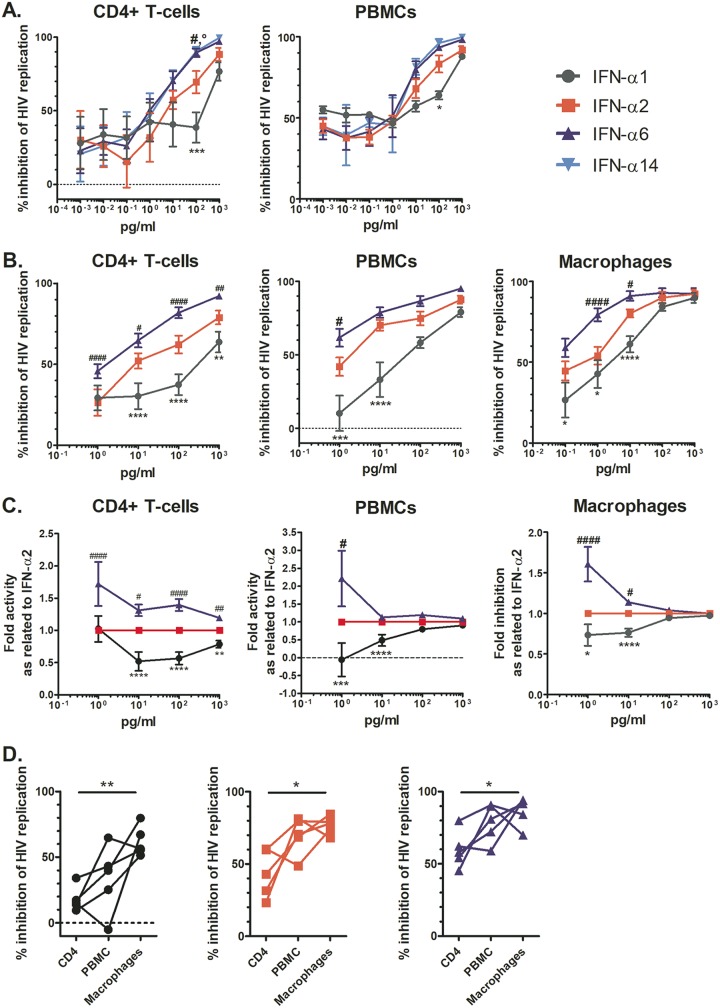
FIG 2.
Dose-dependent HIV-inhibitory activity of IFN-α subtypes as examined in primary cells infected ex vivo. (A and B) CD4+ T cells, PBMCs, or MDMs were pretreated with the indicated IFN-α subtype for 2 h and then inoculated with HIV YU-2 overnight. The next day, the cultures were washed and the IFN-αs added back. At days 0, 4, 8, and 12, supernatant was harvested to monitor HIV replication by quantifying p24 Ag. The area under the curve of the p24 Ag over time was calculated and normalized to that of the control (i.e., no IFN-α). (A) Data exploring anti-HIV activities of IFN-α1, -α2, -α6, and -α14 in subsets of six donors’ CD4+ T cells and three donors’ PBMCs at an extended dose range. (B) Data for IFN-α1, -α2, and -α6 in cells from larger numbers of donors (12, 9, and 9 donors, respectively), focusing on higher dosages of the IFN-α subtypes. Responses were compared to those measured in the IFN-α2-treated groups by significance testing with RM two-way ANOVAs, comparing all groups to the IFN-α2 group. Symbols for comparisons with IFN-α2 are as follows: *, IFN-α1; #, IFN-α6. (C) Data for fold changes in anti-HIV activities compared to that of IFN-α2 for IFN-α subtypes and donor cells as described in the legend to panel B. (D) Percentages of inhibition in donor-matched cell subsets for IFN-α1, -α2, and -α6 at 10 pg/ml. Significance testing was done for each IFN-α subtype using RM one-way ANOVAs, comparing the responses in each cell type to one another.