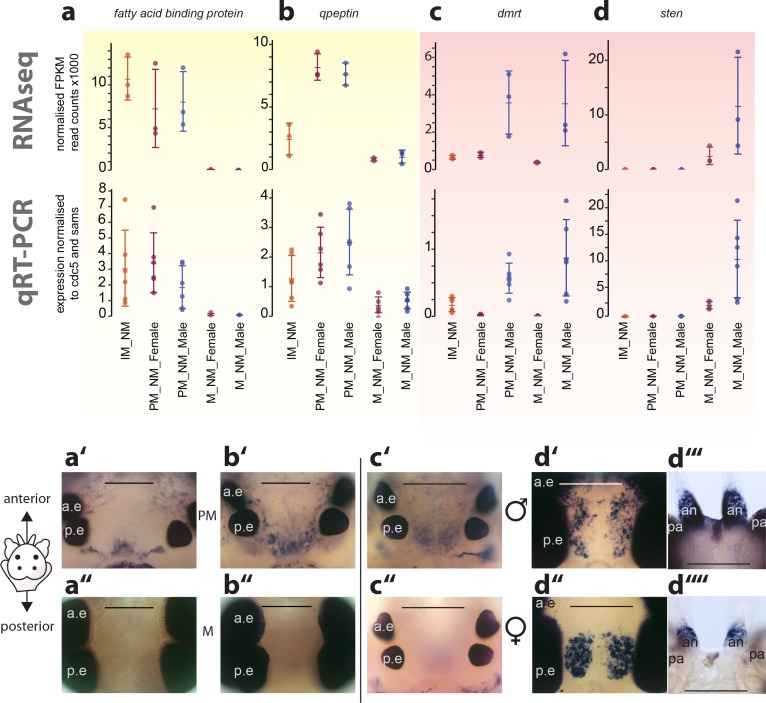
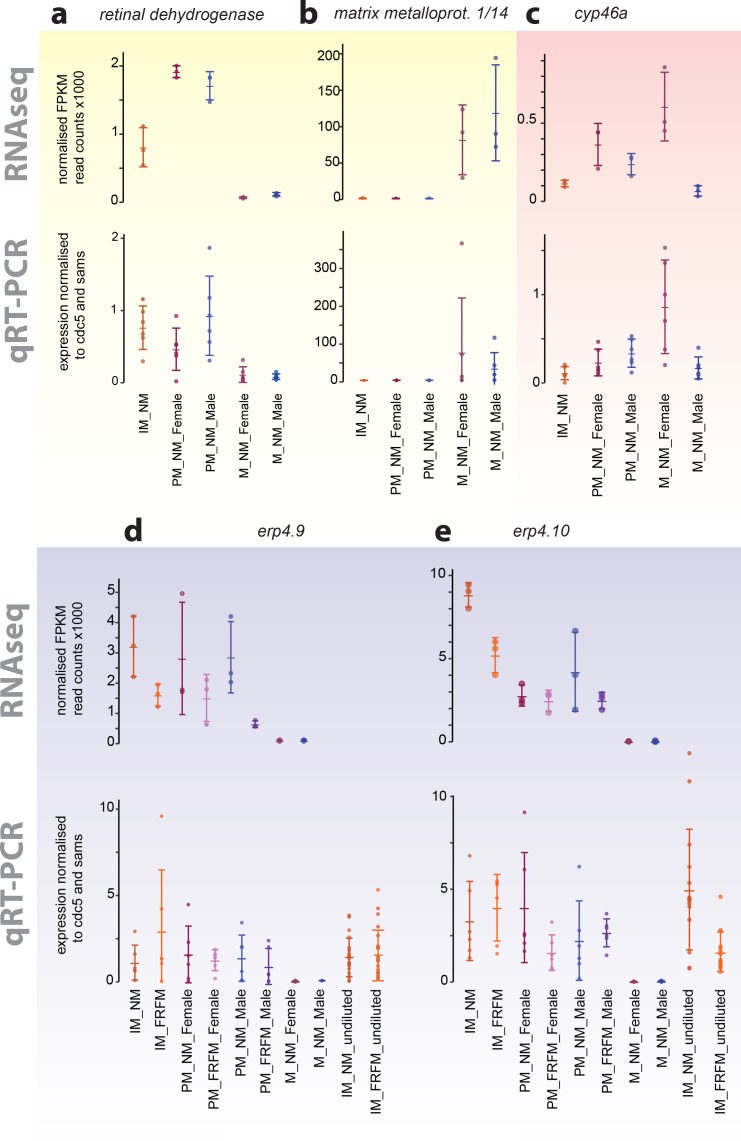
Figure 4. Exemplary validation of candidate genes by qRT-PCR and expression domains in the head.
(a–a’’,b–b’’) Maturation markers fatty acid binding protein and qpeptin. (c–c’’,d–d’’) Sexual differentiation markers dmrt and sten. (a–d): qRT-PCR validation of the candidates relative to the arithmetic mean of the reference genes cdc5 and sams. All graphs show the arithmetic mean with standard deviation, and the individual data points. (a’–d’’) Whole mount in situ hybridisations of the respective genes, comparing premature animals (PM, (a’,b’) with mature animals (M, a’’,b’’), and males (c’,d’,d’’’) with females (c’’,d’’, d’’’), respectively. All images except d’’’and d’’’’: dorsal views, anterior to the top, scale bar: 250 µm. d’’’ and d’’’’: ventral views, anterior top, scale bar: 200 µm. Also see Figure 4—figure supplement 1 for further validations. a.e.: anterior eye; p.e.: posterior eye, an: antenna, pa: palpa.