Abstract
Jersey and Kashmiri cattle are important dairy breeds that contribute significantly to the total milk production of the Indian northern state of Jammu and Kashmir. The Kashmiri cattle germplasm has been extensively diluted through crossbreeding with Jersey cattle with the goal of enhancing its milk production ability. However, crossbred animals are prone to diseases resulting to unsustainable milk production. This study aimed to provide a comprehensive transcriptome profile of mammary gland epithelial cells at different stages of lactation and to find key differences in genes and pathways regulating milk traits between Jersey and Kashmiri cattle. Mammary epithelial cells (MEC) isolated from milk obtained from six lactating cows (three Jersey and three Kashmiri cattle) on day 15 (D15), D90 and D250 in milk, representing early, mid and late lactation, respectively were used. RNA isolated from MEC was subjected to next-generation RNA sequencing and bioinformatics processing. Casein and whey protein genes were found to be highly expressed throughout the lactation stages in both breeds. Largest differences in differentially expressed genes (DEG) were between D15 vs D90 (1,805 genes) in Kashmiri cattle and, D15 vs D250 (3,392 genes) in Jersey cattle. A total of 1,103, 1,356 and 1,397 genes were differentially expressed between Kashmiri and Jersey cattle on D15, D90 and D250, respectively. Antioxidant genes like RPLPO and RPS28 were highly expressed in Kashmiri cattle. Differentially expressed genes in both Kashmiri and Jersey were enriched for multicellular organismal process, receptor activity, catalytic activity, signal transducer activity, macromolecular complex and developmental process gene ontology terms. Whereas, biological regulation, endopeptidase activity and response to stimulus were enriched in Kashmiri cattle and, reproduction and immune system process were enriched in Jersey cattle. Most of the pathways responsible for regulation of milk production like JAK-STAT, p38 MAPK pathway, PI3 kinase pathway were enriched by DEG in Jersey cattle only. Although Kashmiri has poor milk production efficiency, the present study suggests possible physicochemical and antioxidant properties of Kashmiri cattle milk that needs to be further explored.
Introduction
Mammary gland development and the physiological control of its dynamics are a vital part of the mammalian reproduction strategy [1–2]. Milk evolved as an essential source of nutrients and immune factors including immune-modulatory, anti-inflammatory and anti-microbial agents that offer protection against infections [3–4]. Milk yield and quality are important economic traits. An increase in the efficiency of milk synthesis both in terms of quality and quantity is a highly desirable goal for the dairy industry [5]. The mammary gland displays a high level of developmental plasticity with the ability to undergo repeated cycles of growth and regression [6]. Lactation is a dynamic physiological process characterized by an initial rapid increase in milk yield during early lactation, which peaks around 6 weeks into lactation, followed by a gradual decrease until the end of lactation [7]. The knowledge of gene expression involved in lactation informs on the biological mechanisms underlying mammary morphogenesis and metabolic activities as well as enhances our understanding of milk composition [8–9]. The ability to manipulate lactation performance in less improved breeds is an area of increasing interest, and knowledge of the biological pathways and mechanisms that govern mammary gland development and lactation may help to increase the lactation performance of dairy animals. Recent developments in “omics” technologies like transcriptomics make it possible to comprehensively and systematically identify the potential factors or processes that may influence lactation [10–11]. Using high throughput RNA sequencing technique, a high number of genes were identified as differentially expressed between different stages of lactation, and the expression alterations may play crucial roles in the regulation of lactation [9–12]. Thus, a thorough and deeper understanding of the genes and biological networks that regulate bovine milk composition is required.
Cow milk contains a heterogeneous population of somatic cells consisting of lymphocytes, neutrophils, macrophages and exfoliated epithelial cells [13]. Mammary epithelial cells (MEC) are unique in that they are involved in the synthesis and secretion of milk. Although milk somatic cells have been widely used to analyse the expression of genes involved in milk synthesis in ruminants [14–16], it is known that some milk trait genes of interest (e.g. genes in apoptosis pathway) are not solely expressed in MEC, but also by other cell types like leucocytes [17]. Thus, compared with MEC, there is the possibility to study genes not specifically expressed in MEC when milk somatic cells are used to study the expression of genes involved in milk synthesis. Moreover, Sciascia et al. [18] reported that milk somatic cells are not suitable for measuring milk protein expression in lactating ruminants. Although many studies have examined the physicochemical properties of cow milk and the genes expressed in the bovine mammary gland [19–22], limited research has detailed the characterization of genes expressed in milk epithelial cells. Therefore, identification and characterisation of milk quality and yield related genes expressed at different stages of lactation in MEC may represent an important step towards understanding of the complex biology of the milk production process.
The Jersey breed is amongst top milk producers in the world and it is routinely used to upgrade the milk producing capacity of the Kashmiri local cattle of North India. Kashmiri cattle are poor-performing and not improved for milk production, and differ greatly from Jersey in dairy production characteristics. Given the importance of the Kashmiri cattle in crossbreeding programs for augmenting milk production, this study aimed to compare its MEC transcriptome, using RNA Seq, with that of Jersey breed to gain a better understanding of the genes and pathways underlying the different milk producing abilities of the two breeds. We therefore report for the first time the MEC transcriptome of Kashmiri cattle at different stages of lactation using RNA-seq. We also present a characterization of the gene expression profile and differences between the MEC transcriptomes of Kashmiri and Jersey cattle.
Materials and methods
Animals and sampling
Animal care and use procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee of Sher-e-Kashmir University of Agricultural Sciences and Technology of Kashmir. Three healthy Kashmiri and three Jersey cows in their 3rd lactation at the Share-Kashmir University of Agricultural Sciences and Technology dairy farm, Mountain Livestock Research Institute (MLRI), Kashmir, India were selected for the study. The animals were kept in free stall housing, fed with balanced ration and had ad libitum access to water. Fresh milk samples (1.5 L) were aseptically collected by milking equally the four quarters of the cows on day 15 (D15), D90 and D250 in milk representing early lactation, mid-lactation and late lactation stages, respectively. Under the management conditions at the MLRI dairy farm, the lactation stages for Jersey cattle are D1-D80 (early lactation), D81-D185 (mid-lactation) and D186-D300 (late lactation). The corresponding periods for Kashmiri cattle are D1-70 (early lactation), D71 to D180 (mid-lactation) and D181-D280 (late lactation). Thus D15, D90 and D250 were chosen to represent early, mid and late lactation stages, respectively in both breeds. In total, nine samples per breed were collected. The milk samples were immediately transported to the laboratory in ice cooled containers. For milk quality analysis, the different parameters like milk yield/day, fat and protein content were recorded for ±7 days relative to day of sampling (i.e. seven days before day of sampling, day of sampling and seven days after day of sampling) for each lactation stage. The fat and protein contents were determined by Milk auto-analyser (Speedy Lab, Astori, Italy).
Isolation of milk epithelial cells and purity check
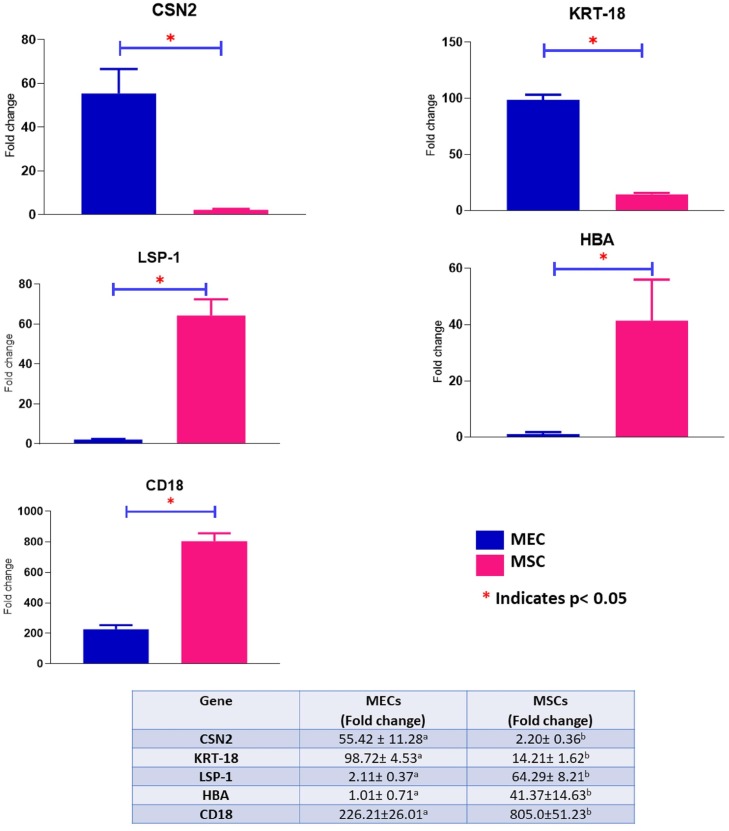
Milk epithelial cells were isolated from whole fresh milk following the protocol of Boutinaud et al. [13] with some modifications. Milk sample (1.5 L/cow) was aliquoted (125 ml) into each of six 250 ml centrifuge tubes, and 100 ml cold (4°C) diethylpyrocarbonate (DEPC) treated 1 x phosphate buffered saline (PBS) buffer added. The samples were defatted by centrifugation for 20 min at 2800 x g at 4°C. The fat layer and whey portion were carefully removed and the remaining fraction (1 ml) at the bottom containing the cell pellet was mixed with 800 μl cold 1 x PBS and transferred into a 2 ml tube. After adding 200 μl EDTA (0.5 M pH 8.0, 4°C), the sample was centrifuged at 14,000 x g for 1 min at 4°C. The supernatant was discarded, and pellets of the same sample were pooled and resuspended in 200 μl cold 1 x PBS and centrifuged at 5100 x g for 5 min at 4°C. The supernatant was discarded and the pellet was resuspended in 1.25 ml cold 1 x PBS containing 1% bovine serum albumin (BSA, Sigma, USA). A portion (500 μl) of the resuspended milk somatic cells (MSC) was used for RNA isolation while the other portion was further purified to obtain MEC. Specific anti-cytokeratin peptide 18 antibody (KRT18, Clone KS-B17.2, Sigma–Aldrich, USA) coated beads (Dynabeads Pan Mouse IgG, Invitrogen, USA) were used to separate MEC from other cell types according to Boutinaud et al.,[13]. Briefly, 25 μl of Dynabeads was transferred to a 1.5 ml tube and washed twice with 1 ml 1% BSA–PBS to remove the preservative. The Dynabeads were resuspended in 1 ml 1% BSA–PBS and transferred to a 1.5 ml tube containing 3 μl of KRT18 antibodies. The suspension was incubated for 30 min at 4°C on a Sample Mixer (Rotospin, Tarson,-India). Then, the tube was placed in the magnetic particle concentrator (Dyna Mag 5, Invitrogen, USA) for 30 sec. After another wash step and aspiration of the supernatant containing unbound antibodies, the antibody-coated Dynabeads were resuspended in 250 μl 1% BSA–PBS and transferred to the 1.25 ml cell suspension and incubated for 1 h at 4°C on the Sample Mixer. Finally, specifically bound cells were collected by magnetic incubation for 1 min. The bead bound cell pellet was washed (1 ml 1 x PBS added followed by centrifugation at 4000g for 1 min) and immediately used for RNA extraction. Possible contamination of purified MEC was checked by quantification of the expression of marker genes for various MSC types like beta casein (CSN2, mammary epithelial cell marker), cytokeratin 18 (KRT18, epithelial cell marker), lymphocyte-specific protein one (LSP1, leucocyte specific cell marker), haemoglobin sub-unit alpha (HBA, red blood cell marker) and CD18 (macrophage cell marker) [23–24] in samples collected on D90 by real time quantitative PCR (qPCR) (S1 Table).
RNA extraction and sequencing
Total RNA extraction from MEC and MSC was accomplished by Trizol method (Ambion, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. RNA was quantified by spectrophotometer (ThermoFisher, USA) and the quality and integrity was assessed by Bioanalyzer (Agilent, USA). The RNA integrity number (RIN) of samples ranged from 6.5–9.3. Only those samples having RIN values above 8 were used for library construction. The RNA isolation process was repeated for samples with lower RIN values until a RIN value of ≥8 was achieved.
Illumina TruSeq stranded mRNA sample preparation kit was used to generate cDNA libraries according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Total RNA (4μg/sample) was used to prepare the libraries. Poly-A containing mRNA molecules were purified using poly-T oligo-attached magnetic beads. Following purification, RNA was fragmented into small pieces of 300 bp size using divalent cations under elevated temperature. The cleaved RNA fragments was used to synthesize first strand cDNA using reverse transcriptase and random primers (Illumina, USA) followed by second strand cDNA synthesis using DNA Polymerase I and RNase H. After adenylation of 3’ ends of DNA fragments, hybridisation was initiated by ligating Illumina paired-end adapter and index. cDNA fragments (200bp) were generated and were selectively enriched to construct the final sequencing paired end library using Illumina PCR Primer Cocktail. Libraries were pooled in equimolar amounts and paired end sequenced (126 bp) on three lanes (6/lane) on a High Throughput Model flow cell on an Illumina HiSeq 2500 platform by SciGenom, Cochin, Kerela-India.
Sequence data processing, alignment and identification of expressed genes
Raw data (reads) in fastq format were first processed by removing adapter sequences and reads having a phred score <30 with Trimmomatic software v0.32. Clean reads were aligned to the bovine reference genome, UMD3.1 version 85 (ftp://ftp.ensembl.org/pub/release-85/gtf/bos_taurus/Bos_taurus.UMD3.1.85.gtf.gz) with Bowtie v2.0.6. Also, a data-base of splice junctions was generated by TopHat v2.1.1[25–26] (http://tophat.cbcb.umd.edu/) based on gene model annotation file 77 (ftp://ftp.ensembl.org/pub/release-77/gtf/bos_taurus).
Differential gene expression analysis
Aligned reads were assembled with Cufflinks and differentially expressed genes (DEG) between lactation stages and breed were detected and quantified with Cuffdiff [26]. Negative binomial distribution was used to calculate gene expression which was normalized in fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads (FPKM). T-test was used to identify significantly differentially expressed genes and gene expression differences were declared significant at p-values < 0.05 after Benjamini-Hochberg correction.
Gene ontology (GO) and KEGG analysis of differentially expressed genes
GO and pathway enrichment analysis of DEG was accomplished with Gene Ontology Consortium data base (http://www.geneontology.org) [27]. GO terms and KEGG pathways (http://www.genome.jp/kegg/) with Benjamini and Hochberg corrected p-values < 0.05 were considered significantly enriched.
Protein-protein interaction networks of differentially expressed genes
Protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks were constructed on the basis of information from STRING v10.5 (https://string-db.org), using the Ensemble gene identifiers of DEG as input and Bos taurus as background which provides critical assessment and integration of protein-protein interactions, including direct (physical) and indirect (functional) associations [28]. The top 20 DEG and DEG for milk traits from lactation stage comparisons in Kashmiri and Jersey cattle were used in protein-protein interaction analysis. Credible interactions (combined_score ≥ 0.4) were further visualized using CytoScape [29].
Quantitative real time PCR
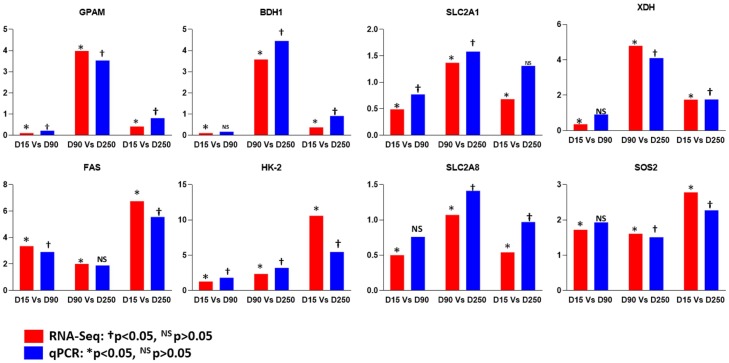
Real time quantitative PCR was performed to verify the expression levels of eight DEG (GPAM, BDH1, SLC2A1, SLC2A8, HK2, SOS2, FAS and XDH) involved in different milk synthesis pathways. cDNA was synthesized from 0.5 μg of the same total RNA used in RNA sequencing using the Revert Aid First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Thermo Scientific, USA) as per the manufacturer’s protocol. Primers were designed using Primer3 Plus software (https://primer3plus.com/cgi-bin/dev/primer3plus.cgi). qPCR was performed on a Light Cycler 480 II Real-Time PCR System (Roche, Switzerland). The reaction volume of 20 μl included 10 μL of 2X SYBR Green MasterMix reagent (Thermo Scientific, USA), 1μl of cDNA and 0.2 μL of each primer (10μM). The sequences of the primers and annealing temperatures are shown in S1 Table. All reactions were conducted in triplicates and included negative controls with no template. The expression levels of genes were normalized with GAPDH and UXT. GAPDH and UXT were initially tested and shown to be stable under the experimental conditions. The relative gene expression was calculated using the 2-ΔΔCt method [30].
Results
Milk yield traits
Milk yield (kg/day), fat and protein contents were determined for ±7 days relative to day of sampling for each lactation stage. The milk yield per day varied significantly between lactation stages in both Kashmiri and Jersey cattle. The mid lactation was characterised by highest milk yield (p<0.05), whereas protein and fat contents were maximum (p<0.05) during initial stages of lactation in both breeds, except that early lactation protein content (3.21±0.58) was similar to late lactation protein content (3.11±0.39) in Kashmiri cattle (Table 1). As expected, the milk yield of Jersey cattle was higher than that of Kashmiri cattle at all lactation stages. The fat and protein contents in Jersey cattle ranged from 4.10% to 4.85% and 2.91% to 3.36%, respectively. The corresponding values for Kashmiri cattle were 3.20%-3.94% and 2.81%-3.21%, respectively.
Table 1. Milk yield and component traits1 in Kashmiri and Jersey cattle at different stages of lactation.
| Lactation stage | Jersey cattle | Kashmiri cattle | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Milk yield (kg/day) | Protein (%) | Fat (%) | Milk yield (kg/day) | Protein (%) | Fat (%) | |
| Early lactation | 8.2±0.95a | 3.36±0.72a | 4.85±0.93a | 4.12±0.89d | 3.21±0.58d | 3.94±0.62d |
| Mid lactation | 10.5±1.1b | 2.91±0.36b | 4.10±0.78b | 5.20±0.99e | 2.81±0.49e | 3.20±0.77e |
| Late lactation | 6±0.81c | 3.21±0.78b | 4.63±0.62c | 3.82±0.62f | 3.11±0.39d | 3.46±0.99e |
1Values are the means ± standard deviation of data collected ±7 days relative to day of sampling at each lactation stage (D15, D90 and D250).
a, b, c, d, eFor each parameter and breed, column means with different superscripts differ significantly.
Sequencing and expressed genes in mammary epithelial cells
To test the purity of isolated MEC and validate its use in transcriptional studies of milk trait genes, the expression of marker genes for specific cell types was compared between MEC and MSC. The expression levels of marker genes were normalised against GAPDH and UXT housekeeping genes. The mRNA expression levels of KRT18 and CSN2 were significantly higher (p<0.05) in the isolated MEC as compared to MSC (Fig 1). Furthermore, the expression of LSP1, HBA and CD18, chosen as markers for cell types other than MEC, were significantly higher (p<0.05) in MSC as compared to MEC (Fig 1).
Fig 1. Comparison of the expression levels of different cell type marker genes in isolated mammary epithelial cells (MEC) as compared to milk somatic cells (MSC).
Sequencing of 18 libraries generated a total of 1.65 billion reads (range 68,43–136,83 million reads/library) (S2 Table). Out of this number, 1.47 billion reads (95.82%) passed quality control and were aligned to the bovine genome UMD3.1. A total of 1.44 billion uniquely mapped reads were further processed while reads that mapped to multiple positions, unaligned and discordant reads were discarded (S2 Table). Mapped genes with FPKM ≤0.01 were discarded and the remainder divided into a low expression group (< 10 FPKM), a moderate expression group (10 FPKM to 500 FPKM) and a high expression group (> 500 FPKM) (S3 Table). For both breeds, the highest number of expressed genes with FPKM >0.01 was during late lactation (D250) in Jersey (13,835 genes) and Kashmiri cattle (14,464 genes) (S3 Table).
Top most expressed genes at each stage of lactation in Kashmiri and Jersey cattle
The numbers of genes with the highest FPKM values (> 500) in each breed and lactation day are shown in S3 Table. For both breeds, 13 top expressed genes at each lactation day accounted for ~70% of the total FPKM values (Table 2). The top expressed genes at each stage of lactation were similar for both breeds, except RPS12 and CCL14, which were highly expressed in Kashmiri cattle only or Jersey cattle only, respectively.
Table 2. Highly expressed genes in mammary epithelial cells with FPKM values >2000 at three different stages of lactation in Kashmiri and Jersey cattle1.
| Genes | Kashmiri | Jersey | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15 | D90 | D250 | D15 | D90 | D250 | |
| CSN1S1 | 151,546 | 128,456.2 | 194,567.1 | 164,564.5 | 156,743.9 | 234,598.2 |
| CSN1S2 | 71,398.8 | 89,764.6 | 125,657 | 150,945 | 167,512.3 | 182,657.2 |
| CSN3 | 161,987.2 | 159,574.6 | 192,456.5 | 181,457.6 | 150,675.1 | 231,241.7 |
| CSN2 | 211,651.8 | 185,657.23 | 227,861.2 | 243,561.9 | 200,165 | 245,241.9 |
| LGB | 147,876.25 | 98,365.7 | 148,641.1 | 137,645.7 | 100,387 | 140,034.5 |
| LALBA | 34,224.31 | 37,937.7 | 52,945.3 | 41,669.1 | 40,597.8 | 45,782.2 |
| RPLP1 | 21,400.1 | 15,712.7 | 7,041 | 9,184.13 | 3,006.93 | 3,774.83 |
| RPS28 | 17,835.6 | 9,313.4 | 3,436.38 | 8,888.89 | - | - |
| RPS20/snoU54 | 14,922.6 | 6,510.56 | - | 8,756.15 | - | - |
| RPLPO | 11,925.8 | - | 3,133.07 | 5,337.15 | - | - |
| RPS12 | - | - | - | - | 3,089.68 | 2,494.05 |
| B2M | - | 7,468.17 | 2,723.17 | - | 10,721 | 14,357.5 |
| CCL14 | - | - | - | - | 7,509.43 | 10,501.5 |
1Mammary epithelia cells were isolated from milk obtained from Kashmiri (n = 3) and Jersey (n = 3) cows at D15 (15 days in milk) (early lactation), D90 (mid-lactation) and D250 (late-lactation) and subjected to RNA-sequencing.
‘-’Indicate that the genes have FPKM values less than the threshold values (See S3 Table for FPKM values of all genes).
Differentially expressed genes between lactation stages in Kashmiri and Jersey cattle
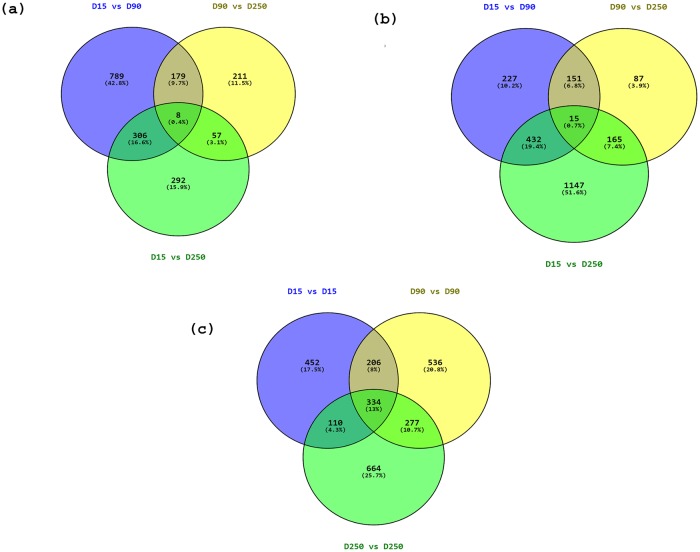
A total of 1,282, 455 and 665 genes were differentially expressed (FDR<0.05) between D15 vs D90, D90 vs D250, and D15 vs D250, respectively in Kashmiri cattle (Fig 2a, S4 Table). Likewise, 826, 418 and 1,765 genes were differentially expressed (FDR<0.05) between D15 vs D90, D90 vs D250, and D15 vs D250, respectively in Jersey cattle (Fig 2b, S4 Table). The largest number of DEG were observed between D15 vs D90 in Kashmiri (1,282 genes) and between D15 vs D250 in Jersey (1,765 genes). The number of DEG that were common to all lactation stages were 8 and 15 in Kashmiri and Jersey, respectively. The top ten DEG with highest fold changes for each breed are listed in Table 3.
Fig 2. Significantly differentially expressed genes between D15 vs D90, D15 vs D250 and D90 vs D250 in mammary epithelial cells in (a) Kashmiri and (b) Jersey cattle and (c) D15, D90 and D250 between Jersey and Kashmiri cattle.
Table 3. Top 10 differentially expressed genes in mammary epithelial cells with highest fold changes between lactation stages in Kashmiri and Jersey cattle1.
| Gene | D15 vs D90 | D90 vs D250 | D15 vs D250 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log2Fold change | p-value | FDR2 | Gene | Log2Fold change | p-value | FDR | Gene | Log2Fold change | p-value | FDR | |
| Kashmiri cattle | |||||||||||
| SNORD50 | -11.066 | 5E-05 | 0.001 | B3GNT6 | 7.031 | 0.001 | 0.010 | PEAR1 | 7.008 | 0.003 | 0.031 |
| TMEM232 | -11.216 | 5E-05 | 0.001 | PEAR1 | 5.771 | 0.0003 | 0.006 | DMP1 | 6.936 | 0.001 | 0.018 |
| ATP6V0D2 | 6.038 | 0.005 | 0.044 | TMEM232 | 5.117 | 0.003 | 0.032 | SLC18B1 | 6.768 | 0.003 | 0.0288 |
| CPM | 5.144 | 0.0001 | 0.002 | LMO7 | 5.106 | 5.0E-05 | 0.001 | SNORD50 | -12.055 | 5E-05 | 0.0013 |
| SPDEF | -6.378 | 5E-05 | 0.001 | ME1 | 4.856 | 0.004 | 0.038 | TMEM232 | -10.875 | 0.001 | 0.016 |
| FHOD3 | -5.217 | 0.001 | 0.019 | PLEKHF1 | -4.857 | 5.0E-05 | 0.001 | MAP2 | 6.291 | 5.0E-05 | 0.001 |
| MROH2B | -5.151 | 0.0002 | 0.004 | F3 | 4.846 | 5.0E-05 | 0.001 | B4GALT6 | 6.193 | 0.0009 | 0.013 |
| INSC | -4.979 | 5E-05 | 0.001 | DCN | 4.787 | 0.001 | 0.020 | ESR1 | 6.072 | 0.0005 | 0.008 |
| HACD4 | 4.905 | 0.0004 | 0.006 | CLDN1 | 4.772 | 5.0E-05 | 0.001 | CLDN1 | 6.038 | 0.001 | 0.020 |
| LRRC66 | 4.886 | 0.002 | 0.028 | HSPB8 | 4.530 | 5.0E-05 | 0.001 | CPM | 5.924 | 5.0E-05 | 0.001 |
| Jersey cattle | |||||||||||
| TMSB4X | 5.724 | 0.0002 | 0.004 | SLC27A6 | 6.504 | 0.0003 | 0.005 | CD69 | 7.777 | 5E-05 | 0.001 |
| IL1A | 5.131 | 5E-05 | 0.0014 | SLC25A21 | 5.843 | 0.001 | 0.019 | P2RY14 | 7.148 | 0.001 | 0.015 |
| SPATA3 | -6.557 | 0.004 | 0.036 | CCDC13 | 5.589 | 0.001 | 0.012 | ND6 | 6.565 | 0.0003 | 0.006 |
| IRX1 | -6.382 | 5E-05 | 0.0014 | MAPK4 | 5.587 | 0.0003 | 0.005 | KMO | 6.330 | 0.003 | 0.029 |
| SLC27A6 | -6.382 | 0.0002 | 0.004 | HHATL | 5.512 | 0.002 | 0.021 | STRA8 | 6.070 | 0.0001 | 0.002 |
| SLC38A3 | -6.150 | 0.005 | 0.047 | SLC38A3 | 5.422 | 0.005 | 0.048 | NFAT5 | 6.072 | 5.0E-05 | 0.001 |
| SLC7A4 | -6.122 | 5.0E-05 | 0.001 | RUNDC3B | 5.387 | 0.0005 | 0.008 | TANK | 5.975 | 5.0E-05 | 0.001 |
| HPN | -5.994 | 5.0E-05 | 0.001 | SCARF2 | 5.301 | 5.0E-05 | 0.001 | CCDC146 | 5.928 | 5.0E-05 | 0.001 |
| ADIRF | -5.913 | 0.0005 | 0.008 | BCAS1 | 5.237 | 0.0001 | 0.003 | CCDC83 | 5.772 | 0.0009 | 0.013 |
| BDH1 | -5.850 | 0.0002 | 0.004 | KRT24 | 5.233 | 0.0001 | 0.003 | BIRC2 | 5.744 | 5.0E-05 | 0.001 |
1Mammary epithelia cells were isolated from milk obtained from Kashmiri (n = 3) and Jersey (n = 3) cows at D15 (early lactation), D90(mid-lactation) and D250 (late-lactation) and subjected to RNA-sequencing.
2FDR: Benjamini and Hockberg corrected p-values
A comparison between Kashmiri vs Jersey cattle indicated that 1,103, 1,356 and 1,397 genes were differentially expressed between the two breeds on D15, D90 and D250, respectively (Fig 2c, S4 Table) while 334 DEG were common to all stages. The top 10 DEG at each lactation stage between the two breeds are shown in Table 4.
Table 4. Top differentially expressed genes in mammary epithelial cells with highest fold changes between Kashmiri and Jersey cattle1.
| Stage | Genes | Log2Fold change | p-value | FDR2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15 | SLC18B1 | 9.809 | 0.001 | 0.014 |
| bta-mir-223 | 8.261 | 1.0E-05 | 0.002 | |
| CD-207 | 7.411 | 5.0E-05 | 0.004 | |
| SNORD50 | -12.531 | 5.0E-05 | 0.001 | |
| TMEM237 | -9.963 | 5.0E-05 | 0.006 | |
| TPT1 | -6.971 | 0.003 | 0.037 | |
| NOS2 | 6.158 | 0.002 | 0.031 | |
| RBP4 | 5.906 | 5.0E-05 | 0.004 | |
| CXCL12 | -5.825 | 5.0E-05 | 0.001 | |
| LRRC66 | 5.717 | 0.001 | 0.020 | |
| D90 | NLRP12 | 8.333 | 0.005 | 0.048 |
| DMXL2 | 8.260 | 5.0E-05 | 0.001 | |
| MGLL | 7.729 | 5.0E-05 | 0.011 | |
| STEAP4 | 7.394 | 5.0E-05 | 0.001 | |
| GPR84 | 7.318 | 5.0E-05 | 0.001 | |
| CXCL12 | -7.173 | 0.005 | 0.048 | |
| TMSB4X | 6.952 | 0.0009 | 0.013 | |
| MCEMP1 | 6.920 | 5.0E-05 | 0.001 | |
| B3GNT6 | 6.798 | 0.001 | 0.019 | |
| OCSTAMP | 6.798 | 5.0E-05 | 0.001 | |
| D250 | NLRP12 | 8.906 | 0.0004 | 0.007 |
| bta-mir-223 | 8.360 | 0.001 | 0.019 | |
| PTX3 | 8.334 | 0.005 | 0.049 | |
| GPR84 | 8.148 | 5.0E-05 | 0.001 | |
| STEAP4 | 7.895 | 5.0E-05 | 0.001 | |
| G0S2 | 7.797 | 5.0E-05 | 0.001 | |
| BCL2A1 | 7.769 | 5.0E-05 | 0.001 | |
| TIAM2 | 7.491 | 0.0005 | 0.008 | |
| SNORA17 | 7.362 | 0.0002 | 0.004 | |
| TG | 7.346 | 0.001 | 0.021 |
1Mammary epithelia cells were isolated from milk obtained from Kashmiri (n = 3) and Jersey (n = 3) cows at D15 (15 days in milk) (early lactation), D90 (mid-lactation) and D250 (late-lactation) and subjected to RNA-sequencing.
2FDR: Benjamini and Hockberg corrected p-values
Candidate genes related to milk quality and yield traits
The expression levels of about 42 genes for milk traits (fat, protein and milk yield traits) in Kashmiri and Jersey cattle are shown in Table 5. It was observed that the major candidate genes for fat synthesis like GPAM, ABCG2, ACSS2, FABP3, THRSP, FASN, SPHK2 and BDH1 showed higher up-regulation at D250 (D90 vs D250) in both Kashmiri and Jersey cattle. The major milk protein genes (CSN1S1, CSN1S2, CSN2, CSN3, LALBA and LGB showed up-regulated expression at D250 (D15 vs D250 and D90 vs D250) in both breeds and genes responsible for milk yield like SLC2A4 was highly expressed at D90 (D15 vs D90) and D250 (D15 vs D250) in Kashmiri cattle and SLC2A1 at D250 (D15 vs D250) in Jersey cattle (Table 5).
Table 5. Differentially expressed milk candidate genes in mammary epithelial cells for milk quality and yield traits between different stages of lactation in Kashmiri and Jersey1.
| Genes | Kashmiri cattle (Log2Fold change) | Jersey (Log2Fold change) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15 vs D90 | D90 vs D250 | D15 vs D250 | D15 vs D90 | D90 vs D250 | D15 vs D250 | |
| LPL | -2.724 | 0.842 | -1.881 | 0.028 | -0.268 | -0.24 |
| GPAM | -3.258 | 1.993 | -1.264 | -3.694 | 3.73 | 0.035 |
| VLDLR | -1.825 | 1.999 | 0.174 | 0.506 | 0.64 | 1.147 |
| DGAT1 | 0.16 | -1.014 | -0.853 | -0.184 | 0.473 | 0.289 |
| ABCA1 | 1.477 | 2.015 | 3.492 | 1.168 | -0.424 | 0.744 |
| LPIN1 | -3.204 | 1.287 | -1.917 | 0.05 | 0.906 | 0.957 |
| ABCG2 | -2.178 | 1.251 | -0.927 | -3.76 | 3.929 | 0.16 |
| INSIG1 | -0.036 | -0.301 | -0.337 | 0.858 | 0.255 | 1.114 |
| ACSS1 | -1.258 | -0.238 | -1.496 | -2.283 | 0.095 | -2.187 |
| INSIG2 | 0.505 | 0.111 | 0.617 | 1.565 | -0.344 | 1.22 |
| ACSS2 | -1.859 | 1.834 | -0.024 | -2.762 | 2.558 | -0.211 |
| SCAP | 0.211 | -1.124 | -0.913 | -0.967 | -0.727 | -1.694 |
| ACSL1 | -1.035 | 1.346 | 0.311 | 0.521 | 0.333 | 0.854 |
| SREBF1 | -1.441 | -0.346 | -1.788 | -1.085 | 0.529 | -0.556 |
| SREBF2 | 0.607 | -0.849 | -0.241 | 0.242 | 0.224 | 0.466 |
| FABP3 | -2.29 | 1.638 | -0.652 | -3.9 | 3.218 | -0.682 |
| THRSP | -1.005 | 1.792 | 0.786 | -3.396 | 3.451 | 0.055 |
| PPARG | 4.542 | 0.55 | 5.092 | 1.01 | -0.738 | 0.272 |
| ACACA | -3.482 | 2.24 | -1.241 | -3.72 | 2.546 | -1.173 |
| PPARGC1A | 0.543 | 2.242 | 2.785 | -2.58 | 3.503 | 0.922 |
| FADS1 | -0.808 | 0.725 | -0.082 | 1.83 | -0.525 | 1.305 |
| PPARGC1B | 1.585 | 0.307 | 1.893 | -0.035 | 0.546 | 0.51 |
| FADS2 | 0.521 | 0.4 | 0.922 | 2.094 | -1.832 | 0.262 |
| FASN | -2.541 | 2.166 | -0.374 | -4.247 | 4.523 | 0.275 |
| SPTLC1 | -0.243 | 0.862 | 0.619 | 1.159 | 0.753 | 1.912 |
| SPTLC2 | 0.739 | 0.06 | 0.8 | 0.688 | 0.024 | 0.712 |
| SPHK2 | -1.347 | 0.817 | -0.529 | -1.157 | 0.224 | -0.933 |
| XDH | -2.595 | 2.311 | -0.284 | -1.451 | 2.262 | 0.811 |
| SGPL1 | 1.392 | 0.512 | 1.905 | 1.32 | -0.271 | 1.048 |
| UGCG | 0.862 | 0.809 | 1.671 | 1.293 | 2.355 | 3.649 |
| OSBP | -0.142 | -0.785 | -0.927 | -0.523 | 0.022 | -0.501 |
| BDH1 | -3.248 | 1.839 | -1.408 | -5.85 | 3.008 | -2.842 |
| OSBPL2 | -1.212 | 0.174 | -1.038 | -0.11 | 0.401 | 0.29 |
| OXCT1 | 0.161 | 0.757 | 0.919 | 0.756 | 0.223 | 0.98 |
| CSN1S1 | -0.238 | 0.598 | 0.36 | -0.07 | 0.581 | 0.511 |
| CSN1S2 | 0.33 | 0.485 | 0.815 | 0.15 | 0.124 | 0.275 |
| CSN3 | -0.021 | 0.27 | 0.248 | -0.268 | 0.617 | 0.349 |
| CSN2 | -0.189 | 0.295 | 0.106 | -0.283 | 0.293 | 0.009 |
| LGB | -0.588 | 0.5956 | 0.007 | 0.957 | 0.698 | 1.656 |
| LALBA | 0.148 | 0.48 | 0.629 | -0.037 | 0.173 | 0.135 |
| HK2 | 0.355 | 1.232 | 1.587 | -1.157 | 0.224 | -0.933 |
| SLC2A1 | -1.006 | 0.456 | -0.549 | 0.995 | 0.44 | 1.435 |
| SLC2A4 | 1.655 | 0.48 | 2.136 | -1.311 | -0.377 | -1.688 |
| SLC2A8 | -0.986 | 0.101 | -0.884 | -1.506 | -0.902 | -2.408 |
1Mammary epithelia cells were isolated from milk obtained from Kashmiri (n = 3) and Jersey (n = 3) cows at D15 (early lactation), D90 (mid-lactation) and D250 (late-lactation) and subjected to RNA-sequencing.
Protein-protein interaction
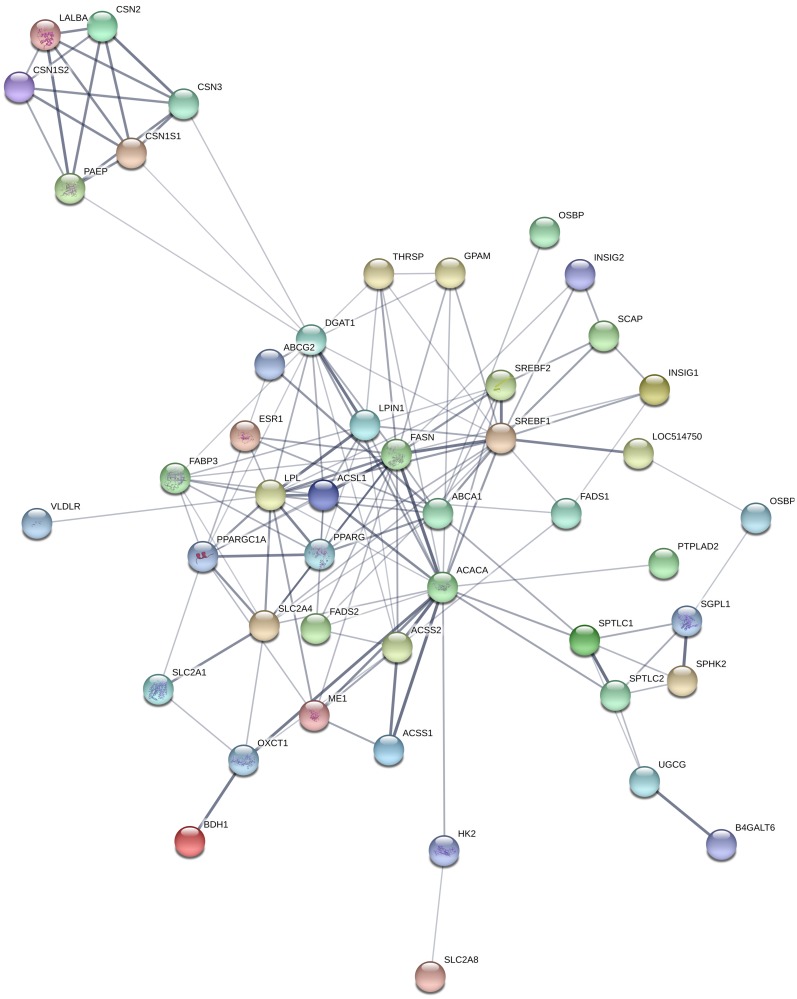
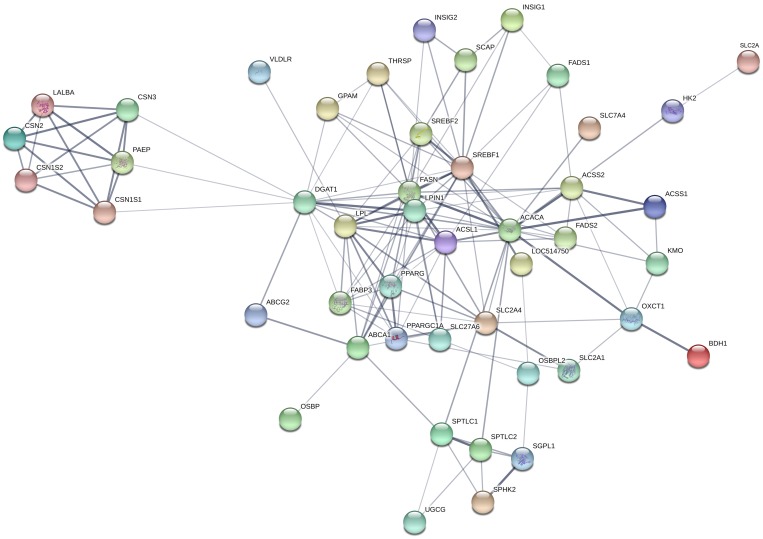
We examined possible interactions between top 20 differentially expressed genes (Table 3 and S4 Table) and candidate genes for milk yield and quality traits (Table 5) at each lactation stage comparisons (D15 vs D90, D90 vs D250 and D15 vs D250) in Kashmir and Jersey cattle using the STRING database [26]. Out of 60 DEG (20 top genes from each lactation stage comparison) in Kashmiri cattle, only ME1, B4GALT6 and ESR1 showed protein interactions with major milk candidate genes (Fig 3) with interaction confidence > 0.4. Whereas in Jersey cattle, SLC27A6, BDH1 and KMO showed multiple interactions with various milk candidate genes (Fig 4). The details of string analysis are shown in supplementary file (S5 Table).
Fig 3. Protein-protein interactions among top 20 differentially expressed candidate genes and differentially expressed genes for milk traits from lactation stage comparisons in Kashmiri cattle.
In the network view, nodes are proteins while edges represent predicted functional interactions; the low interaction nodes are hidden.
Fig 4. Protein-protein interactions among top 20 differentially expressed candidate genes and differentially expressed genes for milk traits from lactation stage comparisons in Jersey cattle.
In the network view, nodes are proteins while edges represent predicted functional interactions; the low interaction nodes are hidden.
Gene ontology and pathway enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes
According to lactation stage comparisons, a total of 12 (localization, biological regulation, response to stimulus, multicellular organismal process, endopeptidase activity, binding, receptor activity, signal transducer activity, catalytic activity, transporter activity, cell junction and macromolecular complex), 5 (cellular process, developmental process, biological adhesion, cell junction and macromolecular complex) and 4 (biological regulation, response to stimulus, multicellular organismal process and extracellular region) GO terms were significantly enriched (FDR < 0.05) by DEG at D15 vs D90, D90 vs D250 and D15 vs D250, respectively in Kashmiri cattle (Table 6 and S6 Table). Similarly, 7 (reproduction, developmental process, multicellular organismal process, locomotion, receptor activity, signal transducer activity and catalytic activity), 3 (signal transducer activity, synapse and macromolecular complex) and 10 (localization, reproduction, multicellular organismal process, metabolic process, immune system process, receptor activity, signal transducer activity, catalytic activity, cell part and organelle) GO terms were significantly enriched (FDR < 0.05) by DEG at D15 vs D90, D90 vs D250 and D15 vs D250, respectively in Jersey cattle (Table 6 and S6 Table). Only 6 GO terms (multicellular organismal process, receptor activity, signal transducer activity, catalytic activity, macromolecular complex and multicellular organismal process) were commonly enriched by DEG in Kashmiri and Jersey cattle.
Table 6. Significantly enriched gene ontology (GO) terms associated with identified differentially expressed genes in mammary epithelial cells in Kashmiri and Jersey cattle1.
| Comparison | Kashmiri | Jersey | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO term | GO ID | Genes | FE | P-value | FDR2 | GO term | GO ID | Genes | FE | P-value | FDR | |
| D15 VS D90 | Biological function | |||||||||||
| Localization | GO:0051179 | 188 | 1.26 | 0.002 | 0.019 | Reproduction | GO:0000003 | 3 | 0.22 | 0.001 | 0.017 | |
| Biological regulation | GO:0065007 | 233 | 0.69 | 4.0E-07 | 2.0E-05 | Developmental process | GO:0032502 | 102 | 1.33 | 0.005 | 0.047 | |
| Response to stimulus | GO:0050896 | 157 | 0.69 | 4.0E-07 | 2.0E-05 | Multicellular organismal process | GO:0032501 | 52 | 0.6 | 7.4E-05 | 0.003 | |
| Multicellular organismal process | GO:0032501 | 91 | 0.67 | 5.2E-05 | 0.001 | Locomotion | GO:0040011 | 27 | 2.09 | 6.4E-04 | 0.013 | |
| Endopeptidase activity | GO:0010950 | 3 | 1.24 | 0.000 | 0.050 | Metabolic process | GO:0008152 | 307 | 1.14 | 0.012 | 0.141 | |
| Molecular function | ||||||||||||
| Binding | GO:0005488 | 303 | 0.83 | 3.2E-04 | 0.006 | Receptor activity | GO:0004872 | 39 | 0.54 | 1.7E-05 | 0.001 | |
| Receptor activity | GO:0004872 | 62 | 0.54 | 1.0E-07 | 9.6E-06 | Signal transducer activity | GO:0004871 | 37 | 0.6 | 8.7E-04 | 0.021 | |
| Signal transducer activity | GO:0004871 | 51 | 0.52 | 3.7E-07 | 2.4E-05 | Catalytic activity | GO:0003824 | 258 | 1.21 | 9.3E-04 | 0.020 | |
| Catalytic activity | GO:0003824 | 408 | 1.22 | 2.8E-05 | 8.9E-04 | Antioxidant activity | GO:0016209 | 5 | 3.23 | 0.026 | 0.261 | |
| Transporter activity | GO:0005215 | 100 | 1.36 | 0.004 | 0.050 | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| Cellular component | ||||||||||||
| Synapse | GO:0045202 | 9 | 2.05 | 0.051 | 0.134 | Synapse | GO:0045202 | 8 | 2.88 | 0.010 | 0.318 | |
| Cell junction | GO:0030054 | 17 | 2.3 | 0.003 | 0.020 | Extracellular region | GO:0005576 | 41 | 1.43 | 0.034 | 0.267 | |
| Macromolecular complex | GO:0032991 | 122 | 0.71 | 6.9E-05 | 0.001 | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| D90 VS D250 | Biological function | |||||||||||
| Cellular process | GO:0009987 | 278 | 1.22 | 2.6E-05 | 6.2E-04 | Localization | GO:0051179 | 71 | 1.43 | 0.003 | 0.134 | |
| Developmental process | GO:0032502 | 86 | 1.98 | 2.9E-09 | 7.2E-07 | Multicellular organismal process | GO:0032501 | 29 | 0.64 | 0.011 | 0.228 | |
| Rhythmic process | GO:0048511 | 2 | 7.05 | 0.041 | 0.227 | |||||||
| Biological adhesion | GO:0022610 | 27 | 3.25 | 2.8E-07 | 1.4E-05 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Locomotion | GO:0040011 | 15 | 2.06 | 0.013 | 0.103 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Molecular function | ||||||||||||
| Binding | GO:0005488 | 153 | 1.17 | 0.034 | 0.269 | Receptor activity | GO:0004872 | 22 | 0.58 | 0.005 | 0.129 | |
| Receptor activity | GO:0004872 | 28 | 0.68 | 0.032 | 0.266 | Signal transducer activity | GO:0004871 | 13 | 0.4 | 1.4E-04 | 0.026 | |
| Structural molecule activity | GO:0005198 | 28 | 1.81 | 0.004 | 0.06 | Transporter activity | GO:0005215 | 39 | 1.59 | 0.007 | 0.154 | |
| Signal transducer activity | GO:0004871 | 22 | 0.63 | 0.021 | 0.22 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Cellular component | ||||||||||||
| Synapse | GO:0045202 | 5 | 3.18 | 0.025 | 0.158 | Synapse | GO:0045202 | 6 | 4.1 | 0.005 | 0.050 | |
| Cell junction | GO:0030054 | 21 | 7.91 | 4.8E-12 | 2.9E-10 | Macromolecular complex | GO:0032991 | 31 | 0.54 | 1.1E-04 | 0.007 | |
| Macromolecular complex | GO:0032991 | 39 | 0.63 | 0.002 | 0.024 | Extracellular matrix | GO:0031012 | 7 | 2.65 | 0.020 | 0.106 | |
| D15 VS D250 | Biological function | |||||||||||
| Biological regulation | GO:0065007 | 118 | 0.74 | 3.0E-04 | 0.009 | Cellular process | GO:0009987 | 951 | 1.07 | 0.013 | 0.066 | |
| Response to stimulus | GO:0050896 | 75 | 0.63 | 5.0E-06 | 2.0E-04 | Localization | GO:0051179 | 271 | 1.3 | 3.9E-05 | 7.4E-04 | |
| Multicellular organismal process | GO:0032501 | 44 | 0.61 | 4.7E-04 | 0.013 | Reproduction | GO:0000003 | 15 | 0.49 | 0.003 | 0.023 | |
| Biological adhesion | GO:0022610 | 21 | 1.72 | 0.0197 | 0.178 | Response to stimulus | GO:0050896 | 283 | 0.89 | 0.038 | 0.148 | |
| positive regulation of peptidase activity | GO:0010952 | 3 | 1.20 | 0.000 | 0.081 | Multicellular organismal process | GO:0032501 | 91 | 048 | 2.0E-15 | 1.2E-13 | |
| - | - | - | - | - | - | Metabolic process | GO:0008152 | 718 | 1.2 | 7.7E-08 | 2.3E-06 | |
| - | - | - | - | - | - | Immune system process | GO:0002376 | 49 | 1.56 | 0.006 | 0.035 | |
| Molecular function | ||||||||||||
| Binding | GO:0005488 | 160 | 0.83 | 0.008 | 0.141 | Binding | GO:0005488 | 560 | 1.09 | 0.022 | 0.147 | |
| Receptor activity | GO:0004872 | 36 | 0.6 | 7.6E-04 | 0.029 | Receptor activity | GO:0004872 | 98 | 0.61 | 1.8E-07 | 1.7E-05 | |
| Structural molecule activity | GO:0005198 | 33 | 1.45 | 0.041 | 0.365 | Signal transducer activity | GO:0004871 | 70 | 0.51 | 6.5E-10 | 1.2E-07 | |
| Transporter activity | GO:0005215 | 52 | 1.34 | 0.045 | 0.388 | Catalytic activity | GO:0003824 | 570 | 1.21 | 1.7E-06 | 1.0E-04 | |
| Cellular function | ||||||||||||
| Extracellular matrix | GO:0031012 | 9 | 2.16 | 0.042 | 0.242 | Macromolecular complex | GO:0032991 | 273 | 1.14 | 0.035 | 0.131 | |
| Extracellular region | GO:0005576 | 42 | 1.76 | 7.6E-04 | 0.012 | Cell part | GO:0044464 | 732 | 1.11 | 0.001 | 0.013 | |
| - | - | - | - | - | - | Organelle | GO:0043226 | 464 | 1.14 | 0.004 | 0.051 | |
1Mammary epithelia cells were isolated from milk obtained from Kashmiri (n = 3) and Jersey (n = 3) cows at D15 (15 days in milk) (early lactation), D90 (mid-lactation) and D250 (late-lactation) and subjected to RNA-sequencing.
2FDR: Benjamini and Hockberg corrected p-values
Pathway enrichment analysis at different stages of lactation indicated that 5 pathways (transcription regulation by bZIP transcription factor, Toll receptor signalling pathway, VEGF signalling pathway, CCKR signalling pathway and chemokine and cytokine signalling pathway) and 11 pathways (JAK/STAT signalling pathway, p38 MAPK pathway, B cell activation, Toll receptor signalling pathway, interleukin signalling pathway, apoptosis signalling pathway, inflammation mediated by chemokine and cytokine signalling, phosphatidylinositol-3-kinases (PI3) pathway, Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) signalling pathway, T cell activation and cholecystokinin receptor (CCKR) signalling pathway were significantly enriched (FDR < 0.05) by DEG of D15 vs D90 and D15 vs D250, respectively in Jersey cattle while only two pathways, purine metabolism (FDR = 0.095) and p38 MAPK pathway (FDR = 0.063) (D15 vs D90) tended towards significance in Kashmiri cattle (Table 7 and S7 Table).
Table 7. Enriched KEGG pathways for differentially expressed genes in mammary epithelial cells between lactation stages in Kashmiri and Jersey cattle1.
| Kashmiri | Jersey | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pathway | ID | Genes | Fold enrichment | P-value | FDR2 | Pathway | ID | Genes | Fold enrichment | P-value | FDR |
| D15 VS D90 | |||||||||||
| Purine metabolism | P02769 | 6 | 7.6 | 0.000 | 0.095 | Salvage pyrimidine deoxyribonucleotides | P02774 | 2 | 14.63 | 0.017 | 0.258 |
| 2-arachidonoylglycerol biosynthesis | P05726 | 3 | 5.97 | 0.025 | 0.685 | Cholesterol biosynthesis | P00014 | 4 | 5.85 | 0.008 | 0.149 |
| Pyrimidine Metabolism | P02771 | 5 | 4.35 | 0.011 | 0.451 | Plasminogen activating cascade | P00050 | 5 | 4.99 | 0.005 | 0.132 |
| Cholesterol biosynthesis | P00014 | 4 | 3.71 | 0.034 | 0.706 | Axon guidance mediated by Slit/Robo | P00008 | 4 | 3.99 | 0.025 | 0.313 |
| p38 MAPK pathway | P05918 | 11 | 3.56 | 0.000 | 0.063 | Transcription regulation by bZIP transcription factor | P00055 | 11 | 3.66 | 0.000 | 0.0199 |
| Axon guidance mediated by Slit/Robo | P00008 | 5 | 3.16 | 0.031 | 0.733 | p38 MAPK pathway | P05918 | 7 | 3.57 | 0.005 | 0.116 |
| Blood coagulation | P00011 | 9 | 2.67 | 0.011 | 0.378 | Toll receptor signalling pathway | P00054 | 10 | 3.48 | 0.001 | 0.033 |
| Hypoxia response via HIF activation | P00030 | 6 | 2.46 | 0.048 | 0.793 | VEGF signalling pathway | P00056 | 11 | 3.26 | 0.001 | 0.037 |
| Apoptosis signalling pathway | P00006 | 3 | 0.31 | 0.037 | 0.670 | Enkephalin release | P05913 | 5 | 3.05 | 0.031 | 0.346 |
| - | - | - | - | - | CCKR signalling map | P06959 | 23 | 2.64 | 0.000 | 0.003 | |
| - | - | - | - | - | Inflammation mediated by chemokine and cytokine signalling pathway | P00031 | 29 | 2.58 | 0.000 | 0.002 | |
| - | - | - | - | - | Apoptosis signalling pathway | P00006 | 13 | 2.13 | 0.013 | 0.222 | |
| - | - | - | - | - | p53 pathway | P00059 | 9 | 2.12 | 0.044 | 0.427 | |
| - | - | - | - | - | EGF receptor signalling pathway | P00018 | 13 | 1.88 | 0.034 | 0.347 | |
| - | - | - | - | - | Angiogenesis | P00005 | 15 | 1.87 | 0.029 | 0.346 | |
| D90 VS D250 | |||||||||||
| Purine metabolism | P02769 | 2 | 7.05 | 0.041 | 0.668 | Pyrimidine Metabolism | P02771 | 3 | 7.82 | 0.009 | 0.305 |
| p38 MAPK pathway | P05918 | 4 | 3.61 | 0.030 | 0.613 | Purine metabolism | P02769 | 2 | 7.59 | 0.036 | 0.651 |
| T cell activation | P00053 | 9 | 3.23 | 0.002 | 0.229 | Plasminogen activating cascade | P00050 | 4 | 7.59 | 0.002 | 0.240 |
| EGF receptor signalling pathway | P00018 | 11 | 2.81 | 0.00284 | 0.154 | Angiotensin II-stimulated signalling through G proteins and beta-arrestin | P05911 | 5 | 5.09 | 0.004 | 0.233 |
| Cadherin signalling pathway | P00012 | 10 | 2.73 | 0.005 | 0.169 | Interferon-gamma signalling pathway | P00035 | 3 | 4.64 | 0.032 | 0.661 |
| B cell activation | P00010 | 5 | 2.69 | 0.044 | 0.660 | Inflammation mediated by chemokine and cytokine signalling pathway | P00031 | 16 | 2.7 | 0.000 | 0.0827 |
| p53 pathway | P00059 | 6 | 2.5 | 0.038 | 0.703 | Cytoskeletal regulation by Rho GTPase | P00016 | 6 | 2.78 | 0.025 | 0.589 |
| Integrin signalling pathway | P00034 | 11 | 2.41 | 0.008 | 0.223 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Inflammation mediated by chemokine and cytokine signalling pathway | P00031 | 13 | 2.04 | 0.016 | 0.376 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| D15 VS D250 | |||||||||||
| Purine metabolism | P02769 | 3 | 7.19 | 0.013 | 0.534 | JAK/STAT signalling pathway | P00038 | 10 | 4.96 | 0.000 | 0.003 |
| Blood coagulation | P00011 | 7 | 3.93 | 0.003 | 0.549 | ATP synthesis | P02721 | 4 | 3.97 | 0.033 | 0.226 |
| - | - | - | - | - | p38 MAPK pathway | P05918 | 17 | 3.92 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| - | - | - | - | - | Vitamin D metabolism and pathway | P04396 | 6 | 3.72 | 0.012 | 0.116 | |
| - | - | - | - | - | B cell activation | P00010 | 25 | 3.45 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| - | - | - | - | - | Cholesterol biosynthesis | P00014 | 5 | 3.31 | 0.030 | 0.219 | |
| - | - | - | - | - | Toll receptor signalling pathway | P00054 | 20 | 3.15 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| - | - | - | - | - | Interferon-gamma signalling pathway | P00035 | 8 | 2.94 | 0.012 | 0.110 | |
| - | - | - | - | - | Interleukin signalling pathway | P00036 | 27 | 2.88 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| - | - | - | - | - | Apoptosis signalling pathway | P00006 | 36 | 2.67 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| - | - | - | - | - | Inflammation mediated by chemokine and cytokine signalling pathway | P00031 | 64 | 2.57 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| - | - | - | - | - | PI3 kinase pathway | P00048 | 16 | 2.56 | 0.002 | 0.0257 | |
| - | - | - | - | - | PDGF signalling pathway | P00047 | 38 | 2.48 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| - | - | - | - | - | T cell activation | P00053 | 26 | 2.39 | 0.000 | 0.003 | |
| - | - | - | - | - | CCKR signalling map | P06959 | 43 | 2.23 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| - | - | - | - | - | Ubiquitin proteasome pathway | P00060 | 14 | 2.2 | 0.014 | 0.128 | |
| - | - | - | - | - | Ras Pathway | P04393 | 16 | 2.12 | 0.009 | 0.106 | |
| - | - | - | - | - | Transcription regulation by bZIP transcription factor | P00055 | 14 | 2.1 | 0.017 | 0.142 | |
| - | - | - | - | - | Integrin signalling pathway | P00034 | 29 | 1.63 | 0.020 | 0.150 | |
1Mammary epithelia cells were isolated from milk obtained from Kashmiri (n = 3) and Jersey (n = 3) cows at D15 (15 days in milk) (early lactation), D90 (mid-lactation) and D250 (late-lactation) and subjected to RNA-sequencing.
2FDR: Benjamini and Hockberg corrected p-values
Real time quantitative PCR validation of the RNA-seq expression results
Results of qPCR analysis of the expression of 8 DEG involved in different milk synthesis pathways (GPAM, BDH1, SLC2A1, SLC2A8, HK-2, FAS, SOS2 and XDH) and data obtained by RNA-Seq are shown in Fig 5. The expression levels of genes by qPCR and RNA-Seq were highly correlated (Pearson’s correlation coefficient = 0.87) thus validating the RNA-Seq results.
Fig 5. Comparison of the expression levels of eight differentially expressed genes obtained by RNA-seq and qPCR detection methods.
Discussion
In this study, we investigated the transcriptome profile of bovine MEC at different stages of lactation in Kashmiri and Jersey cattle by the method of high throughput RNA sequencing. Purified RNA from MEC, which represents a non-invasive source of material for assessing gene expression in mammary gland [24] was used. The quality of RNA from milk isolated MEC can be sensitive to degradation (due to several long processing steps) resulting in a wide range of RIN values (4 to 9) [24,31,32]. Using RNA from MEC with RIN of 6, Canovas et al. [24] reported discrepancies in gene expression when compared with other sources of mammary RNA (mammary gland tissue, milk somatic cells, laser micro dissected mammary epithelial cells and milk fat globules) [24]. Consequently, Boutinaud et al. [17] advised that the quality of isolated MEC RNA should be assessed before use in gene expression analysis. In this study, the RIN values of isolated MEC RNA ranged from 7.4 to 9.1 suggesting that the RNA was of high quality with minimal degradation. Therefore, the low RIN 6 reported by Canovas et al. [24] could explain the relatively low levels of CSN2, CSN3, CSN1S1 and CSN2S2 when compared with our data, suggesting that the antibody-captured milk MEC technique used by these authors was probably not optimal. The validity of gene expression results obtained by using purified MEC has been demonstrated in cows and buffalo [31, 33–36] and supported by our data. The advantages of purified MEC as a non-invasive source of RNA for mammary gland transcriptome analysis include but not limited to possibility for repeat sampling over a period of time on the same animals without causing damage to mammary tissue and ability to specifically study milk secreting cells.
The qPCR results of CSN2, KRT18, LSP1, HBA and CD18 suggest that the purified MEC in this study share characteristics with typical mammary gland epithelial cells and were minimally contaminated with other cell types like macrophages, leucocytes and red blood cells as we detected very low mRNA abundance of LSP1, HBA and CD18 in isolated MEC (Fig 1). However, our results contrast findings by Cánovas et al. [24] who showed the possibility of higher contamination of purified MEC by macrophages, further supporting our suggestion that the antibody-captured milk MEC technique was not optimally applied in that study.
The RNA sequencing results were validated by real time qPCR of eight genes which showed high correlation (r = 0.87) in their expression levels with RNA sequencing data. Further validation of DEG in milk synthesis related pathways between the two breeds in a larger population is necessary. Such validation could not be performed within this study due to the limited sample size. The transcriptome results revealed that the majority of genes were lowly expressed (FPKM<10) (S3 Table). This observation is in agreement with previous reports on the mammary gland transcriptome of Canadian Holsteins and transgenic goats [10,37,38]. The read counts of highly expressed genes (Table 2) constituted about 70% of total read counts in both breeds. The caseins (CSN1S1, CSN1S2, CSN3, CSN2) and whey protein genes (LGB, LALB) were amongst the top expressed genes as expected. Our observation is in agreement with Ibeagha-Awemu et al. [38].
The DEG profile between lactation stages in this study followed the dynamics of a typical lactation curve. It was found that the highest numbers of genes were expressed in early lactation in both breeds. A higher protein and fat content observed in this study during the initial stages of lactation and supported by a previous report [39] could be a possible reason for this observation. Casein and whey protein gene expression remained almost constant throughout lactation in both breeds. However, the expression was higher in Jersey cattle as compared to Kashmiri cattle. It is likely that the casein and whey protein genes have been fixed through long term genetic selection for increased milk production and consequently accounted for their increased frequencies in Jersey cattle. Apart from the casein and whey protein genes, other genes like RPLP1, RPS28, RPLPO and B2M were also highly expressed in the two breeds. RPLP1 gene encodes a ribosomal phosphoprotein that is a component of the 60S ribosomal subunit and plays an important role in the synthesis of proteins, protein folding and transport [40]. Deficiency of RPS28 and RPLPO proteins has been shown to cause cell death through reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation and MAPK1/ERK2 signalling pathway activation [41]. In this study, RPS28 was highly expressed during all three lactation stages in Kashmiri cattle while in Jersey, it was expressed only at early lactation. Similarly, RPLPO was highly expressed during early and late lactation in Kashmiri cattle and during early lactation in Jersey cows. The expression patterns of RPS28 and RPLPO suggests a possible higher antioxidant activity of milk from Kashmiri cattle as compared to Jersey cattle. B2M gene is among highly expressed genes (higher expression in Jersey cattle) and encodes for the beta-2-microglobulin protein, an integral component of the Fc receptor heterodimer involved in transferring IgG from blood into milk across mammary epithelial cells [42]. Some B2M haplotypes have been reported to be related to higher concentrations of IgG1 in bovine milk [43]. Increasing IgG levels in milk could become important as IgG enhanced dairy products are in demand by consumers to obtain protective immunity [44]. CCL14, a small cytokine belonging to the CC chemokine family was highly expressed during mid and late lactation stages in Jersey cows. CCL14 is involved in cellular calcium homeostasis, immune response and positive regulation of cell proliferation [45].
Differential gene expression analysis indicated that more genes were differentially expressed in Jersey as compared to Kashmiri cattle. In Kashmiri cattle, only three genes, SNORD50, PEAR1 and TMEM232, were amongst top DEG between lactation stages. The membrane protein, PEAR1, shows specific expression in endothelial and platelets cells and plays significant roles in platelet activity and cardiovascular disease [46,47]. TMEM232 has been reported to be co-expressed with SLC25A46 and NAA10. Through genome wide association studies, TMEM232 along with SLC25A46 have been found to dysregulate IgE concentration [48] and are associated with various allergic conditions, while NAA10 was found to regulate mTOR pathway which regulates milk protein synthesis [49].
In Jersey, TMSB4X, which was highly up-regulated at D90, is involved in T-cell activation [50], pathogen clearance and anti-inflammatory effects [51]. SLC27A6 was found to be highly up-regulated during early and late lactation in Jersey and is involved in fatty acid uptake by mammary epithelial cells. SLC27A6 is the major isoform of solute carrier group of genes expressed in bovine MEC and its expression was highly up-regulated with the onset of lactation [52,53].
The expression of all the top DEG between Kashmiri and Jersey cattle (Table 4) were higher in Jersey except SNORD50 and TMEM237, which were expressed at a higher rate in Kashmiri cattle during early lactation. Bos taurus microRNA-223 (bta-miR-223) was differentially expressed between Kashmiri and Jersey and has known roles in immunity, immune cell lineage differentiation, and granulopoiesis [53]. Bta-miR-223 has been implicated in cancer progression, HIV-1 infection, IL-17–induced inflammation [54,55], general delay in alternative NF-κB activation in innate immune cells [56] and negative regulation of proliferation and differentiation of neutrophils through down-regulation of the transcription factor, Mef2c, as well as up-regulation during bovine mammary gland infections like mastitis [57]. SNORD50 is involved in maturation of ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) within the nucleolus [58,59] and its overexpression inhibits colony formation of human breast and prostate cancer cell lines in vitro, suggesting its role as a tumor suppressor [60,61]. PTX3 play roles in the regulation of resistance to pathogens, inflammatory reaction, clearance of self-components and female fertility [62,63,64]. GPR84 is expressed mainly in immune-related tissues and plays significant roles in inflammatory processes [65]. It is also expressed in adipose tissue [66]. It enhances insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells [67,68] and increases the release of gut peptides, glucagon-like peptide 1 from intestinal neuroendocrine L-cells [69].
The candidate genes for milk quality and yield traits a were expressed at higher rates in Jersey cattle as compared to Kashmiri cattle (Tables 4 and 5). This observation is supported by milk yield, and milk fat and protein contents which were higher in Jersey at all stages of lactation as compared to Kashmiri cattle. Similar differential expression patterns were also reported by Lee et al., [70] in lactating yaks.
The relative expression of the major milk protein genes (CSN1S1, CSN1S2, LALBA CSN3, CSN2 and LGB) showed highest fold changes at D250 (late-lactation) in both Kashmiri and Jersey cattle. Our findings are in agreement with Sigl et al. [33] and Colitti and Farinacci [71]. Similar to our results, Colitti and Pulina [72] recorded higher expression for CSN1S1, CSN3 and CSN2 during late lactation in dairy ewes. Amongst the glucose transporter genes (SLC2A1, SLC2A4 and SLC2A8, and HK2), only SLC2A1 was up-regulated at mid-lactation in Kashmiri cattle which could be attributed to increased demand for glucose during mid-lactation period [73]. SLC2A8, another major solute carrier that plays a significant role in glucose transport in mammary gland indicated higher expression during mid-lactation (D90). SLC2A8 mRNA in mammary gland is developmentally regulated during lactation in both mouse and cows [74]. SLC2A4 expression, unlike SLC2A1 expression was found to be higher during late lactation and could influence the insulin action on mammary tissue during involution [75].
Data on protein-protein interaction indicated that ME1 protein had varying degrees of interactions with milk candidate genes (ACSS1, ACSS2, PPARGC1A, LPL and FSN) with critical roles in metabolic pathways, insulin signalling, fatty acid synthesis and metabolism. ME1 gene encodes a cytosolic NADP-dependent enzyme that generates NADPH used by FASN for long chain fatty acid synthesis [76]. B4GALT6 interacted (confidence score = 0.905) with UGCG milk candidate gene. B4GALT6, a galactosyltransferase gene of the sphingolipid metabolic pathway encodes for a lactosyl ceramide synthase enzyme that is required for cell apoptosis [77] and lactose biosynthesis (occurs exclusively in the mammary gland) [78]. ESR1 protein interacted with lipogenic proteins (LPL, ABCA1, FASN and PPARGC1A) with confidence scores varying from 0.5 to 0.61. ESR1 plays a key regulatory role in lipid biosynthesis in mammary epithelial cells through activation of various lipogenic genes (SREBF1, SREBF2, PPARG, INSIG1, and PPARGC1A) [79]. SLC27A6 interacted with ACSL1 and LPIN1 with confidence score of 0.63 and 0.66, respectively. SLC27A6 is an integral transmembrane protein that enhance the uptake of long-chain and very long chain fatty acids into cells by activating LC-acyl-CoA primarily via ACSL1 [80]. BDH1 showed protein-protein interaction only with OXCT1 (confidence score > 0.9). Both BDH1 and OXCT1 are involved in ketone body utilization through synthesis and degradation of ketone bodies pathway, which utilize β-hydroxybutyrate for de novo fatty acid synthesis in mammary epithelial cells [81].
In mammals, the maintenance of lactogenic process is because of the balance between different processes like mammary development and involution pathways [82]. In relation to these physiological processes, many of the enriched GO terms in our data are related to developmental processes (GO:0032502). With respect to involution, this mechanism produces changes in mammary gland architecture through extra cellular matrix remodelling, collapse of alveoli and differentiation of adipocytes [83]. Cell junction (GO:0030054) and synapse (GO:0045202) which are related to cellular components of ECM were enriched in Kashmiri and Jersey cattle, respectively. The enriched genes for these terms (MEGF9, HAPLN3, ELN, LAMB3, GAS6, VCAN, TIMP1) have been associated with the onset of mammary gland involution and mammary gland morphogenesis [84,85]. Our results did not show a direct relationship with prolactin signalling, which is important for the process of lactogenesis. However, a significant GO term, response to stimulus (GO:0050896), is a parent term to insulin and growth factor stimulus. It is remarkable that both insulin and growth hormone are known to increase prolactin lactogenic effect [85]. Additionally, it is important to highlight that the significant GO term related to organelle (GO:0043226) (includes endoplasmic reticulum lumen) was significantly enriched at D250 (D15 vs D250) of lactation in Jersey. This organelle is linked to the lipid secretor mechanism of mammary epithelial cells [86]. The GO term, endopeptidase activity (GO: 0010950) was highly enriched in Kashmiri cattle (D15 vs D90) and may have special effects on the physico-chemical characteristics of milk [87] and flavour of dairy products [88] in this breed. Moreover, the immune system process (GO:0002376) GO term was significantly enriched by DEG in Jersey (D15 vs D250). Subclinical infections elicit elevated somatic cell counts (SCC) but other variables like breed have been shown to influence milk SCC levels [89].
The pathway enrichment analysis indicated that a total of 16 pathways were enriched (FDR<0.05) for DEG in Jersey and only two pathways (purine metabolism and p38 MAPK pathway) tended (FDR<0.1) to be significant in Kashmiri cattle. Among enriched pathways, the bZIP transcription factor regulates the transcriptional activity of various protein coding genes like GTF2B, CREB1, POLR2L which play critical roles in the regulation of mammary epithelial cell proliferation [90]. P13 kinase regulates mammary epithelial cell differentiation through prolactin action. The mammary differentiation due to P13K-AKT activation results in autocrine prolactin secretion which in turn activates JAK-STAT pathway [91]. Lemay et al. [92] observed that P13K-AKT pathway was highly significantly enriched during lactation in mouse mammary gland. JAK-STAT pathway plays important roles in the regulation of milk protein synthesis in non-ruminants [93]. Besides protein synthesis, STAT3, JAK2 and JAK3 are important for mammary gland development [94]. In bovine, STAT3 responds to lactogenic factors and its activity increases during lactation [95]. The p38-MAPK pathway is another signalling pathway which plays a critical role in mammary epithelial cell development and enhances milk production by modulating alveolar cell proliferation and branching [96]. A number of immune related pathways (B cell activation, Toll receptor signalling pathway, T cell activation) were significantly enriched in Jersey cattle and may play an important role in milk production by protecting offspring and cell secreting organs [97].
Conclusion
This study represents a cohesive comparison of the milk epithelial cell transcriptome profiles at different stages of lactation between Kashmiri and Jersey cattle. The results revealed higher gene expression profiles of candidate genes for milk synthesis and yield traits in Jersey compared to Kashmiri cattle. More genes were differentially expressed between lactation days in Jersey cattle as compared to Kashmiri cattle. Sixteen pathways were significantly enriched by DEG in Jersey cattle while no pathway was found to be significantly enriched in Kashmiri cattle. On the other hand, varied numbers of GO terms were enriched between lactation stages in both Kashmiri and Jersey cattle. The presence of enriched GO terms like endopeptidase and antioxidant activity in Kashmiri cattle suggests special effects on the physico-chemical characteristics of milk from Kashmiri cattle. Such properties may lead to the development of certain niche products and thereby help in the conservation of this unique germplasm which has been diluted through extensive cross breeding programmes. The results provide a significant advance in our knowledge of Kashmiri cow lactating mammary gland gene expression and valuable information for future studies and breed improvement.
Supporting information
Genes and primer sequences for purity check of isolated mammary epithelial cells (a). Genes and primer sequences used for validation of RNA-Seq data by qPCR (b).
(DOCX)
(DOCX)
(XLSX)
(XLSX)
(XLSX)
(XLSX)
(XLSX)
Acknowledgments
We are highly thankful to the Vice-Chancellor, Shar-e-Kashmir University of Agricultural Sciences and Technology of Kashmir for his guidance and support. We appreciate the In-charge, Mountain Livestock Research Institute (MLRI), Kashmir for his assistance. We are entirely grateful to the local participant farmers who volunteered their animals for the study.
Data Availability
The sequencing data is available in NCBI under accession number GSE107366.
Funding Statement
The study was supported by the Department of Biotechnology, Ministry of Science and Technology, Government of India under grant BT/PR11408/AAQ/1/591/2014. The funding agency had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Capuco AV, Akers RM. The origin and evolution of lactation. Journal of biology. 2009;8(4):37 10.1186/jbiol139 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Goldman AS, Chheda S, Garofalo R. Evolution of immunologic functions of the mammary gland and the postnatal development of immunity. Pediatric Research. 1998;43(2):155 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Goldman AS. Modulation of the gastrointestinal tract of infants by human milk. Interfaces and interactions. An evolutionary perspective. The Journal of nutrition. 2000;130(2):426S–31S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Séverin S, Wenshui X. Milk biologically active components as nutraceuticals. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition. 2005;45(7–8):645–56. 10.1080/10408690490911756 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bionaz M, Periasamy K, Rodriguez-Zas SL, Everts RE, Lewin HA, Hurley WL, et al. Old and new stories: revelations from functional analysis of the bovine mammary transcriptome during the lactation cycle. PloS one. 2012;7(3):e33268 10.1371/journal.pone.0033268 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.McGinley JN, Thompson HJ. Quantitative assessment of mammary gland density in rodents using digital image analysis. Biological procedures online. 2011;13(1):4 10.1186/1480-9222-13-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Strucken EM, Laurenson YC, Brockmann GA. Go with the flow—biology and genetics of the lactation cycle. Frontiers in genetics. 2015; 6:118 10.3389/fgene.2015.00118 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Suárez-Vega A, Gutiérrez-Gil B, Klopp C, Robert-Granie C, Tosser-Klopp G, Arranz JJ. Characterization and comparative analysis of the milk transcriptome in two dairy sheep breeds using RNA sequencing. Scientific reports. 2015. December 18; 5:18399 10.1038/srep18399 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Do DN, Li R, Dudemaine PL, Ibeagha-Awemu EM. MicroRNA roles in signalling during lactation: an insight from differential expression, time course and pathway analyses of deep sequence data. Scientific reports. 2017; 7:44605 10.1038/srep44605 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wickramasinghe S, Rincon G, Islas-Trejo A, Medrano JF. Transcriptional profiling of bovine milk using RNA sequencing. BMC genomics. 2012;13(1):45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cui X, Hou Y, Yang S, Xie Y, Zhang S, Zhang Y. Transcriptional profiling of mammary gland in Holstein cows with extremely different milk protein and fat percentage using RNA sequencing. BMC genomics. 2014;15(1):226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Li Z, Liu H, Jin X, Lo L, Liu J. Expression profiles of microRNAs from lactating and non-lactating bovine mammary glands and identification of miRNA related to lactation. BMC genomics. 2012;13(1):731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Boutinaud M, Jammes H. Potential uses of milk epithelial cells: a review. Reproduction Nutrition Development. 2002;42(2):133–47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Murrieta CM, Hess BW, Scholljegerdes EJ, Engle TE, Hossner KL, Moss GE, et al. Evaluation of milk somatic cells as a source of mRNA for study of lipogenesis in the mammary gland of lactating beef cows supplemented with dietary high-linoleate safflower seeds. Journal of Animal Sciences. 2006; 84: 2399–2405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mura MC, Daga C, Bodano S, Paludo M, Luridiana S, Pazzola M, et al. Development of a RNA extraction method from milk for gene expression study in the mammary gland of sheep. Molecular Biology Reports. 2013; 40: 2169–2173.6 10.1007/s11033-012-2276-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bai WL, Yin RH, Jiang WQ, Ajayi OO, Zhao SJ, Luo GB, et al. Molecular analysis of αs1-, β-, αs2- and κ-casein transcripts reveals differential translational efficiency in yak lactating mammary gland. Livestock Science. 2013; 152: 74–78. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Boutinaud M, Herve L and Lollivier V. Mammary epithelial cells isolated from milk are a valuable, non-invasive source of mammary transcripts. Frontiers in Genetics. 2015; 6: 323 10.3389/fgene.2015.00323 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sciascia Q, Pacheco D, SennaSalerno M, Blair HT and McCoard SA. Milk somatic cells are not suitable biomarkers of lactating ruminant mammary gland function. Proceedings of New Zealand Society of Animal Production. 2012; 72: 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Finucane KA, McFadden TB, Bond JP, Kennelly JJ, Zhao FQ. Onset of lactation in the bovine mammary gland: gene expression profiling indicates a strong inhibition of gene expression in cell proliferation. Functional & integrative genomics. 2008;8(3):251–64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Imran M, Khan H, Hassan SS, and Khan R. Physicochemical characteristics of various milk samples available in Pakistan. Journal of Zhejiang University Science B. 2008; 9(7): 546 551. 10.1631/jzus.B0820052 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.McCarthy OJ, Singh H. Physico-chemical properties of milk InAdvanced dairy chemistry 2009;691–758. Springer, New York, NY. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Jelen P. Physico-chemical properties of milk and whey in membrane processing. Journal of Dairy Science. 1979;62(8):1343–51. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wang T, Lim JN, Bok JD, Kim JH, Kang SK, Lee SB et al. Association of protein expression in isolated milk epithelial cells and cis-9, trans-11 conjugated linoleic acid proportions in milk from dairy cows. J. Sci. Food. Agric. 2014; 94, 1835–1843. 10.1002/jsfa.6502 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Cánovas A, Rincón G, Bevilacqua C, Islas-Trejo A, Brenaut P, Hovey RC, Boutinaud M, Morgenthaler C, VanKlompenberg MK, Martin P and Medrano JF. Comparison of five different RNA sources to examine the lactating bovine mammary gland transcriptome using RNA-Sequencing. Scientific reports. 2014; 4:5297 10.1038/srep05297 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Trapnell C, Pachter L, Salzberg SL. TopHat: discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics. 2009;25(9):1105–11. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp120 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Trapnell C, Roberts A, Goff L, Pertea G, Kim D, Kelley DR, et al. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nature protocols. 2012;7(3):562 10.1038/nprot.2012.016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Thomas PD, Campbell MJ, Kejariwal A, Mi H, Karlak B, Daverman R, et al. PANTHER: a library of protein families and subfamilies indexed by function. Genome research. 2003;1;13(9):2129–41. 10.1101/gr.772403 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S, Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, et al. STRING v10: protein–protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic acids research. 2014;28;43(D1):D447–52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Shannon P. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Research. 2003;13, 2498–2504. 10.1101/gr.1239303 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. methods. 2001;25(4):402–8. 10.1006/meth.2001.1262 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Boutinaud M, BenChedly MH, Delamaire E and Guinard-Flament J. Milking and feed, restriction regulate transcripts of mammary epithelial cells purified from milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2008; 91, 988–998. 10.3168/jds.2007-0587 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Angulo J, Mahecha L, Nuernberg K, Nuernberg G, Dannenberger D, Olivera M, et al. Effects of polyunsaturated fatty acids from plant oils and algae on milk fat yield and composition are associated with mammary lipogenic and SREBF1gene expression. Animal. 2012; 6, 1961–1972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sigl T, Meyer HHD and Wiedemann S. Gene expression of six major milk proteins in primary bovine mammary epithelial cells isolated from milk during the first twenty weeks of lactation. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2012; 57, 469–480. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sigl T, Meyer HH and Wiedemann S. Gene expression analysis of protein synthesis pathways in bovine mammary epithelial cells purified from milk during lactation and short-term restricted feeding. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2014; 98, 84–95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Yadav P, Kumar P, Mukesh M, Kataria RS, Yadav A, Mohanty AK, et al. Kinetics of lipogenic genes expression in milk purified mammary epithelial cells(MEC) across lactation and their correlation with milk and fat yield in buffalo. Res.Vet.Sci. 2015; 99, 129–136. 10.1016/j.rvsc.2015.01.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Yadav P, Singh DD, Mukesh M, Kataria RS, Yadav A, Mohanty AK, Mishra BP. Expression profiling of glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) and apoptotic genes (BAX and BCL2) in milk enriched mammary epithelial cells (MEC) in riverine buffalo during lactation. Animal biotechnology. 2014; 3;25(3):151–9. 10.1080/10495398.2013.836530 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lin J, Bao ZK, Zhang Q, Hu WW, Yu QH, Yang Q. Transcriptome analysis of the mammary gland from GH transgenic goats during involution. Gene. 2015;565(2):228–34. 10.1016/j.gene.2015.04.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ibeagha-Awemu EM, Li R, Ammah AA, Dudemaine PL, Bissonnette N, Benchaar C, et al. Transcriptome adaptation of the bovine mammary gland to diets rich in unsaturated fatty acids shows greater impact of linseed oil over safflower oil on gene expression and metabolic pathways. BMC genomics. 2016;17(1):104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Gao Y, Lin X, Shi K, Yan Z, Wang Z. Bovine Mammary Gene Expression Profiling during the Onset of Lactation. PLoS ONE. 2013; 8(8): e70393 10.1371/journal.pone.0070393 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Perucho L, Artero-Castro A, Guerrero S, Cajal SR, LLeonart ME, Wang ZQ. RPLP1, a crucial ribosomal protein for embryonic development of the nervous system. PloS one. 2014;24;9(6): e99956 10.1371/journal.pone.0099956 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Artero-Castro A, Perez-Alea M, Feliciano A, Leal JA, Genestar M, Castellvi J, Peg V, Ramón y Cajal S, LLeonart ME. Disruption of the ribosomal P complex leads to stress-induced autophagy. Autophagy. 2015;11(9):1499–519. 10.1080/15548627.2015.1063764 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Anderson CL, Chaudhury C, Kim J, Bronson CL, Wani MA, Mohanty S. Perspective–FcRn transports albumin: relevance to immunology and medicine. Trends in immunology. 2006;1;27(7):343–8. 10.1016/j.it.2006.05.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zhao S, Liu G, Wang J, Zhang C, Bu D, Liu K, Zhou L. Association of polymorphisms of beta-2-microglobulin gene (β2m) with milk IgG1 content in Chinese Holstein dairy cows. Livestock Science. 2012;143(2):289–92. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Hurley WL, Theil PK. Perspectives on immunoglobulins in colostrum and milk. Nutrients. 2011;3(4):442–74. 10.3390/nu3040442 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Piantoni P, Wang P, Drackley JK, Hurley WL, Loor JJ. Expression of metabolic, tissue remodeling, oxidative stress, and inflammatory pathways in mammary tissue during involution in lactating dairy cows. Bioinformatics and biology insights. 2010;4:BBI-S5850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Yang WY, Petit T, Cauwenberghs N, Zhang ZY, Sheng CS, Thijs L, et al. PEAR1 is not a major susceptibility gene for cardiovascular disease in a Flemish population. BMC medical genetics. 2017;18(1):45 10.1186/s12881-017-0411-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Izzi B, Pistoni M, Cludts K, Akkor P, Lambrechts D, Verfaillie C, et al. Allele-specific DNA methylation reinforces PEAR1 enhancer activity. Blood. 2016;128(7):1003–12. 10.1182/blood-2015-11-682153 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Granada M, Wilk JB, Tuzova M, Strachan DP, Weidinger S, Albrecht E, et al. A genome-wide association study of plasma total IgE concentrations in the Framingham Heart Study. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 2012;129(3):840–5. 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.09.029 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Wang M, Xu B, Wang H, Bu D, Wang J, Loor JJ. Effects of arginine concentration on the in vitro expression of casein and mTOR pathway related genes in mammary epithelial cells from dairy cattle. PLoS One. 2014;9(5):e95985 10.1371/journal.pone.0095985 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Low TL, Goldstein AL. Thymosins: structure, function and therapeutic applications. Thymus. 1984;6(1–2):27–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Girardi M, Sherling MA, Filler RB, Shires J, Theodoridis E, Hayday AC, et al. Anti‐inflammatory effects in the skin of thymosin‐β4 splice‐variants. Immunology. 2003;1;109(1):1–7. 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2003.01616.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Bionaz M, Loor JJ. ACSL1, AGPAT6, FABP3, LPIN1, and SLC27A6 are the most abundant isoforms in bovine mammary tissue and their expression is affected by stage of lactation. The Journal of Nutrition. 2008;1;138(6):1019–24. 10.1093/jn/138.6.1019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Bionaz M, Loor JJ. Gene networks driving bovine milk fat synthesis during the lactation cycle. BMC genomics. 2008;9(1):366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Poon KS, Palanisamy K, Chang SS, Sun KT, Chen KB, Li PC, Lin TC, Li CY. Plasma exosomal miR-223 expression regulates inflammatory responses during cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass. Scientific Reports. 2017;7(1):10807 10.1038/s41598-017-09709-w [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Jeffrey AD, Syed R, Duggineni D, Rutsky J, Rengasamy P, Zhang J, et al. Visceral Adipose MicroRNA 223 Is Upregulated in Human and Murine Obesity and Modulates the Inflammatory Phenotype of Macrophages. PlosOne. 2016; 11(11). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Lukens JR, Gurung P, Shaw PJ, Barr MJ, Zaki MH, Brown SA, et al. The NLRP12 sensor negatively regulates auto inflammatory disease by modulating interleukin-4 production in T cells. Immunity. 2015; 21;42(4):654–64. 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.03.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Li R., Zhang C. L., Liao X. X., Chen D., Wang W. Q., Zhu Y. H., … & Yang Z. P. Transcriptome microRNA profiling of bovine mammary glands infected with Staphylococcus aureus. International journal of molecular sciences. 2015;16(3):4997–5013. 10.3390/ijms16034997 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Matera AG, Terns RM, Terns MP. Non-coding RNAs: lessons from the small nuclear and small nucleolar RNAs. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology. 2007;8(3):209 10.1038/nrm2124 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Williams GT, Farzaneh F. Are snoRNAs and snoRNA host genes new players in cancer? Nature reviews cancer. 2012;12(2):84 10.1038/nrc3195 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Dong XY, Rodriguez C, Guo P, Sun X, Talbot JT, Zhou W, Petros J, Li Q, Vessella RL, Kibel AS, Stevens VL. SnoRNA U50 is a candidate tumor-suppressor gene at 6q14. 3 with a mutation associated with clinically significant prostate cancer. Human molecular genetics. 2008;17;17(7):1031–42. 10.1093/hmg/ddm375 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Dong XY, Guo P, Boyd J, Sun X, Li Q, Zhou W, Dong JT. Implication of snoRNA U50 in human breast cancer. Journal of Genetics and Genomics. 2009; 31;36(8):447–54. 10.1016/S1673-8527(08)60134-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Mantovani A, Garlanda C, Bottazzi B. Pentraxin 3, a non-redundant soluble pattern recognition receptor involved in innate immunity. Vaccine. 2003; June 1;21:S43–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Pepys MB, Baltz ML. Acute phase proteins with special reference to C-reactive protein and related proteins (pentaxins) and serum amyloid A protein InAdvances in immunology. 1983; January 1 (Vol. 34, pp. 141–212). Academic Press. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.May L, Kuningas M, Bodegom DV, Meij HJ, Frolich M, Slagboom PE, Mantovani A, Westendorp RG. Genetic variation in pentraxin (PTX) 3 gene associates with PTX3 production and fertility in women. Biology of reproduction. 2010;1;82(2):299–304. 10.1095/biolreprod.109.079111 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Zhang Q, Yang H, Li J, Xie X. Discovery and Characterization of a Novel Small-Molecule Agonist for Medium-Chain Free Fatty Acid Receptor G Protein–Coupled Receptor 84. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 2016;1;357(2):337–44. 10.1124/jpet.116.232033 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Brown AJ, Goldsworthy SM, Barnes AA, Eilert MM, Tcheang L, Daniels D, et al. The Orphan G protein-coupled receptors GPR41 and GPR43 are activated by propionate and other short chain carboxylic acids. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2003; 28;278(13):11312–9. 10.1074/jbc.M211609200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Briscoe CP, Tadayyon M, Andrews JL, Benson WG, Chambers JK, Eilert MM, et al. , The orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR40 is activated by medium and long chain fatty acids. Journal of Biological chemistry. 2003; 28;278(13):11303–11. 10.1074/jbc.M211495200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Itoh Y, Kawamata Y, Harada M, Kobayashi M, Fujii R, Fukusumi S, et al. , Letters to Nature-Free fatty acids regulate insulin secretion from pancreatic 0 cells through GPR40. Nature. 2003;422(6928):173–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Overton HA, Babbs AJ, Doel SM, Fyfe MC, Gardner LS, Griffin G, Jackson HC, Procter MJ, Rasamison CM, Tang-Christensen M, Widdowson PS. Deorphanization of a G protein-coupled receptor for oleoylethanolamide and its use in the discovery of small-molecule hypophagic agents. Cell metabolism. 2006;3(3):167–75. 10.1016/j.cmet.2006.02.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Lee JN, Wang Y, Xu YO, Li YC, Tian F, Jiang MF. Characterisation of gene expression related to milk fat synthesis in the mammary tissue of lactating yaks. Journal of Dairy Research. 2017;84(3):283–8. 10.1017/S0022029917000413 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Colitti M., Farinacci M. Cell turnover and gene activities in sheep mammary glands prior to lambing to involution. Tissue and Cell. 2009; 41, 326–333. 10.1016/j.tice.2009.02.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Colitti M., Pulina G. Short communication: Expression profile of caseins, estrogen and prolactin receptors in mammary glands of dairy ewes. Italian Journal of Animal Science. 2010; 9, 285–289. [Google Scholar]
- 73.Komatsu T, Itoh F, Kushibiki S, Hodate K. Changes in gene expression of glucose transporters in lactating and nonlactating cows 1. Journal of animal science. 2005;1;83(3):557–64. 10.2527/2005.833557x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Zhao FQ, Miller PJ, Wall EH, Zheng YC, Dong B, Neville MC, McFadden TB. Bovine glucose transporter GLUT8: cloning, expression, and developmental regulation in mammary gland. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Gene Structure and Expression. 2004; 21;1680(2):103–13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Mattmiller SA, Corl CM, Gandy JC, Loor JJ, Sordillo LM. Glucose transporter and hypoxia-associated gene expression in the mammary gland of transition dairy cattle. Journal of Dairy Science. 2011; 94: 2912–2922. 10.3168/jds.2010-3936 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Al-Dwairi A, Pabona JM, Simmen RC, Simmen FA. Cytosolic malic enzyme 1 (ME1) mediates high fat diet-induced adiposity, endocrine profile, and gastrointestinal tract proliferation-associated biomarkers in male mice. PLoS One. 2012; 7: e46716 10.1371/journal.pone.0046716 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Martin S, Williams N, Chatterjee S. Lactosylceramide is required in apoptosis induced by N-Smase. Glycoconjugate journal. 2006; 23: 147–157. 10.1007/s10719-006-7920-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Amado M, Almeida R, Schwientek T, Clausen H. Identification and characterization of large galactosyltransferase gene families: galactosyltransferases for all functions. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1999; 1473: 35–53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Mahmoud AM and Morey WH. Regulation of lipid synthesis genes and milk fat production in human mammary epithelial cells during secretory activation. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2013. 15; 305(6): E700–E716. 10.1152/ajpendo.00052.2013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Stahl A. A current review of fatty acid transport proteins (SLC27). Pflugers Arch. 2004. February;447(5):722–7. 10.1007/s00424-003-1106-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Robinson AM, Williamson DH. Physiological roles of ketone bodies as substrates and signals in mammalian tissues. Physiological reviews. 1980;60(1):143–87. 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.1.143 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Raven LA, Cocks BG, Goddard ME, Pryce JE and Hayes BJ. Genetic variants in mammary development, prolactin signalling and involution pathways explain considerable variation in bovine milk production and milk composition. Genetics Selection Evolution. 2014;46, 29-9686-46-29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Maller O, Martinson H and Schedin P. Extracellular matrix composition reveals complex and dynamic stromal-epithelial interactions in the mammary gland. Journal of mammary gland biology and neoplasia. 2010;15, 301–318. 10.1007/s10911-010-9189-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Nemir M, Bhattacharyya D, Li X, Singh K, Mukherjee AB, Mukherjee BB. Targeted inhibition of osteopontin expression in the mammary gland causes abnormal morphogenesis and lactation deficiency. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2000;14;275(2):969–76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Macias H, Hinck L. Mammary gland development. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Developmental Biology. 2012;1;1(4):533–57. 10.1002/wdev.35 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Ghosal D, Shappell NW and Keenan TW. Endoplasmic reticulum lumenal proteins of rat mammary gland. Potential involvement in lipid droplet assembly during lactation. Biochimica et. Biophysica Acta. 1994; 1200, 175–181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Marino R, Considine T, Sevi A, McSweeney P and Kelly A. Contribution of proteolytic activity associated with somatic cells in milk to cheese ripening. International Dairy Journal. 2005;15, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar]
- 88.McSweeney P. Biochemistry of cheese ripening. International Journal of Dairy Technology. 2004;57, 127–144. [Google Scholar]
- 89.Lurueña-Martínez MA, Revilla I, Severiano-Pérez P and Vivar-Quintana AM. The influence of breed on the organoleptic characteristics of Zamorano sheep’s raw milk cheese and its assessment by instrumental analysis. International Journal of Dairy Technology. 2010; 63, 216–223. [Google Scholar]
- 90.Talukder Amjad H, W Rui-An and K Rakesh. Expression and transactivating functions of the bZIP transcription factor GADD153 in mammary epithelial cells. Oncogene. 2002; 21, 4289 ± 4300 10.1038/sj.onc.1205529 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Chen CC, Stairs DB, Boxer RB, Belka GK, Horseman ND, Alvarez JV, et al. Autocrine prolactin induced by the Pten–Akt pathway is required for lactation initiation and provides a direct link between the Akt and Stat5 pathways. Genes & development. 2012; 1;26(19):2154–68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Lemay DG, Lynn DJ, Martin WF, Neville MC, Casey TM, Rincon G, et al. The bovine lactation genome: insights into the evolution of mammalian milk. Genome biology. 2009;10(4): R43 10.1186/gb-2009-10-4-r43 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Liu X, Robinson GW, Wagner KU, Garrett L, Wynshaw-Boris A, et al. Stat5a is mandatory for adult mammary gland development and lactogenesis. Genes and Development. 1997; 11: 179–186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Barash I. Stat5 in the mammary gland: controlling normal development and cancer. Journal of cellular physiology. 2006;1;209(2):305–13. 10.1002/jcp.20771 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Yang J, Kennelly JJ, Baracos VE. The activity of transcription factor Stat5 responds to prolactin, growth hormone, and IGF-1 in rat and bovine mammary explants culture. Journal of Animal Science. 2000; 78: 3114–25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Fata Jimmie E, et al. The MAPK ERK-1, 2 pathway integrates distinct and antagonistic signals from TGFα and FGF7 in morphogenesis of mouse mammary epithelium. Developmental biology. 2007; 306(1): 193–207. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.03.013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Alsaweed M, Hartmann PE, Geddes DT and Kakulas F. MicroRNAs in breastmilk and the lactating breast: potential immunoprotectors and developmental regulators for the infant and the mother. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2015;12, 13981–14020. 10.3390/ijerph121113981 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Genes and primer sequences for purity check of isolated mammary epithelial cells (a). Genes and primer sequences used for validation of RNA-Seq data by qPCR (b).
(DOCX)
(DOCX)
(XLSX)
(XLSX)
(XLSX)
(XLSX)
(XLSX)
Data Availability Statement
The sequencing data is available in NCBI under accession number GSE107366.