135 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Dayan V, Yannarelli G, Billia F, Filomeno P, Wang X-H, Davies JE, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells mediate a switch to alternatively activated monocytes/macrophages after acute myocardial infarction. Basic Res Cardiol. (2011) 106:1299–310. 10.1007/s00395-011-0221-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Ishikane S, Hosoda H, Yamahara K, Akitake Y, Kyoungsook J, Mishima K, et al. Allogeneic transplantation of fetal membrane-derived mesenchymal stem cell sheets increases neovascularization and improves cardiac function after myocardial infarction in rats. Transplantation (2013) 96:697–706. 10.1097/TP.0b013e31829f753d [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Protti A, Mongue-Din H, Mylonas KJ, Sirker A, Sag CM, Swim MM, et al. Bone marrow transplantation modulates tissue macrophage phenotype and enhances cardiac recovery after subsequent acute myocardial infarction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2016) 90:120–8. 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2015.12.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Sarig U, Sarig H, de-Berardinis E, Chaw S-Y, Nguyen EBV, Ramanujam VS, et al. Natural myocardial ECM patch drives cardiac progenitor based restoration even after scarring. Acta Biomater. (2016) 44:209–20. 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.08.031 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Castellano D, Blanes M, Marco B, Cerrada I, Ruiz-Saurí A, Pelacho B, et al. A comparison of electrospun polymers reveals poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) fiber as a superior scaffold for cardiac repair. Stem Cells Dev. (2014) 23:1479–90. 10.1089/scd.2013.0578 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Levy DE, Darnell JE, Jr. Stats: transcriptional control and biological impact. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2002) 3:651–62. 10.1038/nrm909 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Grote K, Luchtefeld M, Schieffer B. JANUS under stress–role of JAK/STAT signaling pathway in vascular diseases. Vascul Pharmacol. (2005) 43:357–63. 10.1016/j.vph.2005.08.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Sun H, Wang Y. Interferon regulatory factors in heart: stress response beyond inflammation. Hypertension (2014) 63:663–4. 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.113.02795 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Martinez FO, Helming L, Gordon S. Alternative activation of macrophages: an immunologic functional perspective. Annu Rev Immunol. (2009) 27:451–83. 10.1146/annurev.immunol.021908.132532 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Meraz MA, White JM, Sheehan KC, Bach EA, Rodig SJ, Dighe AS, et al. Targeted disruption of the Stat1 gene in mice reveals unexpected physiologic specificity in the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Cell (1996) 84:431–42. 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81288-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Darnell JE, Jr, Kerr IM, Stark GR. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science (1994) 264:1415–21. 10.1126/science.8197455 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Ohmori Y, Hamilton TA. IL-4-induced STAT6 suppresses IFN-gamma-stimulated STAT1-dependent transcription in mouse macrophages. J Immunol. (1997) 159:5474–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Buckley CD, Gilroy DW, Serhan CN. Proresolving lipid mediators and mechanisms in the resolution of acute inflammation. Immunity (2014) 40:315–27. 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.02.009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Joo M, Sadikot RT. PGD synthase and PGD2 in immune resposne. Mediators Inflamm. (2012) 2012:503128. 10.1155/2012/503128 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Sandig H, Pease JE, Sabroe I. Contrary prostaglandins: the opposing roles of PGD2 and its metabolites in leukocyte function. J Leukoc Biol. (2007) 81:372–82. 10.1189/jlb.0706424 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Rajakariar R, Hilliard M, Lawrence T, Trivedi S, Colville-Nash P, Bellingan G, et al. Hematopoietic prostaglandin D2 synthase controls the onset and resolution of acute inflammation through PGD2 and 15-deoxyDelta12 14 PGJ2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2007) 104:20979–84. 10.1073/pnas.0707394104 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Kong D, Shen Y, Liu G, Zuo S, Ji Y, Lu A, et al. PKA regulatory IIalpha subunit is essential for PGD2-mediated resolution of inflammation. J Exp Med. (2016) 213:2209–26. 10.1084/jem.20160459 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Murray PJ. Understanding and exploiting the endogenous interleukin-10/STAT3-mediated anti-inflammatory response. Curr Opin Pharmacol. (2006) 6:379–86. 10.1016/j.coph.2006.01.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Williams L, Bradley L, Smith A, Foxwell B. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 is the dominant mediator of the anti-inflammatory effects of IL-10 in human macrophages. J Immunol. (2004) 172:567–76. 10.4049/jimmunol.172.1.567 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Krausgruber T, Blazek K, Smallie T, Alzabin S, Lockstone H, Sahgal N, et al. IRF5 promotes inflammatory macrophage polarization and TH1-TH17 responses. Nat Immunol. (2011) 12:231–8. 10.1038/ni.1990 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Gurish MF, Austen KF. Developmental origin and functional specialization of mast cell subsets. Immunity (2012) 37:25–33. 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.07.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Wernersson S, Pejler G. Mast cell secretory granules: armed for battle. Nat Rev Immunol. (2014) 14:478–94. 10.1038/nri3690 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Sperr WR, Bankl HC, Mundigler G, Klappacher G, Grossschmidt K, Agis H, et al. The human cardiac mast cell: localization, isolation, phenotype, and functional characterization. Blood (1994) 84:3876–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Frangogiannis NG, Burns AR, Michael LH, Entman ML. Histochemical and morphological characteristics of canine cardiac mast cells. Histochem J. (1999) 31:221–9. 10.1023/A:1003541332070 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Dewald O, Ren G, Duerr GD, Zoerlein M, Klemm C, Gersch C, et al. Of mice and dogs: species-specific differences in the inflammatory response following myocardial infarction. Am J Pathol. (2004) 164:665–77. 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63154-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Monis B, Weinberg T. Aminopeptidase activity in myocardial infarction of man. A histochemical study. Am J Pathol. (1964) 44:867–76. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Engels W, Reiters PH, Daemen MJ, Smits JF, van der Vusse GJ. Transmural changes in mast cell density in rat heart after infarct induction in vivo. J Pathol. (1995) 177:423–9. 10.1002/path.1711770414 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Somasundaram P, Ren G, Nagar H, Kraemer D, Mendoza L, Michael LH, et al. Mast cell tryptase may modulate endothelial cell phenotype in healing myocardial infarcts. J Pathol. (2005) 205:102–11. 10.1002/path.1690 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Hausenloy DJ, Yellon DM. Ischaemic conditioning and reperfusion injury. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2016) 13:193–209. 10.1038/nrcardio.2016.5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Xing D, Zhang R, Li S, Huang P, Luo C, Hei Z, et al. Pivotal role of mast cell carboxypeptidase A in mediating protection against small intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats after ischemic preconditioning. J Surg Res. (2014) 192:177–86. 10.1016/j.jss.2014.05.050 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Rehni AK, Bhateja P, Singh N, Jaggi AS. Implication of mast cell degranulation in ischemic preconditioning-induced prevention of cerebral injury. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. (2008) 22:179–88. 10.1111/j.1472-8206.2008.00567.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Wang P, Downey JM, Cohen MV. Mast cell degranulation does not contribute to ischemic preconditioning in isolated rabbit hearts. Basic Res Cardiol. (1996) 91:458–67. 10.1007/BF00788727 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Humphreys RA, Kane KA, Parratt JR. Lack of involvement of mast cell degranulation in the antiarrhythmic effect of preconditioning in rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. (1998) 31:418–23. 10.1097/00005344-199803000-00013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Davani S, Muret P, Royer B, Kantelip B, Frances C, Millart H, et al. Ischaemic preconditioning and mast cell histamine release: microdialysis of isolated rat hearts. Pharmacol Res. (2002) 45:383–90. 10.1006/phrs.2001.0960 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Parikh V, Singh M. Resident cardiac mast cells and the cardioprotective effect of ischemic preconditioning in isolated rat heart. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. (1997) 30:149–56. 10.1097/00005344-199708000-00001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Parikh V, Singh M. Possible role of cardiac mast cells in norepinephrine-induced myocardial preconditioning. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. (1999) 21:269–74. 10.1358/mf.1999.21.4.538177 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Parikh V, Singh M. Possible role of adrenergic component and cardiac mast cell degranulation in preconditioning-induced cardioprotection. Pharmacol Res. (1999) 40:129–37. 10.1006/phrs.1999.0501 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Parikh V, Singh M. Cardiac mast cell stabilization and cardioprotective effect of ischemic preconditioning in isolated rat heart. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. (1998) 31:779–85. 10.1097/00005344-199805000-00018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Rork TH, Wallace KL, Kennedy DP, Marshall MA, Lankford AR, Linden J. Adenosine A2A receptor activation reduces infarct size in the isolated, perfused mouse heart by inhibiting resident cardiac mast cell degranulation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2008) 295:H1825–33. 10.1152/ajpheart.495.2008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Nistri S, Cinci L, Perna AM, Masini E, Mastroianni R, Bani D. Relaxin induces mast cell inhibition and reduces ventricular arrhythmias in a swine model of acute myocardial infarction. Pharmacol Res. (2008) 57:43–8. 10.1016/j.phrs.2007.11.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Nistri S, Cinci L, Perna AM, Masini E, Bani D. Mast cell inhibition and reduced ventricular arrhythmias in a swine model of acute myocardial infarction upon therapeutic administration of relaxin. Inflamm Res. (2008) 57(Suppl. 1):S7–8. 10.1007/s00011-007-0602-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Silver RB, Reid AC, Mackins CJ, Askwith T, Schaefer U, Herzlinger D, et al. Mast cells: a unique source of renin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2004) 101:13607–12. 10.1073/pnas.0403208101 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Mackins CJ, Kano S, Seyedi N, Schafer U, Reid AC, Machida T, et al. Cardiac mast cell-derived renin promotes local angiotensin formation, norepinephrine release, and arrhythmias in ischemia/reperfusion. J Clin Invest. (2006) 116:1063–70. 10.1172/JCI25713 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Aldi S, Marino A, Tomita K, Corti F, Anand R, Olson KE, et al. E-NTPDase1/CD39 modulates renin release from heart mast cells during ischemia/reperfusion: a novel cardioprotective role. FASEB J. (2015) 29:61–9. 10.1096/fj.14-261867 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Headrick JP. Ischemic preconditioning: bioenergetic and metabolic changes and the role of endogenous adenosine. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (1996) 28:1227–40. 10.1006/jmcc.1996.0113 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Koda K, Salazar-Rodriguez M, Corti F, Chan NY, Estephan R, Silver RB, et al. Aldehyde dehydrogenase activation prevents reperfusion arrhythmias by inhibiting local renin release from cardiac mast cells. Circulation (2010) 122:771–81. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.952481 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Marino A, Sakamoto T, Robador PA, Tomita K, Levi R. S1P receptor 1-mediated anti-renin-angiotensin system cardioprotection: pivotal role of mast cell aldehyde dehydrogenase type 2. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. (2017) 362:230–42. 10.1124/jpet.117.241976 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Marino A, Levi R. Salvaging the ischemic heart: Gi-coupled receptors in mast cells activate a PKC/ALDH2 pathway providing anti-RAS cardioprotection. Curr Med Chem. (2018) 25:4416–31. 10.2174/0929867325666180214115127 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Aldi S, Takano K, Tomita K, Koda K, Chan NY, Marino A, et al. Histamine H4-receptors inhibit mast cell renin release in ischemia/reperfusion via protein kinase C epsilon-dependent aldehyde dehydrogenase type-2 activation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. (2014) 349:508–17. 10.1124/jpet.114.214122 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Urata H, Kinoshita A, Misono KS, Bumpus FM, Husain A. Identification of a highly specific chymase as the major angiotensin II-forming enzyme in the human heart. J Biol Chem. (1990) 265:22348–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Wei CC, Hase N, Inoue Y, Bradley EW, Yahiro E, Li M, et al. Mast cell chymase limits the cardiac efficacy of Ang I-converting enzyme inhibitor therapy in rodents. J Clin Invest. (2010) 120:1229–39. 10.1172/JCI39345 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Prosser HC, Forster ME, Richards AM, Pemberton CJ. Cardiac chymase converts rat proAngiotensin-12 (PA12) to angiotensin II: effects of PA12 upon cardiac haemodynamics. Cardiovasc Res. (2009) 82:40–50. 10.1093/cvr/cvp003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Nabah YN, Mateo T, Estelles R, Mata M, Zagorski J, Sarau H, et al. Angiotensin II induces neutrophil accumulation in vivo through generation and release of CXC chemokines. Circulation (2004) 110:3581–6. 10.1161/01.CIR.0000148824.93600.F3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Oyamada S, Bianchi C, Takai S, Chu LM, Sellke FW. Chymase inhibition reduces infarction and matrix metalloproteinase-9 activation and attenuates inflammation and fibrosis after acute myocardial ischemia/reperfusion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. (2011) 339:143–51. 10.1124/jpet.111.179697 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Tejada T, Tan L, Torres RA, Calvert JW, Lambert JP, Zaidi M, et al. IGF-1 degradation by mouse mast cell protease 4 promotes cell death and adverse cardiac remodeling days after a myocardial infarction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2016) 113:6949–54. 10.1073/pnas.1603127113 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Youker KA, Hawkins HK, Kukielka GL, Perrard JL, Michael LH, Ballantyne CM, et al. Molecular evidence for induction of intracellular adhesion molecule-1 in the viable border zone associated with ischemia-reperfusion injury of the dog heart. Circulation (1994) 89:2736–46. 10.1161/01.CIR.89.6.2736 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Frangogiannis NG, Lindsey ML, Michael LH, Youker KA, Bressler RB, Mendoza LH, et al. Resident cardiac mast cells degranulate and release preformed TNF-alpha, initiating the cytokine cascade in experimental canine myocardial ischemia/reperfusion. Circulation (1998) 98:699–710. 10.1161/01.CIR.98.7.699 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Gilles S, Zahler S, Welsch U, Sommerhoff CP, Becker BF. Release of TNF-alpha during myocardial reperfusion depends on oxidative stress and is prevented by mast cell stabilizers. Cardiovasc Res. (2003) 60:608–16. 10.1016/j.cardiores.2003.08.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Liao CH, Akazawa H, Tamagawa M, Ito K, Yasuda N, Kudo Y, et al. Cardiac mast cells cause atrial fibrillation through PDGF-A-mediated fibrosis in pressure-overloaded mouse hearts. J Clin Invest. (2010) 120:242–53. 10.1172/JCI39942 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Helske S, Lindstedt KA, Laine M, Mayranpaa M, Werkkala K, Lommi J, et al. Induction of local angiotensin II-producing systems in stenotic aortic valves. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2004) 44:1859–66. 10.1016/j.jacc.2004.07.054 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Helske S, Syvaranta S, Kupari M, Lappalainen J, Laine M, Lommi J, et al. Possible role for mast cell-derived cathepsin G in the adverse remodelling of stenotic aortic valves. Eur Heart J. (2006) 27:1495–504. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehi706 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Hara M, Ono K, Hwang MW, Iwasaki A, Okada M, Nakatani K, et al. Evidence for a role of mast cells in the evolution to congestive heart failure. J Exp Med. (2002) 195:375–81. 10.1084/jem.20002036 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Matsumoto T, Wada A, Tsutamoto T, Ohnishi M, Isono T, Kinoshita M. Chymase inhibition prevents cardiac fibrosis and improves diastolic dysfunction in the progression of heart failure. Circulation (2003) 107:2555–8. 10.1161/01.CIR.0000074041.81728.79 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Frangogiannis NG, Perrard JL, Mendoza LH, Burns AR, Lindsey ML, Ballantyne CM, et al. Stem cell factor induction is associated with mast cell accumulation after canine myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Circulation (1998) 98:687–98. 10.1161/01.CIR.98.7.687 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Takeshita K, Hayashi M, Iino S, Kondo T, Inden Y, Iwase M, et al. Increased expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in cardiomyocytes contributes to cardiac fibrosis after myocardial infarction. Am J Pathol. (2004) 164:449–56. 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63135-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Kanemitsu H, Takai S, Tsuneyoshi H, Nishina T, Yoshikawa K, Miyazaki M, et al. Chymase inhibition prevents cardiac fibrosis and dysfunction after myocardial infarction in rats. Hypertens Res. (2006) 29:57–64. 10.1291/hypres.29.57 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Koike MK, de Carvalho Frimm C, de Lourdes Higuchi M. Bradykinin B2 receptor antagonism attenuates inflammation, mast cell infiltration and fibrosis in remote myocardium after infarction in rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. (2005) 32:1131–6. 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2005.04309.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Szczeklik A, Sladek K, Szczerba A, Dropinski J. Serum immunoglobulin E response to myocardial infarction. Circulation (1988) 77:1245–9. 10.1161/01.CIR.77.6.1245 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Yamaki T, Iwai-Takano M, Yaoita H, Ogawa K, Tajima H, Takeishi Y, et al. Participation of mast cells in angiogenesis in the border zone of myocardial infarction in rats. J Med Ultrason (2001) (2009) 36:119–27. 10.1007/s10396-009-0229-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Shin K, Watts GF, Oettgen HC, Friend DS, Pemberton AD, Gurish MF, et al. Mouse mast cell tryptase mMCP-6 is a critical link between adaptive and innate immunity in the chronic phase of Trichinella spiralis infection. J Immunol. (2008) 180:4885–91. 10.4049/jimmunol.180.7.4885 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Ngkelo A, Richart A, Kirk JA, Bonnin P, Vilar J, Lemitre M, et al. Mast cells regulate myofilament calcium sensitization and heart function after myocardial infarction. J Exp Med. (2016) 213:1353–74. 10.1084/jem.20160081 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Kwon JS, Kim YS, Cho AS, Cho HH, Kim JS, Hong MH, et al. The novel role of mast cells in the microenvironment of acute myocardial infarction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2011) 50:814–25. 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2011.01.019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Shao Z, Nazari M, Guo L, Li SH, Sun J, Liu SM, et al. The cardiac repair benefits of inflammation do not persist: evidence from mast cell implantation. J Cell Mol Med. (2015) 19:2751–62. 10.1111/jcmm.12703 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Nazari M, Ni NC, Ludke A, Li SH, Guo J, Weisel RD, et al. Mast cells promote proliferation and migration and inhibit differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells through PDGF. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2016) 94:32–42. 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.03.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Rosenberg HF, Dyer KD, Foster PS. Eosinophils: changing perspectives in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. (2013) 13:9–22. 10.1038/nri3341 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Hallgren R, Venge P, Cullhed I, Olsson I. Blood eosinophils and eosinophil cationic protein after acute myocardial infarction or corticosteroid administration. Br J Haematol. (1979) 42:147–54. 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1979.tb03707.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Atkinson JB, Robinowitz M, McAllister HA, Virmani R. Association of eosinophils with cardiac rupture. Hum Pathol. (1985) 16:562–8. 10.1016/S0046-8177(85)80105-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Konishi T, Funayama N, Yamamoto T, Morita T, Hotta D, Nishihara H, et al. Prognostic value of eosinophil to leukocyte ratio in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention. J Atheroscler Thromb. (2017) 24:827–40. 10.5551/jat.37937 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Niccoli G, Schiavino D, Belloni F, Ferrante G, La Torre G, Conte M, et al. Pre-intervention eosinophil cationic protein serum levels predict clinical outcomes following implantation of drug-eluting stents. Eur Heart J. (2009) 30:1340–7. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehp120 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Niccoli G, Sgueglia GA, Conte M, Cosentino N, Minelli S, Belloni F, et al. Eosinophil cationic protein and clinical outcome after bare metal stent implantation. Atherosclerosis (2011) 215:166–9. 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.11.044 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Shiyovich A, Gilutz H, Plakht Y. White blood cell subtypes are associated with a greater long-term risk of death after acute myocardial infarction. Tex Heart Inst J. (2017) 44:176–88. 10.14503/THIJ-16-5768 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Odeberg J, Freitag M, Forssell H, Vaara I, Persson ML, Odeberg H, et al. Influence of pre-existing inflammation on the outcome of acute coronary syndrome: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open (2016) 6:e009968. 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-009968 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Jiang P, Wang DZ, Ren YL, Cai JP, Chen BX. Significance of eosinophil accumulation in the thrombus and decrease in peripheral blood in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Coron Artery Dis. (2015) 26:101–6. 10.1097/MCA.0000000000000186 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Sakai T, Inoue S, Matsuyama TA, Takei M, Ota H, Katagiri T, et al. Eosinophils may be involved in thrombus growth in acute coronary syndrome. Int Heart J. (2009) 50:267–77. 10.1536/ihj.50.267 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Niccoli G, Calvieri C, Flego D, Scalone G, Imaeva A, Sabato V, et al. Allergic inflammation is associated with coronary instability and a worse clinical outcome after acute myocardial infarction. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. (2015) 8:e002554 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.115.002554 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Heredia JE, Mukundan L, Chen FM, Mueller AA, Deo RC, Locksley RM, et al. Type 2 innate signals stimulate fibro/adipogenic progenitors to facilitate muscle regeneration. Cell (2013) 153:376–88. 10.1016/j.cell.2013.02.053 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Goh YP, Henderson NC, Heredia JE, Red Eagle A, Odegaard JI, Lehwald N, et al. Eosinophils secrete IL-4 to facilitate liver regeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2013) 110:9914–9. 10.1073/pnas.1304046110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]