Abstract
Background:
Infant death in KID syndrome is recognized; its association with specific genotypes and pathophysiology is inadequately understood.
Objective:
To discover characteristics that account for poor outcomes in lethal KID syndrome.
Methods:
We collected four new cases and nine previously reported, genotyped cases of lethal KID syndrome. We performed new molecular modeling of the lethal mutants GJB2 p.A88V and GJB2 p.G45E.
Results:
Infant death occurred in all patients with GJB2 p.G45E and p.A88V; it is unusual with other GJB2 mutations. Early death with those two “lethal” mutations is likely multifactorial: during life all had at least one serious infection; most had poor weight gain and severe respiratory difficulties; many had additional anatomic abnormalities. Structural modeling of GJB2 p.G45E identified no impact on the salt bridge previously predicted to account for abnormal central CO2 sensing of GJB2 p.A88V.
Limitations:
Clinical review was retrospective.
Conclusion:
GJB2 p.G45E and p.A88V are the only KID syndrome mutations associated with uniform early lethality. Those electro-physiologically severe mutations in GJB2 reveal abnormalities in many organs in lethal KID syndrome. All KID syndrome patients may have subtle abnormalities beyond eyes, ears and skin. Early genotyping of KID syndrome births will inform prognostic discussion.
Keywords: keratitis, ichthyosis, and deafness syndrome (KID) syndrome, connexin 26 (Cx26), gap junction protein, beta-2 (GJB2)
Introduction
Keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness (KID) syndrome is a rare congenital disorder caused by autosomal dominant mutations in the GJB2 gene that encodes connexin 26 (Cx26). Affected individuals typically are born with erythrokeratoderma and may develop degrees of sensorineural hearing loss and/or progressive vascularizing keratitis. A previous review suggested certain patients with KID syndrome die in infancy due to sepsis, but did not evaluate their specific mutation nor abnormalities in other organ systems1. More recently, cases of “lethal KID syndrome” have been reported with mutations p.A88V and p.G45E in GJB22–6. One group suggested that the p.A88V mutation depresses breathing through centrally impaired CO2 sensing.
When we became aware of four previously unreported infants with KID syndrome who died in infancy despite aggressive antimicrobial prophylaxis, we sought answers to the following questions: 1. Is there evidence that the GJB2 p.A88V and p.G45E mutations are not uniformly lethal in infancy? 2. Do other GJB2 mutations result in infant mortality? 3. Is there a single cause for the lethal outcome associated with those two mutations, and is abnormal CO2 sensing sufficient to account for infant mortality in lethal KID syndrome? 4. In severe cases of KID syndrome, is there evidence for disease in organs other than skin, cornea and inner ear?
Materials and Methods
We reviewed new (cases 2–5) and previously published (cases 1, 6–13) cases of lethal KID syndrome where GJB2 mutations were identified, and contacted the primary providers to obtain detailed clinical information. Primary data including cultures, laboratory and imaging results, and pathology reports were reviewed when available. Two of the new cases had post-mortem exams. One lethal case with a p.S17F mutation8 was excluded because patients with this mutation usually survive into adulthood9.
Of the 16 cases identified, detailed clinical information was available for 13. For 11 of these cases, we confirmed clinical details with the primary dermatologist. For the two remaining cases (cases 6 and 13), we relied on their published case reports1, 2 The Yale Institutional Review Board ruled this project exempt from review.
Structural analyses were performed based on the X-ray crystal structure of Cx26 (PDB Code 2ZW3)10. Structural modeling and figure preparation were performed using Coot11, UCSF Chimera (Resource for Biocomputing, Visualization, and Informatics, University of California, San Francisco), and PyMOL Molecular Graphics System (Version 1.5.0.4, Schrodinger, LLC).
Results
Thirteen patients (nine males and four females) with lethal KID syndrome, six with the GJB2 p.A88V mutation and seven with the GJB2 p.G45E mutation, were identified (Table 1). These patients were from the United States, Japan, France, and Austria. No surviving cases with GJB2 p.A88V or p.G45E mutations were identified based on literature review and diagnostic laboratory data (ClinVar; GeneDx variant database; personal communication, G. Richard). Interestingly, some Japanese individuals with GJB2 p.G45E mutations do not have a cutaneous phenotype, due to the presence of a second, confining mutation on the same GJB2 allele (in cis)3. Recently published GJB2 p.A88V case reports provided more primary clinical information than available for GJB2 p.G45E patients. Four of seven p.G45E patients (cases 8–11) were from a single family.
Table 1.
Key clinical features of KID patients with GJB2 p.A88V and p.G45E variants. Summary of cases by organ system. For the two cases in grey, we relied on the published case reports, as we were not able to communicate with the primary dermatologist. Asterisked cases are from one family.
| Case (citation if previously reported) | Genotype | Gender | Gestational age at birth (weeks + days) | Respiratory | Cardiovascular | Central Nervous System | Gastrointestinal | Skin Ulcerations | Skin Histology | Hematologic | Thymus | Infection Onset (months) | Age at death (months) | Cause of death |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (7) | A88V | M | 37 | apnea requiring intubation at birth; pneumogram demonstrating central apnea; respiratory failure; bronchopneumonia | cardiomegaly, dilated right atrium, dysplastic tricuspid valve | no gag reflex; small interruption of the left internal capsule by gray matter; subacute to chronic germinal matrix hemorrhage | low weight and height; zinc deficiency; thin distal esophagus; difficulty with oral feeds | intertriginous | baseline erythrokeratoderma: hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, mild lymphocytic infiltrate, retained granular layer, impetiginization with cocci ulcer: upper layers of epidermis with parakeratosis and extensive ballooning degeneration and necrosis, chronic inflammatory infiltrate in the dermis | macrocytic anemia | hypoplastic | 1 | 5 | respiratory failure, sepsis |
| 2 | A88V | F | 34 | hypoxia; hypercapnea; pneumogram suggestive of central apnea | patent foramen ovale | poor suck reflex; mild inferior vermian hypogensis | low weight; mild zinc deficiency | inguinal creases | normocytic anemia requiring transfusion; normal flow | 1.75 | respiratory failure, sepsis | |||
| 3 | A88V | M | 33 + 6 | increased work of breathing; acute respiratory acidosis requiring intubation at end of life | small patent ductus arteriorsus, moderately dilated left ventricle | normal brain ultrasound | low weight and height; enteral and parenteral nutritional supplementation | around gastric tube; diaper area; intertriginous | new red urticarial rash on leg: accentuated granular layer, hyperkeratosis, superficial dermal edema with perivascular mixed inflammatory infiltrate | normocytic anemia; immunoglobulins normal | 2 | 6 | fungemia with respiratory failure | |
| 4 | A88V | F | 32 + 6 | increased work of breathing; intermittent apnea | patent foramen ovale v. small secundum atrial septal defect | no gag reflex; Dandy- Walker malformation with small germinal matrix hemorrhage and severe ventriculomegaly | difficulty with oral feeds | intertriginous | ulcer: upper third epidermis with pale cytoplasm | anemia requiring transfusion | 0.5 | 2 | congenital abnormality of the brainstem | |
| 5 | A88V | M | 35–36 | hypoxia; immature lungs with patchy intralveolar; hemorrhage | hypotensive requiring pressors echocardiogram normal | microcephaly; acute hypoxic change in hippocampal neurons | low weight and height; low vitamin A; abnormal maturation of non- keratinized squamous epithelium in esophagus | lower abdomen | normocytic anemia; low IgG and IgA | thymic involution | 0.5 | 0.75 | ||
| 6 (2) | A88V | M | 33 + 4 | apnea; atelectasis; cerebral irritability that required mechanical ventilation | hydrocephalus; intraventricular and parenchymal hemorrhage | scalp | 1 | Klebsiella sepsis | ||||||
| 7 (3) | G45E | F | 36 | suspected aspiration pneumonia and bronchitis | pulmonary artery stenosis | nasogastric tube | perianal and genital | baseline erythrokeratoderma: hyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, focal vacuolar degeneration | 7 | |||||
| * (4, 5) twin | A G45E | M | 31 | failure to thrive despite enteral and parental alimentation | none | orthokeratotic hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, complete absense of granular layer; keratinocytes in the upper part of the epidermis were swollen and sometimes vacuolated | 1 | pseudomonas septicemia | ||||||
| * (4, 5) twin | B G45E | M | 31 | candida and staph pulmonary infection; edema and dyskeratotic laryngeal mucosae | cardiomegaly | dilation of left ventricle | low weight ana height; enteral nutrition for difficulty feeding; dyskeratotic esophageal mucosa | none | orthokeratotic hyperkeratosis with focal parakeratosis, focal granular layer | anemia; immunoglobulin and lymphocyte flow normal | 3 | 5 | candida and staphlococcal pulmonary infection | |
| 10* (5) | G45E | M | 33 | nasogastric tube | none | 1 | candida and staphlococcal septicemia | |||||||
| 11* (5) | G45E | M | 35 | respiratory failure; candida pulmonary infection | none | 0.3 | candida pulmonary infection | |||||||
| 12 (6) | G45E | F | 36 | respiratory insufficency due to aspiration | psychomotor delay | low weight and height | none | hyper- and parakeratosis, intraepidermal neutrophils, abundant bacteria and fungi, no ballooning degeneration | no immunologic incompetence | 1 | 12 | septicemia | ||
| 13 (1) | G45E | M | 36 | viral upper respiratory infection | scalp | immunoglobulins and lymphocyte phenoytype panel wnl | 3.5 | 6 | septicemia |
same family
Clinical Course
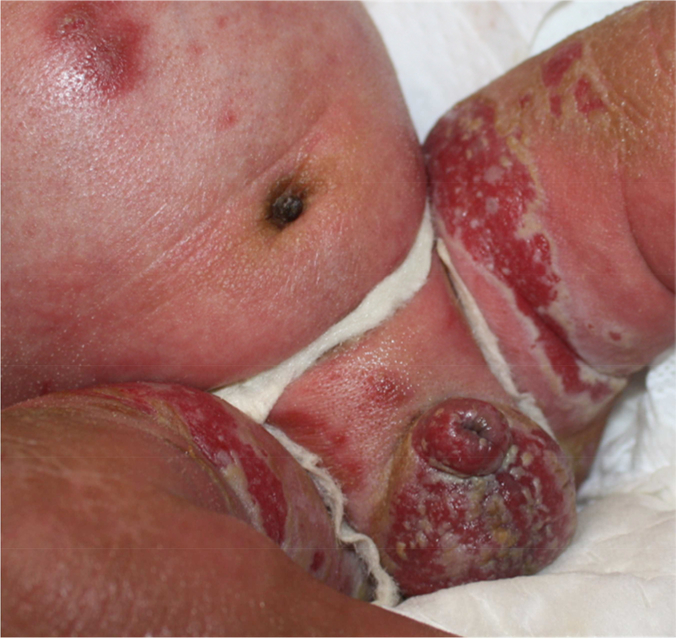
All patients were born prematurely (average, 34 weeks; range, 31–37 weeks). Death occurred between 10 days and 1 year of age (average, 3.5 months). Academic dermatologists cared for all patients during prolonged hospitalizations in tertiary care centers. At birth or shortly thereafter, a diagnosis of KID syndrome was suspected due to skin changes, keratitis, and hearing loss, and was ultimately confirmed by genetic testing. Each patient was born with relatively mild skin disease (i.e., diffuse, thin palmoplantar keratoderma with characteristic grainy surface changes), central facial hyperkeratosis, and diffuse erythrokeratoderma. Among those who survived beyond the neonatal period, all GJB2 p.A88V and two GJB2 p.G45E patients developed increasing hyperkeratosis with fissures. Intertriginous erosions became ulcerations that waxed and waned, but on the whole, progressively worsened (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Late skin findings in lethal KID syndrome.
Intertriginous hyperkeratosis and denudation in a patient with GJB2 p.A88V mutation (case 1).
By 2 months of age, and often earlier, all but two patients experienced serious infection, with the skin and respiratory tract being the usual sites. Many of these patients were eventually diagnosed with septicemia. Candida species and Staphylococcus aureus were the most common organisms cultured. Several patients were evaluated for immunodeficiency, but no consistent immunodeficiency was found.
The vast majority of patients suffered from significant functional abnormalities related to nutrition and breathing, with respiratory difficulties being the single most significant issue. Infection or aspiration pneumonia contributed to these difficulties in some, but not all, patients. All GJB2 p.A88V patients had respiratory problems. Two of these six patients were investigated for and found to have central apnea. All six continued to have respiratory distress (i.e., hypoxia and increased work of breathing) beyond a corrected gestational age of 40 weeks, when apnea of prematurity should have resolved. Three of the six patients were eventually intubated, and mechanical ventilation was needed but deferred in the other three patients due to parent preference for supportive care. Caffeine, which is used to treat apnea of prematurity, was used in cases 1 and 2 with no appreciable improvement.
Seven of the 13 patients were diagnosed with failure to thrive and required nutritional supplementation. Two were found to have mild zinc deficiency, and oral zinc supplementation was thought to temporarily improve the skin in one of them. Half of the patients had mild to moderate anemia.
In addition to the expected changes in skin, eyes and ears, many patients had additional anatomic abnormalities, most commonly in the central nervous system (CNS) and heart (Table).
Skin Histology
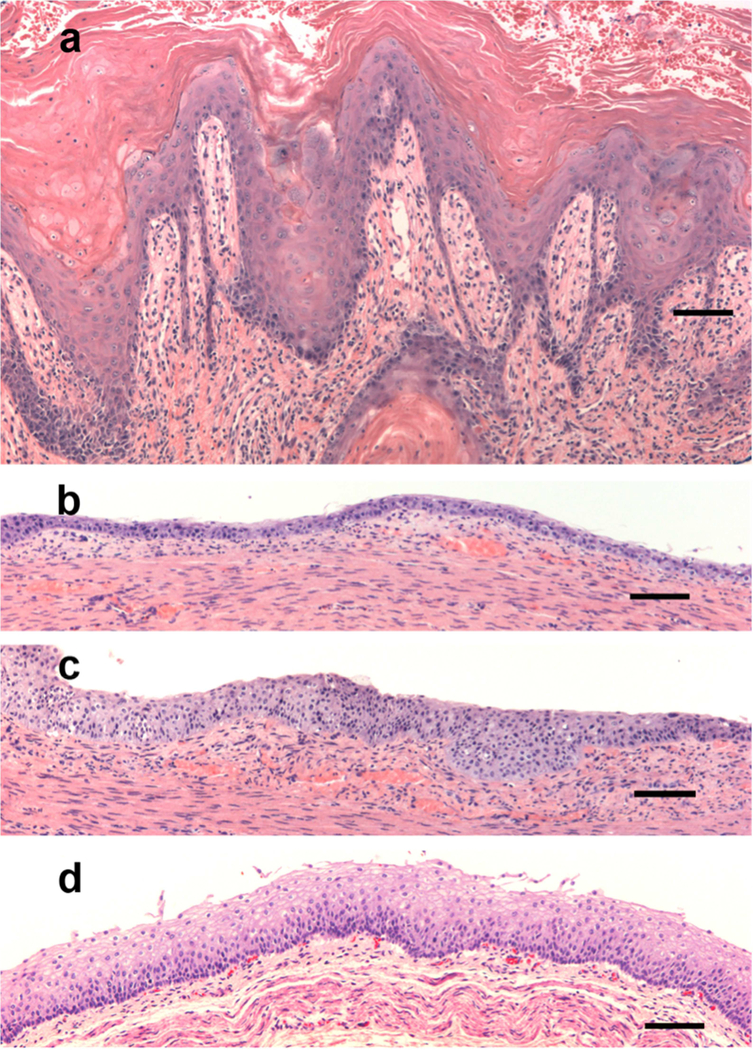
Other than acanthosis and hyperkeratosis, there were no consistent findings on skin biopsy. Papillomatosis, focal parakeratosis, hyper- and hypo-granulosis and, in one case, horn cyst formation were reported. This variability may be related to biopsy site location and its time point in the clinical course. Four of eight biopsies showed pale cytoplasm in the upper epidermis (Figure 2a), suggestive of nutritional deficiency.
Figure 2. Histopathology of skin and esophagus in lethal KID syndrome.
(a) Skin from thigh in Figure 1 shows hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis and focal ballooning degeneration, with pale cytoplasm in keratinocytes of the upper epidermis. (b). Distal esophagus from case 1 shows thin mucosa limited to basal layer with no maturation and hyperchromatic nuclei. (c). Disordered maturation in the few areas where the mucosa is not thin. (d) Matched normal control of distal esophagus from 2-month infant. Hematoxylin and Eosin. Bar = 100um.
Post-Mortem Examination
Two patients underwent post-mortem examination. Both had hypoplastic thymi for their age and abnormal maturation of the squamous epithelium in the esophagus. The distal esophageal epithelium in Case 1 had few layers with poor epithelial maturation and hyperchromatic nuclei (Figure 2b, c). Case 1 had an enlarged adrenal medulla and heart, and case 5 also had early bronchopulmonary dysplasia, pan lobular hepatic microsteatosis, natal teeth, cleft of the secondary palate, a duplicated left renal collecting system, undescended testes, camptodactyly of all digits, and mild microcephaly (5th percentile).
Structural analysis of p.A88Vandp.G45E mutant Cx26
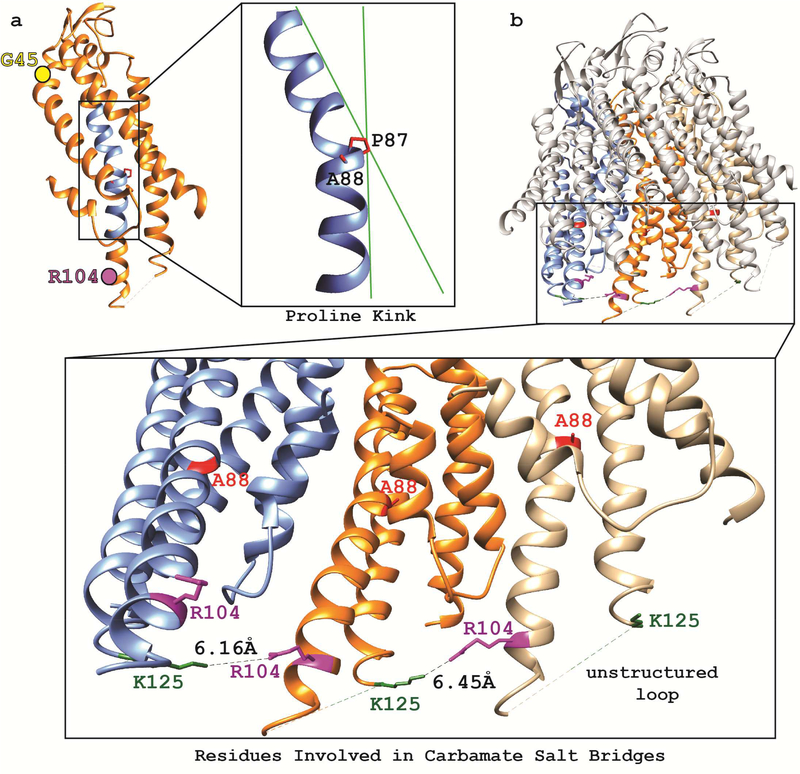
The frequency of serious respiratory difficulties, along with evidence that Cx26 is important for CO2 sensing12, prompted us to model the structural consequences of mutant GJB2 p.A88V and p.G45E proteins. CO2 modulation of Cx26 channel function results from formation of a carbamate bridge on the intracellular surface between Arg104 on one Cx26 molecule, and Lys125 on an adjacent Cx26 molecule, in the hexameric hemichannel7, 12 Pro87 introduces a kink in Cx26 (Figure 3a) that is vital to transduction of voltage gating13 and confers the appropriate spacing to allow the carbamate salt bridge (Figure 3b). Mutant p. A88V protein necessitates a packing rearrangement of the transmembrane helix to avoid unfavorable stereochemical clashes between the new valine and the adjacent proline. The required repacking of Cx26 p.A88V plausibly leads to repositioning of the intracellular end of the transmembrane helix and its proximity to Lys125 on the neighboring Cx26 protomer (Figure 3b). In contrast, modeling suggests the solvent-exposed, pore-lining extracellular mutant p.G45E should not affect CO2 sensing.
Figure 3. Structural analysis of Cx26 containing the p.A88V mutation.
. (a) A single Cx26 protomer (orange) with the transmembrane region of the second transmembrane helix (TM2) highlighted in blue. The critical P87 adjacent to A88 is shown in a zoomed-in image of the TM2 helix and illustrates helical kinking induced by P87 (green lines aid visualization of the altered helical angle). Also shown are the positions of external G45 (yellow sphere) far from the carbamate binding region, and internal R104 on TM2 (purple sphere) involved in carbamate binding. (b) Cx26 hemichannel (top) with zoomed-in image (bottom) of three neighboring Cx26 protomers (colored blue, orange, and tan) showing the R104 (purple) and K125 (green) residues critical to CO2 binding. The distance between these residues ranges from ~ 6.1 to 6.5 Å.
Discussion
Infant mortality in KID syndrome with GJB2 p.A88V or p.G45E mutations appears to be unavoidable despite intensive medical interventions; all succumb to the disease despite modern intensive neonatal care in tertiary academic centers and prophylactic antimicrobials. This information should encourage early genotyping in order to guide management of newborn KID syndrome patients. No abnormalities in a single organ system can account for the early lethality of these Cx26 mutations. Infant death in KID syndrome caused by other GJB2 mutations is rare.
GJB2 mutations encoding p.A88V and p.G45E have far-reaching clinical consequences beyond keratitis, ichthyosis and deafness. KID syndrome patients with those mutations have deficits in many other organ systems as revealed by our post-mortem information on two males, and by detailed imaging and other data from 5 of the remaining eleven. Additional abnormalities likely would have identified if not for the limitations in patient data collection. This should not be surprising since connexin 26 is expressed in many tissues during development and is inducible in skin by inflammation and retinoids14. In adults, transcripts are highly expressed in the esophagus, cervix and vagina15 and protein highly expressed in esophagus, spinal cord and colon16. The striking histopathological changes in esophagus, and unanticipated pre-mortem, should alert us to potential barrier and other functional abnormalities in stratified squamous epithelia in all KID syndrome patients. Dandy-Walker malformations (identified in case 4 here) were previously noted in a large fraction of KID syndrome patients with a variety of GJB2 mutations17–21 yet this information has yet to appear in most reviews of KID syndrome. The current definition of KID syndrome affecting only the skin, eye, and ears is inadequate for lethal and for non-lethal variants, and handicaps evaluation of issues arising in other potentially affected organ systems.
Repeated infections are a serious problem for these KID syndrome patients. The patients with A88V and G45E mutations in GJB2 are profoundly susceptible to and poorly able to respond to infections despite vigorous interventions. To date, no intrinsic adaptive or innate immune abnormalities have been identified in KID syndrome. We question whether the physically diminished epithelial barriers shown in skin and esophagus in our patients (and unexplored in vagina and cervix) are the source of these repeated infections and perhaps account for the frequency of fungemia.
Our current understanding of the expression and physiologic function of normal and mutant Cx2622 explains some, but not all, of the clinical observations in this group of patients. Loss of function mutations in GJB2 cause non-syndromic deafness, while gain of function mutations in GJB2 are responsible for several skin diseases including KID syndrome22. At least 11 GJB2 mutations are associated with KID syndrome, and all tested show leakiness of connexin hemichannels. In electrophysiological or biochemical testing, p.A88V and p.G45E proteins show distinct abnormalities potentially more severe than other Cx26 mutants23, 24 Thus, the progressively increasing hyperkeratosis, late onset of erosions, and upper-epidermal pallor in the histopathology of these KID syndrome patients suggest that irritation or infection upregulates suprabasal expression of mutant Cx26, resulting in hemichannels that leak ATP and calcium, leading to abnormal differentiation, barrier dysfunction, and cell death24, 25.
Understanding of the effect of dominant GJB2 mutations on organs other than skin is even more limited. The frequency of respiratory difficulties in this group of patients is striking. Anatomic abnormalities in lungs of KID syndrome patients have not been demonstrated. Dale and colleagues have shown that connexin 26 is expressed in the central respiratory control center of the medulla oblongata, and that cells sense intracellular CO2 by forming a carbamate bridge that regulates hemichannel opening12. GJB2 p.A88V fails to form the carbamate bridge and the hemichannel malfunctions. In silico structural analysis of p.A88V indicated substitution of valine for alanine at position 88 can alter the intracellular carbamate salt bridge required for CO2 sensing. By contrast, our structural analysis places the p.G45E mutation on the extracellular portion of the molecule, where it would be unlikely to impact the carbamate salt bridge. Thus, as attractive as the central CO2 sensing defect is to explain pulmonary problems in patients with A88V mutations, it does not explain pulmonary problems in patients with G45E mutations.
Our analysis highlights the clinical heterogeneity of KID syndrome, underscores the complex expression and combinatorial cell biology of connexins, and demonstrates that the current definition of KID syndrome obscures the effect of GJB2 mutations on other organ systems. This is likely true for non-lethal as well as lethal variants. We set out to determine whether these severe mutations had a uniformly lethal outcome and if there was a unifying explanation for that outcome. We found that no single problem accounted for the poor outcome, but rather that these individuals had a surprisingly large number of organ systems with developmental and acquired disease, emphasizing the old adage that the severest examples of disease may not be typical, but they can serve to reveal subtle and previously unappreciated abnormalities.
Capsule Summary.
What is already known?
Early lethality in KID syndrome has been attributed to infection or impaired central CO2 sensing.
What this article adds to our knowledge?
Uniform lethality with two mutations in GJB2 had no single cause of death. Many organ systems had abnormalities.
How this information impacts clinical practice and/or changes patient care?
Clinicians should be alert to abnormalities beyond keratitis, ichthyosis and deafness. Early genotyping will guide management.
Acknowledgments
Funding/Support
This work was supported in part by the Dermatology Foundation through a Career Development Award (to C.G.B.), an NIH/NIAMS Dermatology Training Grant to Yale T 32 AR007016 (to C.G.B. and E.L.; PI: Richard Edelson), and an NIH/NIAMS grant 5K08AR070290–02 (to C.G.B).
Footnotes
Conflict of interest: The authors have no conflict of interest to declare
This work was performed in New Haven, Connecticut.
IRB: exempt from review
Prior Presentation: A portion of the structural work was presented in a poster at the Society of Investigative Dermatology in Portland, OR, in 2017.
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- 1.Gilliam A, Williams ML. Fatal septicemia in an infant with keratitis, ichthyosis, and deafness (KID) syndrome. Pediatr Dermatol 2002;19:232–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Koppelhus U, Tranebjaerg L, Esberg G, Ramsing M, Lodahl M, Rendtorff ND et al. A novel mutation in the connexin 26 gene (GJB2) in a child with clinical and histological features of keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness (KID) syndrome. Clin Exp Dermatol 2011;36:142–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ogawa Y, Takeichi T, Kono M, Hamajima N, Yamamoto T, Sugiura K et al. Revertant mutation releases confined lethal mutation, opening Pandora’s box: a novel genetic pathogenesis. PLoS Genet 2014;10:e1004276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Jonard L, Feldmann D, Parsy C, Freitag S, Sinico M, Koval C et al. A familial case of Keratitis- Ichthyosis-Deafness (KID) syndrome with the GJB2 mutation G45E. Eur J Med Genet 2008;51:35–43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sbidian E, Feldmann D, Bengoa J, Fraitag S, Abadie V, de Prost Y et al. Germline mosaicism in keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness syndrome: pre-natal diagnosis in a familial lethal form. Clin Genet 2010;77:587–92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Janecke AR, Hennies HC, Gunther B, Gansl G, Smolle J, Messmer EM et al. GJB2 mutations in keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness syndrome including its fatal form. Am J Med Genet A 2005;133A:128–31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Meigh L, Hussain N, Mulkey DK, Dale N. Connexin26 hemichannels with a mutation that causes KID syndrome in humans lack sensitivity to CO2. Elife 2014;3:e04249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mazereeuw-Hautier J, Chiaverini C, Jonca N, Bieth E, Dreyfus I, Maza A et al. Lethal form of keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness syndrome caused by the GJB2 mutation p.Ser17Phe. Acta Derm Venereol 2014;94:591–2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mazereeuw-Hautier J, Bitoun E, Chevrant-Breton J, Man SY, Bodemer C, Prins C et al. Keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness syndrome: disease expression and spectrum of connexin 26 (GJB2) mutations in 14 patients. Br J Dermatol 2007;156:1015–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Maeda S, Nakagawa S, Suga M, Yamashita E, Oshima A, Fujiyoshi Y et al. Structure of the connexin 26 gap junction channel at 3.5 A resolution. Nature 2009;458:597–602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Emsley P, Cowtan K. Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 2004;60:2126–32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Meigh L, Greenhalgh SA, Rodgers TL, Cann MJ, Roper DI, Dale N. CO(2)directly modulates connexin 26 by formation of carbamate bridges between subunits. Elife 2013;2:e01213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Suchyna TM, Xu LX, Gao F, Fourtner CR, Nicholson BJ. Identification of a proline residue as a transduction element involved in voltage gating of gap junctions. Nature 1993;365:847–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Masgrau-Peya E, Salomon D, Saurat JH, Meda P. In vivo modulation of connexins 43 and 26 of human epidermis by topical retinoic acid treatment. J Histochem Cytochem 1997;45:1207–15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. https://www.gtexportal.org/home/gene/GJB2.
- 16. https://www.proteomicsdb.org/proteomicsdb/-human/proteinDetails/P29033/expression.
- 17.Zhang XB, Wei SC, Li CX, Xu X, He YQ, Luo Q et al. Mutation of GJB2 in a Chinese patient with keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness syndrome and brain malformation. Clin Exp Dermatol 2009;34:309–13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zhang XB, Li CX. A case of keratitis ichthyosis deafness (KID) syndrome associated with Dandy-Walker. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2007;21:706–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Todt I, Mazereeuw-Hautier J, Binder B, Willems PJ. Dandy-Walker malformation in patients with KID syndrome associated with a heterozygote mutation (p.Asp50Asn) in the GJB2 gene encoding connexin 26. Clin Genet 2009;76:404–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Boudghene-Stambouli O, Merad-Boudia A, Abdelali S. [KID syndrome, pachydermatoglyphy and Dandy-Walker syndrome]. Ann Dermatol Venereol 1994;121:99–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cushing SL, MacDonald L, Propst EJ, Sharma A, Stockley T, Blaser SL et al. Successful cochlear implantation in a child with Keratosis, Icthiosis and Deafness (KID) Syndrome and Dandy-Walker malformation. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2008;72:693–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lilly E, Sellitto C, Milstone LM, White TW. Connexin channels in congenital skin disorders. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2016;50:4–12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sanchez HA, Mese G, Srinivas M, White TW, Verselis VK. Differentially altered Ca2+ regulation and Ca2+ permeability in Cx26 hemichannels formed by the A40V and G45E mutations that cause keratitis ichthyosis deafness syndrome. J Gen Physiol 2010;136:47–62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mhaske PV, Levit NA, Li L, Wang HZ, Lee JR, Shuja Z et al. The human Cx26-D50A and Cx26- A88V mutations causing keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness syndrome display increased hemichannel activity. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2013;304:C1150–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mese G, Sellitto C, Li L, Wang HZ, Valiunas V, Richard G et al. The Cx26-G45E mutation displays increased hemichannel activity in a mouse model of the lethal form of keratitis- ichthyosis-deafness syndrome. Mol Biol Cell 2011;22:4776–86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]