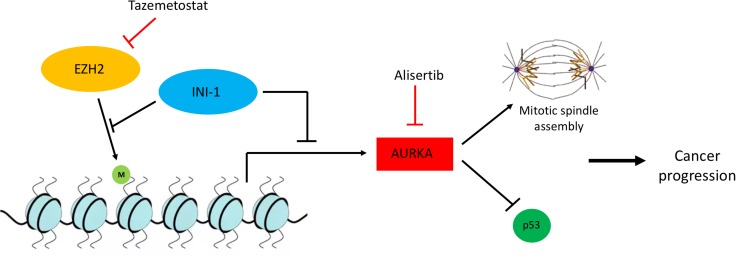
Figure 2.
Oncogenic signaling involving INI‐1 creates novel therapeutic opportunities. INI‐1 as part of the SWItch/Sucrose Non‐Fermentable complex and EZH2 as part of the PRC2 complex have antagonistic roles in the methylation of histones and gene expression. Particularly, EZH2 induces H3K27 trimethylation, whereas INI‐1 inhibits this activity. In the setting of INI‐1 deficiency, EZH2 activity is upregulated, rendering these tumors particularly sensitive to EZH2 inhibitors such as tazemetostat. Similarly, INI‐1 suppresses the expression of AurkA, which is implicated in the stability of the mitotic spindle and the degradation of p53, promoting cancer progression. Thus, INI‐1‐deficient tumors are also sensitive to AurkA inhibition by agents such as alisertib. Abbreviations: AurkA, Aurora kinase A; EZH2, enhancer of zeste homolog 2; INI‐1, integrase interactor 1.