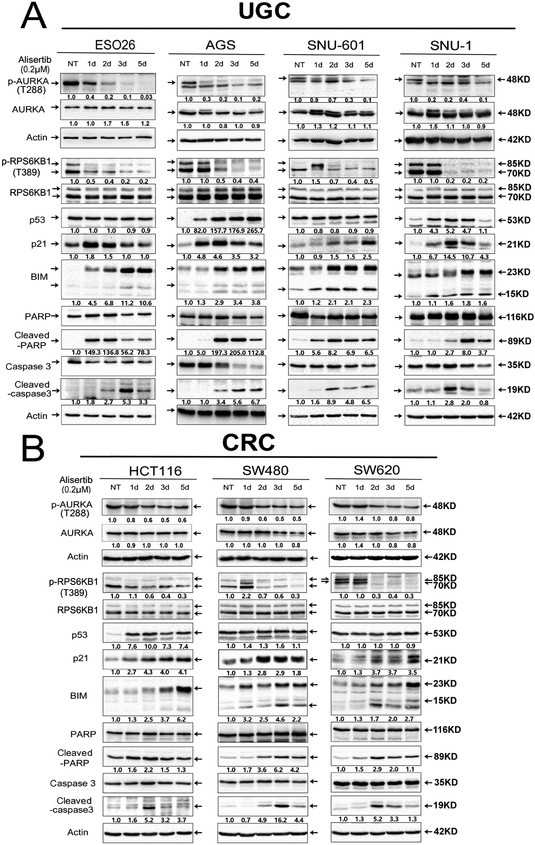
Figure 2. AURKA inhibition downregulates RPS6KB1 protein phosphorylation at Thr-389, and upregulates protein expression of pro-apoptotic mediators in KRAS-driven GI cancer cells.
A, Upper GI cancer cells (ESO26, AGS, SNU-1, SNU-601) were treated with alisertib (0.2 μM) for 1, 2, 3, and 5 days, and cell lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis. The data showed that 1 or 2 days of alisertib treatment led to a decrease in the levels of p-RPS6KB1 (T389) and an increase in p53 (only in p53 WT cell lines), p21, BIM, cleaved PARP, and cleaved caspase 3. B, Colorectal cancer (CRC) cells (HCT116, SW480, SW620) were treated as described in A. Gel loading was normalized for equal β-Actin; representative blots from one of two independent experiments. The relative density of bands is shown under each immunoblot, after normalization to the levels of actin). Quantification of Western blot data is included in Supplementary Figure S1A. Black arrows indicate the molecular weight of proteins.