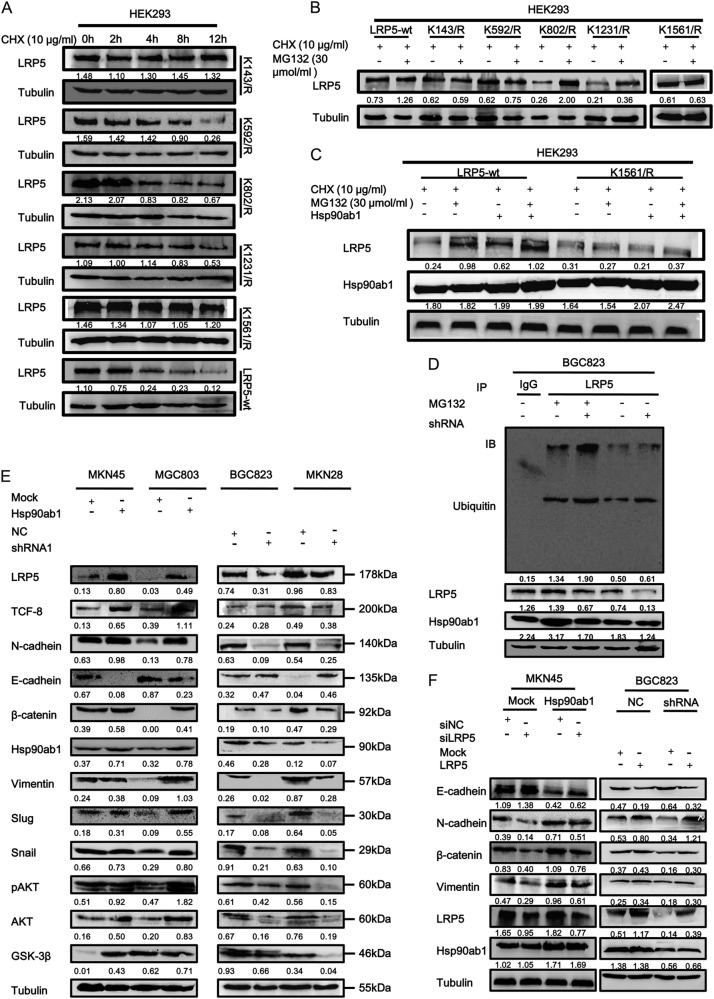
Fig. 7.
Hsp90ab1 inhibited the ubiquitin degradation of LRP5 and promoted the proliferation and invasion of GC cells by activating AKT and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. a HEK 293 T cells were transiently transfected with LRP5-wt plasmid or the K142R, K592R, K802R, K1231R, and K1561R mutants, and treated with CHX at 10 μg/ml for the indicated times. Cell lysates were assessed by Western blot analysis. b HEK 293 T cells were transiently transfected with LRP5-wt plasmid or the K142R, K592R, K802R, K1231R and K1561R mutants, and treated with CHX at 10 μg/ml and MG132 at 30 μM for 12 h. Cell lysates were assessed by Western blot analysis. c HEK 293 T cells were transiently co-transfected with LRP5-wt plasmid or the K1561R mutants and Hsp90ab1, and treated with CHX at 10 μg/ml and MG132 at 30 μM for 12 h. Cell lysates were assessed by Western blot analysis. d Hsp90ab1 increased the LRP5 level by inhibiting its ubiquitin-mediated degradation in BGC823 cells. e Western blotting analyses of the levels of Akt, Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways and classical EMT markers in GC cells treated with Hsp90ab1 or shRNA1. f Western blotting analyses of the levels of Hsp90ab1, LRP5 and classical EMT markers in GC cells treated with co-transfection of Hsp90ab1 and siLRP5 or shHsp90ab1 and LRP5