Figure 3.
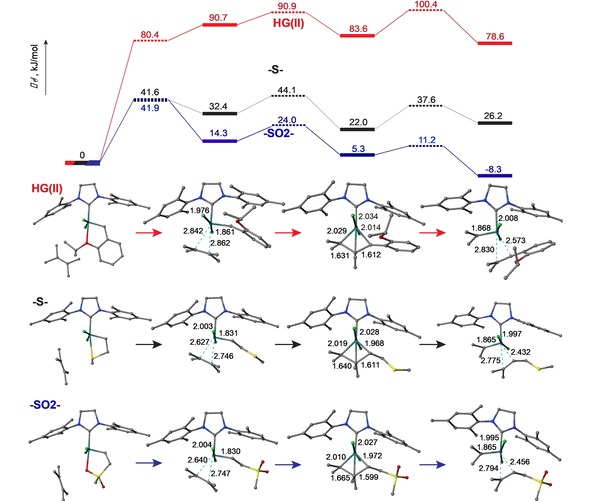
Top: Free energy profile of interaction of 2,3‐dimethyl‐2‐butene 4 S with HG(II), [Ru]=CH−CH2−S−CH3 and [Ru]=CH−CH2−SO2−CH3, shown using red, black, and blue colors, respectively [DLPNO‐CCSD(T)/def2‐TZVP//M06‐L/def2‐SV(P)+PCM(MeCN)]. Bottom: Calculated initial chelate structures of the HG(II) precatalyst and ruthenium β‐chalcogenide carbene complexes are aligned along the left edge, the corresponding key intermediates in the reaction coordinate pathways are correlated within columns directly below the composite free energy profiles, and selected bond lengths are associated with the computed structures. It is noted that the transition state free energy of the π‐complex formation involving HG(II) lies below the free energy of the resulting π‐complex due to the entropy correction (no such effect is present on the corresponding potential energy surface diagram).
