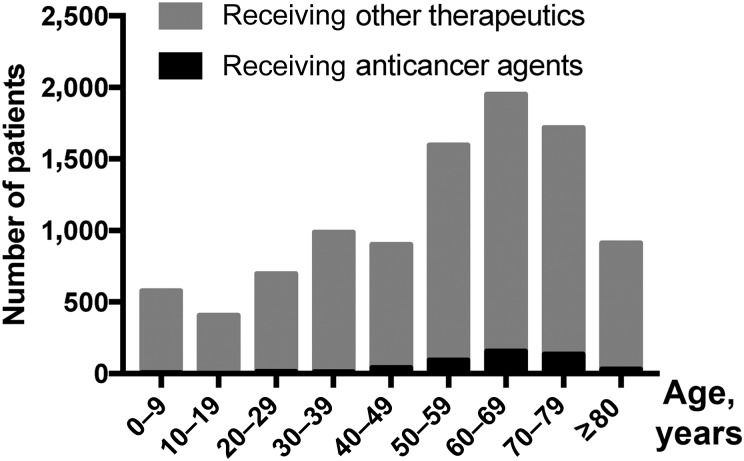
Figure 1.
Relationship between age and the prevalence of life‐threatening skin toxicities. The cohort included patients with Stevens‐Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis (n = 9,738). Age groups are defined in 10‐year bands or age of more than 80 years. The highest prevalence of drug‐induced skin toxicity was noted among patients aged 50–79 years, both among patients receiving anticancer agents and among those receiving non‐anticancer therapeutics. In this cohort of patients with drug‐induced life‐threatening skin toxicity, an anticancer agent was identified as the causative drug in 5.8%, 7.9%, and 7.8% of patients aged 50–59, 60–69, and 70–79 years, respectively, compared with only 3.4% and 2.0% of patients aged above 80 years or below 50 years, respectively.