Abstract
IMPORTANCE
Thrombocytopenia and intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) are common among very-low-birth-weight (VLBW) infants. Survey results suggest that US neonatologists frequently administer platelet transfusions to VLBW infants with mild to moderate thrombocytopenia.
OBJECTIVES
To characterize platelet transfusion practices in US neonatal intensive care units (NICUs), to determine whether severity of illness influences platelet transfusion decisions, and to examine the association between platelet count (PCT) and the risk for IVH in the first 7 days of life.
DESIGN, SETTING, AND PARTICIPANTS
This multicenter, retrospective cohort study included 972 VLBW infants treated in 6 US NICUs, with admission dates from January 1, 2006, to December 31, 2007. Data were collected from all infants until NICU discharge or death (last day of data collected, December 4, 2008). Data were entered into the central database, cleaned, and analyzed from May 1, 2009, to February 11, 2016.
INTERVENTION
Platelet transfusion.
MAIN OUTCOMES AND MEASURES
Number of platelet transfusions and incidence of IVH.
RESULTS
Among the 972 VLBW infants (520 [53.5%] male; mean [SD] gestational age, 28.2 [2.9] weeks), 231 received 1002 platelet transfusions (mean [SD], 4.3 [6.0] per infant; range, 1–63 per infant). The pretransfusion PCT was at least 50 000/μL for 653 of 998 transfusions (65.4%) with this information. Two hundred eighty-one transfusions (28.0%) were given during the first 7 days of life. During that period, platelet transfusions were given on 35 of 53 days (66.0%) when the patient had a PCT less than 50 000/μL and on 203 of 436 days (46.6%) when the patient had a PCT of 50 000/μL to 99 000/μL. At least 1 marker of severe illness was present on 198 of 212 patient-days (93.4%) with thrombocytopenia (PCT, <100 000/μL) when a platelet transfusion was given compared with 113 of 190 patient-days (59.5%) with thrombocytopenia when no platelet transfusion was given. Thrombocytopenia was a risk factor for intraventricular hemorrhage during the first 7 days of life (hazard ratio, 2.17; 95% CI, 1.53–3.08; P < .001). However, no correlation was found between severity of thrombocytopenia and risk for IVH. After controlling for significant clinical factors and thrombocytopenia, platelet transfusions did not have a significant effect on the incidence of IVH (hazard ratio, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.49–1.73; P = .80).
CONCLUSIONS AND RELEVANCE
A large proportion of platelet transfusions were given to VLBW infants with PCT greater than 50 000/μL. Severity of illness influenced transfusion decisions. However, the severity of thrombocytopenia did not correlate with the risk for IVH, and platelet transfusions did not reduce this risk.
Thrombocytopenia, defined as a platelet count (PCT) less than 150 000/μL (to convert to ×109 per liter, multiply by 0.001), affects 18% to 35% of patients admitted to neonatal intensive care units (NICUs).1–3 The incidence of thrombocytopenia is inversely related to gestational age (GA) and approaches 70% among infants who weigh less than 1000 g.4 An estimated 5% to 9% of patients admitted to US NICUs receive at least 1 platelet transfusion in an attempt to prevent hemorrhage, particularly intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH).5
The only randomized clinical trial of platelet transfusion thresholds in neonates6 was published more than 20 years ago. One hundred fifty-two very-low-birth-weight (VLBW) neonates with a PCT of 50 000/μL to 150 000/μL during the first 72 hours of life were randomized to receive platelet transfusions for any PCT less than 50 000/μL or less than 150 000/μL during the first 7 days of life.6 These investigators found no differences in the incidence or severity of IVH between the 2 groups,indicatingthattransfusionsgivenforPCTsof50 000/μL to 150 000/μL do not decrease the risk for hemorrhage in VLBW neonates.6
In the absence of other platelet transfusion trials, lingering uncertainty about the risk associated with neonatal thrombocytopenia has resulted in substantial variability in neonatal platelet transfusion practices worldwide. Survey results have suggested that US neonatologists often administer platelet transfusions at significantly higher PCTs than do their European counterparts.7,8 However, whether these survey results reflect actual transfusion practices in US NICUs remains unknown.
Liberal platelet transfusion practices are of particular concern in the context of reports showing that neonates receiving platelet transfusions have a greater risk for death than neonates who do not receive transfusions.5,9–11 However, whether this association is related to sicker infants being more likely to receive platelet transfusions is unclear.
The present study focused on VLBW neonates admitted to 6 US NICUs. We designed the study with the following objectives: (1) to characterize actual platelet transfusion practices in this patient population; (2) to determine whether severity of illness and clinical factors associated with increased bleeding risk influence platelet transfusion decisions; and (3) to examine the association between the degree of thrombocytopenia and subsequent risk for IVH during the first 7 days of life.
Methods
Study Population
This retrospective cohort study included 972 VLBW neonates admitted to 6 US NICUs (Boston Children’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts; University of Iowa Children’s Hospital, Iowa City; and the following 4 NICUs affiliated with Intermountain Health Care, Utah: LDS Hospital, Salt Lake City; McKay Dee Hospital, Ogden; Utah Valley Regional Medical Center, Provo; and Primary Children’s Medical Center, Salt Lake City) from January 1, 2006, to December 31, 2007. Information about the sites is presented in eTable 1 in the Supplement. The VLBW neonates admitted during that period were identified through review of each NICU’s admission records. Infants who received transfusions were identified by cross-referencing VLBW infants with blood bank records. Institutional review board approval was obtained at each institution, and informed consent was waived by the institutional review boards at all institutions owing to the retrospective nature of this study.
Data Collection
Medical records from neonates who received and did not receive transfusions were reviewed, and the data were collected by neonatal nurses using uniform data collection forms. Laboratory data and results of ultrasonography of the head were obtained from each institution’s electronic medical records. Diagnoses, ventilator support, medications, and any indication of moderate or severe bleeding were obtained from the medical record. For all infants, regardless of transfusion status, every PCT during the first 7 days of life was recorded.
Each infant in the study had a baseline set of admission and maternal data. For each platelet transfusion administered and for each day with a PCT of 100 000/μL or less during the first 7 days of life, information was collected regarding markers of severity of illness at that time (eg, use of mechanical ventilation or vasopressors), risk factors for bleeding (eg, use of anticoagulants or medications that affect platelet function, abnormal coagulation test results), surgery, or recent prior hemorrhage. The site and severity of bleeding were recorded following predefined criteria (eMethods in the Supplement).
Statistical Analysis
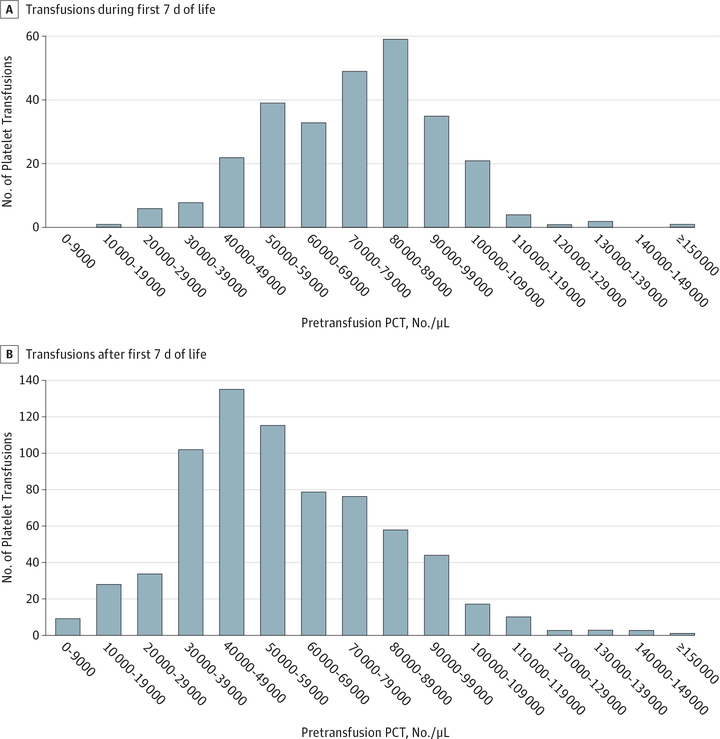
Data were assessed from May 1, 2009, to February 11, 2016. Data were entered into a centralized Access database (Microsoft Corp) and validated. Demographic comparisons of infants in the transfusion vs nontransfusion groups and analyses of pretransfusion PCTs (Figure 1) used data from the patient cohort throughout their NICU admissions. Because the risk for IVH is highest in the first 7 days of life, and because data collection for the later period was limited to days on which platelet transfusions were administered, all other analyses were limited to the first 7 days of life.
Figure 1.
Distribution of Pretransfusion Platelet Counts (PCTs) in Very-Low-Birth-Weight Neonates Receiving Platelet Transfusions
Generalized linear models accounted for potential correlations between different patient-days for the same patient and were used to investigate whether the degree of thrombocytopenia was associated with the decision to give a platelet trans-fusion. Analysis was restricted to infants with any PCT less than 150 000/μL during the first 7 days of life. The unit of analysis was each patient-day for which at least 1 PCT was available. If the patient-day did not include a transfusion, the lowest PCT of the day was analyzed. If the patient-day included a platelet transfusion, the pretransfusion PCT was used for this analysis.
To determine whether clinical factors associated with severe illness or a higher risk for bleeding influenced platelet transfusion decisions, we used generalized linear models to evaluate whether the presence of predefined markers of severe illness (mechanical ventilation and use of vasopressors) and/or factors associated with an increased risk for bleeding (use of medications, coagulopathy [determined by international normalized ratio, fibrinogen level, or partial thromboplastin time12], surgery, history of hemorrhage, or ultrasono-graphic findings consistent with IVH13) (Table 1) were associated with the administration of a platelet transfusion on days when the PCT was less than 100 000/μL, taking into account within-person correlation. Infants with significant congenital anoma lies, heart defects, or known genetic disorders were excluded from this and the following analyses.
Table 1.
Association Between Markers of Severe Illness or Increased Risk for Bleeding and Platelet Transfusion on Days During the First 7 Days of Life With a Platelet Count <100 000/μL
| Presence of Marker, No. (%) of Patient-days | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| With Platelet Transfusion (n = 212) |
Without Platelet Transfusion (n = 190) |
||
| Conventional mechanical ventilation, high-frequency oscillator, or high-frequency jet ventilation | 192 (90.6) | 96 (50.5) | <.001 |
| Hemodynamic support consisting of dopamine hydrochloride or dobutamine hydrochloride, ≥5 μg/kg/min, or epinephrine at any dose | 68 (32.1) | 18 (9.5) | .001 |
| Administration of indomethacin or ibuprofen for patent ductus arteriosus or heparin sodium for anticoagulation (ie, not for line patency) within the prior 24 h | 17 (8.0) | 14 (7.4) | .90 |
| Coagulopathy indicated by INR >2, fibrinogen level <100 mg/dL, or PTT >1.5 × mean reference value for age12 within the prior 48 h | 21 (9.9) | 9 (4.7) | .14 |
| Surgery or other invasive procedures within the prior 72 h or the subsequent 24 h | 28 (13.2) | 7 (3.7) | .007 |
| Pulmonary, Gl, GU, wound, or other hemorrhage during the prior 48 h (not including IVH) | 42 (19.8) | 6 (3.2) | <.001 |
| Ultrasonographic findings consistent with the diagnosis or extension of IVH by Papile et al13 grading system within the prior 7 d | 97 (45.8) | 39 (20.5) | .005 |
| Any marker | 198 (93.4) | 113 (59.5) | <.001 |
Abbreviations: GI, gastrointestinal tract; GU, genitourinary; INR, international normalized ratio; IVH, intraventricular hemorrhage; PTT, partial thromboplastin time.
SI conversion factor: To convert fibrinogen to micromoles per liter, multiply by 0.0294.
P values were calculated using a generalized linear model, taking into account potential correlations between different patient-days for the same patient.
Cox regression models, stratified by site to account for potential confounding, were used to determine whether the nadir PCT, treated as a time-varying categorical variable, was associated with a risk for subsequent IVH during the first 7 days of life (ie, the lowest PCT on day 1 was considered in determining the risk for IVH on day 2 for participants who did not already have an IVH; the lowest PCT from days 1 and 2 was considered in determining the risk for IVH on day 3 for participants who did not already have an IVH; and so on). Stratified Cox regression models were also used to assess the association between platelet transfusion (as a dichotomous time-varying covariate) and the subsequent diagnosis of IVH during the first 7 days of life. This analysis was conducted with the first diagnosis of any grade IVH as the outcome and with the first diagnosis of (or progression to) grade III or IV IVH as the outcome. To assess whether the association between trans-fusion and IVH could be explained by other patient characteristics, the unadjusted association was compared with the association adjusted for baseline covariates (sex; GA <28 vs ≥28 weeks; 5-minute APGAR <7 vs ≥7; use of antenatal corticosteroids; and pregnancy-induced hypertension as delivery indication) and for nadir PCT (dichotomized at 150 000/μL as a time-varying covariate). Because the purpose of these analyses was to generate hypotheses to be tested in future randomized trials, for all analyses a 2-sided P < .05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Patient Demographics
Of the 972 VLBW neonates in this cohort, 231 (23.8%) received at least 1 platelet transfusion during their NICU admission. Infants in the transfusion group were more likely to be male than those in the nontransfusion group, with 141 of 231 infants in the transfusion group (61.0%) vs 379 of 740 infants in the nontransfusion group (51.2%) (P = .01). Sex was not recorded for 1 infant. In addition, infants in the transfusion group were more premature (mean [SD] GA, 26.3 [3.0] vs 28.8 [2.6] weeks; P < .001) and smaller (mean [SD] birth weight, 805 [284] vs 1113 [264] g; P < .001) than those in the nontransfusion group.
Platelet Transfusions
The 231 VLBW infants in the transfusion group received a total of 1002 platelet transfusions, with a mean (SD) of 4.3 (6.0) and a range from 1 to 63 transfusions per infant. Ninety-four infants (40.7%) had transfusions only during the first 7 days of life; 76 infants (32.9%), only after the first 7 days of life; and 61 infants (26.4%), during both periods. Two hundred eighty-one platelet transfusions (28.0% of transfusions) were given during the first 7 days of life, and the remaining 721 (72.0%) were given after day 7. When we omitted 4 platelet transfusions that were administered without a prior platelet count, 653 of 998 transfusions (65.4%) had a pretransfusion PCT of at least 50 000/μL, including 244 of 281 (86.8%) during the first 7 days of life and 409 of 717 (57.0%) later transfusions (Figure 1).
Figure 2 shows the association between the degree of thrombocytopenia in the first 7 days of life and whether or not a platelet transfusion was administered on that day. Among the 395 infants with any platelet count less than 150 000/μL during the first 7 days of life, 1891 patient-days had PCT information available. At least 1 platelet transfusion occurred on 35 of 53 days (66.0%) with a PCT less than 50 000/μL, on 203 of 436 days (46.6%) with a PCT of 50 000/μL to 99 000/μL, on 26 of 735 days (3.5%) with a PCT of 100 000/μL to 149 000/μL, and 1 of 667 days (0.1%) with a PCT greater than 150 000/μL. In the generalized linear model for whether or not platelet transfusion occurred on a given day with thrombocytopenia, taking into account PCT category, NICU site, and within-person correlation, the PCT category and site were significantly associated with transfusion (P < .001 and P = .004, respectively; eTable 2 in the Supplement).
Figure 2.
Association Between Platelet Count (PCT) and Occurrence of Platelet Transfusion
Platelet Transfusions and Illness Severity
In the first 7 days of life, 189 VLBW infants had a total of 402 days with a PCT less than 100 000/μL. At least 1 platelet trans-fusion was given on 212 (52.7%) of those days. Of these 212 patient-days with at least 1 platelet transfusion, 198 (93.4%) had at least 1 marker of severe illness or bleeding risk. Of the 190 patient-days without a platelet transfusion, 113 (59.5%) had at least 1 such marker (P < .001) (Table 1). We found significant differences among the 6 study sites for several clinical markers examined (eTable 3 in the Supplement), likely reflecting a combination of different patient populations and practice variations.
Thrombocytopenia and Risk for IVH
The risk for IVH was evaluated based on the lowest PCT on any day before the diagnosis of IVH. Compared with PCTs of at least 150 000/μL, the hazard ratio for the development of IVH was 2.17 for any PCT less than 150 000/μL (95% CI, 1.53–3.08; P < .001), indicating that infants with thrombocytopenia were at higher risk for IVH than those without thrombocytopenia. However, among the 314 infants with at least 1 PCT of less than 150 000/μL during the first 7 days of life, no association was found between severity of thrombocytopenia and the risk for subsequent IVH (Table 2; overall P = .79).
Table 2.
Association Between Lowest PCT to Date and Risk for IVHa
| Lowest PCT Category, No./μL | HR(95%CI) | P Valueb |
|---|---|---|
| 10 000–39 000 | 0.93 (0.22–4.00) | .92 |
| 40 000–49 000 | 1.39 (0.47–4.11) | .55 |
| 50 000–59 000 | 0.26 (0.04–1.95) | .19 |
| 60 000–69 000 | 0.30 (0.04–2.29) | .25 |
| 70000–79 000 | 1.26 (0.48–3.31) | .64 |
| 80 000–89 000 | 1.28 (0.43–3.88) | .66 |
| 90 000–99 000 | 1.35 (0.57–3.16) | .50 |
| 100 000–149 000 | 1.10(0.66–1.83) | .73 |
| ≥150 000 | 1 [Reference] | NA |
Abbreviations: HR, hazard ratio; IVH, intraventricular hemorrhage; NA, not applicable; PCT, platelet count.
SI conversion factor: To convert PCT to ×109 per liter, multiply by 0.001.
Analysis includes 314 very-low-birth-weight infants with thrombocytopenia (≥1 PCT <150 000/μL during the first 7 days of life) compared with infants who had not yet had thrombocytopenia (reference group).
Overall P = .79 from test with 8 degrees of freedom for degree of thrombocytopenia.
Platelet Transfusions and Risk for IVH
To determine whether platelet transfusions given to VLBW infants in the first 7 days of life protected against the development or progression of IVH, we performed a Cox regression analysis in 756 infants. In the first 7 days of life, 134 (17.7%) of these infants had an IVH, including a grade III or IV IVH in 62(8.2%). Table 3 shows a significant association between platelet transfusion and subsequent IVH, with infants in the trans-fusion group at higher risk (P = .004).
Table 3.
Association Between Prior Platelet Transfusion and Risk for IVH Outcomes During the First 7 Days of Life
| IVH Outcome | Prior Platelet Transfusion as a Risk Factor for IVH | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unadjusted Model | Model for Adjusted Clinical Covariatesa |
Model for Adjusted Clinical Covariates and Nadir PCTb |
||||
| HR(95%CI) | P Value | HR(95%CI) | P Value | HR (95% Cl) | P Value | |
| Any grade IVH (134 of 756 neonates)c | 2.25 (1.30–3.89) | .004 | 1.47 (0.83–2.62) | .19 | 0.92 (0.49–1.73) | .80 |
| Grade III or IV IVH (62 of 772 neonates)d | 4.05 (2.16–7.60) | <.001 | 2.43 (1.24–4.77) | .01 | 1.24(0.59–2.60) | .57 |
Abbreviations: HR, hazard ratio; IVH, intraventricular hemorrhage; PCT, platelet count.
Includes sex, gestational age less than 28 vs at least 28 weeks, 5-minute Apgar score less than 7 vs at least 7, antenatal corticosteroid treatment, and pregnancy-induced hypertension as an indication for delivery. All models are restricted to infants who have no missing data for any of the clinical covariates.
Includes all variables listed in footnote “a,” plus whether the nadir PCT to date is less than 150 000/μL or at least 150 000/μL (to convert to ×109 per liter, multiply by 0.001).
Omits infants with any IVH on the first day of life.
Omits infants with grade III or IV IVH on the first day of life.
Next, we examined baseline demographic and clinical factors to determine which were associated with a significantly increased or decreased risk for IVH when considered separately. Factors that were significantly associated with an increased risk for IVH included male sex, GA less than 28 weeks, and 5-minute APGAR score less than 7. Two factors, antenatal corticosteroid therapy and pregnancy-induced hypertension as indication for delivery, were significantly associated with a decreased risk of IVH. Table 3 also shows the association between platelet transfusion and subsequent IVH outcomes from a multivariable regression model that adjusted for the positive and negative clinical factors that were individually associated with IVH. Table 3 also shows the association between platelet transfusion and subsequent IVH outcomes from a multivariable regression model that adjusted for the clinical factors and for whether the infant had yet experienced any PCT of less than 150 000/μL. In both models, the effect of platelet transfusion on the development of any IVH was attenuated and became non-significant. Similar findings were observed when only grades III and IV IVH were considered, although only in the model ad justing for clinical factors and thrombocytopenia did platelet transfusion become nonsignificant.
Discussion
Multiple studies have highlighted the variability in platelet transfusion thresholds used in the NICU.5,9,14 Survey results,7 in particular, suggested that neonatologists in North America frequently administer transfusions to nonbleeding preterm neonates with PCTs of 50 000/μL to 149 000/μL. A comparison of the survey responses of US and European neonatologists8 suggested that US neonatologists administer transfusions at significantly higher PCTs and concluded that practice differences alone would result in the administration of 1.8 times more platelet transfusions in US NICUs.
The primary goal of this study was to describe actual platelet transfusion practices in US NICUs. We confirmed that a high percentage of VLBW neonates (23.8% in our cohort) received platelet transfusions during their NICU stay, with a mean (SD) of 4.3 (6.0) transfusions per infant (range, 1–63 transfusions per infant). These findings were concordant with those of prior single-institution observational studies that reported approximately 50% of infants undergoing transfusion receive at least 2 platelet transfusions.5,14 We also demonstrated that a large pro-portion (65.2%) of platelet transfusions were given for pretrans-fusion PCTs of at least 50 000/μL. This finding was in contrast to UK NICUs, in which the median PCT at which transfusions were administered was 27 000/μL.15 Together these studies confirmed that US neonatologists generally follow more liberal transfusion thresholds than do European neonatologists.
The reasons underlying the liberal US approach to platelet transfusions are likely multifactorial and might include the limited evidence to guide neonatal transfusion decisions, concerns about neonatal platelet function, and differences in health care systems. In regard to neonatal platelet function, investigators16–20 have established that platelets from neonates are hyporeactive in response to most agonists. However, tests of whole-blood primary hemostasis consistently indicate that term neonates have increased hemostasis compared with adults,21–23 a finding explained by the high levels of von Willebrand factor and hematocrit and the high mean corpuscular volume in the blood of neonates.21 Data on platelet function in preterm neonates are scarce. However, although bleeding and closure times are longer in preterm compared with term neonates, the available studies suggest that premature infants have adequate primary hemostasis.24,25 Furthermore, the hyporeactivity of neonatal platelets significantly improves by the 10th day of life,18,20,26 thus providing no support for the use of liberal transfusion thresholds after this period.
Because nearly all intracranial hemorrhages occur within the first 7 days of life,27 many neonatologists attempt to maintain higher PCTs during this period, as evident in our study (Figure 1). The reasons underlying the predisposition of pre-term infants to IVH are multifactorial, however, and include the fragility of the periventricular capillary bed and susceptibility to hemodynamic instability. In the present study, thrombocytopenia was associated with an increased risk for IVH. However, the risk for IVH among infants with thrombocytopenia was not correlated with the severity of thrombocytopenia, consistent with other recent studies.15,28–31 Similar observations were recently reported in a cohort of pediatric patients with chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia.32 Taken together, these studies support the conclusion that, although thrombocytopenia is associated with an increased risk for bleeding, the association does not imply causality and the PCT is not the main determinant of bleeding, thus questioning the benefit of platelet transfusions given to VLBW infants with mild to moderate thrombocytopenia. In a prospective observational study of neonates with PCTs less than 60 000/μL, GA less than 34 weeks, postnatal age less than 14 days, and necrotizing enterocolitis were more important risk factors for bleeding than the PCT.15,29
An issue to consider is the potential for platelet transfusions to have deleterious effects, particularly given the reported correlation between the number of platelet transfusions and neonatal morbidity and mortality.5,10 However, whether this association reflects any negative effects of platelet transfusions or whether sicker infants are more likely to receive platelet transfusions had not been determined. We addressed this question and observed that 1 or more markers of severe illness or factors associated with bleeding risk were present on 93.4% of patient-days with thrombocytopenia when at least 1 platelet transfusion was administered, compared with 59.5% of patient-days with thrombocytopenia without a trans-fusion. This finding indicates that severity of illness influences transfusion decisions and may be a confounding factor when investigating the association between platelet transfusions and outcomes. Along these lines, our NICUs represented a mixture of academic and nonacademic practices, which displayed significant variability in platelet transfusion practices and in the presence of markers of severity of illness. The units with the highest platelet transfusion rates and the highest percentages of infants with at least 1 marker of illness severity or bleeding risk were those with an exclusive out-born population.
Nevertheless, platelet transfusions are not without risks. Bacterial infections are associated with platelet transfusions more than any other blood product owing to the need to store platelets at room temperature.33,34 Transfusion-transmitted infections with the potential for long-term consequences (ie, Chagas disease) are also more relevant in neonates than in older patients.35,36 Other transfusion complications, such as trans-fusion-related acute lung injury, might be underrecognized in sick neonates.
We recognize that our study had limitations. Because it was retrospective, data collection was limited to information obtained as part of standard care. For example, ultrasonography of the head was obtained per routine clinical practice. Thus, we could not determine when an IVH occurred, and our analysis was based on the time of IVH diagnosis. Also, because the study was not randomized, causation or lack of causation cannot be assessed. Although we adjusted for factors in our data set associated with IVH risk, platelet transfusions may have been given to infants who were at increased risk owing to factors not included in the data set. If so, platelet transfusions may have reduced the risk for IVH compared with what it would have been without transfusion. In addition, because infants in our study often underwent transfusion for PCTs of 50 000/μL to 150 000/μL, the number of patient-days with PCTs less than 50 000/μL was low. Thus, the degree to which our findings are generalizable to infants with more severe thrombocytopenia is unclear. Finally, data for this study were collected approximately 8 years ago, and practices might have changed since. However, to our knowledge, no high-level evidence likely to change practice substantially (ie, a randomized clinical trial) has been published during this period.
Conclusions
We demonstrated that infants with thrombocytopenia admitted to US NICUs frequently receive platelet transfusions for mild to moderate thrombocytopenia, although the degree of thrombocytopenia did not correlate with IVH. We also showed that infants with thrombocytopenia are more likely to receive platelet transfusions if they are sicker, which may partly explain the association between platelet transfusions and poor outcomes. After adjusting for relevant variables, we found no evidence that platelet transfusions significantly affected the incidence of IVH in our study population. These observations highlight the need to conduct randomized clinical trials to conclusively establish the risks and benefits of different platelet transfusion thresholds in this population.
Supplementary Material
Key Points.
Question What is the association between platelet count and risk for intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH)?
Findings In this multicenter cohort study of 972 very-low-birth-weight (VLBW) infants, thrombocytopenia was a risk factor for IVH, but no correlation was found between severity of thrombocytopenia and risk for IVH, and platelet transfusions did not have a significant effect on the incidence of IVH.
Meaning Platelet transfusions were frequently given to VLBW infants with mild to moderate thrombocytopenia, but severity of thrombocytopenia was not associated with the risk of IVH and platelet transfusions did not reduce this risk.
Acknowledgments
Funding/Support:
This study was supported by grants R21 HL087150 and P01 HL046925 from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health.
Role of the Funder/Sponsor:
The funding source had no role in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Footnotes
Conflict of Interest Disclosures:
None reported.
Previous Presentations: Preliminary data for this study were previously presented at the annual Pediatric Academic Societies Meeting; April 30, 2012; Boston, Massachusetts.
REFERENCES
- 1.Andrew M, Castle V, Saigal S, Carter C, Kelton JG. Clinical impact of neonatal thrombocytopenia. J Pediatr. 1987;110(3):457–464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Castle V, Andrew M, Kelton J, Giron D, Johnston M, Carter C. Frequency and mechanism of neonatal thrombocytopenia. J Pediatr. 1986;108(5, pt 1): 749–755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mehta P, Vasa R, Neumann L, Karpatkin M. Thrombocytopenia in the high-risk infant. J Pediatr. 1980;97(5):791–794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Christensen RD, Henry E, Wiedmeier SE, et al. Thrombocytopenia among extremely low birth weight neonates: data from a multihospital healthcare system. J Perinatol. 2006;26(6):348–353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Del Vecchio A, Sola MC, Theriaque DW, et al. Platelet transfusions in the neonatal intensive care unit: factors predicting which patients will require multiple transfusions. Transfusion. 2001;41(6):803–808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Andrew M, Vegh P, Caco C, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of platelet transfusions in thrombocytopenic premature infants. J Pediatr. 1993;123(2):285–291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Josephson CD, Su LL, Christensen RD, et al. Platelet transfusion practices among neonatologists in the United States and Canada: results of a survey. Pediatrics. 2009;123(1):278–285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Cremer M, Sola-Visner M, Roll S, et al. Platelet transfusions in neonates: practices in the United States vary significantly from those in Austria, Germany, and Switzerland. Transfusion. 2011;51(12): 2634–2641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Garcia MG, Duenas E, Sola MC, Hutson AD, Theriaque D, Christensen RD. Epidemiologic and outcome studies of patients who received platelet transfusions in the neonatal intensive care unit. J Perinatol. 2001;21(7):415–420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Baer VL, Lambert DK, Henry E, Snow GL, Sola-Visner MC, Christensen RD. Do platelet transfusions in the NICU adversely affect survival? analysis of 1600 thrombocytopenic neonates in a multihospital healthcare system. J Perinatol. 2007; 27(12):790–796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bonifacio L, Petrova A, Nanjundaswamy S, Mehta R. Thrombocytopenia related neonatal outcome in preterms. Indian J Pediatr. 2007;74(3): 269–274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Nathan DG, Oski FA. Hematology of Infancy and Childhood. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders; 1992. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Papile LA, Burstein J, Burstein R, Koffler H. Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: a study of infants with birth weights less than 1,500 gm. J Pediatr. 1978; 92(4):529–534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Murray NA, Howarth LJ, McCloy MP, Letsky EA, Roberts IA. Platelet transfusion in the management of severe thrombocytopenia in neonatal intensive care unit patients. Transfus Med. 2002;12(1):35–41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Stanworth SJ, Clarke P, Watts T, et al. ; Platelets and Neonatal Transfusion Study Group. Prospective, observational study of outcomes in neonates with severe thrombocytopenia. Pediatrics. 2009;124(5):e826–e834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Israels SJ, Odaibo FS, Robertson C, McMillan EM, McNicol A. Deficient thromboxane synthesis and response in platelets from premature infants. Pediatr Res. 1997;41(2):218–223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Setzer ES, Webb IB, Wassenaar JW, Reeder JD, Mehta PS, Eitzman DV. Platelet dysfunction and coagulopathy in intraventricular hemorrhage in the premature infant. J Pediatr. 1982;100(4):599–605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sitaru AG, Holzhauer S, Speer CP, et al. Neonatal platelets from cord blood and peripheral blood. Platelets. 2005;16(3–4):203–210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Rajasekhar D, Kestin AS, Bednarek FJ, Ellis PA, Barnard MR, Michelson AD. Neonatal platelets are less reactive than adult platelets to physiological agonists in whole blood. Thromb Haemost. 1994;72 (6):957–963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bednarek FJ, Bean S, Barnard MR, Frelinger AL, Michelson AD. The platelet hyporeactivity of extremely low birth weight neonates is age-dependent. Thromb Res. 2009;124(1):42–45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Andrew M, Paes B, Bowker J, Vegh P. Evaluation of an automated bleeding time device in the newborn. Am J Hematol. 1990;35(4):275–277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Boudewijns M, Raes M, Peeters V, et al. Evaluation of platelet function on cord blood in 80 healthy term neonates using the Platelet Function Analyser (PFA-100): shorter in vitro bleeding times in neonates than adults. Eur J Pediatr. 2003;162(3): 212–213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Israels SJ, Cheang T, McMillan-Ward EM, Cheang M. Evaluation of primary hemostasis in neonates with a new in vitro platelet function analyzer. J Pediatr. 2001;138(1):116–119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Del Vecchio A, Latini G, Henry E, Christensen RD. Template bleeding times of 240 neonates born at 24 to 41 weeks gestation. J Perinatol. 2008;28 (6):427–431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Saxonhouse MA, Garner R, Mammel L, et al. Closure times measured by the platelet function analyzer PFA-100 are longer in neonatal blood compared to cord blood samples. Neonatology. 2010;97(3):242–249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Uçar T, Gurman C, Arsan S, Kemahli S. Platelet aggregation in term and preterm newborns. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2005;22(2):139–145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Horbar JD, Badger GJ, Carpenter JH, et al. ; Members of the Vermont Oxford Network. Trends in mortality and morbidity for very low birth weight infants, 1991–1999. Pediatrics. 2002;110(1, pt 1): 143–151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.von Lindern JS, van den Bruele T, Lopriore E, Walther FJ. Thrombocytopenia in neonates and the risk of intraventricular hemorrhage: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Pediatr. 2011;11(1):16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Muthukumar P, Venkatesh V, Curley A, et al. ; Platelets Neonatal Transfusion Study Group. Severe thrombocytopenia and patterns of bleeding in neonates: results from a prospective observational study and implications for use of platelet transfusions. Transfus Med. 2012;22(5):338–343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Baer VL, Lambert DK, Henry E, Christensen RD. Severe thrombocytopenia in the NICU. Pediatrics. 2009;124(6):e1095–e1100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.von Lindern JS, Hulzebos CV, Bos AF, Brand A, Walther FJ, Lopriore E. Thrombocytopaenia and intraventricular haemorrhage in very premature infants: a tale of two cities. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2012;97(5):F348–F352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Josephson CD, Granger S, Assmann SF, et al. Bleeding risks are higher in children versus adults given prophylactic platelet transfusions for treatment-induced hypoproliferative thrombocytopenia. Blood. 2012;120(4):748–760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Christensen RD, ed. Blood Banking and Transfusion Issues in Perinatal Medicine. Philadelphia, PA: WB Saunders; 2000. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kuehnert MJ, Roth VR, Haley NR, et al. Transfusion-transmitted bacterial infection in the United States, 1998 through 2000. Transfusion. 2001;41(12):1493–1499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Benjamin RJ, Stramer SL, Leiby DA, Dodd RY, Fearon M, Castro E. Trypanosoma cruzi infection in North America and Spain: evidence in support of transfusion transmission. Transfusion. 2012;52(9): 1913–1921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Agapova M, Busch MP, Custer B. Cost-effectiveness of screening the US blood supply for Trypanosoma cruzi. Transfusion. 2010;50 (10):2220–2232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.