ABSTRACT
Background
Mitochondrial dysfunction is an important component of the aging process and has been implicated in the development of many human diseases. Mitochondrial DNA copy number (mtDNAcn), an indirect biomarker of mitochondrial function, is sensitive to oxidative damage. Few population-based studies have investigated the impact of fruit and vegetable consumption and cigarette smoke (2 major sources of exogenous antioxidants and oxidants) on leukocyte mtDNAcn.
Objectives
We investigated the association between fruit and vegetable consumption, cigarette smoke, and leukocyte mtDNAcn based on data from the Nurses’ Health Study (NHS).
Methods
Data from 2769 disease-free women in the NHS were used to examine the cross-sectional associations between dietary sources of antioxidants, cigarette smoke, and leukocyte mtDNAcn. In vitro cell-based experiments were conducted to support the findings from the population-based study.
Results
In the multivariable-adjusted model, both whole-fruit consumption and intake of flavanones (a group of antioxidants abundant in fruit) were positively associated with leukocyte mtDNAcn (P-trend = 0.005 and 0.02, respectively), whereas pack-years of smoking and smoking duration were inversely associated with leukocyte mtDNAcn (P-trend = 0.01 and 0.007, respectively). These findings are supported by in vitro cell-based experiments showing that the administration of naringin, a major flavanone in fruit, led to a substantial increase in mtDNAcn in human leukocytes, whereas exposure to nicotine-derived nitrosamine ketone, a key carcinogenic ingredient of cigarette smoke, resulted in a significant decrease in mtDNAcn of cells (all P < 0.05). Further in vitro studies showed that alterations in leukocyte mtDNAcn were functionally linked to the modulation of mitochondrial biogenesis and function.
Conclusions
Fruit consumption and intake of dietary flavanones were associated with increased leukocyte mtDNAcn, whereas cigarette smoking was associated with decreased leukocyte mtDNAcn, which is a promising biomarker for oxidative stress–related health outcomes.
Keywords: cigarette smoke, fruit, mitochondrial DNA copy number, oxidative stress; leukocyte
Introduction
Oxidative stress reflects a state of physiologic imbalance between production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and a biological system's antioxidant defense to repair the resulting damage (1). Mitochondria are intracellular organelles in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic organisms with a number of functions, including energy metabolism, free-radical production, and apoptosis (2). Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is known to be more sensitive to oxidative damage than nuclear DNA due to its lack of protective histones, introns, and efficient DNA repair mechanisms. Increased oxidative stress may contribute to alterations in the copy number and integrity of mtDNA in human cells (3–7).
Within a certain level, ROS may induce stress responses by altering the expression of specific nuclear genes in order to uphold the energy metabolism to rescue the cell. Once beyond the threshold, ROS may cause oxidative damage to the mtDNA of the affected cells (8). In contrast, antioxidants have been shown to reduce mitochondrial damage and increase mitochondrial biogenesis and mtDNA copy number (mtDNAcn) (9, 10). Both mitochondrial structural and functional alterations have been implicated in the pathogenesis of human diseases, including premature aging, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disease (1, 11–15). Epidemiologic studies have linked reduced leukocyte mtDNAcn with a range of adverse clinical outcomes, including all-cause mortality, coronary heart disease and sudden cardiac death, metabolic syndrome, and chronic kidney disease (16–20). Therefore, mtDNAcn may serve as a promising biomarker for oxidative stress–related health outcomes.
Although alterations in leukocyte mtDNAcn have been associated with several environmental and lifestyle factors, including plasma antioxidants and pro-oxidants (21) and BMI and weight change (22), the spectrum of factors that affect mtDNAcn is not fully understood. In particular, few population-based studies to date have investigated in detail the impact of fruit and vegetable consumption and cigarette smoke on leukocyte mtDNAcn. Because fruit and vegetable consumption and smoking are major sources of exogenous antioxidants (e.g., flavonoids, vitamin C) and oxidants, respectively (23–26), we hypothesized that 1) fruit and vegetable consumption would be associated with higher leukocyte mtDNAcn and 2) cigarette smoking would be associated with lower leukocyte mtDNAcn. In particular, flavonoids are a group of phytochemicals (e.g., flavanonols, flavones, flavanones, flavan-3-ols, anthocyanidins) with antioxidant properties (25, 27). To address the questions of interest, we investigated the associations between fruit and vegetables, dietary antioxidants, cigarette smoke, and leukocyte mtDNAcn using data on 2769 healthy women from the Nurses’ Health Study (NHS).
We sought to find evidence to support the above population-based findings using in vitro cell-based experimental models: exposing human peripheral blood–derived leukocytes to naringin, a major flavanone in citrus fruit, and 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone [nicotine-derived nitrosamine ketone (NNK)], a key ingredient of cigarette smoke, which are representative active components of such exogenous antioxidants and oxidants. We considered cellular ROS as a potential candidate to link environmental factors and mtDNAcn, because mtDNAcn is closely associated with cellular ROS and redox status (3–5, 9, 10, 21) and fruit consumption and cigarette smoke are considered to be the primary sources of exogenous antioxidants and oxidants, respectively, which ultimately contribute to alterations in cellular ROS generation and redox potential (23–25).
Methods
Study population
Our study was designed as a cross-sectional study based on the NHS, established in 1976 when 121,700 registered nurses aged 30–50 y residing in 11 US states completed a baseline questionnaire related to risk factors for cardiovascular disease and cancer and thereafter have been updating their information on environmental and lifestyle factors and medical history biennially. Between 1989 and 1990, blood samples were collected from 32,826 members of the NHS. Women who provided blood samples were similar demographically to those who did not (28). In this study, we included controls (n = 2769) from 3 nested case-control studies for lung cancer (n = 321), skin cancer (including basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma; n = 1385), and colorectal cancer (n = 1063) from the NHS (22, 29, 30). A flow chart for derivation of the study population is shown in Supplemental Figure 1. All participants are Caucasian women with both dietary intake and smoking information at blood collection. The institutional review board of Brigham and Women's Hospital approved this study.
Assessment of dietary factors, smoking, and other covariates in the NHS
A detailed description is provided in Supplemental Methods. Briefly, dietary data assessed using a validated food-frequency questionnaire (FFQ) were derived from the questionnaire administered in 1990, with missing information substituted from the 1986 questionnaire. Participants were asked how often, on average (never to ≥6 servings/d), during the previous year they had consumed each food item on the FFQ. Total fruit and vegetable intakes were calculated as the sum of intakes of 16 and 27 items, respectively; the intake of citrus products was calculated as the sum of intakes of oranges, orange juice, grapefruit, and grapefruit juice. Using the food-composition database of the USDA, we calculated the total intake of each nutrient (i.e., flavonoids and vitamins C and E) by summing the nutrient content for a specific amount of each food during the previous year multiplied by a weight proportional to the frequency of its consumption. Dietary intake collected using the FFQ as mentioned above has been shown to be a valid estimate of relative food and nutrient intakes when compared with multiple diet records (31, 32). For example, the overall mean correlation coefficient comparing intakes of 18 nutrients measured by the FFQ and by diet record was 0.60 (32).
Lifestyle and anthropometric data were derived from the questionnaire administered closest to the time of blood draw, with missing information substituted from previous questionnaires. Smoking status (never, past, or current) and number of cigarettes smoked among current smokers were assessed biennially starting at baseline (1976). Duration of smoking was calculated as the difference between age at smoking initiation and current age for current smokers and between ages at onset and cessation for past smokers. We multiplied the number of packs of cigarettes smoked per day by the number of years of smoking to estimate pack-years of smoking. The number of years since cessation was obtained for past smokers by deducting the age at which they quit smoking from their current age.
Assessment of mtDNAcn in leukocytes in the NHS
For blood samples from the NHS participants, genomic DNA was extracted from buffy-coat fractions using the QIAmp (Qiagen) 96-spin blood protocol. DNA concentrations were determined via pico-green quantitation using a Molecular Devices 96-well spectrophotometer. Relative leukocyte mtDNAcn was determined using a quantitative polymerase chain reaction–based method. More details are shown in Supplemental Methods.
In vitro laboratory experiments
The detailed descriptions with regard to in vitro cell culture, chemical treatment, measurements of mtDNAcn, and biomarkers of mitochondrial biogenesis and function (e.g., mRNA and ATP levels), as well as measurement of redox status and cellular ROS, are provided in Supplemental Methods. Briefly, total DNA was extracted from the human peripheral blood–derived leukocyte cell line HL-60. The cells were grown in Roswell Park Memorial Institute 1640 medium (Thermo Scientific, Inc.). Naringin and NNK were added to the cultured cells for 24 h. We used real-time polymerase chain reaction to quantify mtDNAcn. Four genes, including nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide dehydrogenase subunit 1 (ND1), nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide dehydrogenase subunit 2 (ND2), cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (COI), and cytochrome c oxidase subunit II (COII), were used to represent mtDNAcn (33, 34). Total RNA isolated from HL-60 cells was used to measure mRNA levels for a mitochondrial fusion gene, Opa1, and a mitochondrial fission gene, Drp1 (35, 36). We determined the concentrations of total glutathione (GSH), oxidized glutathione (GSSG), NAD(P)H, lipid peroxidation products (thiobarbituric acid reactive substances), and intracellular peroxide (H2O2) using the previously described methods (37–40).
Statistical analysis
Leukocyte mtDNAcn was measured in various batches over several data sets in the NHS. To minimize the influence of potential batch effect on mtDNAcn measurements across different data sets, we calculated z scores of log-transformed mtDNAcn for each sample on the basis of their relative distribution in each data set (22). Levene's test for homogeneity showed statistically homogeneous distributions of the z scores from different data sets (P = 0.99).
We calculated age-adjusted participant demographic and lifestyle characteristics and age- and energy-adjusted nutrient intakes across quartiles of the leukocyte mtDNAcn z score. Spearman's age-adjusted partial rank correlation coefficients were calculated to examine the correlations of leukocyte mtDNAcn with dietary and smoking-related variables. Multivariable-adjusted generalized linear regression models were used to evaluate the associations between dietary factors, cigarette smoke, and leukocyte mtDNAcn, controlling for a range of covariates. We calculated least-squares mean leukoctye mtDNAcn z scores over categories of dietary factors and cigarette smoke with adjustment for the same covariates. We tested for linear trend across quartiles for a given continuous variable by assigning median values for these quartiles and treating the new variable as a continuous term in the models. Bonferroni correction for P values was applied for multiple comparisons for individual food item, nutrient, and smoking variables, and was calculated as 0.05/n (n = 6, 8, and 3, respectively). We also examined the potential interaction between fruit consumption and smoking by adding a cross-product interaction term in the model with the main effects of these 2 variables.
For data obtained from the in vitro experiments, Wilcoxon's rank-sum test was used to examine the difference between the treatment group and control group. All of the analyses were performed using SAS 9.2 software, and significance was set at P < 0.05 (2-sided).
Results
Participant characteristics
Table 1 shows the descriptive characteristics of the 2769 women according to leukocyte mtDNAcn quartiles. Leukocyte mtDNAcn z-score quartiles were generally similar with respect to age and total calorie intake, whereas there were decreasing trends in the proportion of current smokers, pack-years of smoking, and smoking duration and increasing trends in smoking cessation and intakes of total fruit and flavanones across the leukocyte mtDNAcn quartiles. Conversely, there was an increasing trend in leukocyte mtDNAcn z score across the total fruit consumption quartiles (Supplemental Table 1).
TABLE 1.
Age-standardized characteristics at blood draw by quartiles of mitochondrial DNA copy number (z score) in 2769 women in the Nurses’ Health Study (1990)1
| Quartile 1 (n = 692) | Quartile 2 (n = 692) | Quartile 3 (n = 693) | Quartile 4 (n = 692) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median of z score | −1.10 | −0.32 | 0.27 | 1.10 |
| Age at blood draw, y | 58.9 ± 6.7 | 58.4 ± 6.7 | 58.8 ± 6.9 | 58.5 ± 6.7 |
| BMI at blood draw, kg/m2 | 25.7 ± 4.8 | 25.6 ± 4.8 | 25.5 ± 4.4 | 25.1 ± 4.4 |
| Physical activity, METs/wk | 14.6 ± 17.8 | 13.7 ± 15.9 | 16.1 ± 19.1 | 15.8 ± 18.2 |
| Postmenopausal hormone use,2 % | 47.3 | 47.1 | 41.7 | 45.2 |
| Dietary factors | ||||
| Total calories, kcal/d | 1747 ± 490 | 1764 ± 501 | 1785 ± 521 | 1747 ± 495 |
| Alcohol, g/d | 5.6 ± 10.3 | 5.2 ± 9.3 | 5.2 ± 9.4 | 6.0 ± 10.4 |
| Total fruit, servings/d | 2.4 ± 1.5 | 2.5 ± 1.5 | 2.5 ± 1.4 | 2.5 ± 1.3 |
| Whole fruit, servings/d | 1.7 ± 1.3 | 1.7 ± 1.1 | 1.8 ± 1.1 | 1.7 ± 1.0 |
| Fruit juices, servings/d | 0.7 ± 0.7 | 0.7 ± 0.8 | 0.7 ± 0.7 | 0.7 ± 0.7 |
| Citrus products, servings/d | 0.8 ± 0.8 | 0.8 ± 0.7 | 0.9 ± 0.7 | 0.8 ± 0.7 |
| Total vegetables, servings/d | 3.9 ± 2.0 | 3.9 ± 1.9 | 4.0 ± 2.2 | 3.9 ± 2.0 |
| Total flavonoids, mg/d | 376 ± 380 | 373 ± 352 | 356 ± 321 | 361 ± 331 |
| Flavonols, mg/d | 18.9 ± 13.3 | 18.6 ± 12.5 | 18.5 ± 12.4 | 18.5 ± 11.9 |
| Flavones, mg/d | 1.8 ± 1.4 | 1.8 ± 1.4 | 1.8 ± 1.4 | 1.8 ± 1.4 |
| Flavanones, mg/d | 37.4 ± 36.9 | 37.7 ± 33.5 | 39.7 ± 35.3 | 40.8 ± 35.5 |
| Flavan-3-ols, mg/d | 59.8 ± 85.6 | 59.2 ± 78.8 | 54.1 ± 70.6 | 55.6 ± 73.4 |
| Anthocyanidins, mg/d | 11.1 ± 14.7 | 10.3 ± 11.7 | 10.0 ± 10.4 | 10.5 ± 11.6 |
| Vitamin C, mg/d | 330.8 ± 382.1 | 313.1 ± 343.8 | 319.7 ± 333.9 | 322.6 ± 371.2 |
| Vitamin E, mg/d | 72.7 ± 159.5 | 79.3 ± 179.0 | 81.4 ± 177.0 | 87.2 ± 193.2 |
| Cigarette smoking | ||||
| Never smoker, % | 41.6 | 40.4 | 46.9 | 44.4 |
| Past smoker, % | 36.0 | 38.4 | 39.7 | 39.8 |
| Current smoker, % | 22.4 | 21.2 | 13.4 | 15.7 |
| Pack-years3 | 28.8 (21.5) | 28.4 (21.6) | 24.4 (21.1) | 25.0 (21.3) |
| Smoking duration,3 y | 27.1 (12.6) | 26.6 (13.1) | 23.9 (12.5) | 24.8 (13.0) |
| Smoking cessation,4 y | 14.9 (11.3) | 16.0 (11.2) | 16.7 (10.7) | 16.4 (10.7) |
1Values are means ± SDs or percentages and are standardized to the age distribution of the study population. MET, metabolic equivalent task.
2Among postmenopausal women.
3Among ever smokers.
4 Among past smokers.
Correlations between dietary factors, cigarette smoke, and leukocyte mtDNAcn
Age-adjusted Spearman correlation analyses showed modest but significant positive correlations between leukocyte mtDNAcn and the consumption of total fruit, whole fruit, citrus products, flavones, and flavanones (Table 2). Leukocyte mtDNAcn was also negatively correlated with pack-years of smoking and smoking duration among ever smokers. After correction for multiple comparisons, the significant correlations remained for total fruit, whole fruit, flavanones, pack-years of smoking, and smoking duration.
TABLE 2.
Age-adjusted Spearman correlations between dietary factors, cigarette smoking, and mitochondrial DNA copy number (z score) in 2769 women in the Nurses’ Health Study
| Correlation coefficient | Nominal P | |
|---|---|---|
| Food items | ||
| Total fruit | 0.05 | 0.0061 |
| Whole fruit | 0.06 | 0.0041 |
| Fruit juices | 0.02 | 0.22 |
| Citrus products | 0.05 | 0.009 |
| Total vegetables | 0.01 | 0.67 |
| Nutrients | ||
| Total flavonoids | 0.01 | 0.71 |
| Flavonols | 0.01 | 0.74 |
| Flavones | 0.04 | 0.02 |
| Flavanones | 0.06 | 0.0031 |
| Flavan-3-ols | −0.001 | 0.98 |
| Anthocyanidins | 0.01 | 0.47 |
| Vitamin C | 0.02 | 0.40 |
| Vitamin E | 0.01 | 0.60 |
| Cigarette smoking | ||
| Pack-years2 | −0.08 | 0.0021 |
| Smoking duration,2 y | −0.08 | 0.0021 |
| Smoking cessation,3 y | 0.05 | 0.08 |
1Significant after correction for multiple comparisons: P < 0.008, 0.006, and 0.017 for food items, nutrients, and smoking variables, respectively.
2Among ever smokers.
3Among past smokers.
Associations between dietary factors, cigarette smoke, and leukocyte mtDNAcn
We found a significant positive association between total fruit consumption and leukocyte mtDNAcn in the model adjusting for age, smoking, and other dietary and lifestyle factors (P-trend = 0.02; Table 3). Interestingly, this association between total fruit and leukocyte mtDNAcn z score appeared to be driven by whole fruit (P-trend = 0.005) but not fruit juices, and only whole fruit remained significant after correction for multiple comparisons. Among dietary nutrients, the intake of flavanones was significantly and positively associated with leukocyte mtDNAcn (P-trend = 0.02), and the major food source of flavanones, citrus products, was also positively associated with leukocyte mtDNAcn (P-trend = 0.04). Individual fruit items, however, showed less-consistent associations with leukocyte mtDNAcn and lost significance after the correction for multiple comparisons (Supplemental Table 2).
TABLE 3.
Least-squares means of mitochondrial DNA copy number (z score) according to dietary factors in 2769 women in the Nurses’ Health Study1
| Quartile 1 | Quartile 2 | Quartile 3 | Quartile 4 | Nominal P- trend | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SE | P | Mean ± SE | P | Mean ± SE | P | Mean ± SE | P | ||
| Food items | |||||||||
| Total fruit | −0.09 ± 0.05 | Ref | 0.02 ± 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.005 ± 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.07 ± 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| Whole fruit | −0.06 ± 0.05 | Ref | −0.05 ± 0.04 | 0.79 | 0.02 ± 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.09 ± 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.0052 |
| Fruit juices | −0.002 ± 0.04 | Ref | −0.07 ± 0.05 | 0.23 | 0.03 ± 0.04 | 0.56 | 0.03 ± 0.04 | 0.58 | 0.16 |
| Citrus products | −0.11 ± 0.04 | Ref | 0.05 ± 0.04 | 0.004 | 0.01 ± 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 ± 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.04 |
| Total vegetables | 0.01 ± 0.05 | Ref | −0.05 ± 0.04 | 0.30 | 0.04 ± 0.04 | 0.49 | −0.002 ± 0.05 | 0.89 | 0.76 |
| Nutrients | |||||||||
| Total flavonoids | −0.02 ± 0.04 | Ref | 0.04 ± 0.04 | 0.22 | 0.003 ± 0.04 | 0.61 | −0.02 ± 0.04 | 0.94 | 0.62 |
| Flavonols | −0.03 ± 0.04 | Ref | 0.01 ± 0.04 | 0.47 | 0.05 ± 0.04 | 0.17 | −0.03 ± 0.04 | 0.91 | 0.71 |
| Flavones | −0.09 ± 0.04 | Ref | 0.02 ± 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.05 ± 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.09 |
| Flavanones | −0.06 ± 0.04 | Ref | −0.01 ± 0.04 | 0.35 | −0.002 ± 0.04 | 0.27 | 0.07 ± 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Flavan-3-ols | −0.001 ± 0.04 | Ref | 0.02 ± 0.04 | 0.64 | 0.002 ± 0.04 | 0.97 | −0.03 ± 0.04 | 0.63 | 0.42 |
| Anthocyanidins | −0.04 ± 0.04 | Ref | 0.01 ± 0.04 | 0.41 | 0.05 ± 0.04 | 0.13 | −0.03 ± 0.04 | 0.85 | 0.99 |
| Vitamin C, mg/d | −0.04 ± 0.04 | Ref | −0.003 ± 0.04 | 0.55 | 0.06 ± 0.04 | 0.07 | −0.03 ± 0.04 | 0.89 | 0.65 |
| Vitamin E, IU/d | −0.004 ± 0.05 | Ref | −0.02 ± 0.04 | 0.74 | −0.01 ± 0.04 | 0.90 | 0.04 ± 0.04 | 0.45 | 0.26 |
1Generalized linear regression models with adjustment for age at blood draw, pack-years of smoking, menopausal status, postmenopausal hormone use, BMI, physical activity, and intakes of total calories and alcohol were used. Ref, reference.
2Significant after correction for multiple comparisons: P < 0.008 and 0.006 for food items and nutrients, respectively.
We found a generally consistent association pattern for smoking-related variables and leukocyte mtDNAcn z score (Table 4). Pack-years of smoking and smoking duration were significantly and inversely associated with leukocyte mtDNAcn z score (P-trend = 0.01 and 0.007, respectively), but only smoking duration remained significant after correction for multiple comparisons. There was no significant interaction between fruit consumption and smoking for their potential effects on mtDNAcn (data not shown).
TABLE 4.
Least-squares means of mitochondrial DNA copy number (z score) according to cigarette smoking in 2769 women in the Nurses’ Health Study1
| Mean ± SE | P | Nominal P-trend | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smoking status | — | ||
| Never | 0.03 ± 0.04 | Ref | |
| Past | 0.03 ± 0.04 | 0.93 | |
| Current: 1–24 cigarettes/d | −0.17 ± 0.06 | 0.001 | |
| Current: ≥25 cigarettes/d | −0.11 ± 0.09 | 0.12 | |
| Pack-years | 0.01 | ||
| Never | 0.03 ± 0.04 | Ref | |
| 1–15 | 0.06 ± 0.05 | 0.60 | |
| 16–30 | −0.11 ± 0.06 | 0.02 | |
| >30 | −0.06 ± 0.05 | 0.05 | |
| Smoking duration, y | 0.0072 | ||
| Never | 0.04 ± 0.04 | Ref | |
| 1–15 | 0.06 ± 0.05 | 0.64 | |
| 16–30 | −0.002 ± 0.05 | 0.49 | |
| >30 | −0.10 ± 0.05 | 0.007 | |
| Smoking cessation,3 y | 0.74 | ||
| Never | 0.03 ± 0.04 | Ref | |
| >30 | 0.001 ± 0.05 | 0.65 | |
| 16–30 | 0.07 ± 0.05 | 0.42 | |
| 1–15 | −0.05 ± 0.10 | 0.45 |
1Generalized linear regression models with adjustment for age at blood draw, menopausal status, postmenopausal hormone use, BMI, physical activity, and intakes of total calories, alcohol, and whole fruit were used. Ref, reference.
2Significant after correction for multiple comparisons, P < 0.017.
3Never smokers were excluded from the trend test.
In vitro experiments for dietary antioxidants, cigarette smoke, and leukocyte mtDNAcn
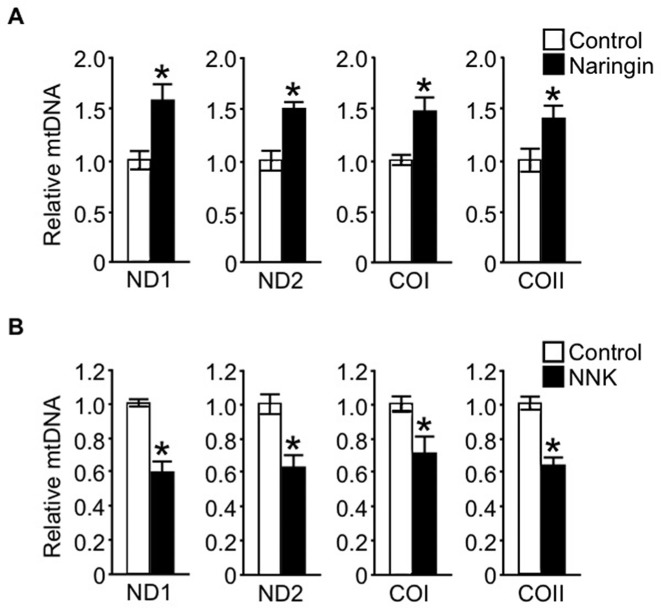
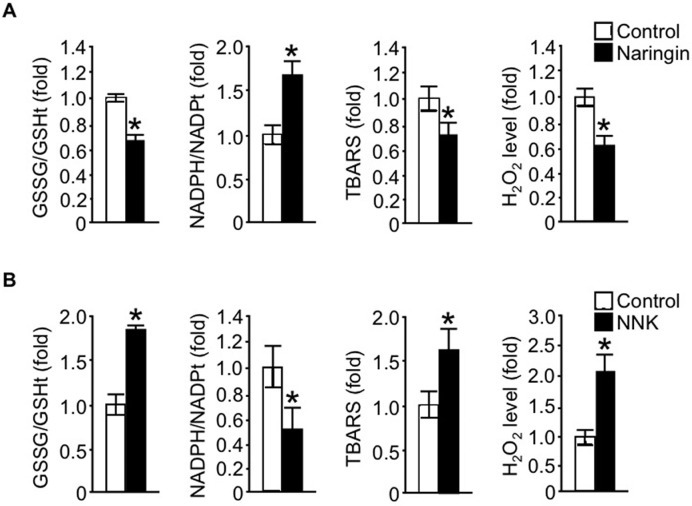
To provide an insight into the nature of the associations reported herein, we examined the direct beneficial effect of naringin, a major flavanone in citrus fruit, on mtDNAcn in the human peripheral blood–derived leukocyte cell line HL-60. Our results showed that naringin treatment resulted in a marked increase in mtDNAcn (Figure 1A) as well as mitochondrial biogenesis and function (Supplemental Figure 2A) compared with that in control cells. The positive association of naringin with mtDNAcn correlated with redox status and subsequent intracellular ROS production of the cells. As shown in Figure 2A, naringin significantly improved the cellular redox status as reflected by increases in GSH and NAD(P)H levels and decreased levels of lipid peroxidation (thiobarbituric acid reactive substances), an indicative marker of cellular oxidative stress, compared with that in control cells, which consequently led to a substantial reduction in cellular ROS generation.
FIGURE 1.
Effect of naringin and NNK on mtDNAcn in HL-60 cells. Cells were treated with 100 μM naringin (A) or 200 μM NNK (B) for 24 h, and the relative mtDNAcn was analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR with a specific primer against mtDNA and β-actin, as described in Methods. The mtDNA genes ND1, ND2, COI, and COII were used to represent mtDNAcn. Values are means ± SDs from 3 independent experiments. *Different from control, P < 0.05 (Wilcoxon's rank-sum test). COI, cytochrome c oxidase subunit I; COII, cytochrome c oxidase subunit II; mtDNAcn, mitochondrial DNA copy number; ND1, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide dehydrogenase subunit 1; ND2, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide dehydrogenase subunit 2; NNK, nicotine-derived nitrosamine ketone; PCR, polymerase chain reaction.
FIGURE 2.
Effect of naringin and NNK on intracellular ROS in the leukocytes. The ratio of GSSG compared with total GSH concentration, ratio of NAD(P)H compared with total NAD(P) concentration, TBARS assay for assessment of lipid peroxidation products, and intracellular peroxide production were measured in the HL-60 cells after the treatment with 100 μM naringin (A) or 200 μM NNK (B) for 24 h. Values represent the fold change over the levels observed in the control and are shown as means ± SDs of 3 independent experiments. *Different from control, P < 0.05 (Wilcoxon's rank-sum test). GSH, glutathione; GSHt, total glutathione; GSSG, oxidized glutathione; H2O2, intracellular peroxide; NADPt, total NAD(P); NNK, nicotine-derived nitrosamine ketone; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TBARS, thiobarbituric acid reactive substance.
In contrast, a substantial decrease in mtDNAcn (Figure 1B), consistent with defective mitochondrial biogenesis and impaired mitochondrial function (Supplemental Figure 2B), was observed in comparison to the control when the leukocytes were exposed to NNK, the key carcinogenic ingredient of cigarette smoke. Furthermore, the results in Figure 2B showed that exposure of the cells to NNK led to an impairment in the cellular redox status compared with that in the control in parallel with excessive production of intracellular ROS and ROS-related oxidative stress, indicating the causal relation between the cellular-redox imbalance and the decrease in mtDNAcn induced by NNK exposure.
Discussion
On the basis of detailed data on 2769 healthy women from a well-characterized cohort, our study provided a comprehensive evaluation of the association between fruit and vegetables, dietary antioxidants, and cigarette smoke and leukocyte mtDNAcn, a potential biomarker of oxidative stress–related clinical outcomes. Our study found that fruit consumption was positively associated with leukocyte mtDNAcn, whereas cigarette smoke was inversely associated with leukocyte mtDNAcn. In addition, the consumption of whole fruit and the intake of flavanones were both positively associated with leukocyte mtDNAcn. These findings observed in NHS participants are supported by in vitro cell-based experiments showing that exposure to a major flavanone in the fruit (i.e., naringin) could result in an increase in mtDNAcn in human peripheral blood–derived leukocytes, whereas exposure to a key carcinogenic ingredient of cigarette smoke, specifically NNK, could cause a decrease in mtDNAcn of the cells. Moreover, our in vitro studies showed that alterations in mtDNAcn were functionally linked to the modulation of mitochondrial biogenesis and function in leukocytes.
Oxidative stress is characterized by the presence of a large number of ROS such as superoxide anions and hydroxyl radicals, which can be generated by cigarette smoke (41). Cigarette smoke can release multiple toxic compounds to cause a series of cellular abnormalities, including DNA damage, inflammation, and oxidative stress (42). Mitochondria are sensitive to oxidative stress and cannot remove or repair DNA damage caused to them by ROS. To compensate for this damage, healthy mitochondria increase their DNA copy number in response to trans-acting factors (i.e., potential factors that regulate the replication and transcription of mtDNA and the processing of mtRNA) encoded by nuclear DNA (8, 43). However, extensive oxidative stress may surpass mitochondrial capacity to compensate for oxidative damage and reduce mtDNA content. A previous human study determined that, compared with nonsmokers, the mtDNA content in the lung tissue of light smokers was slightly higher but among heavy smokers was significantly lower (6). In support of this, an animal study also found that perinatal environmental tobacco smoke exposure resulted in significantly increased oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction and damage, which were accompanied by significantly decreased mitochondrial antioxidant capacity and mtDNAcn in vascular tissue along with increased mitochondrial damage in buffy-coat tissues in nonhuman primates (7).
Smoking is a risk factor for a wide range of clinical conditions, including cardiovascular disease (26), diabetes (44), metabolic syndrome (45), chronic kidney disease (46), and neurodegenerative disease (47); and smoking-related oxidative stress has been implicated in the pathogenesis of many of these diseases (26, 42, 48). As a promising biomarker of oxidative stress, alterations in leukocyte mtDNAcn have been associated with increased risk of a range of adverse clinical outcomes (16, 17, 19, 20, 49, 50). Our study provides a relatively comprehensive evaluation of the association between smoking and leukocyte mtDNAcn using detailed information on smoking status, pack-years of smoking, smoking duration, and smoking cessation and found generally consistent negative correlations and inverse associations between these smoking measures and leukocyte mtDNAcn. Pending further investigation, our results add to the promise of leukocyte mtDNAcn as a biomarker for smoking-related clinical outcomes.
We also found a positive association of leukocyte mtDNAcn with fruit consumption but not with vegetable consumption, suggesting that some fruit-specific antioxidants may play a role. This is consistent with the finding that the intake of flavanones, a group of antioxidant phytochemicals that are abundant in citrus products (25), was significantly and positively associated with leukocyte mtDNAcn. In support of this, we also found a positive association between the consumption of citrus products and leukocyte mtDNAcn. Citrus flavanones have been shown to elicit substantial antioxidant effects (25, 51), and the consumption of citrus products can reduce oxidative stress levels (52). However, the association between fruit consumption and leukocyte mtDNAcn was driven by whole fruit but not fruit juice in our study. The null association between fruit juice consumption and leukocyte mtDNAcn may relate to the lower amounts of antioxidant phytochemicals. For example, different juice-processing techniques have been shown to influence the contents of beneficial phytochemicals in fresh fruit (53).
To provide a mechanistic foundation for the potential association between fruit consumption and cigarette smoke and leukocyte mtDNAcn, the human peripheral blood–derived leukocyte cell line HL-60 was treated with naringin and NNK, the major flavanone in the citrus species and the major ingredient of tobacco-specific nitrosamines, respectively. The results showed that leukocyte mtDNAcn was markedly increased after the administration of naringin, whereas exposure to NNK led to a significant decrease in mtDNAcn in comparison to normal cells, providing evidence for the association between fruit consumption, cigarette smoke, and mtDNAcn identified in the NHS participants. In particular, the data clearly indicated that cellular ROS play a pivotal role at the interface between fruit consumption, cigarette smoke, and mtDNAcn. These in vitro experimental results further strengthen the validity of our population-based epidemiologic findings.
Our study has several strengths, including detailed information on dietary factors, cigarette smoke, and other covariates; the health care background of the participants; and mutual confirmation of population and laboratory data. Nevertheless, our study also has several limitations. First, the population-based part of the study has a cross-sectional design and thus does not support causal inference. Nevertheless, results of in vitro experiments support the major findings from the population-based analyses. Second, there is the possibility of unmeasured confounding due to other potential factors that could affect the oxidative stress, although we controlled for a number of dietary and lifestyle factors in the data analysis. Third, we were not able to measure biomarkers of oxidative stress in our study participants and therefore are unsure if the level of mtDNAcn was correlated with the level of oxidative stress appropriately. However, in our previous study using the same study population, we found that mtDNAcn was strongly positively correlated with telomere length, another biomarker of peripheral blood leukocytes related to oxidative stress (22), which supports the validity of mtDNAcn measured in our study. Fourth, our study participants were exclusively white women, and therefore the findings may not be generalizable to men or other ethnicities. However, restricting the sample to white female health professionals also reduces the possibility of introducing confounding related to socioeconomic status, which is common in multiethnic studies.
In conclusion, our study suggests that fruit consumption is associated with higher leukocyte mtDNAcn, whereas cigarette smoke is associated with lower leukocyte mtDNAcn. Flavanones, a group of antioxidant phytochemicals abundant in citrus products, may be the key factor behind the association between fruit consumption and mtDNAcn, which is supported by the in vitro experiments showing the alterations in leukocyte mtDNAcn accompanied by relevant changes in mitochondrial biogenesis and function in human peripheral blood–derived leukocytes. This study provides the first evidence, to our knowledge, that fruit consumption and cigarette smoke may affect the levels of leukocyte mtDNAcn, a promising biomarker for oxidative stress–related clinical outcomes. The results further support the benefits of fruit consumption in promoting health and the adverse impact of cigarette smoke. Additional prospective studies are warranted to investigate the significance of leukocyte mtDNAcn as a biomarker of oxidative stress–related clinical outcomes in different populations, and future experimental studies are also warranted to further elucidate the underlying mechanism and signaling pathway involved in the relations between fruit consumption, cigarette smoke, and mtDNAcn as reported herein.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
The authors’ responsibilities were as follows—SW, JHL, and HN: acquisition of data (provided animals, acquired and managed patients, provided facilities, etc.) and study supervision: SW, HN, and JHL: writing, review, and/or revision of the manuscript: and SW, XL, SM, TF, ATC, GL, EG, IDV, JHL, and HN: analysis and interpretation of data (e.g., statistical analysis, biostatistics, computational analysis); drafting of the manuscript; and administrative, technical, or material support (i.e., reporting or organizing data, constructing databases); and all authors: read and approved the final manuscript. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Notes
Supported in part by NIH grants UM1 CA186107, R01 CA49449, and P01 CA87969 and by the National Research Foundation of Korea grant NRF-2015R1C1A1A01053746 from the Korean government, Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning (MSIP) of South Korea. SW is supported by start-up funding from Peking University Health Science Center (no. BMU20160549) and “Young Thousand Talents Program” of China.
Supplemental Figures 1 and 2, Supplemental Methods, and Supplemental Tables 1 and 2 are available from the “Supplementary data” link in the online posting of the article and from the same link in the online table of contents at https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/.
Abbreviation used: FFQ, food-frequency questionnaire; mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA; mtDNAcn, mitochondrial DNA copy number; NHS, Nurses’ Health Study; NNK, nicotine-derived nitrosamine ketone; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
References
- 1. Ramalingam M, Kim S-J. Reactive oxygen/nitrogen species and their functional correlations in neurodegenerative diseases. J Neural Transm. 2012;119(8):891–910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Wallace DC. Mitochondrial DNA mutations in disease and aging. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2010;51(5):440–50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Chen XJ, Butow RA. The organization and inheritance of the mitochondrial genome. Nat Rev Genet. 2005;6(11):815–25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Larsen NB, Rasmussen M, Rasmussen LJ. Nuclear and mitochondrial DNA repair: similar pathways?. Mitochondrion. 2005;5(2):89–108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Lee H-C, Wei Y-H. Mitochondrial biogenesis and mitochondrial DNA maintenance of mammalian cells under oxidative stress. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005;37(4):822–34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Lee H-C, Lu C-Y, Fahn H-J, Wei Y-H. Aging-and smoking-associated alteration in the relative content of mitochondrial DNA in human lung. FEBS Lett. 1998;441(2):292–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Westbrook DG, Anderson PG, Pinkerton KE, Ballinger SW. Perinatal tobacco smoke exposure increases vascular oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage in non-human primates. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2010;10(3):216–26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Lee HC, Wei YH. Mitochondrial biogenesis and mitochondrial DNA maintenance of mammalian cells under oxidative stress. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005;37(4):822–34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Valdecantos MP, Pérez‐Matute P, González‐Muniesa P, Prieto‐Hontoria PL, Moreno‐Aliaga MJ, Martínez JA. Lipoic acid improves mitochondrial function in nonalcoholic steatosis through the stimulation of Sirtuin 1 and Sirtuin 3. Obesity. 2012;20(10):1974–83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Fernández-Galilea M, Pérez-Matute P, Prieto-Hontoria PL, Houssier M, Burrell MA, Langin D, Martínez JA, Moreno-Aliaga MJ. α-Lipoic acid treatment increases mitochondrial biogenesis and promotes beige adipose features in subcutaneous adipocytes from overweight/obese subjects. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2015;1851(3):273–81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Akhmedov AT, Marín-García J. Mitochondrial DNA maintenance: an appraisal. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015;409(1-2):283–305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Cadenas S, Aragonés J, Landázuri MO. Mitochondrial reprogramming through cardiac oxygen sensors in ischaemic heart disease. Cardiovasc Res. 2010;88(2):219–28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Supale S, Thorel F, Merkwirth C, Gjinovci A, Herrera PL, Scorrano L, Meda P, Langer T, Maechler P. Loss of prohibitin induces mitochondrial damages altering beta-cell function and survival and is responsible for gradual diabetes development. Diabetes. 2013;62(10):3488–99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Lin MT, Beal MF. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature. 2006;443(7113):787–95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Coskun PE, Wyrembak J, Derbereva O, Melkonian G, Doran E, Lott IT, Head E, Cotman CW, Wallace DC. Systemic mitochondrial dysfunction and the etiology of Alzheimer's disease and down syndrome dementia. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010;20(Suppl 2):S293–310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Ashar FN, Moes A, Moore AZ, Grove ML, Chaves PH, Coresh J, Newman AB, Matteini AM, Bandeen-Roche K, Boerwinkle E et al.. Association of mitochondrial DNA levels with frailty and all-cause mortality. J Mol Med (Berl). 2015;93(2):177–86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Chen S, Xie X, Wang Y, Gao Y, Xie X, Yang J, Ye J. Association between leukocyte mitochondrial DNA content and risk of coronary heart disease: a case-control study. Atherosclerosis. 2014;237(1):220–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Zhang Y, Guallar E, Ashar FN, Longchamps RJ, Castellani CA, Lane J, Grove ML, Coresh J, Sotoodehnia N, Ilkhanoff L et al.. Association between mitochondrial DNA copy number and sudden cardiac death: findings from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study (ARIC). Eur Heart J. 2017;38(46):3443–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Kim J-H, Im J-A, Lee D-C. The relationship between leukocyte mitochondrial DNA contents and metabolic syndrome in postmenopausal women. Menopause. 2012;19(5):582–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Tin A, Grams ME, Ashar FN, Lane JA, Rosenberg AZ, Grove ML, Boerwinkle E, Selvin E, Coresh J, Pankratz N. Association between mitochondrial DNA copy number in peripheral blood and incident CKD in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;27(8):2467–73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Liu C-S, Tsai C-S, Kuo C-L, Chen H-W, Lii C-K, Ma Y-S, Wei Y-H. Oxidative stress-related alteration of the copy number of mitochondrial DNA in human leukocytes. Free Radic Res. 2003;37(12):1307–17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Meng S, Wu S, Liang L, Liang G, Giovannucci E, De Vivo I, Nan H. Leukocyte mitochondrial DNA copy number, anthropometric indices, and weight change in US women. Oncotarget. 2016;7(37):60676–86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Gramza-Michałowska A, Człapka-Matyasik M. Evaluation of the antiradical potential of fruit and vegetable snacks. ACTA Scientiarum Polonorum Technologia Alimentaria. 2011;10(1):63–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Sun J, Chu YF, Wu X, Liu RH. Antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of common fruits. J Agric Food Chem. 2002;50(25):7449–54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Barreca D, Gattuso G, Bellocco E, Calderaro A, Trombetta D, Smeriglio A, Lagana G, Daglia M, Meneghini S, Nabavi SM. Flavanones: citrus phytochemical with health-promoting properties. Biofactors. 2017;43(4):495–506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Csordas A, Wick G, Laufer G, Bernhard D. An evaluation of the clinical evidence on the role of inflammation and oxidative stress in smoking-mediated cardiovascular disease. Biomarker Insights. 2008;3:127–39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Cazarolli LH, Zanatta L, Alberton EH, Figueiredo MS, Folador P, Damazio RG, Pizzolatti MG, Silva FR. Flavonoids: prospective drug candidates. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2008;8(13):1429–40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Hankinson SE, Colditz GA, Hunter DJ, Manson JE, Willett WC, Stampfer MJ, Longcope C, Speizer FE. Reproductive factors and family history of breast cancer in relation to plasma estrogen and prolactin levels in postmenopausal women in the Nurses' Health Study (United States). Cancer Causes Control. 1995;6(3):217–24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Meng S, De Vivo I, Liang L, Hu Z, Christiani DC, Giovannucci E, Han J. Pre-diagnostic leukocyte mitochondrial DNA copy number and risk of lung cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7(19):27307–12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Meng S, De Vivo I, Liang L, Giovannucci E, Tang JY, Han J. Pre-diagnostic leukocyte mitochondrial DNA copy number and skin cancer risk. Carcinogenesis. 2016;37(9):897–903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Salvini S, Hunter DJ, Sampson L, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA, Rosner B, Willett WC. Food-based validation of a dietary questionnaire: the effects of week-to-week variation in food consumption. Int J Epidemiol. 1989;18(4):858–67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Willett W, Reynolds R, Cottrell-Hoehner S, Sampson L, Browne M. Validation of a semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire: comparison with a 1-year diet record. J Am Diet Assoc. 1987;87(1):43–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Mei H, Sun S, Bai Y, Chen Y, Chai R, Li H. Reduced mtDNA copy number increases the sensitivity of tumor cells to chemotherapeutic drugs. Cell Death Dis. 2015;6:e1710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Morino K, Petersen KF, Dufour S, Befroy D, Frattini J, Shatzkes N, Neschen S, White MF, Bilz S, Sono S et al.. Reduced mitochondrial density and increased IRS-1 serine phosphorylation in muscle of insulin-resistant offspring of type 2 diabetic parents. J Clin Invest. 2005;115(12):3587–93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Peng K, Tao Y, Zhang J, Wang J, Ye F, Dan G, Zhao Y, Cai Y, Zhao J, Wu Q et al.. Resveratrol regulates mitochondrial biogenesis and fission/fusion to attenuate rotenone-induced neurotoxicity. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:6705621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Prieto J, Leon M, Ponsoda X, Sendra R, Bort R, Ferrer-Lorente R, Raya A, Lopez-Garcia C, Torres J. Early ERK1/2 activation promotes DRP1-dependent mitochondrial fission necessary for cell reprogramming. Nat Comm. 2016;7:11124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Akerboom TP, Sies H. Assay of glutathione, glutathione disulfide, and glutathione mixed disulfides in biological samples. Methods Enzymol. 1981;77:373–82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Anderson ME. Determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide in biological samples. Methods Enzymol. 1985;113:548–55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Zerez CR, Lee SJ, Tanaka KR. Spectrophotometric determination of oxidized and reduced pyridine nucleotides in erythrocytes using a single extraction procedure. Anal Biochem. 1987;164(2):367–73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Jiang ZY, Hunt JV, Wolff SP. Ferrous ion oxidation in the presence of xylenol orange for detection of lipid hydroperoxide in low density lipoprotein. Anal Biochem. 1992;202(2):384–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Tsuchiya M, Suzuki YJ, Cross CE, Packer L. Superoxide generated by cigarette smoke damages the respiratory burst and induces physical changes in the membrane order and water organization of inflammatory cells. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1993;686(1):39–52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Csiszar A, Podlutsky A, Wolin MS, Losonczy G, Pacher P, Ungvari Z. Oxidative stress and accelerated vascular aging: implications for cigarette smoking. Front Biosci. 2009;14:3128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Yu M. Generation, function and diagnostic value of mitochondrial DNA copy number alterations in human cancers. Life Sci. 2011;89(3):65–71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Pan A, Wang Y, Talaei M, Hu FB, Wu T. Relation of active, passive, and quitting smoking with incident type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015;3(12):958–67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Cena H, Fonte ML, Turconi G. Relationship between smoking and metabolic syndrome. Nutr Rev. 2011;69(12):745–53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Jones-Burton C, Seliger SL, Scherer RW, Mishra SI, Vessal G, Brown J, Weir MR, Fink JC. Cigarette smoking and incident chronic kidney disease: a systematic review. Am J Nephrol. 2007;27(4):342–51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Durazzo TC, Mattsson N, Weiner MW. Smoking and increased Alzheimer's disease risk: a review of potential mechanisms. Alzheimers Dement. 2014;10(3 Suppl):S122–45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. La Maestra S, Kisby GE, Micale RT, Johnson J, Kow YW, Bao G, Sheppard C, Stanfield S, Tran H, Woltjer RL et al.. Cigarette smoke induces DNA damage and alters base-excision repair and tau levels in the brain of neonatal mice. Toxicol Sci. 2011;123(2):471–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Lee JW, Park KD, Im JA, Kim MY, Lee DC. Mitochondrial DNA copy number in peripheral blood is associated with cognitive function in apparently healthy elderly women. Clin Chim Acta. 2010;411(7-8):592–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Mengel-From J, Thinggaard M, Dalgard C, Kyvik KO, Christensen K, Christiansen L. Mitochondrial DNA copy number in peripheral blood cells declines with age and is associated with general health among elderly. Hum Genet. 2014;133(9):1149–59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Ferreira PS, Spolidorio LC, Manthey JA, Cesar TB. Citrus flavanones prevent systemic inflammation and ameliorate oxidative stress in C57BL/6J mice fed high-fat diet. Food Funct. 2016;7(6):2675–81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Codoner-Franch P, Lopez-Jaen AB, De La Mano-Hernandez A, Sentandreu E, Simo-Jorda R, Valls-Belles V. Oxidative markers in children with severe obesity following low-calorie diets supplemented with mandarin juice. Acta Paediatr. 2010;99(12):1841–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Uckoo RM, Jayaprakasha GK, Balasubramaniam V, Patil BS. Grapefruit (Citrus paradisi Macfad) phytochemicals composition is modulated by household processing techniques. J Food Sci. 2012;77(9):C921–C6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.