Abstract
Study Design
A retrospective study.
Purpose
We report our experience with 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA)–assisted resection of spinal cord ependymomas in adults.
Overview of Literature
Ependymoma is the most frequent primary spinal cord tumor in adults. Surgery is the treatment of choice in most cases. However, while complete resection is achieved in approximately 80% of cases, clinical improvement is achieved in 15% only. Five-ALA fluorescence–guided surgery seems to be useful for this tumor type.
Methods
We studied 14 patients undergoing 5-ALA fluorescence-guided surgery for spinal cord ependymomas in our service. The modified McCormick classification was used to determine clinical status and the degree of resection was assessed with magnetic resonance imaging.
Results
Of the 14 patients, the tumor showed an intense emission of fluorescence in 12 and the fluorescence was weak and nonuniform in two. Complete resection was achieved in 11 cases. According to the McCormick classification, 10 patients improved, two remained the same, and two deteriorated.
Conclusions
Our results confirm that 5-ALA fluorescence-guided resection is useful in spinal cord ependymoma resection. Although the rate of complete resections is similar to that in published series without 5-ALA, clinical results are better when using 5-ALA with a lower percentage of clinical deterioration.
Keywords: Spinal cord, Ependymoma, Aminolevulinic acid, Fluorescence guided surgery
Introduction
Spinal cord tumors represent 5% to 10% of primary tumors in the central nervous system. Ependymomas account for 50% to 60% of primary spinal cord tumors in adults [1] and 2% of all central nervous system tumors [2]. Surgery is the treatment of choice, especially in cases of neurologic deficit. However, while it is possible to achieve complete resection in approximately 80% of patients, 15% only of cases show clinical improvement [3].
5-Aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA) fluorescence-guided resection is a useful technique for the resection of malignant gliomas as well as other tumors, such as meningiomas, metastases, spinal cord tumors, subependymomas, and hemangioblastomas [4-12].
To date, only some cases and small series of 5-ALA–assisted resection of spinal cord ependymomas have been reported [5,7,9,12-14]. We report our experience in what we believe is the largest series of 5-ALA assisted resection of spinal cord ependymomas in adults.
Materials and Methods
We reviewed the histories of all adults who underwent 5-ALA–assisted surgery for an intramedullary ependymoma, including those of the conus medullaris and excluding those of the filum terminale, at University Hospital Complex of Badajoz, Spain between June 2009 and May 2016. The neurologic status of the patients was graded according to the modified McCormick classification preoperatively [15], at discharge, and during the last available follow-up. All the patients underwent preoperative magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) including T1- and T2-weighted sequences and contrast-enhanced T1 sequence. The pattern of contrast enhancement, presence and location of any cystic component, and existence of associated syringomyelia were considered. The extent of resection was estimated by comparison between preoperative and postoperative MRIs. The evolution of tumor rests or any tumor recurrence, when resection was considered complete, was evaluated with sequential MRI studies during follow-up. Neuroradiologists at our institution, who were blinded to the surgical technique used, evaluated all MRIs.
All the patients received dexamethasone preoperatively. Three hours before anesthetic induction, they were given a solution containing 20 mg/kg 5-ALA orally. Surgery was performed with the patient under general anesthesia and orotracheal intubation. Standard microsurgical technique was used, with neurophysiologic monitoring in 11 patients since this technique was not available to us at that time. Fluoroscopy was used to locate the lesion level intraoperatively. Laminectomy or laminoplasty was performed according to surgeon preferences and patient age. A modified neurosurgical microscope (Pentero; Carl Zeiss Co., Oberkochen, Germany) with blue light emission was used during the surgery. When present, fluorescence (graded as strong, mild, or none) was used to guide the myelotomy in the pure intramedullary tumors. During resection, white and blue light alternated to determine the limits of the tumor and scar tissue in the reoperated patients. When the surgeon determined that the tumor resection was finished using white light, the surgical bed was explored under blue light to search for any remnant tumor exhibiting fluorescence. To avoid toxicity induced by 5-ALA photosensitivity, the patients were protected from any light source for 24 hours and they wore dark glasses.
This study was performed with the approval of othe institutional review board of University Hospital Complex of Badajoz, Spain.
Results
A total of 14 patients (seven males, seven females; median age, 50.6 years) with a spinal cord ependymoma underwent surgery between June 2009 and May 2016 (Table 1). Three patients had been operated previously for ependymoma, two at another level and the other had a true recurrence 7 years after an apparent complete resection without the aid of 5-ALA.
Table 1.
Characteristics of the 14 patients included in the study
| Case | Sex | Age (yr) | Level | McCormick | Time until surgery (mo) | Resection grade | Fluorescence | Ki-67 (%) | Neurophysiological monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F | 58 | C1–C2 | III | 36 | Complete | Intense | 1 | Not available |
| 2 | F | 46 | D8–D12 | II | 1 | Subtotal | Intense | 15 (AE) | Not available |
| 3 | F | 72 | D12–L1 | II | 18 | Complete | Intense | 1 | Not available |
| 4 | M | 50 | D4 | II | - | Complete | Intense | 4 | No alterations |
| 5 | M | 52 | C7 | Ib | - | Complete | Intense | 2 | No alterations |
| 6 | F | 18 | D9–D10 | Ib | 2 | Complete | Mild | 5 | No alterations |
| 7 | F | 50 | C4–D1 | II | 24 | Complete | Intense | 2 | No alterations |
| 8 | F | 62 | C5–C6 | Ib | 180 | Complete | Mild | 2 | Improvement of SEPs |
| 9 | M | 44 | L1 | II | 4 | Subtotal | Intense | 1 | Decrease of SEPs |
| 10 | M | 42 | C6–D6 | III | 5 | Complete | Intense | 10 | No alterations |
| 11 | M | 15 | L1–L3 | III | 9 | Complete | Intense | 5 | No alterations |
| 12 | M | 62 | L2 | Ib | 2 | Subtotal | Intense | 5 | Decrease of SEPs |
| 13 | M | 49 | L1 | Ib | 2 | Complete | Intense | 2 | No alterations |
| 14 | F | 56 | D11 | Ib | 24 | Complete | Intense | 2 | No alterations |
F, female; M, male; AE, anaplastic ependymoma; SEPs, somatosensory evoked potentials.
The most frequent clinical manifestation was a sensory deficit in 11 of 14 patients, followed by pain with radicular distribution in nine. Motor and sphincter disturbances or gait difficulties occurred in four patients. No patient was asymptomatic at presentation. According to the McCormick classification, six patients had grade Ib, five grade II, and three grade III disease. The median duration of symptoms was 7 months. The most common lesion location was dorsal and in five patients the conus medullaris was affected. MRI showed uniform contrast enhancement of the tumor in 12 patients and nonuniform enhancement in two. Four patients had associated tumoral cysts and three had syringomyelia.
The tumor emitted an intense fluorescence in 12 patients, while in two the fluorescence was mild and scattered. Intraoperative complete resection was achieved in 11 patients with no visible fluorescence in the surgical bed, and this was confirmed on postoperative MRI. The remaining three patients had minimal residual tumor with fluorescence emission that was deemed unsafe to remove.
Neurophysiologic monitoring was available for 11 of 14 patients: eight had no modification of the potentials during the surgery, improvement was observed in one, and in two with subtotal resection a decrease in somatosensory potentials was noticed and, facing the risk of permanent neurologic consequences, the surgery was stopped. The other case with subtotal resection confirmed with 5-ALA and postoperative MRI did not undergo neurophysiologic monitoring; however, the location at the conus medullaris prompted us to end the operation.
No complications related to the surgery or administration of 5-ALA were observed.
Pathologic diagnoses were ependymoma grade I in three patients, grade II in nine, and grade III in one. Median Ki-67 index was 5%, 2%, and 15%, respectively. There was no correlation between cell proliferation index and intraoperative fluorescence emission.
At discharge, five patients (two grade Ib, two grade II, and one grade III cases) were unchanged, five (four grade Ib and one grade III) were improved, and four (three grade II and one grade III) deteriorated (Table 2). After a median 20-month follow-up, some patients showed continuous improvement, five of the six with McCormick grade Ib improved to grade I, and one deteriorated to grade II. Among the five patients with McCormick grade II, two remained stable, two improved to grades I and Ib, and one deteriorated to grade IV. This last patient was diagnosed with anaplastic ependymoma. All the three patients with grade III disease, including the patient with grade IV at discharge, improved to grade I (one patient) or grade II (two patients) (Table 3).
Table 2.
Comparison of the grade on the modified McCormick classification before surgery and at discharge
| M cCormick preoperative | McCormick at discharge |
Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | Ib | II | III | IV | ||
| I | 0 | |||||
| Ib | 4 | 2 | 6 | |||
| II | 2 | 3 | 5 | |||
| III | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | ||
| IV | 0 | |||||
| Total | 5 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 14 |
Table 3.
Comparison of the grade on the modified McCormick classification before surgery and at the last follow-up
| M cCormick preoperative | McCormick during follow-up |
Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | Ib | II | III | IV | ||
| I | 0 | |||||
| Ib | 5 | 1 | 6 | |||
| II | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 5 | |
| III | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
| IV | 0 | |||||
| Total | 7 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 14 |
Seven of the nine patients with preoperative radicular pain improved. This improvement did not change with time. Sensory deficits were stable in all the patients at discharge but three improved long-term until they became free of this deficit. Of the four patients with preoperative motor deficits, one showed complete recovery postoperatively, two remained unchanged (one of them had a complete recovery throughout the follow-up), and one worsened, showing a dense tetraparesis at discharge that improved to monoparesis during follow-up. Three patients without any motor deficit preoperatively suffered a motor deficit in the immediate postoperative period, being transient in one of them. Sphincter disturbances were unchanged in three patients and improved to normal function in one patient. The remaining patient suffered a profound, permanent deterioration of bladder control until it disappeared completely during follow-up. Postoperatively, one patient presented with urinary deterioration with no posterior resolution.
Discussion
Spinal cord ependymoma is a potentially curable tumor due to its good prognosis and low recurrence rate as long as complete resection is achieved [16-22]. Advances in microsurgery, neuroimaging, and intraoperative monitoring have enabled safer surgical resection. However, despite this, a high morbidity rate remains in the immediate postoperative period [19,22] This occurs first because sometimes the plane between normal tissue and the tumor is not distinguished easily, which is especially evident at the zone of the conus medullaris. Second, during ventral dissection of the tumor, there is a risk of microvasculature disruption, which, in conjunction with surgical manipulation, may lead to edema and ischemia of the spinal cord and subsequent clinical deterioration [16,22].
5-ALA is a useful tool to treat malignant brain gliomas as well as other tumors. The usefulness of 5-ALA in ependymomas already has been reported in the literature [5,7,9,12-14]. Our results showed that 5-ALA helps to identify the dissection plane between normal tissue and the tumor. This would lead to a high rate of complete resections, even in cases where the fluorescence was not intense, and minimization of damage to healthy neural tissue. The complete resection rate was 79% in our series and 70% and 80% in two series on 5-ALA [12,14]. In other wider series, in which 5-ALA was not used, the rate varies between 65% and 91.5% [15,17,20,21,23].
Regarding the functional result, 10 patients (71.4%) showed improvement, two only (14.3%) deteriorated (one had anaplastic ependymoma with subtotal resection and posterior recurrence), and two remained the same (14.3%). Millesi et al. [12] reported no data about the functional result. However, Inoue et al. [14] reported a stability rate of 30% on the McCormick classification at the end of follow-up, and an improvement rate of 70%, similar to our results. In reported series in which 5-ALA is not used, the long-term deterioration is 13.9% to 35.8% [15,16,18,24-27].
Moreover, 5-ALA also is useful as an indicator of the extent of tumor resection. In our cases in which fluorescence remained in the surgical cavity, postoperative MRI confirmed the presence of residual tumor; therefore, 5-ALA also is useful as an indicator of the extent of tumor resection (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
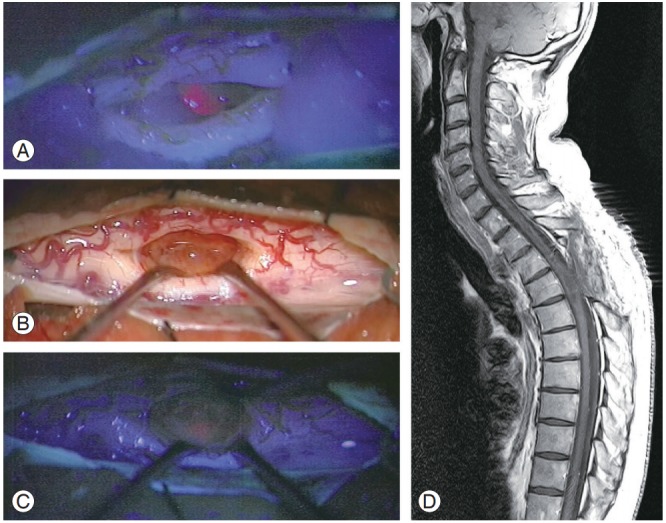
Case 4. (A) Intraoperative image with blue light showing the intense fluorescence emitted by the lesion. (B) Intraoperative image with white light in which the tumor bed is seen. (C) Intraoperative image with blue light in which no fluorescence emission is seen in the tumor bed. (D) Sagittal dorsal postoperative magnetic resonance imaging shows complete resection.
Pathologic diagnosis confirmed tumor presence in all the samples showing fluorescence emission, indicating a positive predictive value of 100%. No correlation of fluorescence with proliferation index was observed. The same occurs with other tumors of the central nervous system, such as meningiomas [28].
Deterioration of sensory function is inevitable due to the myelotomy, and studies have shown a correlation between the length of the myelotomy and postoperative sensory deficit [29,30]. As we reported previously [9], 5-ALA can help to locate the point to perform the myelotomy as well as to determine its length, which, in turn, may lead to a minor sensory function deficit (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
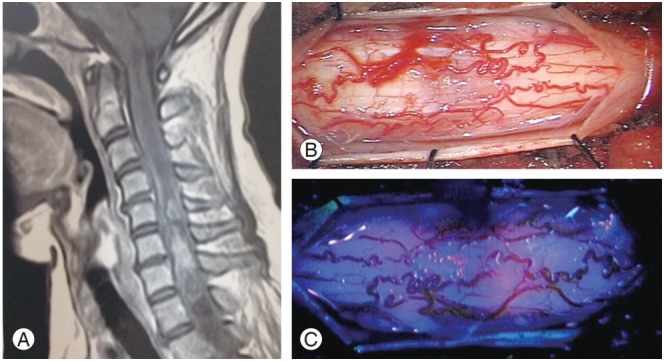
Case 7. (A) Sagittal cervicodorsal magnetic resonance imaging with gadolinium shows the lesion. (B) Intraoperative image with white light shows the spinal cord with numerous pathologic vessels on its surface. (C) Intraoperative image with blue light shows fluorescence emission before myelotomy.
Our study has some limitations. First, it is a retrospective study with a small cohort. In addition, it is not a comparative study; therefore, we believe that prospective studies comparing cohorts without and with 5-ALA are necessary.
Conclusions
5-ALA fluorescence-guided resection seems to be a useful tool for the resection of spinal cord ependymomas, because it permits identification of the plane of cleavage between the tumor and normal tissue and minimizes the risks of a spinal cord lesion. In many cases, it showed us the point to perform the myelotomy.
Footnotes
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Author contributions
Conception and design: Rafael García Moreno, Luis Miguel Bernal García; data acquisition: Rafael García Moreno, Hyaissa Ippolito Bastidas, Carlos Andrés Mondragón Tirado, Aurora Moreno Flores, Juan Pablo Sosa Cabezas; analysis of data: Rafael García Moreno, Hyaissa Ippolito Bastidas; drafting of the manuscript: Rafael García Moreno, José Manuel Cabezudo Artero; critical revision: Rafael García Moreno, Luis Miguel Bernal García, Hyaissa Ippolito Bastidas, Carlos Andrés Mondragón Tirado, Aurora Moreno Flores, Juan Pablo Sosa Cabezas, José Manuel Cabezudo Artero; and supervision: José Manuel Cabezudo Artero
References
- 1.Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK. WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. 4th ed. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer Press; 2007. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Miller DC. Surgical pathology of intramedullary spinal cord neoplasms. J Neurooncol. 2000;47:189–94. doi: 10.1023/a:1006496204396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Samii M, Klekamp J. Surgical results of 100 intramedullary tumors in relation to accompanying syringomyelia. Neurosurgery. 1994;35:865–73. doi: 10.1227/00006123-199411000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Stummer W, Pichlmeier U, Meinel T, et al. Fluorescence-guided surgery with 5-aminolevulinic acid for resection of malignant glioma: a randomised controlled multicentre phase III trial. Lancet Oncol. 2006;7:392–401. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(06)70665-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Arai T, Tani S, Isoshima A, et al. Intraoperative photodynamic diagnosis for spinal ependymoma using 5-aminolevulinic acid: technical note. No Shinkei Geka. 2006;34:811–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kajimoto Y, Kuroiwa T, Miyatake S, et al. Use of 5-aminolevulinic acid in fluorescence-guided resection of meningioma with high risk of recurrence: case report. J Neurosurg. 2007;106:1070–4. doi: 10.3171/jns.2007.106.6.1070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Shimizu S, Utsuki S, Sato K, Oka H, Fujii K, Mii K. Photodynamic diagnosis in surgery for spinal ependymoma: case illustration. J Neurosurg Spine. 2006;5:380. doi: 10.3171/spi.2006.5.4.380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Utsuki S, Miyoshi N, Oka H, et al. Fluorescence-guided resection of metastatic brain tumors using a 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced protoporphyrin IX: pathological study. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2007;24:53–5. doi: 10.1007/s10014-007-0223-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bernal-Garcia LM, Cabezudo-Artero JM, Ortega-Martinez M, et al. Fluorescence-guided resection with 5-aminolevulinic acid of an intramedullary tumor. Neurocirugia (Astur) 2010;21:312–6. doi: 10.4321/s1130-14732010000400004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bernal Garcia LM, Cabezudo Artero JM, Marcelo Zamorano MB, Gilete Tejero I. Fluorescence-guided resection with 5-aminolevulinic acid of subependymomas of the fourth ventricle: report of 2 cases: technical case report. Neurosurgery. 2015;11 Suppl 2:E364–71. doi: 10.1227/NEU.0000000000000682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Utsuki S, Oka H, Sato K, Shimizu S, Suzuki S, Fujii K. Fluorescence diagnosis of tumor cells in hemangioblastoma cysts with 5-aminolevulinic acid. J Neurosurg. 2010;112:130–2. doi: 10.3171/2009.5.JNS08442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Millesi M, Kiesel B, Woehrer A, et al. Analysis of 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced fluorescence in 55 different spinal tumors. Neurosurg Focus. 2014;36:E11. doi: 10.3171/2013.12.FOCUS13485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Eicker SO, Floeth FW, Kamp M, Steiger HJ, Hanggi D. The impact of fluorescence guidance on spinal intradural tumour surgery. Eur Spine J. 2013;22:1394–401. doi: 10.1007/s00586-013-2657-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Inoue T, Endo T, Nagamatsu K, Watanabe M, Tominaga T. 5-Aminolevulinic acid fluorescence-guided resection of intramedullary ependymoma: report of 9 cases. Neurosurgery. 2013;72(2 Suppl Operative):ons159–68. doi: 10.1227/NEU.0b013e31827bc7a3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Aghakhani N, David P, Parker F, Lacroix C, Benoudiba F, Tadie M. Intramedullary spinal ependymomas: analysis of a consecutive series of 82 adult cases with particular attention to patients with no preoperative neurological deficit. Neurosurgery. 2008;62:1279–85. doi: 10.1227/01.neu.0000333299.26566.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chang UK, Choe WJ, Chung SK, Chung CK, Kim HJ. Surgical outcome and prognostic factors of spinal intramedullary ependymomas in adults. J Neurooncol. 2002;57:133–9. doi: 10.1023/a:1015789009058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lin YH, Huang CI, Wong TT, et al. Treatment of spinal cord ependymomas by surgery with or without postoperative radiotherapy. J Neurooncol. 2005;71:205–10. doi: 10.1007/s11060-004-1386-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kucia EJ, Bambakidis NC, Chang SW, Spetzler RF. Surgical technique and outcomes in the treatment of spinal cord ependymomas, part 1: intramedullary ependymomas. Neurosurgery. 2011;68(1 Suppl Operative):57–63. doi: 10.1227/NEU.0b013e318208f181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Constantini S, Miller DC, Allen JC, Rorke LB, Freed D, Epstein FJ. Radical excision of intramedullary spinal cord tumors: surgical morbidity and long-term follow-up evaluation in 164 children and young adults. J Neurosurg. 2000;93(2 Suppl):183–93. doi: 10.3171/spi.2000.93.2.0183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Nakamura M, Ishii K, Watanabe K, et al. Surgical treatment of intramedullary spinal cord tumors: prognosis and complications. Spinal Cord. 2008;46:282–6. doi: 10.1038/sj.sc.3102130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Raco A, Esposito V, Lenzi J, Piccirilli M, Delfini R, Cantore G. Long-term follow-up of intramedullary spinal cord tumors: a series of 202 cases. Neurosurgery. 2005;56:972–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Nagasawa DT, Smith ZA, Cremer N, Fong C, Lu DC, Yang I. Complications associated with the treatment for spinal ependymomas. Neurosurg Focus. 2011;31:E13. doi: 10.3171/2011.7.FOCUS11158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bostrom A, von Lehe M, Hartmann W, et al. Surgery for spinal cord ependymomas: outcome and prognostic factors. Neurosurgery. 2011;68:302–8. doi: 10.1227/NEU.0b013e3182004c1e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Klekamp J. Spinal ependymomas: part 1: intramedullary ependymomas. Neurosurg Focus. 2015;39:E6. doi: 10.3171/2015.5.FOCUS15161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hanbali F, Fourney DR, Marmor E, et al. Spinal cord ependymoma: radical surgical resection and outcome. Neurosurgery. 2002;51:1162–72. doi: 10.1097/00006123-200211000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ohata K, Takami T, Gotou T, et al. Surgical outcome of intramedullary spinal cord ependymoma. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1999;141:341–6. doi: 10.1007/s007010050309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lee J, Parsa AT, Ames CP, McCormick PC. Clinical management of intramedullary spinal ependymomas in adults. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2006;17:21–7. doi: 10.1016/j.nec.2005.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Della Puppa A, Rustemi O, Gioffre G, et al. Predictive value of intraoperative 5-aminolevulinic acidinduced fluorescence for detecting bone invasion in meningioma surgery. J Neurosurg. 2014;120:840–5. doi: 10.3171/2013.12.JNS131642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ebner FH, Roser F, Falk M, Hermann S, Honegger J, Tatagiba M. Management of intramedullary spinal cord lesions: interdependence of the longitudinal extension of the lesion and the functional outcome. Eur Spine J. 2010;19:665–9. doi: 10.1007/s00586-009-1232-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Li TY, Chu JS, Xu YL, et al. Surgical strategies and outcomes of spinal ependymomas of different lengths: analysis of 210 patients: clinical article. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014;21:249–59. doi: 10.3171/2014.3.SPINE13481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


